Identification of Growth Factors, Cytokines and Mediators Regulated by Artemisia annua L. Polyphenols (pKAL) in HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells: TGF-β1 and NGF-β Attenuate pKAL-Induced Anticancer Effects via NF-κB p65 Upregulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. pKAL Induces Intracelluar and Extracelluar Vesicles in HCT116 Cells
2.2. Identification of Growth Factors, Cytokines and Signaling Mediators Regulated by pKAL
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3.1. Expression Heatmap and Keywords for pKAL-Regulated Proteins
2.3.2. Gene Category Classification for pKAL-Regulated Proteins
2.3.3. Protein–Protein Interaction Network for pKAL-Regulated Proteins
2.4. TGF-β1 Inhibits pKAL-Induced Anticancer Effect
2.5. NGF-β Inhibits pKAL-Induced Anticancer Effect through PI3K Signaling
2.6. TGF-β1 and NGF-β Attenuate pKAL-Induced Cell Death through Upregulation of NF-κB p65 and Cyclin D1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. pKAL Compounds
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Viability Analysis
4.5. Phase-Contrast Microscopy
4.6. Phase-Contrast Microscopy of Hematoxylin-Stained Cells
4.7. Sample Preparation for Antibody Array
4.8. Antibody Array Analysis
4.9. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, R.; Bhatt, L.K.; Johnston, T.P.; Prabhavalkar, K.S. Colon cancer stem cells: Potential target for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1068–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Zhu, Y. Colorectal cancer stem cell: A potential therapeutic target. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2011, 13, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xia, L.; Wang, H.; Oyang, L.; Su, M.; Liu, Q.; Lin, J.; Tan, S.; Tian, Y.; Liao, Q.; et al. Cancer stem cells in progression of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33403–33415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadanandam, A.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Homicsko, K.; Collisson, E.A.; Gibb, W.J.; Wullschleger, S.; Ostos, L.C.; Lannon, W.A.; Grotzinger, C.; Del Rio, M.; et al. A colorectal cancer classification system that associates cellular phenotype and responses to therapy. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganesan, K.; Jayachandran, M.; Xu, B. Diet-Derived Phytochemicals Targeting Colon Cancer Stem Cells and Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.Y.; Chao, T.C.; Su, Y. The Stemness-High Human Colorectal Cancer Cells Promote Angiogenesis by Producing Higher Amounts of Angiogenic Cytokines via Activation of the Egfr/Akt/Nf-kappaB Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabkeviciene, D.; Jonusiene, V.; Zitkute, V.; Zalyte, E.; Grigaitis, P.; Kirveliene, V.; Sasnauskiene, A. The role of interleukin-8 (CXCL8) and CXCR2 in acquired chemoresistance of human colorectal carcinoma cells HCT116. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, F.; Hosseini, R.; Saso, L.; Firuzi, O. Modulation of neurotrophic signaling pathways by polyphenols. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorzynik-Debicka, M.; Przychodzen, P.; Cappello, F.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Knap, N.; Wozniak, M.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, I.; Sharma, M.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Combinatorial Epigenetics Impact of Polyphenols and Phytochemicals in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uddin, M.S.; Mamun, A.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Jeandet, P.; Alexiou, A.; Behl, T.; Sarwar, M.S.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Ashraf, G.M.; Sayed, A.A.; et al. Natural Products for Neurodegeneration: Regulating Neurotrophic Signals. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8820406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.J.; Lee, W.S.; Paramanantham, A.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.M.; Ryu, C.H.; Hong, S.C.; Chung, K.H.; et al. P53 Enhances Artemisia annua L. Polyphenols-Induced Cell Death Through Upregulation of p53-Dependent Targets and Cleavage of PARP1 and Lamin A/C in HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.J.; Paramanantham, A.