Thymoquinone Suppresses Angiogenesis in DEN-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting miR-1-3p
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
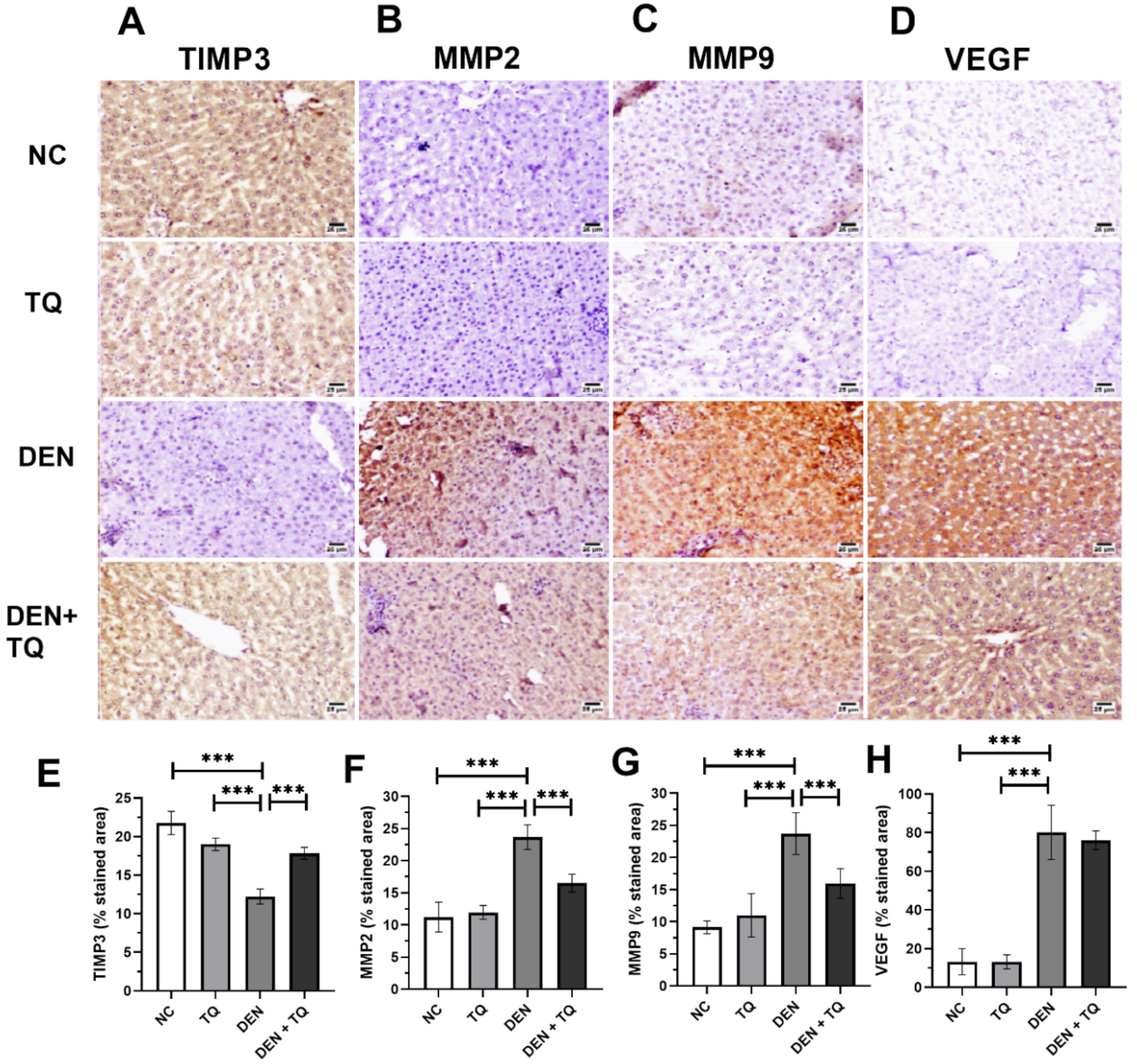
2.1. TQ Decreases the Angiogenesis in DEN-Intoxicated Rats
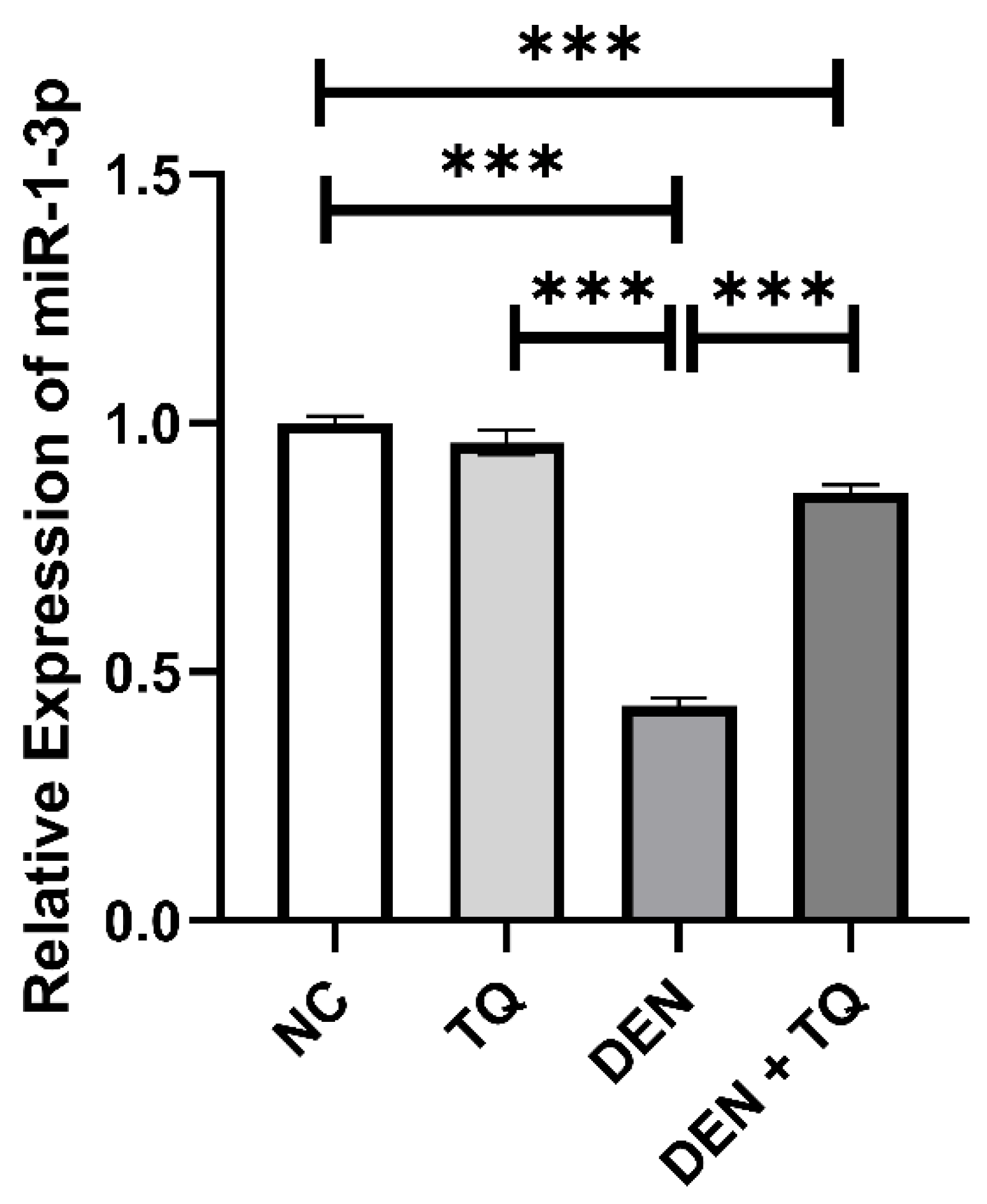
2.2. MiR-1-3p Level Increased in TQ-Treated Rats
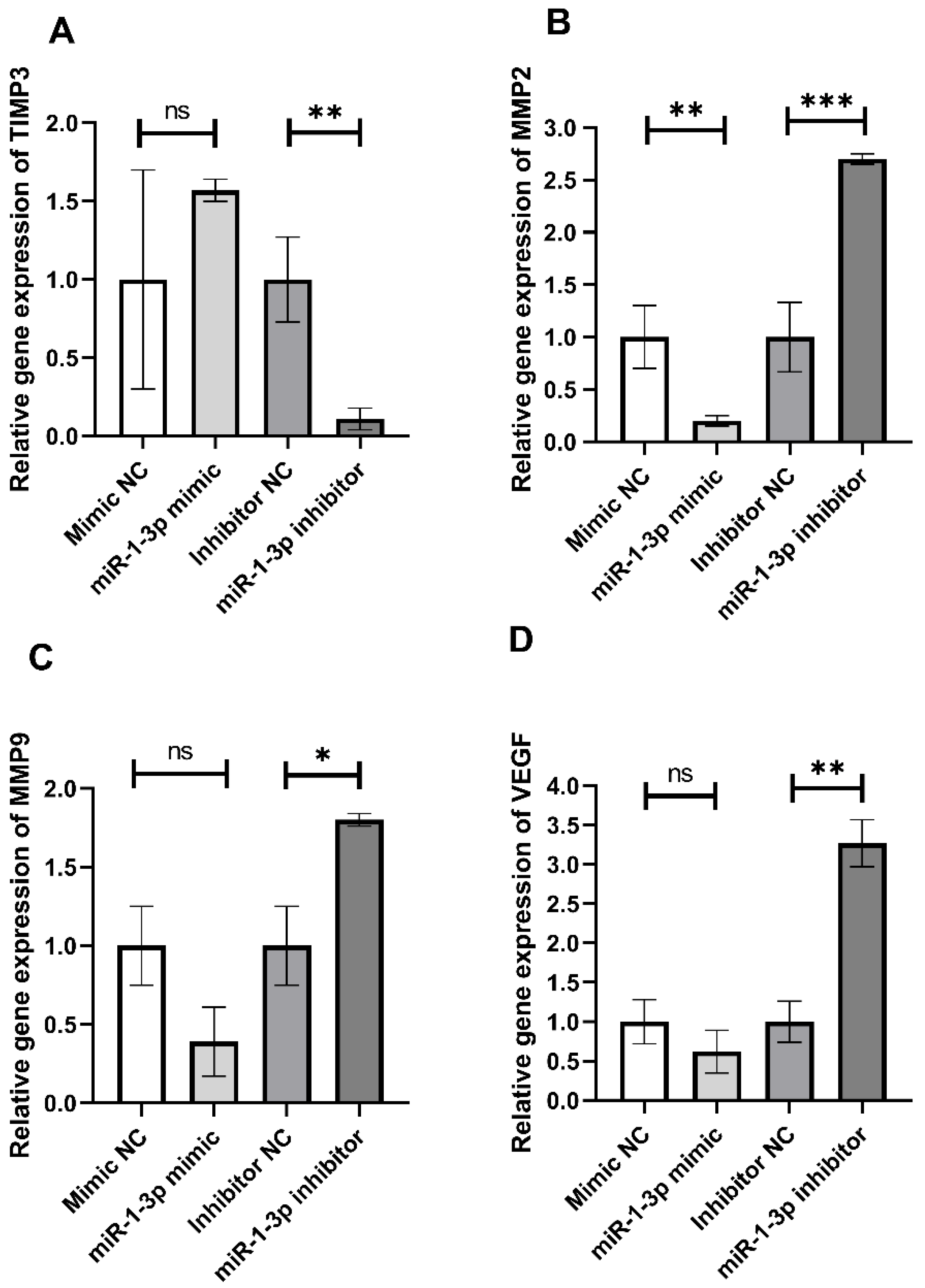
2.3. In Vitro Effect of miR-1-3p on Retardation of HepG2 Cell Migration
2.4. Prediction of Target Genes and Pathway Prediction Analysis for miR-1-3p
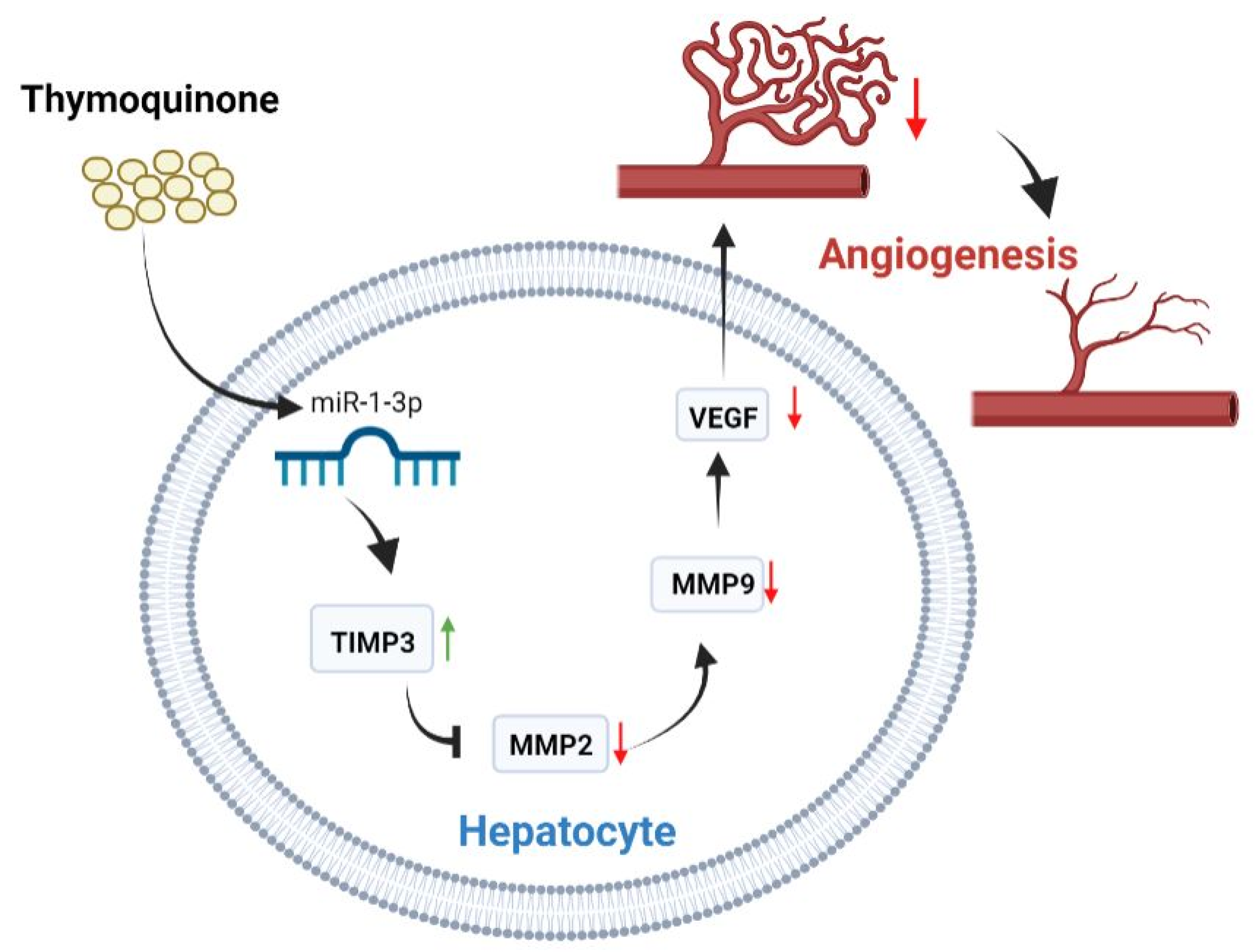
3. Discussion
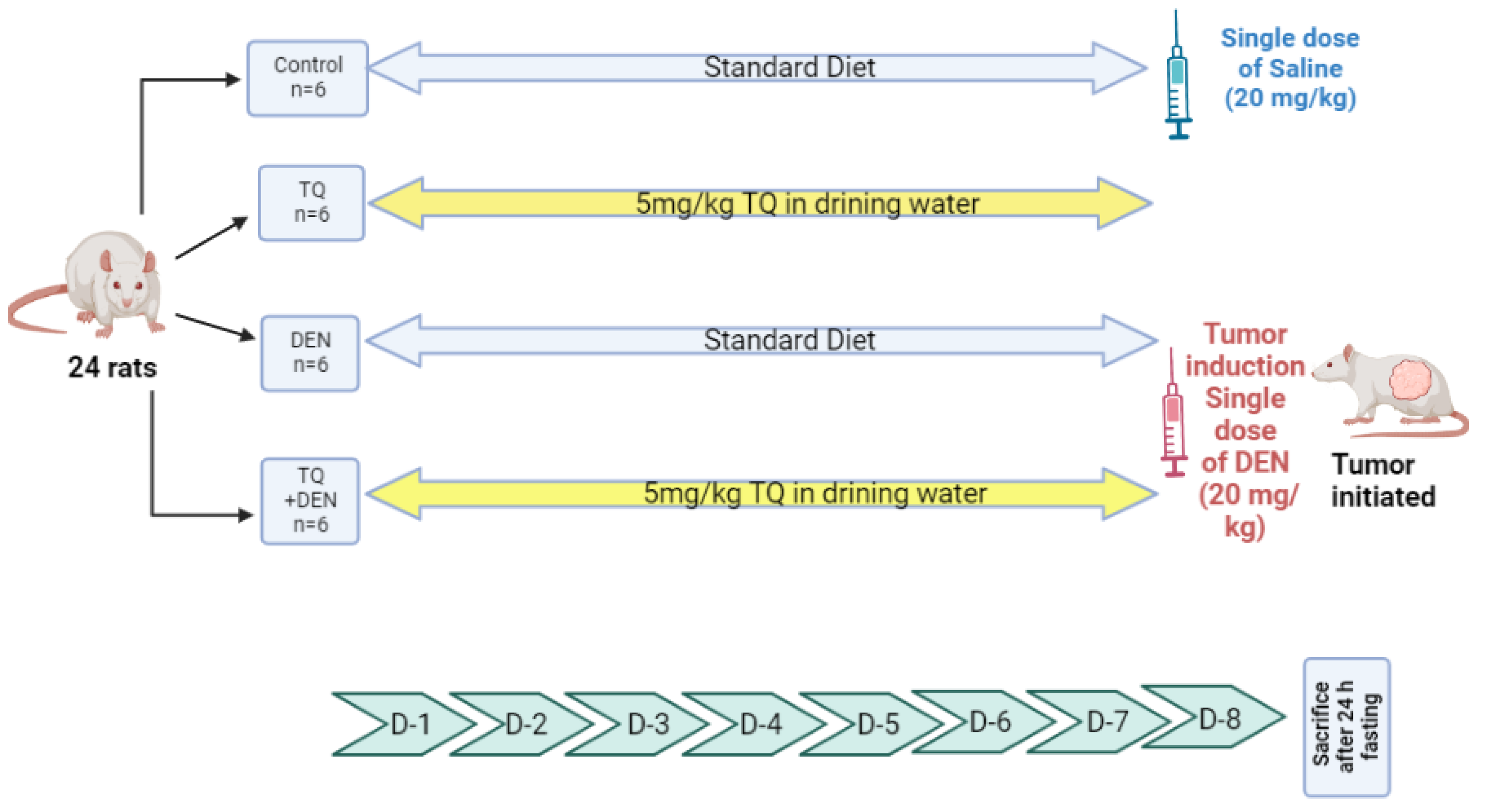
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. DEN Liver Injury Model
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Cell Lines
4.5. Transfecting Cells with Mimic or Inhibitor of miR-1-3p
4.6. RNA Isolation and Gene Expression Levels of miR-1-3p, TIMP3, MMP2, MMP9, and VEGF by RT-qPCR
4.7. Wound Healing Assay
4.8. Relationship between miR-1-3p and TIMP3 at Post-Transcriptional Level
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; El-Serag, H.B.; Debakey, M.E. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Consider the population. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moawad, A.W.; Szklaruk, J.; Lall, C.; Blair, K.J.; Kaseb, A.O.; Kamath, A.; Rohren, S.A.; Elsayes, K.M. Angiogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Pathophysiology, Targeted Therapy, and Role of Imaging. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2020, 7, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Burroughs, A.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2003, 362, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaseb, A.O.; Hanbali, A.; Cotant, M.; Hassan, M.M.; Wollner, I.; Philip, P.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of literature. Cancer 2009, 115, 4895–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.D.; Lazaryan, A.; Aucejo, F.; Eghtesad, B.; Pelley, R.; Fung, J.; Miller, C.; Yerian, L. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFr2) expression and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma following liver transplantation: The Cleveland Clinic experience. J. Liver Transl. 2008, 26, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadabadi, M.R.; Mozafari, M.R. Enhanced efficacy and bioavailability of thymoquinone using nanoliposomal dosage form. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 47, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, I.I.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Volceanov, A.; Andronescu, E. Nanobiomaterials Used in Cancer Therapy: An Up-To-Date Overview. Molecules 2019, 24, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashmawy, N.E.; Khedr, E.G.; Ebeid, E.Z.M.; Salem, M.L.; Zidan, A.A.A.; Mosalam, E.M. Enhanced anticancer effect and reduced toxicity of doxorubicin in combination with thymoquinone released from poly-N-acetyl glucosamine nanomatrix in mice bearing solid Ehrlish carcinoma. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaufi, O.M.; Noorwali, A.; Zahran, F.; Al-Abd, A.M.; Al-Attas, S. Cytotoxicity of thymoquinone alone or in combination with cisplatin (CDDP) against oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayoonfal, M.; Asemi, Z.; Yousefi, B. Targeting microRNAs with thymoquinone: A new approach for cancer therapy. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2021, 26, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkat, M.A.; Harshita; Ahmad, J.; Khan, M.A.; Beg, S.; Ahmad, F.J. Insights into the Targeting Potential of Thymoquinone for Therapeutic Intervention against Triple-negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thummuri, D.; Jeengar, M.K.; Shrivastava, S.; Nemani, H.; Ramavat, R.N.; Chaudhari, P.; Naidu, V.G.M. Thymoquinone prevents RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis activation and osteolysis in an in vivo model of inflammation by suppressing NF-KB and MAPK Signalling. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relles, D.; Chipitsyna, G.I.; Gong, Q.; Yeo, C.J.; Arafat, H.A. Thymoquinone Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Cell Death and Reduction of Tumor Size through Combined Inhibition of Histone Deacetylation and Induction of Histone Acetylation. Adv. Prev. Med. 2016, 2016, 1407840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulasli, S.S.; Celik, S.; Gunay, E.; Ozdemir, M.; Hazman, O.; Ozyurek, A.; Koyuncu, T.; Unlu, M. Anticancer effects of thymoquinone, caffeic acid phenethyl ester and resveratrol on A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells exposed to benzo(a)pyrene. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 6159–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, A.E.; Abd-Allah, A.R.; Korashy, H.M.; Attia, S.M.; Alzahrani, A.Z.; Saquib, Q.; Bakheet, S.A.; Abdel-Hamied, H.E.; Jamal, S.; Rishi, A.K. Thymoquinone suppression of the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth involves inhibition of IL-8 expression, elevated levels of TRAIL receptors, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 389, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Fahim, S.A.; Tadros, S.A.; Badary, O.A. Suppressive effects of thymoquinone on the initiation stage of diethylnitrosamine hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. The Role of Thymoquinone in Inflammatory Response in Chronic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ruan, J.; Liu, X.; Xiao, C.; Xiong, J. MicroRNA-301a-3p suppressed the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting VGLL4. Pathol.—Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.B.; Tan, X.L.; Dong, K.S.; Zhang, H.W.; Chen, X.P.; Chu, L.; Zhang, B. xiang miRNA-448 inhibits cell growth by targeting BCL-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Si, M.; Yang, N.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Yan, K.; Zong, Y.; Zhu, N.; Wei, Y. MicroRNA-506 suppresses invasiveness and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting IL8. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1586. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, Z.J.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Wen, J.; Gao, Y.F.; Liu, Y.J. miR-1306–3p targets FBXL5 to promote metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through suppressing snail degradation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ma, X.; Guan, G.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Niu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Bian, C.; Zang, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-766 promotes cancer progression by targeting NR3C2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, K.; Miyaaki, H.; Ichikawa, T. Antitumor function of microRNA-122 against hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meral, I.; Pala, M.; Akbas, F.; Ustunova, S.; Yildiz, C.; Demirel, M.H. Effects of thymoquinone on liver miRNAs and oxidative stress in Ehrlich acid mouse solid tumor model. Biotech. Histochem. 