Targeted Suppression of Lipoprotein Receptor LSR in Astrocytes Leads to Olfactory and Memory Deficits in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Lsr Deletion and Downregulation of Cholesterol-Related Gene Expression in cKO Mice
2.2. Activity and Anxiety in Astroglial Lsr cKO Mice
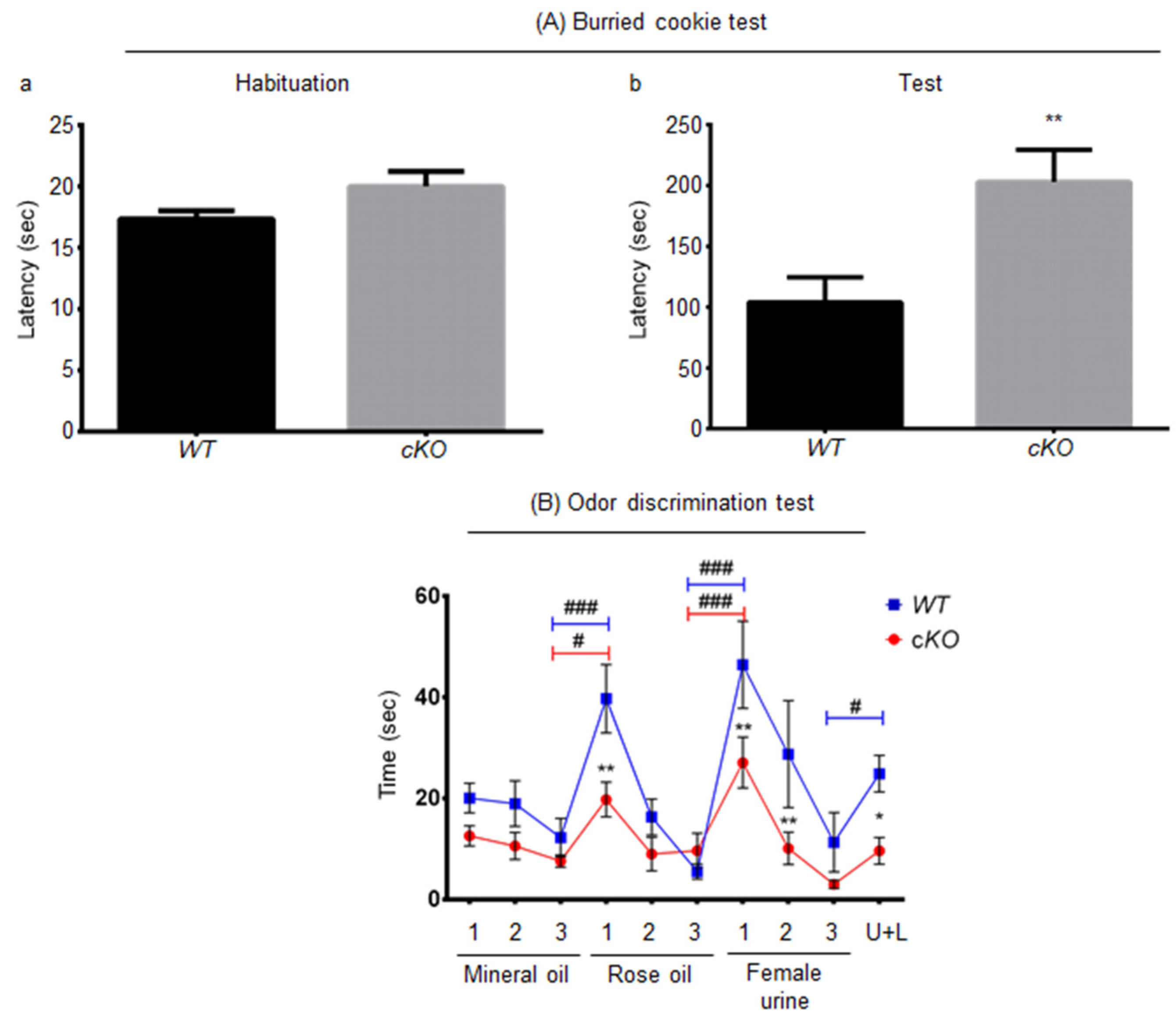
2.3. Olfaction in Astroglial Lsr cKO Mice
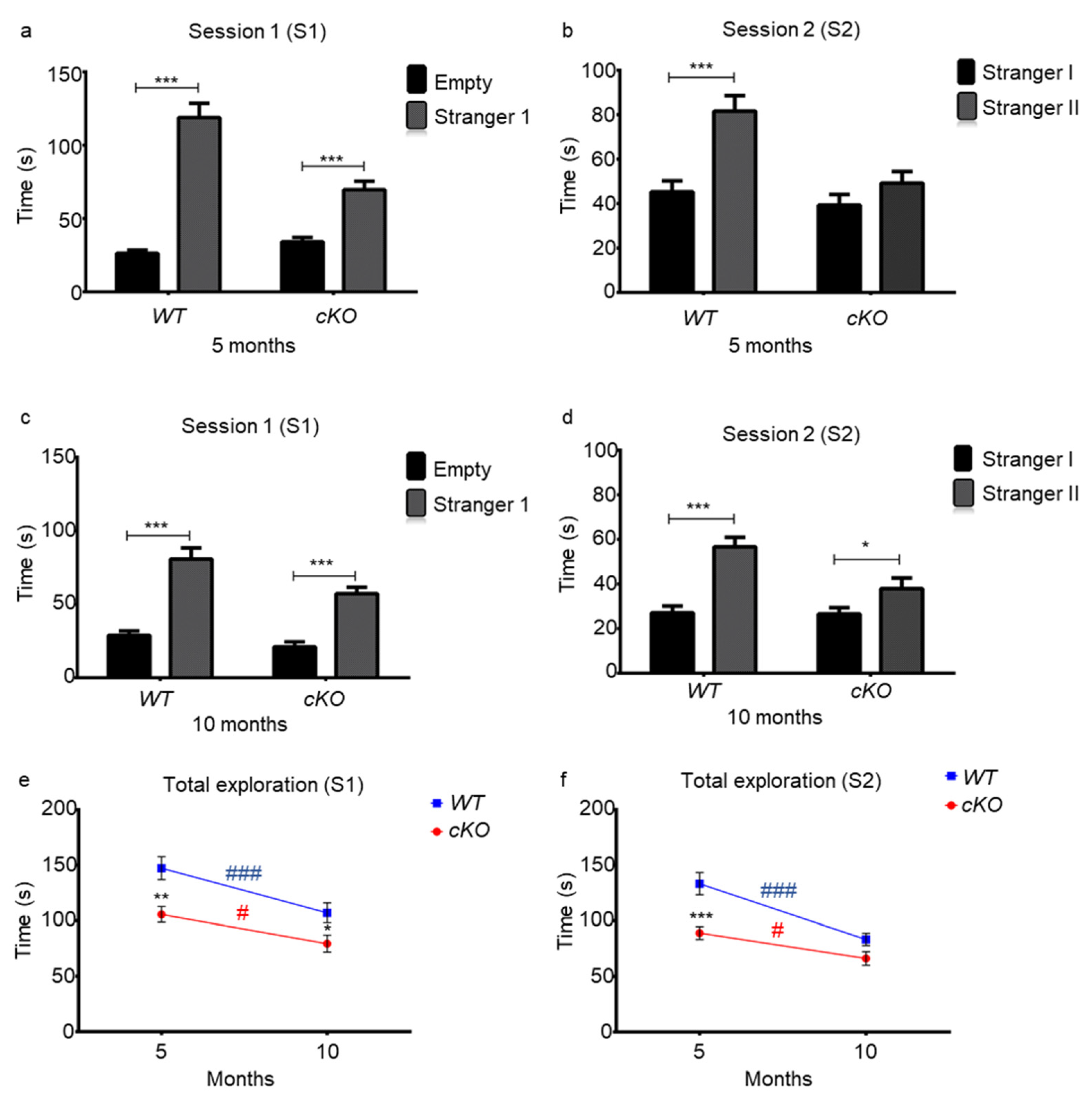
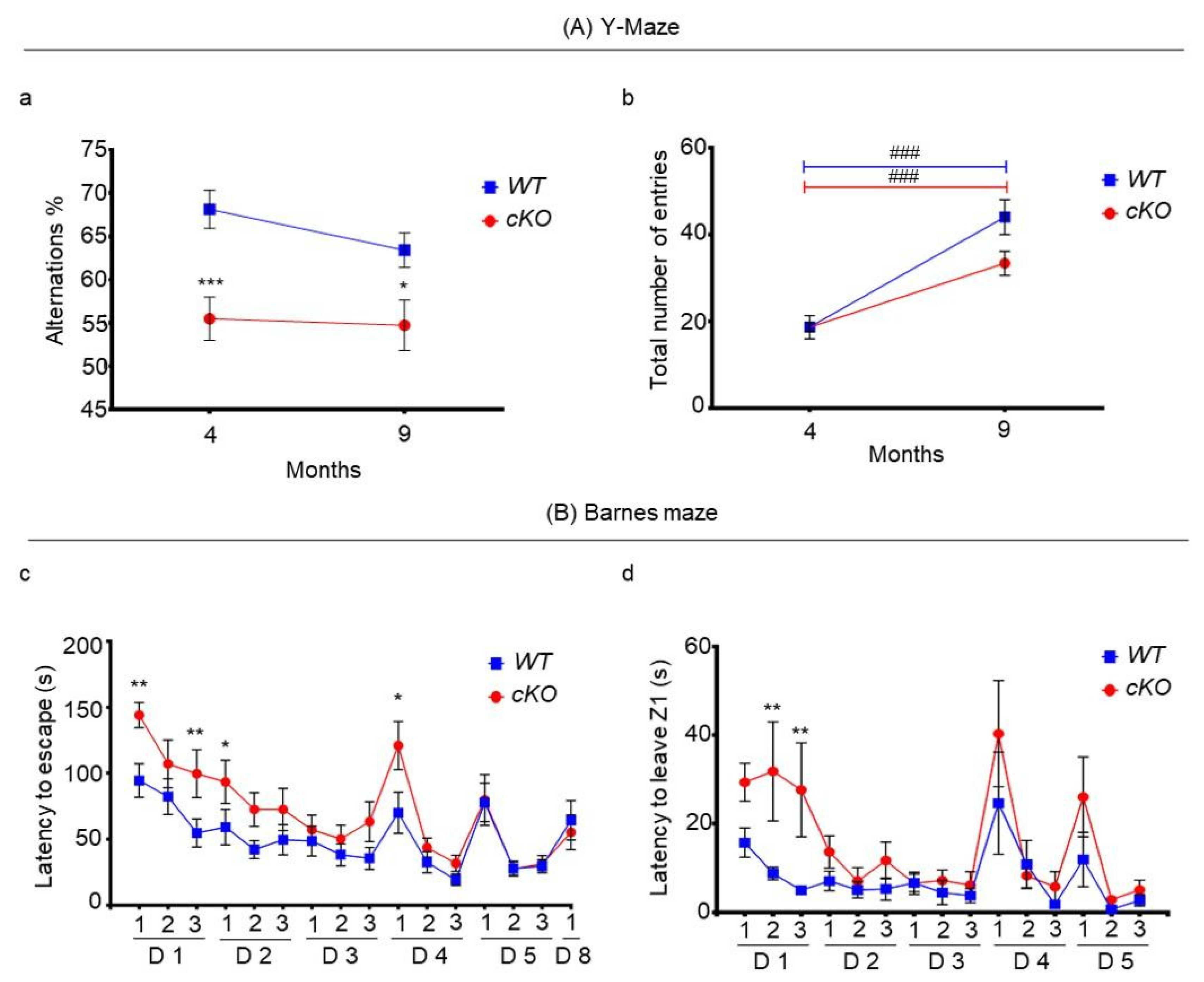
2.4. Memory in Astroglial Lsr cKO Mice
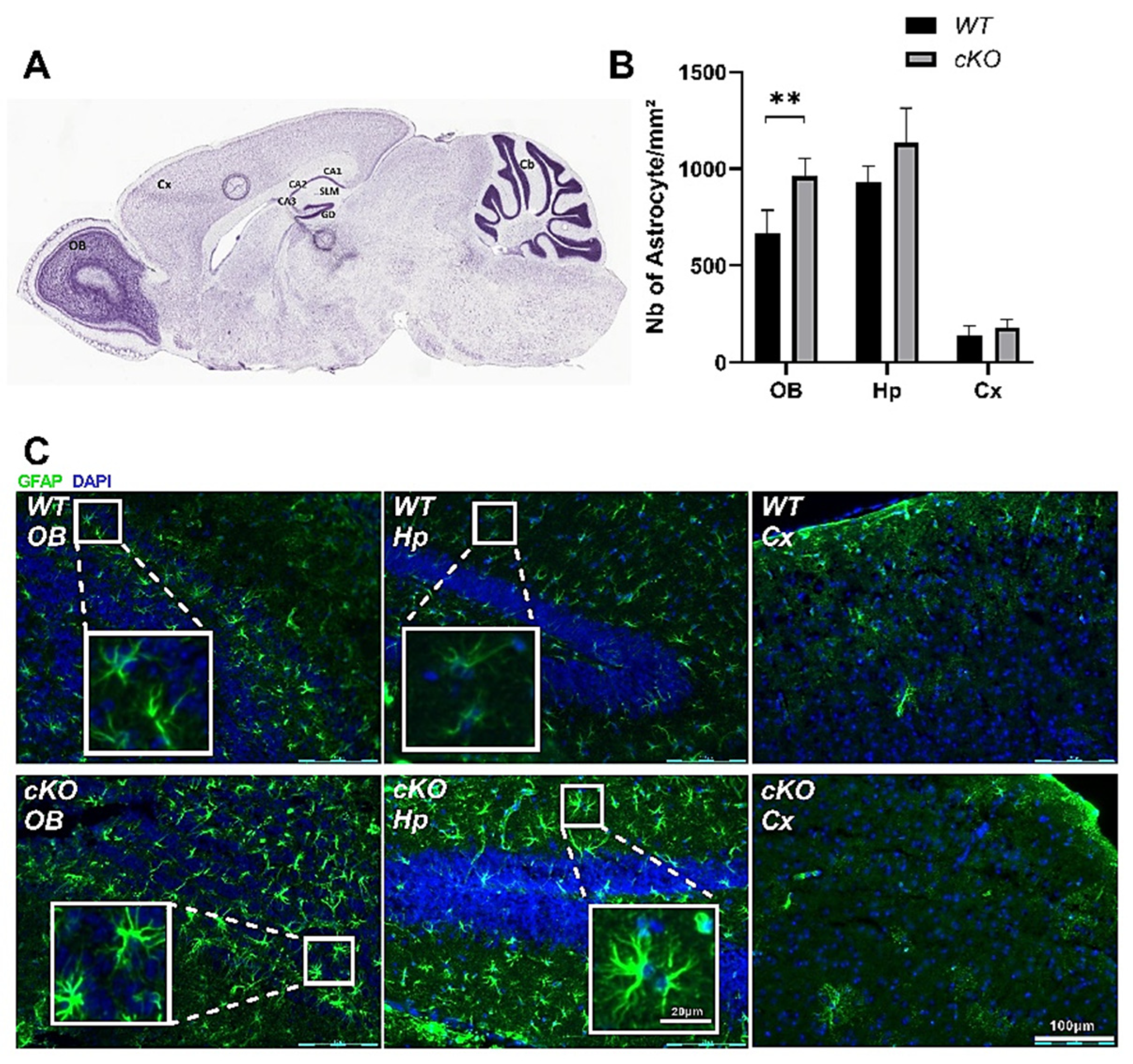
2.5. Astroglial Activation in cKO Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Tamoxifen (TAM)-Induced Activation of CreERT2
4.3. Behavioral Tests
4.3.1. Activity and Anxiety
Home Cage Activity Test
Open Field Test
Free Exploratory Paradigm Test
4.3.2. Olfaction
Buried Cookie Test
Habituation/Cross-Habituation Test
4.3.3. Memory
Object Recognition Test
Three-Chamber Sociability and Social Novelty Test
Y-Maze Test
Barnes Maze
4.4. RNA Extraction and Real-Time (RT) Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.5. Blood Glucose Test
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 |
| ABCG1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease; Apo, apolipoprotein |
| BB | blood brain barrier |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| cKO | astroglial Lsr knock-out |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| C3 | complement component 3 |
| Cre | Cre-recombinase |
| Cx | cortex |
| Cyp46A1 | cytochrome P450 family 46 subfamily A member 1 |
| EIF3F | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit F |
| ERT2 | estrogen receptor inducible promoter |
| fl | flox |
| EEF2 | eukaryotic elongation factor 2 |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| GLAST | glial glutamate transporter |
| hmgcr | HMG CoA reductase |
| Hp | hippocampus |
| LSR | lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor |
| MCI | mild cognitive impairment |
| OB | olfactory bulb |
| PPIA | peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase A |
| RT-qPCR | real-time quantitative PCR |
| S1, S2 | session 1, session 2 |
| S100β | S100 calcium-binding protein β |
| srebp1 | sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 |
