Severe Acute Hepatic Dysfunction Induced by Ammonium Acetate Treatment Results in Choroid Plexus Swelling and Ventricle Enlargement in the Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
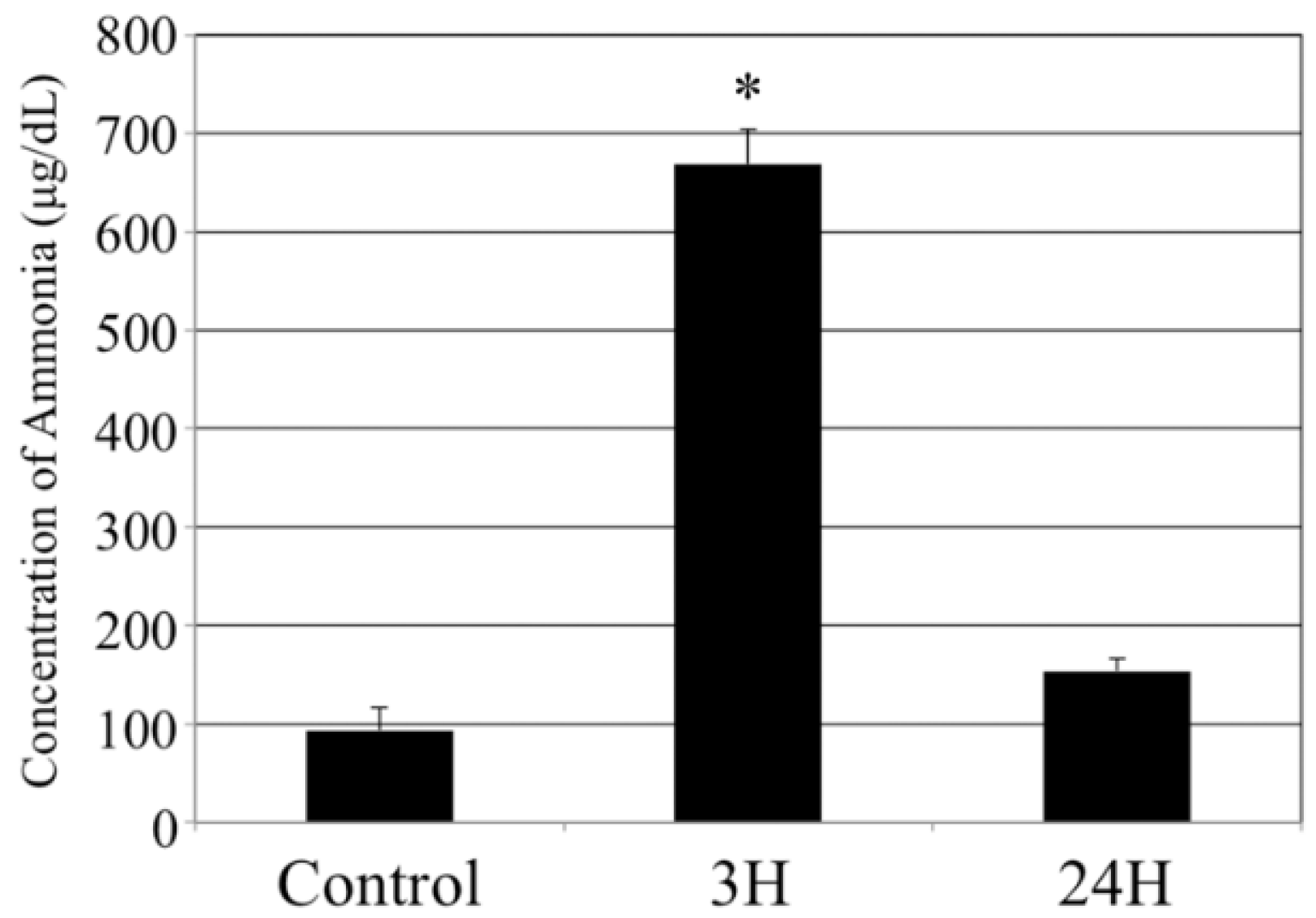
2.1. Biochemical Analyses
2.2. Sequential Macroscopic Anatomical Changes in the Brain following Hepatic Encephalopathy
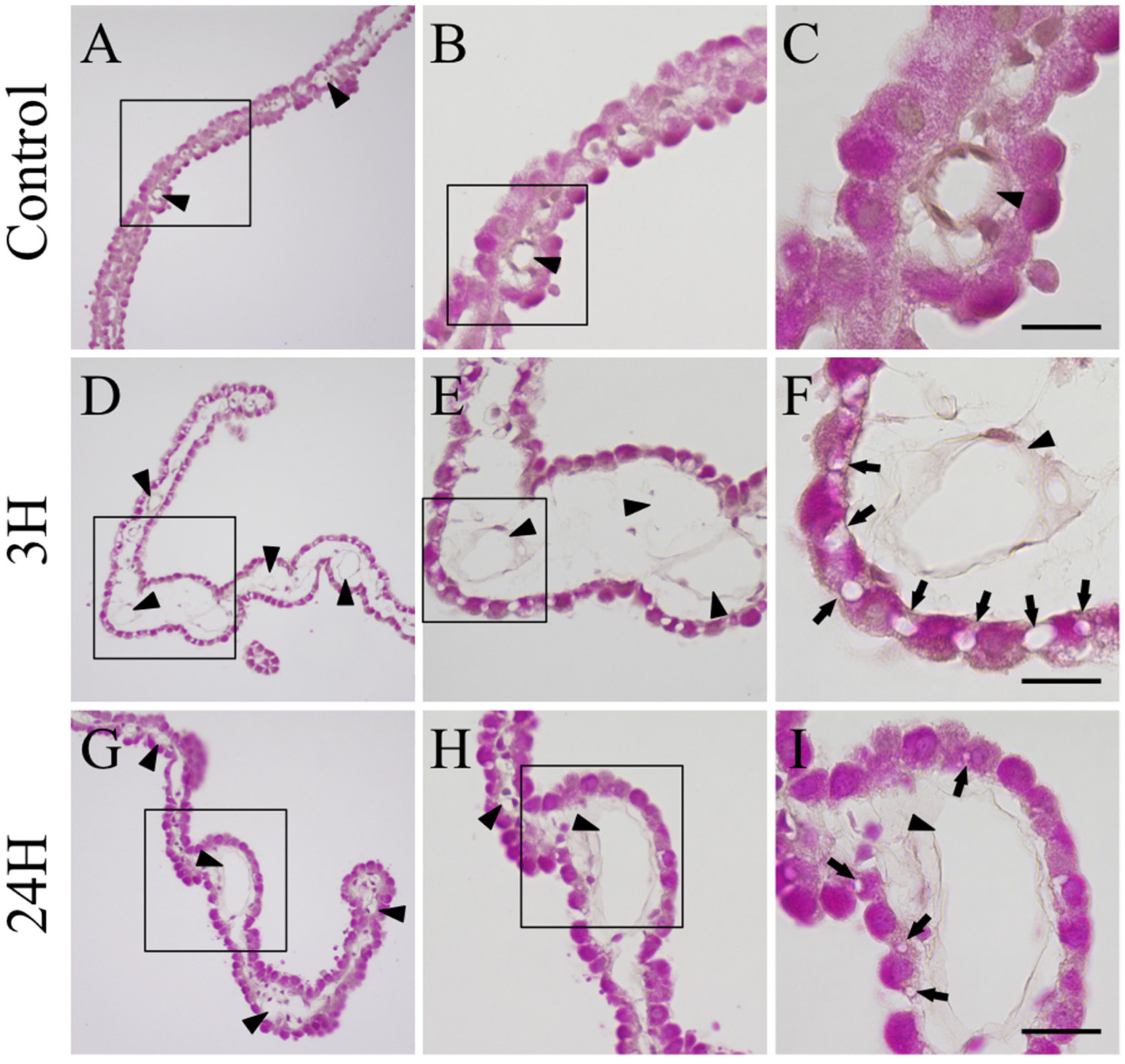
2.3. Histopathological Evaluation of the Changes in the Choroid Plexus in Response to Hepatic Encephalopathy
2.4. Ultrastructural Changes in the Choroid Plexus in Response to Hepatic Encephalopathy
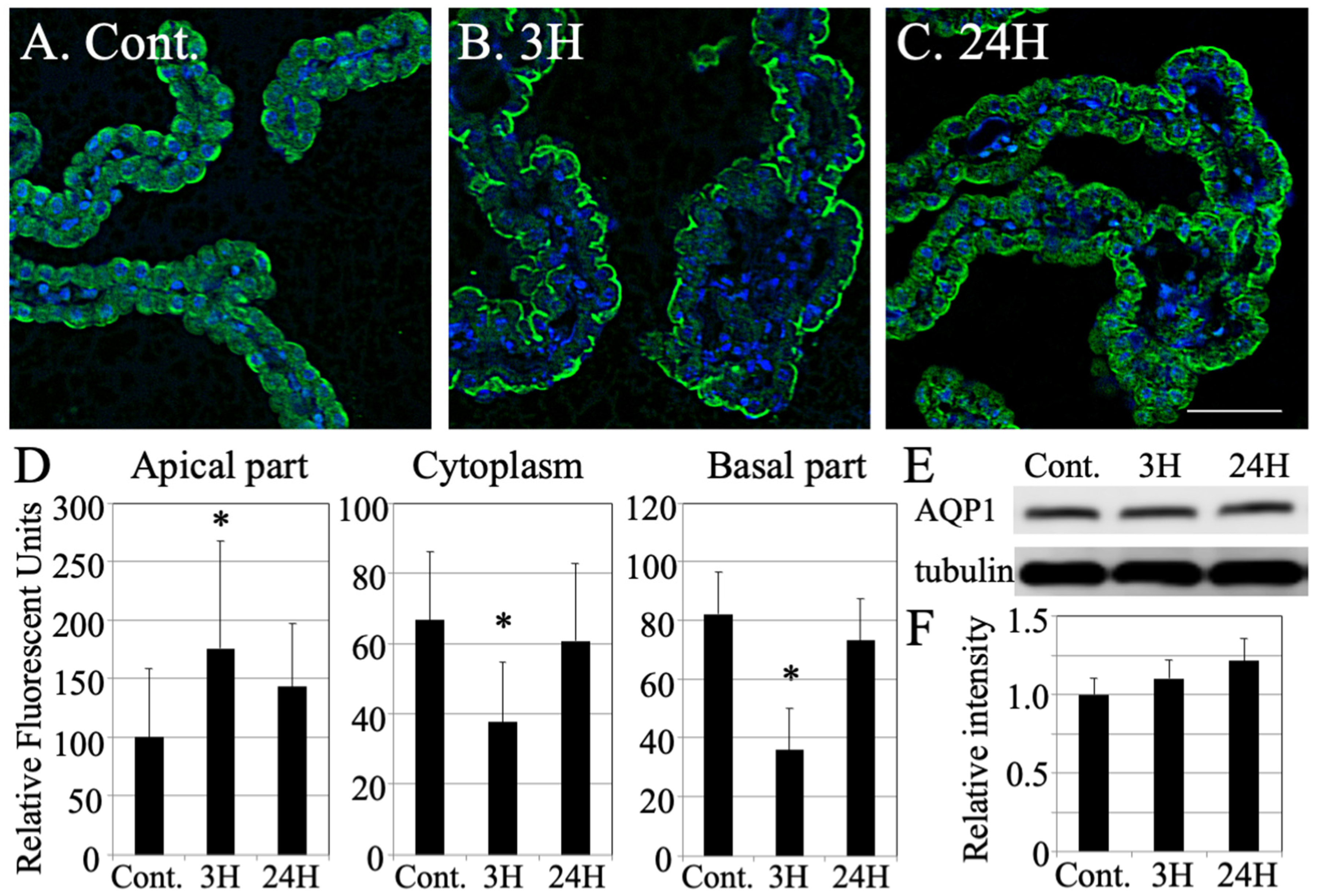
2.5. Changes in the Distribution of Aquaporin 1 across the Choroid Plexus after Hepatic Encephalopathy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Inducing Acute Liver Failure Induction
4.3. Biochemical Analysis
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Tissue Preparation
4.6. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.7. Electron Microscopy
4.8. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bemeur, C.; Cudalbu, C.; Dam, G.; Thrane, A.S.; Cooper, A.J.; Rose, C.F. Brain edema: A valid endpoint for measuring hepatic encephalopathy? Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, J.A.; Kalb, T. Neurological management of fulminant hepatic failure. Neurocrit. Care 2011, 14, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, S.J.; Robinson, M.; Northrup, B.; Bell, R.; Moritz, M.; Jarrell, B.; Martin, P.; Maddrey, W.C. Elevated intracranial pressure and computed tomography of the brain in fulminant hepatocellular failure. Hepatology 1991, 13, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stravitz, R.T.; Kramer, A.H.; Davern, T.; Shaikh, A.O.; Caldwell, S.H.; Mehta, R.L.; Blei, A.T.; Fontana, R.J.; McGuire, B.M.; Rossaro, L.; et al. Intensive care of patients with acute liver failure: Recommendations of the U.S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosoi, C.R.; Rose, C.F. Brain edema in acute liver failure and chronic liver disease: Similarities and differences. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unterberg, A.W.; Stover, J.; Kress, B.; Kiening, K.L. Edema and brain trauma. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norenberg, M.D.; Rao, K.V.; Jayakumar, A.R. Mechanisms of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Metab. Brain Dis. 2005, 20, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.R.; Rao, K.V.; Murthy, C.R.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama Rao, K.V.; Norenberg, M.D. Aquaporin-4 in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2007, 22, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrane, A.S.; Rangroo Thrane, V.; Nedergaard, M. Drowning stars: Reassessing the role of astrocytes in brain edema. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovira, A.; Grive, E.; Pedraza, S.; Rovira, A.; Alonso, J. Magnetization transfer ratio values and proton MR spectroscopy of normal-appearing cerebral white matter in patients with liver cirrhosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Cordoba, J.; Alonso, J.; Rovira, A.; Jacas, C.; Sanpedro, F.; Castells, L.; Vargas, V.; Margarit, C.; Kulisewsky, J.; Esteban, R.; et al. The development of low-grade cerebral edema in cirrhosis is supported by the evolution of (1)H-magnetic resonance abnormalities after liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Oatridge, A.; Hajnal, J.V.; Burroughs, A.K.; McIntyre, N.; deSouza, N.M. MR imaging of the basal ganglia in chronic liver disease: Correlation of T1-weighted and magnetisation transfer contrast measurements with liver dysfunction and neuropsychiatric status. Metab. Brain Dis. 1995, 10, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, N. Magnetic resonance image segmentation using pattern recognition, and applied to image registration and quantitation. NMR Biomed. 1998, 11, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; White, S.; Dhanjal, N.S.; Oatridge, A.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Changes in brain size in hepatic encephalopathy: A coregistered MRI study. Metab. Brain Dis. 2004, 19, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, E.M.; Bauer, R.M.; Berman, M.D.; Guth, J.C.; Maas, M.B.; Naidech, A.M.; Rosenberg, N.F. Acute changes in ventricular volume during treatment for hepatic and renal failure. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2014, 4, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamamoto Filho, P.T.; Fogaroli, M.O.; Oliveira, M.A.C.; Oliveira, C.C.; Batah, S.S.; Fabro, A.T.; Vulcano, L.C.; Bazan, R.; Zanini, M.A. A Rat Model of Neurocysticercosis-Induced Hydrocephalus: Chronic Progressive Hydrocephalus with Mild Clinical Impairment. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, e535–e544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, K.; Tanaka, S.; Ribot, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Nakadate, K.; Watanabe, Y. Preservation of functional architecture in visual cortex of cats with experimentally induced hydrocephalus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosoi, C.R.; Rose, C.F. Identifying the direct effects of ammonia on the brain. Metab. Brain Dis. 2009, 24, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, P.S.; Runyon, B.A. Serum ammonia level for the evaluation of hepatic encephalopathy. JAMA 2014, 312, 643–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.P.; Aggarwal, A.; Krieger, D.; Easley, K.A.; Karafa, M.T.; Van Lente, F.; Arroliga, A.C.; Mullen, K.D. Correlation between ammonia levels and the severity of hepatic encephalopathy. Am. J. Med. 2003, 114, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damkier, H.H.; Brown, P.D.; Praetorius, J. Cerebrospinal fluid secretion by the choroid plexus. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1847–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boassa, D.; Stamer, W.D.; Yool, A.J. Ion channel function of aquaporin-1 natively expressed in choroid plexus. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7811–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Praetorius, J.; Damkier, H.H. Transport across the choroid plexus epithelium. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C673–C686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johanson, C.; Stopa, E.; McMillan, P.; Roth, D.; Funk, J.; Krinke, G. The distributional nexus of choroid plexus to cerebrospinal fluid, ependyma and brain: Toxicologic/pathologic phenomena, periventricular destabilization, and lesion spread. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 39, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimy, J.K.; Duran, D.; Hu, J.K.; Gavankar, C.; Gaillard, J.R.; Bayri, Y.; Rice, H.; DiLuna, M.L.; Gerzanich, V.; Marc Simard, J.