2018, 93, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.O.; El-Mesery, M.E.; Anwer, R.; Eissa, L.A. Thymoquinone potentiates miR-16 and miR-375 expressions in hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.M.; Wu, H.L.; Yu, X.; Tang, K.; Wang, S.G.; Ye, Z.Q.; Hu, J. The putative tumour suppressor miR-1-3p modulates prostate cancer cell aggressiveness by repressing E2F5 and PFTK1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, K.; Shi, L. MicroRNA-1-3p inhibits the proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting DKK1. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yan, P.; Guo, F.F.; Liu, H.J.; Zhao, Z.F. MiR-1-3p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by regulating BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway in bladder cancer. Neoplasma 2018, 65, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, D.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Tao, H.; Chen, Q. miR-1-3p and miR-206 sensitizes HGF-induced gefitinib-resistant human lung cancer cells through inhibition of c-Met signalling and EMT. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Huang, J.C.; Chen, G.; Wei, D.M. Expression level and potential target pathways of miR-1-3p in colorectal carcinoma based on 645 cases from 9 microarray datasets. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5013–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagawa, T.; Shirai, Y.; Oda, S.; Yokoi, T. Identification of Specific MicroRNA Biomarkers in Early Stages of Hepatocellular Injury, Cholestasis, and Steatosis in Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 166, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, L.; Gu, H.; Chen, J.; Guo, R.; Liu, Y. Downregulation of MicroRNA-1 is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Lab. 2015, 61, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, L.; Qiao, Z.; Yu, M.; Yu, B.; Yang, T. miR-1-3p suppresses proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting SOX9. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Cho, S.G.; Yi, Z.; Pang, X.; Rodriguez, M.; Wang, Y.