Antimicrobial Peptide LCN2 Inhibited Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection in Bladder Cells in a High-Glucose Environment through JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
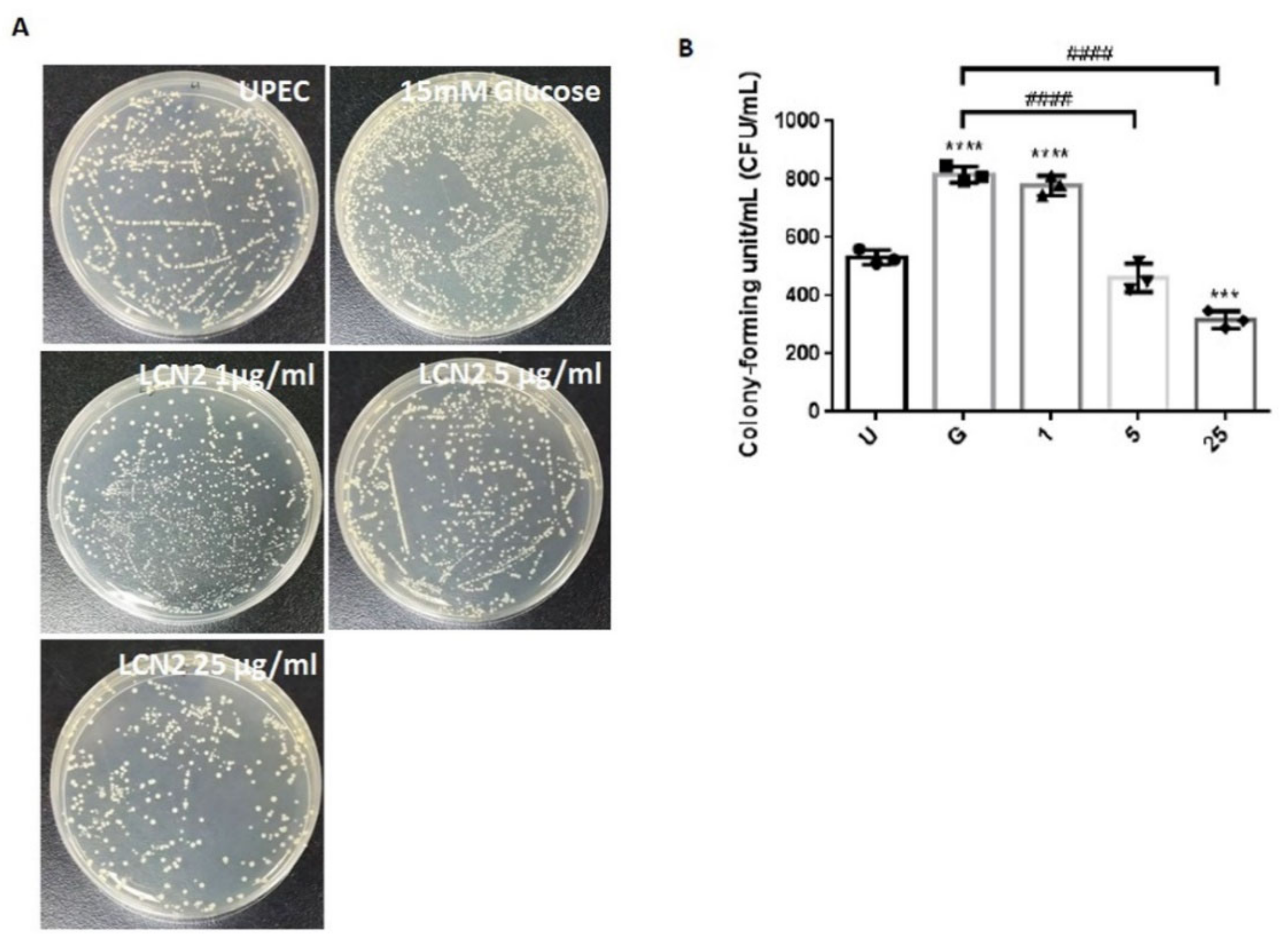
2.1. LCN2 Suppresses UPEC Infections in Bladder Cells in a High-Glucose Environment
2.2. LCN2 Suppresses UPEC Infections and Downregulates the Expression of STAT1/3 and TLR-4 in SV-HUC-1 Cells
2.3. LCN2 Reduces the UPEC-Induced Exogenous Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion
2.4. LCN2-Mediated Suppression in UPEC Infection and Inflammatory Responses in Bladder Cells Is Related to Downregulation of the JAK/STAT Pathway and TLR-4 Expression
2.5. LCN2 Decreased UPEC Infections in Bladder Cells, Which May Be Associated with the Regulation of the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway
2.6. Increased UPEC Infections in Bladder Cells in a High-Glucose Environment Were Inhibited by LCN2 Downregulating the JAK/STAT-Pathway-Related Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain
4.2. Bladder Cell Culture, LCN2 Pretreatment, and UPEC Infection
4.3. UPEC Infection and Quantification by Colony-Forming Unit (CFU) Counting and Fluorescence Microscopy
4.4. Cell Protein Extraction
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Cytometric Bead Array (CBA) Immunoassay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geerlings, S.E. Urinary tract infections in patients with diabetes mellitus: Epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31 (Suppl. 1), S54–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerius, N.H.; Eff, C.; Hansen, N.E.; Karle, H.; Nerup, J.; Soeberg, B.; Sorensen, S.F. Neutrophil and lymphocyte function in patients with diabetes mellitus. Acta Med. Scand. 1982, 211, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dielubanza, E.J.; Schaeffer, A.J. Urinary tract infections in women. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 95, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quint, H.J.; Drach, G.W.; Rappaport, W.D.; Hoffmann, C.J. Emphysematous cystitis: A review of the spectrum of disease. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, A. Urinary tract infections in patients with diabetes. Am. J. Med. 2002, 113 (Suppl. 1A), 80S–84S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyota, N.; Ogawa, D.; Ishii, K.; Hirata, K.; Wada, J.; Shikata, K.; Makino, H. Emphysematous cystitis in a patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Med. Okayama 2011, 65, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.L.; Neild, G.H. Urinary tract infection. Medicine 2007, 35, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naber, K.G.; Schito, G.; Botto, H.; Palou, J.; Mazzei, T. Surveillance Study in Europe and Brazil on Clinical Aspects and Antimicrobial Resistance Epidemiology in Females with Cystitis (ARESC): Implications for Empiric Therapy. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.; Arianayagam, M.; Rashid, P. Bacterial cystitis in women. Aust. Fam. Physician 2010, 39, 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, I.; Dicks, B.; Kim, N.N.; Hartzell, R. Multidisciplinary Overview of Vaginal Atrophy and Associated Genitourinary Symptoms in Postmenopausal Women. Sex. Med. 2013, 1, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tseng, C.C.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, M.C.; Hor, L.I.; Ko, Y.H.; Huang, J.J. Host and bacterial virulence factors predisposing to emphysematous pyelonephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Halagappa, V.K.; Riazi, S.; Hu, X.; Ecelbarger, C.A. Reduced expression of insulin receptors in the kidneys of insulin-resistant rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2661–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becknell, B.; Schwaderer, A.; Hains, D.S.; Spencer, J.D. Amplifying renal immunity: The role of antimicrobial peptides in pyelonephritis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paragas, N.; Kulkarni, R.; Werth, M.