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid hypersecretion in pediatric hydrocephalus. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 41, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, G.; Soper, R.; Brooks, H.F.; Stadlbauer, V.; Vairappan, B.; Davies, N.A.; Andreola, F.; Hodges, S.; Moss, R.F.; Davies, D.C.; et al. Role of aquaporin-4 in the development of brain oedema in liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama Rao, K.V.; Jayakumar, A.R.; Tong, X.; Curtis, K.M.; Norenberg, M.D. Brain aquaporin-4 in experimental acute liver failure. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eefsen, M.; Jelnes, P.; Schmidt, L.E.; Vainer, B.; Bisgaard, H.C.; Larsen, F.S. Brain expression of the water channels aquaporin-1 and -4 in mice with acute liver injury, hyperammonemia and brain edema. Metab. Brain Dis. 2010, 25, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaut, J.; Lasbennes, F.; Magistretti, P.J.; Regli, L. Aquaporins in brain: Distribution, physiology, and pathophysiology. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2002, 22, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.F.; Zhu, S.M.; Zheng, Y.Y. Ammonia induces upregulation of aquaporin-4 in neocortical astrocytes of rats through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2010, 123, 1888–1892. [Google Scholar]
- Bonomini, F.; Rezzani, R. Aquaporin and blood brain barrier. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosu, G.C.; Pirici, I.; Grigorie, A.A.; Istrate-Ofiteru, A.M.; Iovan, L.; Tudorica, V.; Pirici, D. Distribution of Aquaporins 1 and 4 in the Central Nervous System. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2019, 45, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.Y.; Huang, G.Q.; Du, Q.; Zhou, L.Q.; Zhou, J.H. The dynamic expression of aquaporins 1 and 4 in rats with hydrocephalus induced by subarachnoid haemorrhage. Folia Neuropathol. 2019, 57, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, B.; Hsu, Y.; Schneller, B.; Hobbs, J.G.; Mehta, A.I.; Linninger, A. Hydrocephalus: The role of cerebral aquaporin-4 channels and computational modeling considerations of cerebrospinal fluid. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 41, E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul, L.; Madan, M.; Rammling, M.; Chigurupati, S.; Chan, S.L.; Pattisapu, J.V. Expression of aquaporin 1 and 4 in a congenital hydrocephalus rat model. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roales-Bujan, R.; Paez, P.; Guerra, M.; Rodriguez, S.; Vio, K.; Ho-Plagaro, A.; Garcia-Bonilla, M.; Rodriguez-Perez, L.M.; Dominguez-Pinos, M.D.; Rodriguez, E.M.; et al. Astrocytes acquire morphological and functional characteristics of ependymal cells following disruption of ependyma in hydrocephalus. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakadate, K.; Imamura, K.; Watanabe, Y. Cellular and subcellular localization of alpha-1 adrenoceptors in the rat visual cortex. Neuroscience 2006, 141, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakadate, K. Developmental changes in the flotillin-1 expression pattern of the rat visual cortex. Neuroscience 2015, 292, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakadate, K.; Kamata, S. Severe Acute Hepatic Dysfunction Induced by Ammonium Acetate Treatment Results in Choroid Plexus Swelling and Ventricle Enlargement in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042010
Nakadate K, Kamata S. Severe Acute Hepatic Dysfunction Induced by Ammonium Acetate Treatment Results in Choroid Plexus Swelling and Ventricle Enlargement in the Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(4):2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042010
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakadate, Kazuhiko, and Sumito Kamata. 2022. "Severe Acute Hepatic Dysfunction Induced by Ammonium Acetate Treatment Results in Choroid Plexus Swelling and Ventricle Enlargement in the Brain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 4: 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042010
APA StyleNakadate, K., & Kamata, S. (2022). Severe Acute Hepatic Dysfunction Induced by Ammonium Acetate Treatment Results in Choroid Plexus Swelling and Ventricle Enlargement in the Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(4), 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042010





