Quantitative In-Depth Transcriptome Analysis Implicates Peritoneal Macrophages as Important Players in the Complement and Coagulation Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
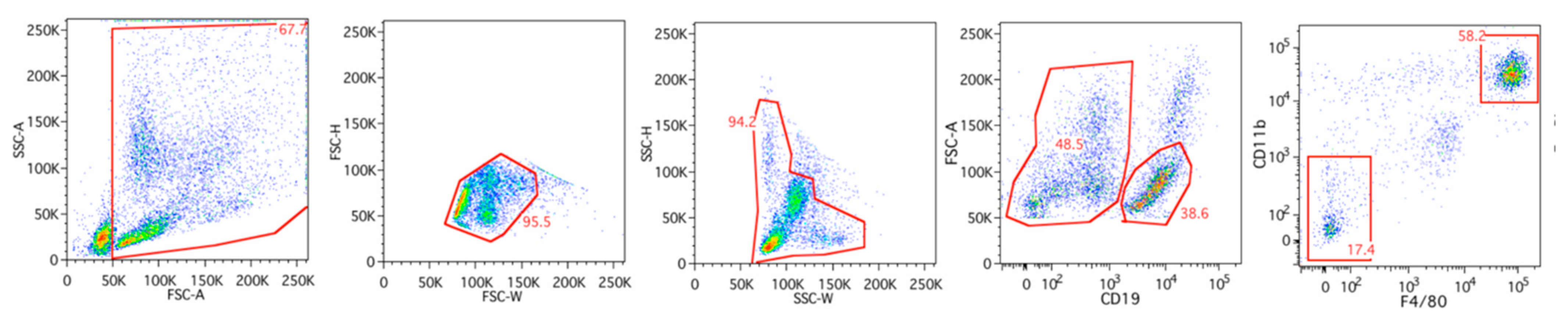
2.1. Preparation of RNA from Mouse Tissues, Purified Peritoneal Cell Fractions, and Purified Human Peripheral Blood Monocytes
2.2. Analysis of Transcript Levels in Mouse Peritoneal MΦs and Human Peripheral Blood Monocytes
2.3. Analysis of Transcript Levels for a Panel of Pattern Recognition Receptors and Proteins Involved in Angiogenesis
2.4. Analysis of Transcript Levels in the Mouse Liver
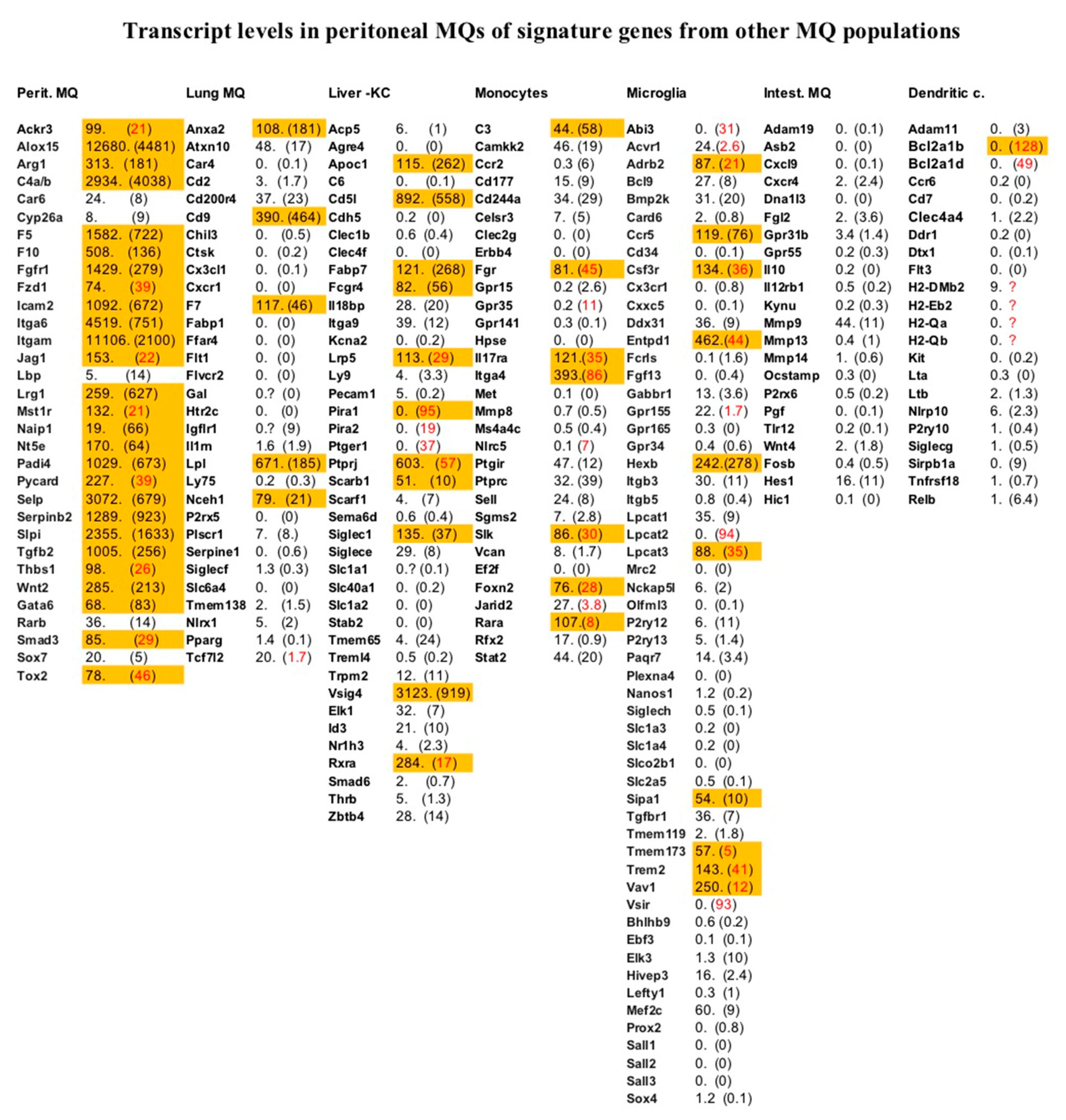
2.5. Analysis of Transcripts Representing a Panel of Signature Genes Identified by Single Cell Analysis of Monocytes, Dendritic Cells, and MΦs from Different Tissues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
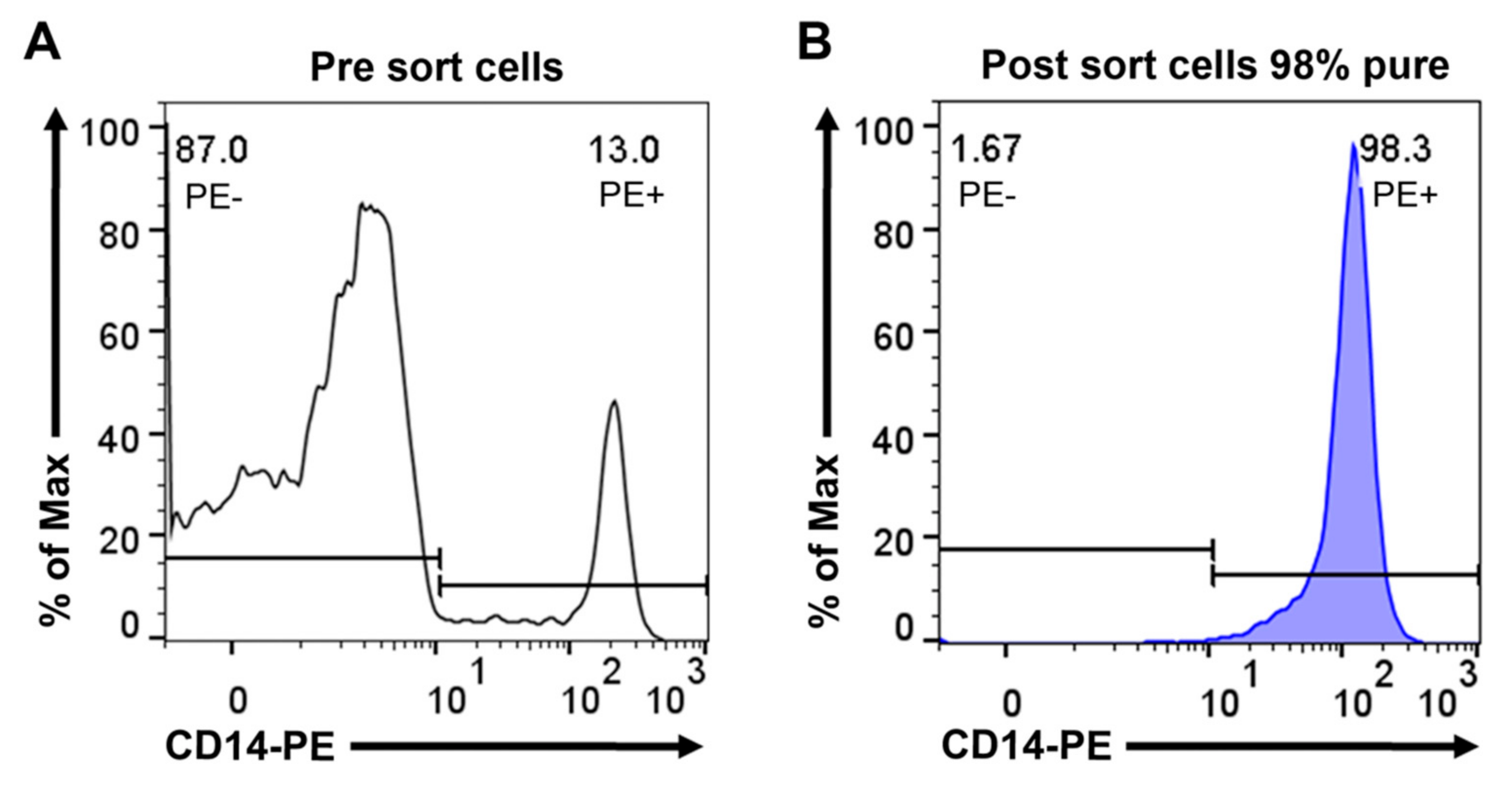
4.2. Peritoneal Cell Extraction and FACS Sorting of Peritoneal Macrophages and B Cells
4.3. Isolation of Human Peripheral Blood Monocytes by Magnetic Cell Sorting
4.4. RNA Isolation
4.5. Analysis of the Transcriptome by RNA-seq and by the Thermo Fisher Ampliseq Chip and PCR-Based Method
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordon, S.; Pluddemann, A. Tissue macrophages: Heterogeneity and functions. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyama, S.; Nakahashi-Oda, C.; Abe, F.; Wang, Y.; Sato, K.; Shibuya, A. Identification and isolation of splenic tissue-resident macrophage sub-populations by flow cytometry. Int. Immunol. 2018, 31, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sieweke, M.H.; Allen, J.E. Beyond stem cells: Self-renewal of differentiated macrophages. Science 2013, 342, 1242974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit, I.; Winter, D.R.; Jung, S. The role of the local environment and epigenetics in shaping macrophage identity and their effect on tissue homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdiguero, E.G.; Klapproth, K.; Schulz, C.; Busch, K.; de Bruijn, M.; Rodewald, H.R.; Geissmann, F. The Origin of Tissue-Resident Macrophages: When an Erythro-myeloid Progenitor Is an Erythro-myeloid Progenitor. Immunity 2015, 43, 1023–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeffel, G.; Chen, J.; Lavin, Y.; Low, D.; Almeida, F.F.; See, P.; Beaudin, A.E.; Lum, J.; Low, I.; Forsberg, E.C.; et al. C-Myb(+) erythro-myeloid progenitor-derived fetal monocytes give rise to adult tissue-resident macrophages. Immunity 2015, 42, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginhoux, F.; Greter, M.; Leboeuf, M.; Nandi, S.; See, P.; Gokhan, S.; Mehler, M.F.; Conway, S.J.; Ng, L.G.; Stanley, E.R.; et al. Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science 2010, 330, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kierdorf, K.; Erny, D.; Goldmann, T.; Sander, V.; Schulz, C.; Perdiguero, E.G.; Wieghofer, P.; Heinrich, A.; Riemke, P.; Holscher, C.; et al. Microglia emerge from erythromyeloid precursors via Pu.1- and Irf8-dependent pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, C.C.; Bravo-Blas, A.; Scott, C.L.; Perdiguero, E.G.; Geissmann, F.; Henri, S.; Malissen, B.; Osborne, L.C.; Artis, D.; Mowat, A.M. Constant replenishment from circulating monocytes maintains the macrophage pool in the intestine of adult mice. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeffel, G.; Ginhoux, F. Fetal monocytes and the origins of tissue-resident macrophages. Cell Immunol. 