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M.; Forster, C.; Deng, R.; Zhang, Q.; Singer, E.; Klose, A.D.; Shen, T.H.; et al. alpha-Intercalated cells defend the urinary system from bacterial infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2963–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eichler, T.E.; Becknell, B.; Easterling, R.S.; Ingraham, S.E.; Cohen, D.M.; Schwaderer, A.L.; Hains, D.S.; Li, B.; Cohen, A.; Metheny, J.; et al. Insulin and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway regulate Ribonuclease 7 expression in the human urinary tract. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, A.T.; LaBarge, S.A.; McCurdy, C.E.; Schenk, S. Knockout of STAT3 in skeletal muscle does not prevent high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtha, M.J.; Eichler, T.; Bender, K.; Metheny, J.; Li, B.; Schwaderer, A.L.; Mosquera, C.; James, C.; Schwartz, L.; Becknell, B.; et al. Insulin receptor signaling regulates renal collecting duct and intercalated cell antibacterial defenses. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 5634–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. AKT/PKB signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell 2007, 129, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.X.; Lou, K.; Chen, L.J.; Liu, S.D.; Pang, S.G. Lipocalin-2: A role in hepatic gluconeogenesis via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.H.; Liu, S.P.; Fan, C.K.; Tzou, K.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Cheng, P.C. Insulin Downregulated the Infection of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) in Bladder Cells in a High-Glucose Environment through JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Plenge, R.J.I. JAK and STAT signaling molecules in immunoregulation and immune-mediated disease. Immunity 2012, 36, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashili, F.; Chibalin, A.V.; Krook, A.; Zierath, J.R.J.D. Constitutive STAT3 phosphorylation contributes to skeletal muscle insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.H.; Choi, S.E.; Ha, E.S.; Jung, J.G.; Han, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, K.W. IL-6 induction of TLR-4 gene expression via STAT3 has an effect on insulin resistance in human skeletal muscle. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Fang, J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.; Su, S.B. High glucose induces and activates Toll-like receptor 4 in endothelial cells of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2015, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devaraj, S.; Dasu, M.R.; Rockwood, J.; Winter, W.; Griffen, S.C.; Jialal, I. Increased toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 expression in monocytes from patients with type 1 diabetes: Further evidence of a proinflammatory state. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.H.; Fan, C.K.; Wu, C.C.; Yu, H.J.; Liu, H.T.; Chen, K.C.; Liu, S.P.; Cheng, P.C. Enhanced uropathogenic Escherichia coli-induced infection in uroepithelial cells by sugar through TLR-4 and JAK/STAT1 signaling pathways. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.H.; Fan, C.K.; Yu, H.J.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, K.C.; Liu, S.P.; Cheng, P.C. Testosterone suppresses uropathogenic Escherichia coli invasion and colonization within prostate cells and inhibits inflammatory responses through JAK/STAT-1 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.H.; Liao, P.W.; Fan, C.K.; Liu, S.P.; Cheng, P.C. RNase 7 Inhibits Uropathogenic Escherichia coli-Induced Inflammation in Bladder Cells under a High-Glucose Environment by Regulating the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, D.; Yoruk, E.; Kalayci-Yuksek, F.; Uz, G.; Topal-Sarikaya, A.; Ang-Kucuker, M. The Effects of Insulin and Glucose on Different Characteristics of a UPEC: Alterations in Growth Rate and Expression Levels of some Virulence Genes. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.H.; Lu, Y.C.; Fan, C.K.; Yu, H.J.; Liu, H.T.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, K.C.; Liu, S.P.; Cheng, P.C. Testosterone regulates the intracellular bacterial community formation of uropathogenic Escherichia coli in prostate cells via STAT3. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 310, 151450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigedal, M.; Marstad, A.; Haug, M.; Damas, J.K.; Strong, R.K.; Roberts, P.L.; Himpsl, S.D.; Stapleton, A.; Hooton, T.M.; Mobley, H.L.; et al. Lipocalin 2 imparts selective pressure on bacterial growth in the bladder and is elevated in women with urinary tract infection. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 6081–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kluber, P.; Meurer, S.K.; Lambertz, J.; Schwarz, R.; Zechel-Gran, S.; Braunschweig, T.; Hurka, S.; Domann, E.; Weiskirchen, R. Depletion of Lipocalin 2 (LCN2) in Mice Leads to Dysbiosis and Persistent Colonization with Segmented Filamentous Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Jin, M.; Li, H.; Li, S. miR-383 reduces keratinocyte proliferation and induces the apoptosis in psoriasis via disruption of LCN2-dependent JAK/STAT pathway activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.Y.; Kim, D.B.; Ko, S.H.; Jo, Y.H.; Kim, M.J. Induction mechanism of lipocalin-2 expression by co-stimulation with interleukin-1beta and interferon-gamma in RINm5F beta-cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, I.; Save, S.; Kruse, R.; Persson, K. Expression of suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 (SOCS3) in human bladder epithelial cells infected with uropathogenic Escherichia coli. APMIS 2013, 121, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Naka, T.; Kubo, M. SOCS proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.A. The Jak/STAT pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parmar, T.; Parmar, V.M.; Arai, E.; Sahu, B.; Perusek, L.; Maeda, A. Acute Stress Responses Are Early Molecular Events of Retinal Degeneration in Abca4-/-Rdh8-/- Mice After Light Exposure. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 3257–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, G.; Wilting, J.; Hess, C.F.; Ramadori, G.; Malik, I.A. PECAM-1 modulates liver damage induced by synergistic effects of TNF-alpha and irradiation. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3336–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana, Z.; De la Cruz, M.A.; Carrillo-Casas, E.M.; Duran, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hernandez-Castro, R.; Puente, J.L.; Daaka, Y.; Giron, J.A. Production of the Escherichia coli common pilus by uropathogenic E. coli is associated with adherence to HeLa and HTB-4 cells and invasion of mouse bladder urothelium. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berry, R.E.; Klumpp, D.J.; Schaeffer, A.J. Urothelial cultures support intracellular bacterial community formation by uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2762–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baune, B.T.; Ponath, G.; Golledge, J.; Varga, G.; Arolt, V.; Rothermundt, M.; Berger, K. Association between IL-8 cytokine and cognitive performance in an elderly general population—The MEMO-Study. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhabhar, F.S.; Viswanathan, K. Short-term stress experienced at time of immunization induces a long-lasting increase in immunologic memory. Am. J. Physiology. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 289, R738–R744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.-C.; Ho, C.-H.; Fan, C.-K.; Liu, S.-P.; Cheng, P.-C. Antimicrobial Peptide LCN2 Inhibited Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection in Bladder Cells in a High-Glucose Environment through JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415763
Chen P-C, Ho C-H, Fan C-K, Liu S-P, Cheng P-C. Antimicrobial Peptide LCN2 Inhibited Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection in Bladder Cells in a High-Glucose Environment through JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415763
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Pei-Chi, Chen-Hsun Ho, Chia-Kwung Fan, Shih-Ping Liu, and Po-Ching Cheng. 2022. "Antimicrobial Peptide LCN2 Inhibited Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection in Bladder Cells in a High-Glucose Environment through JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415763
APA StyleChen, P.-C., Ho, C.-H., Fan, C.-K., Liu, S.-P., & Cheng, P.-C. (2022). Antimicrobial Peptide LCN2 Inhibited Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection in Bladder Cells in a High-Glucose Environment through JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415763






