Roles of Resolvins in Chronic Inflammatory Response
Abstract
:1. Introduction
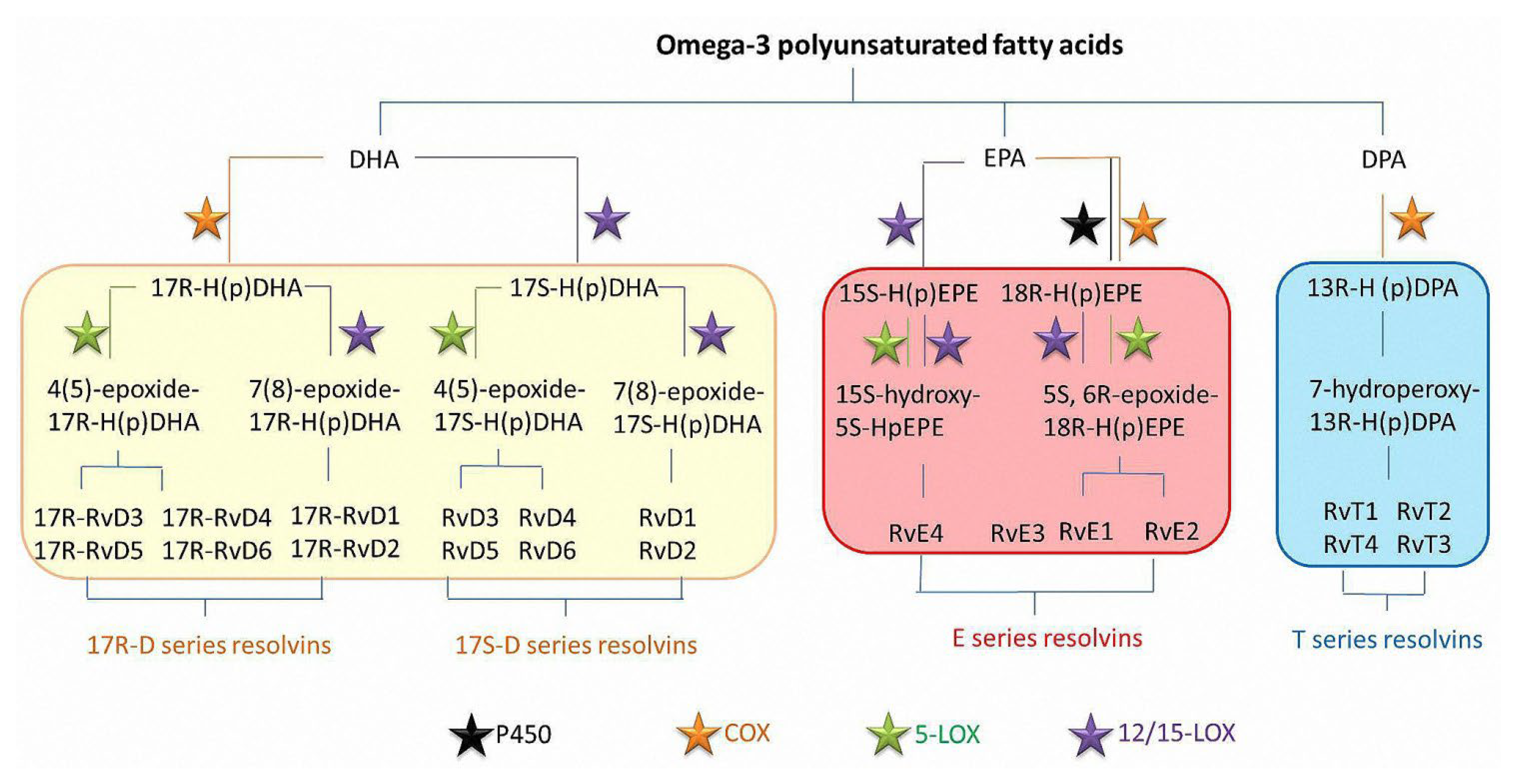
2. Production and Characteristics of Resolvins
3. Resolvins Receptors
4. Effects of Resolvins on Target Cells in Chronic Inflammatory Response
4.1. Effects on Neutrophils
4.2. Effects on Macrophages
4.3. Effects on Lymphocytes
4.4. Effects on Astrocytes
4.5. Effects on Endothelial Cells
4.6. Effects on Cancer Cells
5. Mechanism and Clinical Translation of Resolvins for Chronic Inflammatory Diseases Treatment
5.1. Effects on Pain
5.2. Effects on Atherosclerosis
5.3. Effects on Diabetes
5.4. Effects on Anti-Depression and Wound Healing
5.5. Effects on Rheumatoid Arthritis
5.6. Application of Resolvins in the Treatment of Pre-Diseases
6. Further Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sochocka, M.; Diniz, B.S.; Leszek, J. Inflammatory Response in the CNS: Friend or Foe? Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 8071–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balta, M.G.; Loos, B.G.; Nicu, E.A. Emerging Concepts in the Resolution of Periodontal Inflammation: A Role for Resolvin E1. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kazemi, S.; Shirzad, H.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Recent Findings in Molecular Basis of Inflammation and Anti-inflammatory Plants. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Levy, B.D. Resolvins in inflammation: Emergence of the pro-resolving superfamily of mediators. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdolmaleki, F.; Kovanen, P.T.; Mardani, R.; Gheibi-Hayat, S.M.; Bo, S.; Sahebkar, A. Resolvins: Emerging Players in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 58, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredman, G.; Serhan, C.N. Specialized proresolving mediator targets for RvE1 and RvD1 in peripheral blood and mechanisms of resolution. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente-Cebrian, S.; Costa, A.G.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Zabala, M.; Laiglesia, L.M.; Martinez, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J. An update on the role of omega-3 fatty acids on inflammatory and degenerative diseases. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaudez, F.; Ivanovski, S.; Fournier, B.; Vaquette, C. The utilisation of resolvins in medicine and tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtzelis, I.; Li, X.; Mitroulis, I.; Grosser, D.; Kajikawa, T.; Wang, B.; Grzybek, M.; von Renesse, J.; Czogalla, A.; Troullinaki, M.; et al. DEL-1 promotes macrophage efferocytosis and clearance of inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannaway, M.; Torrens, C.; Warner, J.A.; Sampson, A.P. Resolvin E1, resolvin D1 and resolvin D2 inhibit constriction of rat thoracic aorta and human pulmonary artery induced by the thromboxane mimetic U46619. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, B.; Obeng, M.; Nauroth, J.M.; Chung, G.; Bailey-Hall, E.; Hallenbeck, T.; Arterburn, L.M. Metabolism and biological production of resolvins derived from docosapentaenoic acid (DPAn-6). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiurchiu, V.; Leuti, A.; Maccarrone, M. Bioactive Lipids and Chronic Inflammation: Managing the Fire Within. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.; Lu, Y. Omega-3 fatty acid-derived resolvins and protectins in inflammation resolution and leukocyte functions: Targeting novel lipid mediator pathways in mitigation of acute kidney injury. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnardottir, H.; Pawelzik, S.C.; Sarajlic, P.; Quaranta, A.; Kolmert, J.; Religa, D.; Wheelock, C.E.; Back, M. Immunomodulation by intravenous omega-3 fatty acid treatment in older subjects hospitalized for COVID-19: A single-blind randomized controlled trial. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, P.L.; Kalstad, A.A.; Tveit, S.H.; Laake, K.; Schmidt, E.B.; Smith, P.; Nilsen, D.W.; Tveit, A.; Solheim, S.; Arnesen, H.; et al. Changes in eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid and risk of cardiovascular events and atrial fibrillation: A secondary analysis of the OMEMI trial. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famenini, S.; Rigali, E.A.; Olivera-Perez, H.M.; Dang, J.; Chang, M.T.; Halder, R.; Rao, R.V.; Pellegrini, M.; Porter, V.; Bredesen, D.; et al. Increased intermediate M1-M2 macrophage polarization and improved cognition in mild cognitive impairment patients on omega-3 supplementation. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Proudman, S.M.; Cleland, L.G.; Metcalf, R.G.; Sullivan, T.R.; Spargo, L.D.; James, M.J. Plasma n-3 fatty acids and clinical outcomes in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerlach, B.D.; Marinello, M.; Heinz, J.; Rymut, N.; Sansbury, B.E.; Riley, C.O.; Sadhu, S.; Hosseini, Z.; Kojima, Y.; Tang, D.D.; et al. Resolvin D1 promotes the targeting and clearance of necroptotic cells. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, W.; Cao, Q.; Shu, Y. Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 inhibits TGF-beta1-induced EMT through the inhibition of the mTOR pathway by reducing the expression of PKM2 and is closely linked to oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasturk, H.; Abdallah, R.; Kantarci, A.; Nguyen, D.; Giordano, N.; Hamilton, J.; Van Dyke, T.E. Resolvin E1 (RvE1) Attenuates Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation in Diet and Inflammation-Induced Atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Kebir, D.; Gjorstrup, P.; Filep, J.G. Resolvin E1 promotes phagocytosis-induced neutrophil apoptosis and accelerates resolution of pulmonary inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14983–14988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, X.; Lee, H.N.; Surh, Y.J. RvD1 inhibits TNF alpha-induced c-Myc expression in normal intestinal epithelial cells and destabilizes hyper-expressed c-Myc in colon cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.T.; Duan, X.R.; Hu, F.; Poorun, D.; Liu, X.X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gan, L.; He, M.W.; Zhu, K.; et al. Resolvin D1 attenuates imiquimod-induced mice psoriasiform dermatitis through MAPKs and NF-kappa B pathways. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 89, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyama, S.; Shimoda, K.; Suzuki, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Ishimura, K.; Fukuda, H.; Hitora-Imamura, N.; Ide, S.; Satoh, M.; Kaneda, K.; et al. Resolvin E1/E2 ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behaviors via ChemR23. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisicchia, E.; Sasso, V.; Catanzaro, G.; Leuti, A.; Besharat, Z.M.; Chiacchiarini, M.; Molinari, M.; Ferretti, E.; Viscomi, M.T.; Chiurchiu, V. Resolvin D1 Halts Remote Neuroinflammation and Improves Functional Recovery after Focal Brain Damage Via ALX/FPR2 Receptor-Regulated MicroRNAs. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6894–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Easley, J.T.; Nelson, J.W.; Mellas, R.E.; Sommakia, S.; Wu, C.; Trump, B.; Baker, O.J. Aspirin-Triggered Resolvin D1 Versus Dexamethasone in the Treatment of Sjogren’s Syndrome-Like NOD/ShiLtJ Mice—A Pilot Study. J. Rheum. Dis. Treat. 2015, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, H.M.; Thatcher, T.H.; Levy, E.P.; Fulton, R.A.; Owens, K.M.; Phipps, R.P.; Sime, P.J. Resolvin D1 Attenuates Polyinosinic-Polycytidylic Acid-Induced Inflammatory Signaling in Human Airway Epithelial Cells via TAK1. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 4980–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, R.R.; Xu, Z.Z.; Strichartz, G.; Serhan, C.N. Emerging roles of resolvins in the resolution of inflammation and pain. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serhan, C.N.; Libreros, S.; Nshimiyimana, R. E-series resolvin metabolome, biosynthesis and critical role of stereochemistry of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) in inflammation-resolution: Preparing SPMs for long COVID-19, human clinical trials, and targeted precision nutrition. Semin. Immunol. 2022, 101597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Liu, D.X.; Shi, X.X.; Xu, N.; Li, R.G. Efficacy of vitamin D2 on severe diabetic peripheral neuropathy of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A multicenter random double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes-Metab. Res. Rev. 2017, 33, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Dalli, J.; Colas, R.A.; Serhan, C.N. Novel n-3 immunoresolvents: Structures and actions. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellmann, J.; Sansbury, B.E.; Wong, B.; Li, X.F.; Singh, M.; Nuutila, K.; Chiang, N.; Eriksson, E.; Serhan, C.N.; Spite, M. Biosynthesis of D-Series Resolvins in Skin Provides Insights into their Role in Tissue Repair. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werz, O.; Gerstmeier, J.; Libreros, S.; De la Rosa, X.; Werner, M.; Norris, P.C.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Human macrophages differentially produce specific resolvin or leukotriene signals that depend on bacterial pathogenicity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, A.; Komshian, S.; Sansbury, B.E.; Wu, B.; Mottola, G.; Chen, M.; Spite, M.; Conte, M.S. Biosynthesis of proresolving lipid mediators by vascular cells and tissues. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3393–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- See, V.H.L.; Mas, E.; Prescott, S.L.; Beilin, L.J.; Burrows, S.; Barden, A.E.; Huang, R.C.; Mori, T.A. Effects of prenatal n-3 fatty acid supplementation on offspring resolvins at birth and 12 years of age: A double-blind, randomised controlled clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, N.; Sugiyama, T.; Morita, M.; Suganuma, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Total Synthesis of Resolvin D5. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.P.; Chiurchiu, V.; Perruche, S.; You, S. Regulation of T-Cell Immune Responses by Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 768133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.W.; Libreros, S.; De La Rosa, X.; Sansbury, B.E.; Norris, P.C.; Chiang, N.; Fichtner, D.; Keyes, G.S.; Wourms, N.; Spite, M.; et al. Frontline Science: Structural insights into Resolvin D4 actions and further metabolites via a new total organic synthesis and validation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnardottir, H.H.; Dalli, J.; Norling, L.V.; Colas, R.A.; Perretti, M.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin D3 Is Dysregulated in Arthritis and Reduces Arthritic Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giera, M.; Ioan-Facsinay, A.; Fau-Toes, R.; Toes, R.; Fau-Gao, F.; Gao, F.; Fau-Dalli, J.; Dalli, J.; Fau-Deelder, A.M.; Deelder, A.; et al. Lipid and lipid mediator profiling of human synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis patients by means of LC-MS/MS. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarghi, A.; Rao, P.N.; Knaus, E.E. Design and synthesis of new rofecoxib analogs as selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors: Replacement of the methanesulfonyl pharmacophore by a N-acetylsulfonamido bioisostere. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. Publ. Can. Soc. Pharm. Sci. Soc. Can. Sci. Pharm. 2007, 10, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Petasis, N.A.; Serhan, C.N.; Gao, H. Protective actions of aspirin-triggered (17R) resolvin D1 and its analogue, 17R-hydroxy-19-para-fluorophenoxy-resolvin D1 methyl ester, in C5a-dependent IgG immune complex-induced inflammation and lung injury. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3769–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima-Garcia, J.F.; Dutra, R.C.; Silva, K.D.; Motta, E.M.; Campos, M.M.; Calixto, J.B. The precursor of resolvin D series and aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 display anti-hyperalgesic properties in adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weylandt, K.H.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Gomolka, B.; Waechter, S.F.; Wiedenmann, B.; Wiedenmann, B. Omega-3 fatty acids and their lipid mediators: Towards an understanding of resolvin and protectin formation. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2012, 97, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.F.; Vickery, T.W.; Serhan, C.N. Chiral lipidomics of E-series resolvins: Aspirin and the biosynthesis of novel mediators. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2011, 1811, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Artiach, G.; Carracedo, M.; Plunde, O.; Wheelock, C.E.; Thul, S.; Sjövall, P.; Franco-Cereceda, A.; Laguna-Fernandez, A.; Arnardottir, H.; Bäck, M. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Decrease Aortic Valve Disease Through the Resolvin E1 and ChemR23 Axis. Circulation 2020, 142, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, Y.; Sato, Y.; Fukuda, H.; Ishimura, K.; Ikeda, H.; Watanabe, M.; Tansho-Nagakawa, S.; Ubagai, T.; Shuto, S.; Ono, Y. Resolvin E1, but not resolvins E2 and E3, promotes fMLF-induced ROS generation in human neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 2706–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Libreros, S.; Shay, A.E.; Nshimiyimana, R.; Fichtner, D.; Martin, M.J.; Wourms, N.; Serhan, C.N. A New E-Series Resolvin: RvE4 Stereochemistry and Function in Efferocytosis of Inflammation-Resolution. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 631319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature 2014, 510, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Primdahl, K.G.; Aursnes, M.; Walker, M.E.; Colas, R.A.; Serhan, C.N.; Dalli, J.; Hansen, T.V.; Vik, A. Synthesis of 13(R)-Hydroxy-7Z,10Z,13R,14E,16Z,19Z Docosapentaenoic Acid (13R-HDPA) and Its Biosynthetic Conversion to the 13-Series Resolvins. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.R.; Spur, B.W. First total syntheses of the pro-resolving lipid mediators 7(S),13(R),20(S)-Resolvin T1 and 7(S),13(R)-Resolvin T4. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.R.; Spur, B.W. First total synthesis of the pro-resolving lipid mediator 7(S),12(R),13(S)-Resolvin T2 and its 13(R)-epimer. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalli, J.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Elucidation of novel 13-series resolvins that increase with atorvastatin and clear infections. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalli, J.; Winkler, J.W.; Colas, R.A.; Arnardottir, H.; Cheng, C.-Y.C.; Chiang, N.; Petasis, N.A.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin D3 and aspirin-triggered resolvin D3 are potent immunoresolvents. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, N.; Fredman, G.; Backhed, F.; Oh, S.F.; Vickery, T.; Schmidt, B.A.; Serhan, C.N. Infection regulates pro-resolving mediators that lower antibiotic requirements. Nature 2012, 484, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos, H.T.; Nam, K.; Maslow, F.; Trump, B.; Baker, O.J. Specialized pro-resolving receptors are expressed in salivary glands with Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2022, 56, 151865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; Recchiuti, A.; Chiang, N.; Fredman, G.