2018, 330, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeksema, M.A.; Glass, C.K. Nature and nurture of tissue-specific macrophage phenotypes. Atherosclerosis 2019, 281, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hume, D.A.; Irvine, K.M.; Pridans, C. The Mononuclear Phagocyte System: The Relationship between Monocytes and Macrophages. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilliams, M.; Thierry, G.R.; Bonnardel, J.; Bajenoff, M. Establishment and Maintenance of the Macrophage Niche. Immunity 2020, 52, 434–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, S.J.; Hume, D.A. Homeostasis in the mononuclear phagocyte system. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Lowell, C.A. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage activation and signal transduction in the absence of Src-family kinases Hck, Fgr, and Lyn. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Matsuura, M.; Hirai, Y. Regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-12 production by activation of repressor element GA-12 through hyperactivation of the ERK pathway. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xaus, J.; Comalada, M.; Barrachina, M.; Herrero, C.; Gonalons, E.; Soler, C.; Lloberas, J.; Celada, A. The expression of MHC class II genes in macrophages is cell cycle dependent. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 6364–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ting, J.P.; Trowsdale, J. Genetic control of MHC class II expression. Cell 2002, 109, S21–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Summers, K.M.; Bush, S.J.; Hume, D.A. Network analysis of transcriptomic diversity amongst resident tissue macrophages and dendritic cells in the mouse mononuclear phagocyte system. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, E.E.; Cassado, A.A.; Govoni, G.R.; Fukuhara, T.; Yang, Y.; Monack, D.M.; Bortoluci, K.R.; Almeida, S.R.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Herzenberg, L.A. Two physically, functionally, and developmentally distinct peritoneal macrophage subsets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conceicao-Silva, F.; Reis, C.S.M.; De Luca, P.M.; Leite-Silva, J.; Santiago, M.A.; Morrot, A.; Morgado, F.N. The Immune System Throws Its Traps: Cells and Their Extracellular Traps in Disease and Protection. Cells 2021, 10, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, J.T.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Wilson, M.S.; Mentink-Kane, M.M.; Thompson, R.W.; Cheever, A.W.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Wynn, T.A. Retnla (relmalpha/fizz1) suppresses helminth-induced Th2-type immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akula, S.; Paivandy, A.; Fu, Z.; Thorpe, M.; Pejler, G.; Hellman, L. Quantitative In-Depth Analysis of the Mouse Mast Cell Transcriptome Reveals Organ-Specific Mast Cell Heterogeneity. Cells 2020, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Min, Q.; Ikawa, T.; Yasuda, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Tsubata, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.Y. Kelch-like protein 14 promotes B-1a but suppresses B-1b cell development. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, J.M.B.; Felippe, M.J.B. Development, phenotype, and function of non-conventional B cells. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 54, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, M. The ontogeny of murine B-1a cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2020, 111, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, L.; Smedsrod, B.; Sandberg, H.; Pettersson, U. Secretion of coagulant factor VIII activity and antigen by in vitro cultivated rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Br. J. Haematol. 