Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms of Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (SSADHD): Towards the Development of SSADH-Targeted Medicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
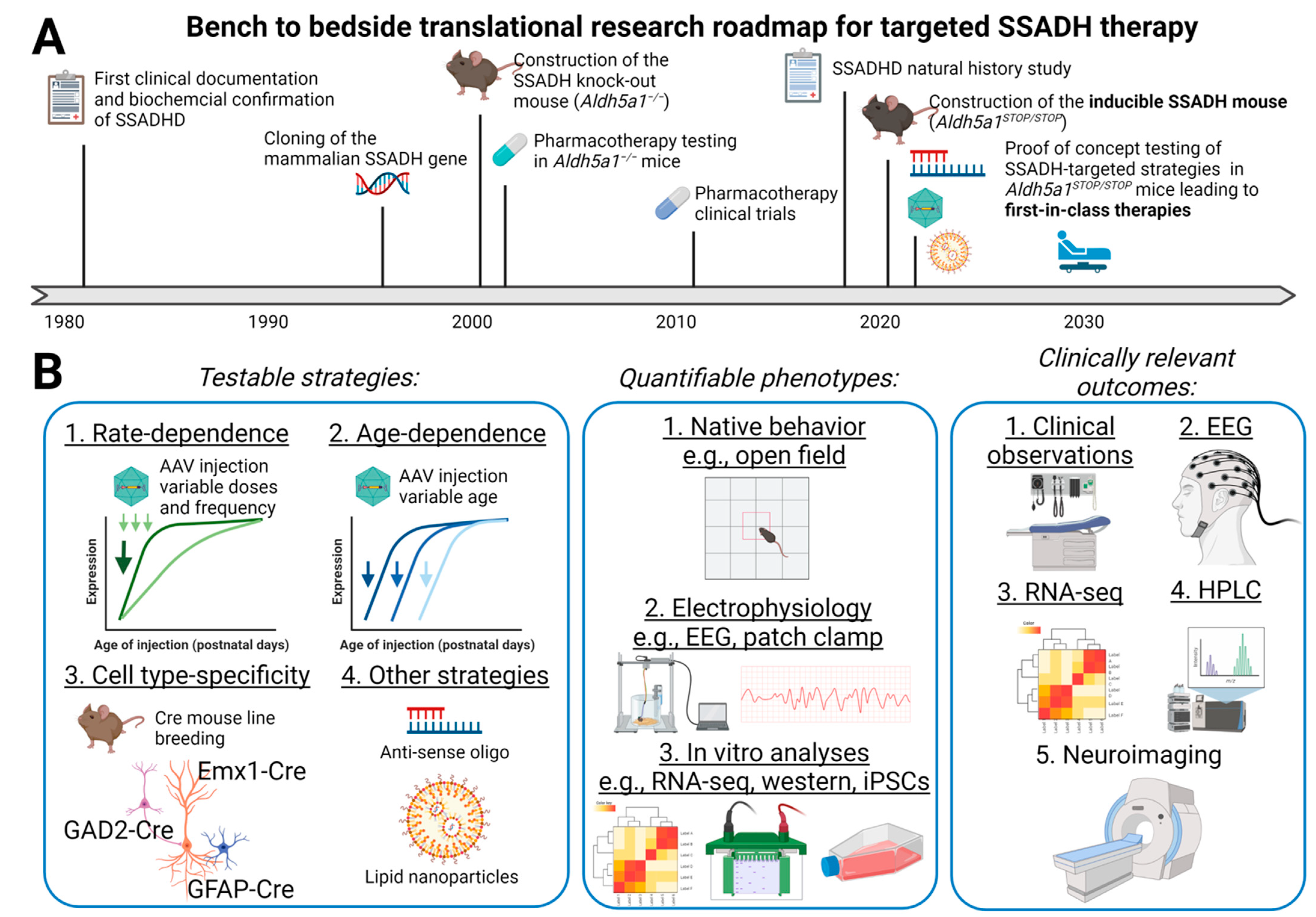
2. A Brief History and Update on SSADHD Research
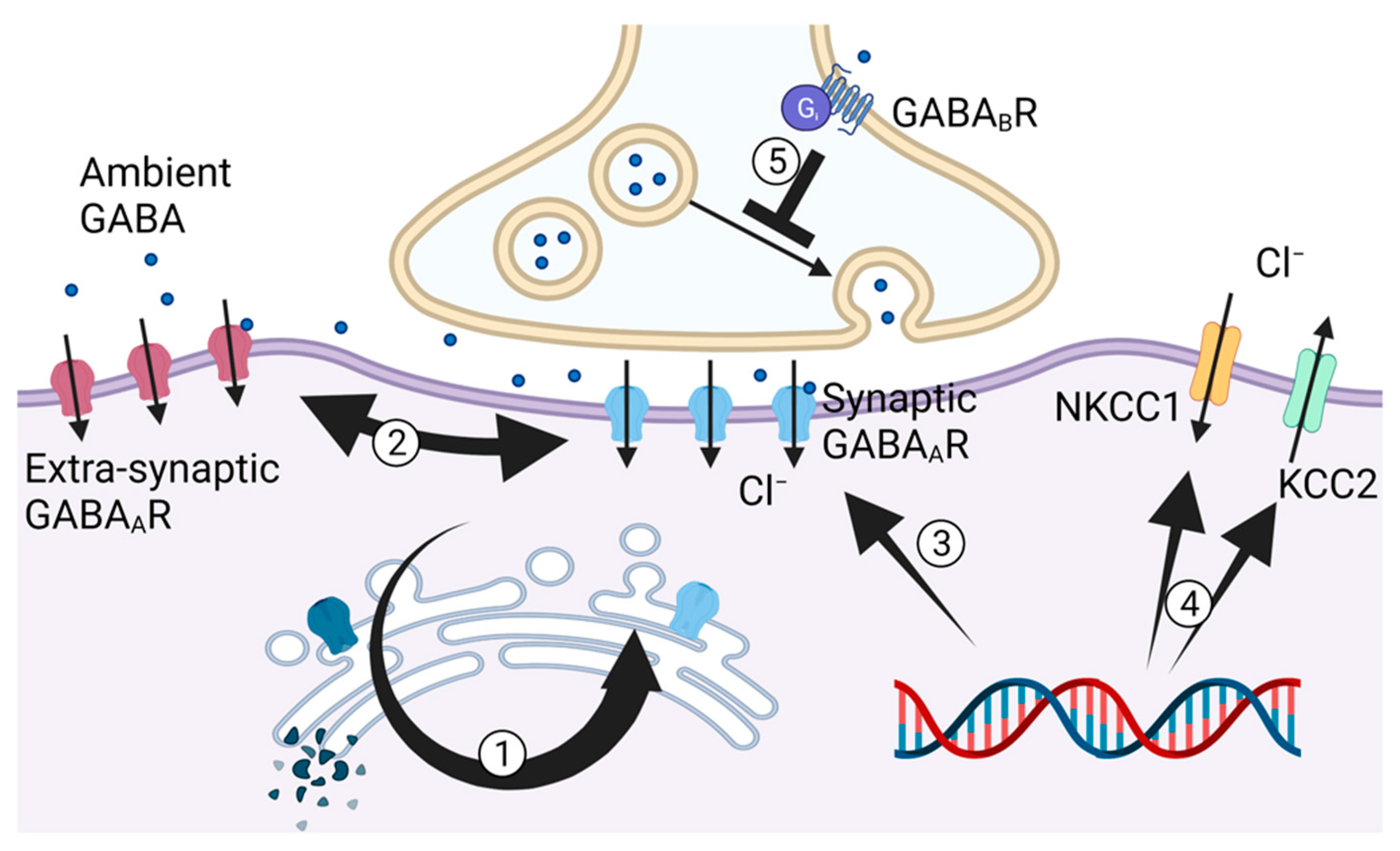
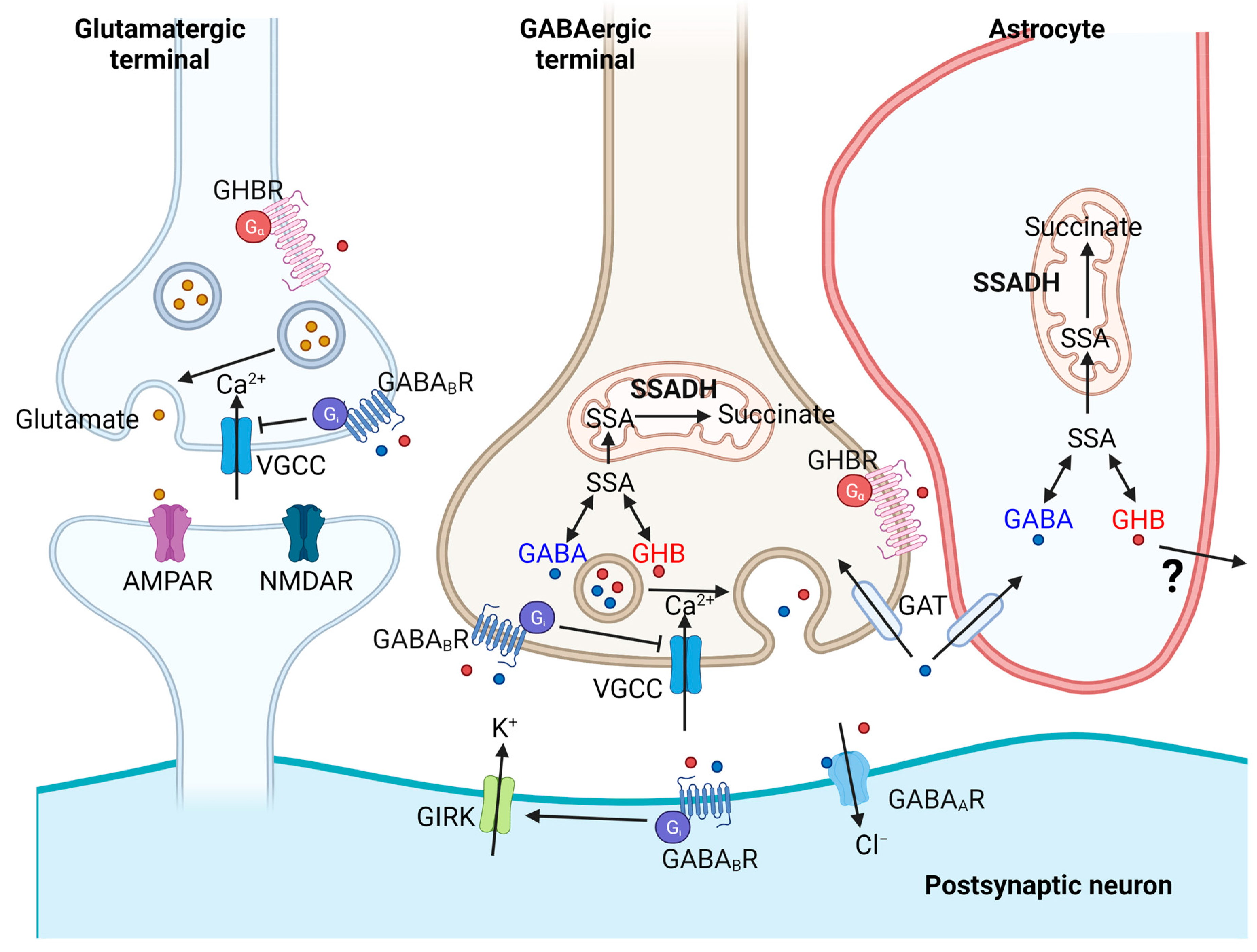
3. GABA, Chloride Homeostasis and GHB Signaling in Neuronal Inhibitory Control
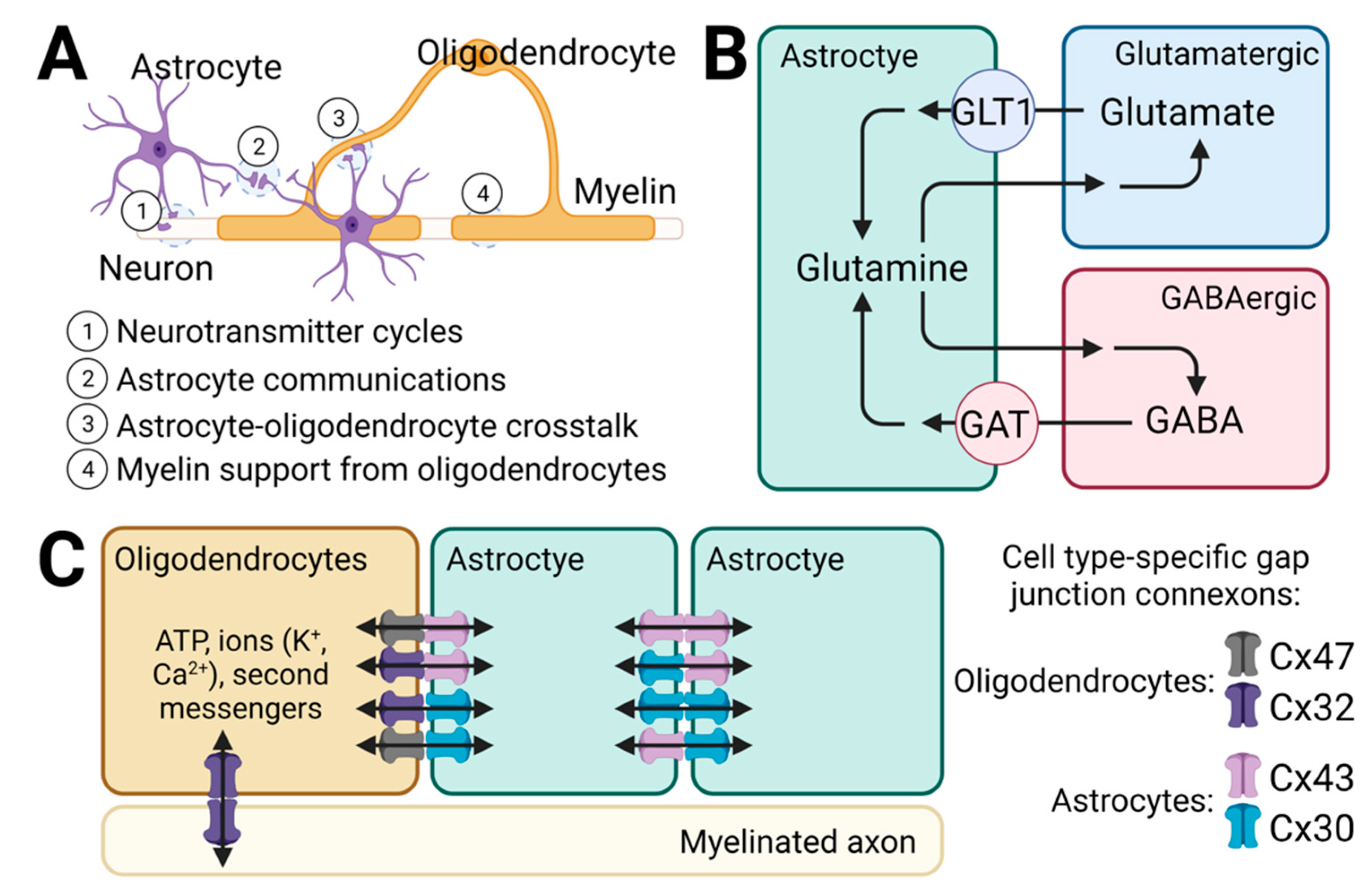
4. Astrocyte and Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in SSADHD
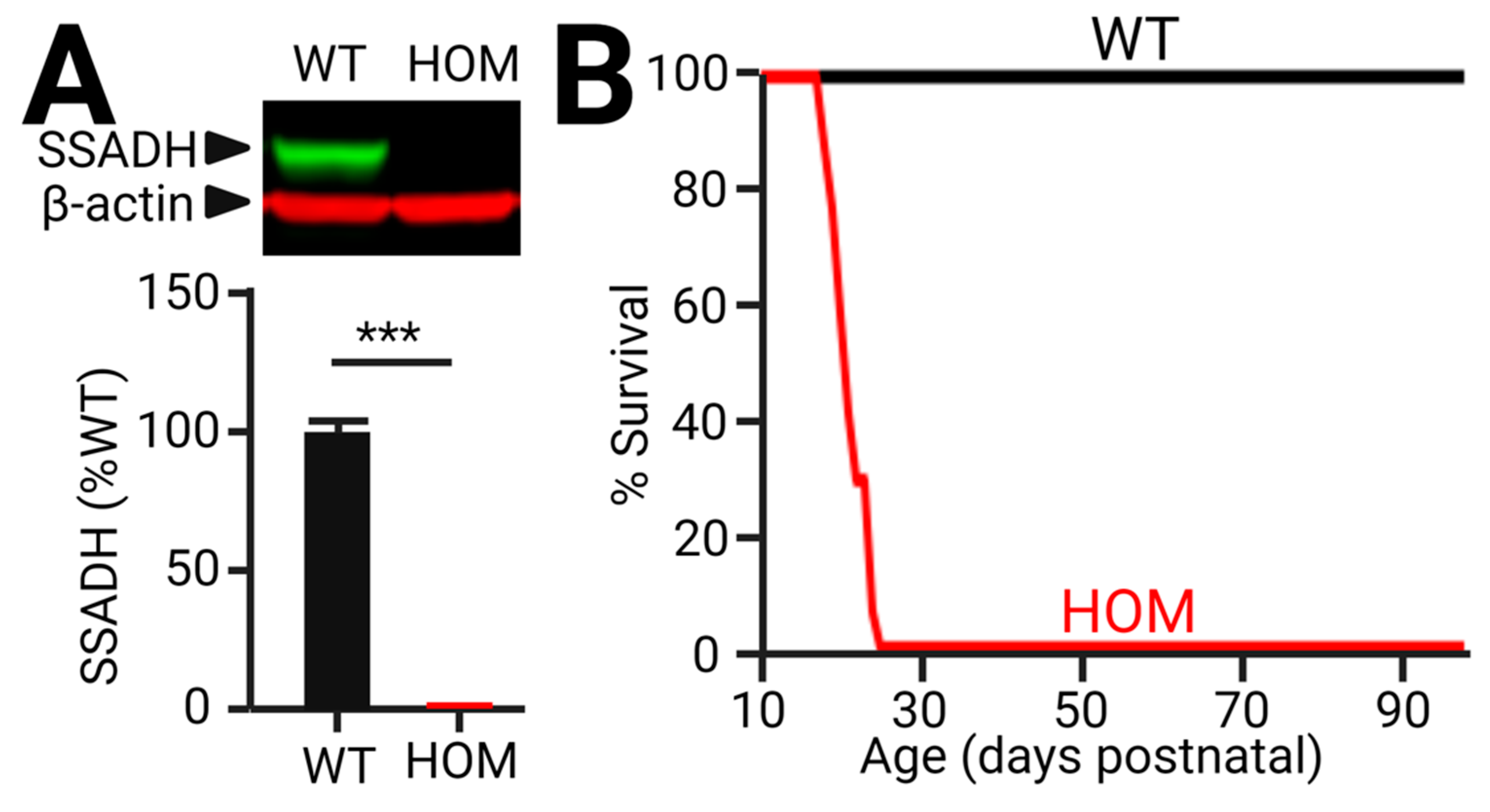
5. The Novel SSADHD Mouse Model, aldh5a1STOP/STOP
6. Concluding Remarks
7. Materials and Methods
7.1. Animal Use and Institutional Assurance
7.2. Western Blot Analyses
7.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jakobs, C.; Bojasch, M.; Monch, E.; Rating, D.; Siemes, H.; Hanefeld, F. Urinary excretion of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in a patient with neurological abnormalities. The probability of a new inborn error of metabolism. Clin. Chim. Acta 1981, 111, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, K.M.; Sweetman, L.; Nyhan, W.L.; Jakobs, C.; Rating, D.; Siemes, H.; Hanefeld, F. Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency: An inborn error of gamma-aminobutyric acid metabolism. Clin. Chim. Acta 1983, 133, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, K.M.; Baumann, C.; Ogier, H.; Rossier, E.; Vollmer, B.; Jakobs, C. Pre- and postnatal diagnosis of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency using enzyme and metabolite assays. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1994, 17, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernocchi, G.; Barni, S.; Biggiogera, M. Electron-cytochemical localization of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity in Purkinje neurons and hepatocytes of the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1986, 17, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambliss, K.L.; Caudle, D.L.; Hinson, D.D.; Moomaw, C.R.; Slaughter, C.A.; Jakobs, C.; Gibson, K.M. Molecular cloning of the mature NAD(+)-dependent succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase from rat and human. cDNA isolation, evolutionary homology, and tissue expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, T.; Kajita, M.; Sekido, Y.; Ishiguro, Y.; Tsuge, I.; Kimura, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Watanabe, K.; Shimokata, K.; Niwa, T. Mutation analysis in a patient with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency: A compound heterozygote with 103-121del and 1460T > A of the ALDH5A1 gene. Hum. Hered. 2002, 53, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaboshi, S.; Hogema, B.M.; Novelletto, A.; Malaspina, P.; Salomons, G.S.; Maropoulos, G.D.; Jakobs, C.; Grompe, M.; Gibson, K.M. Mutational spectrum of the succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH5A1) gene and functional analysis of 27 novel disease-causing mutations in patients with SSADH deficiency. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 22, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Kong, X.D.; Kan, Q.C.; Shi, H.R.; Wu, Q.H.; Zhuo, Z.H.; Bai, Q.L.; Jiang, M. Mutation analysis and prenatal diagnosis in a Chinese family with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase and a systematic review of the literature of reported ALDH5A1 mutations. J. Perinat. Med. 2016, 44, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, S.; Capo, C.; Ciminelli, B.M.; Iacovelli, F.; Menduti, G.; Funghini, S.; Donati, M.A.; Falconi, M.; Rossi, L.; Malaspina, P. SSADH deficiency in an Italian family: A novel ALDH5A1 gene mutation affecting the succinic semialdehyde substrate binding site. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Lin, Y.T.; Jiang, M.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Li, D.; Hu, H.; Liu, L. Novel mutations in a Chinese family with two patients with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2020, 36, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBacco, M.L.; Pop, A.; Salomons, G.S.; Hanson, E.; Roullet, J.B.; Gibson, K.M.; Pearl, P.L. Novel ALDH5A1 variants and genotype: Phenotype correlation in SSADH deficiency. Neurology 2020, 95, e2675–e2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, P.L.; Wiwattanadittakul, N.; Roullet, J.B.; Gibson, K.M. Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, K.M.; Christensen, E.; Jakobs, C.; Fowler, B.; Clarke, M.A.; Hammersen, G.; Raab, K.; Kobori, J.; Moosa, A.; Vollmer, B.; et al. The clinical phenotype of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (4-hydroxybutyric aciduria): Case reports of 23 new patients. Pediatrics 1997, 99, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, P.L.; Gibson, K.M.; Acosta, M.T.; Vezina, L.G.; Theodore, W.H.; Rogawski, M.A.; Novotny, E.J.; Gropman, A.; Conry, J.A.; Berry, G.T.; et al. Clinical spectrum of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Neurology 2003, 60, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knerr, I.; Gibson, K.M.; Jakobs, C.; Pearl, P.L. Neuropsychiatric morbidity in adolescent and adult succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency patients. CNS Spectr. 2008, 13, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, K.M.; Gupta, M.; Pearl, P.L.; Tuchman, M.; Vezina, L.G.; Snead, O.C., III; Smit, L.M.; Jakobs, C. Significant behavioral disturbances in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH) deficiency (gamma-hydroxybutyric aciduria). Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, P.L.; Shukla, L.; Theodore, W.H.; Jakobs, C.; Michael Gibson, K. Epilepsy in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency, a disorder of GABA metabolism. Brain Dev. 2011, 33, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBacco, M.L.; Roullet, J.B.; Kapur, K.; Brown, M.N.; Walters, D.C.; Gibson, K.M.; Pearl, P.L. Age-related phenotype and biomarker changes in SSADH deficiency. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, D.C.; Lawrence, R.; Kirby, T.; Ahrendsen, J.T.; Anderson, M.P.; Roullet, J.B.; Murphy, E.J.; Gibson, K.M.; Consortium, S.D.I. Postmortem Analyses in a Patient With Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (SSADHD): II. Histological, Lipid, and Gene Expression Outcomes in Regional Brain Tissue. J. Child Neurol. 2021, 36, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogema, B.M.; Akaboshi, S.; Taylor, M.; Salomons, G.S.; Jakobs, C.; Schutgens, R.B.; Wilcken, B.; Worthington, S.; Maropoulos, G.; Grompe, M.; et al. Prenatal diagnosis of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency: Increased accuracy employing DNA, enzyme, and metabolite analyses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2001, 72, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropman, A. Vigabatrin and newer interventions in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54 (Suppl. S6), S66–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergezinger, K.; Jeschke, R.; Frauendienst-Egger, G.; Korall, H.; Gibson, K.M.; Schuster, V.H. Monitoring of 4-hydroxybutyric acid levels in body fluids during vigabatrin treatment in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matern, D.; Lehnert, W.; Gibson, K.M.; Korinthenberg, R. Seizures in a boy with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency treated with vigabatrin (gamma-vinyl-GABA). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1996, 19, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanadia, E.; Gibson, K.M.; Pearl, P.L.; Trapolino, E.; Mangano, S.; Vanadia, F. Therapeutic efficacy of magnesium valproate in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. JIMD Rep. 2013, 8, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kratz, S.V. Sensory integration intervention: Historical concepts, treatment strategies and clinical experiences in three patients with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH) deficiency. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2009, 32, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, K.R.; Pearl, P.L.; Theodore, W.H.; McCarter, R.C.; Jakobs, C.; Gibson, K.M. Thirty years beyond discovery--clinical trials in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency, a disorder of GABA metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogema, B.M.; Gupta, M.; Senephansiri, H.; Burlingame, T.G.; Taylor, M.; Jakobs, C.; Schutgens, R.B.; Froestl, W.; Snead, O.C.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; et al. Pharmacologic rescue of lethal seizures in mice deficient in succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Wu, Y.; Gibson, K.M.; Snead, O.C., III. Absence seizures in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficient mice: A model of juvenile absence epilepsy. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 79, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, K.M.; Jakobs, C.; Pearl, P.L.; Snead, O.C. Murine succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH) deficiency, a heritable disorder of GABA metabolism with epileptic phenotype. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, L.S.; Nylen, K.J.; Persinger, M.A.; Cortez, M.A.; Gibson, K.M.; Snead, O.C., III. Circadian distribution of generalized tonic-clonic seizures associated with murine succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency, a disorder of GABA metabolism. Epilepsy Behav. 2008, 13, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Greven, R.; Jansen, E.E.; Jakobs, C.; Hogema, B.M.; Froestl, W.; Snead, O.C.; Bartels, H.; Grompe, M.; Gibson, K.M. Therapeutic intervention in mice deficient for succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (gamma-hydroxybutyric aciduria). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.R.; Ainslie, G.R.; McConnell, A.; Roullet, J.B.; Gibson, K.M. Toxicologic/transport properties of NCS-382, a gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) receptor ligand, in neuronal and epithelial cells: Therapeutic implications for SSADH deficiency, a GABA metabolic disorder. Toxicol. In Vitr. 2018, 46, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, K.R.; Ainslie, G.R.; Gibson, K.M. mTOR inhibitors rescue premature lethality and attenuate dysregulation of GABAergic/glutamatergic transcription in murine succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (SSADHD), a disorder of GABA metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, K.R.; Ainslie, G.R.; Jansen, E.E.; Salomons, G.S.; Gibson, K.M. Torin 1 partially corrects vigabatrin-induced mitochondrial increase in mouse. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylen, K.; Velazquez, J.L.; Likhodii, S.S.; Cortez, M.A.; Shen, L.; Leshchenko, Y.; Adeli, K.; Gibson, K.M.; Burnham, W.M.; Snead, O.C., III. A ketogenic diet rescues the murine succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficient phenotype. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nylen, K.; Velazquez, J.L.; Sayed, V.; Gibson, K.M.; Burnham, W.M.; Snead, O.C., III. The effects of a ketogenic diet on ATP concentrations and the number of hippocampal mitochondria in Aldh5a1(−/−) mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, P.L.; Schreiber, J.; Theodore, W.H.; McCarter, R.; Barrios, E.S.; Yu, J.; Wiggs, E.; He, J.; Gibson, K.M. Taurine trial in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency and elevated CNS GABA. Neurology 2014, 82, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, J.M.; Pearl, P.L.; Dustin, I.; Wiggs, E.; Barrios, E.; Wassermann, E.M.; Gibson, K.M.; Theodore, W.H. Biomarkers in a Taurine Trial for Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency. JIMD Rep. 2016, 30, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, J.M.; Wiggs, E.; Cuento, R.; Norato, G.; Dustin, I.H.; Rolinski, R.; Austermuehle, A.; Zhou, X.; Inati, S.K.; Gibson, K.M.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of SGS-742, a gamma-aminobutyric acid B (GABA-B) Receptor Antagonist, for Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency. J. Child Neurol. 2021, 36, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Jansen, E.E.; Senephansiri, H.; Jakobs, C.; Snead, O.C.; Grompe, M.; Gibson, K.M. Liver-directed adenoviral gene transfer in murine succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.R.; Ainslie, G.R.; Walters, D.C.; McConnell, A.; Dhamne, S.C.; Rotenberg, A.; Roullet, J.B.; Gibson, K.M. Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency, a disorder of GABA metabolism: An update on pharmacological and enzyme-replacement therapeutic strategies. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulaklak, K.; Gersbach, C.A. The once and future gene therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, J.S. Best hope or broken promise? After a decade, gene therapy goes on trial. US News World Rep. 2000, 128, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Papanikolaou, E.; Bosio, A. The Promise and the Hope of Gene Therapy. Front. Genome Ed. 2021, 3, 618346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connock, M.; Juarez-Garcia, A.; Frew, E.; Mans, A.; Dretzke, J.; Fry-Smith, A.; Moore, D. A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapies for Fabry’s disease and mucopolysaccharidosis type 1. Health Technol. Assess. 2006, 10, iii–iv, ix–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safary, A.; Akbarzadeh Khiavi, M.; Mousavi, R.; Barar, J.; Rafi, M.A. Enzyme replacement therapies: What is the best option? Bioimpacts 2018, 8, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, P.L.; DiBacco, M.L.; Papadelis, C.; Opladen, T.; Hanson, E.; Roullet, J.B.; Gibson, K.M. Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency: Review of the Natural History Study. J. Child Neurol. 2021, 36, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.H.C.; Pearl, P.L.; Rotenberg, A. Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency: Relevance in gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Plasticity. J. Child Neurol. 2021, 36, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevot, T.; Sibille, E. Altered GABA-mediated information processing and cognitive dysfunctions in depression and other brain disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Q.; Barberis, A.; Higley, M.J. Preserving the balance: Diverse forms of long-term GABAergic synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, K.K.; Larsson, O.M.; Schousboe, A. Regulation of excitation by GABA neurotransmission: Focus on metabolism and transport. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2008, 44, 201–221. [Google Scholar]
