Developmental and Reproductive Impacts of Four Bisphenols in Daphnia magna
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
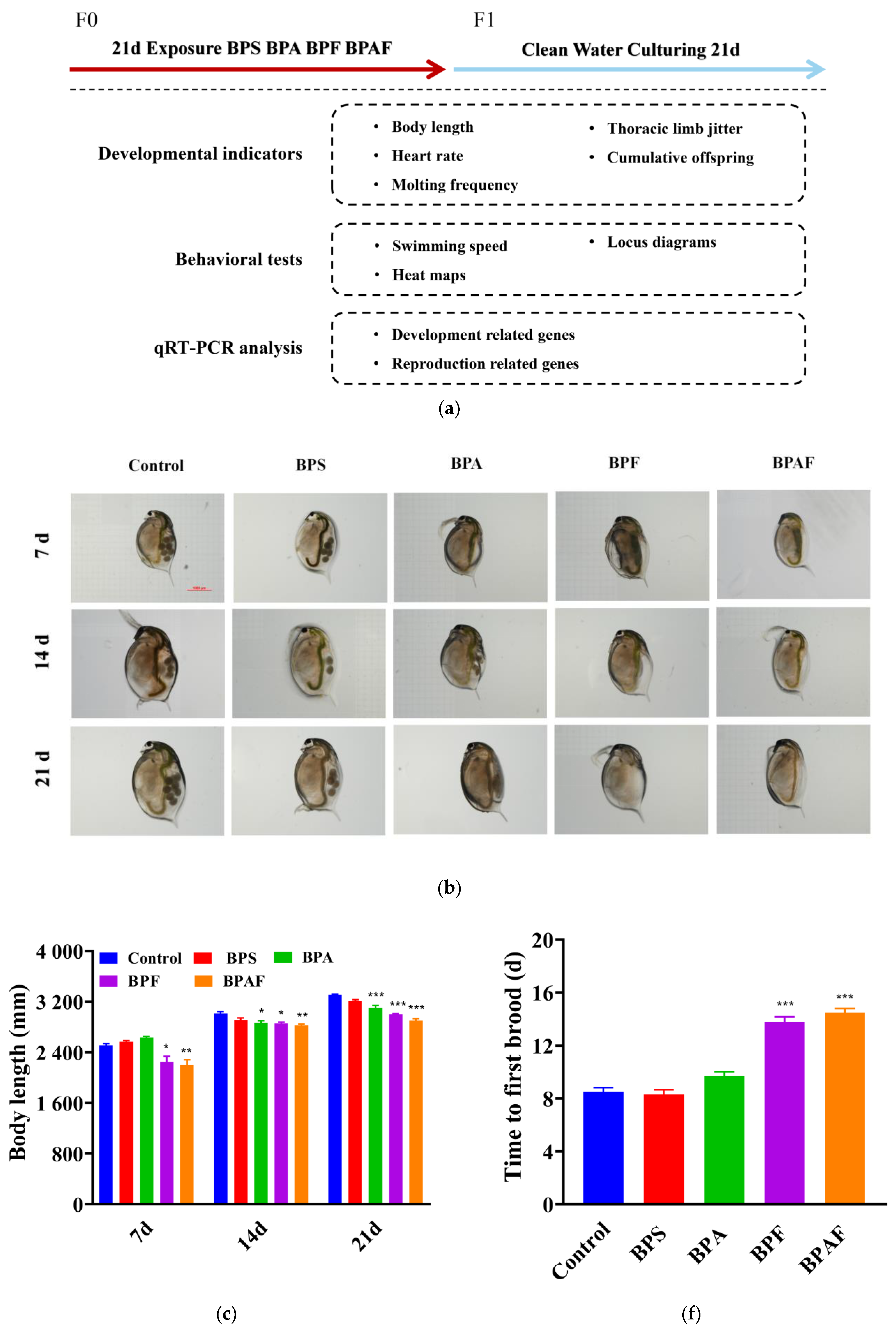
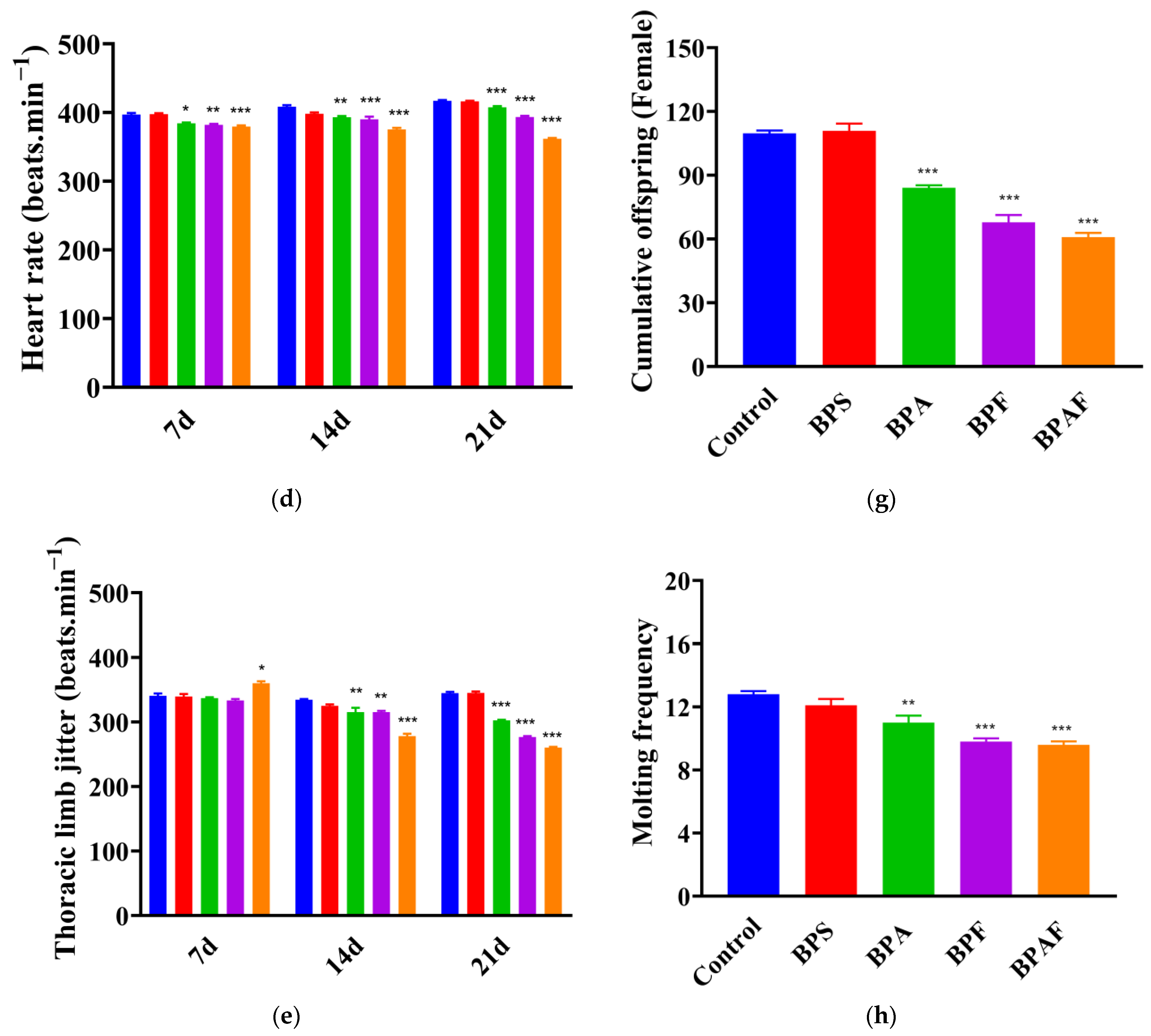
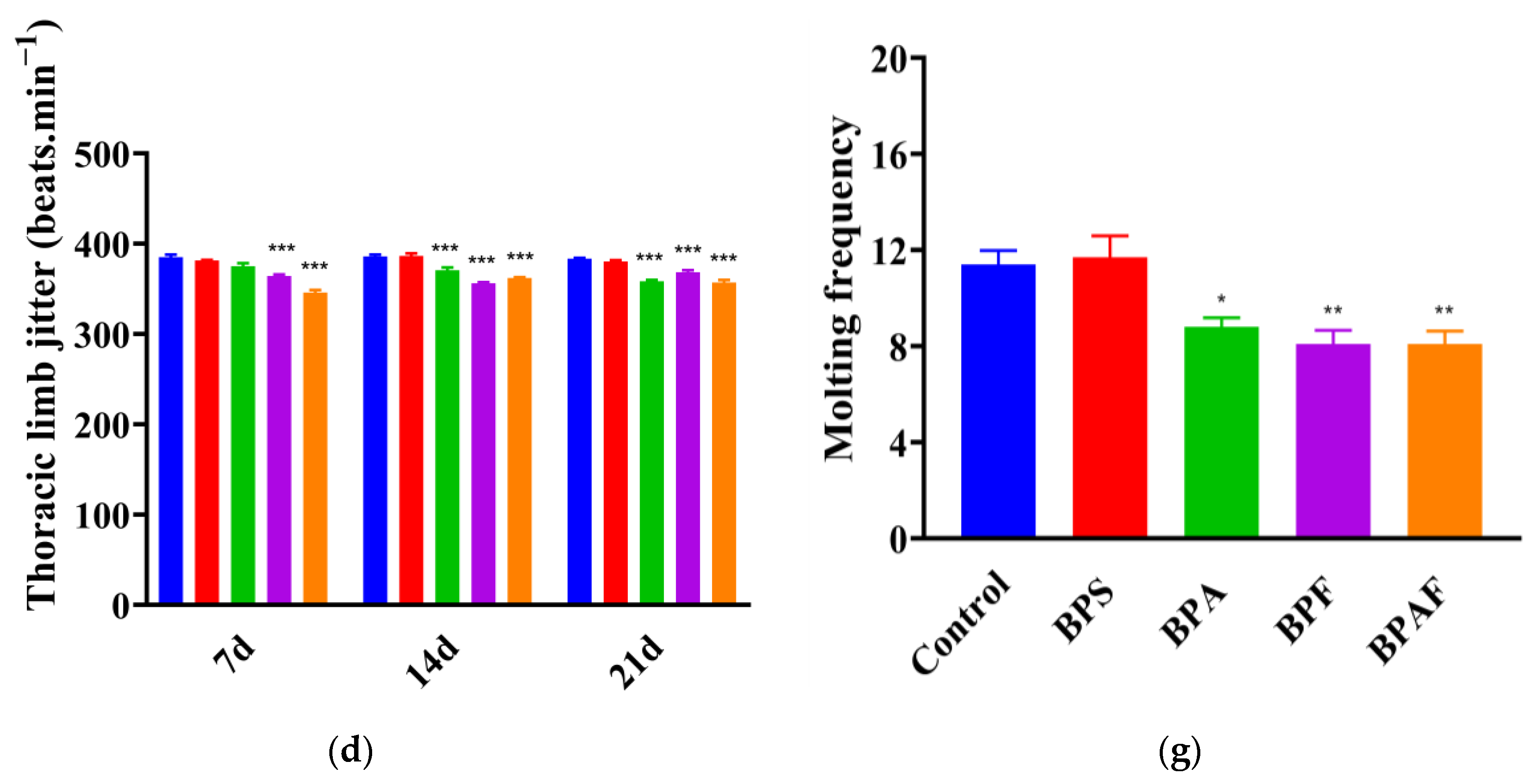
2.1. Development and Reproduction of the F0 Generation
2.2. Development and Reproduction of the F1 Generation
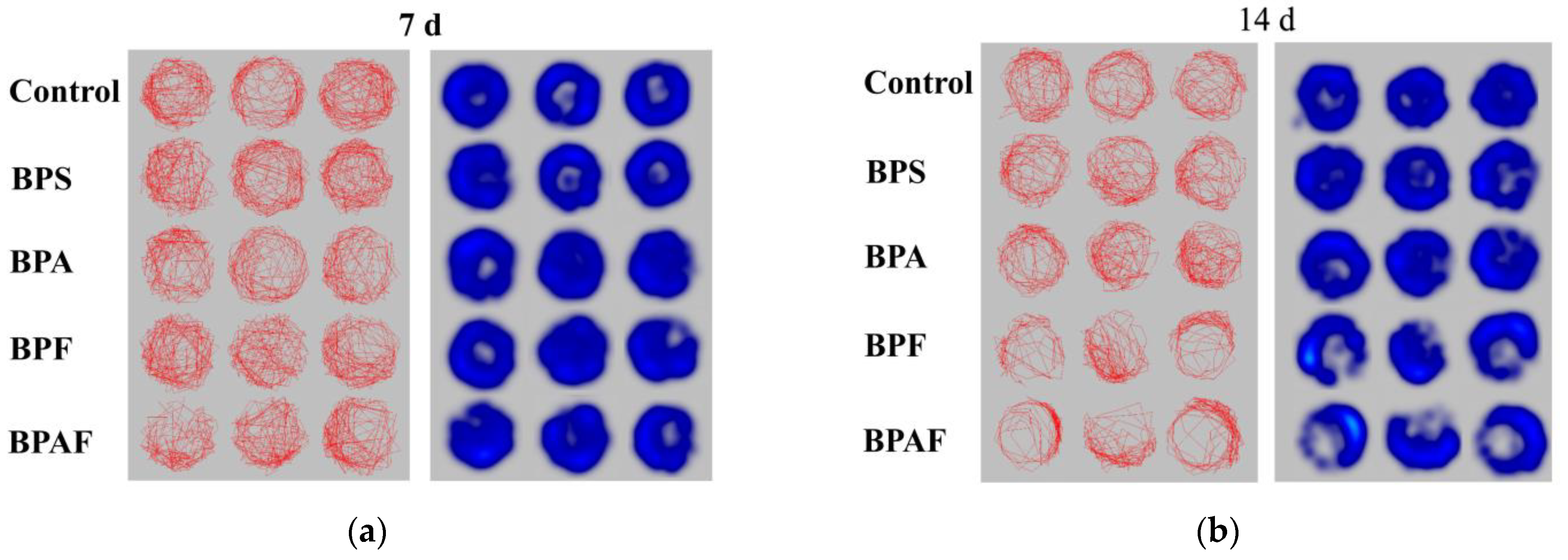
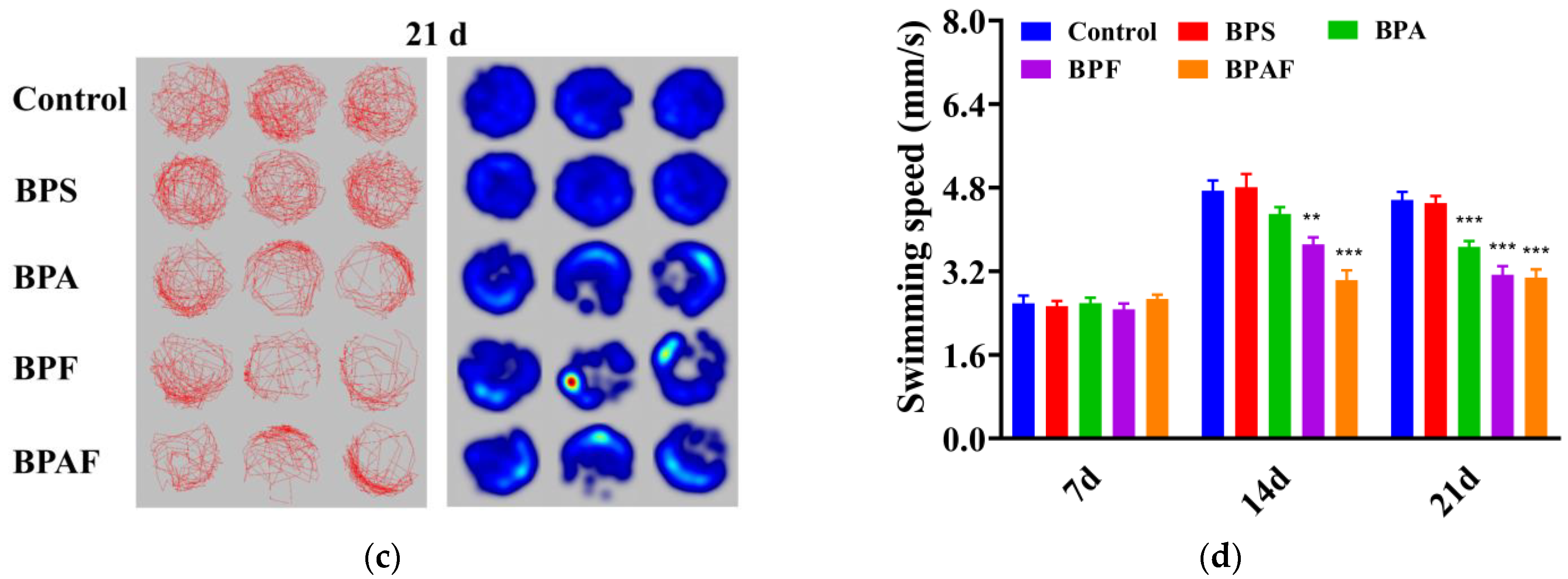
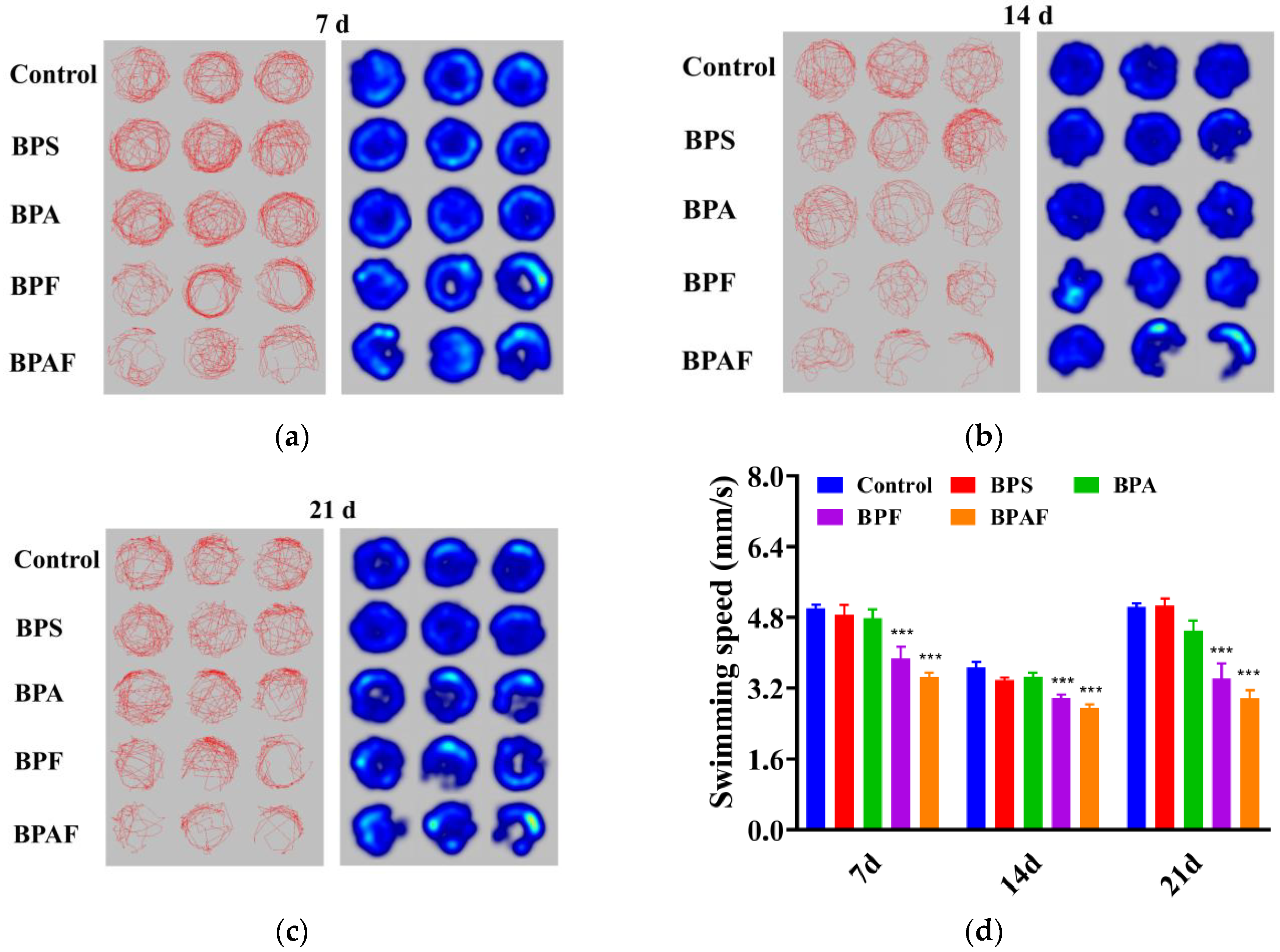
2.3. Behavioral Response
2.4. Reflection of Antioxidant Enzymatic Activity
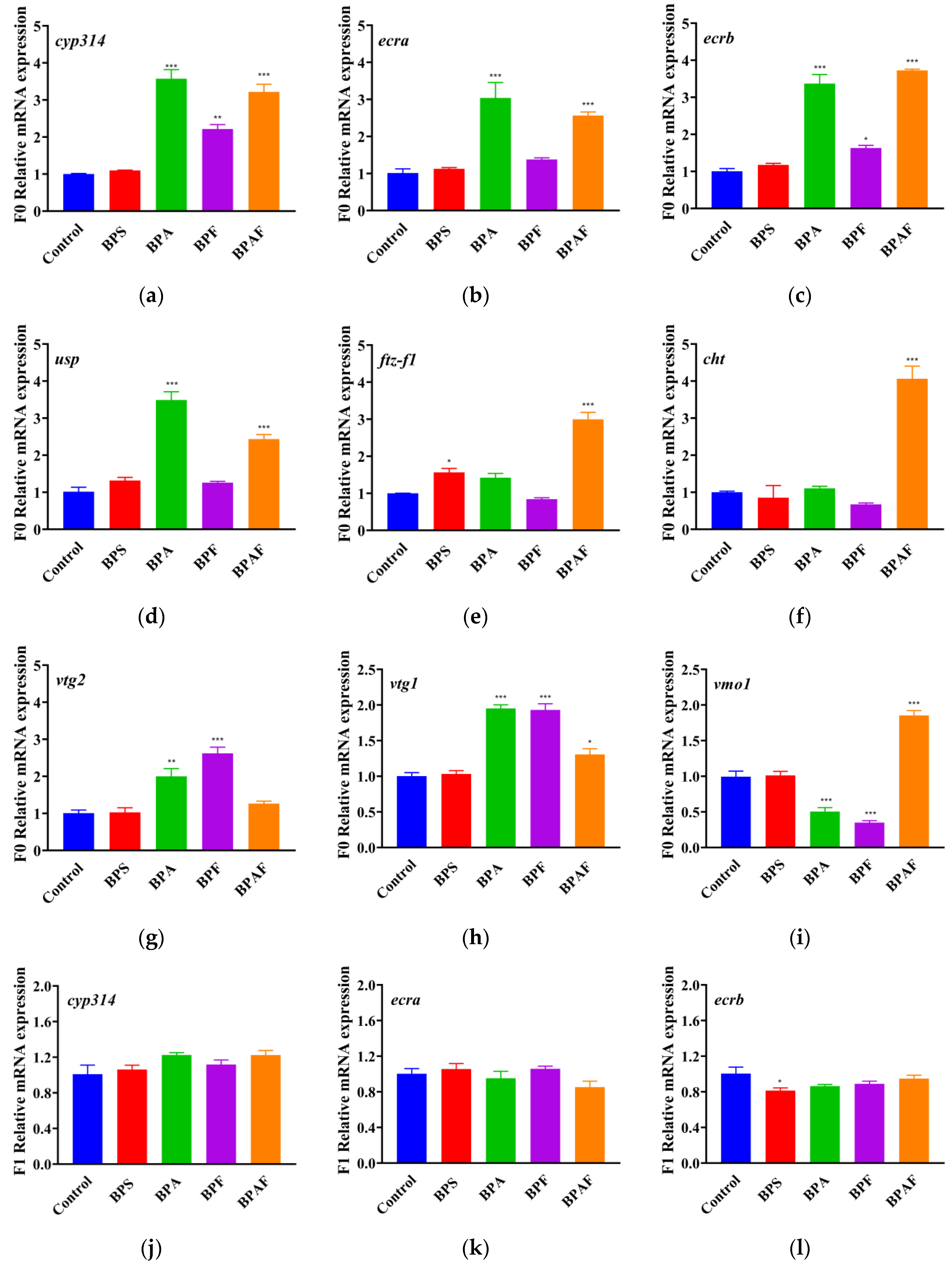
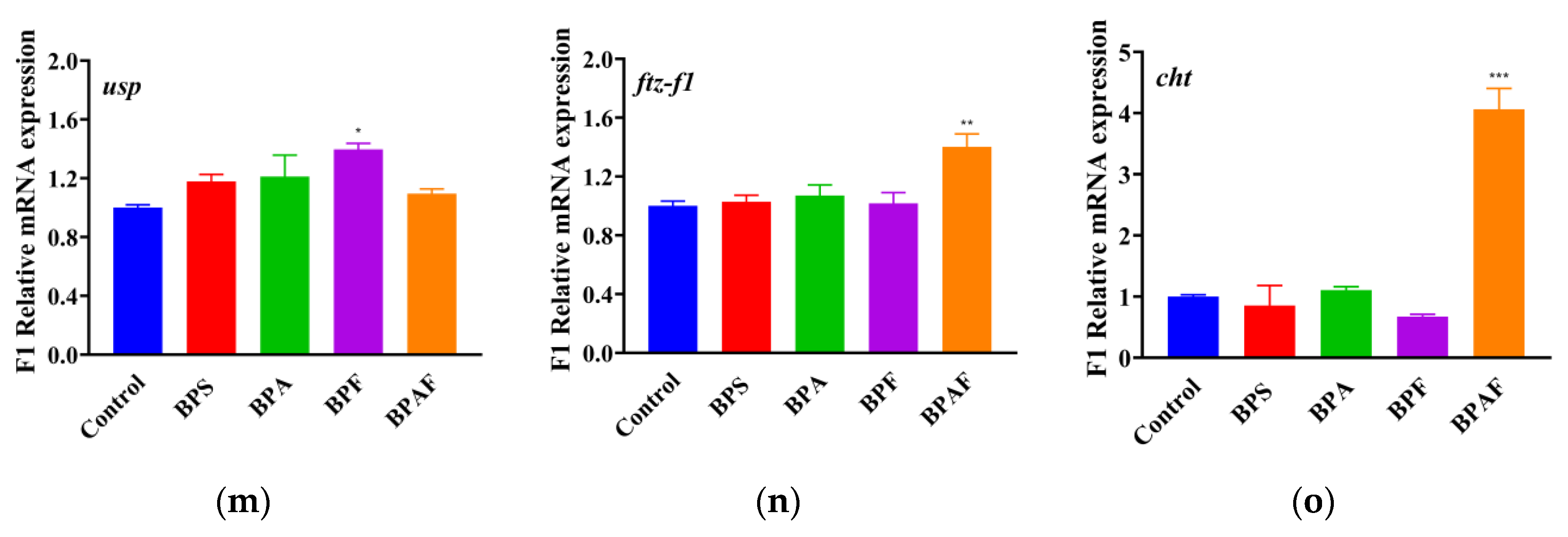
2.5. Expressions of Genes Related to Development and Reproduction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Chemicals and Test Solutions
4.3. Chronic Toxicity Test
4.4. Heartbeat, Body Length, and Thoracic Limb Beat Frequency Measurement
4.5. Behavioral Tests
4.6. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Determination of Antioxidant Enzymatic Activity
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fischnaller, M.; Bakry, R.; Bonn, G.K. A simple method for the enrichment of bisphenols using boron nitride. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipelli, R.; Harries, L.; Okuda, K.; Yoshihara, S.; Melzer, D.; Galloway, T. Bisphenol A modulates the metabolic regulator oestrogen-related receptor-alpha in T-cells. Reproduction 2014, 147, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Q.; Wong, C.K.; Zheng, J.S.; Bouwman, H.; Barra, R.; Wahlstrom, B.; Neretin, L.; Wong, M.H. Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: A review of sources, environmental levels, and potential human health impacts. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Adegoke, E.O.; Pang, M.G. Drivers of owning more BPA. J Hazard Mater. 