Biocompatible Gas Plasma Treatment Affects Secretion Profiles but Not Osteogenic Differentiation in Patient-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantification of Reactive Species in Cell Culture Media
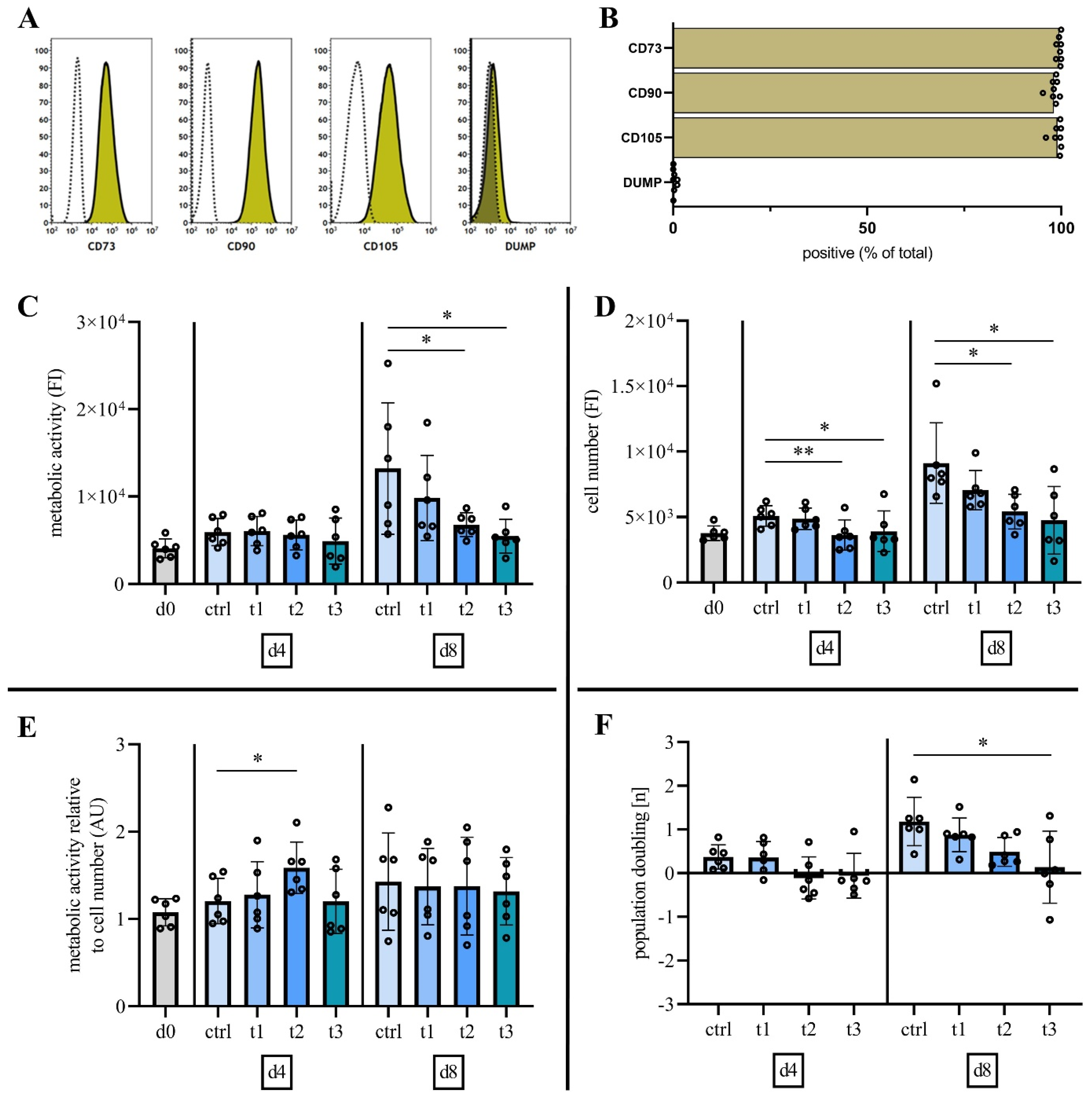
2.2. Characterization of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
2.3. Cold Physical Plasma Alters Cell Viability and Proliferation Capacity
2.4. Exposure to Cold Physical Plasma Affects hBM-MSC Morphology
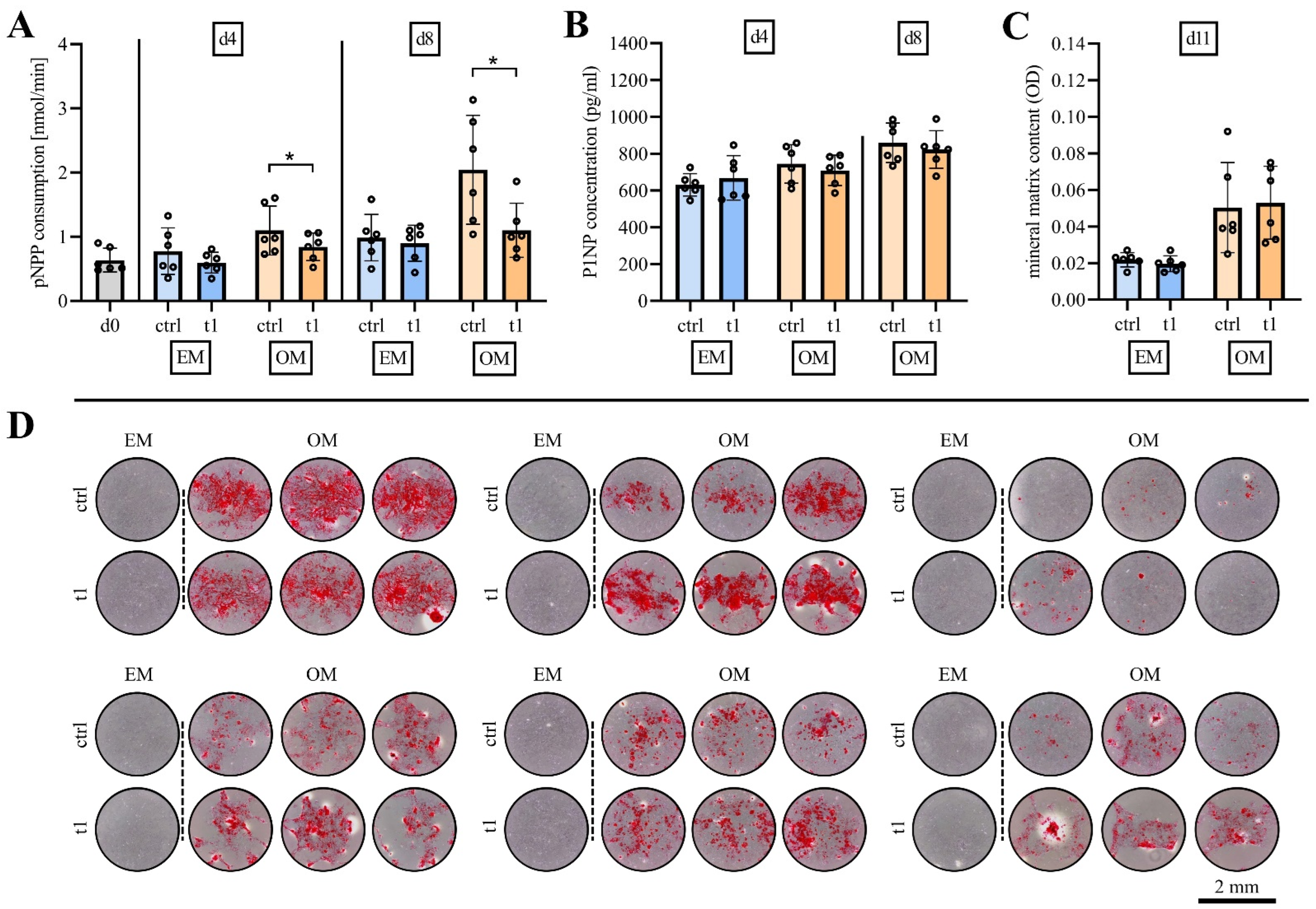
2.5. Matrix Mineralization Was Not Affected by Exposure to Cold Physical Plasma
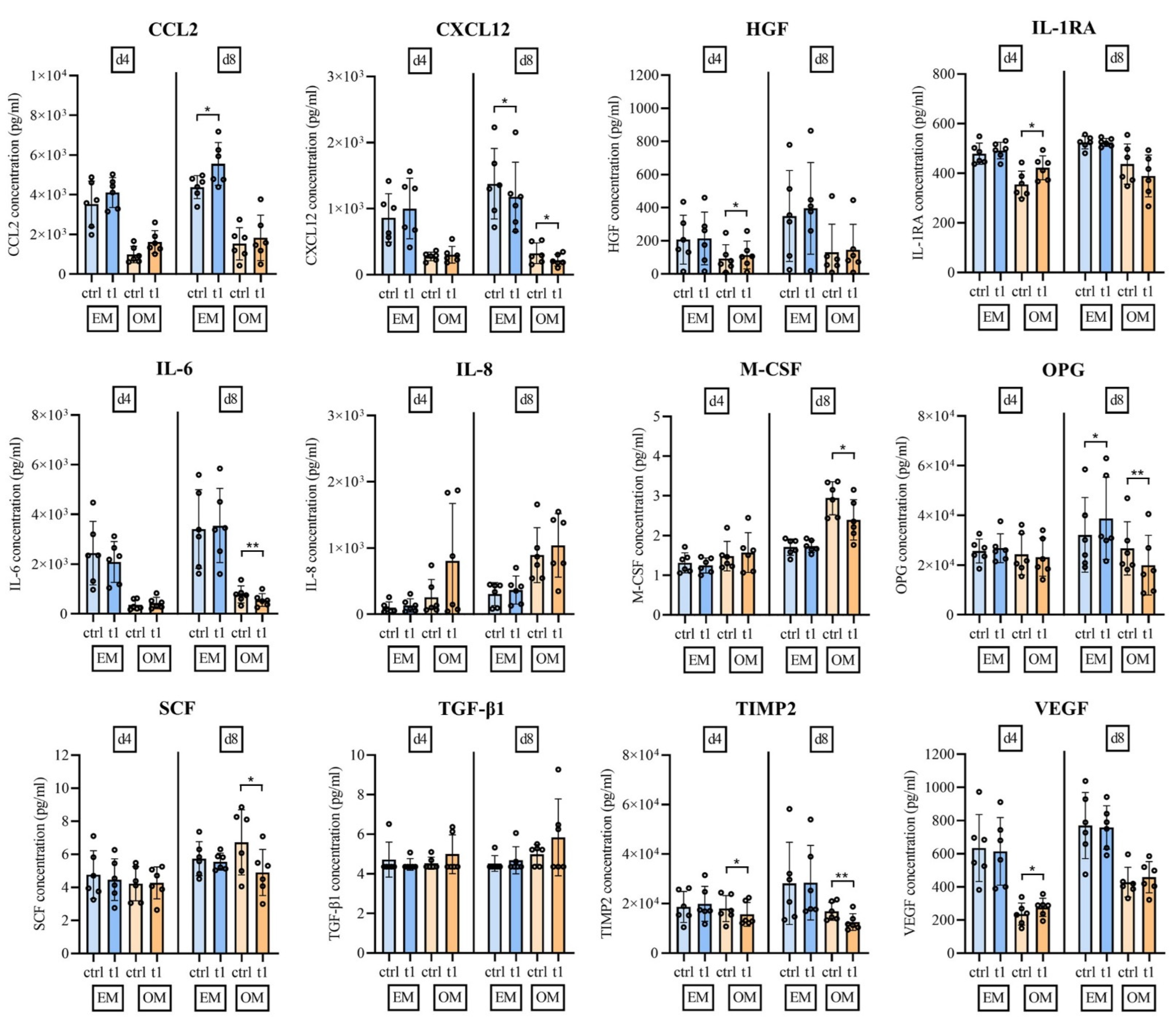
2.6. Soluble Mediator Multiplex Analysis of Major MSC Secreted Signaling Molecules
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Patient Recruitment and Sample Harvest
4.2. Cell Isolation, Cultivation and Characterization
4.3. In Vitro Exposure to Cold Physical Plasma
4.4. Quantification of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species
4.5. Cell Viability and Proliferation
4.6. High Content Fluorescence Imaging
4.7. In Vitro Stimulation of Osteogenic Differentiation
4.8. Quantification of the Osteogenic Differentiation Potential
4.9. Soluble Mediator Multiplex Analysis
4.10. Data Analysis, Presentation, and Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bekeschus, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Emmert, S.; Schmidt, A. Medical gas plasma-stimulated wound healing: Evidence and mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2021, 46, 102116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weltmann, K.; von Woedtke, T. Plasma medicine—Current state of research and medical application. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2016, 59, 014031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, W.L.; Perrotti, V.; Iaculli, F.; Piattelli, A.; Quaranta, A. The emerging role of cold atmospheric plasma in implantology: A review of the literature. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebli, N.; Krebs, J.; Stich, H.; Schawalder, P.; Walton, M.; Schwenke, D.; Gruner, H.; Gasser, B.; Theis, J.C. In vivo comparison of the osseointegration of vacuum plasma sprayed titanium- and hydroxyapatite-coated implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2003, 66, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duske, K.; Koban, I.; Kindel, E.; Schröder, K.; Nebe, B.; Holtfreter, B.; Jablonowski, L.; Weltmann, K.D.; Kocher, T. Atmospheric plasma enhances wettability and cell spreading on dental implant metals. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Genova, T.; Mandracci, P.; Mussano, F.; Abundo, R.; Fiorellini, J.P. Morphometric Changes Induced by Cold Argon Plasma Treatment on Osteoblasts Grown on Different Dental Implant Surfaces. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2017, 37, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Woedtke, T.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K.; Weltmann, K.D. Plasma Medicine: A Field of Applied Redox Biology. Vivo 2019, 33, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T. The plasma jet kINPen—A powerful tool for wound healing. Clin. Plasma Med. 2016, 4, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, E.; Liedtke, K.R.; van der Linde, J.; Metelmann, H.-R.; Heidecke, C.-D.; Partecke, L.-I.; Bekeschus, S. Physical plasma-treated saline promotes an immunogenic phenotype in CT26 colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, A.; Wende, K.; Bundscherer, L.; Hasse, S.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Lindequist, U.; Masur, K. Nonthermal plasma increases expression of wound healing related genes in a keratinocyte cell line. Plasma Med. 2013, 3, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, K.; Koban, I.; Tresp, H.; Jablonowski, L.; Schröder, K.; Kramer, A.; Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T.; Kocher, T. Atmospheric pressure plasma: A high-performance tool for the efficient removal of biofilms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Poschkamp, B.; van der Linde, J. Medical gas plasma promotes blood coagulation via platelet activation. Biomaterials 2020, 278, 120433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daeschlein, G.; Napp, M.; Lutze, S.; Arnold, A.; von Podewils, S.; Guembel, D.; Jünger, M. Skin and wound decontamination of multidrug-resistant bacteria by cold atmospheric plasma coagulation. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2015, 13, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daeschlein, G.; Scholz, S.; Emmert, S.; von Podewils, S.; Haase, H.; von Woedtke, T.; Junger, M. Plasma medicine in dermatology: Basic antimicrobial efficacy testing as prerequisite to clinical plasma therapy. Plasma Med. 2012, 2, 33–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallo, J.; Raska, M.; Kriegova, E.; Goodman, S.B. Inflammation and its resolution and the musculoskeletal system. J. Orthop. Transl. 2017, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.C.; Larrouture, Q.C.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Beer-Stoltz, D.; Liu, L.; Tuan, R.S.; Robinson, L.J.; Schlesinger, P.H.; Nelson, D.J. Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Matrix Formation In Vivo and In Vitro. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2017, 23, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tominami, K.; Kanetaka, H.; Sasaki, S.; Mokudai, T.; Kaneko, T.; Niwano, Y. Cold atmospheric plasma enhances osteoblast differentiation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uccelli, A.; Moretta, L.; Pistoia, V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, G.; Ankrum, J.A.; Kamhieh-Milz, J.; Bieback, K.; Ringden, O.; Volk, H.D.; Geissler, S.; Reinke, P. Intravascular Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cell Therapy Product Diversification: Time for New Clinical Guidelines. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oryan, A.; Kamali, A.; Moshiri, A.; Eslaminejad, M.B. Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Bone Regenerative Medicine: What Is the Evidence? Cells Tissues Organs 2017, 204, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, G.C.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, S.; Song, K. Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Efficiently Promotes the Proliferation of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells by Activating NO-Response Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miletić, M.; Mojsilović, S.; Đorđević, I.O.; Maletić, D.; Puač, N.; Lazović, S.; Malović, G.; Milenković, P.; Petrović, Z.L.; Bugarski, D. Effects of non-thermal atmospheric plasma on human periodontal ligament mesenchymal stem cells. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 345401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Masur, K.; Kolata, J.; Wende, K.; Schmidt, A.; Bundscherer, L.; Barton, A.; Kramer, A.; Broker, B.; Weltmann, K.D. Human Mononuclear Cell Survival and Proliferation is Modulated by Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jet. Plasma Process. Polym. 2013, 10, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, G.C.; Kim, S.S.; Han, S.; Song, K. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma is an excellent tool to activate proliferation in various mesoderm-derived human adult stem cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 134, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.R.; Xu, G.M.; Shi, X.M.; Zhang, G.J. Low temperature plasma promoting fibroblast proliferation by activating the NF-kappaB pathway and increasing cyclinD1 expression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przekora, A.; Audemar, M.; Pawlat, J.; Canal, C.; Thomann, J.S.; Labay, C.; Wojcik, M.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Terebun, P.; Ginalska, G.; et al. Positive Effect of Cold Atmospheric Nitrogen Plasma on the Behavior of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cultured on a Bone Scaffold Containing Iron Oxide-Loaded Silica Nanoparticles Catalyst. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, B.; Marciniak, J.; Deschner, J.; Stope, M.B.; Mustea, A.; Kramer, F.J.; Nokhbehsaim, M. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Promotes Regeneration-Associated Cell Functions of Murine Cementoblasts In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbeck, M.J.; Chernets, N.; Zhang, J.; Kurpad, D.S.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Freeman, T.A. Skeletal cell differentiation is enhanced by atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinpflug, J.; Pfeiffenberger, M.; Damerau, A.; Schwarz, F.; Textor, M.; Lang, A.; Schulze, F. Journey into Bone Models: A Review. Genes 2018, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoon, J.; Hesse, B.; Rakow, A.; Ort, M.J.; Lagrange, A.; Jacobi, D.; Winter, A.; Huesker, K.; Reinke, S.; Cotte, M.; et al. Metal-Specific Biomaterial Accumulation in Human Peri-Implant Bone and Bone Marrow. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundscherer, L.; Wende, K.; Ottmuller, K.; Barton, A.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Hasse, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; Masur, K.; Lindequist, U. Impact of non-thermal plasma treatment on MAPK signaling pathways of human immune cell lines. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, S.B.; Gallo, J. Periprosthetic Osteolysis: Mechanisms, Prevention and Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernhardsson, M.; Sandberg, O.; Aspenberg, P. Experimental models for cancellous bone healing in the rat. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 745–750. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, M.M.; Wilson, B.M.; Ross, R.D.; Virdi, A.S.; Sumner, D.R. Arthrotomy-based preclinical models of particle-induced osteolysis: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2017, 35, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, J.S.; Choi, S.H.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, K.M.; Chu, P.K. Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Amine-Functionalized Titanium Using Humidified Ammonia Supplied Nonthermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, C.E.B.; Neto, M.F.Q.; Braz, J.; de Medeiros Aires, M.; Farias, N.B.S.; Barboza, C.A.G.; Cavalcanti, G.B., Jr.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Alves, C., Jr. Effect of plasma-nitrided titanium surfaces on the differentiation of pre-osteoblastic cells. Artif. Organs 2019, 43, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guastaldi, F.P.; Yoo, D.; Marin, C.; Jimbo, R.; Tovar, N.; Zanetta-Barbosa, D.; Coelho, P.G. Plasma treatment maintains surface energy of the implant surface and enhances osseointegration. Int. J. Biomater. 