CCL4 Regulates Eosinophil Activation in Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
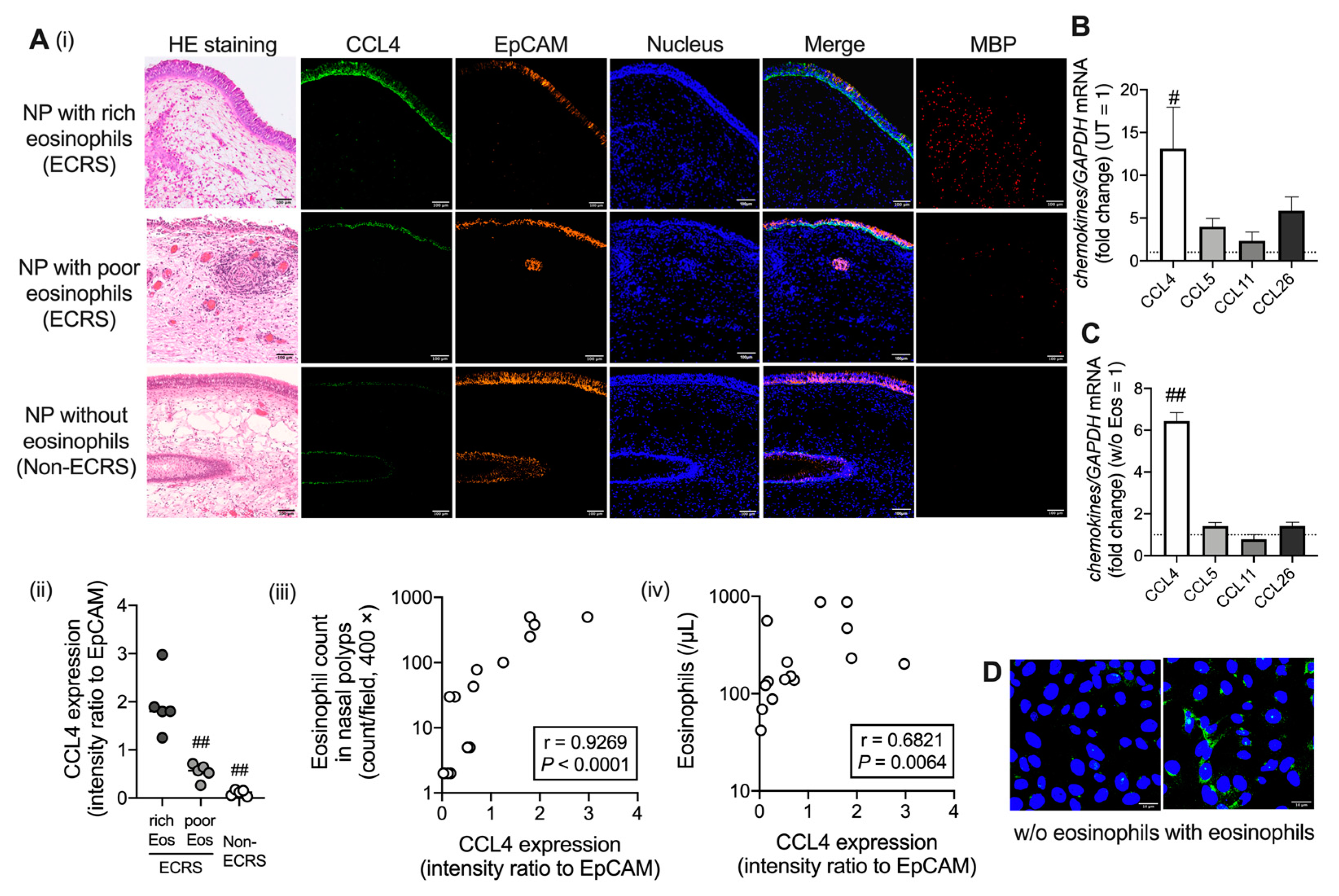
2.1. CCL4 Expression Increases in Airway Epithelial Cells under Eosinophilic Inflammation
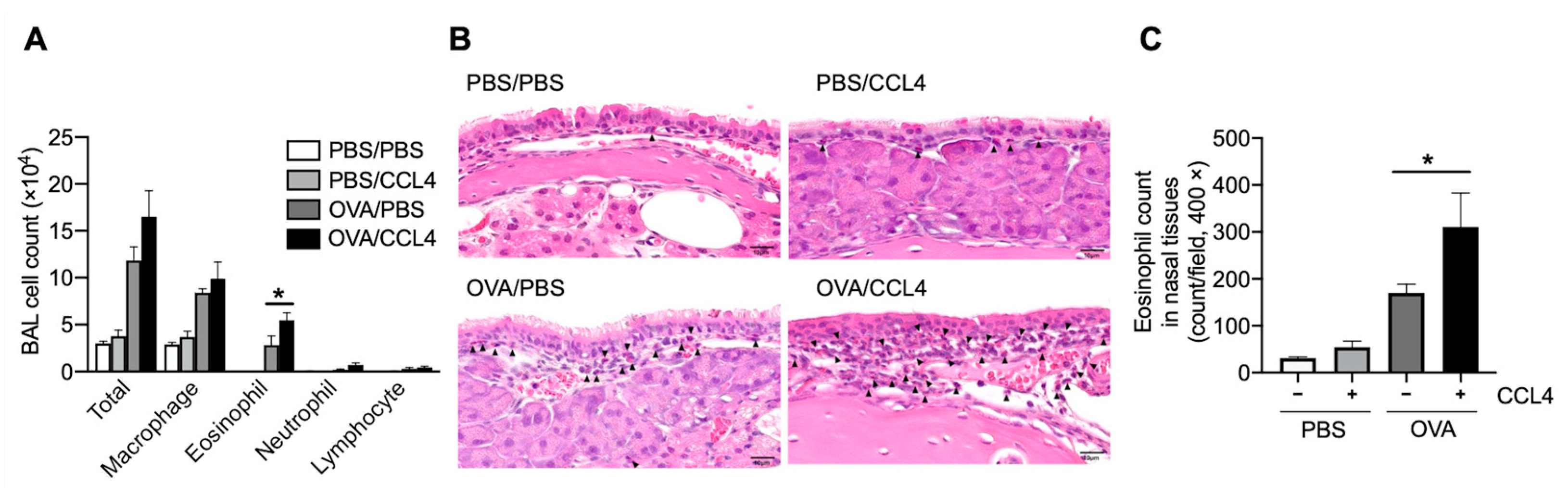
2.2. CCL4 Enhances Eosinophil Accumulation into the Local Allergic Inflammatory Site
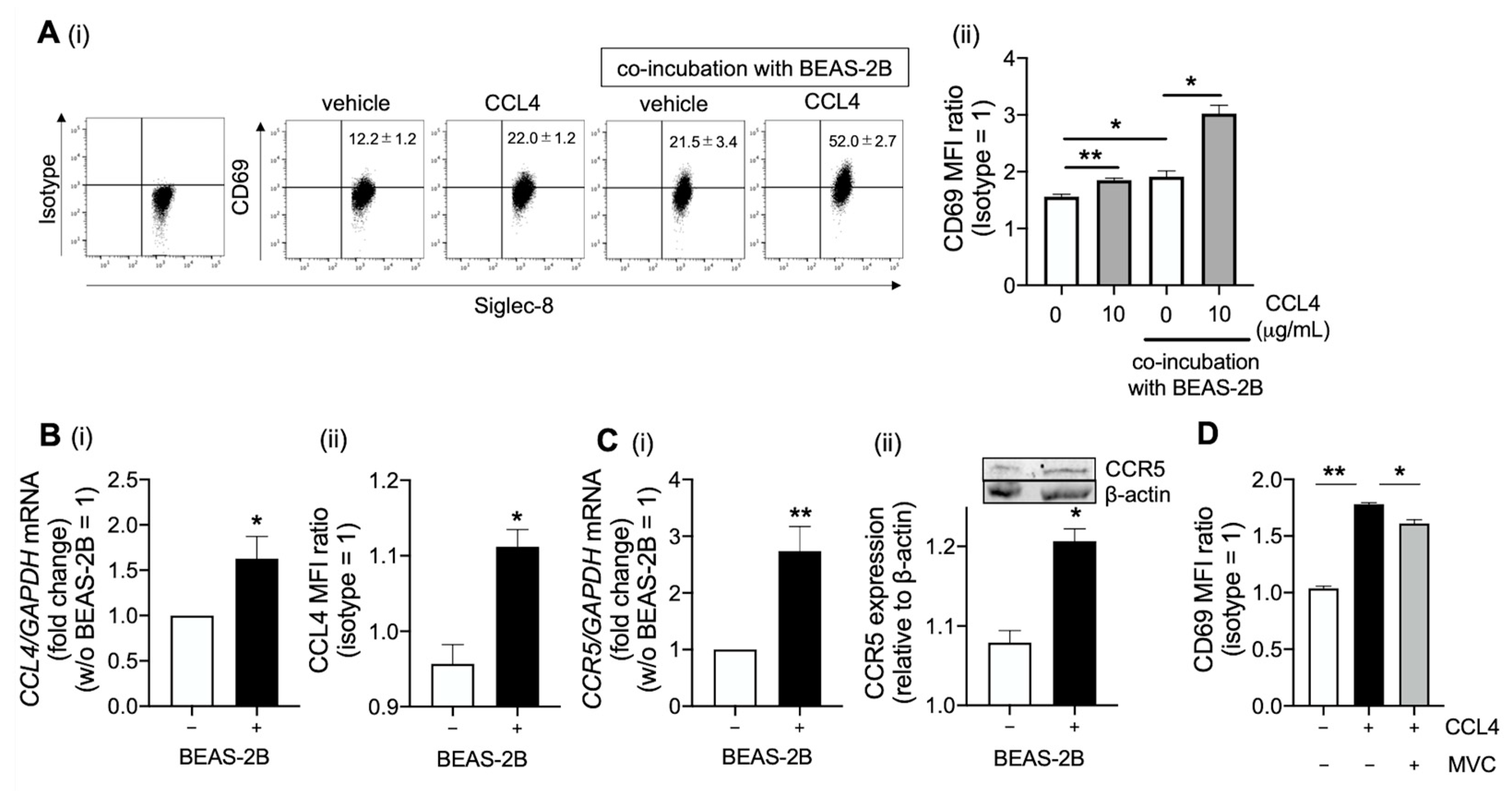
2.3. CCL4 Activates Eosinophils in the Airway
2.4. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor (PDGFR)β and Src Family Are Involve in CCL4-Mediated Eosinophil Activation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Preparation
4.2. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.3. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.5. Cell Survival
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Human Phosphor-Kinase Array
4.8. Animals
4.9. Sensitization and Airway Challenge
4.10. CCL4 and Soluble CD69 Immunoassay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishitoya, J.; Sakuma, Y.; Tsukuda, M. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan. Allergol. Int. 2010, 59, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeno, S.; Hirakawa, K.; Ishino, T. Pathological mechanisms and clinical features of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in the Japanese population. Allergol. Int. 2010, 59, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, S.; Imoto, Y.; Kato, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Tokunaga, T.; Tsutsumiuchi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Kidoguchi, M.; Takabayashi, T. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, T.; Sakashita, M.; Haruna, T.; Asaka, D.; Takeno, S.; Ikeda, H.; Nakayama, T.; Seki, N.; Ito, S.; Murata, J.; et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: The JESREC Study. Allergy 2015, 70, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Okada, N.; Tsurumoto, T.; Mitsuyoshi, R.; Takaishi, S.; Asaka, D.; Kojima, H.; Yoshikawa, M.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. JESREC score and mucosal eosinophilia can predict endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kanda, A.; Yun, Y.; Dan Van, B.; Suzuki, K.; Sawada, S.; Asako, M.; Iwai, H. Reduced local response to corticosteroids in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with asthma. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Yi, X.; Liu, S.; Holtappels, G.; Bachert, C.; Zhang, N. The development of nasal polyp disease involves early nasal mucosal inflammation and remodelling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takabayashi, T.; Schleimer, R.P. Formation of nasal polyps: The roles of innate type 2 inflammation and deposition of fibrin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Ishinaga, H.; Takeuchi, K. Pathogenesis of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Inflamm. 