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Liu, M. Thymoquinone inhibits tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth through suppressing AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Liu, A.; Shen, Y.; Xu, H.Z.; Yang, S.Z.; Ying, X.Z.; Liao, W.; Liu, H.X.; Lin, Z.Q.; Chen, Q.Y.; et al. Antitumor and anti-angiogenesis effects of thymoquinone on osteosarcoma through the NF-κB pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, W. MiR-1-3p Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis by Inhibiting YWHAZ-Mediated Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Li, K.; Gu, F.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, W.; Sun, M.; Hou, B. LINC00242/miR-1-3p/G6PD axis regulates Warburg effect and affects gastric cancer proliferation and apoptosis. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheau, C.; Badarau, I.A.; Costache, R.; Caruntu, C.; Mihai, G.L.; Didilescu, A.C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 9423907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoedel, K.E.; Tyner, V.Z.; Kim, T.H.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Mars, W.M. HGF, MET, and matrix-related proteases in hepatocellular carcinoma, fibrolamellar variant, cirrhotic and normal liver. Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Ding, Y.M.; Fan, P.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.H.; Wang, W.X. Expression and significance of MMP2 and HIF-1α in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heissig, B.; Hattori, K.; Dias, S.; Friedrich, M.; Ferris, B.; Hackett, N.R.; Crystal, R.G.; Besmer, P.; Lyden, D.; Moore, M.A.S.; et al. Recruitment of stem and progenitor cells from the bone marrow niche requires MMP-9 mediated release of Kit-ligand. Cell 2002, 109, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Qin, G.H.; Dang, Y.W.; Yang, J. The prospective role of matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 and transforming growth factor beta 1 in accelerating the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2017, 6, S229–S231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.W.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, W.E.; Yang, S.F. TIMP-3 as a therapeutic target for cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Wang, Y.; Smith, M.R.; Kim, H.; Jacobs, C.; Jackman, J.; Kung, H.F.; Colburn, N.H.; Sun, Y. Suppression of in vivo tumor growth and induction of suspension cell death by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-3. Carcinogenesis 