Chromium Induces Toxicity at Different Phenotypic, Physiological, Biochemical, and Ultrastructural Levels in Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Parameters
2.2. Leaf Gas Exchange Elements
2.3. Chlorophyll Content Analysis
2.4. Stomatal Structure Analysis
2.5. Root Morphology
2.6. H2O2 and MDA Content
2.7. Osmolytes and Antioxidants
2.8. Antioxidant Enzymes
2.9. Concentration, Uptake, and Translocation of Chromium
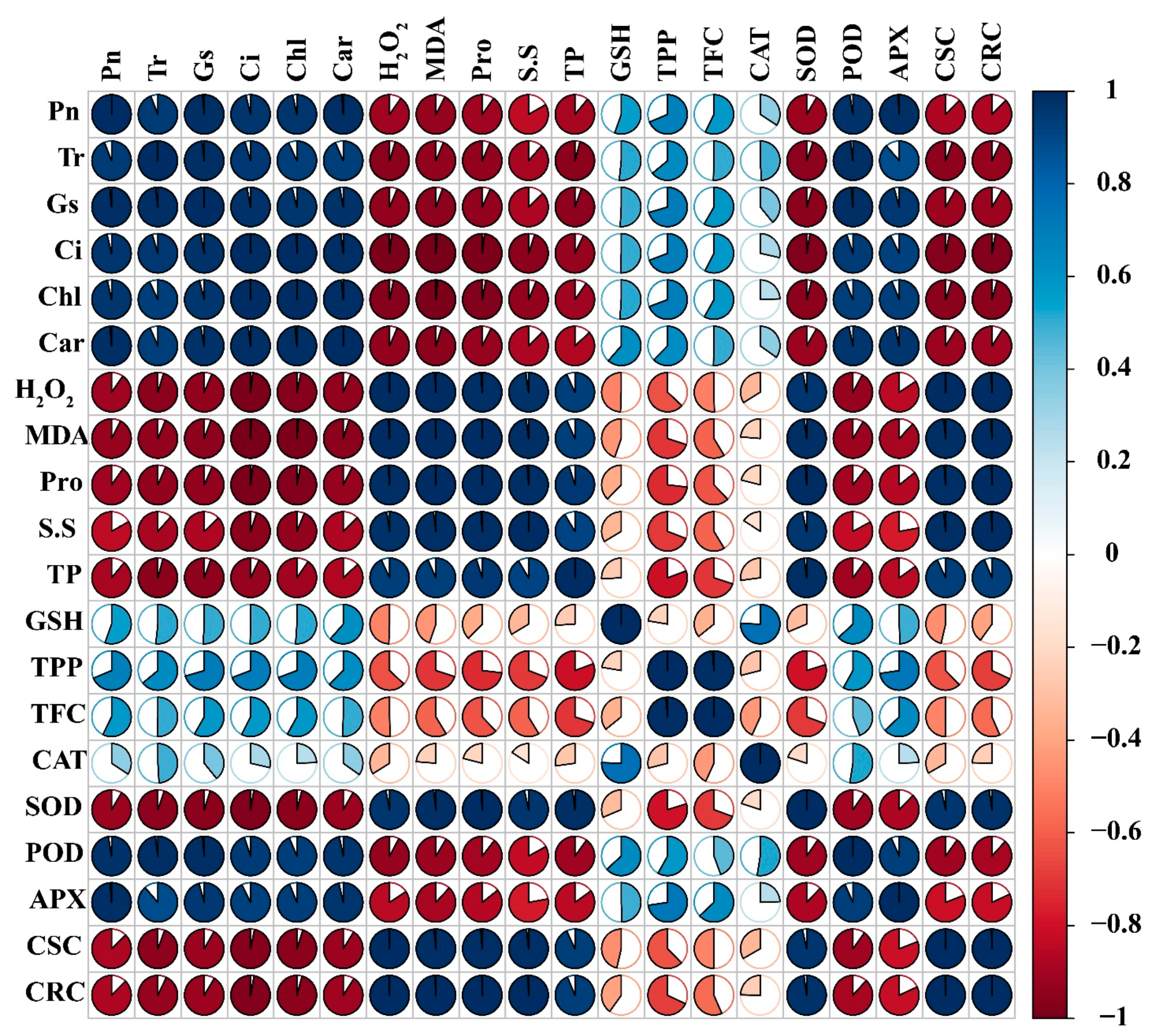
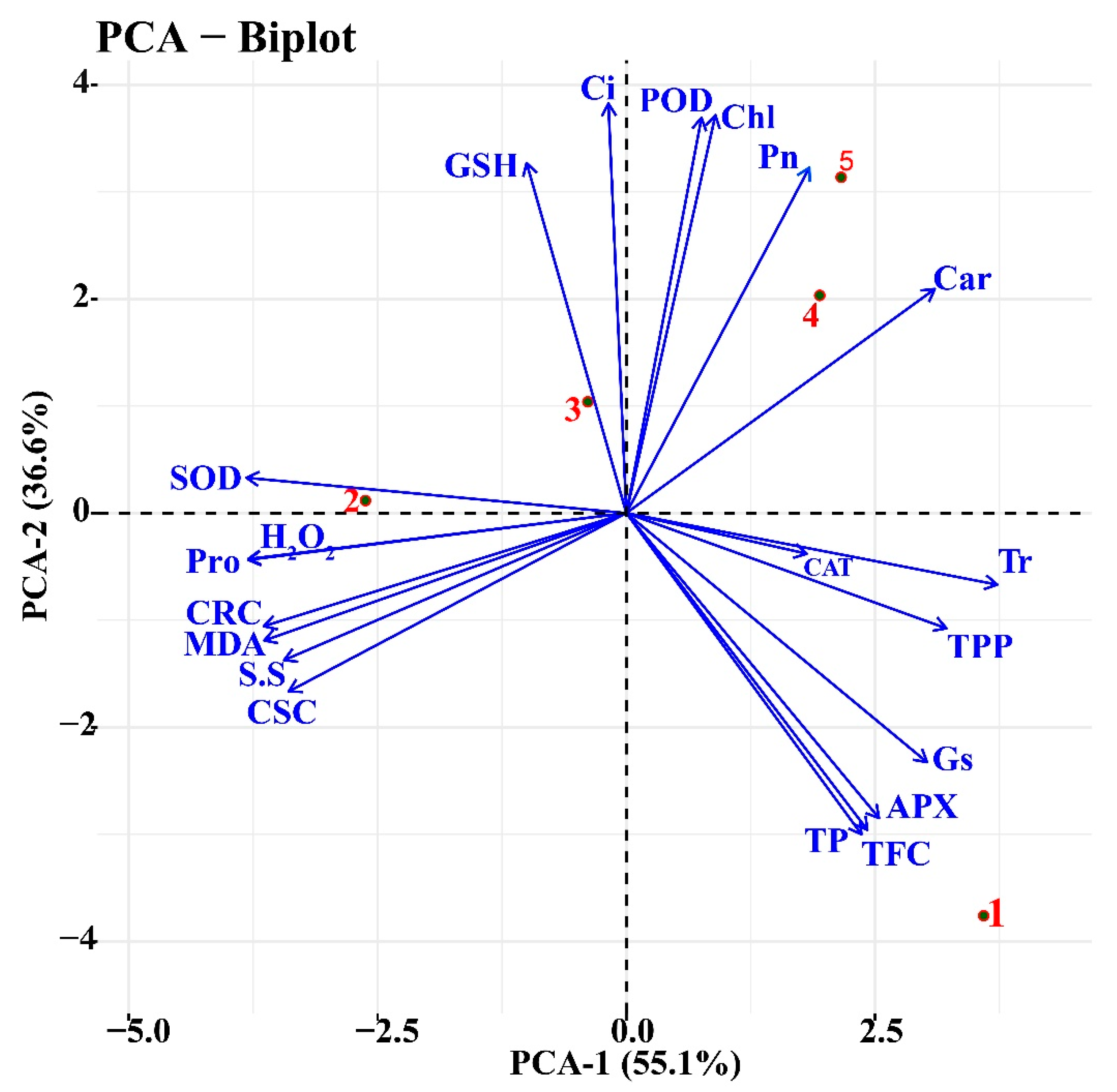
2.10. Correlation and Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Seedling Growth and Treatment
4.2. Growth Variables
Shoot DW (Controlled Plants)
Root DW (Controlled Plants)
4.3. Relative Water Content Analysis
4.4. Gas Exchange Parameters and Root Morphology
4.5. Chlorophyll Measurement
4.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.7. Determination of MDA, H2O2, Proteins, GSH, and Antioxidant Enzymes
4.8. Determination of Proline and Soluble Sugars
4.9. Determination of Total Polyphenols and Flavonoid Content
4.10. Cr Content Analysis
concentration of Cr in the roots
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, Q.; Abbas, F.; Bukhari, S.A.H.; Saeed, R.; Wu, L. Citric acid assisted phytoextraction of chromium by sunflower; morpho-physiological and biochemical alterations in plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habiba, U.; Ali, S.; Hafeez, F.; Rizwan, M.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Hussain, A.; Asad, S.A. Morpho-physiological responses of maize cultivars exposed to chromium stress. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 21, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, H.; Khan, I.; Ahmad, A.; Iqbal, M. Induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant defence system in Brassica juncea and Vigna radiata in response to chromium treatments. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 61, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.A.d.C.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Suzuki, M.S.; Vitória, A.P. Plant chromium uptake and transport, physiological effects and recent advances in molecular investigations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 140, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Sharma, N.L.; Singh, C.K.; Sarkar, S.K.; Singh, I.; Dotaniya, M.L. Effect of chromium (VI) toxicity on morpho-physiological characteristics, yield, and yield components of two chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) varieties. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Bharwana, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Farid, M.; Kanwal, S.; Ali, Q.; Ibrahim, M.; Gill, R.A.; Khan, M.D. Fulvic acid mediates chromium (Cr) tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) through lowering of Cr uptake and improved antioxidant defense system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10601–10609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeel, A.; Xu, M.; Gan, Y. Chromium-induced reactive oxygen species accumulation by altering the enzymatic antioxidant system and associated cytotoxic, genotoxic, ultrastructural, and photosynthetic changes in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Xia, J. Chromium contamination accident in China: Viewing environment policy of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8605–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Wise, J.P.; Bassig, B.A.; Zhou, A.; Savitz, D.A.; Xiong, C.; Zhao, J.; et al. A case-control study of maternal exposure to chromium and infant low birth weight in China. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Xue, N.; Han, Z. A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Adhikari, S.; Ghosh, S.; Azahar, I.; Shaw, A.K.; Roy, D.; Roy, S.; Saha, S.; Hossain, Z. Imbalance of redox homeostasis and antioxidant defense status in maize under chromium (VI) stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 169, 103873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka, E.; Jurkowska, K.; Piwowar, A. Chromium (III) and chromium (VI) as important players in the induction of genotoxicity—current view. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Shamshad, S.; Rafiq, M.; Khalid, S.; Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C.; Rashid, M.I. Chromium speciation, bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, S.A.; Ashraf, U.; Khan, I.; Tanveer, M.; Shahid, M.; Shakoor, A.; Wang, L. Phyto-toxicity of chromium in maize: Oxidative damage, osmolyte accumulation, anti-oxidative defense and chromium uptake. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrees, M.; Ali, S.; Iqbal, M.; Aslam, S.; Siddiqi, Z.; Farid, M.; Ali, Q.; Saeed, R.; Rizwan, M. Mannitol alleviates chromium toxicity in wheat plants in relation to growth, yield, stimulation of anti-oxidative enzymes, oxidative stress and Cr uptake in sand and soil media. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, D.; Dey, S.; Raychaudhuri, S. Sen Chromium (VI)—Induced stress response in the plant Plantago ovata Forsk in vitro. Genes Environ. 2018, 40, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Dawood, M.; Farid, M.; Hussain, A.; Wijaya, L.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates chromium stress on cauliflower by restricting its uptake and enhancing antioxidative system. Physiol. Plant. 2019, 168, ppl.13001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Ma, Z.; Ye, Z.; Guo, X.; Qiu, R. Heavy metal (Pb, Zn) uptake and chemical changes in rhizosphere soils of four wetland plants with different radial oxygen loss. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, S.; Hussain, S.; Saud, S.; Hassan, S.; Shan, D.; Chen, Y.; Deng, N.; Khan, F.; Wu, C.; Wu, W.; et al. Grain cadmium and zinc concentrations in maize influenced by genotypic variations and zinc fertilization. CLEANSoil Air Water 2015, 43, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Santos, C.; Azevedo, R.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Correia, C.; Dias, M.C. Chromium (VI) induces toxicity at different photosynthetic levels in pea. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 53, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, R.A.; Zang, L.; Ali, B.; Farooq, M.A.; Cui, P.; Yang, S.; Ali, S.; Zhou, W. Chromium-induced physio-chemical and ultrastructural changes in four cultivars of Brassica napus L. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, A. Phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in plants growing under heavy metal stress. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ke, W.; Hou, H. Effect of salt stress on growth, physiological parameters, and ionic concentration of water dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 660409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Zhou, K.; Khan, S.; Ke, W.; Hou, H. Investigation of an antioxidative system for salinity tolerance in Oenanthe javanica. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Y.N.; Lee, L.K.; Zakaria, N.A.; Foo, K.Y. Phytotoxic effects of trivalent chromium-enriched water irrigation in Vigna unguiculata seedling. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.A.; Zhang, N.; Ali, B.; Farooq, M.A.; Xu, J.; Gill, M.B.; Mao, B.; Zhou, W. Role of exogenous salicylic acid in regulating physio-morphic and molecular changes under chromium toxicity in black- and yellow- seeded Brassica napus L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 20483–20496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadif, W.M.; Rahim, S.A.; Sahid, I.; Rahman, A.; Ibrahima, I. Influence of chromium metal on chlorophyll content in leaves of paddy Oryza sativa L. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2015, 13, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajpayee, P.; Tripathi, R.; Rai, U.; Ali, M.; Singh, S. Chromium (VI) accumulation reduces chlorophyll biosynthesis, nitrate reductase activity and protein content in Nymphaea alba L. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, P.; Kumar, V.; Joshi, U.N. Effect of chromium(VI) toxicity on enzymes of nitrogen metabolism in xlusterbean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.). Enzyme Res. 2014, 2014, 784036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, V.; Vajpayee, P.; Singh, S.N.; Mehrotra, S. Effect of chromium accumulation on photosynthetic pigments, oxidative stress defense system, nitrate reduction, proline level and eugenol content of Ocimum tenuiflorum L. Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, O.P.; Dubey, S.; Rai, U.N. Preferential accumulation of cadmium and chromium: Toxicity in Bacopa monnieri L. under mixed metal treatments. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 78, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iese, V.; Holland, E.; Wairiu, M.; Havea, R.; Patolo, S.; Nishi, M.; Hoponoa, T.; Bourke, R.M.; Dean, A.; Waqainabete, L. Facing food security risks: The rise and rise of the sweet potato in the Pacific Islands. Glob. Food Sec. 2018, 18, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, R.; Sivasankar, S. Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas [L.] Lam)—A valuable medicinal food: A review. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussoline, W.A.; Bohac, J.R.; Boman, B.J.; Trupia, S.; Wilkie, A.C. Agronomic productivity, bioethanol potential and postharvest storability of an industrial sweetpotato cultivar. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 95, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurie, S.M.; Faber, M.; Claasen, N. Incorporating orange-fleshed sweet potato into the food system as a strategy for improved nutrition: The context of South Africa. Food Res. Int. 2018, 104, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Mishra, D.; Buragohain, A.