1989, 73, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, S.; Rubin, K.; Hook, M.; Ahlgren, T.; Seljelid, R. In vitro biosynthesis of cold insoluble globulin (fibronectin) by mouse peritoneal macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1979, 105, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassado Ados, A.; D’Imperio Lima, M.R.; Bortoluci, K.R. Revisiting mouse peritoneal macrophages: Heterogeneity, development, and function. Front Immunol. 2015, 6, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takenaka, E.; Van Vo, A.; Yamashita-Kanemaru, Y.; Shibuya, A.; Shibuya, K. Selective DNAM-1 expression on small peritoneal macrophages contributes to CD4(+) T cell costimulation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, D.G.; Rubio, A.J.; Mata, J.; Munoz, S.; Gallegos, A.; Walker, W.E. Large Peritoneal Macrophages and Transitional Premonocytes Promote Survival during Abdominal Sepsis. Immunohorizons 2021, 5, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorch, S.K.; Surewaard, B.G.; Hossain, M.; Peiseler, M.; Deppermann, C.; Deng, J.; Bogoslowski, A.; van der Wal, F.; Omri, A.; Hickey, M.J.; et al. Peritoneal GATA6+ macrophages function as a portal for Staphylococcus aureus dissemination. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4643–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo, R.; Pridans, C.; Langlais, D.; Hume, D.A. Transcriptional mechanisms that control expression of the macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor locus. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2161–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mouse Peritoneal MΦs | H-Monocytes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RNA-Seq | Ampliseq | Ampliseq | |
| A. Amyloids and General Transcripts | |||
| Saa3 (serum amyloid, apolipoprotein) | 10,137 | 7412 | 0 |
| Saa1 (serum amyloid, apolipoprotein) | 9084 | 0 * | 0 |
| Saa2 (serum amyloid, apolipoprotein) | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Saa4 (serum amyloid, apolipoprotein) | 16 | 0 | 0 |
| Actb (beta actin) | 3425 | 7060 | 19,693 |
| Tcn2 (Transcobalmin) | (1027) | 5383 | 21 |
| Wfdc17 (WAP protein domain protein-activated MQ) | 4897 | 4064 | 0 |
| Tln1 (Talin 1 cytoskeletal membrane connector) | 370 | 1971 | 248 |
| Itsn1 (Intersectin 1 membrane trafficking) | (276) | 1359 | 0 |
| Grn (Granulin) | 1817 | 2744 | 588 |
| Bst1 (ADP-ribosyl cyclase 2) | 159 | 1204 | 100 |
| Gda (Guanine deaminase) | 523 | 1232 | 0 |
| Hamp (Hepsidin Iron import) | 148 | 876 | 1 |
| Ninj1 (Ninjurin 1 apoptosis signal?) | 390 | 1122 | 578 |
| Hal (Histidine ammonia lyase) | 335 | 1561 | 0 |
| Hdc (Histidine decarboxylase) | 21 | 42 | 0 |
| Hrg (Histidine rich glycoprotein) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B. Extracellular Matrix | |||
| Fn1 (Fibronectin) | (10,119) | 25,920 | 0 |
| Prg4 (Proteoglycan 4, Lubricin) | 3921 | 3606 | 0 |
| Srgn (Serglycin-proteoglycan core protein) | 1022 | 2803 | 3855 |
| Sdc3 (Syndecan 3) | 873 | 3205 | 5 |
| Ecm1 (Extracellular matrix protein 1) | (1876) | 3180 | 1 |
| C. Antimicrobial Proteins | |||
| Lyz1 (M-Lysozyme) | 8354 | 791 | 27,394 |
| Lyz2 (P-Lysozyme) | 0 | 104,081 * | - |
| Defb (Beta-defensins) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Camp (Cathelicidin) | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Cybb (Cytochr.b-245 (Nox2) Cytb558) | 1018 | 2664 | 1081 |
| Padi4 (Peptidyl arginine deiminase type IV) | 673 | 1029 | 77 |
| Flnb (Filamin B, fagocytosis) | (419) | 2235 | 9 |
| Flna (Filamin A) | (287) | 1458 | 1175 |