2013, 2013, 354125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildemann, B.; Ignatius, A.; Leung, F.; Taitsman, L.A.; Smith, R.M.; Pesantez, R.; Stoddart, M.J.; Richards, R.G.; Jupiter, J.B. Non-union bone fractures. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer. 2021, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; Unger, P.; Berneburg, M.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Karrer, S. Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) activates angiogenesis-related molecules in skin keratinocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells and improves wound angiogenesis in an autocrine and paracrine mode. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 89, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, T.; Semmler, M.L.; Schäfer, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Emmert, S.; Boeckmann, L. Plasma Medicine: Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma in Dermatology. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3873928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, A.R.R.; Dahlke, M.H. Immunomodulation by Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Mechanisms of Action of Living, Apoptotic, and Dead MSCs. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eggers, B.; Marciniak, J.; Memmert, S.; Kramer, F.J.; Deschner, J.; Nokhbehsaim, M. The beneficial effect of cold atmospheric plasma on parameters of molecules and cell function involved in wound healing in human osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Odontology 2020, 108, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrell, C.R.; Markovic, B.S.; Fellabaum, C.; Arsenijevic, N.; Djonov, V.; Volarevic, V. The role of Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in mesenchymal stem cell-based tissue repair and regeneration. Biofactors 2020, 46, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, D.S.; Caplice, N.M.; Clover, A.J.P. Mesenchymal stromal cell derived CCL2 is required for accelerated wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, J.; Das, R.; Nylen, E.; Chinnadurai, R.; Galipeau, J. CCL2 and CXCL12 Derived from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Cooperatively Polarize IL-10+ Tissue Macrophages to Mitigate Gut Injury. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1923–1934.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mun, S.H.; Park, P.S.U.; Park-Min, K.H. The M-CSF receptor in osteoclasts and beyond. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1239–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udagawa, N.; Koide, M.; Nakamura, M.; Nakamichi, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Uehara, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Furuya, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Fukuda, C.; et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2021, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borciani, G.; Montalbano, G.; Baldini, N.; Cerqueni, G.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Ciapetti, G. Co-culture systems of osteoblasts and osteoclasts: Simulating in vitro bone remodeling in regenerative approaches. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kang, H.; Lu, J.; Dai, Y.; Wang, F. Experimental study of the effects of hypoxia simulator on osteointegration of titanium prosthesis in osteoporotic rats. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckermann, B.M.; Kallifatidis, G.; Groth, A.; Frommhold, D.; Apel, A.; Mattern, J.; Salnikov, A.V.; Moldenhauer, G.; Wagner, W.; Diehlmann, A.; et al. VEGF expression by mesenchymal stem cells contributes to angiogenesis in pancreatic carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Seo, D.W. TIMP-2: An endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis. Trends Mol. Med. 2005, 11, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrzejewska, A.; Catar, R.; Schoon, J.; Qazi, T.H.; Sass, F.A.; Jacobi, D.; Blankenstein, A.; Reinke, S.; Kruger, D.; Streitz, M.; et al. Multi-Parameter Analysis of Biobanked Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Shows Little Influence for Donor Age and Mild Comorbidities on Phenotypic and Functional Properties. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.D. The kINPen—A review on physics and chemistry of the atmospheric pressure plasma jet and its applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 233001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakow, A.; Schoon, J.; Dienelt, A.; John, T.; Textor, M.; Duda, G.; Perka, C.; Schulze, F.; Ode, A. Influence of particulate and dissociated metal-on-metal hip endoprosthesis wear on mesenchymal stromal cells in vivo and in vitro. Biomaterials 2016, 98, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ode, A.; Schoon, J.; Kurtz, A.; Gaetjen, M.; Ode, J.E.; Geissler, S.; Duda, G.N. CD73/5′-ecto-nucleotidase acts as a regulatory factor in osteo-/chondrogenic differentiation of mechanically stimulated mesenchymal stromal cells. Eur. Cells Mater. 2013, 25, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient | Age | Sex | Indication for Surgery | Surgical Treatment | Long-Term Medication | Comorbidities | BM Weight (g) | Number of BM-MNCs Isolated (×106) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| donor 1 | 75.7 | w | hip osteoarthritis | primary THA | pantoprazole, lisinopril, bisoprolol, allopurinol, prednisolone | polymyalgia rheumatica, art. hypertension, anxiety disorder | 10.56 | 144 |