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Chakraborty, N. Comparative analysis of phytochemicals and nutrient availability in two contrasting cultivars of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Food Chem. 2015, 173, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.F.; Tu, Z.C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wen, Q.H.; Huang, T. Antioxidant activities and polyphenols of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) leaves extracted with solvents of various polarities. Food Biosci. 2016, 15, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, K.; Toyama, J.; Yoshimoto, M. Nutrition and utilization of a new sweetpotato cultivar for tops. In Proceedings of the 13th ISTRC Symposium, Arusha, Tanzania, 10–14 November 2007; pp. 550–553. [Google Scholar]
- Kurata, R.; Adachi, M.; Yamakawa, O.; Yoshimoto, M. Growth suppression of human cancer cells by polyphenolics from sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.) leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Mu, T.; Xi, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J. Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) leaves as nutritional and functional foods. Food Chem. 2014, 156, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwanga, R.O.M.; Andrade, M.I.; Carey, E.E.; Low, J.W.; Yencho, G.C.; Grüneberg, W.J. Sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.). In Genetic Improvement of Tropical Crops; Campos, H., Caligari, P.D.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 181–218. ISBN 978-3-319-59817-8. [Google Scholar]
- Altaf, M.A.; Shu, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Mumtaz, M.A.; Wang, Z. Vanadium toxicity induced changes in growth, antioxidant profiling, and vanadium uptake in pepper (Capsicum annum L.) seedlings. Horticulturae 2021, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Jiménez, A.; Trejo-Téllez, L.I.; Guillén-Sánchez, D.; Gómez-Merino, F.C. Vanadium stimulates pepper plant growth and flowering, increases concentrations of amino acids, sugars and chlorophylls, and modifies nutrient concentrations. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, X.; Qing, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X. Selenium alleviated chromium stress in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. Pekinensis) by regulating root morphology and metal element uptake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilon-Smits, E.A.; Quinn, C.F.; Tapken, W.; Malagoli, M.; Schiavon, M. Physiological functions of beneficial elements. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña-Sánchez, W.D.; León-Morales, J.M.; López-Bibiano, Y.; Hernández-Hernández, M.; Langarica-Velázquez, E.C.; García-Morales, S. Effect of V, Se, and Ce on growth, photosynthetic pigments, and total phenol content of tomato and pepper seedlings. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.T.; Qiu, R.L.; Zeng, X.W.; Ying, R.R.; Yu, F.M.; Zhou, X.Y. Lead, zinc, cadmium hyperaccumulation and growth stimulation in Arabis paniculata Franch. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 66, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Jia, Y.; Gou, M.; Zeyer, J. Toxicity of vanadium in soil on soybean at different growth stages. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, M.; An, W.; Li, W.; Perumal, V.; Wu, C.; Sahi, S.V.; Sarkar, S.K. Chromium detoxification mechanism induced growth and antioxidant responses in vetiver (Chrysopogon zizanioides(L.) Roberty). J. Cent. South Univ. 2019, 26, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukta, R.H.; Khatun, M.R.; Nazmul Huda, A.K.M. Calcium induces phytochelatin accumulation to cope with chromium toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Interact. 2019, 14, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Kapoor, D.; Wang, J.; Shahzad, B.; Kumar, V.; Bali, A.S.; Jasrotia, S.; Zheng, B.; Yuan, H.; Yan, D. Chromium bioaccumulation and its impacts on plants: An overview. Plants 2020, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Gil-Díaz, M.; Lobo, M.C. Response of two barley cultivars to increasing concentrations of cadmium or chromium in soil during the growing period. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 163, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, M.A.; Wang, X.; Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A.; Ashraf, S.; Samreen, T.; Nadeem, S.M.; Jamil, M. Biochar mediated-alleviation of chromium stress and growth improvement of different maize cultivars in tannery polluted soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Tang, Y. Accumulation and biotransformation of vanadium in Opuntia microdasys. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, M.; Mohammadian, F. Vanadium effects on phenolic content and photosynthetic pigments of sunflower. South-Western J. Hortic. Biol. Environ. 2018, 9, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Gill, R.A.; Islam, F.; Farooq, M.A.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W. Ecotoxicological and interactive effects of copper and chromium on physiochemical, ultrastructural, and molecular profiling in Brassica napus L. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9248123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaheer, I.E.; Ali, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Yousaf, H.S.; Malik, A.; Abbas, Z.; Rizwan, M.; Abualreesh, M.H.; Alatawi, A.; Wang, X. Combined application of zinc and iron-lysine and its effects on morpho-physiological traits, antioxidant capacity and chromium uptake in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, S.; Kiran, S.; Fahad, S.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, M.A.; Tahir, F.A.; Rasheed, M.K.; Shahzad, K.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; et al. Alleviation of chromium toxicity in maize by Fe fortification and chromium tolerant ACC deaminase producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.A.; Ashraf, U.; Khan, I.; Saleem, M.F.; Wang, L.C. Chromium toxicity induced alterations in growth, photosynthesis, gas exchange attributes and yield formation in maize. Pakistan J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 53, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lv, C.; Xu, M.; Chen, G.; Lv, C.; Gao, Z. Photosynthesis performance, antioxidant enzymes, and ultrastructural analyses of rice seedlings under chromium stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhara Chary, N.; Kamala, C.T.; Samuel Suman Raj, D. Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 69, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.N.