The Histamine H4 Receptor Participates in the Neuropathic Pain-Relieving Activity of the Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist GSK189254
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
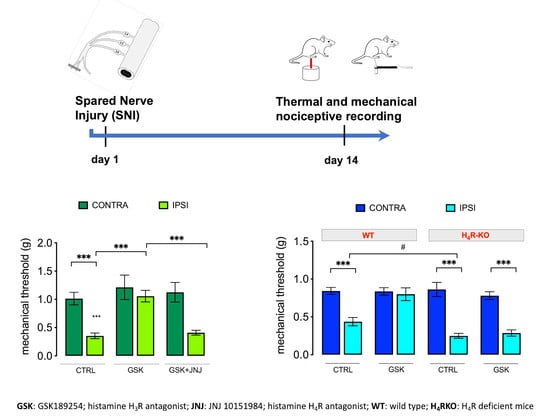
2.1. GSK189254 Attenuates Pain Hypersensitivity in SNI Mice through H4R Activation
2.2. Lack of Contribution of H4R to the Anorexiant Effect of GSK 189254
2.3. Lack of Locomotor Side Effects
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Animals
4.4. Microinjection into the Locus Coeruleus
4.5. Intrathecal Injection
4.6. Spared Nerve Injury (SNI)
4.7. Nociceptive Behaviour
4.7.1. Von Frey Test
4.7.2. Hargreaves’ Plantar Test
4.8. Locomotor Activity
4.8.1. Rotarod Test
4.8.2. Hole-Board Test
4.9. Evaluation of Food Consumption
4.10. Immunofluorescence
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Hecke, O.; Austin, S.K.; Khan, R.A.; Smith, B.H.; Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 2014, 155, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, E.; Mammana, S.; Nicoletti, F.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The neuropathic pain: An overview of the current treatment and future therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 2058738419838383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaumette, T.; Chapuy, E.; Berrocoso, E.; Llorca-Torralba, M.; Bravo, L.; Mico, J.A.; Chalus, M.; Eschalier, A.; Ardid, D.; Marchand, F.; et al. Effects of S 38093, an antagonist/inverse agonist of histamine H3 receptors, in models of neuropathic pain in rats. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanna, M.D.; Mello, T.; Ghelardini, C.; Galeotti, N. Inhibition of spinal ERK1/2-c-JUN signaling pathway counteracts the development of low doses morphine-induced hyperalgesia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 764, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, I.; Telezhkin, V.; Alrashdi, I.; Chazot, P.L. Histamine, histamine receptors, and neuropathic pain relief. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 580–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, K.E.; Chazot, P.L.; Hann, V.; Shenton, F.; Hough, L.B.; Rice, F.L. Immunohistochemical localization of histamine H3 receptors in rodent skin, dorsal root ganglia, superior cervical ganglia, and spinal cord: Potential antinociceptive targets. Pain 2007, 129, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrang, J.M.; Drutel, G.; Schwartz, J.-C. Characterization of histamine H3 receptors regulating acetylcholine release in rat entorhinal cortex. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 114, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellenbroek, B.A. Histamine H3 receptors, the complex interaction with dopamine and its implications for addiction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlicker, E.; Schunack, W.; Göthert, M. Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in pig retina discs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1990, 342, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threlfell, S.; Cragg, S.J.; Kalló, I.; Turi, G.F.; Coen, C.W.; Greenfield, S.A. Histamine H3 receptors inhibit serotonin release in substantia nigra pars reticulata. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8704–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, G.C.; Chandran, P.; Salyers, A.K.; Pai, M.; Zhu, C.Z.; Wensink, E.J.; Witte, D.G.; Miller, T.R.; Mikusa, J.P.; Baker, S.J.; et al. H4 receptor antagonism exhibits anti-nociceptive effects in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 95, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Łażewska, D.; Latacz, G.; Olejarz, A.; Makuch, W.; Stark, H.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Mika, J. Antinociceptive effects of novel histamine H3 and H4 receptor antagonists and their influence on morphine analgesia of neuropathic pain in the mouse. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cowart, M.; Hsieh, G.; Black, L.A.; Zhan, C.; Gomez, E.J.; Pai, M.; Strakhova, M.; Manelli, A.; Carr, T.; Wetter, J.; et al. Pharmacological characterization of A-960656, a histamine H3 receptor antagonist with efficacy in animal models of osteoarthritis and neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 684, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhurst, A.D.; Briggs, M.A.; Bruton, G.; Calver, A.R.; Chessell, I.; Crook, B.; Davis, J.B.; Davis, R.P.; Foley, A.G.; Heslop, T.; et al. Structurally novel histamine H3 receptor antagonists GSK207040 and GSK334429 improve scopolamine-induced memory impairment and capsaicin-induced secondary allodynia in rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangam, E.B.; Jemima, E.A.; Singh, H.; Baig, M.S.; Khan, M.; Mathias, C.B.; Church, M.K.; Saluja, R. The role of histamine and histamine receptors in mast cell-mediated allergy and inflammation: The hunt for new therapeutic targets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanna, M.D.; Lucarini, L.; Durante, M.; Ghelardini, C.