Fabrication of Fragment Antibody–Enzyme Complex as a Sensing Element for Immunosensing
Abstract
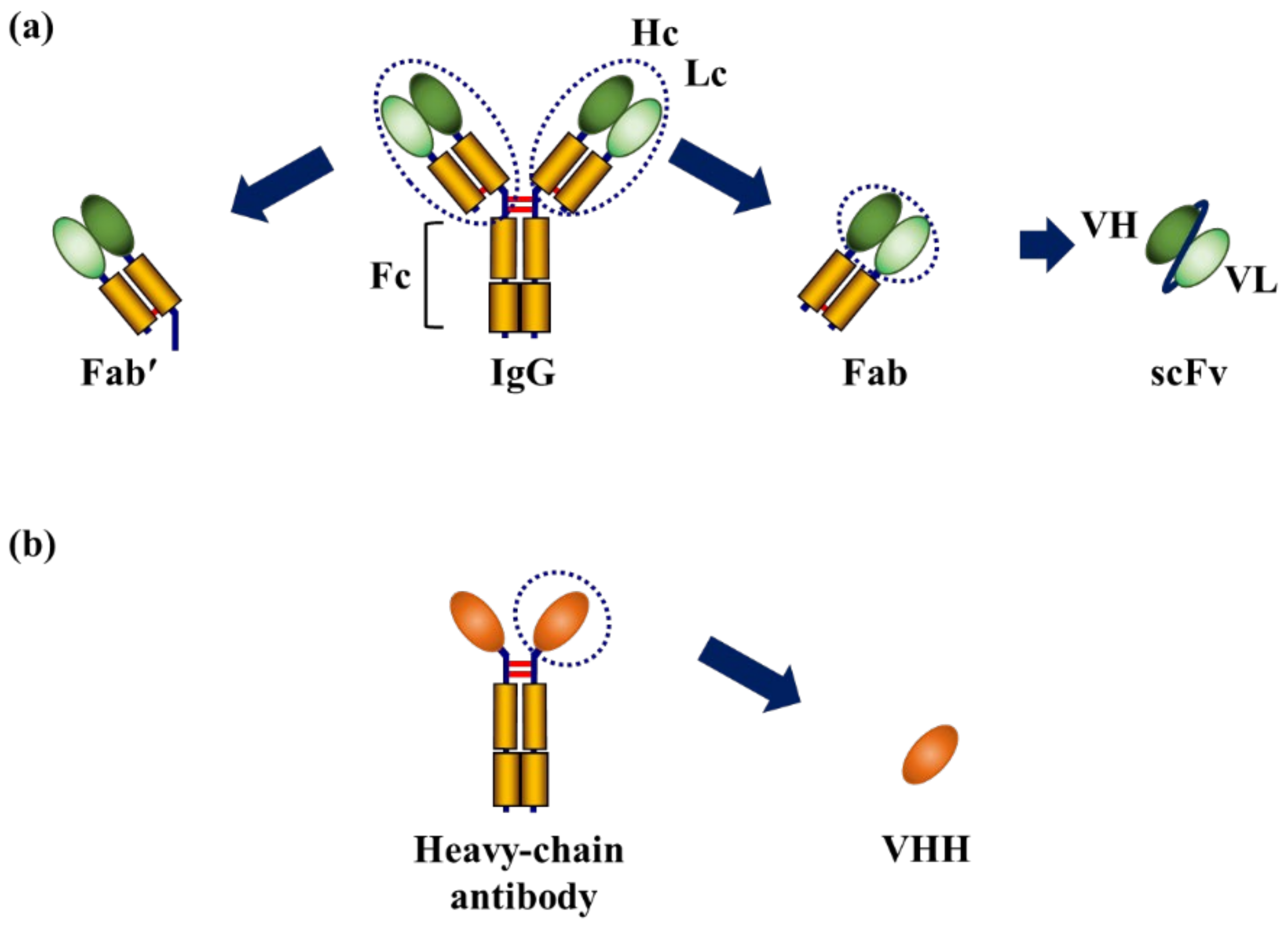
:1. Introduction
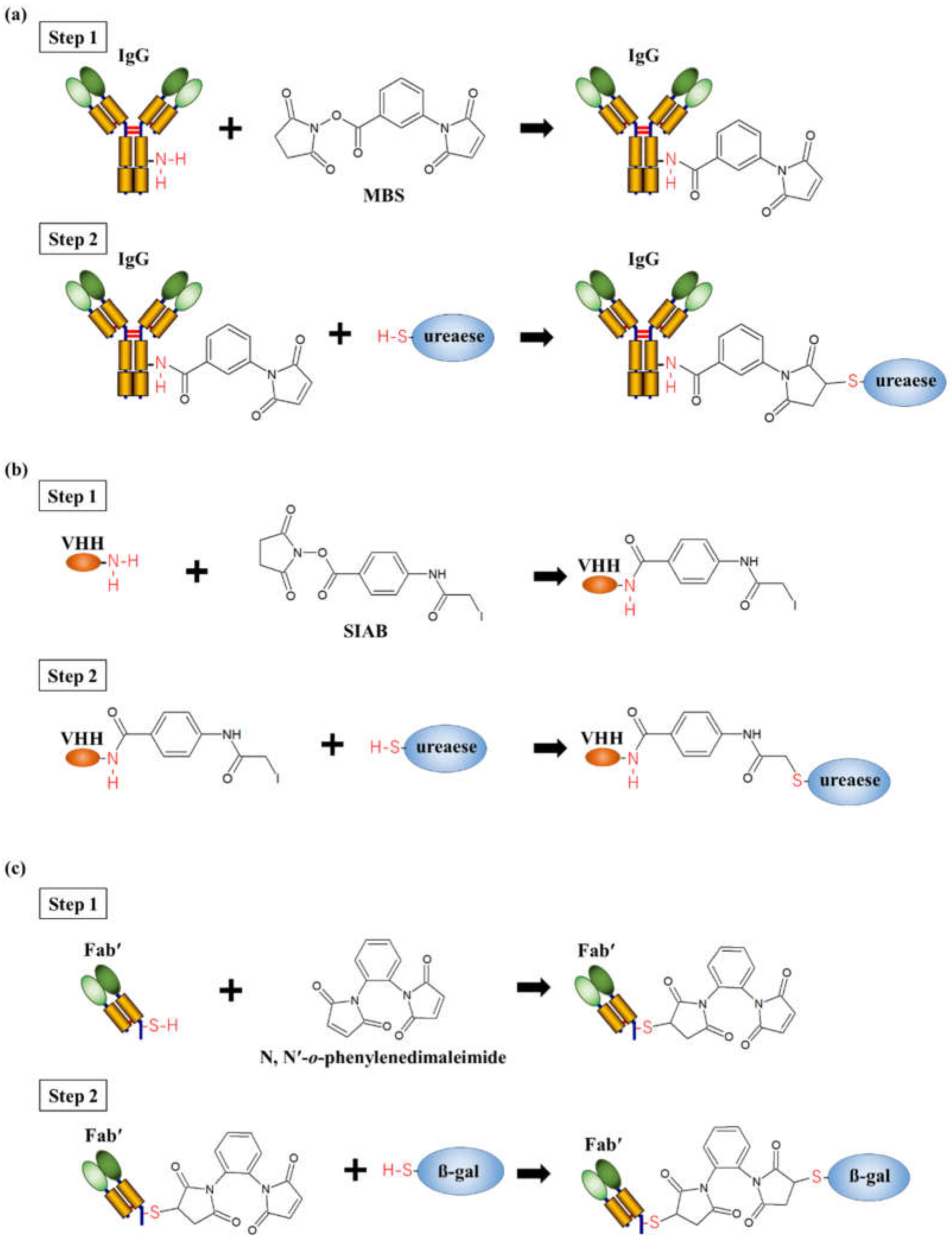
2. Chemical Conjugation
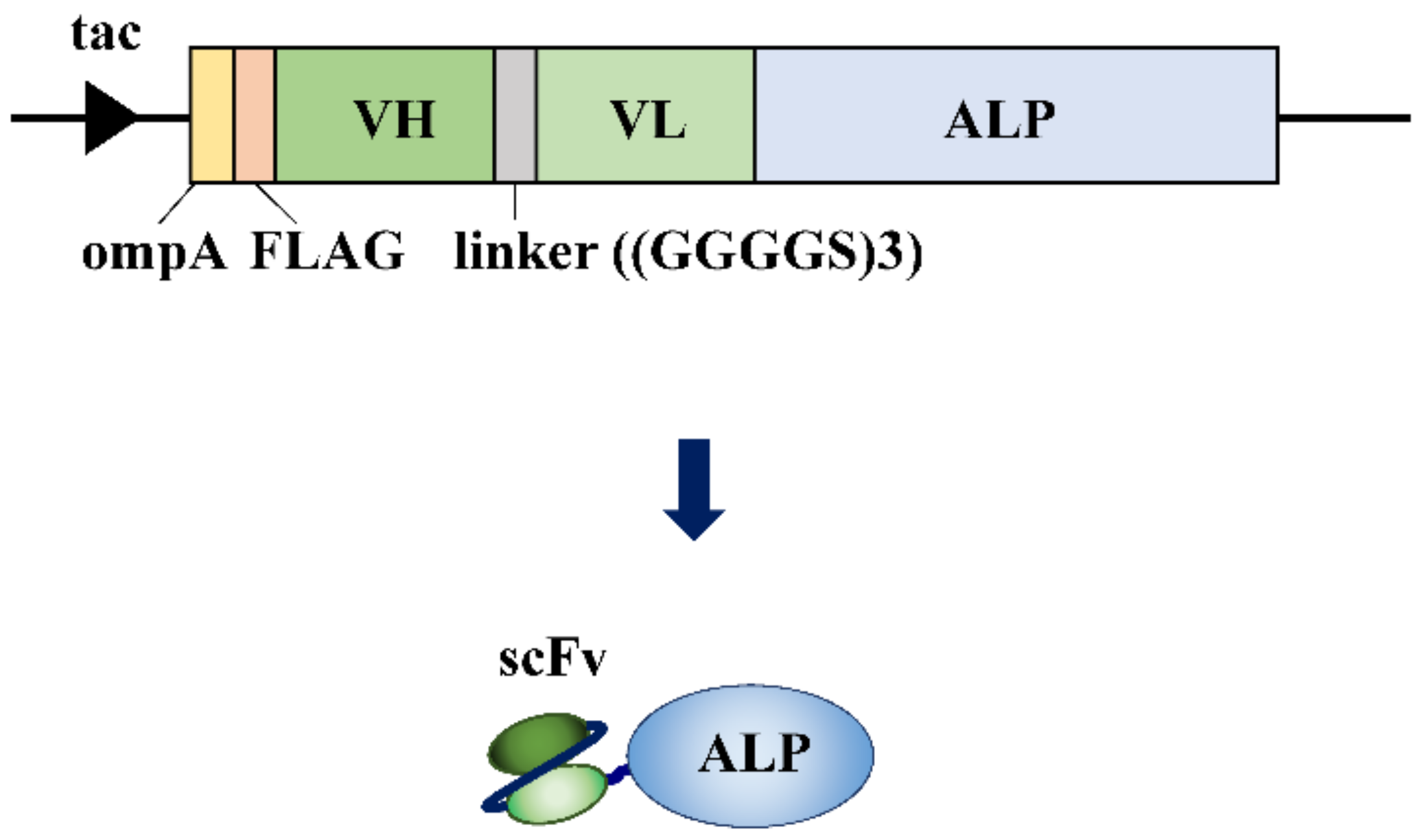
3. Direct Fusion
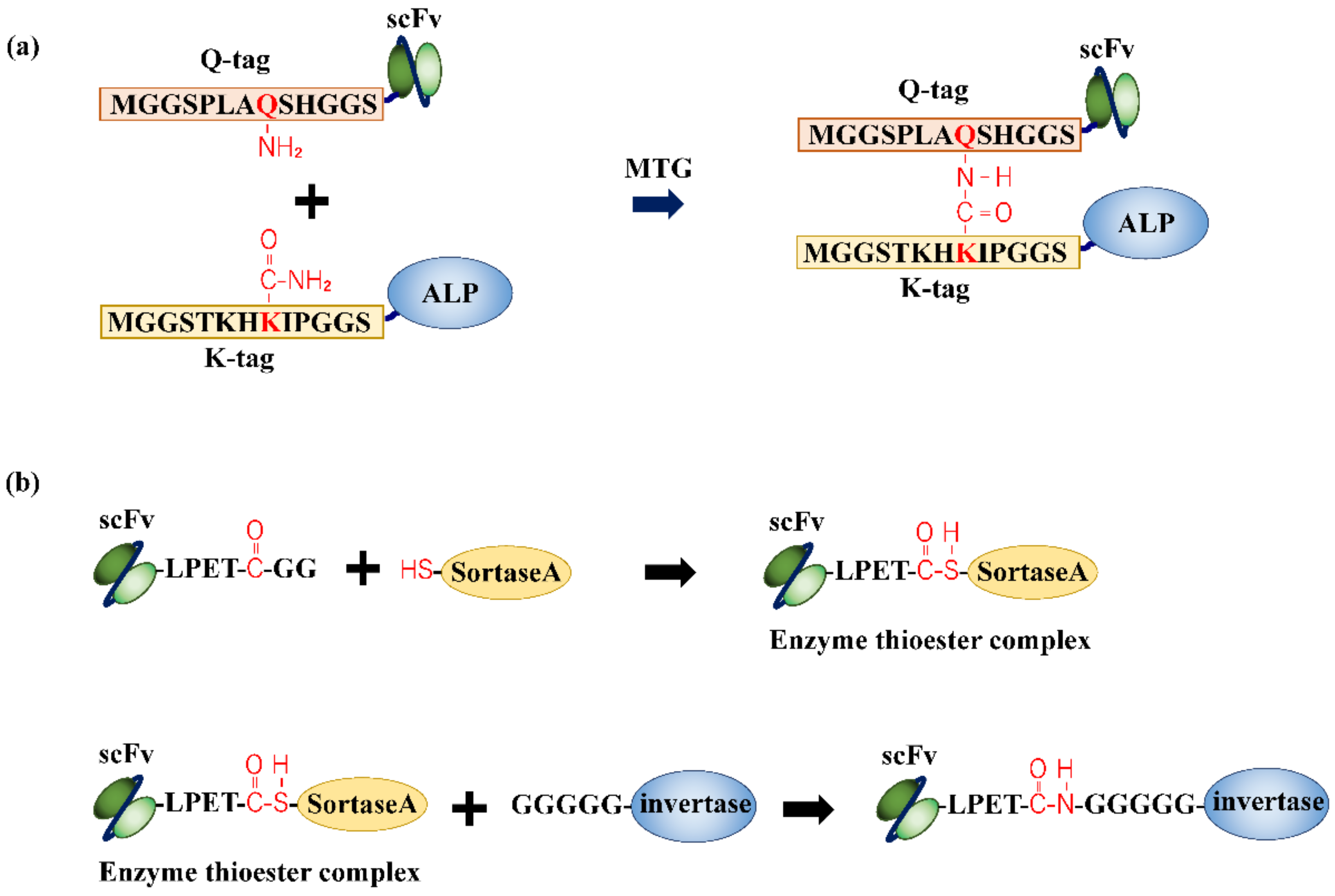
4. Enzymatic Conjugation
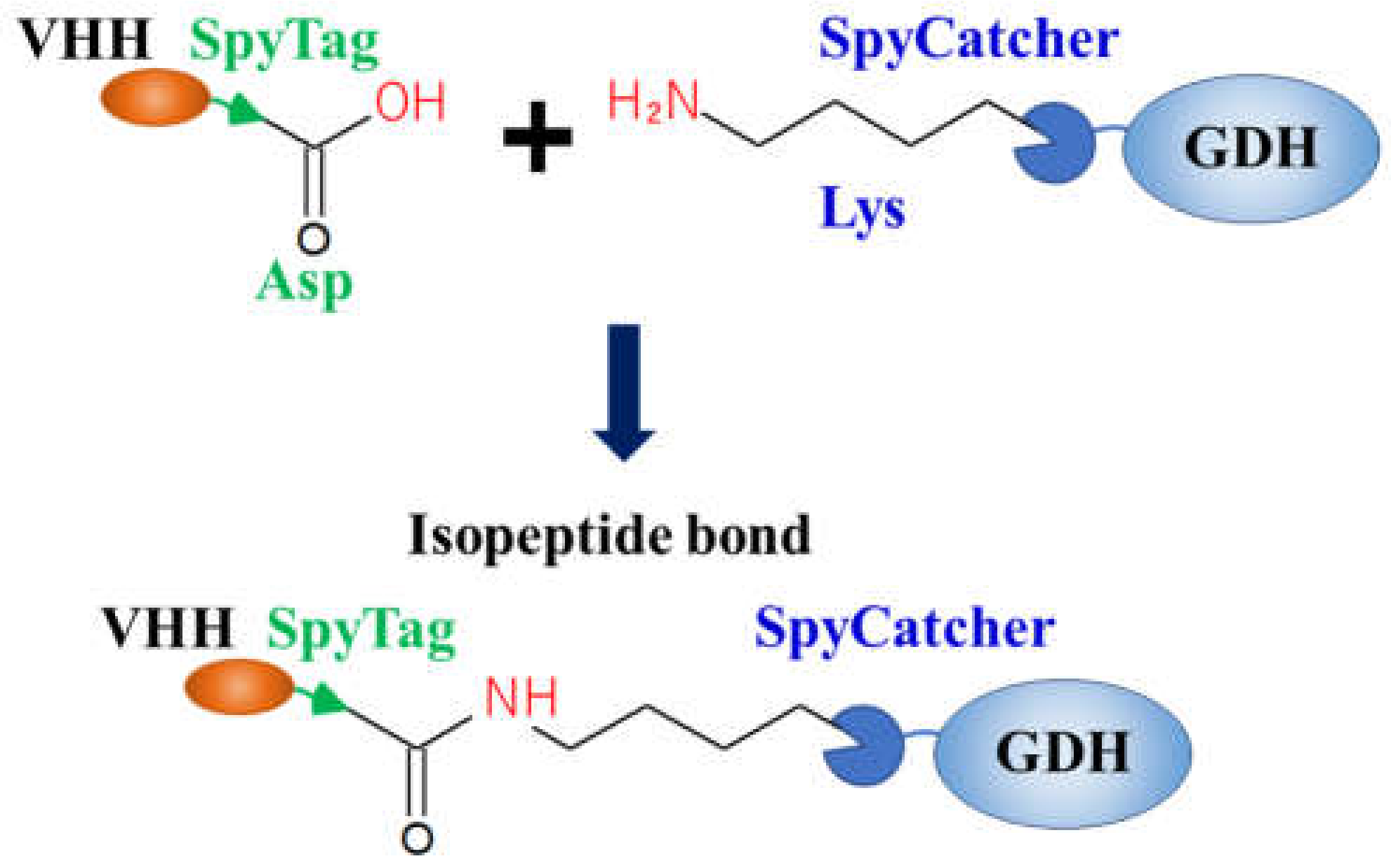
5. Catcher/Tag System
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hock, B. Antibodies for immunosensors: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 347, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schots, A.; van der Wolf, J.M. Green fluorescent protein fluobody immunosensors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2002, 183, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Ueda, H. Recent advances in quenchbody, a fluorescent immunosensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; He, J.; Shi, W.; Zhao, W.; Shen, J. Application of quantum dot−antibody conjugates for detection of sulfamethazine residue in chicken muscle tissue. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6139–6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.P.; Ngatia, S.N.; van Duyne, R.P. LSPR biosensor signal enhancement using nanoparticle-antibody conjugates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wisdom, G.B. Enzyme-immunoassay. Clin. Chem. 1976, 22, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, E.; Imagawa, M.; Hashida, S.; Yoshitake, S.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Ueno, T. Enzyme-labeling of antibodies and their fragments for enzyme immunoassay and immunohistochemical staining. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 1983, 4, 209–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, C.; Molokova, E.; Minja, F.; Geis, S.; Loscher, T.; Maboko, L.; Koulchin, V.; Hoelscher, M. Detection of mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan with an antigen-capture ELISA in unprocessed urine of Tanzanian patients with suspected tuberculosis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 99, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, T.E.; Sheppard, J.I.; Moore, J.C.; Sigouin, C.S.; Kelton, J.G. Quantitative interpretation of optical density measurements using PF4-dependent enzyme-immunoassays. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Dauner, A.L.; Mitra, I.; Forshey, B.M.; Garcia, P.; Morrison, A.C.; Halsey, E.S.; Kochel, T.J.; Wu, S.J.L. Evaluation of dengue NS1 antigen rapid tests and ELISA kits using clinical samples. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.L.; Ren, H.L.; Li, Y.S.; Hu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.S.; Yan, D.M.; Hui, Q.; Liu, D.; Lin, C.; et al. A magnetic particles-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for rapid detection of ovalbumin. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 459, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul Azim, M.A.; Hasan, M.; Ansari, I.H.; Nasreen, F. Chemiluminescence immunoassay: Basic mechanism and applications. Bangladesh J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 18, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawachi, S.; Matsushita, T.; Sato, T.; Nunoi, H.; Noguchi, H.; Ota, S.; Kanemoto, N.; Nakatani, K.; Nishiguchi, T.; Yuge, A.; et al. Multicenter prospective evaluation of a novel rapid immunochromatographic diagnostic kit specifically detecting influenza A H1N1 2009 virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 51, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.; Ainsworth, M.; Anand, R.; Andersson, M.I.; Auckland, K.; Baillie, J.K.; Barnes, E.; Beer, S.; Bell, J.I.; Berry, T.; et al. Antibody testing for COVID-19: A report from the national COVID scientific advisory panel. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, A.; Cavalera, S.; Di Nardo, F.; Calabria, D.; Rosati, S.; Simoni, P.; Colitti, B.; Baggiani, C.; Roda, M.; Anfossi, L. Dual lateral flow optical/chemiluminescence immunosensors for the rapid detection of salivary and serum IgA in patients with COVID-19 disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lin, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Song, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Song, H.; Hao, R. Multichannel immunosensor platform for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A(H1N1) virus. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 22262–22270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, L.; Saroglia, M.; Galatà, G.; de Santis, R.; Fillo, S.; Luca, V.; Faggioni, G.; D’Amore, N.; Regalbuto, E.; Salvatori, P.; et al. Magnetic beads combined with carbon black-based screen-printed electrodes for COVID-19: A reliable and miniaturized electrochemical immunosensor for SARS-CoV-2 detection in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, H.; Takasaki, W.; Tsukamoto, R.; Nambara, T. Sensitivity of steroid enzyme immunoassays. comparison of alkaline phosphatase, β-galactosidase and horseradish peroxidase as labels in a colorimetric assay system. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 3336–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, I.; Rishpon, J. Alkaline phosphatase as a label for a heterogeneous immunoelectrochemical sensor: An electrochemical study. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1989, 258, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalado, C.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Duarte-Vázquez, M.A. Biotechnological applications of peroxidases. Phytochem. Rev. 2004, 3, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kang, Y.C.; Lee, J.K. Eco-friendly composite of Fe3O4-reduced graphene oxide particles for efficient enzyme immobilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Su, P.; Huang, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles coated with immobilized alkaline phosphatase for enzymolysis and enzyme inhibition assays. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1749–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; Turner, A.P.F. Glucose oxidase: An ideal enzyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1992, 7, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skládal, P. Advances in electrochemical immunosensors. Electroanalysis 1997, 9, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinke, A.; Benkert, A.; Scheller, F.W. Electrochemical immunoassays. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 366, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaul Haque, A.M.; Kwon, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, N.S.; Ho Yoon, Y.; Yang, H. Sensitive and low-background electrochemical immunosensor employing glucose dehydrogenase and 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fernández, B.; Mercader, J.V.; Checa-Orrego, B.I.; De La Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Costa-García, A. A monoclonal antibody-based immunosensor for the electrochemical detection of imidacloprid pesticide. Analyst 2019, 144, 2936–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, K.N.; Seong, W.K. Electrochemical