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Liu, J.; Rizwan, M.; Fahad, S.; Xu, Z.; Hu, L. Seed priming with melatonin coping drought stress in rapeseed by regulating reactive oxygen species detoxification: Antioxidant defense system, osmotic adjustment, stomatal traits and chloroplast ultrastructure perseveration. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucińska-Sobkowiak, R. Water relations in plants subjected to heavy metal stresses. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, V.; Kohli, S.K.; Kapoor, D.; Bakshi, P.; Sharma, P.; Arora, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Ahmad, P. Stress protective effect of Rhododendron arboreum leaves (MEL) on chromium-treated Vigna radiata plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, S.; Varghese, T.; Kumari, M. Effect of chromium on morphological features of tomato and brinjal. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 8, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Balasaraswathi, K.; Jayaveni, S.; Sridevi, J.; Sujatha, D.; Phebe Aaron, K.; Rose, C. Cr–induced cellular injury and necrosis in Glycine max L.: Biochemical mechanism of oxidative damage in chloroplast. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 118, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.; Kumar, R.G.; Verma, S.; Dubey, R. Effect of cadmium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide anion generation and activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice seedlings. Plant Sci. 2001, 161, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbarian, R.; Azizi, E.; Behdad, A.; Mirblook, A. Effects of chromium on enzymatic/nonenzymatic antioxidants and oxidant levels of Portulaca oleracea L. J. Med. Plants By-Prod. 2019, 8, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčik, J.; Babula, P.; Klejdus, B.; Hedbavny, J. Chromium uptake and consequences for metabolism and oxidative stress in chamomile plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7864–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qados, A.M.S.A. Effect of salt stress on plant growth and metabolism of bean plant Vicia faba (L.). J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2011, 10, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rastgoo, L.; Alemzadeh, A. Biochemical responses of Gouan (Aeluropus littoralis) to heavy metals stress. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza-Cózatl, D.G.; Moreno-Sánchez, R. Control of glutathione and phytochelatin synthesis under cadmium stress. Pathway modeling for plants. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 238, 919–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izbiańska, K.; Arasimowicz-Jelonek, M.; Deckert, J. Phenylpropanoid pathway metabolites promote tolerance response of lupine roots to lead stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisa, D.; Kayır, Ö.; Sağlam, N.; Şahin, S.; Öztürk, L.; Elmastaş, M. Changes of phenolic compounds in tomato associated with the heavy metal stress. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2019, 2, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- André, C.M.; Schafleitner, R.; Legay, S.; Lefèvre, I.; Aliaga, C.A.A.; Nomberto, G.; Hoffmann, L.; Hausman, J.; Larondelle, Y.; Evers, D. Gene expression changes related to the production of phenolic compounds in potato tubers grown under drought stress. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Saxena, R.; Singh, S. Chromium induced lipid peroxidation in the plants of Pistia stratiotes L.: Role of antioxidants and antioxidant enzymes. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, A.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ishaque, W.; Rasool, N.; Rehman, M.Z.; Bashir, A.; Abid, M.; Wu, L. Management of tannery wastewater for improving growth attributes and reducing chromium uptake in spinach through citric acid application. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10848–10856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, M.M.; Diao, X.-p.; ur Rehman, A.; Imtiaz, M.; Shakoor, A.; Altaf, M.A.; Younis, H.; Fu, P.; Ghani, M.U. Effect of vanadium on growth, photosynthesis, reactive oxygen species, antioxidant enzymes, and cell death of rice. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 2643–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Zhou, K.; Hou, H.; Ke, W.; Yang, J. Phenotypic, nutritional, and antioxidant characterization of blanched Oenanthe javanica for preferable cultivar. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 639639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Bahadur, S.; Hussain, A.; Saeed, S.; Khuram, I.; Ullah, M.; Shao, J.; Akhtar, N. Foliar epidermal micromorphology and its taxonomic significance in Polygonatum (Asparagaceae) using scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2020, 83, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, G.; Bishopp, A.; Heenatigala, P.P.M.; Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Kumar, S.; Duan, P.; Yao, L.; et al. A comparison of growth on mercuric chloride for three Lemnaceae species reveals differences in growth dynamics that effect their suitability for use in either monitoring or remediating ecosystems contaminated with mercury. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Qayyum, A.; Zhou, K.; Ke, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, G. Influence of blanching on the gene expression profile of phenylpropanoid, flavonoid and vitamin biosynthesis, and their accumulation in Oenanthe javanica. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
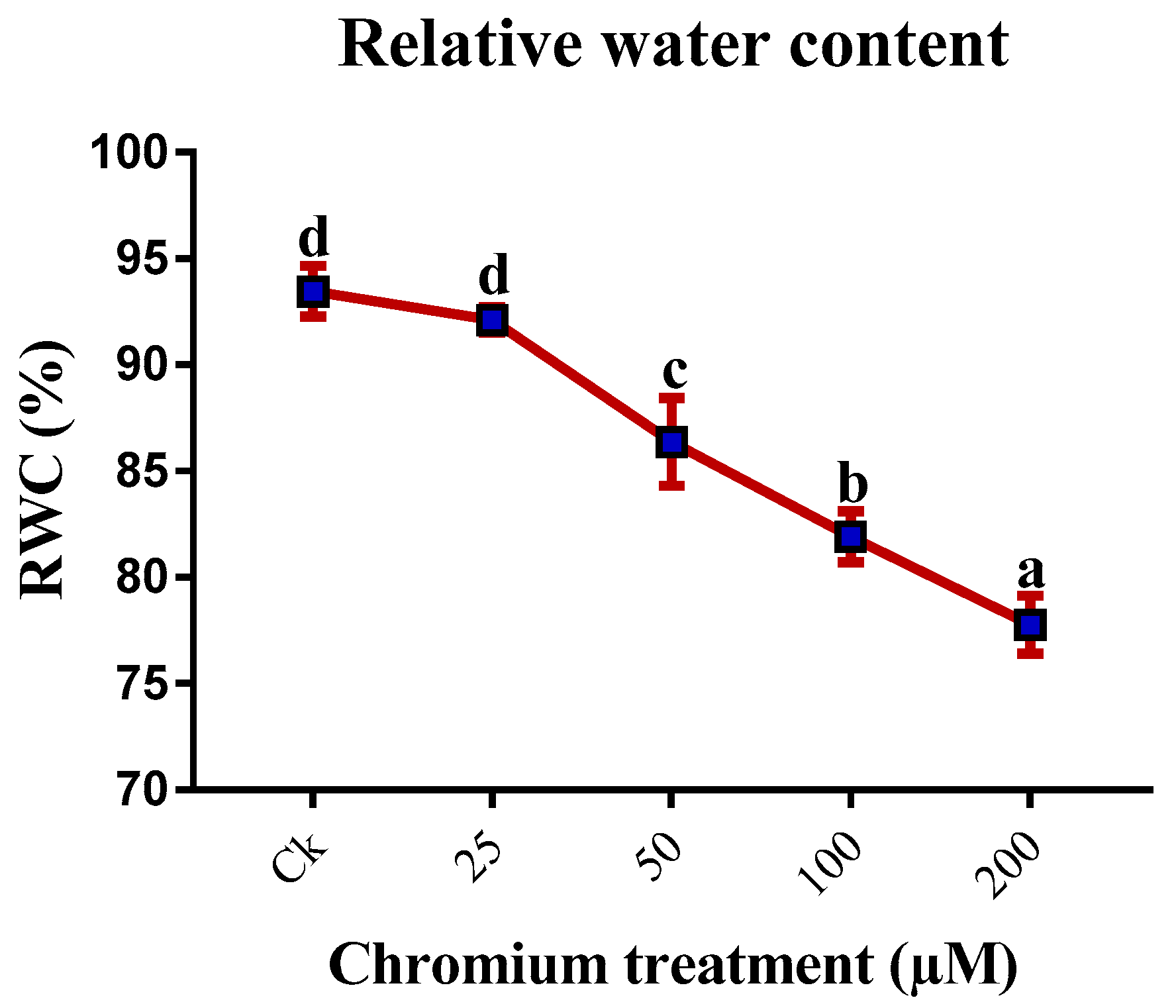
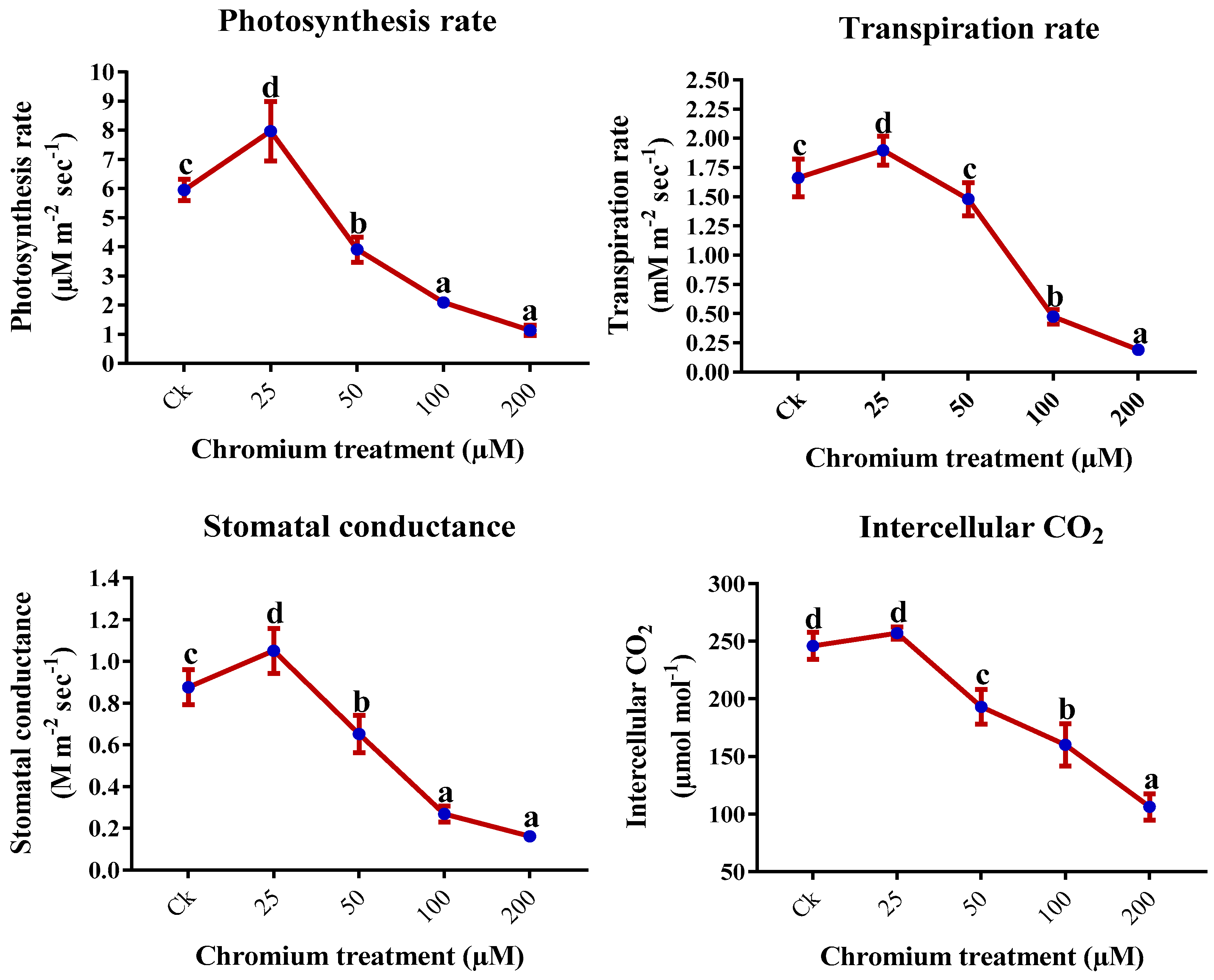
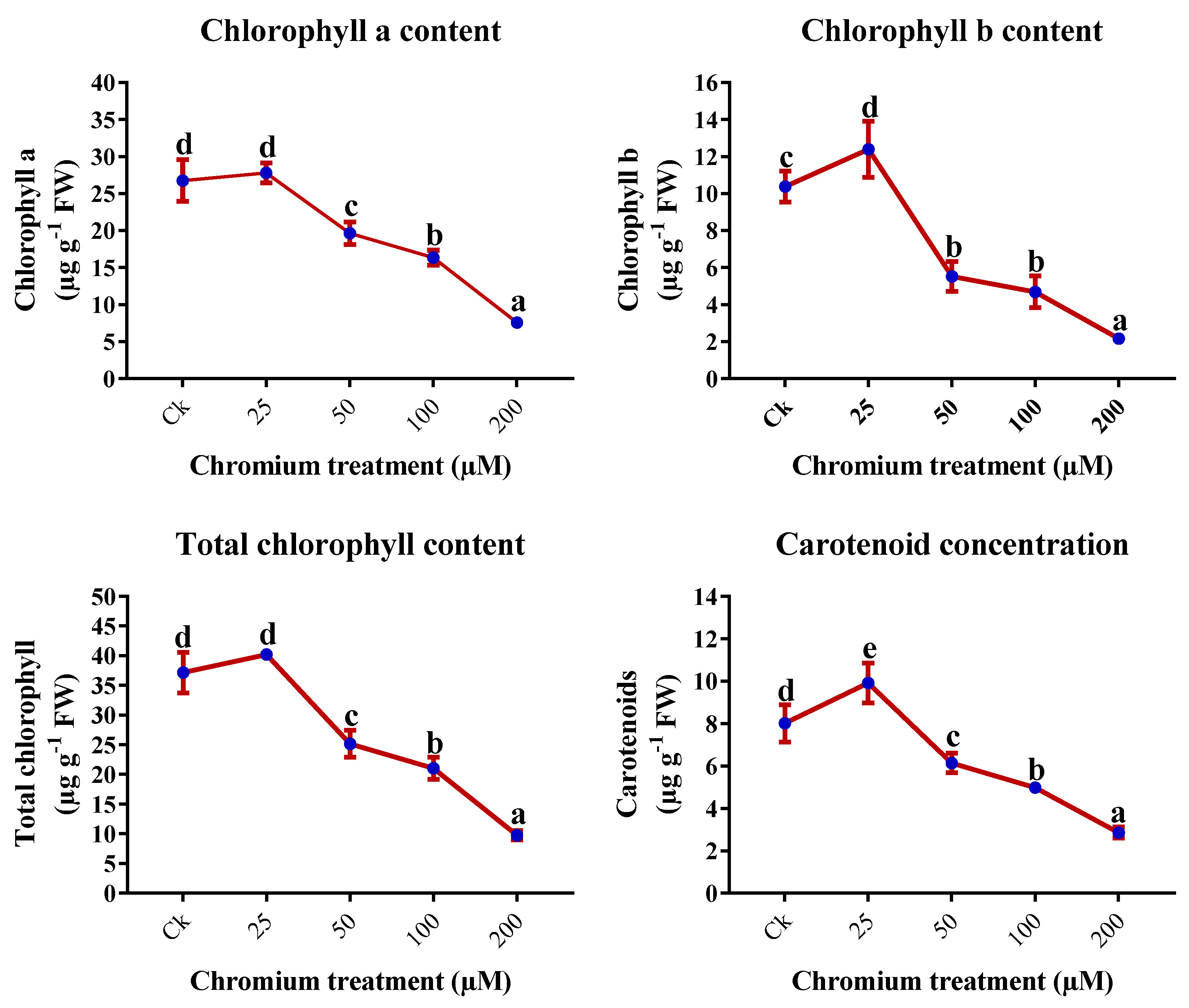
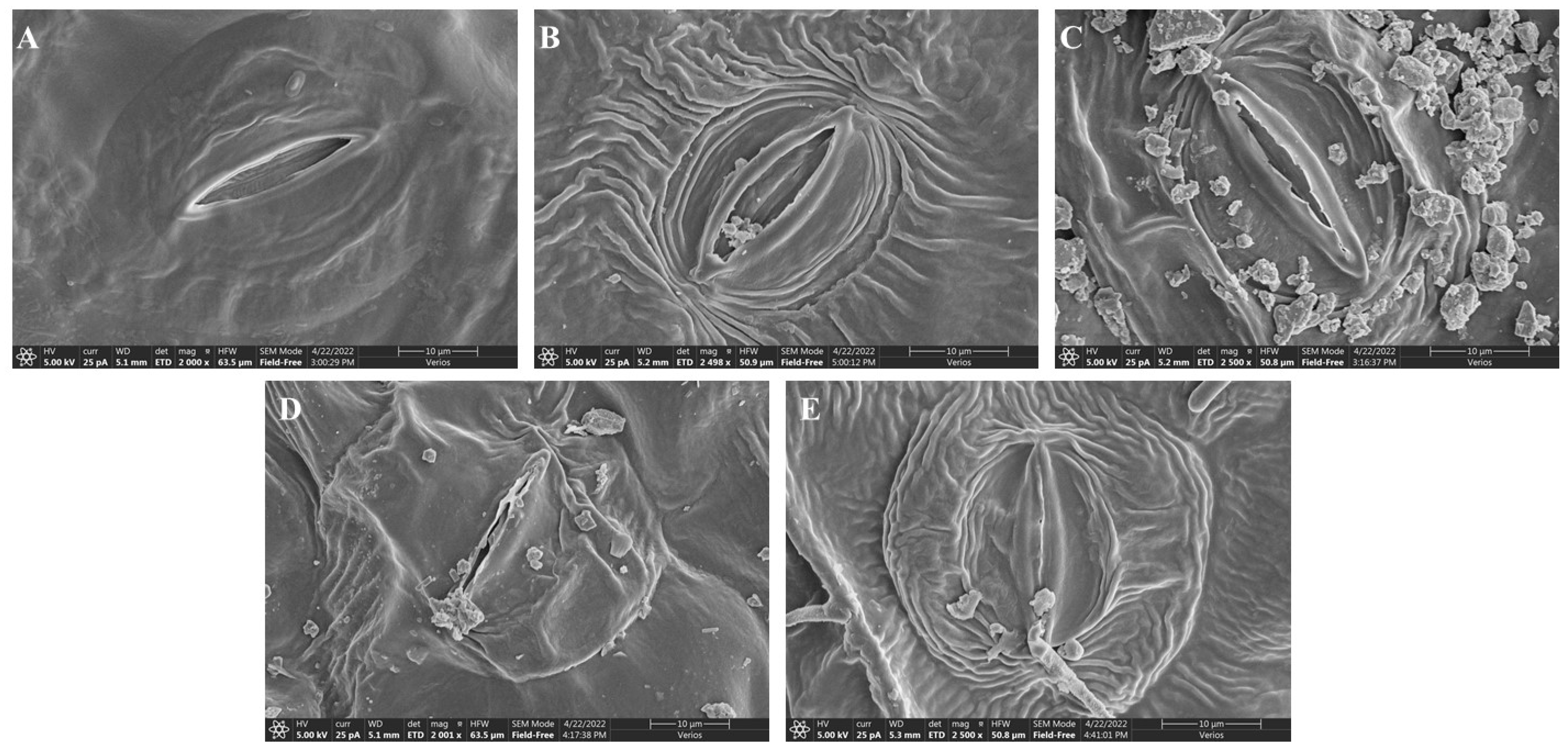
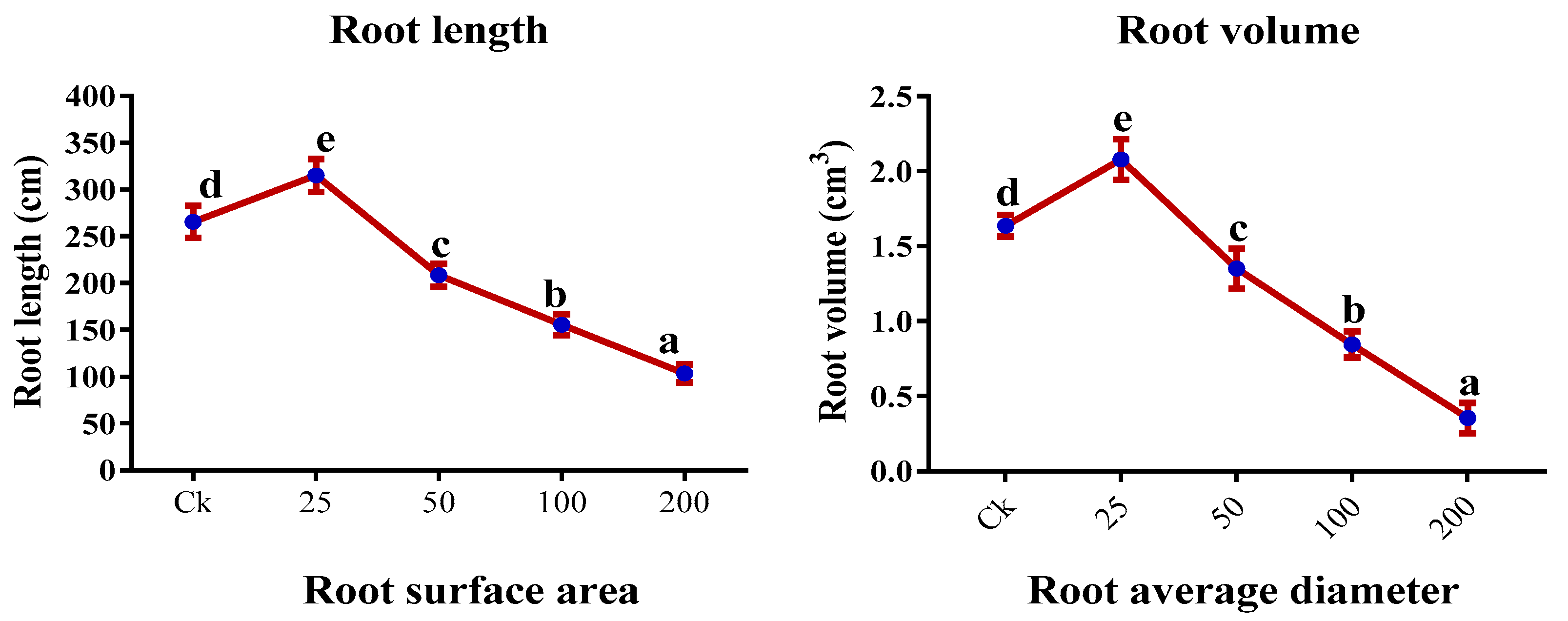
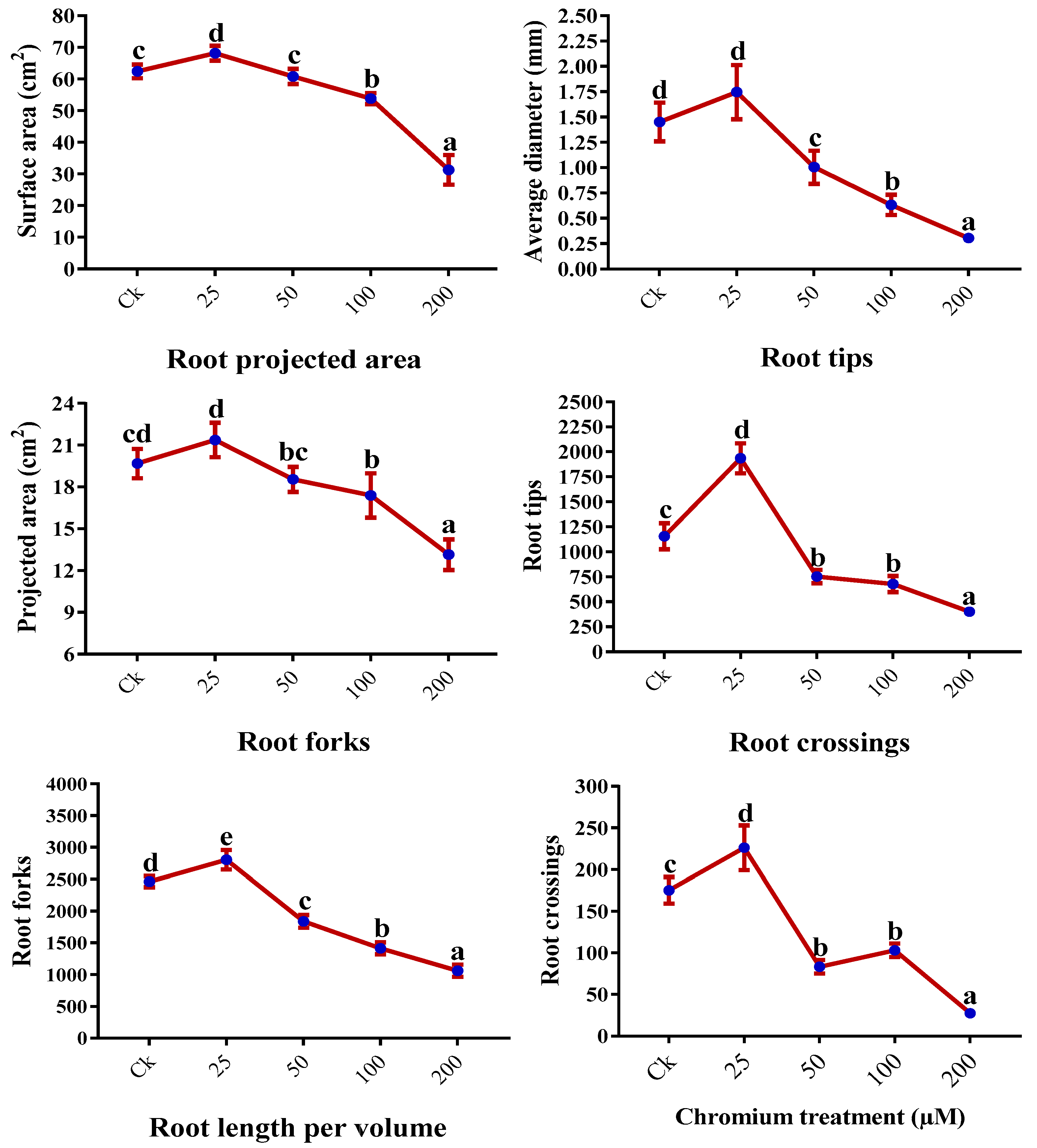
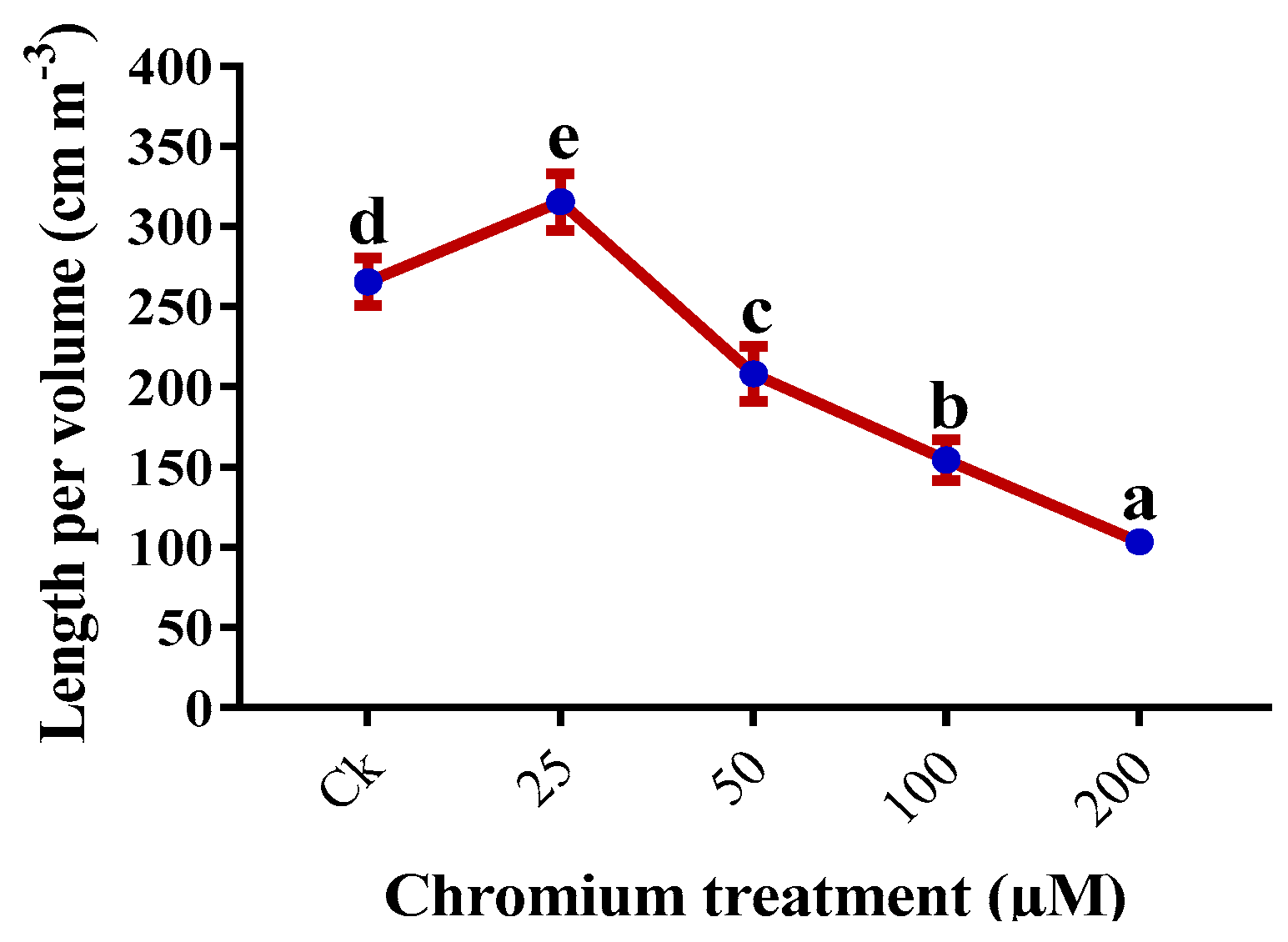

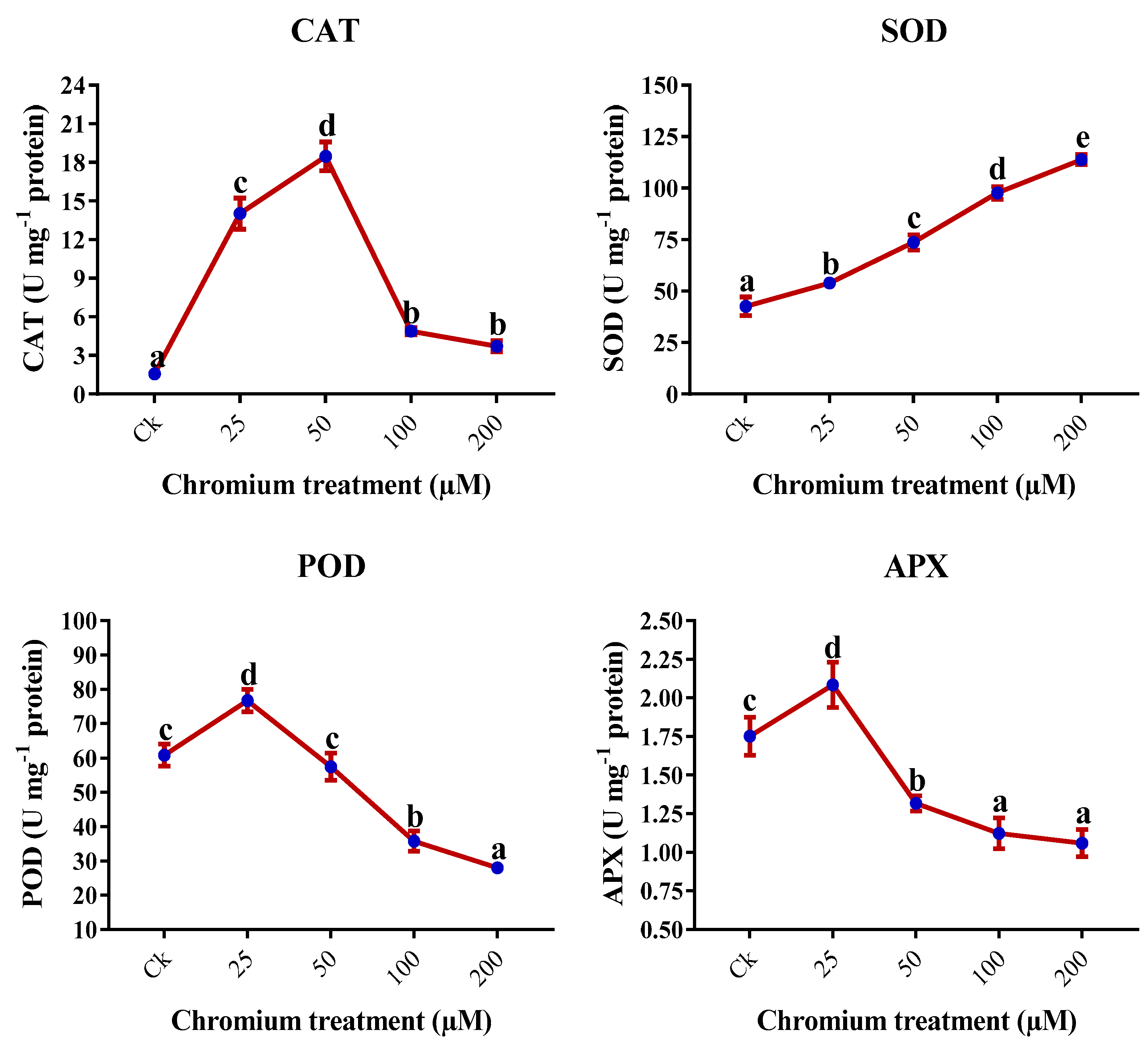
| Chromium (µM) | Height (cm) | Number of leaves | Leaf Area (cm2) | Shoot FW (g) | Root FW (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ck | 49.2 ± 3.4 c | 8.7 ± 0.6 c | 53.1 ± 3.2 c | 6.62 ± 0.4 d | 3.20 ± 0.5 cd |
| 25 | 57.0 ± 4.7 d | 9.3 ± 0.6 c | 60.5 ± 3.7 c | 7.14 ± 0.5 e | 3.54 ± 0.5 d |
| 50 | 44.5 ± 3.2 bc | 6.0 ± 1.0 b | 48.4 ± 5.0 b | 5.86 ± 0.7 c | 2.09 ± 0.2 bc |
| 100 | 39.6 ± 3.8 b | 4.7 ± 0.6 b | 42.5 ± 6.7 b | 4.31 ± 0.4 b | 1.60 ± 0.1 b |
| 200 | 24.9 ± 5.1 a | 3.7 ± 0.6 a | 33.9 ± 5.7 a | 3.43 ± 0.4 a | 1.12 ± 0.1 a |
| Chromium (µM) | Shoot DW (g) | Root DW (g) | SDSI | RDSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ck | 0.786 ± 0.09 d | 0.317 ± 0.02 d | 100 | 100 |