1996, 17, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.W.; Huang, Y.W.; Chen, M.K.; Su, S.C.; Yang, S.F.; Lin, C.W. Polymorphisms and Plasma Levels of Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-3: Impact on Genetic Susceptibility and Clinical Outcome of Oral Cancer. Medicine 2015, 94, e2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.F.; Yang, C.; Liang, L.H.; Liu, B.; Zhou, B.; Li, B.; Han, Z.C. Inhibition of human leukemia xenograft in nude mice by adenovirus-mediated tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3. Leukemia 2006, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Munoz, W.; Sanchez, O.H.; Di Grappa, M.; English, J.L.; Hill, R.P.; Khokha, R. Enhanced metastatic dissemination to multiple organs by melanoma and lymphoma cells in timp-3−/− mice. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6489–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, A.K.; Vairappan, B. Role of zonula occludens in gastrointestinal and liver cancers. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 3647–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Tu, F.; Qiang, Y.; Nie, C. Decreased expression of ZO-1 is associated with tumor metastases in liver cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 17, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, A.K.; Vairappan, B.; Srinivas, B.H. Nimbolide inhibits tumor growth by restoring hepatic tight junction protein expression and reduced inflammation in an experimental hepatocarcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 7131–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, E.; Burek, M.; Förster, C.Y. Tight Junctions and the Tumor Microenvironment. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2016, 4, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brokalaki, E.I.; Weber, F.; Sotiropoulos, G.C.; Daoudaki, M.; Cicinnati, V.R.; Beckebaum, S. Claudin-7 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 2737–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, Y.; Yoon, C.H.; Kim, R.K.; Lim, E.J.; Oh, Y.S.; Hwang, S.G.; An, S.; Yoon, G.; Gye, M.C.; Yi, J.M.; et al. Claudin-1 induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition through activation of the c-Abl-ERK signaling pathway in human liver cells. Oncogene 2012, 32, 