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.M.; Ryu, C.H.; Hong, S.C.; Chung, K.H.; Kim, C.W.; et al. Artemisia annua L. Polyphenol-Induced Cell Death Is ROS-Independently Enhanced by Inhibition of JNK in HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Chen, T.; Zheng, X.; Yang, S.; Xu, K.; Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Colorectal cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles establish an inflammatory premetastatic niche in liver metastasis. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.Y.; Naora, H. Extracellular Vesicle Membrane-Associated Proteins: Emerging Roles in Tumor Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenesis Therapy Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S. Insulin signaling, resistance, and the metabolic syndrome: Insights from mouse models into disease mechanisms. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, T1–T23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Bai, J.; Qin, T.; Wang, Z.; Han, L. NGF from pancreatic stellate cells induces pancreatic cancer proliferation and invasion by PI3K/AKT/GSK signal pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5901–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Descamps, S.; Toillon, R.A.; Adriaenssens, E.; Pawlowski, V.; Cool, S.M.; Nurcombe, V.; Le Bourhis, X.; Boilly, B.; Peyrat, J.P.; Hondermarck, H. Nerve growth factor stimulates proliferation and survival of human breast cancer cells through two distinct signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17864–17870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torrealba, N.; Vera, R.; Fraile, B.; Martinez-Onsurbe, P.; Paniagua, R.; Royuela, M. TGF-beta/PI3K/AKT/mTOR/NF-kB pathway. Clinicopathological features in prostate cancer. Aging Male 2020, 23, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.W.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Shin, J.M.; Lee, H.M. Apigenin alleviates TGF-beta1-induced nasal mucosa remodeling by inhibiting MAPK/NF-kB signaling pathways in chronic rhinosinusitis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudlsperger, C.; Bian, Y.; Contag Wise, S.; Burnett, J.; Coupar, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Van Waes, C. TGF-beta and NF-kappaB signal pathway cross-talk is mediated through TAK1 and SMAD7 in a subset of head and neck cancers. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, C.; Shields, M.D.; Elborn, J.S.; Schock, B.C. A20 regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB: Perspectives for inflammatory lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jong, H.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Im, Y.H.; Park, J.W.; Kim, N.K.; Bang, Y.J. Attenuation of transforming growth factor beta-induced growth inhibition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines by cyclin D1 overexpression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 292, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitisin, K.; Ganesan, N.; Tang, Y.; Jogunoori, W.; Volpe, E.A.; Kim, S.S.; Katuri, V.; Kallakury, B.; Pishvaian, M.; Albanese, C.; et al. Disruption of transforming growth factor-beta signaling through beta-spectrin ELF leads to hepatocellular cancer through cyclin D1 activation. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7103–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.F.; Chen, D.; Wu, Q.; Chen, M.; Sheu, T.J.; Schwarz, E.M.; Drissi, H.; Zuscik, M.; O’Keefe, R.J. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates cyclin D1 expression through activation of beta-catenin signaling in chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21296–21304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bian, X.; Xiao, Y.T.; Wu, T.; Yao, M.; Du, L.; Ren, S.; Wang, J. Microvesicles and chemokines in tumor microenvironment: Mediators of intercellular communications in tumor progression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrochers, L.M.; Antonyak, M.A.; Cerione, R.A. Extracellular Vesicles: Satellites of Information Transfer in Cancer and Stem Cell Biology. Dev. Cell 2016, 37, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucchetti, D.; Ricciardi Tenore, C.; Colella, F.; Sgambato, A. Extracellular Vesicles and Cancer: A Focus on Metabolism, Cytokines, and Immunity. Cancers 2020, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maacha, S.; Bhat, A.A.; Jimenez, L.; Raza, A.; Haris, M.; Uddin, S.; Grivel, J.C. Extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication: Roles