2021, 417, 126076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Zhan, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Wong, M.; Xu, B.; Zheng, C. The occurrence, potential toxicity, and toxicity mechanism of bisphenol S, a substitute of bisphenol A: A critical review of recent progress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, P.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Rapid method for the separation and recovery of endocrine-disrupting compound bisphenol AP from wastewater. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3968–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wan, Y.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of bisphenols, bisphenol A diglycidyl ethers (BADGEs), and novolac glycidyl ethers (NOGEs) in indoor air from Albany, New York, USA, and its implications for inhalation exposure. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Zhu, L. Occurrence and partitioning of bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from Liaohe River Basin and Taihu Lake, China. Water Res. 2016, 103, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, B. Determination of seven bisphenol analogues in reed and Callitrichaceae by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 953–954, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Hong, Y.; Cai, Z. Occurrence and Partitioning of Bisphenol Analogues in Adults’ Blood from China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guan, J.; Yin, J.; Shao, B.; Li, H. Urinary levels of bisphenol analogues in residents living near a manufacturing plant in south China. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.-F.; Qu, G.-B.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.-W.; Shi, J.-B.; Jiang, G.-B. Tetrabromobisphenol-A/S and nine novel analogs in biological samples from the Chinese Bohai Sea: Implications for trophic transfer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4203–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotimi, O.A.; Olawole, T.D.; De Campos, O.C.; Adelani, I.B.; Rotimi, S.O. Bisphenol A in Africa: A review of environmental and biological levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Shan, G.; Chen, P.; Cui, S.; Yi, S.; Zhu, L. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of emerging bisphenol analogues in aquatic organisms from Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Guo, M.; Yin, X.; Huang, C.; Qian, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Ji, G. A systematic comparison of neurotoxicity of bisphenol A and its derivatives in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, D.; Sharin, T.; Chiu, S.; O’Brien, J.M. In Vitro Screening of 21 Bisphenol A Replacement Alternatives: Compared with Bisphenol A, the Majority of Alternatives Are More Cytotoxic and Dysregulate More Genes in Avian Hepatocytes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Fol, V.; Ait-Aissa, S.; Sonavane, M.; Porcher, J.M.; Balaguer, P.; Cravedi, J.P.; Zalko, D.; Brion, F. In vitro and in vivo estrogenic activity of BPA, BPF and BPS in zebrafish-specific assays. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Qi, S.; Wang, H.; Yuan, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Qiu, J. Bisphenol analogues induced metabolic effects through eliciting intestinal cell heterogeneous response. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L.; Fan, D.; Shi, L.; Wang, J.; Ji, G. Bisphenol F exposure impairs neurodevelopment in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Gu, J.; Guo, M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.; Shi, L.; Gu, A. A systematic comparison of the developmental vascular toxicity of bisphenol A and its alternatives in vivo and in vitro. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 2, 132936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Li, L.; Yin, X.; Liang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhou, L.; Fan, D.; Shi, L.; Ji, G. Long-term exposure of zebrafish to bisphenol F: Adverse effects on parental reproduction and offspring neurodevelopment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 248, 106190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Saili, K.S.