| Timd4 (Binds Phosphatidyl serine, apoptotic cells) | 933 | 1244 | 0 |
| D. Lipid Mediators and Metabolism | |||
| Alox1 (Arachinodate-15-lipoxygenase) | 4481 | 12,680 | 0 |
| Pla2g7 (Phosplipase A2) | 1325 | 1549 | 15 |
| Alox5ap (Arachinodate-5-lipoxygenase activating protein) | (1058) | 1296 | 111 |
| Ptgis (Prosaglandin I syntase) | 387 | 1283 | 0 |
| Alox5 (Arachinodate-5-lipoxygenase) | 178 | 494 | 190 |
| Dpep2 (Dipeptidase 2 membrane bound, incl. PGD4) | (360) | 1243 | 77 |
| ApoE (Apolipoprotein E) | (14,181) | 2413 | 2 |
| Pltp (Phospholipid transfer protein) | 2036 | 5788 | 1 |
| Plin2 (Perilipin2 cytopl. lipid droplet binding) | 426 | 1370 | 777 |
| Retnla (Resistin like alpha, cholesterol hom?) | 609 | 1223 | 0 |
| Smpdl3a (Sphingomyelin Phosphodiesterase acid-like 3) | 1103 | 2505 | 3 |
| Lipn (Lipase important for keratinocytes) | 34 | 11 | 11 |
| E. Complement Proteins and Their Receptors | |||
| Cfp (Complement factor P, Properdin) | 2941 | 5225 | 991 |
| C1qa (Complement factor C1q A) | 3661 | 4 * | 7 |
| C1qb (Complement factor C1q B) | 2123 | 3978 | 3 |
| C1qc (Complement factor C1q C) | 2127 | 128 * | 1 |
| C4b (Complement factor 4B) | 3087 | 2934 | 0.1 |
| C4a (Complement factor 4A) | 951 | 28 * | 1 |
| Cfh (Complement factor H) | 739 | 1980 | 0 |
| Fcna (Ficolin A) (human Ficolin 1, Fcn1) | 1428 | 1306 | 3198 |
| Vsig4 (V-Ig domain cont.4 Comp C3b rec) | 919 | 3123 | 5 |
| C3 (Complement factor 3) | 58 | 44 | 2 |
| CFB (Complement factor B) | 205 | 0 * | 0.2 |
| C2 (Complement factor 2) | 4 | 5 | 14 |
| C3ar1 (C3a receptor) | 139 | 290 | 41 |
| C5ar1 (C5a receptor 1) | (104) | 68 | 0 |
| F. Coagulation Proteins | |||
| F5 (Coagulation factor V) | 722 | 1582 | 40 |
| F10 (Coagulation factor X) | (266) | 508 | 0 |
| F7 (Coagulation factor VII) | 46 | 117 | 0 |
| F12 (Coagulation factor XII) | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| F9 (Coagulation factor IX) | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| F2 (Thrombin) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| G. Proteases | |||
| Mmp19 (Matrix metalloprotease 19) | (18) | 81 | 1 |
| Mmp9 (Matrix metalloprotease 9) | 11 | 42 | 9 |
| Mmp27 (Matrix metalloprotease 27) | 6 | 10 | 0 |
| Mmp12 (Matrix metalloprotease 12) | 3 | 0.3 | 0 |
| H. Protease Inhibitors | |||
| Cst3 (Cystatin C) | 3497 | 5347 | 3704 |
| SLPI (Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor) | 1633 | 2355 | 0.4 |
| Serpinb2 (Serpin B2) | (915) | 1289 | 38 |
| Timp2 (Metalloproteinase Inhibitor 2) | 821 | 2135 | 283 |
| Timp1 (Metalloproteinase Inhibitor 1) | 0.1 | 0 | 725 |
| Serpinb9 (Serpin B9) | 6 | 13 | 111 |
| I. Lysosomal Proteins | |||
| Laptm5 (Lysosomal membrane protein 5) | 1938 | 6638 | 6180 |
| Psap (Prosaposin glycosphingolipids) | (2039) | 3559 | 12,296 |
| Man2b1 (Alpha-mannosidase) | 708 | 1621 | 5 |
| Ctsb (Cathepsin B) | 1175 | 4250 | 814 |
| Ctsd (Cathepsin D) | 3251 | 3595 | 1171 |
| Ctsl (Cathepsin L) | 451 | 2369 | 19 |
| Ctsa (Cathepsin A) | (652) | 2308 | 192 |
| Ctss (Cathepsin S) | (1575) | 1445 | 5290 |
| Ctsz (Cathepsin Z) | 360 | 571 | 1415 |
| Ctsh (Cathepsin H) | (116) | 316 | 329 |
| Ctsc (Cathepsin C) | 63 | 205 | 145 |
| Ctso (Cathepsin O) | 50 | 63 | 9 |
| Ctsf (Cathepsin F) | 48 | 53 | 1 |
| Ctse (Cathepsin E) | 21 | 76 | 0 |
| J. Immunoglobulin Receptors | |||
| FcgRIII (Fc gamma receptor 3) | 773 | 1968 | - |
| Fcgrt (FcRN) | 484 | 1786 | 380 |
| Fcgr4 (Fc gamma receptor 4) | 56 | 82 | - |
| Fcgr1 (Fc gamma receptor 1, high affinity) | 17 | 35 | 51 |
| Fcgr2b (Fc gamma receptor 2B, inhibiting) | (449) | 9 * | 59 |
| Fcgr2a (Fc gamma receptor 2A) | - | - | 580 |
