Dual CXCR4/IL-10 Gene-Edited Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exhibit Robust Therapeutic Properties in Chronic Wound Healing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
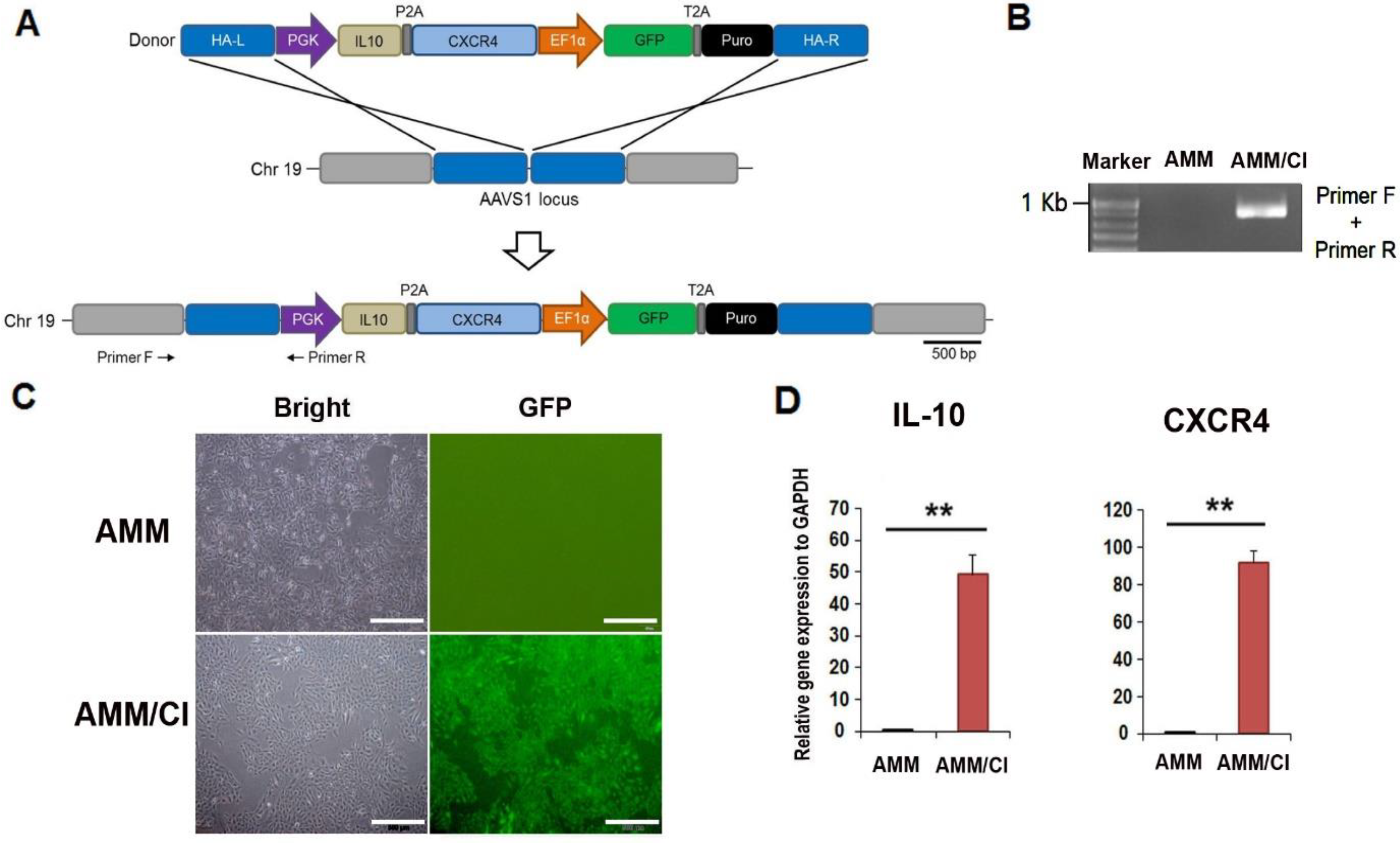
2.1. Generation of an CXCR4/IL-10 Knock-in AMM Line
2.2. Factors Secreted by AMM/CI Promoted Matrigel Tube Formation
2.3. Factors Secreted by AMM/CI Promoted Phagocytosis
2.4. Factors Secreted by AMM/CI Showed an Anti-Inflammatory Effect
2.5. AMM/CI Strongly Promoted Wound Healing
2.6. AMM/CI Induced Multiple Biological Factors for Wound Healing
2.7. AMM/CI Maintained High Re-Epithelialization Potential in Wounds
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Donor Construction, Transfection and Selection
4.3. Quantitative Real-Time (qRT)-PCR Analysis
4.4. Culture Medium Preparation
4.5. Matrigel Tube Formation Assay
4.6. Phagocytic Assay
4.7. Neutral Red Phagocytic Activity
4.8. Nitric Oxide (NO) Assay
4.9. Generation of Type 1 Diabetes Mice Model
4.10. Excisional Wound Mouse Model and Cell Injection
4.11. Wound Analysis
4.12. Histological Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, P.; Nunan, R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound healing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuss, S.; Becher, E.; Woltje, M.; Tietze, L.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Functional expression of HGF and HGF receptor/c-met in adult human mesenchymal stem cells suggests a role in cell mobilization, tissue repair, and wound healing. Stem Cells 2004, 22, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Scott, P.G.; Tredget, E.E. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through differentiation and angiogenesis. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 2648–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suh, W.; Kim, K.L.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, I.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Jang, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Byun, J.; Choi, J.H.; et al. Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells accelerates dermal wound healing with increased recruitment of monocytes/macrophages and neovascularization. Stem Cells 2005, 23, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, D.; Xiao, H.; Wu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, F. Paracrine effects of adipose-derived stem cells in cutaneous wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Wound Care 2022, 31 (Suppl. 3), S29–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukomska, B.; Stanaszek, L.; Zuba-Surma, E.; Legosz, P.; Sarzynska, S.; Drela, K. Challenges and Controversies in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 9628536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirhaj, M.; Labbaf, S.; Tavakoli, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Emerging treatment strategies in wound care. Int. Wound J. 2022, 19, 1934–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golchin, A.; Shams, F.; Basiri, A.; Ranjbarvan, P.; Kiani, S.; Sarkhosh-Inanlou, R.; Ardeshirylajimi, A.; Gholizadeh-Ghaleh Aziz, S.; Sadigh, S.; Rasmi, Y. Combination Therapy of Stem Cell-derived Exosomes and Biomaterials in the Wound Healing. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 1892–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettet, G.; Chaplain, M.A.; McElwain, D.L.; Byrne, H.M. On the role of angiogenesis in wound healing. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1996, 263, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar]