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Bai, C.; Tanguay, R.L.; Dong, Q.; Huang, C. Developmental bisphenol A exposure impairs sperm function and reproduction in zebrafish. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Liang, C.; Li, W.; Letcher, R.J.; Liu, C. A comprehensive system for detection of behavioral change of D. magna exposed to various chemicals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, A.; Yamamuro, M.; Tatarazako, N. Acute toxicity of 50 metals to Daphnia magna. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Huang, B.; Chen, Z.; Lv, X.; Qian, W.; Zhu, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z. Behavioural and chronic toxicity of fullerene to Daphnia magna: Mechanisms revealed by transcriptomic analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255 Pt 1, 113181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Berge, W.F. Breeding Daphnia magna. Hydrobiologia 1978, 59, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 211: Daphnia Magna Reproduction Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cano, A.M.; Maul, J.D.; Saed, M.; Shah, S.A.; Green, M.J.; Canas-Carrell, J.E. Bioaccumulation, stress, and swimming impairment in Daphnia magna exposed to multiwalled carbon nanotubes, graphene, and graphene oxide. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seda, B.C.; Ke, P.C.; Mount, A.S.; Klaine, S.J. Toxicity of aqueous C70-gallic acid suspension in Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Z.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Guo, R. Food up-take and reproduction performance of Daphnia magna under the exposure of Bisphenols. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, J.T.; Taylor, J.A.; Shetty, S.R.; Edwards, M.; Connelly, J.J.; Rissman, E.F. Gestational exposure to low dose bisphenol A alters social behavior in juvenile mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreman, J.; Lee, O.; Trznadel, M.; David, A.; Kudoh, T.; Tyler, C.R. Acute Toxicity, Teratogenic, and Estrogenic Effects of Bisphenol A and Its Alternative Replacements Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F, and Bisphenol AF in Zebrafish Embryo-Larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12796–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, T.Y.; Yoon, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.D. Mode of action characterization for adverse effect of propranolol in Daphnia magna based on behavior and physiology monitoring and metabolite profiling. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, M.; Ishibashi, H.; Matsumura, N.; Nagao, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Watanabe, A.; Onikura, N.; Kishi, K.; Arizono, K. Acute Toxicity Responses of Two Crustaceans, Americamysis bahia and Daphnia magna, to Endocrine Disrupters. J. Heath Sci. 2004, 50, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.G.; Orcutt, J.D.; Gerritsen, J. Functional Response and Fitness in a Generalist Filter Feeder, Daphnia Magna (Cladocera: Crustacea). Ecology 1983, 64, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.-H.; Sserwadda, A.; Song, K.; Zang, Y.-N.; Shen, H.-S. Cloning and Expression of Ecdysone Receptor and Retinoid X Receptor from Procambarus clarkii: Induction by Eyestalk Ablation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Colon, E.; Chawla, S.; Vandenberg, L.N.; Suvorov, A. Endocrine disruptors alter social behaviors and indirectly influence social hierarchies via changes in body weight. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, J.T.; Goldsby, J.A.; Rissman, E.F. Transgenerational effects of prenatal bisphenol A on social recognition. Horm. Behav. 