| TAM | tamoxifen |
| WT | wild-type |
| Z1,2,3 | zones 1, 2, 3 |
References
- Söderberg, M.; Edlund, C.; Kristensson, K.; Dallner, G. Lipid compositions of different regions of the human brain during aging. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennerholm, L.; Gottfries, C.G. Membrane lipids, selectively diminished in Alzheimer brains, suggest synapse loss as a primary event in early-onset form (type I) and demyelination in late-onset form (type II). J. Neurochem. 1994, 62, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; Fabelo, N.; Ferrer, I.; Marín, R. “Lipid raft aging” in the human frontal cortex during nonpathological aging: Gender influences and potential implications in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 67, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ledesma, M.D.; Martin, M.G.; Dotti, C.G. Lipid changes in the aged brain: Effect on synaptic function and neuronal survival. Prog. Lipid Res. 2012, 51, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.; Dotti, C.G.; Ledesma, M.D. Brain cholesterol in normal and pathological aging. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, D.A.; Nalivaeva, N.N.; Turner, A.J. Lipid rafts and Alzheimer’s disease: Protein-lipid interactions and perturbation of signaling. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitas, R.E.; Boyles, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Hui, D.; Weisgraber, K.H. Lipoproteins and their receptors in the central nervous system. Characterization of the lipoproteins in cerebrospinal fluid and identification of apolipoprotein B,E(LDL) receptors in the brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 14352–14360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeske, D.J.; Dietschy, J.M. Regulation of rates of cholesterol synthesis in vivo in the liver and carcass of the rat measured using [3H]water. J. Lipid Res. 1980, 21, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, A.M.; Holtzman, D.M.; Munson, G.; Mathur, T.; Schneider, D.; Chang, L.K.; Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A.; Lukens, J.; Shah, J.A.; et al. Unique lipoproteins secreted by primary astrocytes from wild type, apoE (−/−), and human apoE transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30001–30007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Kusumo, H.; Costa, L.G.; Guizzetti, M. Cholesterol efflux is differentially regulated in neurons and astrocytes: Implications for brain cholesterol homeostasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bihain, B.E.; Yen, F.T. The lipolysis stimulated receptor: A gene at last. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1998, 9, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, F.T.; Roitel, O.; Bonnard, L.; Notet, V.; Pratte, D.; Stenger, C.; Magueur, E.; Bihain, B.E. Lipolysis stimulated lipoprotein receptor: A novel molecular link between hyperlipidemia, weight gain, and atherosclerosis in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25650–25659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenger, C.; Pinçon, A.; Hanse, M.; Royer, L.; Comte, A.; Koziel, V.; Olivier, J.L.; Pillot, T.; Yen, F.T. Brain region-specific immunolocalization of the lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor (LSR) and altered cholesterol distribution in aged LSR+/− mice. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvekar, P.; Berriel Diaz, M.; Krones-Herzig, A.; Hardeland, U.; Strzoda, D.; Stöhr, S.; Frohme, M.; Herzig, S. Liver-specific loss of lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor triggers systemic hyperlipidemia in mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesli, S.; Javorschi, S.; Bérard, A.M.; Landry, M.; Priddle, H.; Kivlichan, D.; Smith, A.J.; Yen, F.T.; Bihain, B.E.; Darmon, M. Distribution of the lipolysis stimulated receptor in adult and embryonic murine tissues and lethality of LSR−/− embryos at 12.5 to 14.5 days of gestation. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohet, F.; Lin, C.; Munji, R.N.; Lee, S.Y.; Ruderisch, N.; Soung, A.; Arnold, T.D.; Derugin, N.; Vexler, Z.S.; Yen, F.T.; et al. LSR/angulin-1 is a tricellular tight junction protein involved in blood-brain barrier formation. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, S.; Parton, R.G. Lipid droplets: A unified view of a dynamic organelle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, A.; Yen, F.T.; Oster, T.; Malaplate, C.; Pauron, L.; Corbier, C.; Lanhers, M.C.; Claudepierre, T. Age-related changes in regiospecific expression of Lipolysis Stimulated Receptor (LSR) in mice brain. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slezak, M.; Göritz, C.; Niemiec, A.; Frisén, J.; Chambon, P.; Metzger, D.; Pfrieger, F.W. Transgenic mice for conditional gene manipulation in astroglial cells. Glia 2007, 55, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streicher, R.; Kotzka, J.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Siemeister, G.; Munck, M.; Avci, H.; Krone, W. SREBP-1 mediates activation of the low-density lipoprotein receptor promoter by insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7128–7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, B.P.; Lu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Stemerman, M.B.; Chien, S.; Shyy, J.Y. Shear stress activation of SREBP1 in endothelial cells is mediated by integrins. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinçon, A.; Thomas, M.H.; Huguet, M.; Allouche, A.; Colin, J.C.; Georges, A.; Derrien, A.; Lanhers, M.C.; Malaplate-Armand, C.; Oster, T.; et al. Increased susceptibility of dyslipidemic LSR+/− mice to amyloid stress is associated with changes in cortical cholesterol levels. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 45, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, A.; Verret, L.; Bozon, B.; El Tannir El Tayara, N.; Ly, M.; Kober, F.; Dhenain, M.; Rampon, C.; Delatour, B. Impaired neurogenesis, neuronal loss, and brain functional deficits in the APPxPS1-Ki mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filali, M.; Lalonde, R.; Rivest, S. Anomalies in social behaviors and exploratory activities in an APPswe/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djelti, F.; Braudeau, J.; Hudry, E.; Dhenain, M.; Varin, J.; Bièche, I.; Marquer, C.; Chali, F.; Ayciriex, S.; Auzeil, N.; et al. CYP46A1 inhibition, brain cholesterol accumulation and neurodegeneration pave the way for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2015, 138, 2383–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruthirakuhan, M.; Herrmann, N.; Vieira, D.; Gallagher, D.; Lanctôt, K.L. The roles of apathy and depression in predicting Alzheimer Disease: A longitudinal