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Histamine H4 receptor agonist-induced relief from painful peripheral neuropathy is mediated by inhibition of spinal neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strakhova, M.I.; Nikkel, A.L.; Manelli, A.M.; Hsieh, G.C.; Esbenshade, T.A.; Brioni, J.D.; Bitner, R.S. Localization of histamine H4 receptors in the central nervous system of human and rat. Brain Res. 2009, 1250, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, M.D.; Ghelardini, C.; Thurmond, R.L.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Behavioural phenotype of histamine H4 receptor knockout mice: Focus on central neuronal functions. Neuropharmacology 2017, 114, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeotti, N.; Sanna, M.D.; Ghelardini, C. Pleiotropic effect of histamine H4 receptor modulation in the central nervous system. Neuropharmacology 2013, 71, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, M.D.; Stark, H.; Lucarini, L.; Ghelardini, C.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Histamine H4 receptor activation alleviates neuropathic pain through differential regulation of ERK, JNK, and P38 MAPK phosphorylation. Pain 2015, 156, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.E.; Ganellin, C.R. Histamine and its receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, S127–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medhurst, A.D.; Atkins, A.R.; Beresford, I.J.; Brackenborough, K.; Briggs, M.A.; Calver, A.R.; Cilia, J.; Cluderay, J.E.; Crook, B.; Davis, J.B.; et al. GSK189254, a novel H3 receptor antagonist that binds to histamine H3 receptors in Alzheimer’s disease brain and improves cognitive performance in preclinical models. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 321, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Łażewska, D.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Progress in the development of histamine H3 receptor antagonists/inverse agonists: A patent review (2013–2017). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Alamilla, G.; Márquez-Gómez, R.; García-Gálvez, A.M.; Morales-Figueroa, G.E.; Arias-Montaño, J.A. The histamine H3 receptor: Structure, pharmacology, and function. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 649–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz, N.F.; Flores-Herrera, H.; García-López, G.; Molina-Hernández, A. Central Histamine, the H3-Receptor and Obesity Therapy. CNS Neurol. Disord.Drug Targets 2019, 18, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medhurst, S.J.; Collins, S.D.; Billinton, A.; Bingham, S.; Dalziel, R.G.; Brass, A.; Roberts, J.C.; Medhurst, A.D.; Chessell, I.P. Novel histamine H3 receptor antagonists GSK189254 and GSK334429 are efficacious in surgically-induced and virally-induced rat models of neuropathic pain. Pain 2008, 138, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaraughty, S.; Chu, K.L.; Cowart, M.D.; Brioni, J.D. Antagonism of supraspinal histamine H3 receptors modulates spinal neuronal activity in neuropathic rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, K.E.; Nalwalk, J.W.; Stadel, R.; Ge, P.; Lawson, D.; Silos-Santiago, I.; Hough, L.B. Activation of spinal histamine H3 receptors inhibits mechanical nociception. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 470, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, L.B.; Rice, F.L. H3 receptors and pain modulation: Peripheral, spinal, and brain interactions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 336, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanna, M.D.; Borgonetti, V.