Cytokine Profiling in Different SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
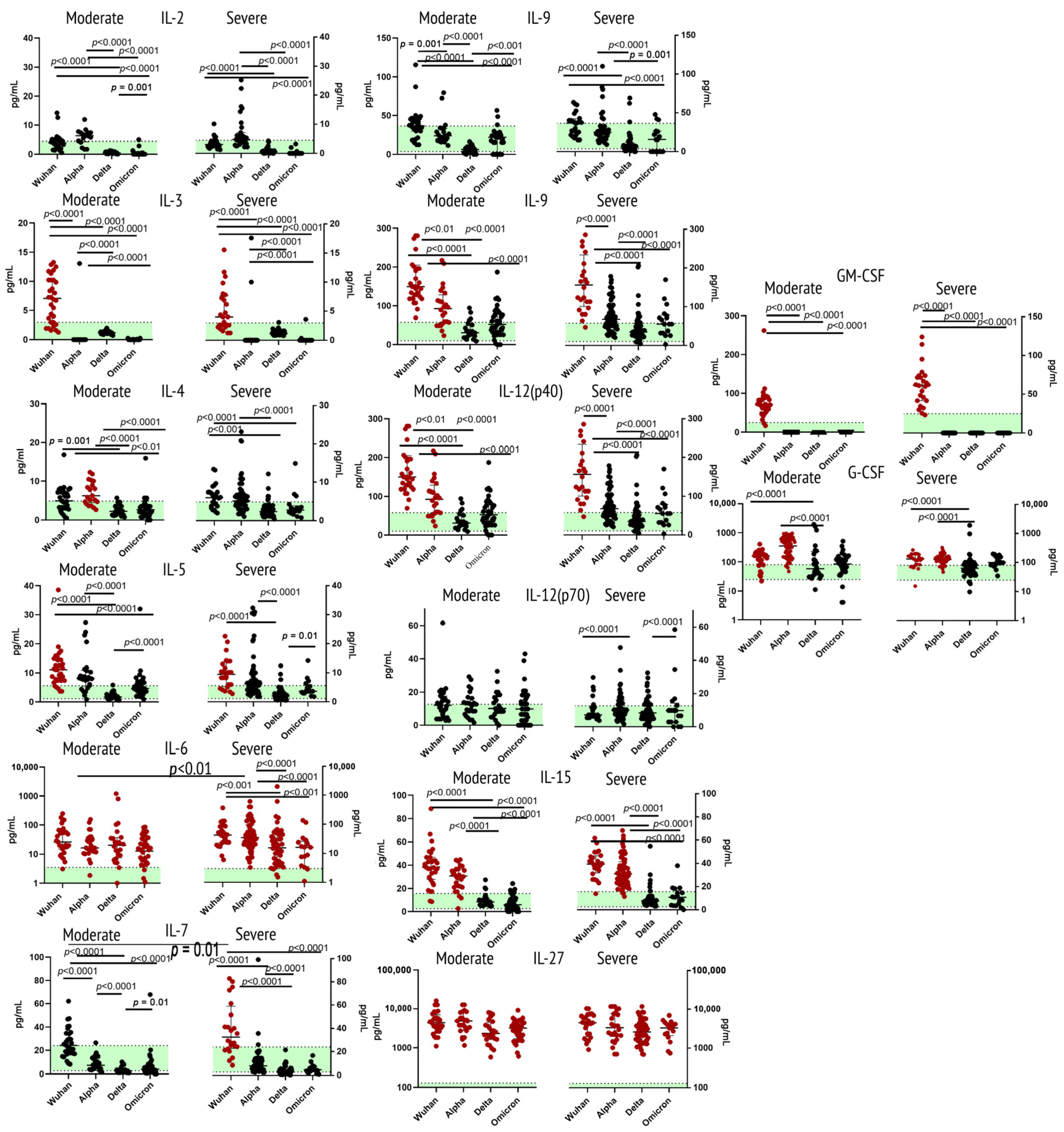
2. Results
2.1. Cytokines of Type I Receptor Family
2.2. Cytokines of Type II Receptor Family & TNF Receptor Superfamily
2.3. Cytokines of Immunoglobulin Superfamily
2.4. Cytokines/Growth Factors of Other Receptor Families
3. Discussion
3.1. Cytokines of Type I Receptor Family
3.1.1. Interleukin 2
3.1.2. Interleukin 3
3.1.3. Interleukin 4
3.1.4. Interleukin 5
3.1.5. Interleukin 6
3.1.6. Interleukin 7
3.1.7. Interleukin 9
3.1.8. Interleukin 12 (p40 & p70)
3.1.9. Interleukin 15
3.1.10. Interleukin 27
3.1.11. G-CSF and GM-CSF
3.2. Cytokines of Type II Receptor Family and TNF Receptor Superfamily
3.2.1. Interleukin 10
3.2.2. Interleukin 22
3.2.3. Interferons α and γ
3.2.4. Tumor Necrosis Factors α and β
3.3. Cytokines of Immunoglobulin Superfamily
3.3.1. Interleukin 1 (α and β) and Its Receptor Antagonist
3.3.2. Interleukin 18
3.3.3. Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
3.3.4. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (AA and AA/BB)
3.4. Cytokines/Growth Factors of Other Receptor Families
3.4.1. Interleukin-17A
3.4.2. Epidermal Growth Factor
3.4.3. Fibroblast Growth Factor-2
3.4.4. Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase 3 Ligand
3.4.5. Transforming Growth Factor Alpha
3.4.6. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
3.5. Constant Markers of COVID-19 Infection (IL-6, IL-10, IL-18, IL-27)
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genetic Testing
4.2. Patients
4.3. Disease Severity Assessment
4.4. Cytokine Concentrations Measurement
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72,314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebecca, H. A Case Fatality Rate. Encyclopedia Britannica, 5 May 2020. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/case-fatality-rate (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- WHO. COVID-19 Monitoring. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Melo, A.K.G.; Milby, K.M.; Caparroz, A.L.M.A.; Pinto, A.C.P.N.; Santos, R.R.P.; Rocha, A.P.; Ferreira, G.A.; Souza, V.A.; Valadares, L.D.A.; Vieira, R.M.R.A.; et al. Biomarkers of cytokine storm as red flags for severe and fatal COVID-19 cases: A living systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Pan, H.; Li, R.; He, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L. Increased Circulating Cytokines Have a Role in COVID-19 Severity and Death With a More Pronounced Effect in Males: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 802228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulchandani, R.; Lyngdoh, T.; Kakkar, A.K. Deciphering the COVID-19 cytokine storm: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazersaheb, S.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S.M.; Hejazi, M.S.; Tarhriz, V.; Farjami, A.; Ghasemian Sorbeni, F.; Farahzadi, R.; Ghasemnejad, T. COVID-19 infection: An overview on cytokine storm and related interventions. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. COVID-19 Clinical Management: Living Guidance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-clinical-2021-2 (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Arsentieva, N.A.; Liubimova, N.E.; Batsunov, O.K.; Korobova, Z.R.; Stanevich, O.V.; Lebedeva, A.A.; Vorobyov, E.A.; Vorobyova, S.V.; Kulikov, A.N.; Lioznov, D.A.; et al. Plasma cytokines in patients with COVID-19 during acute phase of the disease and following complete recovery. Med. Immunol. 