analysis in older adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2019, 27, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawas, C.H.; Corrada, M.M.; Brookmeyer, R.; Morrison, A.; Resnick, S.M.; Zonderman, A.B.; Arenberg, D. Visual memory predicts Alzheimer’s disease more than a decade before diagnosis. Neurology 2003, 60, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, H. Memory loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Pertzov, Y.; Nicholas, J.M.; Henley, S.M.D.; Crutch, S.; Woodward, F.; Leung, K.; Fox, N.C.; Husain, M. Visual short-term memory binding deficit in familial Alzheimer’s disease. Cortex 2016, 78, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Didic, M.; Felician, O.; Barbeau, E.J.; Mancini, J.; Latger-Florence, C.; Tramoni, E.; Ceccaldi, M. Impaired visual recognition memory predicts Alzheimer’s disease in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 35, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirova, A.M.; Bays, R.B.; Lagalwar, S. Working memory and executive function decline across normal aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 748212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.M.; Lu, D.; Liu, L.P.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhou, Y.Y. Olfactory dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Starkstein, S.E.; Jorge, R.; Mizrahi, R.; Robinson, R.G. A prospective longitudinal study of apathy in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nobis, L.; Husain, M. Apathy in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2018, 22, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyketsos, C.G.; Carrillo, M.C.; Ryan, J.M.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Trzepacz, P.; Amatniek, J.; Cedarbaum, J.; Brashear, R.; Miller, D.S. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.C.; Liu, C.C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LaDu, M.J.; Falduto, M.T.; Manelli, A.M.; Reardon, C.A.; Getz, G.S.; Frail, D.E. Isoform-specific binding of apolipoprotein E to beta-amyloid. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23403–23406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bales, K.R.; Du, Y.; Holtzman, D.; Cordell, B.; Paul, S.M. Neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease: Critical roles for cytokine/Abeta-induced glial activation, NF-kappaB, and apolipoprotein E. Neurobiol. Aging. 