in the tumor microenvironment and anti-cancer drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Namee, N.M.; O’Driscoll, L. Extracellular vesicles and anti-cancer drug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.W.; Ab-Mutalib, N.S.; Abdullah, N.M.A.; Jamal, R.; Abu, N. Extracellular Vesicle-derived circular RNAs confers chemoresistance in Colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atale, N.; Gupta, S.; Yadav, U.C.; Rani, V. Cell-death assessment by fluorescent and nonfluorescent cytosolic and nuclear staining techniques. J. Microsc. 2014, 255, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlyukov, M.S.; Yu, H.; Bastola, S.; Minata, M.; Shender, V.O.; Lee, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Komarova, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Apoptotic Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Malignancy of Glioblastoma Via Intercellular Transfer of Splicing Factors. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mileo, A.M.; Nistico, P.; Miccadei, S. Polyphenols: Immunomodulatory and Therapeutic Implication in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Guan, P.; Hu, X.; Yang, L.; He, L.; Lin, Q.; Luo, F.; Li, J.; He, X.; Du, Z.; et al. Natural Polyphenols as Targeted Modulators in Colon Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Applications. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 635484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowehl, R.A.; Burke, S.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Pettet, D.W., 3rd; Rowehl, L.; Li, E.; Antoniou, E.; Zhang, Y.; Bergamaschi, R.; Shroyer, K.R.; et al. Establishment of highly tumorigenic human colorectal cancer cell line (CR4) with properties of putative cancer stem cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Qiao, Y.; Concepcion, W.; Thakor, A.S. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Role in oncogenic processes, bioengineering potential, and technical challenges. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, Q.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Zhou, L.; Sui, H.; Yan, L.; Jiang, H.; Ren, J.; Cai, J.; Li, Q. Resveratrol suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer through TGF-beta1/Smads signaling pathway mediated Snail/E-cadherin expression. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; He, X.; Huang, H.; He, Y.; Lan, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T. Nerve growth factor orchestrates NGAL and matrix metalloproteinases activity to promote colorectal cancer metastasis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 24, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Desta, K.T.; Kim, G.S.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Jin, J.S.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Shin, H.C.; Shim, J.H.; et al. Polyphenolic profile and antioxidant effects of various parts of Artemisia annua L. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
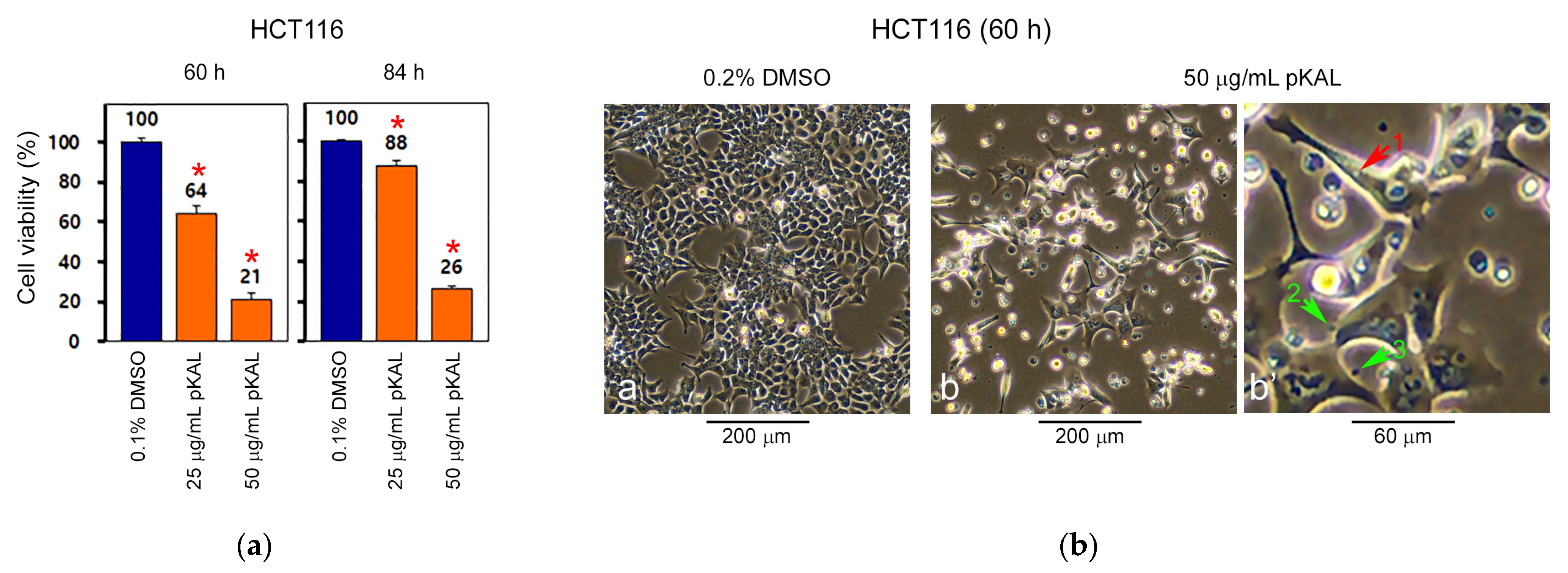
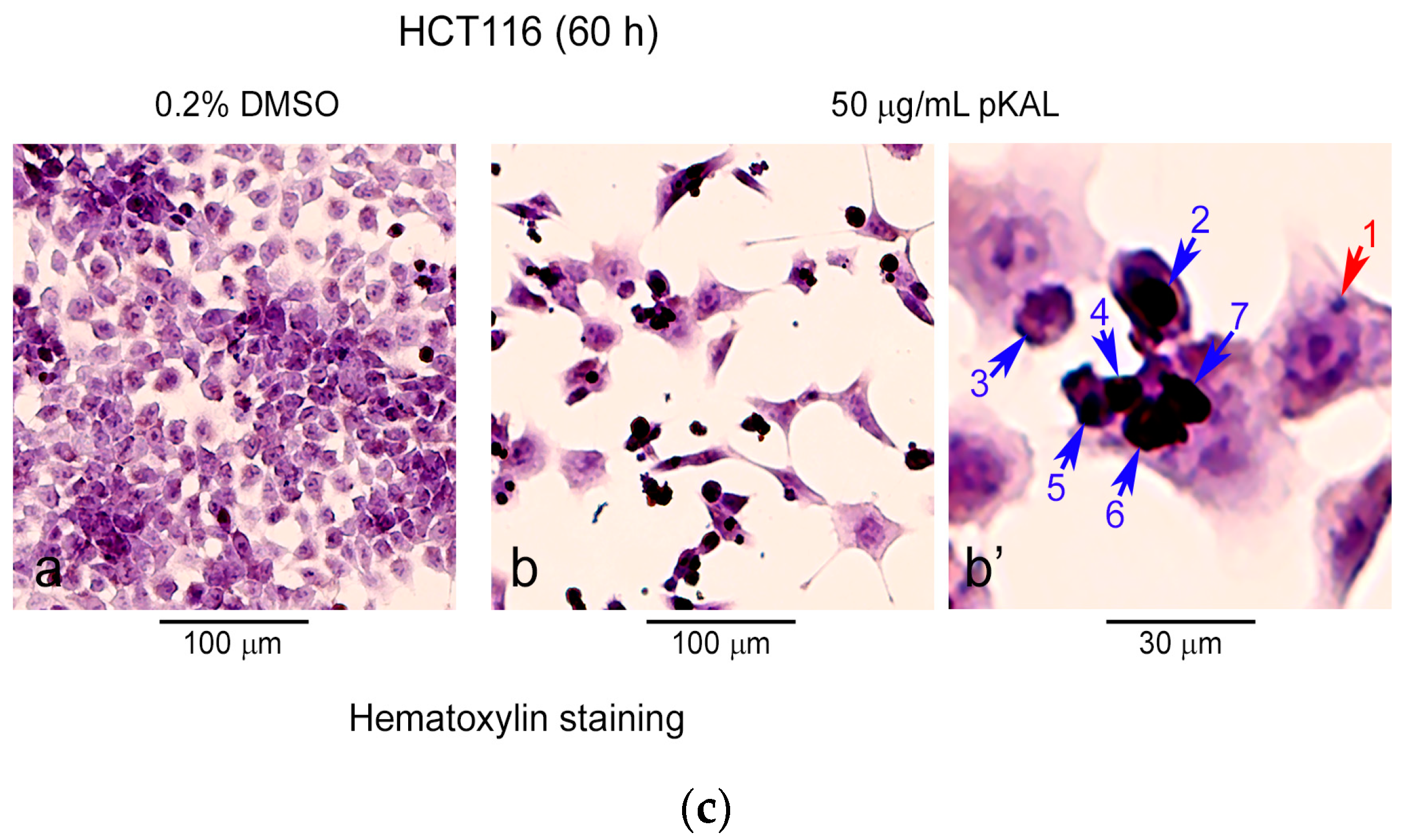
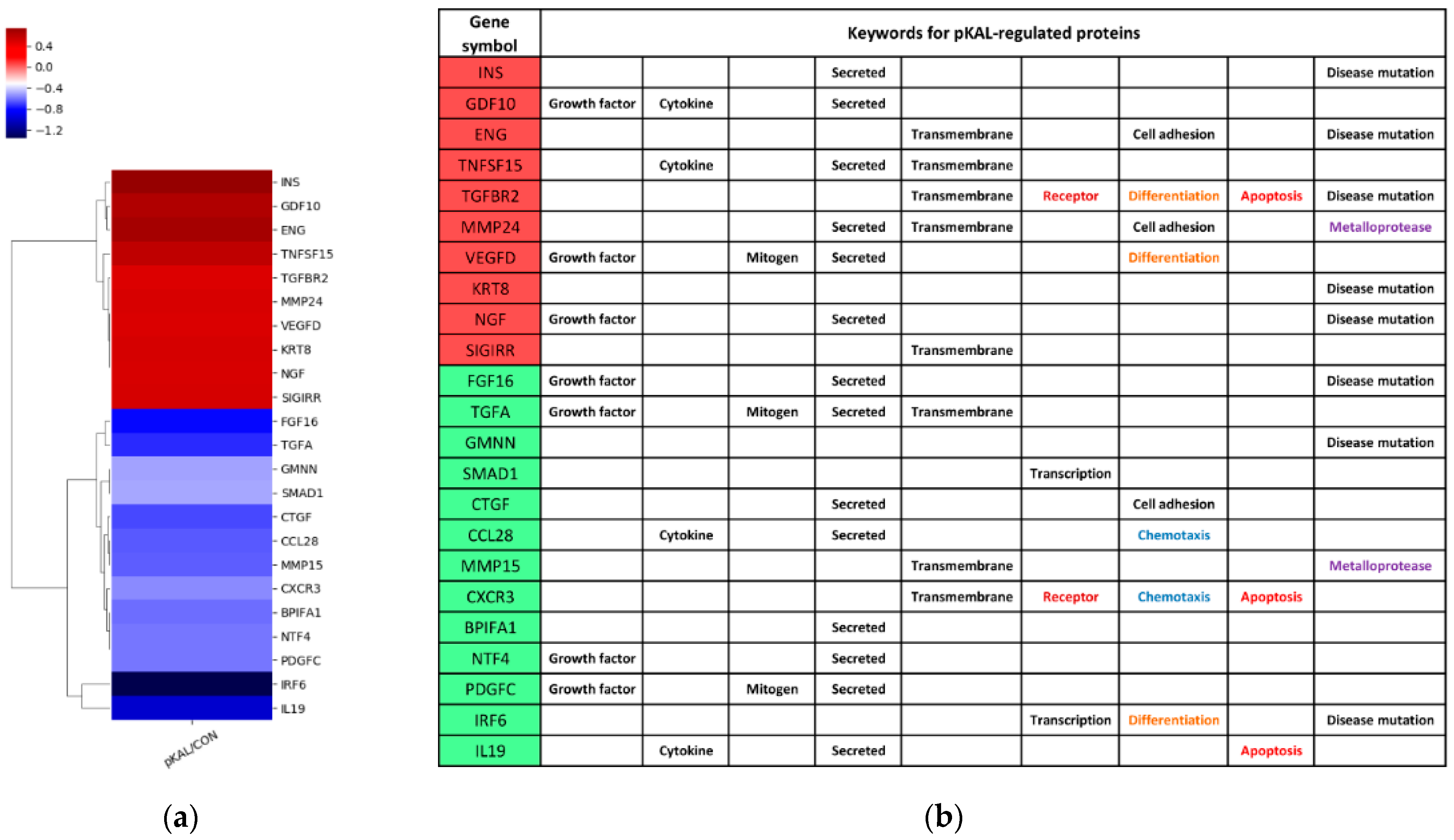
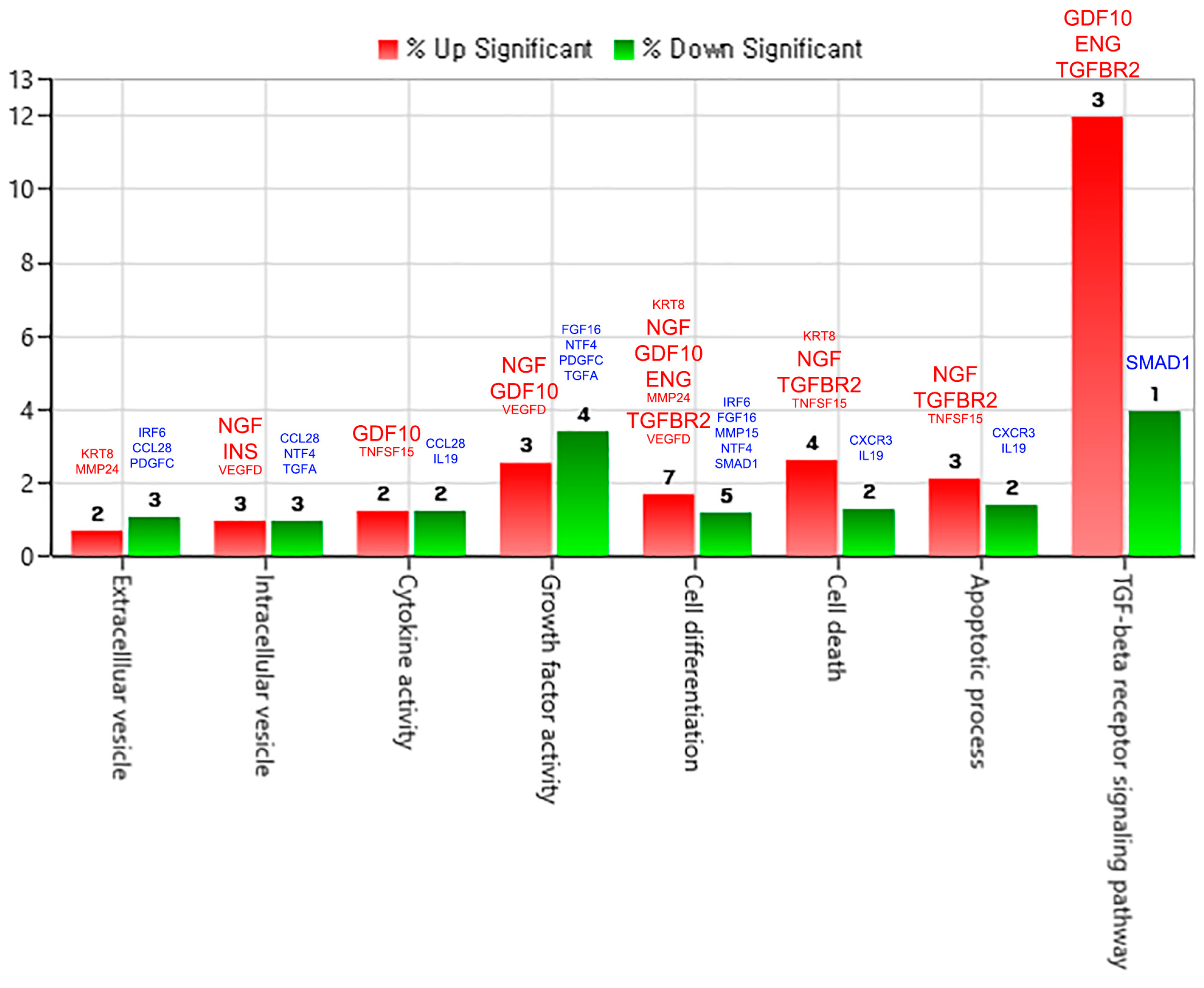
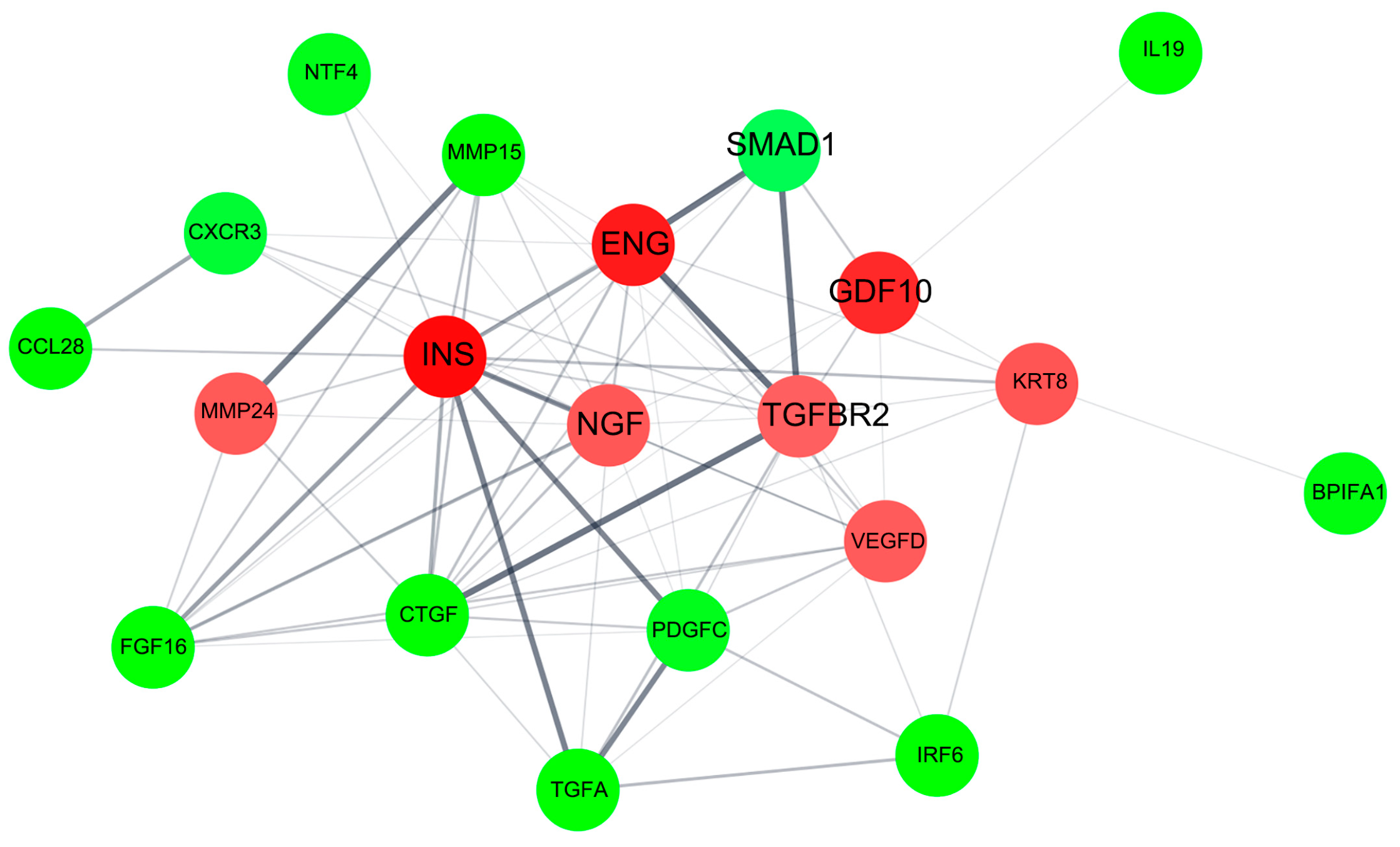
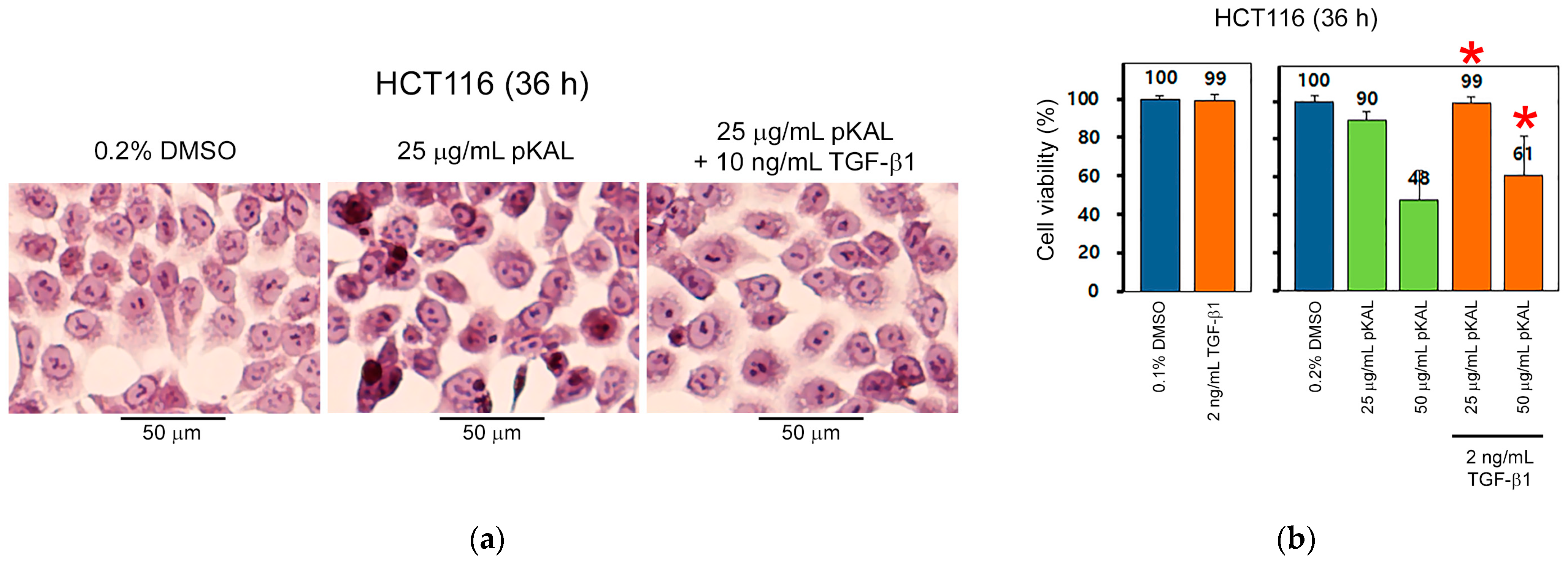


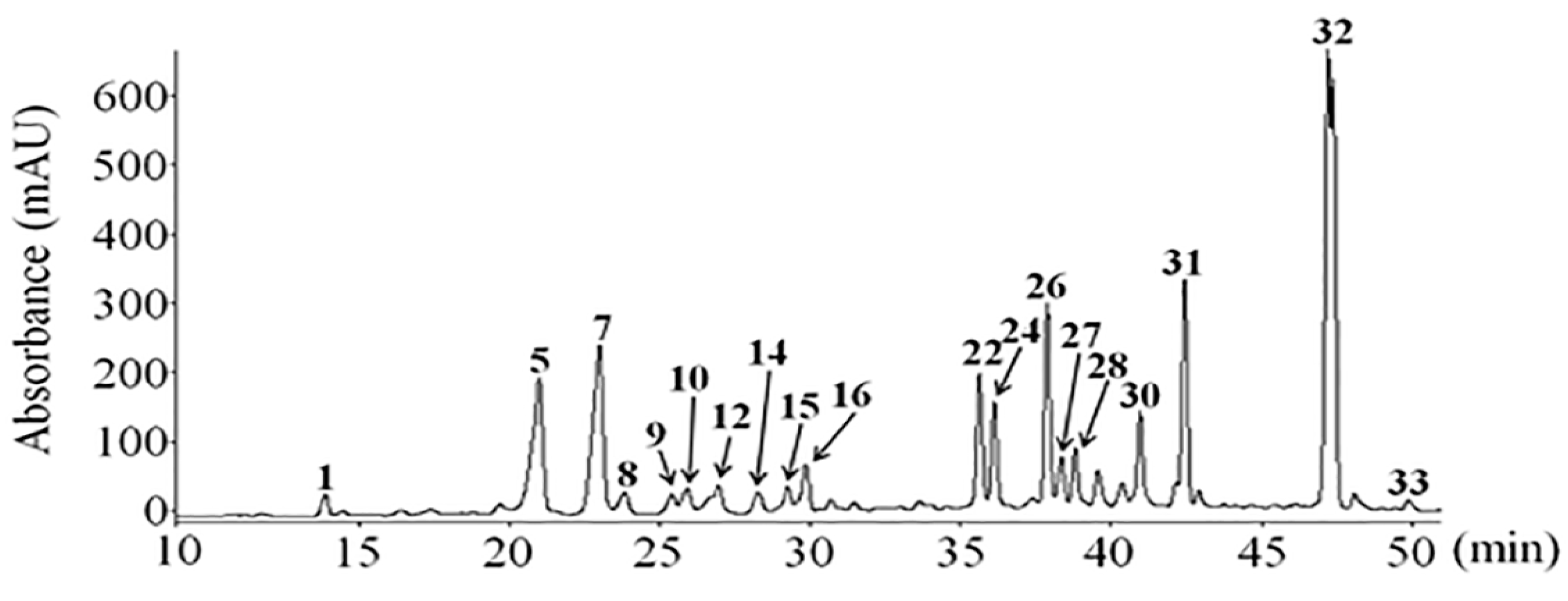
| Gene Symbol | Upregulated Proteins by pKAL | Fold Change pKAL/CON | Normalized Control | Normalized pKAL | Mass (Da) | UniProt ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INS | Insulin | 1.677 | 874.2 | 1466.3 | 11,981 | P01308 |
| ENG | Endoglin | 1.62 | 553 | 895.9 | 70,578 | P17813 |
| GDF10 | Growth/differentiation factor 10 | 1.573 | 528.7 | 831.7 | 53,122 | P55107 |
| TNFSF15 | Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15 | 1.512 | 592 | 895.4 | 28,087 | O95150 |
| Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8 | ||||||
| KRT8 | Single Ig IL-1-related receptor | 1.438 | 581.8 | 836.8 | 53,704 | P05787 |
| SIGIRR | Beta-nerve growth factor | 1.434 | 524.2 | 751.7 | 45,679 | Q6IA17 |
| NGF | Matrix metalloproteinase-24 | 1.43 | 440.5 | 630 | 26,959 | P01138 |
| MMP24 | Vascular endothelial growth factor D | 1.425 | 703.6 | 1002.7 | 73,231 | Q9Y5R2 |
| VEGFD | TGF-beta receptor type-2 | 1.42 | 499 | 708.5 | 40,444 | O43915 |
| TGFBR2 | 1.407 | 523.8 | 736.8 | 64,568 | P37173 |