| Fcer1g (Fc-epsilon receptor gamma, signaling) | 546 | 1318 | 1173 |
| K. MHC Classes I and II | |||
| B2m (beta-2 Microglobulin) | 3358 | 5791 | 5521 |
| H2-K1 (H2-K MHC Class I) | 0 * | 2606 | - |
| H2-D1 (H2-D MHC Class I) | 0 * | 973 | - |
| HLA-A | - | - | 1548 |
| HLA-B | - | - | 6 |
| HLA-C | - | - | 2979 |
| HLA-E | - | - | 2984 |
| HLA-DRB1 | - | - | 3023 |
| HLA-DRA | - | - | 5490 |
| HLA-DPA1 | - | - | 2375 |
| HLA-DPB1 | - | - | 1029 |
| HLA-DPB2 | - | - | 0 |
| HLA-DQB2 | - | - | 0 |
| HLA-DQA1 | - | - | 103 |
| HLA-DQA2 | - | - | 0 |
| H2-DMa (H2-DM alpha chain) | 0 * | 53 | - |
| H2-DMb2 | 0 * | 9 | - |
| H2-Aa (H2-IA) | 0 * | 52 | - |
| L. Classical Surface Receptors/Markers | |||
| CD14 | 560 | 627 | 1697 |
| CD40 | (25) | 79 | 6 |
| CD28 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| CD86 (B7-2) | 63 | 257 | 236 |
| CD80 (B7-1) | 27 | 10 | 2 |
| CD83 (Activation marker for dendritic cells) | (0.7) | 0.1 | 18 |
| CD244 (KIR2DL4) | 29 | 34 | 31 |
| CD84 (Ig superfamily, unknown function) | (244) | 31 | 20 |
| Mcemp1(Mast cell expressed membrane protein 1) | 425 | 1140 | 0 |
| CD209b (Receptor possibly involved in phagocytosis) | (227) | 1125 | 4 (CD209) |
| CD209a | 86 | 110 | - |
| CD5l (CD5 like very specific for MQ, bind CD36) | 558 | 892 | 0 |
| Adgre1 (F4/80, Emr1, GPCR mucin like) | 1178 | 373 | 87 |
| Retnla (Relma, Fizz1, suppresses TH2 responses) | 609 | 1223 | 30 |
| M. Scavenger Receptors | |||
| Marco (MARCO) | 16 | 28 | 1 |
| CD163 (Scavenger receptor, bind hemo-haptoglobin and complement) | 9 | 30 | 225 |
| CD36 (Scarb3) (Lung 1230) | 100 | 562 | 250 |
| CD68 (Binds oxidized LDL) | 425 | 638 | 1273 |
| CD177 | 9 | 15 | 0.3 |
| Scara3 and 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Scarb2 | 119 | 103 | 28 |
| Scarb1 | 10 | 51 | 22 |
| N. Cytokine, Chemokine, and Endothelin Receptors | |||
| Fgfr1 (FGF receptor 1) | (279) | 1429 | 0.1 |
| Csf1r (M-CSF receptor) | 678 | 1343 | 129 |
| Csf2ra (GM-CSF receptor alpha chain) | 277 | 838 | 47 |
| Csf3r (G-CSF receptor CD114) | (73) | 134 | 1236 |
| Ccr5 (CCR-5 receptor) | 76 | 119 | 2 |
| Ccr1 (CCR-1 receptor) | 228 | 91 | 34 |
| Tnfrsf1b (TNF receptor Subfamily 1b) | 66 | 399 | 1515 |
| Tnfrsf1a (TNF receptor Subfamily 1a) | 133 | 133 | 199 |
| Tnfrsf11a (TNF receptor Subfamily 11a) | 10 | 90 | 0.5 |
| Tnfrsf21 (TNF receptor Subfamily 21) | 28 | 80 | 25 |
| Tnfrsf14 (TNF receptor Subfamily 14) | 33 | 70 | 41 |
| Il10ra (IL-10 receptor alpha) | (67) | 280 | 609 |
| Il15ra (IL-15 receptor alpha) | (8) | 36 | 14 |
| Il6ra (IL-6 receptor alpha) | (86) | 34 | 80 |
| Il4ra (IL-4 receptor alpha) | 17 | 21 | 42 |
| IL3ra (IL-3 receptor alpha) | 21 | 17 | 8 |
| Il13ra1 (Il-13 receptor alpha1) | 13 | 10 | 123 |
| EGFR (EGF receptor HER1) | (2 | 6 | 0 |
| IL21r (IL-21 receptor) | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| IL27ra (IL-27 receptor alpha) | 14 | 5 | 32 |
| Il2rg (IL-2 receptor gamma) | (63) | 4 | 47 |
| Il2rb (IL-2 receptor beta) | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Il1r1 (Receptor 1 for IL1 alpha) | (1) | 1.4 | 2 |
| Ednrb (Endothelin B receptor) | (1162) | 1402 | 0.2 |
| O. Toll-Like Receptors and Accessory Proteins | |||
| Tlr4 (TLR-4) | 29 | 200 | 24 |
| Ly96 (MD2 LPS binding together with TLR4) | (74) | 30 | 8 |
| Tlr13 (TLR-13) | 137 | 108 | 0? |
| Tlr7 (TLR-7) | (49) | 84 | 9 |
| Tlr1 (TLR-1) | (25) | 71 | 6 |
| Tlr8 (TLR-8) | (57) | 65 | 46 |
| Tlr2 (TLR-2) | 43 | 26 | 40 |
| Tlr3 (TLR-3) | 8 | 18 | 0 |
| Tlr6 (TLR-6) | 18 | 3 | 2 |
| Nlrc4 (Inflammasome related) | 12 | 15 | 4 |
| P. Cell Adhesion | |||
| Itgam (Integrin alpha m, CD11b) | (2100) | 11,106 | 245 |