immunoassay based on indium tin oxide Activity toward a alkaline phosphatase. Biochip J. 2019, 13, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.; Bradbury, A.R.M.; Knappik, A.; Plückthun, A.; Borrebaeck, C.A.K.; Dübel, S. Animal-free alternatives and the antibody iceberg. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saerens, D.; Huang, L.; Bonroy, K.; Muyldermans, S. Antibody fragments as probe in biosensor development. Sensors 2008, 8, 4669–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvanayagam, Z.E.; Neuzil, P.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Sridhar, U.; Singh, M.; Ho, L.C. An ISFET-based immunosensor for the detection of β-bungarotoxin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Wong, W.Y.; Hegmann, E.; Gaspar, K.; Kumar, P.; Chao, H. Production and characterization of a camelid single domain antibody–urease enzyme conjugate for the treatment of cancer. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Fukui, H.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Ishikawa, E. Enzyme-linked immunoassay: Conjugation of the Fab′ fragment of rabbit IgG with β-D-galactosidase from E. coli and its use for immunoassay. J. Immunol. 1976, 116, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wels, W.; Harwerth, I.-M.; Zwickl, M.d; Hardman, N.; Groner, B.; Hynes, N.E. Construction, bacterial expression and characterization of a bifunctional single–chain antibody–phosphatase fusion protein targeted to the human ERBB–2 receptor. Nat. BioTechnol. 