4873–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Hepatic Hippo signaling inhibits development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.; Janse Van Rensburg, H.J.; Lightbody, E.D.; Neveu, B.; Champagne, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Kay, V.R.; Hao, Y.; Shen, H.; Yeung, B.; et al. A LATS biosensor screen identifies VEGFR as a regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dituri, F.; Gigante, G.; Scialpi, R.; Mancarella, S.; Fabregat, I.; Giannelli, G. Proteoglycans in Cancer: Friends or Enemies? A Special Focus on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Njah, K.; Pobbati, A.V.; Lim, Y.B.; Raju, A.; Lakshmanan, M.; Tergaonkar, V.; Lim, C.T.; Hong, W. Agrin as a Mechanotransduction Signal Regulating YAP through the Hippo Pathway. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 2464–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Njah, K.; Hong, W. Agrin Mediates Angiogenesis in the Tumor Microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranenburg, O.; Gebbink, M.F.B.G.; Voest, E.E. Stimulation of angiogenesis by Ras proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Rev. Cancer 2004, 1654, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, Y.; Gan, P.; Yao, Q.; Ran, F.M.; Tan, J. Downregulation of Rap1 promotes 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.J.; Der, C.J. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3291–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhao, G.D.; Shi, Z.; Qi, L.L.; Zhou, L.Y.; Fu, Z.X. The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and its role in the occurrence and development of HCC. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmikanthan, S.; Sobczak, M.; Chun, C.; Henschel, A.; Dargatz, J.; Ramchandran, R.; Chrzanowska-Wodnicka, M. Rap1 promotes VEGFR2 activation and angiogenesis by a mechanism involving integrin αvβ3. Blood 2011, 118, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara-Romeo, I.; Martinez, P.; Blasco, M.A. Mice lacking RAP1 show early onset and higher rates of DEN-induced hepatocellular carcinomas in female mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, J.R.; Xu, T.; Huang, J.; Xu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.M. MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| KEGG Signaling Pathway | Number of Genes (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Rap1 signaling pathway | 25 (2.9%) | 7.4 × 10−5 |