| donor 2 | 81.5 | w | hip osteoarthritis | primary THA | amlodipine, olmesartan | art. hypertension | 6.56 | 62 |
| donor 3 | 79.5 | w | hip osteoarthritis | primary THA | acetylsalicylic acid, bisoprolol, ramipril, torsemide, cholecalciferol | art. hypertension, osteoporosis, chronic kidney disease | 4.12 | 149 |
| donor 4 | 53.2 | w | developmental dysplasia of the hip | primary THA | - | - | 6.31 | 210 |
| donor 5 | 68.1 | m | hip osteoarthritis | primary THA | allopurinol, pantoprazole | dyslipidemia | 7.53 | 230 |
| donor 6 | 77.1 | m | hip osteoarthritis | primary THA | ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid, simvastatin, candesartan, hydrochlorothiazide | B-cell-lymphoma, art. hypertension, chronic back pain, stroke, lumbar disc disease | 6.33 | 279 |
| donor 7 | 76.4 | w | hip osteoarthritis | primary THA | acetylsalicylic acid, carvedilol, amlodipine, trimipramine, ezetimibe/simvastatin, candesartan | art. hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, depression, aortic valve insufficiency | 2.23 | 104 |
| donor 8 | 75.3 | m | hip osteoarthritis | primary THA | irbesartan, hydrochlorothiazide, carvedilol | art. hypertension, obesity | 8.55 | 203 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fischer, M.; Schoon, J.; Freund, E.; Miebach, L.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Bekeschus, S.; Wassilew, G.I. Biocompatible Gas Plasma Treatment Affects Secretion Profiles but Not Osteogenic Differentiation in Patient-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042038
Fischer M, Schoon J, Freund E, Miebach L, Weltmann K-D, Bekeschus S, Wassilew GI. Biocompatible Gas Plasma Treatment Affects Secretion Profiles but Not Osteogenic Differentiation in Patient-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(4):2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042038
Chicago/Turabian StyleFischer, Maximilian, Janosch Schoon, Eric Freund, Lea Miebach, Klaus-Dieter Weltmann, Sander Bekeschus, and Georgi I. Wassilew. 2022. "Biocompatible Gas Plasma Treatment Affects Secretion Profiles but Not Osteogenic Differentiation in Patient-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 4: 2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042038
APA StyleFischer, M., Schoon, J., Freund, E., Miebach, L., Weltmann, K.-D., Bekeschus, S., & Wassilew, G. I. (2022). Biocompatible Gas Plasma Treatment Affects Secretion Profiles but Not Osteogenic Differentiation in Patient-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(4), 2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042038