2013, 64, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalowicz, J.; Mokra, K.; Bak, A. Bisphenol A and its analogs induce morphological and biochemical alterations in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (in vitro study). Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.D.; Huang, B.W.; Tsuji, Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huc, L.; Lemarie, A.; Gueraud, F.; Helies-Toussaint, C. Low concentrations of bisphenol A induce lipid accumulation mediated by the production of reactive oxygen species in the mitochondria of HepG2 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Suk, K.; Kim, I.K.; Jang, I.S.; Park, J.W.; Johnson, V.J.; Kwon, T.K.; Choi, B.J.; Kim, S.H. Signaling pathways of bisphenol A-induced apoptosis in hippocampal neuronal cells: Role of calcium-induced reactive oxygen species, mitogen-activated protein kinases, and nuclear factor-kappaB. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 2932–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, M.J. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in aquatic invertebrates: Recent advances and future directions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 48, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyzack, J.D.; Kirchmair, J. Computational methods and tools to predict cytochrome P450 metabolism for drug discovery. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Villeneuve, D.L.; Toyota, K.; Iguchi, T.; Tollefsen, K.E. Ecdysone Receptor Agonism Leading to Lethal Molting Disruption in Arthropods: Review and Adverse Outcome Pathway Development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4142–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Dong, H.-Q.; Tian, H.-S.; Ma, L.; Li, X.-L.; Wu, G.-L.; Zhu, C.-L. Cytochrome P450 genes expressed in the deltamethrin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Culex pipiens pallens. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2003, 75, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Yuan, S.; Li, J.; Liu, C. Greater toxic potency of bisphenol AF than bisphenol A in growth, reproduction, and transcription of genes in Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 25218–25227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Henrich, V.C. Arthropod nuclear receptors and their role in molting. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6128–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyoum, A.; Pradhan, A.; Jass, J.; Olsson, P.E. Perfluorinated alkyl substances impede growth, reproduction, lipid metabolism and lifespan in Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houde, M.; Douville, M.; Giraudo, M.; Jean, K.; Lepine, M.; Spencer, C.; De Silva, A.O. Endocrine-disruption potential of perfluoroethylcyclohexane sulfonate (PFECHS) in chronically exposed Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Bao, C.; Huang, H.; Ye, H. Vitellogenin2: Spermatozoon specificity and immunoprotection in mud crabs. Reproduction 2016, 152, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudo, M.; Douville, M.; Cottin, G.; Houde, M. Transcriptomic, cellular and life-history responses of Daphnia magna chronically exposed to benzotriazoles: Endocrine-disrupting potential and molting effects. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, C.; Yu, K.; Zhou, B. Chronic effects of water-borne PFOS exposure on growth, survival and hepatotoxicity in zebrafish: A partial life-cycle test. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, K.; Kim, Y.; Oh, S.; Ahn, B.; Jo, H.; Choi, K. Toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid and perfluorooctanoic acid on freshwater macroinvertebrates (Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa) and fish (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Li, H.; Dang, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of triphenyl phosphate on growth, reproduction and transcription of genes of Daphnia magna. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 195, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blewett, T.A.; Delompre, P.L.; He, Y.; Folkerts, E.J.; Flynn, S.L.; Alessi, D.S.; Goss, G.G. Sublethal and Reproductive Effects of Acute and Chronic Exposure to Flowback and Produced Water from Hydraulic Fracturing on the Water Flea Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3032–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Pan, B.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Nie, X. Adverse effects in Daphnia magna exposed to e-waste leachate: Assessment based on life trait changes and responses of detoxification-related genes. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Li, S. Influences of bisphenol AF on the reproduction and growth of Daphnia magna. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 4394–4400. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, L.; Chen, C.; Guo, L.; Deng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X. Developmental and Reproductive Impacts of Four Bisphenols in Daphnia magna. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314561
Qian L, Chen C, Guo L, Deng J, Zhang X, Zheng J, Wang G, Zhang X. Developmental and Reproductive Impacts of Four Bisphenols in Daphnia magna. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314561
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Lingling, Chen Chen, Liguo Guo, Junping Deng, Xiangling Zhang, Jiexiang Zheng, Genmei Wang, and Xiaofei Zhang. 2022. "Developmental and Reproductive Impacts of Four Bisphenols in Daphnia magna" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314561
APA StyleQian, L., Chen, C., Guo, L., Deng, J., Zhang, X., Zheng, J., Wang, G., & Zhang, X. (2022). Developmental and Reproductive Impacts of Four Bisphenols in Daphnia magna. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314561