- Seeger, F.H.; Rasper, T.; Koyanagi, M.; Fox, H.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. CXCR4 expression determines functional activity of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells for therapeutic neovascularization in acute ischemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima e Silva, R.; Shen, J.; Hackett, S.F.; Kachi, S.; Akiyama, H.; Kiuchi, K.; Yokoi, K.; Hatara, M.C.; Lauer, T.; Aslam, S.; et al. The SDF-1/CXCR4 ligand/receptor pair is an important contributor to several types of ocular neovascularization. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 3219–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.; Balaji, S.; Le, L.D.; Crombleholme, T.M.; Keswani, S.G. Regenerative Wound Healing: The Role of Interleukin-10. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, G.; Ceilley, R. Chronic Wound Healing: A Review of Current Management and Treatments. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frykberg, R.G.; Banks, J. Challenges in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 560–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, V.W.; Gurtner, G.C. Tissue engineering for the management of chronic wounds: Current concepts and future perspectives. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benabdellah, K.; Sanchez-Hernandez, S.; Aguilar-Gonzalez, A.; Maldonado-Perez, N.; Gutierrez-Guerrero, A.; Cortijo-Gutierrez, M.; Ramos-Hernandez, I.; Tristan-Manzano, M.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Herrera, C.; et al. Genome-edited adult stem cells: Next-generation advanced therapy medicinal products. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeo, M.; Lee, W.; Ito, M. Wound healing and skin regeneration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a023267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Huang, G.; Wei, Z.; Nie, K.; Liu, Z.; Deng, C.; Wang, D. IL-10 Gene-Modified Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Augment Regenerative Wound Healing by Multiple Synergistic Effects. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 9158016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Teng, L.; Lu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhao, M. Interleukin-10-Modified Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevent Hypertrophic Scar Formation via Regulating the Biological Characteristics of Fibroblasts and Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 6368311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Biswas, S.; Shang, Y.; Collard, E.; Azad, A.; Kauh, C.; Bhasker, V.; Gordillo, G.M.; Sen, C.K.; Roy, S. Macrophage dysfunction impairs resolution of inflammation in the wounds of diabetic mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meszaros, A.J.; Reichner, J.S.; Albina, J.E. Macrophage phagocytosis of wound neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 65, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yu, R.; Cai, T.; Chen, Z.; Lan, M.; Zou, T.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y. Effects of immune cells and cytokines on inflammation and immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 88, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Helming, L.; Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages: An immunologic functional perspective. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.W.; Houge, M.; Brown, M.; Davis, M.E.; Yoon, Y.S. Cultured human bone marrow-derived CD31+ cells are effective for cardiac and vascular repair through enhanced angiogenic, adhesion, and anti-inflammatory effects. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Shin, M.S.; Lee, H.J.; Ko, J.H.; Wee, W.R.; Lee, J.H. The anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic role of mesenchymal stem cells in corneal wound healing following chemical injury. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Han, S.; Kim, S.W. SDF-1-edited human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells stimulate angiogenesis in treating hindlimb ischaemia. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 3726–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, D.S.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, S.W. Anti-Arthritogenic Property of Interleukin 10-Expressing Human Amniotic MSCs Generated by Gene Editing in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Kim, H.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, J.U.; Levit, R.; Yoon, Y.S. Human peripheral blood-derived CD31+ cells have robust angiogenic and vasculogenic properties and are effective for treating ischemic vascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.W.; Zhang, H.Z.; Guo, L.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, M.H. Amniotic mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing in diabetic NOD/SCID mice through high angiogenic and engraftment capabilities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Guo, L.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.W. Characteristics of circulating CD31+ cells from patients with coronary artery disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 2321–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, T.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.K. Pinus densiflora needle supercritical fluid extract suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators iNOS, IL-6 and IL-1beta, and activation of inflammatory STAT1 and STAT3 signaling proteins in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-challenged murine macrophages. Daru 2017, 25, 18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





| Score | Dermal and Epidermal Regeneration | Granulation Tissue Thickness | Re-Epithelization (10 Days Wounds Only) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–3 | Little epidermal and dermal organization | Thin granulation layer | Cytokeratin+ cells < 100/mm2 |
| 4–6 | Moderate dermal and epidermal organization | Moderate granulation layer | Cytokeratin+ cells 100~200/mm2 |
| 7–9 | Complete remodeling of dermis and epidermis | Thick granulation layer | Cytokeratin+ cells < 300/mm2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.-H.; Chae, D.-S.; Kim, S.-W. Dual CXCR4/IL-10 Gene-Edited Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exhibit Robust Therapeutic Properties in Chronic Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315338
Han S-H, Chae D-S, Kim S-W. Dual CXCR4/IL-10 Gene-Edited Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exhibit Robust Therapeutic Properties in Chronic Wound Healing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):15338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315338
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Seong-Ho, Dong-Sik Chae, and Sung-Whan Kim. 2022. "Dual CXCR4/IL-10 Gene-Edited Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exhibit Robust Therapeutic Properties in Chronic Wound Healing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 15338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315338
APA StyleHan, S.-H., Chae, D.-S., & Kim, S.-W. (2022). Dual CXCR4/IL-10 Gene-Edited Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exhibit Robust Therapeutic Properties in Chronic Wound Healing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 15338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315338