2016, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proost, P.; Wuyts, A.; van Damme, J. The role of chemokines in inflammation. Int. J. Clin. Lab. Res. 1996, 26, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.W.; Ocampo, C.J.; Berdnikovs, S.; Sakashita, M.; Mahdavinia, M.; Suh, L.; Takabayashi, T.; Norton, J.E.; Hulse, K.E.; Conley, D.B.; et al. Cytokines in chronic rhinosinusitis. Role in eosinophilia and aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, P.F.; Spencer, L.A. Functions of tissue-resident eosinophils. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, A.; Yun, Y.; Bui, D.V.; Nguyen, L.M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Mitani, A.; Sawada, S.; Hamada, S.; Asako, M.; et al. The multiple functions and subpopulations of eosinophils in tissues under steady-state and pathological conditions. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesnil, C.; Raulier, S.; Paulissen, G.; Xiao, X.; Birrell, M.A.; Pirottin, D.; Janss, T.; Starkl, P.; Ramery, E.; Henket, M.; et al. Lung-resident eosinophils represent a distinct regulatory eosinophil subset. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3279–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Kanda, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Van Bui, D.; Suzuki, K.; Sawada, S.; Baba, K.; Yagi, M.; Asako, M.; Okazaki, H.; et al. Increased CD69 expression on activated eosinophils in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis correlates with clinical findings. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, A.; Yasutaka, Y.; Van Bui, D.; Suzuki, K.; Sawada, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Asako, M.; Iwai, H. Multiple biological aspects of eosinophils in host defense, eosinophil-associated diseases, immunoregulation, and homeostasis: Is their role beneficial, detrimental, regulator, or bystander? Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, A.; Hirahara, K.; Kiuchi, M.; Nakayama, T. Eosinophils: Cells known for over 140 years with broad and new functions. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Shibano, M.; Saito, T.; Gatto, W.; Kamiya, H.; Hirai, K.; Sumida, M.; Yoshie, O. Airway epithelial cells promote transmigration of eosinophils in a new three-dimensional chemotaxis model. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soragni, A.; Yousefi, S.; Stoeckle, C.; Soriaga, A.B.; Sawaya, M.R.; Kozlowski, E.; Schmid, I.; Radonjic-Hoesli, S.; Boutet, S.; Williams, G.J.; et al. Toxicity of eosinophil MBP is repressed by intracellular crystallization and promoted by extracellular aggregation. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Wong, C.K.; Tsang, M.S.; Chu, I.M.; Liu, D.; Zhu, J.; Chu, M.; Lam, C.W. Activation of eosinophils interacting with bronchial epithelial cells by antimicrobial peptide LL-37: Implications in allergic asthma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, B.G.; Scheffold, A.; Rolph, M.S.; Huser, M.B.; Kaufmann, S.H.; Radbruch, A.; Flesch, I.E.; Kroczek, R.A. MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, RANTES, and ATAC/lymphotactin function together with IFN-gamma as type 1 cytokines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6181–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin-Cocon, L.; Agaugue, S.; Diaz, O.; Vanbervliet, B.; Dollet, S.; Guironnet-Paquet, A.; Andre, P.; Lotteau, V. Th1 disabled function in response to TLR4 stimulation of monocyte-derived DC from patients chronically-infected by hepatitis C virus. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzysiek, R.; Lefevre, E.A.; Zou, W.; Foussat, A.; Bernard, J.; Portier, A.; Galanaud, P.; Richard, Y. Antigen receptor engagement selectively induces macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1 alpha) and MIP-1 beta chemokine production in human B cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 4455–4463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Konno, Y.; Kanda, A.; Yamada, Y.; Yasuba, H.; Sakata, Y.; Fukuchi, M.; Tomoda, K.; Iwai, H.; Ueki, S. Critical role of CCL4 in eosinophil recruitment into the airway. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchimizu, H.; Matsuwaki, Y.; Kato, M.; Otori, N.; Kojima, H. Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin, elastase, and cytokine profile in effusion from eosinophilic otitis media. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, S18–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Fukushima, K.; Mukae, H.; Kadota, J.I.; Kohno, S.; Matsukura, S. Elevated chemokine levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.E., Jr.; Lannigan, J.A.; Kim, P.; Lee, J.J.; Fu, S.M.; Sung, S.S. Murine lung eosinophil activation and chemokine production in allergic airway inflammation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.F.; Wong, C.K.; Lam, C.W. Molecular mechanisms of cytokine and chemokine release from eosinophils activated by IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-23: Implication for Th17 lymphocytes-mediated allergic inflammation. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5625–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, H.F.; Dyer, K.D.; Foster, P.S. Eosinophils: Changing perspectives in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.; Rothenberg, M.E. Biology of the eosinophil. Adv. Immunol. 