Anti-HIV Activity of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2s: Updates for New Enzymes and Different Virus Strains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PLA2s from Snake Venoms
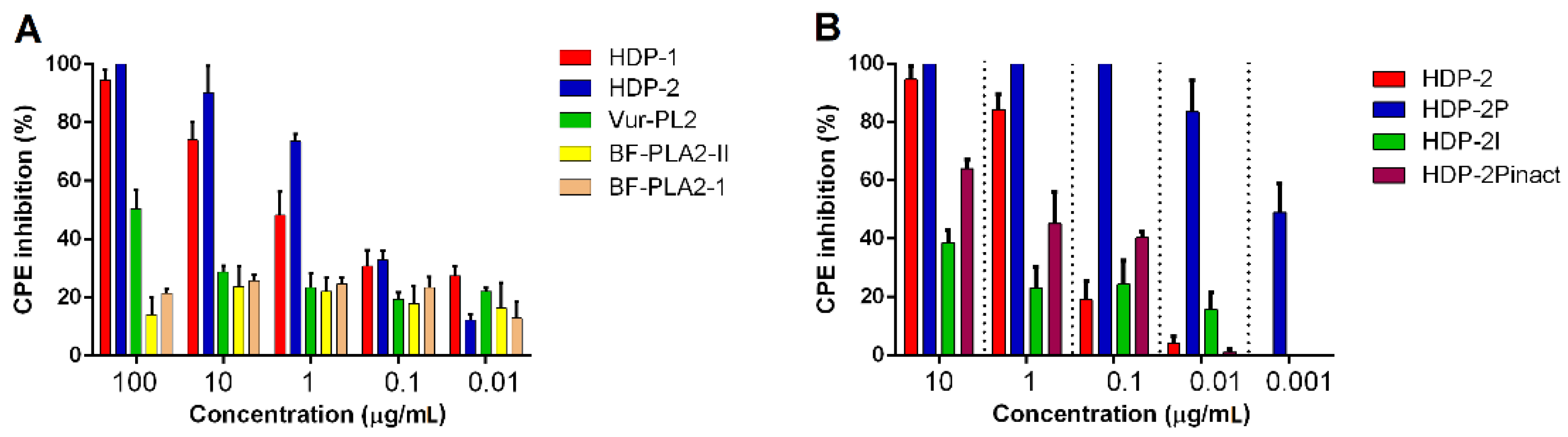
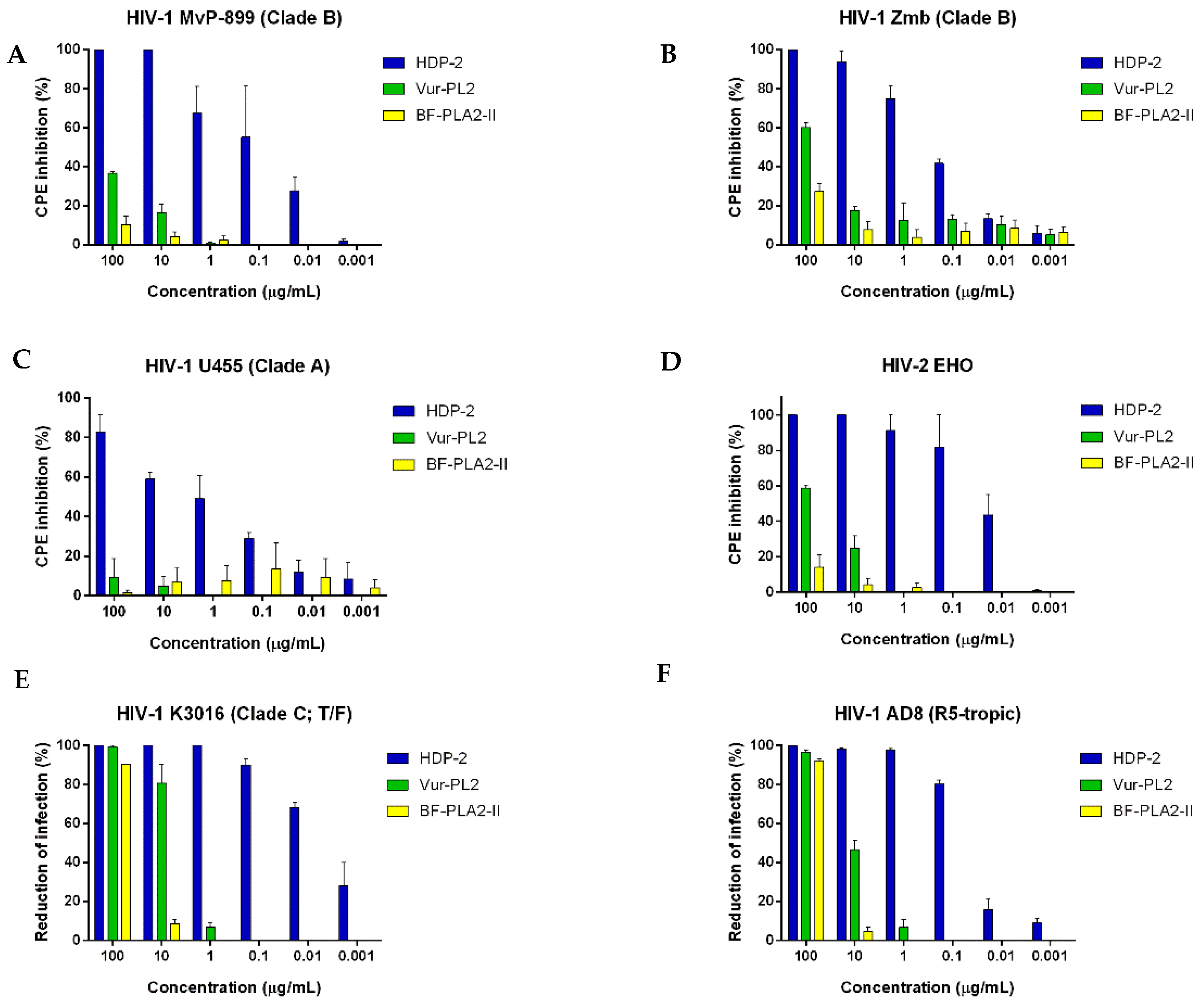
2.2. Antiretroviral Activity of Snake Venom PLA2s
2.3. Effect of PLA2s on Syncytium Formation in Co-Cultures of HIV-1 Chronically Infected and Sup-T1 Cells
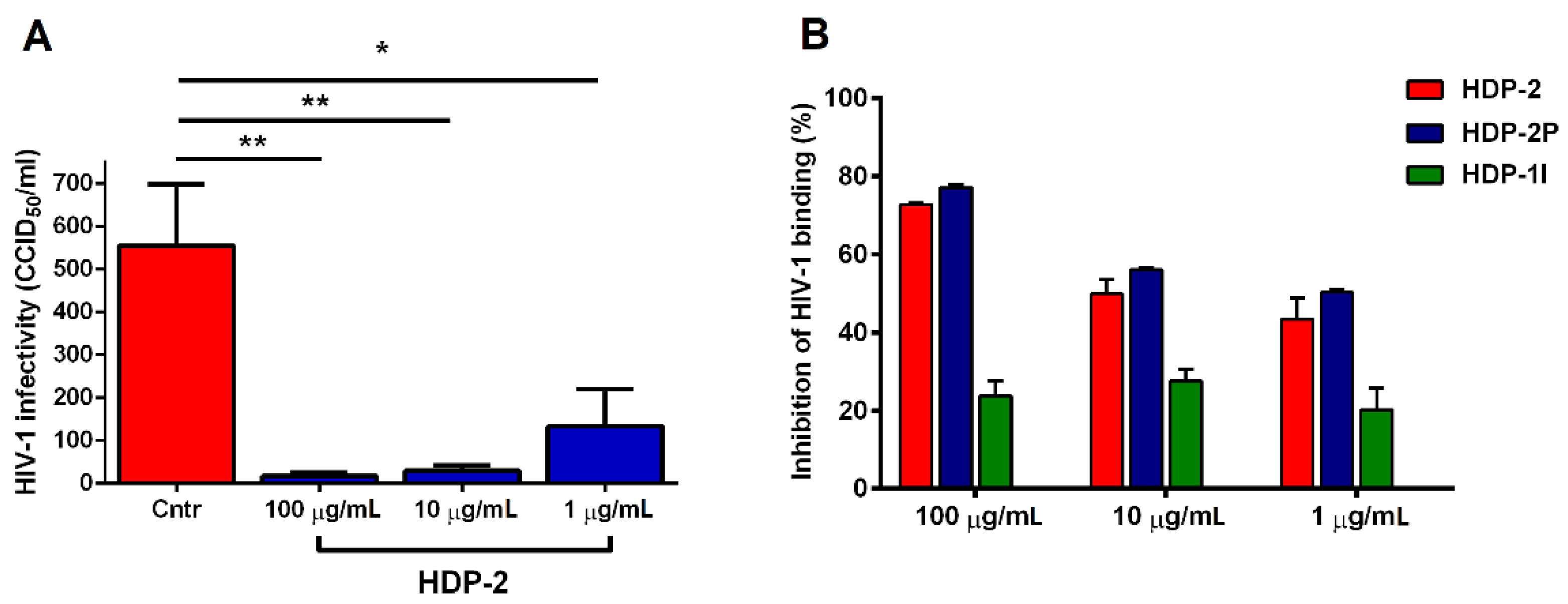
2.4. Dimeric PLA2s Possess Virucidal Activity and Block HIV-1 Adsorption
2.5. Synergistic Activity of HDP-2 and HIV Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Viruses
4.2. Phospholipases A2
4.3. Anti-Retrovirus Assay
4.4. Syncytium Formation Assay
4.5. Virucidal Assay
4.6. Virus Adsorption Assay
4.7. Construction and Production of HIV-1 Env-Functional Clones
4.8. Drug Susceptibility Assay against of HIV-1 Env-Functional Clones
4.9. Analysis of Drug Combination and Synergy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharp, P.M.; Hahn, B.H. Origins of HIV and the AIDS pandemic. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, A006841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Vajdy, M. Mucosal HIV transmission and vaccination strategies through oral compared with vaginal and rectal routes. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilen, C.B.; Tilton, J.C.; Doms, R.W. HIV: Cell binding and entry. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, E.A.; Doms, R.W.; Fenyö, E.M.; Korber, B.T.; Littman, D.R.; Moore, J.P.; Sattentau, Q.J.; Schuitemaker, H.; Sodroski, J.; Weiss, R.A. A new classification for HIV-1. Nature 1998, 391, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keele, B.F.; Giorgi, E.E.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Decker, J.M.; Pham, K.T.; Salazar, M.G.; Sun, C.; Grayson, T.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; et al. Identification and characterization of transmitted and early founder virus envelopes in primary HIV-1 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7552–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sagar, M. Origin of the transmitted virus in HIV infection: Infected cells versus cell-free virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, S667–S673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutartre, H.; Clavière, M.; Journo, C.; Mahieux, R. Cell-Free versus Cell-to-Cell Infection by Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 and Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1: Exploring the Link among Viral Source, Viral Trafficking, and Viral Replication. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7607–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bracq, L.; Xie, M.; Benichou, S.; Bouchet, J. Mechanisms for Cell-to-Cell Transmission of HIV-1. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Pang, H.B.; Kay, M.S. Peptide mimic of the HIV envelope gp120-gp41 interface. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 376, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Checkley, M.A.; Luttge, B.G.; Freed, E.O. HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein biosynthesis, trafficking, and incorporation. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 410, 582–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaitseva, E.; Zaitsev, E.; Melikov, K.; Arakelyan, A.; Marin, M.; Villasmil, R.; Margolis, L.B.; Melikyan, G.B.; Chernomordik, L.V. Fusion Stage of HIV-1 Entry Depends on Virus-Induced Cell Surface Exposure of Phosphatidylserine. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 99–110.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ambrose, Z.; Aiken, C. HIV-1 uncoating: Connection to nuclear entry and regulation by host proteins. Virology 2014, 454–455, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Craigie, R.; Bushman, F.D. HIV DNA integration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bailey, P.; Wilce, J. Venom as a source of useful biologically active molecules. Emerg. Med. 2001, 13, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, J.B.; Scott-Davey, T. Secreted phospholipases A2 of snake venoms: Effects on the peripheral neuromuscular system with comments on the role of phospholipases A2 in disorders of the CNS and their uses in industry. Toxins 2013, 5, 2533–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burke, J.E.; Dennis, E.A. Phospholipase A2 structure/function, mechanism, and signaling. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S237–S242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dennis, E.A.; Cao, J.; Hsu, Y.H.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: Physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, H.; Taketomi, Y.; Isogai, Y.; Miki, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Masuda, S.; Hosono, T.; Arata, S.; Ishikawa, Y.; Ishii, T.; et al. Group III secreted phospholipase A2 regulates epididymal sperm maturation and fertility in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1400–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dennis, E.A. Diversity of group types, regulation, and function of phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 13057–13060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula, R.C.; Castro, H.C.