| Gene Symbol | Downregulated Proteins by pKAL | Fold Change pKAL/CON | Normalized Control | Normalized pKAL | Mass (Da) | UniProt ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRF6 | Interferon regulatory factor 6 | 0.391 | 2311.8 | 904.6 | 53,130 | O14896 |
| IL19 | Interleukin-19 | 0.504 | 1715.2 | 865.1 | 20,452 | Q9UHD0 |
| FGF16 | Fibroblast growth factor 16 | 0.573 | 2972.8 | 1703 | 23,759 | O43320 |
| TGFA | Protransforming growth factor alpha | 0.602 | 920 | 554 | 17,006 | P01135 |
| CTGF | Connective tissue growth factor | 0.625 | 778.2 | 486.2 | 38,091 | P29279 |
| CCL28 | C-C motif chemokine 28 | 0.638 | 6431.9 | 4104.8 | 14,280 | Q9NRJ3 |
| MMP15 | Matrix metalloproteinase-15 | 0.643 | 745 | 479 | 75,807 | P51511 |
| BPIFA1 | BPI fold-containing family A member 1 | 0.66 | 1417 | 935.4 | 26,713 | Q9NP55 |
| NTF4 | Neurotrophin-4 | 0.665 | 963.3 | 640.7 | 22,427 | P34130 |
| PDGFC | Platelet-derived growth factor C | 0.666 | 1023.3 | 681.3 | 39,029 | Q9NRA1 |
| CXCR3 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 3 | 0.685 | 893.2 | 611.5 | 40,660 | P49682 |
| GMNN | Geminin | 0.709 | 2321.9 | 1646.7 | 23,565 | O75496 |
| SMAD1 | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1 | 0.713 | 752.8 | 537 | 52,260 | Q15797 |
| Compounds | [M − H]− | Fragments (m/z) |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeic acid (1) | 179 | 179 135 |
| Quercetin-3-O-galactoside (5) | 463 | 463 301 175 151 121 |
| Mearnsetin-glucoside (7) | 493 | 493 331 315 287 270 181 |
| Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside (8) | 447 | 447 285 |
| Quercetin-3-O-glucoside (9) | 463 | 301 300 178 175 151 121 107 |
| Mearnsetin-glucoside (10) | 493 | 493 331 315 287 270 181 |
| Ferulic acid (12) | 193 | 193 178 161 149 134 |
| Isorhamnetin-glucoside (14) | 477 | 477 462 446 315 314 313 300 299 287 271 |
| Diosmetin-7-O-d-glucoside (15) | 461 | 461 341 299 |
| Luteolin-7-O-glucoside (16) | 447 | 447 285 255 227 |
| Quercetin (22) | 301 | 301 273 179 151 121 107 |
| Quercetagetin-3-O-methyl ether (24) | 331 | 331 316 287 271 209 151 179 166 |
| Luteolin (26) | 285 | 285 243 241 217 198 175 151 133 |
| 8-methoxy-kaempferol (27) | 315 | 315 300 285 137 |
| Quercetagetin-5,3-di-O-methyl ether (28) | 345 | 345 330 315 287 |