1992, 10, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier, A.; Ducancel, F.; Settiawan, N.B.; Cattolico, L.; Maillère, B.; Léonetti, M.; Drevet, P.; Ménez, A.; Boulain, J.C. Recombinant antibody-alkaline phosphatase conjugates for diagnosis of human IgGs: Application to anti-HBsAg detection. J. Immunol. Methods 1995, 181, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliasnikov, O.V.; Grigorenko, V.G.; Egorov, A.M.; Lange, S.; Schmid, R.D. Recombinant production of horseradish peroxidase conjugates with Fab antibodies in Pichia pastoris for analytical applications. Acta Naturae 2011, 3, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takazawa, T.; Kamiya, N.; Ueda, H.; Nagamune, T. Enzymatic labeling of a single chain variable fragment of an antibody with alkaline phosphatase by microbial transglutaminase. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 86, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, H.; Adachi, M.; Umeda, K.; Matsuura, A.; Nonaka, M.; Uchio, R.; Tanaka, H.; Motoki, M. Purification and characteristics of a novel transglutaminase derived from microorganisms. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 2613–2617. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, N.F.; Lim, T.S. Site-specific ScFv labelling with invertase via sortase a mechanism as a platform for antibody-antigen detection using the personal glucose meter. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Liu, G.; Ton-That, H.; Schneewind, O. Staphylococcus aureus sortase, an enzyme that anchors surface proteins to the cell wall. Science 1999, 285, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.J.; Fascione, M.A.; Webb, M.E.; Turnbull, W.B. Efficient N-terminal labeling of proteins by use of sortase. Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 9511–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Asano, R.; Tsukamoto, N.; Tsugawa, W.; Sode, K. Convenient and universal fabrication method for antibody-enzyme complexes as sensing elements using the SpyCatcher/SpyTag system. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 14500–14506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zakeri, B.; Fierer, J.O.; Celik, E.; Chittock, E.C.; Schwarz-Linek, U.; Moy, V.T.; Howarth, M. Peptide tag forming a rapid covalent bond to a protein, through engineering a bacterial adhesin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E690–E697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H.; Miura, D.; Tsugawa, W.; Ikebukuro, K.; Sode, K.; Asano, R. Rapid and homogeneous electrochemical detection by fabricating a high affinity bispecific antibody-enzyme complex using two Catcher/Tag systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, D.; Kimura, H.; Tsugawa, W.; Ikebukuro, K.; Sode, K.; Asano, R. Rapid, convenient, and highly sensitive detection of human hemoglobin in serum using a high-affinity bivalent antibody–enzyme complex. Talanta 2021, 234, 122638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Li, H.P.; Zhang, J.B.; Liu, J.L.; Hu, Z.Q.; Gong, A.D.; Huang, T.; Liao, Y.C. Chicken single-chain antibody fused to alkaline phosphatase detects Aspergillus pathogens and their presence in natural samples by direct sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10992–10999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fabrication Method | Antibody Format | Enzyme | Detection Target | Detection Method | Detection Limit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical conjugation | IgG | Urease | β-BuTX | ELISA (ISFET) | 15.6 ng/mL | [31] |
| Fab’ | β-gal | Human IgG | ELISA | 0.3 fmoles (45 pg *) | [33] | |
| Direct fusion | scFv | ALP | Human erbB-2 receptors | Immunostaining (Fluorescence) | - | [34] |
| Fab/scFv | ALP | Human IgG | ELISA | No data | [35] | |