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Melo, P.A.; Fuly, A.L. Structural and pharmacological features of phospholipases A2 from snake venoms. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazanova, A.S.; Zavada, L.L.; Starkov, V.G.; Kovyazina, I.V.; Subbotina, T.F.; Kostyukhina, E.E.; Dementieva, I.N.; Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Utkin, Y.N. Heterodimeric neurotoxic phospholipases A2--the first proteins from venom of recently established species Vipera nikolskii: Implication of venom composition in viper systematics. Toxicon 2008, 51, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, B.S. Phospholipase A2 as targets for anti-cancer drugs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.V.; Siniavin, A.E.; Hoang, A.N.; Le, M.T.T.; Pham, C.D.; Phung, T.V.; Nguyen, K.C.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Weng, C.F.; et al. Phospholipase A2 from krait Bungarus fasciatus venom induces human cancer cell death in vitro. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nevalainen, T.J.; Graham, G.G.; Scott, K.F. Antibacterial actions of secreted phospholipases A2. Review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Aoki-Utsubo, C.; Kameoka, M.; Deng, L.; Terada, Y.; Kamitani, W.; Sato, K.; Koyanagi, Y.; Hijikata, M.; Shindo, K.; et al. Broad-spectrum antiviral agents: Secreted phospholipase A2 targets viral envelope lipid bilayers derived from the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, V.D.; Soares, R.O.; dos Santos, N.N., Jr.; Trabuco, A.C.; Cintra, A.C.; Figueiredo, L.T.; Caliri, A.; Sampaio, S.V.; Aquino, V.H. Phospholipase A2 isolated from the venom of Crotalus durissus terrificus inactivates dengue virus and other enveloped viruses by disrupting the viral envelope. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenes, H.; Loría, G.D.; Lomonte, B. Potent virucidal activity against Flaviviridae of a group IIA phospholipase A2 isolated from the venom of Bothrops asper. Biologicals 2020, 63, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenard, D.; Lambeau, G.; Valentin, E.; Lefebvre, J.C.; Lazdunski, M.; Doglio, A. Secreted phospholipases A(2), a new class of HIV inhibitors that block virus entry into host cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.O.; Chakrabarti, B.K.; Guha-Niyogi, A.; Louder, M.K.; Mascola, J.R.; Ganesh, L.; Nabel, G.J. Lysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by a specific secreted human phospholipase A2. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bbosa, N.; Kaleebu, P.; Ssemwanga, D. HIV subtype diversity worldwide. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2019, 14, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothlichet, J.; Rose, T.; Bugault, F.; Jeammet, L.; Meola, A.; Haouz, A.; Saul, F.; Geny, D.; Alcami, J.; Ruiz-Mateos, E.; et al. PLA2G1B is involved in CD4 anergy and CD4 lymphopenia in HIV-infected patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2872–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurin, T.; Fenard, D.; Lambeau, G.; Doglio, A. An envelope-determined endocytic route of viral entry allows HIV-1 to escape from secreted phospholipase A2 entry blockade. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, V.D.; Russo, R.R.; Cintra, A.C.; Sartim, M.A.; De Melo Alves-Paiva, R.; Figueiredo, L.T.; Sampaio, S.V.; Aquino, V.H. Crotoxin and phospholipases A2 from Crotalus durissus terrificus showed antiviral activity against dengue and yellow fever viruses. Toxicon 2012, 59, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniavin, A.E.; Streltsova, M.A.; Nikiforova, M.A.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Grinkina, S.D.; Gushchin, V.A.; Mozhaeva, V.A.; Starkov, V.G.; Osipov, A.V.; Lummis, S.C.R.; et al. Snake venom phospholipase A2s exhibit strong virucidal activity against SARS-CoV-2 and inhibit the viral spike glycoprotein interaction with ACE2. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 7777–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.M. Excitement ahead: Structure, function and mechanism of snake venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. Toxicon 2003, 42, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenard, D.; Lambeau, G.; Maurin, T.; Lefebvre, J.C.; Doglio, A. A peptide derived from bee venom-secreted phospholipase A2 inhibits replication of T-cell tropic HIV-1 strains via interaction with the CXCR4 chemokine receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rytik, P.G.; Kutcherov, I.I.; Muller, W.E.; Poleschuk, N.N.; Duboiskaya, G.P.; Kruzo, M.; Podolskaya, I.A. Small animal model of HIV-1 infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 31, S83–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürtler, L.G.; Hauser, P.H.; Eberle, J.; von Brunn, A.; Knapp, S.; Zekeng, L.; Tsague, J.M.; Kaptue, L. A new subtype of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (MVP-5180) from Cameroon. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1581–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timilsina, U.; Ghimire, D.; Timalsina, B.; Nitz, T.J.; Wild, C.T.; Freed, E.O.; Gaur, R. Identification of potent maturation inhibitors against HIV-1 clade C. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, I.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Cheng, A.C.; Starkov, V.; Osipov, A.; Nikitin, I.; Makarova, Y.; Ziganshin, R.; Utkin, Y. cDNA cloning, structural, and functional analyses of venom phospholipases A2 and a Kunitz-type protease inhibitor from steppe viper Vipera ursinii renardi. Toxicon 2011, 57, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radvanyi, F.; Jordan, L.; Russo-Marie, F.; Bon, C. A sensitive and continuous fluorometric assay for phospholipase A2 using pyrene-labeled phospholipids in the presence of serum albumin. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 177, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Obando, D.; Díaz, C.; Angulo, Y.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Role of enzymatic activity in muscle damage and cytotoxicity induced by Bothrops asper Asp49 phospholipase A2 myotoxins: Are there additional effector mechanisms involved? PeerJ 2014, 2, e569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pannecouque, C.; Daelemans, D.; De Clercq, E. Tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay for the detection of HIV replication inhibitors: Revisited 20 years later. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoins. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witvrouw, M.; Fikkert, V.; Pluymers, W.; Matthews, B.; Mardel, K.; Schols, D.; Raff, J.; Debyser, Z.; De Clercq, E.; Holan, G.; et al. Polyanionic (i.e., polysulfonate) dendrimers can inhibit the replication of human immunodeficiency virus by interfering with both virus adsorption and later steps (reverse transcriptase/integrase) in the virus replicative cycle. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Revilla, A.; Delgado, E.; Christian, E.C.; Dalrymple, J.; Vega, Y.; Carrera, C.; González-Galeano, M.; Ocampo, A.; de Castro, R.O.; Lezaún, M.J.; et al. Construction and phenotypic characterization of HIV type 1 functional envelope clones of subtypes G and F. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2011, 27, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamov, E.; Epremyan, K.; Siniavin, A.; Zhernov, Y.; Cuevas, M.T.; Delgado, E.; Sánchez-Martínez, M.; Carrera, C.; Kornilaeva, G.; Turgiev, A.; et al. HIV-1 Genetic Diversity in Recently Diagnosed Infections in Moscow: Predominance of AFSU, Frequent Branching in Clusters, and Circulation of the Iberian Subtype G Variant. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2018, 34, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Li, J.; Zeng, Y. Comparison of three quantification methods for the TZM-bl pseudovirus assay for screening of anti-HIV-1 agents. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 233, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: Visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W488–W493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| MT-4/HIV-1 IIIB | IC50 (µg/mL) with 95% CI * |
|---|---|
| HDP-2 | 0.25 (0.18–0.35) |
| HDP-2P | 0.0008 (0.0005–0.001) |
| HDP-2I | >10 |
| HDP-2Pinact | 0.1 (0.04–0.3) |
| Cell/Virus System | IC50 (µg/mL) with 95% CI * | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HDP-2 | Vur-PL2 | BF-PLA2-II | |
| MT-4/HIV-1 MvP-899 | 0.1 (0.006–0.01) | - ** | - |
| MT-4/HIV-1 Zmb | 0.22 (0.15–0.32) | 16.45 (3.9–68.1) | - |
| MT-4/HIV-1 U455 | 0.9 (0.32–2.6) | - | - |
| MT-4/HIV-2 EHO | 0.016 (0.008–0.03) | ~10.41 | - |
| TZM-bl/HIV-1 K3016 | 0.009 (0.006–0.015) | 4.37 (3.2–5.9) | ~12.21 |
| TZM-bl/HIV-1 AD8 | 0.046 (0.037–0.057) | 10.29 (8.8–11.9) | ~14.26 |
| PLA2 | IC50 (µg/mL) with 95% CI * | |
|---|---|---|
| HIV-1 A6 | HIV-1 CRF02_AG/A6 | |
| HDP-1 | 0.009 (0.008–0.01) | 0.046 (0.038–0.056) |
| HDP-2 | 0.008 (0.007–0.009) | 0.04 (0.034–0.047) |
| Vur-PL2 | 0.007 (0.006–0.01) | 0.1 (0.07–0.16) |
| BF-PLA2-II | 3.22 (1.78–5.84) | ~31.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siniavin, A.; Grinkina, S.; Osipov, A.; Starkov, V.; Tsetlin, V.; Utkin, Y. Anti-HIV Activity of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2s: Updates for New Enzymes and Different Virus Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031610
Siniavin A, Grinkina S, Osipov A, Starkov V, Tsetlin V, Utkin Y. Anti-HIV Activity of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2s: Updates for New Enzymes and Different Virus Strains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031610
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiniavin, Andrei, Svetlana Grinkina, Alexey Osipov, Vladislav Starkov, Victor Tsetlin, and Yuri Utkin. 2022. "Anti-HIV Activity of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2s: Updates for New Enzymes and Different Virus Strains" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031610
APA StyleSiniavin, A., Grinkina, S., Osipov, A., Starkov, V., Tsetlin, V., & Utkin, Y. (2022). Anti-HIV Activity of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2s: Updates for New Enzymes and Different Virus Strains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031610