- Mohler, H. GABA(A) receptor diversity and pharmacology. Cell Tissue Res. 2006, 326, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terunuma, M. Diversity of structure and function of GABAB receptors: A complexity of GABAB-mediated signaling. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2018, 94, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, T.C.; Moss, S.J.; Jurd, R. GABA(A) receptor trafficking and its role in the dynamic modulation of neuronal inhibition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tritsch, N.X.; Granger, A.J.; Sabatini, B.L. Mechanisms and functions of GABA co-release. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickley, S.G.; Mody, I. Extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors: Their function in the CNS and implications for disease. Neuron 2012, 73, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, M.; Dorovykh, V.; Thomas, P.; Smart, T.G. Physiological role for GABAA receptor desensitization in the induction of long-term potentiation at inhibitory synapses. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Kayal, A.R.; Russek, S.J. Regulation of GABAA Receptor Gene Expression and Epilepsy. In Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies, 4th ed.; Noebels, J.L., Avoli, M., Rogawski, M.A., Olsen, R.W., Delgado-Escueta, A.V., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann, M.; Bettler, B. Regulation of neuronal GABA(B) receptor functions by subunit composition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, M.; Costa, R.O.; Duarte, C.B. Alterations in GABAA-Receptor Trafficking and Synaptic Dysfunction in Brain Disorders. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.G.; Bottiglieri, T.; Snead, O.C., III. GABA, gamma-hydroxybutyric acid, and neurological disease. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54 (Suppl. S6), S3–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, E.E.; Vogel, K.R.; Salomons, G.S.; Pearl, P.L.; Roullet, J.B.; Gibson, K.M. Correlation of blood biomarkers with age informs pathomechanisms in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (SSADHD), a disorder of GABA metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afacan, O.; Yang, E.; Lin, A.P.; Coello, E.; DiBacco, M.L.; Pearl, P.L.; Warfield, S.K.; Consortium, S.D.I. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Spectroscopy in Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency. J. Child Neurol. 2021, 36, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboyama, M.; Liu, J.; Kaye, H.; DiBacco, M.; Pearl, P.L.; Rotenberg, A. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency: A Measure of Maturational Trajectory of Cortical Excitability. J. Child Neurol. 2021, 36, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, P.L.; Gibson, K.M.; Quezado, Z.; Dustin, I.; Taylor, J.; Trzcinski, S.; Schreiber, J.; Forester, K.; Reeves-Tyer, P.; Liew, C.; et al. Decreased GABA-A binding on FMZ-PET in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Neurology 2009, 73, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ari, Y.; Khalilov, I.; Kahle, K.T.; Cherubini, E. The GABA excitatory/inhibitory shift in brain maturation and neurological disorders. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 467–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Deeb, T.Z.; Walker, J.A.; Davies, P.A.; Moss, S.J. NMDA receptor activity downregulates KCC2 resulting in depolarizing GABAA receptor-mediated currents. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, R.; Van Hout, M.C. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB): A scoping review of pharmacology, toxicology, motives for use, and user groups. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2014, 46, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Wei, Y.D.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.X. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) for narcolepsy in adults: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2019, 64, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitre, M. The gamma-hydroxybutyrate signalling system in brain: Organization and functional implications. Prog. Neurobiol. 1997, 51, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, K.M.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Hodson, A.K.; Bottiglieri, T.; Jakobs, C. 4-Hydroxybutyric acid and the clinical phenotype of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency, an inborn error of GABA metabolism. Neuropediatrics 1998, 29, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamampandry, C.; Taleb, O.; Viry, S.; Muller, C.; Humbert, J.P.; Gobaille, S.; Aunis, D.; Maitre, M. Cloning and characterization of a rat brain receptor that binds the endogenous neuromodulator gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB). FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1691–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absalom, N.; Eghorn, L.F.; Villumsen, I.S.; Karim, N.; Bay, T.; Olsen, J.V.; Knudsen, G.M.; Brauner-Osborne, H.; Frolund, B.; Clausen, R.P.; et al. alpha4betadelta GABA(A) receptors are high-affinity targets for gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13404–13409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, T.; Antal, K.; Nyitrai, G.; Emri, Z. gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB) induces GABA(B) receptor independent intracellular Ca2+ transients in astrocytes, but has no effect on GHB or GABA(B) receptors of medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bay, T.; Eghorn, L.F.; Klein, A.B.; Wellendorph, P. GHB receptor targets in the CNS: Focus on high-affinity binding sites. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snead, O.C., III. Evidence for a G protein-coupled gamma-hydroxybutyric acid receptor. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.K.; Snead, O.C., III. Presynaptic gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and gamma-aminobutyric acidB (GABAB) receptor-mediated release of GABA and glutamate (GLU) in rat thalamic ventrobasal nucleus (VB): A possible mechanism for the generation of absence-like seizures induced by GHB. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 273, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, S.G.; Feigenbaum, J.J. Effect of gamma-hydroxybutyrate on central dopamine release in vivo. A microdialysis study in awake and anesthetized animals. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997, 53, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenbaum, J.J.; Howard, S.G. Does gamma-hydroxybutyrate inhibit or stimulate central DA release? Int. J. Neurosci. 1996, 88, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.J.; Eroglu, C. Cell Biology of Astrocyte-Synapse Interactions. Neuron 2017, 96, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarillo, E.; Rizor, A.; Lee, J.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for neurotherapeutics. Neuropharmacology 2019, 161, 107559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schousboe, A.; Bak, L.K.; Waagepetersen, H.S. Astrocytic Control of Biosynthesis and Turnover of the Neurotransmitters Glutamate and GABA. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, M.J.; Gomez, T.M.; Puglielli, L. Glial Cell-Axonal Growth Cone Interactions in Neurodevelopment and Regeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J.; Ronnback, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Kumar, T.P.; Joshee, S.; Kirschestein, T.; Subburaju, S.; Khalili, J.S.; Du, C.; Elkhal, A.; Szabó, G.; Jain, R.K.; et al. Endothelial cell-derived GABA signaling modulates neuronal migration and postnatal behavior. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoog, Q.P.; Holtman, L.; Aronica, E.; van Vliet, E.A. Astrocytes as Guardians of Neuronal Excitability: Mechanisms Underlying Epileptogenesis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 591690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, D.A.; Steinhauser, C. Role of astrocytes in epilepsy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a022434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Yang, T.; Cui, S.; Chen, G. Connexin Hemichannels in Astrocytes: Role in CNS Disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, D.A.; Paul, D.L. Gap junctions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a002576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froes, M.M.; Correia, A.H.; Garcia-Abreu, J.; Spray, D.C.; Campos de Carvalho, A.C.; Neto, M.V. Gap-junctional coupling between neurons and astrocytes in primary central nervous system cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7541–7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallraff, A.; Kohling, R.; Heinemann, U.; Theis, M.; Willecke, K.; Steinhauser, C. The impact of astrocytic gap junctional coupling on potassium buffering in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5438–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, D.K.; Vargas, J.R.; Wilcox, K.S. Increased coupling and altered glutamate transport currents in astrocytes following kainic-acid-induced status epilepticus. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.V.; Contreras, J.E.; Bukauskas, F.F.; Saez, J.C. New roles for astrocytes: Gap junction hemichannels have something to communicate. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, S.; Gritti, L.; Crooks, D.; Dombrowski, Y. Oligodendrocytes in Development, Myelin Generation and Beyond. Cells 2019, 8, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benamer, N.; Vidal, M.; Balia, M.; Angulo, M.C. Myelination of parvalbumin interneurons shapes the function of cortical sensory inhibitory circuits. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wang, J.Y.; Gu, R.; Qu, H.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Liu, R.; Yuan, P. The relationship between the occurrence of intractable epilepsy with glial cells and myelin sheath—An experimental study. Eur Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4516–4524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nualart-Marti, A.; Solsona, C.; Fields, R.D. Gap junction communication in myelinating glia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, G.M.; Gupta, M.; Gibson, K.M.; Patel, A.B.; Behar, K.L. Altered cerebral glucose and acetate metabolism in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase-deficient mice: Evidence for glial dysfunction and reduced glutamate/glutamine cycling. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 2077–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donarum, E.A.; Stephan, D.A.; Larkin, K.; Murphy, E.J.; Gupta, M.; Senephansiri, H.; Switzer, R.C.; Pearl, P.L.; Snead, O.C.; Jakobs, C.; et al. Expression profiling reveals multiple myelin alterations in murine succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelo-Coblijn, G.; Murphy, E.J.; Mills, K.; Winchester, B.; Jakobs, C.; Snead, O.C., III; Gibson, K.M. Lipid abnormalities in succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (Aldh5a1−/-/-) −) deficient mouse brain provide additional evidence for myelin alterations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1772, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, M.; Polinsky, M.; Senephansiri, H.; Snead, O.C.; Jansen, E.E.; Jakobs, C.; Gibson, K.M. Seizure evolution and amino acid imbalances in murine succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH) deficiency. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 16, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; He, M.; Wu, P.; Kim, S.; Paik, R.; Sugino, K.; Kvitsiani, D.; Fu, Y.; Lu, J.; Lin, Y.; et al. A resource of Cre driver lines for genetic targeting of GABAergic neurons in cerebral cortex. Neuron 2011, 71, 995–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorski, J.A.; Talley, T.; Qiu, M.; Puelles, L.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Jones, K.R. Cortical excitatory neurons and glia, but not GABAergic neurons, are produced in the Emx1-expressing lineage. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6309–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorian, C.; Nakashima, J.; Le Belle, J.; Ohab, J.; Kim, R.; Liu, A.; Smith, K.B.; Groszer, M.; Garcia, A.D.; Sofroniew, M.V.; et al. Pten deletion in adult neural stem/progenitor cells enhances constitutive neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1874–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hegarty, S.; Winter, C.; Wang, F.; He, Z. Viral vectors for neuronal cell type-specific visualization and manipulations. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 63, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.Y.; Gan, X.X.; Feng, J.H.; Cai, W.S.; Wang, X.Q.; Shen, L.; Luo, H.T.; Chen, Z.; Guo, M.; Cao, J.; et al. ALDH5A1 acts as a tumour promoter and has a prognostic impact in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2021, 39, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hujber, Z.; Horvath, G.; Petovari, G.; Krencz, I.; Danko, T.; Meszaros, K.; Rajnai, H.; Szoboszlai, N.; Leenders, W.P.J.; Jeney, A.; et al. GABA, glutamine, glutamate oxidation and succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase expression in human gliomas. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, J.K.; Corey, D.R. Silencing disease genes in the laboratory and the clinic. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, C.M.; Anderson, C.B.; Howard, M.T. Antisense-induced ribosomal frameshifting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4302–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scioli Montoto, S.; Muraca, G.; Ruiz, M.E. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Pharmacological and Biopharmaceutical Aspects. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 587997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.H.C.; McGinty, G.E.; Pearl, P.L.; Rotenberg, A. Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms of Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (SSADHD): Towards the Development of SSADH-Targeted Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052606
Lee HHC, McGinty GE, Pearl PL, Rotenberg A. Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms of Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (SSADHD): Towards the Development of SSADH-Targeted Medicine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(5):2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052606
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Henry H. C., Gabrielle E. McGinty, Phillip L. Pearl, and Alexander Rotenberg. 2022. "Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms of Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (SSADHD): Towards the Development of SSADH-Targeted Medicine" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 5: 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052606
APA StyleLee, H. H. C., McGinty, G. E., Pearl, P. L., & Rotenberg, A. (2022). Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms of Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (SSADHD): Towards the Development of SSADH-Targeted Medicine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(5), 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052606