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin D1 Receptor Stereoselectivity and Regulation of Inflammation and Proresolving MicroRNAs. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Tonello, R.; Im, S.T.; Jeon, H.; Park, J.; Ford, Z.; Davidson, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, C.K.; Berta, T. Resolvin D3 controls mouse and human TRPV1-positive neurons and preclinical progression of psoriasis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 12111–12126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.F.; Dona, M.; Fredman, G.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Irimia, D.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin E2 Formation and Impact in Inflammation Resolution. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4527–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.F.; Pillai, P.S.; Recchiuti, A.; Yang, R.; Serhan, C.N. Pro-resolving actions and stereoselective biosynthesis of 18S E-series resolvins in human leukocytes and murine inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Structural elucidation and physiologic functions of specialized pro-resolving mediators and their receptors. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 58, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnig, C.; Frossard, N.; Levy, B.D. Towards targeting resolution pathways of airway inflammation in asthma. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 186, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, B.S.; Hasturk, H.; Kantarci, A.; Freire, M.O.; Nguyen, O.; Kansal, S.; Van Dyke, T.E. Impact of Resolvin E1 on Murine Neutrophil Phagocytosis in Type 2 Diabetes. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Codagnone, M.; Cianci, E.; Lamolinara, A.; Mari, V.C.; Nespoli, A.; Isopi, E.; Mattoscio, D.; Arita, M.; Bragonzi, A.; Iezzi, M.; et al. Resolvin D1 enhances the resolution of lung inflammation caused by long-term Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duvall, M.G.; Levy, B.D. DHA- and EPA-derived resolvins, protectins, and maresins in airway inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, N.; Sakuma, M.; Rodriguez, A.R.; Spur, B.W.; Irimia, D.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin T-series reduce neutrophil extracellular traps. Blood 2022, 139, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidzadeh, K.; Christensen, S.M.; Dalby, E.; Chandrasekaran, P.; Mosser, D.M. Macrophages and the Recovery from Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 567–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oishi, Y.; Manabe, I. Macrophages in inflammation, repair and regeneration. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Vicario, C.; Rius, B.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Garcia-Alonso, V.; Lopategi, A.; Titos, E.; Claria, J. Pro-resolving mediators produced from EPA and DHA: Overview of the pathways involved and their mechanisms in metabolic syndrome and related liver diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamiya, R.; Fukunaga, K.; Arita, M.; Miyata, J.; Seki, H.; Minematsu, N.; Suematsu, M.; Asano, K. Resolvin E1 maintains macrophage function under cigarette smoke-induced oxidative stress. FEBS Open Bio 2012, 2, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dona, M.; Fredman, G.; Schwab, J.M.; Chiang, N.; Arita, M.; Goodarzi, A.; Cheng, G.; von Andrian, U.H.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin E1, an EPA-derived mediator in whole blood, selectively counterregulates leukocytes and platelets. Blood 2008, 112, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, Z.; Marinello, M.; Decker, C.; Sansbury, B.E.; Sadhu, S.; Gerlach, B.D.; Bossardi Ramos, R.; Adam, A.P.; Spite, M.; Fredman, G. Resolvin D1 Enhances Necroptotic Cell Clearance Through Promoting Macrophage Fatty Acid Oxidation and Oxidative Phosphorylation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1062–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Feng, N.; Cui, J.; Wang, S.; Qu, H.; Fu, G.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; et al. Resolvin D1 and D2 inhibit tumour growth and inflammation via modulating macrophage polarization. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 8045–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recchiuti, A.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Fredman, G.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. MicroRNAs in resolution of acute inflammation: Identification of novel resolvin D1-miRNA circuits. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakai, Y.; Kobayashi, M. Lymphocyte ‘homing’ and chronic inflammation. Pathol. Int. 2015, 65, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Ramon, S.; Thatcher, T.H.; Woeller, C.F.; Sime, P.J.; Phipps, R.P. Specialized proresolving mediators (SPMs) inhibit human B-cell IgE production. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizraji, G.; Heyman, O.