| Itga6 (Integrin alpha 6) | (751) | 4519 | 0 |
| Itgb2 (Integrin beta 2) | 1602 | 3683 | 1975 |
| Itgb1(Integrin beta 1) | 718 | 1253 | 161 |
| Itga4 (Integrin alpha 4) | 86 | 393 | 230 |
| Itgb7 (Integrin beta 7) | 49 | 17 | 0? |
| Itgav (Integrin alpha v) | 14 | 31 | 2 |
| Itga9 (Integrin alpha 9) | 12 | 39 | 2 |
| Itgb3 (Integrin beta 3) | 11 | 30 | 3 |
| Itgax (Integrin alpha x, CD11c) | 0.2 | 1 | 249 |
| Selp (P-selectin) | 679 | 3123 | 0 |
| Emilin2 (Elastin microfibril located protein 2) | 1123 | 2777 | 162 |
| Icam2 (ICAM 2) | 672 | 1092 | 39 |
| Lgals3 (Galectin3, MAC2) | 0 | 167 | 249 |
| Q. Chemokines and Cytokines | |||
| Pf4 (Platelet factor 4) | 1437 | 3583 | 3 |
| Ccl6 (Member of MIP-1 family) | 1500 | 2616 | - |
| Ccl9 (Also named MIP-1 gamma) | 332 | 3013 | 0 |
| Cxcl13 (B-cell attracting (BCA-1) | 1253 | 1456 | 0 |
| Ccl24 (Eotaxin-2 or MPIF-2) | 480 | 707 | 1 |
| Cxcl16 (T-cell and NK-cell attracting) | 0 | 73 | 307 |
| Cxcl14 (Attracting activated NK cells) | 25 | 47 | 0 |
| Cxcl2 (Also named MIP2 alpha) | 42 | 22 | 12 |
| Cxcl1 (Neutrophil attractant (Gro-a or NAP-3)) | 27 | 19 | 4 |
| Cxcl12 (also named SDF1) | (30) | 16 | 0 |
| Ccl5 (Rantes attracts T-cells, Eosinophils and Basophils) | 3 | 6 | 8 |
| Ccl11 (Eotaxin 1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tgfb2 (TGF-beta 2) | (256) | 1005 | 0.1 |
| Tgfb1 (TGF-beta 1) | 166 | 650 | 918 |
| Il16 (IL-16) | 19 | 71 | 0 |
| Csf1 (M-CSF, expressed low in most tissues) | (8) | 44 | 6 |
| IL18 (IL-18) | 18 | 38 | 58 |
| Il18bp (IL-18 binding protein) | 20 | 28 | 6 |
| IL1a (IL-1 alpha) | 14 | 31 | 0.2 |
| Il15 (IL-15) | (6) | 16 | 6 |
| IL27 (IL-27) | 3 | 3 | 7 |
| Il13 (IL-13) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Il12a and b (IL-12a and b) | 0 | 0 | 1 and 0 |
| Tnf (TNF-alpha) | 1 | 0.1 | 131 |
| Igf1 (IGF-1) | 11 | 80 | 0 |
| Egf (EGF) | 0.4 | 2 | 0 |
| Pdgfa (PDGF-A) | 5 | 10 | 0.4 |
| Pdgfb (PDGF-B) | 6 | 4 | 0.2 |
| Vegfa (VEGF-A) | 0 | 0 | 183 |
| Vegfb (VEGF-B) | 4 | 1.3 | 11 |
| Vegfd (VEGF-D) | 0 | 0 | 0? |
| R. Signaling Components | |||
| Tyrobp (TYRO protein kinase-binding protein, Myeloid) | 1504 | 2028 | 4617 |
| Dab2 (Disabled homolog 2) | (146) | 1413 | 1 |
| Pde2a (cGMP-dependent cyclic phosphodiesterase) | (228) | 1362 | 5 |
| Slfn4 (Schlafen 4-myeloid signaling) | (361) | 1322 | 0? |
| Btk | 59 | 52 | 50 |
| S. Transcription Factors | |||
| Gata6 (GATA-6) | 83 | 68 | 0 |
| Gata3 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| Gata2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Gata1 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| Mitf | (15) | 36 | 4 |
| Spi1 (Pu.1) | 228 | 536 | 1307 |
| Myb | 0.1 | 0 | 0.2 |
| Runx1 | (9) | 139 | 42 |
| Runx3 | 6 | 7 | 166 |
| Creb3l1 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Zeb2 (Zinc finger corepressor) | (100) | 939 | 242 |
| Tox2 | 46 | 78 | 0.3 |
| Ikzf1 (Ikaros, Zinc finger transcription factor) | 8 | 16 | 54 |
| Foxp3 | 5 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Mouse Balb/c Mice | Human | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MΦs | Mast Cells | B-Cells | Monocytes | |
| A. TLR Rig-1 and MDA5 | ||||
| Rig-1 (Ddx58) | 27 | 44 | 104 | 3 |
| MDA5 (Ifih1) | 58 | 42 | 10 | 4 |
| TLR-4 | 200 | 61 | 26 | 24 |
| TLR-13 | 108 | 13 | 3 | - |
| TLR-9 | 0.4 | 12 | 251 | 1 |
| TLR-11 | 0 | 9 | 0 | - |
| TLR-7 | 84 | 5 | 38 | 9 |
| TLR-3 lung (41) | 18 | 5 | 3 | 0 |
| TLR-1 | 71 | 4 | 151 | 6 |
| TLR-8 | 65 | 4 | 1 | 46 |
| TLR-12 | 0.2 | 3 | 15 | - |
| TLR-6 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| TLR-2 | 26 | 2 | 10 | 40 |