2000, 21, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, A.; Gmeiner, B.; Hüttinger, M. Implication of apoE isoforms in cholesterol metabolism by primary rat hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. Biochimie 2006, 88, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.C.; Mace, B.E.; Moore, S.D.; Sullivan, P.M. Progressive loss of synaptic integrity in human apolipoprotein E4 targeted replacement mice and attenuation by apolipoprotein E2. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sen, A.; Alkon, D.L.; Nelson, T.J. Apolipoprotein E3 (ApoE3) but not ApoE4 protects against synaptic loss through increased expression of protein kinase C epsilon. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15947–15958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. Selective Loss of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Exacerbates Brain Injury by Enhancing Neuroinflammation in Experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae Meningitis. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, K.S. Microglial involvement in the development of olfactory dysfunction. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 19, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhaj, N.; Desor, F.; Gleizes, C.; Denis, F.M.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Soulimani, R.; Linder, M. Anxiolytic-like effect of a salmon phospholipopeptidic complex composed of polyunsaturated fatty acids and bioactive peptides. Mar. Drugs. 2013, 11, 4294–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misslin, R.; Ropartz, P. Effects of lateral amygdala lesions on the responses to novelty in mice. Behav. Processes. 1981, 6, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhabazi, K.; Dicko, A.; Desor, F.; Dalal, A.; Younos, C.; Soulimani, R. Preliminary study on immunological and behavioural effects of Thymus broussonetii Boiss., an endemic species in Morocco. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 103, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, S.M.; Tetreault, N.A.; Mulligan, C.K.; Hutson, C.B.; Masliah, E.; Chesselet, M.F. Olfactory deficits in mice overexpressing human wildtype alpha-synuclein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Crawley, J.N. Simple behavioral assessment of mouse olfaction. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2009, 8, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, N.; Raynaud, A.; Le Bourhis, M.; Grébert, D.; Dewaele, A.; Acquistapace, A.; Bombail, V. The olfactory mucosa, first actor of olfactory detection, is sensitive to glucocorticoid hormone. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 51, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leger, M.; Quiedeville, A.; Bouet, V.; Haelewyn, B.; Boulouard, M.; Schumann-Bard, P.; Freret, T. Object recognition test in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2531–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.C.; Scearce-Levie, K.; Sheng, M. Characterization of social behaviors in caspase-3 deficient mice. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 18335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.A. Memory deficits associated with senescence: A neurophysiological and behavioral study in the rat. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1979, 93, 74–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, J.; Ellenbroek, B.A.; van Eck, I.; Roubos, S.; Verhage, M.; Stiedl, O. Finding the right motivation: Genotype-dependent differences in effective reinforcements for spatial learning. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 226, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boda, E.; Pini, A.; Hoxha, E.; Parolisi, R.; Tempia, F. Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR studies in mouse brain. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2009, 37, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆Ct method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Abca1 | CAACCCCTGCTTCCGTTATCCAA | GAGAACAGGCGAGACACGATGGAC |
| BDNF C3 Cyp46a1 | TGGCCTAACAGTGTTTGCAG AGAGGCAAGTGCTGACCAGT GGCTAAGAAGT TGGTCCTGTTGTAAGA | TGTCAGCTCCACTTAGCCTC ACTGGCTGGAATCTTGATGG GGTGGACATCAGGAACTTCTTGACT |
| EEF2 EIF3F Hmgcr | GTGGTGGACTGTGTGTCTGG CATCAAGGCCTATGTCAGCA CCCCACATTCACTCTTGACGCTCT | CGCTGGAAGGTCTGGTAGAG AGGTCAACTCCAATGCGTTC GCTGGCGGACGCCTGACAT |