2021, 23, 311–326. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, H.; Bayer, W. Changes in Symptoms Experienced by SARS-CoV-2-Infected Individuals—From the First Wave to the Omicron Variant. Front. Virol. 2022, 2, 880707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente-González, M.; Suarez-Ortiz, M.; Landete, P. Evolution and Clinical Trend of SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Open Respir. Arch. 2022, 4, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Veyer, D.; Baidaliuk, A.; Staropoli, I.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Rajah, M.M.; Planchais, C.; Porrot, F.; Robillard, N.; Puech, J.; et al. Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization. Nature 2021, 596, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, A.; Dedkov, V.; Sharova, A.; Klyuchnikova, E.; Sbarzaglia, V.; Arbuzova, T.; Forghani, M.; Ramsay, E.; Dolgova, A.; Shabalina, A.; et al. Uninvited Guest: Arrival and Dissemination of Omicron Lineage SARS-CoV-2 in St. Petersburg, Russia. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendickova, K.; Fric, J. Roles of IL-2 in bridging adaptive and innate immunity, and as a tool for cellular immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle-Mendoza, J.; Tarazona-Castro, Y.; Merino-Luna, A.; Carrillo-Ng, H.; Kym, S.; Aguilar-Luis, M.A.; Del Valle, L.J.; Aquino-Ortega, R.; Martins-Luna, J.; Peña-Tuesta, I.; et al. Comparison of cytokines levels among COVID-19 patients living at sea level and high altitude. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjan, L.H.; Furukawa, K.; Nagano, T.; Kiriu, T.; Nishimura, M.; Arii, J.; Hino, Y.; Iwata, S.; Nishimura, Y.; Mori, Y. Early Differences in Cytokine Production by Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, C.M.; Sieff, C.A.; Mathey-Prevot, B.; Wimperis, J.Z.; Bierer, B.E.; Clark, S.C.; Nathan, D.G. Expression of human interleukin-3 (multi-CSF) is restricted to human lymphocytes and T-cell tumor lines. Blood 1989, 73, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guthridge, M.A.; Stomski, F.C.; Thomas, D.; Woodcock, J.M.; Bagley, C.J.; Berndt, M.C.; Lopez, A.F. Mechanism of Activation of the GM-CSF, IL-3, and IL-5 Family of Receptors. Stem Cells 1998, 16, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bénard, A.; Jacobsen, A.; Brunner, M.; Krautz, C.; Klösch, B.; Swierzy, I.; Naschberger, E.; Podolska, M.J.; Kouhestani, D.; David, P.; et al. Interleukin-3 is a predictive marker for severity and outcome during SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junttila, I.S. Tuning the Cytokine Responses: An Update on Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaz de Paula, C.B.; de Azevedo, M.L.V.; Nagashima, S.; Martins, A.P.C.; Malaquias, M.A.S.; Miggiolaro, A.F.R.D.S.; da Silva Motta Júnior, J.; Avelino, G.; do Carmo, L.A.P.; Carstens, L.B.; et al. IL-4/IL-13 remodeling pathway of COVID-19 lung injury. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobova, Z.R.; Zueva, E.V.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Batsunov, O.K.; Liubimova, N.E.; Khamitova, I.V.; Kuznetsova, R.N.; Rubinstein, A.A.; Savin, T.V.; Stanevich, O.V.; et al. Changes in Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Subclasses over Time and in Association with Disease Severity. Viruses 2022, 14, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouro, T.; Takatsu, K. IL-5- and eosinophil-mediated inflammation: From discovery to therapy. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y.; Tang, X. Relationship between blood eosinophil levels and COVID-19 mortality. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korobova, Z.R.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Liubimova, N.E.; Dedkov, V.G.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Sharova, A.A.; Chernykh, E.I.; Kashchenko, V.A.; Ratnikov, V.A.; Gorelov, V.P.; et al. A Comparative Study of the Plasma Chemokine Profile in COVID-19 Patients Infected with Different SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H. Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Tang, T.X.; Deng, H.; Yang, X.P.; Tang, Z.H. Interleukin-7 Biology and Its Effects on Immune Cells: Mediator of Generation, Differentiation, Survival, and Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 747324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakin, E.A.; Stanevich, O.V.; Chmelevsky, M.P.; Belash, V.A.; Belash, A.A.; Savateeva, G.A.; Bokinova, V.A.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Sayenko, L.F.; Korobenkov, E.A.; et al. A Novel Approach for COVID-19 Patient Condition Tracking: From Instant Prediction to Regular Monitoring. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 744652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, Y.; Sui, Y.; Berzofsky, J.A. IL-7 in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and as a Potential Vaccine Adjuvant. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 737406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Gao, H.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.Z.; Lu, J.H.; Li, L.; Wang, H.B.; Zhao, L.; Rong, Y.X.; et al. Serum IP-10 and IL-7 levels are associated with disease severity of coronavirus disease 2019. Cytokine 2021, 142, 155500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monneret, G.; de Marignan, D.; Coudereau, R.; Bernet, C.; Ader, F.; Frobert, E.; Gossez, M.; Viel, S.; Venet, F.; Wallet, F. Immune monitoring of interleukin-7 compassionate use in a critically ill COVID-19 patient. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, E.; Bopp, T. Amazing IL-9: Revealing a new function for an “old” cytokine. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3857–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazavi, A.; Ganji, A.; Keshavarzian, N.; Rabiemajd, S.; Mosayebi, G. Cytokine profile and disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Cytokine 2021, 137, 155323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, H.; Peng, D.; Hu, Y.; Tang, S.; Li, S.; Huang, Q. Interleukin-9-secreting CD4+ T cells regulate CD8+ T cells cytotoxicity in patients with acute coronary syndromes. APMIS 2021, 129, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; He, C.; Nair, L.; Yeung, J.; Egwuagu, C.E. Interleukin 12 (IL-12) family cytokines: Role in immune pathogenesis and treatment of CNS autoimmune disease. Cytokine 2015, 75, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moll-Bernardes, R.; de Sousa, A.S.; Macedo, A.V.S.; Lopes, R.D.; Vera, N.; Maia, L.C.R.; Feldman, A.; Arruda, G.D.A.S.; Castro, M.J.C.; Pimentel-Coelho, P.M.; et al. IL-10 and IL-12 (P70) Levels Predict the Risk of Covid-19 Progression in Hypertensive Patients: Insights From the BRACE-CORONA Trial. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 702507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethuin, F.; Delarche, C.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A.; Eurin, B.; Jacob, L.; Chollet-Martin, S. Regulation of Interleukin 12 p40 and p70 Production by Blood and Alveolar Phagocytes During Severe Sepsis. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perera, P.Y.; Lichy, J.H.; Waldmann, T.A.; Perera, L.P. The role of interleukin-15 in inflammation and immune responses to infection: Implications for its therapeutic use. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergamaschi, C.; Terpos, E.; Rosati, M.; Angel, M.; Bear, J.; Stellas, D.; Karaliota, S.; Apostolakou, F.; Bagratuni, T.; Patseas, D.; et al. Systemic IL-15, IFN-γ, and IP-10/CXCL10 signature associated with effective immune response to SARS-CoV-2 in BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine recipients. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, J.W.; Bai, X.F. IL27: Its roles in the induction and inhibition of inflammation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2008, 1, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Korobova, Z.R.; Isakov, D.V.; Rubinstein, A.A.; Batsunov, O.K.; Khamitova, I.V.; Kuznetsova, R.N.; Savin, T.V.; Akisheva, T.V.; et al. Heterogenous CD8+ T Cell Maturation and ‘Polarization’ in Acute and Convalescent COVID-19 Patients. Viruses 2022, 14, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Roberts, A.; Das, J.; Xu, G.; Ren, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Z.R.; Tan, H.S.W.; et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and T-cell responses: What we do and don’t know. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, K.N.; Blount, D.G.; Riley, E.M. IL-10: The Master Regulator of Immunity to Infection. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5771–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, P.; Tracey, K.J.; Wang, H. Possible inhibition of GM-CSF production by SARS-CoV-2 spike-based vaccines. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, H.; Chamberlain, T.C.; Mui, A.L.; Little, J.P. Elevated Interleukin-10 Levels in COVID-19: Potentiation of Pro-Inflammatory Responses or Impaired Anti-Inflammatory Action? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 677008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, H.; Dauphars, D.J.; He, Y.W. A Potential Role of Interleukin 10 in COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudakov, J.A.; Hanash, A.M.; van den Brink, M.R. Interleukin-22: Immunobiology and pathology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 747–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, S.; Ju, D.; Lin, Y.; Chen, W. The role of interleukin-22 in lung health and its therapeutic potential for COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 951107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayrak, N.; Orte Cano, C.; Karimi, S.; Dogahe, D.; Van Praet, A.; Godefroid, A.; Del Marmol, V.; Grimaldi, D.; Bondue, B.; Van Vooren, J.P.; et al. Distinct Expression Patterns of Interleukin-22 Receptor 1 on Blood Hematopoietic Cells in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 769839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, M.A.; de Castro, J.T.; Takano, C.Y.; Ho, P.L. Off balance: Interferons in COVID-19 lung infections. EBioMedicine 2021, 73, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallach, D. The Tumor Necrosis Factor Family: Family Conventions and Private Idiosyncrasies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, B.K.; Guevara-Coto, J.; Yogendra, R.; Francisco, E.B.; Long, E.; Pise, A.; Rodrigues, H.; Parikh, P.; Mora, J.; Mora-Rodríguez, R.A. Immune-Based Prediction of COVID-19 Severity and Chronicity Decoded Using Machine Learning. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Evidence that TNF-β (lymphotoxin α) can activate the inflammatory environment in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alefishat, E.; Jelinek, H.F.; Mousa, M.; Tay, G.K.; Alsafar, H.S. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 variants: A focus on severity, susceptibility, and preexisting immunity. J. Infect. Public Health. 2022, 15, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaremi, S.; Asgarzadeh, A.; Kianfar, H.; Mohammadnia, A.; Asghariazar, V.; Safarzadeh, E. The role of IL-1 family of cytokines and receptors in pathogenesis of COVID-19. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 923–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Cardona-Ospina, J.A.; Gutiérrez-Ocampo, E.; Villamizar-Peña, R.; Holguin-Rivera, Y.; Escalera-Antezana, J.P.; Alvarado-Arnez, L.E.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Henao-Martinez, A.F.; et al. Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 34, 101623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahtinen, S.; Tong, A.J.; Himmels, P.; Oh, J.; Paler-Martinez, A.; Kim, L.; Wichner, S.; Oei, Y.; McCarron, M.J.; Freund, E.C.; et al. IL-1 and IL-1ra are key regulators of the inflammatory response to RNA vaccines. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushach, I.; Zlotnik, A. Biological role of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) on cells of the myeloid lineage. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, W.; Wu, T.; Wen, T.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Huang, C.; Jiao, Y.; et al. Serum Cytokine and Chemokine Profile in Relation to the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, G.F.; Mustoe, T.A.; Altrock, B.W.; Deuel, T.F.; Thomason, A. Role of platelet-derived growth factor in wound healing. J. Cell Biochem. 1991, 45, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinina, O.; Golovkin, A.; Zaikova, E.; Aquino, A.; Bezrukikh, V.; Melnik, O.; Vasilieva, E.; Karonova, T.; Kudryavtsev, I.; Shlyakhto, E. Cytokine Storm Signature in Patients with Moderate and Severe COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlallah, S.; Sham Eddin, M.S.; Rahal, E.A. IL-17A in COVID-19 Cases: A meta-analysis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourgholaminejad, A.; Pahlavanneshan, S.; Basiri, M. COVID-19 immunopathology with emphasis on Th17 response and cell-based immunomodulation therapy: Potential targets and challenges. Scand. J. Immunol. 2022, 95, e13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smadja, D.M.; Philippe, A.; Bory, O.; Gendron, N.; Beauvais, A.; Gruest, M.; Peron, N.; Khider, L.; Guerin, C.L.; Goudot, G.; et al. Placental growth factor level in plasma predicts COVID-19 severity and in-hospital mortality. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsapogas, P.; Mooney, C.J.; Brown, G.; Rolink, A. The Cytokine Flt3-Ligand in Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McInnes, C.; Wang, J.; Al Moustafa, A.E.; Yansouni, C.; O’Connor-McCourt, M.; Sykes, B.D. Structure-based minimization of transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-alpha) through NMR analysis of the receptor-bound ligand. Design, solution structure, and activity of TGF-alpha 8-50. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27357–27363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dülger, S.U.; Mutlu, N.; Ceylan, İ.; Özhan, E. The relationship between lung fibrosis, the epidermal growth factor receptor, and disease outcomes in COVID-19 pneumonia: A postmortem evaluation. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y. VEGF-targeted cancer therapeutics-paradoxical effects in endocrine organs. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñaloza, H.F.; Nieto, P.A.; Muñoz-Durango, N.; Salazar-Echegarai, F.J.; Torres, J.; Parga, M.J.; Alvarez-Lobos, M.; Riedel, C.A.; Kalergis, A.M.; Bueno, S.M. Interleukin-10 plays a key role in the modulation of neutrophils recruitment and lung inflammation during infection by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Immunology 2015, 146, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barthelemy, A.; Ivanov, S.; Fontaine, J.; Soulard, D.; Bouabe, H.; Paget, C.; Faveeuw, C.; Trottein, F. Influenza A virus-induced release of interleukin-10 inhibits the anti-microbial activities of invariant natural killer T cells during invasive pneumococcal superinfection. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jablonska, E.; Jablonski, J. Effect of IL-18 on the release of IL-6 and its soluble receptors: sIL-6Ralpha and sgp130 by human neutrophils. Immunol. Investig. 2002, 31, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variant | Wuhan (n = 59) | Alpha (n = 95) | Delta (n = 78) | Omicron (n = 57) | Healthy Donors (n = 51) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years Me (Q25–Q75) | 58 (32–75) | 72 (28–84) | 71 (45–93) | 69 (32–910) | 49 (24–69) | |
| Gender distribution | Female% (n) | 66.1% (n = 39) | 52.7% (n = 50) | 64.1% (n = 50) | 61.4% (n = 35) | 58.8% (n = 30) |
| Male, % (n) | 33.3% (n = 20) | 47.3% (n = 45) | 35.9% (n = 28) | 38.6% (n = 22) | 41.2% (n = 21) | |
| Variant | Patients, Diagnosed with ‘Moderate’ Infection | Patients, Diagnosed with ‘Severe’ Infection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | n | % | n | |
| Ancestral Wuhan | 54.2 | 32 | 45.7 | 27 |
| Alpha | 26.6 | 35 | 73.6 | 60 |
| Delta | 34.6 | 27 | 65.4 | 51 |
| Omicron | 75.4 | 43 | 24.6 | 14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korobova, Z.R.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Liubimova, N.E.; Batsunov, O.K.; Dedkov, V.G.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Sharova, A.A.; Adish, Z.; Chernykh, E.I.; Kaschenko, V.A.; et al. Cytokine Profiling in Different SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214146
Korobova ZR, Arsentieva NA, Liubimova NE, Batsunov OK, Dedkov VG, Gladkikh AS, Sharova AA, Adish Z, Chernykh EI, Kaschenko VA, et al. Cytokine Profiling in Different SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(22):14146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214146
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorobova, Zoia R., Natalia A. Arsentieva, Natalia E. Liubimova, Oleg K. Batsunov, Vladimir G. Dedkov, Anna S. Gladkikh, Alena A. Sharova, Zhansaya Adish, Ekaterina I. Chernykh, Victor A. Kaschenko, and et al. 2022. "Cytokine Profiling in Different SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 22: 14146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214146
APA StyleKorobova, Z. R., Arsentieva, N. A., Liubimova, N. E., Batsunov, O. K., Dedkov, V. G., Gladkikh, A. S., Sharova, A. A., Adish, Z., Chernykh, E. I., Kaschenko, V. A., Ratnikov, V. A., Gorelov, V. P., Stanevich, O. V., Kulikov, A. N., Pevtsov, D. E., & Totolian, A. A. (2022). Cytokine Profiling in Different SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(22), 14146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214146