| TLR-5 lung (10) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 18 |
| Dectin-1 (Clec7a) | 261 | 11 | 2 | 142 |
| Ccl5 lung (130) | 6 | 43 | 15 | 8 |
| B. Angiogenesis related transcripts | ||||
| Vegfa lung (350) | 0 | 65 | 0 | 183 |
| Vegfb | 1 | 35 | 6 | 11 |
| Vegfc | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Vegfd lung (92) | 0 | 1 | 0 | - |
| Angpt1 (Angiopoetin 1) | 0 | 72 | 0 | 0.4 |
| Angpt2 (Angiopoetin 2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ampliseq | ||
|---|---|---|
| Analysis 1 | Analysis 2 | |
| A. Major Liver-Specific Transcripts | ||
| Alb (Albumin, the major plasma protein) | 59,900 | 61,827 |
| Ashg (Alpha 2-HS glycoprotein/fetuin) | 14,707 | 14,423 |
| Hpx (Hemopexin bind heme) | 5626 | 5520 |
| Pzp (Pregnancy zone protein, alpha-2 globin family) | 3975 | 3902 |
| Ambp (Alpha-1-microglobulin) | 3702 | 3830 |
| Gnmt (Glycine-N-methyltransferase) | 2386 | 2501 |
| Vtn1 (Vitronectin) | 2677 | 2721 |
| Fn1 (Fibronectin) | 925 | 1018 |
| Hrg (Histidine-rich glycoprotein) | 934 | 810 |
| Akr1c6 (Aldo-keto reductase) | 457 | 516 |
| Akr1c14 (Alcohol dehydrogenase) | 453 | 421 |
| Tfr2 (Transferrin receptor 2) | 439 | 451 |
| Agt (Angiotensin precursor) | 448 | 509 |
| Hpn (Hepsin, a serine protease) (Kidney 370) | 431 | 460 |
| Tdo2 (Tryptophane 2,3-dioxygenase) | 430 | 396 |
| Afm (Afamin albumin related) | 381 | 377 |
| Sult2a2 (Sulfotransferase family 2A drug metabolism) | 302 | 282 |
| Sds (Serine dehydrase, serine metabolism) | 292 | 303 |
| Cp (Ceruloplasmin copper-carrying protein) | 288 | 247 |
| Dpys (Dihydropyrimidase pyrimidine metabolism) | 272 | 270 |
| Saa4 (Serum amyloid, apolipoprotein) | 233 | 227 |
| Apcs (Serum amyloid P component) | 60 | 52 |
| Msp1 (Macrophage stimulatory protein, also HLP) | 323 | 251 |
| Mup20 (Major urinary protein) | 226 | 218 |
| Cyp2c54 (Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C) | 225 | 228 |
| Amdhd1 (Imidazolonepropionase histidine metabolism) | 222 | 246 |
| Ugt2a3 (UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2A3) | 218 | 217 |
| Sult2a1 (Bile salt sulfotransferase) | 176 | 172 |
| Gckr (Glucokinase regulatory protein) | 175 | 180 |
| Fmo3 (Flavo containing mono-oxidase 3) | 175 | 177 |
| Asgr2 (Asialoglycoprotein receptor, galactose) | 174 | 170 |
| Baat (Bile acid-CoA amino acid N-acyl transferase) | 172 | 159 |
| Lyz2 (P-Lysozyme, probably Lyz1 instead) | 160 | 155 |
| Prodh2 (Hydroxyproline dehydrogenase) | 144 | 146 |
| Clec4f (Kupffer cell galactose receptor lectin) | 121 | 115 |
| Gfra1 (GDNF family receptor alpha 1) | 111 | 113 |
| Inhbc (Inhibin beta C-chain TGF-beta family) | 100 | 103 |
| Cpn2 (Carboxypeptidase N) | 83 | 89 |
| Gck (Glucokinase senses glucose levels) | 83 | 87 |
| Gys2 (Glycogene syntase) | 79 | 82 |
| Fgfr4 (FGF receptor 4) | 58 | 54 |
| Oit3 (Oncoprotein-induced transcript 3) | 54 | 64 |
| A1bg (Alpha-1-B glycoprotein) | 40 | 46 |
| Inhbe (Inhibin beta E chain precursor, TGF family) | 39 | 43 |
| Dnase2b (DNAse 2 beta) | 37 | 41 |
| Igfals (IGF-binding factor, stabilizes IGF in plasma) | 31 | 33 |
| Gdf2 (Bone morphogenic protein BMP-9) | 30 | 29 |
| Fgf21 (FGF-21 hepatokine, regulates sugar intake) | 24 | 29 |
| Il6ra (IL-6 receptor alpha) | 21 | 21 |
| Bmp5 (BMP-5, Bone morphogenic protein 5) | 21 | 24 |
| Thpo (Thrombopoietin regulates platelet production) | 20 | 22 |
| Bco1 (beta carotene metabolism) | 20 | 20 |
| Saa3 (Amyloid) | 2.9 | 2.0 |
| B. Lipid Metabolism and Transport | ||
| Scd (Stearoyl CoA desaturase) | 20,132 | 21,369 |
| Fabp1 (Fatty-acid-binding protein) | 15,683 | 16,162 |
| Apoa1 (Apolipoprotein A1, major part of HDL) | 15,093 | 15,512 |