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Histamine H4 receptor stimulation in the locus coeruleus attenuates neuropathic pain by promoting the coeruleospinal noradrenergic inhibitory pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 868, 172859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venable, J.D.; Cai, H.; Chai, W.; Dvorak, C.A.; Grice, C.A.; Jablonowski, J.A.; Shah, C.R.; Kwok, A.K.; Ly, K.S.; Pio, B.; et al. Preparation and biological evaluation of indole, benzimidazole, and thienopyrrole piperazine carboxamides: Potent human histamine H4 antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 8289–8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, G.C.; Honore, P.; Pai, M.; Wensink, E.J.; Chandran, P.; Salyers, A.K.; Wetter, J.M.; Zhao, C.; Liu, H.; Decker, M.W.; et al. Antinociceptive effects of histamine H3 receptor antagonist in the preclinical models of pain in rats and the involvement of central noradrenergic systems. Brain Res. 2010, 1354, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Mello, R.; Dickenson, A.H. Spinal cord mechanisms of pain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bannister, K.; Patel, R.; Goncalves, L.; Townson, L.; Dickenson, A.H. Diffuse noxious inhibitory controls and nerve injury: Restoring an imbalance between descending monoamine inhibitions and facilitations. Pain 2015, 156, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Viisanen, H.; You, H.J.; Pertovaara, A. Spinal histamine in attenuation of mechanical hypersensitivity in the spinal nerve ligation-induced model of experimental neuropathy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 772, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bharti, N.; Dontukurthy, S.; Bala, I.; Singh, G. Postoperative analgesic effect of intravenous (i.v.) clonidine compared with clonidine administration in wound infiltration for open cholecystectomy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaye, A.D.; Chernobylsky, D.J.; Thakur, P.; Siddaiah, H.; Kaye, R.J.; Eng, L.K.; Harbell, M.W.; Lajaunie, J.; Cornett, E.M. Dexmedetomidine in Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) Protocols for Postoperative Pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2020, 24, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Maitra, S.; Khanna, P.; Baidya, D.K. Clonidine for management of chronic pain: A brief review of the current evidences. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2014, 8, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Linciano, P.; Rossino, G.; Listro, R.; Rossi, D.; Collina, S. Sigma-1 receptor antagonists: Promising players in fighting neuropathic pain. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2020, 9, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlos, M.; Romero, L.; Zamanillo, D.; Plata-Salamán, C.; Vela, J.M. Sigma-1 receptor and pain. Handb Exp Pharm. 2017, 244, 131–161. [Google Scholar]
- Riddy, D.M.; Cook, A.E.; Shackleford, D.M.; Pierce, T.L.; Mocaer, E.; Mannoury la Cour, C.; Sors, A.; Charman, W.N.; Summers, R.J.; Sexton, P.M.; et al. Drug-receptor kinetics and sigma-1 receptor affinity differentiate clinically evaluated histamine H3 receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 2019, 144, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, J.C.; Lilley, E. Implementing guidelines on reporting research using animals (ARRIVE etc.): New requirements for publication in BJP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3189–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charan, J.; Kantharia, N. How to calculate sample size in animal studies? J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2013, 4, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanna, M.D.; Ghelardini, C.; Galeotti, N. Activation of JNK pathway in spinal astrocytes contributes to acute ultra-low-dose morphine thermal hyperalgesia. Pain 2015, 156, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borgonetti, V.; Galeotti, N. The Histamine H4 Receptor Participates in the Neuropathic Pain-Relieving Activity of the Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist GSK189254. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214314
Borgonetti V, Galeotti N. The Histamine H4 Receptor Participates in the Neuropathic Pain-Relieving Activity of the Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist GSK189254. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(22):14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214314
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorgonetti, Vittoria, and Nicoletta Galeotti. 2022. "The Histamine H4 Receptor Participates in the Neuropathic Pain-Relieving Activity of the Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist GSK189254" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 22: 14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214314
APA StyleBorgonetti, V., & Galeotti, N. (2022). The Histamine H4 Receptor Participates in the Neuropathic Pain-Relieving Activity of the Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist GSK189254. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(22), 14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214314