| Hprt | TCAGACTGAAGAGCTACTGTAATGATCA | AAAGTTGAGAGATCATCTCCACCAA |
| Lsr (total) | AGTAATACACTCCACTGTCTCCCCAG | CAGGAGAATCACCATCACAGGAA |
| Lsr α | AAGATCTGGATGGGAACAACGAG | CTTCTGAGGTCCTGCCAAGG |
| Lsr α’ | AAGATCTGGATGGGAACAACGAG | CAAAGAGCCAATCAAGGACAATG |
| Lsr β | AAGATCTGGATGGGAACAACGAG | CCAGCAGCATAAACAAGGACAAT |
| Pgk1 | GAGCCTCACTGTCCAAACTA | CTTTAGCGCCTCCCAAGATA |
| PPIA Srebpf1 S100β | GTCTCCTTCGAGCTGTTTGC GGTCCAGCAGGTCCCAGTTGT AACGAGCTCTCTCACTTCCT | GCGTGTAAAGTCACCACCCT CTGCAGTCTTCACGGTGGCTC AAAGAACTCATGGCAGGCCG |
| Tfrc | GTCTTCTGTTGAAACTTGCCCA | GAAAGGTATCCCTCCAACCACTC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Hajj, A.; Herzine, A.; Calcagno, G.; Désor, F.; Djelti, F.; Bombail, V.; Denis, I.; Oster, T.; Malaplate, C.; Vigier, M.; et al. Targeted Suppression of Lipoprotein Receptor LSR in Astrocytes Leads to Olfactory and Memory Deficits in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042049
El Hajj A, Herzine A, Calcagno G, Désor F, Djelti F, Bombail V, Denis I, Oster T, Malaplate C, Vigier M, et al. Targeted Suppression of Lipoprotein Receptor LSR in Astrocytes Leads to Olfactory and Memory Deficits in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(4):2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042049
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Hajj, Aseel, Ameziane Herzine, Gaetano Calcagno, Frédéric Désor, Fathia Djelti, Vincent Bombail, Isabelle Denis, Thierry Oster, Catherine Malaplate, Maxime Vigier, and et al. 2022. "Targeted Suppression of Lipoprotein Receptor LSR in Astrocytes Leads to Olfactory and Memory Deficits in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 4: 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042049
APA StyleEl Hajj, A., Herzine, A., Calcagno, G., Désor, F., Djelti, F., Bombail, V., Denis, I., Oster, T., Malaplate, C., Vigier, M., Kaminski, S., Pauron, L., Corbier, C., Yen, F. T., Lanhers, M.-C., & Claudepierre, T. (2022). Targeted Suppression of Lipoprotein Receptor LSR in Astrocytes Leads to Olfactory and Memory Deficits in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(4), 2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042049