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Wilensky, A. Resolvin D2 Restrains Th1 Immunity and Prevents Alveolar Bone Loss in Murine Periodontitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, H.; Saegusa, J.; Sendo, S.; Ueda, Y.; Okano, T.; Shinohara, M.; Morinobu, A. Effect of resolvin D5 on T cell differentiation and osteoclastogenesis analyzed by lipid mediator profiling in the experimental arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Ding, S.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Sun, L. Resolvin D1 Improves the Treg/Th17 Imbalance in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through miR-30e-5p. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 668760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oner, F.; Alvarez, C.; Yaghmoor, W.; Stephens, D.; Hasturk, H.; Firatli, E.; Kantarci, A. Resolvin E1 Regulates Th17 Function and T Cell Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 637983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, J.; Arita, M. Role of omega-3 fatty acids and their metabolites in asthma and allergic diseases. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.N.; Kundu, J.K.; Cha, Y.N.; Surh, Y.J. Resolvin D1 stimulates efferocytosis through p50/p50-mediated suppression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 4037–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haworth, O.; Cernadas, M.; Levy, B.D. NK cells are effectors for resolvin E1 in the timely resolution of allergic airway inflammation. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6129–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newcombe, E.A.; Camats-Perna, J.; Silva, M.L.; Valmas, N.; Huat, T.J.; Medeiros, R. Inflammation: The link between comorbidities, genetics, and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiberi, M.; Chiurchiu, V. Specialized Pro-resolving Lipid Mediators and Glial Cells: Emerging Candidates for Brain Homeostasis and Repair. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 673549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Carrasco, J.; Martin-Bermejo, M.J.; Pereyra, G.; Mateo, M.I.; Borroto, A.; Brosseron, F.; Kummer, M.P.; Schwartz, S.; López-Atalaya, J.P.; Alarcon, B.; et al. SFRP1 modulates astrocyte-to-microglia crosstalk in acute and chronic neuroinflammation. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e51696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Bittner, S.; Kaiser, F.M.; Wiendl, H.; Kissler, S. IL-17 silencing does not protect nonobese diabetic mice from autoimmune diabetes. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.Z.; Zhang, B.Z.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhang, Z.Y. Resolvin D1 ameliorates cognitive impairment following traumatic brain injury via protecting astrocytic mitochondria. J. Neurochem. 2020, 154, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R.; Planel, E.; Terrando, N. Impaired Resolution of Inflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelmoaty, S.; Wigerblad, G.; Bas, D.B.; Codeluppi, S.; Fernandez-Zafra, T.; El-Awady, E.-S.; Moustafa, Y.; Abdelhamid Ael, D.; Brodin, E.; Svensson, C.I. Spinal actions of lipoxin A4 and 17(R)-resolvin D1 attenuate inflammation-induced mechanical hypersensitivity and spinal TNF release. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhu, Q.; Wen, S.; Yang, C.X.; Fu, Z.J.; Sun, T. Resolvin D2 Relieving Radicular Pain is Associated with Regulation of Inflammatory Mediators, Akt/GSK-3beta Signal Pathway and GPR18. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 2384–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reglero-Real, N.; Colom, B.; Bodkin, J.V.; Nourshargh, S. Endothelial Cell Junctional Adhesion Molecules: Role and Regulation of Expression in Inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wen, H.X.; Tao, Z.; Li, H.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, L.M.; et al. Resolvin D1 Stimulates Alveolar Fluid Clearance through Alveolar Epithelial Sodium Channel, Na,K-ATPase via ALX/cAMP/PI3K Pathway in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3765–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, R.; Mani, A.M.; Singh, N.K.; Rao, G.N. Resolvin D1 blocks H2O2-mediated inhibitory crosstalk between SHP2 and PP2A and suppresses endothelial-monocyte interactions. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 117, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Gui, P.; Yao, C.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Xie, W.; Yao, S.; Lin, Y.; et al. Resolvin D1 reverts lipopolysaccharide-induced TJ proteins disruption and the increase of cellular permeability by regulating IkappaBalpha signaling in human vascular endothelial cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 185715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamoon, L.; Espitia-Corredor, J.A.; Dongil, P.; Menendez-Ribes, M.; Romero, A.; Valencia, I.; Diaz-Araya, G.; Sanchez-Ferrer, C.F.; Peiro, C. Resolvin E1 attenuates doxorubicin-induced endothelial senescence by modulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 201, 115078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sulciner, M.L.; Serhan, C.N.; Gilligan, M.M.; Mudge, D.K.; Chang, J.; Gartung, A.; Lehner, K.A.