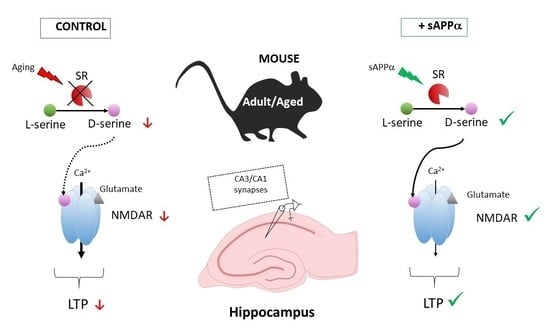
Improved NMDA Receptor Activation by the Secreted Amyloid-Protein Precursor-α in Healthy Aging: A Role for D-Serine?
Abstract
Share and Cite
Billard, J.-M.; Freret, T. Improved NMDA Receptor Activation by the Secreted Amyloid-Protein Precursor-α in Healthy Aging: A Role for D-Serine? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415542
Billard J-M, Freret T. Improved NMDA Receptor Activation by the Secreted Amyloid-Protein Precursor-α in Healthy Aging: A Role for D-Serine? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415542
Chicago/Turabian StyleBillard, Jean-Marie, and Thomas Freret. 2022. "Improved NMDA Receptor Activation by the Secreted Amyloid-Protein Precursor-α in Healthy Aging: A Role for D-Serine?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415542
APA StyleBillard, J.-M., & Freret, T. (2022). Improved NMDA Receptor Activation by the Secreted Amyloid-Protein Precursor-α in Healthy Aging: A Role for D-Serine? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415542