| Kaempferol (30) | 285 | 285 217 151 133 |
| 3,5-dihydroxy-6,7,4′-trimethoxyflavone (31) | 359 | 359 344 329 314 301 286 |
| 3,5-dihydroxy-6,7,3′,4′-tetramethoxyflavone (32) | 373 | 373 358 343 328 315 299 285 |
| Isorhamnetin (33) | 315 | 315 300 271 247 203 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, E.J.; Paramanantham, A.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.-M.; Hong, S.C.; Chung, K.H.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, W.S. Identification of Growth Factors, Cytokines and Mediators Regulated by Artemisia annua L. Polyphenols (pKAL) in HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells: TGF-β1 and NGF-β Attenuate pKAL-Induced Anticancer Effects via NF-κB p65 Upregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031598
Jung EJ, Paramanantham A, Kim HJ, Shin SC, Kim GS, Jung J-M, Hong SC, Chung KH, Kim CW, Lee WS. Identification of Growth Factors, Cytokines and Mediators Regulated by Artemisia annua L. Polyphenols (pKAL) in HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells: TGF-β1 and NGF-β Attenuate pKAL-Induced Anticancer Effects via NF-κB p65 Upregulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031598
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Eun Joo, Anjugam Paramanantham, Hye Jung Kim, Sung Chul Shin, Gon Sup Kim, Jin-Myung Jung, Soon Chan Hong, Ky Hyun Chung, Choong Won Kim, and Won Sup Lee. 2022. "Identification of Growth Factors, Cytokines and Mediators Regulated by Artemisia annua L. Polyphenols (pKAL) in HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells: TGF-β1 and NGF-β Attenuate pKAL-Induced Anticancer Effects via NF-κB p65 Upregulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031598
APA StyleJung, E. J., Paramanantham, A., Kim, H. J., Shin, S. C., Kim, G. S., Jung, J.-M., Hong, S. C., Chung, K. H., Kim, C. W., & Lee, W. S. (2022). Identification of Growth Factors, Cytokines and Mediators Regulated by Artemisia annua L. Polyphenols (pKAL) in HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells: TGF-β1 and NGF-β Attenuate pKAL-Induced Anticancer Effects via NF-κB p65 Upregulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031598