| 25 | 0.831 ± 0.08 e | 0.371 ± 0.04 e | 105.92 ± 2.6 d | 117.0 ± 2.8 d |
| 50 | 0.602 ± 0.06 c | 0.201 ± 0.02 c | 76.74 ± 2.5 c | 63.8 ± 9.5 c |
| 100 | 0.425 ± 0.05 b | 0.148 ± 0.02 b | 54.11 ± 0.6 b | 46.5 ± 4.4 b |
| 200 | 0.322 ± 0.05 a | 0.095 ± 0.01 a | 40.81 ± 2.4 a | 29.8 ± 0.9 a |
| Chromium (µM) | Stomata Length (µm) | Stomata Width (µm) | Stomatal Pore Length (µm) | Stomatal Pore Width (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ck | 26.19 ± 2.25 c | 16.15 ± 1.82 c | 19.47 ± 2.05 d | 3.94 ± 0.73 c |
| 25 | 25.68 ± 2.29 c | 14.97 ± 1.96 c | 19.15 ± 1.61 d | 3.65 ± 0.81 c |
| 50 | 18.43 ± 1.98 b | 8.88 ± 1.34 b | 11.54 ± 1.26 c | 1.51 ± 0.41 b |
| 100 | 15.35 ± 1.58 ab | 6.44 ± 1.07 b | 7.58 ± 1.24 b | 1.28 ± 0.23 b |
| 200 | 12.31 ± 1.13 a | 1.97 ± 0.55 a | 2.89 ± 0.62 a | 0.21 ± 0.08 a |
| Cr (µM) | Proline (µg g−1 FW) | S. Sugars (mg g−1 FW) | T. Proteins (mg g−1) | GSH (mg g−1 prot) | TPC (mg GAE g−1) | TFC (mg CAE g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ck | 15.12 ± 0.99 a | 7.09 ± 0.46 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 38.85 ± 1.89 a | 12.41 ± 0.92 d | 0.49 ± 0.04 c |
| 25 | 22.14 ± 1.74 b | 11.34 ± 1.01 b | 0.09 ± 0.01 ab | 71.44 ± 4.87 c | 9.61 ± 0.60 c | 0.35 ± 0.03 b |
| 50 | 35.49 ± 2.59 c | 14.29 ± 1.21 c | 0.11 ± 0.01 b | 58.11 ± 3.96 b | 7.17 ± 0.54 ab | 0.25 ± 0.01 a |
| 100 | 47.80 ± 4.02 d | 17.35 ± 1.25 d | 0.19 ± 0.02 c | 55.44 ± 3.06 b | 5.99 ± 0.43 a | 0.23 ± 0.02 a |
| 200 | 66.84 ± 4.79 e | 25.80 ± 1.46 e | 0.20 ± 0.02 c | 35.71 ± 2.40 a | 7.68 ± 0.74 b | 0.31 ± 0.02 b |
| Chromium (µM) | Concentration (mg kg−1 DW) | Uptake (mg kg−1 DW) | Translocation (Root to Shoot) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoot | Root | Shoot | Root | ||
| Ck | 0.26 ± 0.02 a | 2.33 ± 0.23 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.24 ± 0.02 a | 0.11 ± 0.02 a |
| 25 | 9.44 ± 0.62 a | 40.35 ± 2.06 b | 0.98 ± 0.05 a | 4.18 ± 0.15 b | 0.23 ± 0.00 b |
| 50 | 25.32 ± 1.16 b | 88.66 ± 9.03 c | 2.63 ± 0.14 b | 9.18 ± 0.80 c | 0.29 ± 0.03 c |
| 100 | 57.67 ± 5.20 c | 152.76 ± 13.94 d | 5.97 ± 0.45 c | 15.82 ± 1.22 d | 0.38 ± 0.01 d |
| 200 | 105.46 ± 12.73 d | 263.82 ± 7.63 e | 10.94 ± 1.41 d | 27.35 ± 1.11 e | 0.40 ± 0.04 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, S.; Wang, M.; Fahad, S.; Qayyum, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G. Chromium Induces Toxicity at Different Phenotypic, Physiological, Biochemical, and Ultrastructural Levels in Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113496
Kumar S, Wang M, Fahad S, Qayyum A, Chen Y, Zhu G. Chromium Induces Toxicity at Different Phenotypic, Physiological, Biochemical, and Ultrastructural Levels in Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113496
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Sunjeet, Mengzhao Wang, Shah Fahad, Abdul Qayyum, Yanli Chen, and Guopeng Zhu. 2022. "Chromium Induces Toxicity at Different Phenotypic, Physiological, Biochemical, and Ultrastructural Levels in Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113496
APA StyleKumar, S., Wang, M., Fahad, S., Qayyum, A., Chen, Y., & Zhu, G. (2022). Chromium Induces Toxicity at Different Phenotypic, Physiological, Biochemical, and Ultrastructural Levels in Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113496