| Apoa2 (Apolipoprotein A1, part of HDL) | 14,210 | 12,233 |
| Apoc1 (Apolipoprotein C1, can be part of HDL) | 12,723 | 12,195 |
| Ttr (Transthyretin, transport thyroxin and retinol) | 12,443 | 11,201 |
| Gc (Gc-globin, vitamin D-binding protein) | 9852 | 9765 |
| Apoc3 (Apolipoprotein C3, can be part of VLDL) | 9755 | 10,184 |
| Rbp4 (Retinol-binding protein) | 6483 | 6138 |
| ApoE (Apolipoprotein E, transport lipids) | 2445 | 2353 |
| Sec14l4 (Sec14-like lipid binding 4, transport) | 260 | 251 |
| C. Protease Inhibitors | ||
| Serpinc1 (Serpin C1) | 4809 | 4845 |
| Fetub (Fetuin b, Cystein protease inhibitor) | 618 | 592 |
| Itih1 (Inter alpha-trypsin inhibitor 1) | 400 | 398 |
| Itih3 (Inter alpha-trypsin inhibitor 3) | 250 | 244 |
| Serpina7 (Serpin A7) | 42 | 46 |
| D. Coagulation Factors | ||
| Fgb) Fibrinogen beta) | 7718 | 7474 |
| Fga (Fibrinogen alpha) | 4817 | 5144 |
| Fgg (Fibrinogen gamma) | 2540 | 2538 |
| F2 (Thrombin) | 3089 | 3507 |
| F10 (Coagulation factor X) | 1007 | 1144 |
| Cpb2 (Carboxypeptidase B2, downregulates fibrinolysis) | 664 | 641 |
| F5 (Coagulation factor V) | 522 | 527 |
| Fgl1 (Fibrinogen-like protein 1) | 452 | 476 |
| F12 (Coagulation factor XII) | 450 | 458 |
| F13b (Coagulation factor XIII-B) | 326 | 315 |
| F7 (Coagulation factor VII) | 150 | 142 |
| F9 (Coagulation factor IX) | 90 | 96 |
| F11 (Coagulation factor XI) | 57 | 49 |
| F8 (Coagulation factor 8, Kidney (3 and 4), Uterus 16) | 17 | 19 |
| E. Complement Factors | ||
| C3 (Complement factor 3) | 5114 | 3902 |
| Cfh (Complement factor H) | 1231 | 1221 |
| C4b (Complement factor 4B) | 777 | 889 |
| C4a (Complement factor 4A) | 26 * | 24 * |
| Cfi (Complement factor I) | 530 | 472 |
| Cfhr1 (Complement factor H-related protein) | 167 | 172 |
| C4bp (C4 binding protein regulatory) | 735 | 671 |
| C8g (Complement factor 8g) | 393 | 398 |
| Hc (Hemolytic component same as C5) | 345 | 298 |
| Crp (C-Reactive protein) | 428 | 433 |
| C1rl (C1r protease) | 232 | 245 |
| C1qbp (C1q binding protein) | 209 | 203 |
| C8b (Complement factor 8 beta chain) | 127 | 119 |
| C9 (Complement component 9) | 119 | 114 |
| C8a (Complement factor 8 alpha chain) | 74 | 44 |
| C1qb (Complement factor C1q beta chain) | 52 | 31 |
| C2 (Complement factor 2) | 51 | 51 |
| Fcna (Ficolin) | 40 | 46 |
| Cfp (Properdin) | 30 | 31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paivandy, A.; Akula, S.; Lara, S.; Fu, Z.; Olsson, A.-K.; Kleinau, S.; Pejler, G.; Hellman, L. Quantitative In-Depth Transcriptome Analysis Implicates Peritoneal Macrophages as Important Players in the Complement and Coagulation Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031185
Paivandy A, Akula S, Lara S, Fu Z, Olsson A-K, Kleinau S, Pejler G, Hellman L. Quantitative In-Depth Transcriptome Analysis Implicates Peritoneal Macrophages as Important Players in the Complement and Coagulation Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031185
Chicago/Turabian StylePaivandy, Aida, Srinivas Akula, Sandra Lara, Zhirong Fu, Anna-Karin Olsson, Sandra Kleinau, Gunnar Pejler, and Lars Hellman. 2022. "Quantitative In-Depth Transcriptome Analysis Implicates Peritoneal Macrophages as Important Players in the Complement and Coagulation Systems" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031185
APA StylePaivandy, A., Akula, S., Lara, S., Fu, Z., Olsson, A.-K., Kleinau, S., Pejler, G., & Hellman, L. (2022). Quantitative In-Depth Transcriptome Analysis Implicates Peritoneal Macrophages as Important Players in the Complement and Coagulation Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031185