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Schmidt, B.; Dalli, J.; et al. Resolvins suppress tumor growth and enhance cancer therapy. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattoscio, D.; Isopi, E.; Lamolinara, A.; Patruno, S.; Medda, A.; De Cecco, F.; Chiocca, S.; Iezzi, M.; Romano, M.; Recchiuti, A. Resolvin D1 reduces cancer growth stimulating a protective neutrophil-dependent recruitment of anti-tumor monocytes. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yao, B.; Chen, T.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Niu, Y.; Song, T.; et al. Resolvin D1 prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition and reduces the stemness features of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting paracrine of cancer-associated fibroblast-derived COMP. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittert, J.; Heinrich, M.A.; Kuninty, P.R.; Storm, G.; Prakash, J. Reprogramming tumor stroma using an endogenous lipid lipoxin A4 to treat pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 420, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, S.; Gao, F. PI3K Mediates the Effect of Resolvin D1 on the Protein Expression of Epithelial Sodium Channel in A549 Cells Treated with Lipopolysaccharide. J. Med. Res. 2013, 42, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, M.K.; Lee, E.J.; Lee, C.H. Resolvin D1 inhibits TGF-beta 1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition of A549 lung cancer cells via lipoxin A4 receptor/formyl peptide receptor 2 and GPR32. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2801–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.; Hua, X.; Zhou, J.; Yang, R. Resolvin D1 and E1 alleviate the progress of hepatitis toward liver cancer in long-term concanavalin A-induced mice through inhibition of NF-κB activity. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valdes, A.M.; Ravipati, S.; Menni, C.; Abhishek, A.; Metrustry, S.; Harris, J.; Nessa, A.; Williams, F.M.K.; Spector, T.D.; Doherty, M.; et al. Association of the resolvin precursor 17-HDHA, but not D- or E-series resolvins, with heat pain sensitivity and osteoarthritis pain in humans. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.L.; Terrando, N.; Xu, Z.Z.; Bang, S.S.; Jordt, S.E.; Maixner, W.; Serhan, C.N.; Ji, R.R. Distinct Analgesic Actions of DHA and DHA-Derived Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators on Post-operative Pain After Bone Fracture in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.M.; Li, C.D.; Zhu, Y.B.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Cao, H. The mechanism of RvD1 alleviates type 2 diabetic neuropathic pain by influencing microglia polarization in rats. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 2017, 33, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Li, L.; Feng, H.; Zhu, J.; et al. Activation of GPR18 by Resolvin D2 Relieves Pain and Improves Bladder Function in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cystitis Through Inhibiting TRPV1. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 4687–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Gu, Y.; Tao, X.; Serhan, C.N.; Ji, R.R. Resolvin D5 Inhibits Neuropathic and Inflammatory Pain in Male But Not Female Mice: Distinct Actions of D-Series Resolvins in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Park, J.Y.; Berta, T.; Yang, R.; Serhan, C.N.; Ji, R.R. Resolvins RvE1 and RvD1 attenuate inflammatory pain via central and peripheral actions. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.H.; Gao, X.; Tang, Y.R.; Chen, F.Q.; Yu, Y.; Sun, M.J.; Li, Y. Resolvin D1 Alleviates Mechanical Allodynia via ALX/FPR2 Receptor Targeted Nod-like Receptor Protein 3/Extracellular Signal-Related Kinase Signaling in a Neuropathic Pain Model. Neuroscience 2022, 494, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasabova, I.A.; Golovko, M.Y.; Golovko, S.A.; Simone, D.A.; Khasabov, S.G. Intrathecal administration of Resolvin D1 and E1 decreases hyperalgesia in mice with bone cancer pain: Involvement of endocannabinoid signaling. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020, 151, 106479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredman, G.; Hellmann, J.; Proto, J.D.; Kuriakose, G.; Colas, R.A.; Dorweiler, B.; Connolly, E.S.; Solomon, R.; Jones, D.M.; Heyer, E.J.; et al. An imbalance between specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and pro-inflammatory leukotrienes promotes instability of atherosclerotic plaques. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salic, K.; Morrison, M.C.; Verschuren, L.; Wielinga, P.Y.; Wu, L.J.; Kleemann, R.; Gjorstrup, P.; Kooistra, T. Resolvin E1 attenuates atherosclerosis in absence of cholesterol-lowering effects and on top of atorvastatin. Atherosclerosis 2016, 250, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, K.J.; Spite, M.; Owens, C.D.; Lancero, H.; Kroemer, A.H.; Pande, R.; Creager, M.A.; Serhan, C.N.; Conte, M.S. Aspirin-triggered lipoxin and resolvin E1 modulate vascular smooth muscle phenotype and correlate with peripheral atherosclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, J.R.; Lemnitzer, P.; Jansen, Y.; Csaba, G.; Winter, C.; Neideck, C.; Silvestre-Roig, C.; Dittmar, G.; Döring, Y.; Drechsler, M.; et al. Resolving Lipid Mediators Maresin 1 and Resolvin D2 Prevent Atheroprogression in Mice. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elajami, T.K.; Colas, R.A.; Dalli, J.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N.; Welty, F.K. Specialized proresolving lipid mediators in patients with coronary artery disease and their potential for clot remodeling. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 2792–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keeley, E.C.; Li, H.J.; Cogle, C.R.; Handberg, E.M.; Merz, C.N.B.; Pepine, C.J. Specialized Proresolving Mediators in Symptomatic Women With Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction (from the Women’s Ischemia Trial to Reduce Events in Nonobstructive CAD [WARRIOR] Trial). Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 162, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.A.; Hasturk, H.; Kantarci, A.; Serhan, C.N.; Van Dyke, T. Atherosclerosis, Periodontal Disease, and Treatment with Resolvins. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, I.; Rabelo, R.A.N.; Barbosa, C.; Rates, M.; Fuentes-Retamal, S.; Gonzalez-Herrera, F.; Guzman-Rivera, D.; Quintero, H.; Kemmerling, U.; Castillo, C.; et al. Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 reduces parasitic cardiac load by decreasing inflammation in a murine model of early chronic Chagas disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lontchi-Yimagou, E.; Sobngwi, E.; Matsha, T.E.; Kengne, A.P. Diabetes mellitus and inflammation. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 13, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barden, A.; Shinde, S.; Phillips, M.; Beilin, L.; Mas, E.; Hodgson, J.M.; Puddey, I.; Mori, T.A. The effects of alcohol on plasma lipid mediators of inflammation resolution in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 133, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevalye, H.; Yorek, M.S.; Coppey, L.J.; Holmes, A.; Harper, M.M.; Kardon, R.H.; Yorek, M.A. Effect of enriching the diet with menhaden oil or daily treatment with resolvin D1 on neuropathy in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 114, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, Q.; Hu, K.; He, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z. Resolvin D1 protects against Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis in diabetes by blocking the MAPK-NF-kappaB pathway. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 216, 108941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Saito, T.; Aoki-Saito, H.; Okada, S.; Ikeda, H.; Nakakura, T.; Fukuda, H.; Arai, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Nakajima, Y.; et al. Resolvin E3 ameliorates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance via the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway in adipocytes. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyama, S.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Shimoda, K.; Ide, S.; Satoh, M.; Minami, M. Resolvin D1 and D2 Reverse Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depression-Like Behaviors Through the mTORC1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Hitora-Imamura, N.; Deyama, S.; Minami, M. Resolvin D2 attenuates chronic pain-induced depression-like behavior in mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2021, 41, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyama, S.; Minami, M.; Kaneda, K. Resolvins as potential candidates for the treatment of major depressive disorder. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 147, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyama, S.; Duman, R.S. Neurotrophic mechanisms underlying the rapid and sustained antidepressant actions of ketamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 188, 172837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyama, S.; Shimoda, K.; Ikeda, H.; Fukuda, H.; Shuto, S.; Minami, M. Resolvin E3 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 138, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Deyama, S.; Shimoda, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Ide, S.; Satoh, M.; Minami, M. Rapid and sustained antidepressant effects of resolvin D1 and D2 in a chronic unpredictable stress model. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 332, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, Y.D.; Omori, K.; Ito, T.; Yamashiro, K.; Nakamura, S.; Okamoto, K.; Ono, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Takashiba, S. Resolvin D2 Induces Resolution of Periapical Inflammation and Promotes Healing of Periapical Lesions in Rat Periapical Periodontitis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; Krzyszczyk, P.; Berthiaume, F. Pro-Resolution Potency of Resolvins D1, D2 and E1 on Neutrophil Migration and in Dermal Wound Healing. Nano Life 2017, 7, 1750002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, T.L.; Kakazu, A.H.; He, J.; Jun, B.; Bazan, N.G.; Bazan, H.E.P. Novel RvD6 stereoisomer induces corneal nerve regeneration and wound healing post-injury by modulating trigeminal transcriptomic signature. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozgul Ozdemir, R.B.; Soysal Gunduz, O.; Ozdemir, A.T.; Akgul, O. Low levels of pro-resolving lipid mediators lipoxin-A4, resolvin-D1 and resolvin-E1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 227, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabdoun, H.A.; Kulbay, M.; Rondon, E.-P.; Vallières, F.; Shi, Q.; Fernandes, J.; Fahmi, H.; Benderdour, M. In vitro and in vivo assessment of the proresolutive and antiresorptive actions of resolvin D1: Relevance to arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Ma, J.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, C.; Zhong, H.; Ling, H.; Xie, Z.; Tian, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T.; et al. Resolvin D1 suppresses pannus formation via decreasing connective tissue growth factor caused by upregulation of miRNA-146a-5p in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flak, M.B.; Koenis, D.S.; Sobrino, A.; Smith, J.; Pistorius, K.; Palmas, F.; Dalli, J. GPR101 mediates the pro-resolving actions of RvD5n-3 DPA in arthritis and infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Funaki, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Okazaki, R.; Yamasaki, A.; Sueda, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Yanai, M.; Fukushima, T.; Harada, T.; Makino, H.; et al. Resolvin E1 Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Resorption by Suppressing IL-17-induced RANKL Expression in Osteoblasts and RANKL-induced Osteoclast Differentiation. Yonago Acta Med. 2018, 61, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattoscio, D.; Ferri, G.; Miccolo, C.; Chiocca, S.; Romano, M.; Recchiuti, A. Gene Expression of the D-Series Resolvin Pathway Predicts Activation of Anti-Tumor Immunity and Clinical Outcomes in Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Name | Structure | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Resolvin D1 | 7S, 8R, 17S-trihydroxy-docosa-4Z, 9E, 11E, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | RvD1 |
| Resolvin D2 | 7S, 16R, 17S-trihydroxy-docosa-4Z, 8E, 10Z, 12E, 14E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | RvD2 |
| Resolvin D3 | 4S, 11R, 17S-trihydroxy-docosa-5Z, 7E, 9E, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | RvD3 |
| Resolvin D4 | 4S, 5R, 17S-trihydroxy-docosa-6E, 8E,10Z, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | RvD4 |
| Resolvin D5 | 7S, 17S-dihydroxy-docosa-4Z, 8E, 10Z, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | RvD5 |
| Resolvin D6 | 4S, 17S-trihydroxy-docosa-5E, 7Z, 10Z, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | RvD6 |
| 17R-Resolvin D1 | 7S, 8R, 17R-trihydroxy-docosa-4Z, 9E, 11E, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | 17R-RvD1 |
| 17R-Resolvin D2 | 7S, 16R, 17R-trihydroxy-docosa-4Z, 8E, 10Z, 12E, 14E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | 17R-RvD2 |
| 17R-Resolvin D3 | 4S, 11R, 17R-trihydroxy-docosa-5Z, 7E, 9E, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | 17R-RvD3 |
| 17R-Resolvin D4 | 4S, 5R, 17R-trihydroxy-docosa-6E, 8E,10Z, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | 17R-RvD4 |
| 17R-Resolvin D5 | 7S, 17R-dihydroxy-docosa-4Z, 8E, 10Z, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | 17R-RvD5 |
| 17R-Resolvin D6 | 4S, 17R-trihydroxy-docosa-5E, 7Z, 10Z, 13Z, 15E, 19Z-hexanoic acid | 17R-RvD6 |
| Resolvin E1 | 5S, 12R, 18R-trihydroxy-eicosa-6Z, 8E, 10E, 14Z, 16E-pentaenoic acid | RvE1 |
| 18S-Resolvin E1 | 5S, 12R, 18S-trihydroxy-eicosa-6Z, 8E, 10E, 14Z, 16E-pentaenoic acid | 18S-RvE1 |
| Resolvin E2 | 5S, 18R-dihydroxy-eicosa-6E, 8Z, 11Z, 14Z, 16E-pentaenoic acid | RvE2 |
| Resolvin E3 | 17R, 18R-dihydroxy-eicosa-5Z, 8Z, 11Z, 13E,15E-pentaenoic acid | RvE3 |
| Resolvin E4 | 5S, 15S-dihydroxy-eicosa-6E, 8Z, 11Z, 13E, 17Z-pentaenoic acid | RvE4 |
| Resolvin T1 | 7S,13R,20S-trihydroxy-8E,10Z,14E,16Z,18E-docosapentaenoicacid | RvT1 |
| Resolvin T2 | 7S,12R,13S-trihydroxy-8Z,10E,14E,16Z,19Z-docosapentaenoic acid | RvT2 |
| Resolvin T3 | 7S,8R,13S-trihydroxy-9E,11E,14E,16Z,19Z-docosapentaenoic acid | RvT3 |
| Resolvin T4 | 7S,13R-dihydroxy-8E,10Z,14E,16Z,19Z-docosapentaenoic acid | RvT4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Fan, D.; Lei, Q.; Lu, A.; He, X. Roles of Resolvins in Chronic Inflammatory Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314883
Liu C, Fan D, Lei Q, Lu A, He X. Roles of Resolvins in Chronic Inflammatory Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314883
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chang, Dancai Fan, Qian Lei, Aiping Lu, and Xiaojuan He. 2022. "Roles of Resolvins in Chronic Inflammatory Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314883
APA StyleLiu, C., Fan, D., Lei, Q., Lu, A., & He, X. (2022). Roles of Resolvins in Chronic Inflammatory Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314883