2009, 101, 81–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yun, Y.; Kanda, A.; Asako, M.; Ueki, S.; Iwai, H. Eosinophilic cholecystitis occurred in a patient with refractory eosinophilic airway inflammation: A case report. Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 10, 2152656719869607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rot, A.; Krieger, M.; Brunner, T.; Bischoff, S.C.; Schall, T.J.; Dahinden, C.A. RANTES and macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha induce the migration and activation of normal human eosinophil granulocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palframan, R.T.; Collins, P.D.; Williams, T.J.; Rankin, S.M. Eotaxin induces a rapid release of eosinophils and their progenitors from the bone marrow. Blood 1998, 91, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunther, C.; Wozel, G.; Meurer, M.; Pfeiffer, C. Up-regulation of CCL11 and CCL26 is associated with activated eosinophils in bullous pemphigoid. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 166, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzaki, Y.; Hamada, K.; Nomi, T.; Ito, T.; Sho, M.; Kai, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Kimura, H. A small-molecule compound targeting CCR5 and CXCR3 prevents airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagome, K.; Nagata, M. Possible mechanisms of eosinophil accumulation in eosinophilic pneumonia. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchimoto, Y.; Kanehiro, A.; Miyahara, N.; Koga, H.; Ikeda, G.; Waseda, K.; Tanimoto, Y.; Ueha, S.; Kataoka, M.; Gelfand, E.W.; et al. Requirement for chemokine receptor 5 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berce, V.; Repnik, K.; Potocnik, U. Association of CCR5-delta32 mutation with reduced risk of nonatopic asthma in Slovenian children. J. Asthma 2008, 45, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, T.N.; Power, C.A.; Shaw, J.P.; Proudfoot, A.E. Chemokine blockers—Therapeutics in the making? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Li, Z. New insights into modes of GPCR activation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopalco, L. CCR5: From natural resistance to a new anti-HIV strategy. Viruses 2010, 2, 574–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoulin, J.B.; Essaghir, A. PDGF receptor signaling networks in normal and cancer cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W. The phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells co-cultured with endothelial cells is modulated by PDGFR-beta/IQGAP1 signaling in LPS-induced intravascular injury. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundra, V.; Escobedo, J.A.; Kazlauskas, A.; Kim, H.K.; Rhee, S.G.; Williams, L.T.; Zetter, B.R. Regulation of chemotaxis by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta. Nature 1994, 367, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Hanaka, S.; Yano, T.; Yamamura, K.; Yoshihara, H.; Nagase, H.; Chihara, J.; Ohta, K. The role of platelet-derived growth factor receptor in eotaxin signaling of eosinophils. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 140 (Suppl. S1), 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlin, A.A.; Lukacs, N.W. Treatment of cockroach allergen asthma model with imatinib attenuates airway responses. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valent, P.; Degenfeld-Schonburg, L.; Sadovnik, I.; Horny, H.P.; Arock, M.; Simon, H.U.; Reiter, A.; Bochner, B.S. Eosinophils and eosinophil-associated disorders: Immunological, clinical, and molecular complexity. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amata, I.; Maffei, M.; Pons, M. Phosphorylation of unique domains of Src family kinases. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Kita, H.; Morikawa, A. Role of tyrosine kinases in human eosinophil degranulation. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1997, 114 (Suppl. S1), 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daub, H.; Weiss, F.U.; Wallasch, C.; Ullrich, A. Role of transactivation of the EGF receptor in signalling by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 1996, 379, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, H.H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Bui, D.V.; Yun, Y.; Nguyen, L.M.; Mitani, A.; Suzuki, K.; Asako, M.; Kanda, A.; Iwai, H. CCL4 Regulates Eosinophil Activation in Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416149
Chu HH, Kobayashi Y, Bui DV, Yun Y, Nguyen LM, Mitani A, Suzuki K, Asako M, Kanda A, Iwai H. CCL4 Regulates Eosinophil Activation in Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):16149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416149
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Hanh Hong, Yoshiki Kobayashi, Dan Van Bui, Yasutaka Yun, Linh Manh Nguyen, Akitoshi Mitani, Kensuke Suzuki, Mikiya Asako, Akira Kanda, and Hiroshi Iwai. 2022. "CCL4 Regulates Eosinophil Activation in Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 16149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416149
APA StyleChu, H. H., Kobayashi, Y., Bui, D. V., Yun, Y., Nguyen, L. M., Mitani, A., Suzuki, K., Asako, M., Kanda, A., & Iwai, H. (2022). CCL4 Regulates Eosinophil Activation in Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 16149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416149