| Fab | HRP | Atrazine | ELISA | 0.1 ng/mL | [36] | |
| Enzymatic conjugation | scFv | ALP | HEL | ELISA | 1 ng/mL | [37] |
| scFv | Invertase | Ubiquitin | ELISA | 0.003 fmol (26 fg *) | [39] | |
| Catcher/Tag system | VHH | GDH | EGFR | ELISA | 3.75 nM (260 ng/mL *) | [42] |
| scFv | GDH | EGFR | ELISA (Fluorescence) ELISA (Amperometry) ELISA (Amperometry, Homogeneous) | 0.079 nM (5.5 ng/mL *) 0.44 nM (31 ng/mL *) 0.2 nM (14 ng/mL *) | [44] | |
| scFv | GDH | Hemoglobin | ELISA (Amperometry, Homogeneous) | 0.54 nM (35 ng/mL *) | [45] |
| Conjugation Efficiency | Reaction Condition | Stoichiometric Conjugation | Note | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical conjugation | High | 0.5~3 h, 25 °C | No | No/Less protein engineering | |
| Direct fusion | - | - | Yes | Single production | |
| Enzymatic conjugation | MTG | Middle | 3 h, 4 °C | No | Less impact on protein function |
| SrtA | Low | 3 h, 25 °C | Yes | ||
| Catcher/Tag system | High | 1~40 h, 4 °C | Yes | High versatility | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oda, M.; Asano, R. Fabrication of Fragment Antibody–Enzyme Complex as a Sensing Element for Immunosensing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031335
Oda M, Asano R. Fabrication of Fragment Antibody–Enzyme Complex as a Sensing Element for Immunosensing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031335
Chicago/Turabian StyleOda, Miho, and Ryutaro Asano. 2022. "Fabrication of Fragment Antibody–Enzyme Complex as a Sensing Element for Immunosensing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031335
APA StyleOda, M., & Asano, R. (2022). Fabrication of Fragment Antibody–Enzyme Complex as a Sensing Element for Immunosensing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031335