| Tight junction | 21 (2.4%) | 1.8 × 10−4 |
| Hippo signaling pathway | 20 (2.3%) | 2 × 10−4 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | 23 (2.7%) | 3.6 × 10−4 |
| Ras signaling pathway | 25 (2.9%) | 4.2 × 10−4 |
| Gene | Primer Sequence | Accession Number | Annealing Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TIMP3 |
F: 5′-TCTGCAACTCCGACATCGT-3′ R: 5′-TTGGTGAAGCCTCGGTACAT-3′ | NM_000362.5 | 59 |
| MMP2 |
F: 5′-AGACAGTGGATGATGCCTTTGC-3′ R: 5′-GGAGTCCGTCCTTACCGTCAAA-3′ | NM_001302510.2 | 61.2 |
| MMP9 |
F: 5′- TTCCAAACCTTTGAGGGCGA-3′ R: 5′-CAAAGGCGTCGTCAATCACC-3′ | NM_004994.3 | 59.8 |
| VEGF |
F: 5’-TCCTCACACCATTGAAACCA-3’ R: 5’-GATCCTGCCCTGTCTCTCTG-3’ | NM_001025366.3 | 56.9 |
| GAPDH |
F: 5′-ACCCACTCCTCCACCTTTGA-3′ R: 5′-CTGTTGCTGTAGCCAAATTCGT-3′ | NM_001357943.2 | 59.7 |
| miR-1-3p | F: 5′-TGGAATGTAAAGAAGT-3′ | MIMAT0000416 | 58 |
| RUN U6B | F: 5′-GGCAGCACATATACTAAAATTGGAA-3′ | M14486.1 | 58 |
| Universal reverse primer | R: 5′-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3′ | N/A | 58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tadros, S.A.; Attia, Y.M.; Maurice, N.W.; Fahim, S.A.; Abdelwahed, F.M.; Ibrahim, S.; Badary, O.A. Thymoquinone Suppresses Angiogenesis in DEN-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting miR-1-3p. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415904
Tadros SA, Attia YM, Maurice NW, Fahim SA, Abdelwahed FM, Ibrahim S, Badary OA. Thymoquinone Suppresses Angiogenesis in DEN-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting miR-1-3p. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415904
Chicago/Turabian StyleTadros, Samer A., Yasmin M. Attia, Nadine W. Maurice, Sally A. Fahim, Fatma M. Abdelwahed, Samar Ibrahim, and Osama A. Badary. 2022. "Thymoquinone Suppresses Angiogenesis in DEN-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting miR-1-3p" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415904
APA StyleTadros, S. A., Attia, Y. M., Maurice, N. W., Fahim, S. A., Abdelwahed, F. M., Ibrahim, S., & Badary, O. A. (2022). Thymoquinone Suppresses Angiogenesis in DEN-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting miR-1-3p. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415904







