Expression and Transcript Localization of star, sf-1, and dax-1 in the Early Brain of the Orange-Spotted Grouper Epinephelus coioides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Grouper Brain star, sf-1 and dax-1
2.2. q-PCR Analysis of sf-1 and dax-1 Transcripts in the Brain of Orange-Spotted Grouper during Developmental Ages
2.2.1. sf-1 mRNA Expression
2.2.2. dax-1 mRNA Expression
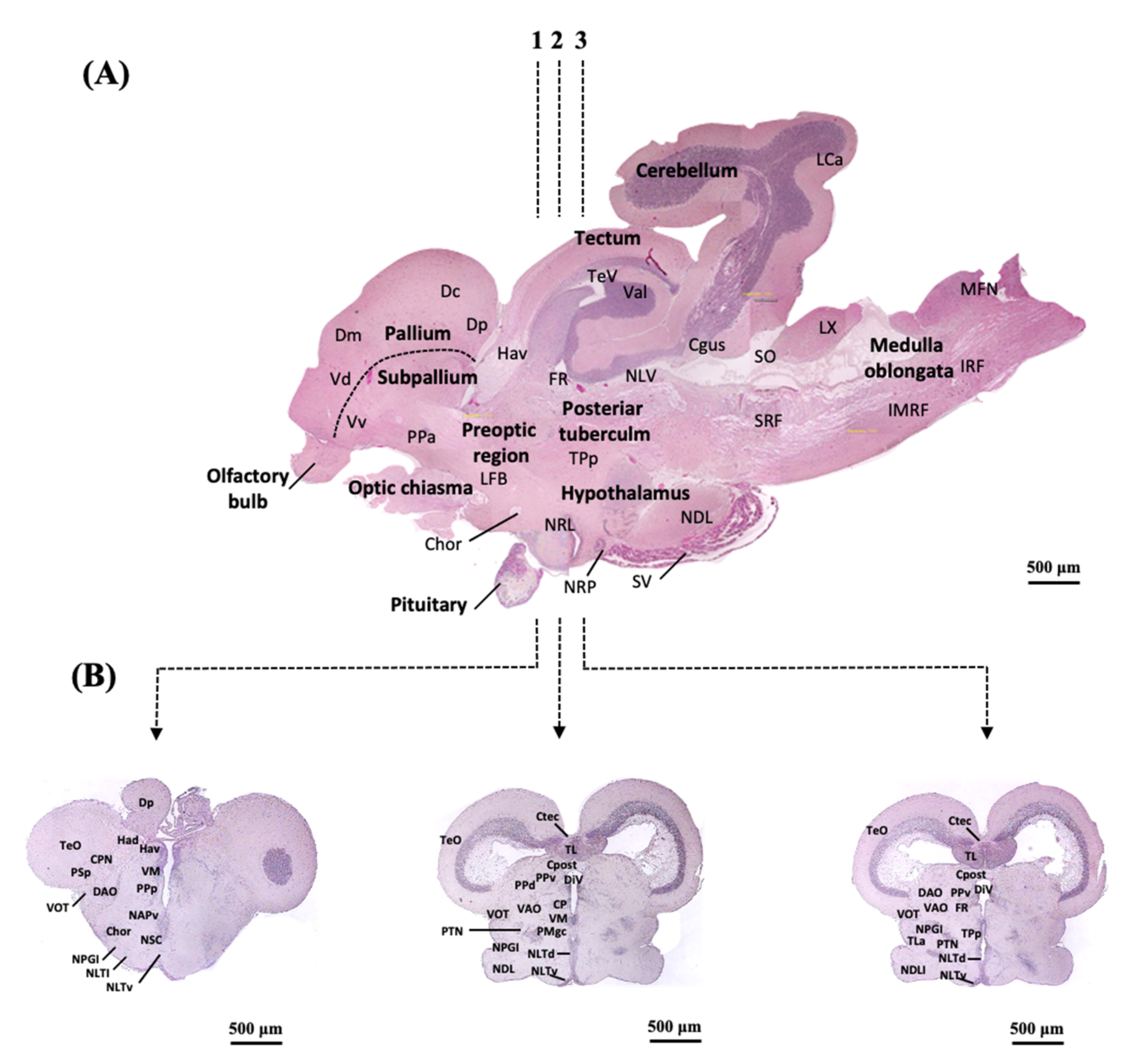
2.3. Localization of sf-1, dax-1 and star Transcripts in the Brain of the Protogynous Orange-Grouper during Different Stages of Developmental
2.4. Effect of E2 on star, sf-1 and dax-1 mRNA Expression in the Grouper Brain In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials & Methods
4.1. Experimental Fish
4.1.1. Experiment 1: Gene Expression Profiles during Gonadal Sex Differentiation
4.1.2. Experiment 2: Localization of sf-1, dax-1 and Star Gene Expression in the Hypothalamus of Orange-Spotted Grouper
4.1.3. Experiment 3: In Vivo Effects of E2 on the Expression of mRNAs Encoding sf-1, dax-1, and Star in the Brain of Grouper
4.2. RNA Extraction, First-Strand cDNA and Molecular Cloning of Genes in the Grouper Brain
4.3. Preparation of Brain Tissue for In Situ Hybridization
4.4. Synthesis of Star, sf-1 and dax-1 RNA Probes
4.5. In Situ Hybridization
4.6. Q-PCR Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plassart-Schiess, E.; Baulieu, E.E. Neurosteroids: Recent findings. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 37, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomy, S.; Wu, G.C.; Huang, H.R.; Dufour, S.; Chang, C.F. Developmental expression of key steroidogenic enzymes in the brain of protandrous black porgy fish Acanthopagrus Schlegeli. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2007, 19, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomy, S.; Wu, G.C.; Huang, H.R.; Chang, C.F. Age-dependent differential expression of genes involved in steroid signalling pathway in the brain of protandrous black porgy Acanthopagrus Schlegeli. Dev. Neurobiol. 2009, 69, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, G.; Tsai, Y.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, C.F. Developmental expression of genes involved in neural estrogen biosynthesis and signaling in the brain of the orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides during gonadal sex differentiation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, G.; Aruna, A.; Chang, C.F. Increase in estrogen signaling in the early brain of orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides: A mini-review. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 39, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, G.; Aruna, A.; Chang, C.F. Neurosteroidogenic enzymes and their regulation in the early brain of the protogynous grouper Epinephelus coioides during gonadal sex differentiation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 181, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizziano-Cantonnet, D.; Anglade, I.; Pellegrini, E.; Gueguen, M.M.; Fostier, A.; Guiguen, Y.; Kah, O. Sexual dimorphism in the brain aromatase expression and activity, and in the central expression of other steroidogenic enzymes during the period of sex differentiation in monosex rainbow trout populations. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 170, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotel, N.; Do Rego, J.L.; Anglade, I.; Vaillant, C.; Pellegrini, E.; Gueguen, M.M.; Mironov, S.; Vaudry, H.; Kah, O. Activity and expression of steroidogenic enzymes in the brain of adult zebrafish. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, D.M. The role of StAR protein in steroidogenesis: Challenges for the future. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 164, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.P.; Bridgham, J.T.; Langenau, D.M.; Johnson, A.L.; Goetz, F.W. Conservation of steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein structure and expression in vertebrates. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2000, 168, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrenberg, U.; Prange-Kiel, J.; Rune, G.M. Steroidogenic factor-1 expression in marmoset and rat hippocampus: Co-localization with StAR and aromatase. J. Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusakabe, M.; Todo, T.; McQuillan, H.J.; Goetz, F.W.; Young, G. Characterization and expression of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein and MLN64 cDNAs in trout. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arukwe, A. Modulation of brain steroidogenesis by affecting transcriptional changes of steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein and cholesterol side chain cleavage (P450scc) in juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) is a novel aspect of nonylphenol toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9791–9798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez, B.S.; Piermarini, P.M.; Evans, A.N.; Applebaum, S.L. Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding steroidogenic acute regulatory protein from freshwater stingrays (Potamotrygon spp.). J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 35, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kocerha, J.; Prucha, M.S.; Kroll, K.J.; Steinhilber, D.; Denslow, N. Regulation of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein transcription in largemouth bass by orphan nuclear receptor signaling pathways. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavorgna, G.; Ueda, H.; Clos, J.; Wu, C. FTZ-F1, a steroid hormone receptor-like protein implicated in the activation of fushi tarazu. Science 1991, 252, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.; Ramayya, M.S.; Chrousos, G.P.; Driggers, P.H.; Parker, K.L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human gene encoding steroidogenic factor 1. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 1996, 11, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingraham, H.A.; Lala, D.S.; Ikeda, Y.; Luo, X.; Shen, W.H.; Nachtigal, M.W.; Abbud, R.; Nilson, J.H.; Parker, K.L. The nuclear receptor SF-1 acts multiple levels of the reproductive axis. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 2302–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, K.L.; Rice, D.A.; Lala, D.S.; Ikeda, Y.; Luo, X.; Wong, M.; Bakke, M.; Zhao, L.; Frigeri, C.; Hanley, N.A.; et al. Steroidogenic factor 1: An essential mediator of endocrine development. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2002, 57, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.A.; Andrews, J.E.; Sinclair, A.H. Gonadal sex differentiation in chicken embryos: Expression of estrogen receptor and aromatase genes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 60, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, P.S.; Harry, J.L.; Marshall Graves, J.A.; Sinclair, A.H. Temperature dependent sex determination in the American alligator: Expression of SF1, WT1 and DAX1 during gonadogenesis. Gene 2000, 241, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, N.A.; Rainey, W.E.; Wilson, D.I.; Ball, S.G.; Parker, K.L. Expression profiles of SF-1, DAX1, and CYP17 in the human fetal adrenal gland: Potential interactions in gene regulation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Shikayama, T.; Mukai, T.; Hisano, S.; Morohashi, K.I. Comparative localization of Dax-1 and Ad4BP/SF-1 during development of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis suggests their closely related and distinct functions. Dev. Dyn. 2001, 220, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, O.; Takayama, K.; Imai, T.; Waterman, M.R.; Takakusu, A.; Omura, T.; Morohashi, K. Sex-dependent expression of a transcription factor, Ad4BP, regulating steroidogenic P-450 genes in the gonads during prenatal and postnatal rat development. Development 1994, 120, 2787–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.C.; Tomy, S.; Chang, C.F. The expression of nr0b1 and nr5a4 during gonad development and sex change in protandrous black porgy fish, Acanthopagrus Schlegeli. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Lu, H.; Sun, C.; Peng, Y.; Meng, F.; Gan, R.; Cui, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. Nr5a homologues in the ricefield eel Monopterus albus: Alternative splicing, tissue-specific expression, and differential roles on the activation of cyp19a1a promoter in vitro. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2021, 312, 113871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofsten, A.H.; Modig, C.; Larsson, A.; Karlsson, J.; Olsson, P.E. Determination of the expression pattern of the dual promoter of zebrafish fushi tarazu factor-1a following microinjections into zebrafish one cell stage embryos. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Shen, W.H.; Ingraham, H.A.; Parker, K.L. Developmental expression of mouse steroidogenic factor 1, an essential regulator of the steroid hydroxylases. Mol. Endocrinol. 1994, 8, 654–662. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, T.; Holt, J.A.; Kiriakidou, M.; Strauss, J.F., 3rd. Steroidogenic factor 1-dependent promoter activity of the human steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) gene. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 9052–9059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.C.; Hsu, N.C.; Pai, C.I.; Wang, C.K.; Chung, B. Functions of the upstream and proximal steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1)-binding sites in the CYP11A1 promoter in basal transcription and hormonal response. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leers-Sucheta, S.; Morohashi, K.; Mason, J.I.; Melner, M.H. Synergistic activation of the human type II 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ5-Δ4 isomerase promoter by the transcription factor steroidogenic factor-1/adrenal 4-binding protein and phorbol ester. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7960–7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lynch, J.P.; Lala, D.S.; Peluso, J.J.; Luo, W.; Parker, K.L.; White, B.A. Steroidogenic factor 1, an orphan nuclear receptor, regulates the expression of the rat aromatase gene in gonadal tissues. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993, 7, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, M.; Tanaka, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Yoshiura, Y.; Oba, Y.; Nagahama, Y. Medaka (Oryzias latipes) FTZ-F1 potentially regulates the transcription of P450 aromatase in ovarian follicles: cDNA cloning and functional characterization. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1999, 149, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiura, Y.; Senthilkumaran, B.; Watanabe, M.; Oba, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Nagahama, Y. Synergistic expression of Ad4BP/SF-1 and cytochrome P-450 aromatase (ovarian type) in the ovary of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, during vitellogenesis suggests transcriptional interaction. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 68, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridevi, P.; Chaitanya, R.K.; Dutta-Gupta, A.; Senthilkumaran, B. FTZ-F1 and FOXL2 up-regulate catfish brain aromatase gene transcription by specific binding to the promoter motifs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, M.; Wang, D.S.; Suzuki, A.; Matsuda, M.; Nagahama, Y.; Shibata, N. Dax1 suppresses P450arom expression in medaka ovarian follicles. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2007, 74, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalli, E.; Bardoni, B.; Zazopoulos, E.; Wurtz, J.M.; Strom, T.M.; Moras, D.; Sas-sone-Corsi, P. A transcriptional silencing domain in DAX-1 whose mutation causes adrenal hypoplasia congenita. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 1950–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Thomsen, J.S.; Johansson, L.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Treuter, E. DAX-1 functions as an LXXLL-containing corepressor for activated estrogen receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39855–39859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanley, N.A.; Stallings, N.; Schimmer, B.P. Steroidogenic factor 1: An essential mediator of endocrine development. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2002, 57, 19–36. [Google Scholar]
- Holter, E.; Kotaja, N.; Makela, S.; Strauss, L.; Kietz, S.; Janne, O.A.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Palvimo, J.J.; Treuter, E. Inhibitions of androgen receptor (AR) function by the reproductive orphan nuclear receptor DAX-1. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Clifford, V.; Western, P.S.; Wilcox, S.A.; BellK, S.; Sinclair, A.H. Cloning and expression of a DAX1 homologue in the chicken embryo. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 24, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pilon, N.; Behdjani, R.; Daneau, I.; Lussier, J.G.; Silversides, D.W. Porcine steroidogenic factor-1 gene (pSF-1) expression and analysis of embryonic pig gonads during sexual differentiation. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 3803–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.J.; Jeffs, B.; Ito, M.; Achermann, J.C.; Yu, R.N.; Hales, D.B.; Jameson, J.L. Aromatase (Cyp19) expression is up-regulated by targeted disruption of Dax1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7988–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawabe, K.; Shikayama, T.; Tsuboi, H.; Oka, S.; Oba, K.; Yanase, T.; Nawata, H.; Morohashi, K. Dax-1 as one of the target genes of Ad4BP/SF-1. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Phelan, J.K.; Wheeler, D.A.; Lin, S.; McCabe, E.R.B. Zebrafish dax1 is required for development of the interrenal organ, the adrenal cortex equivalent. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 2630–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Peng, G. nr0b1 (DAX1) mutation in zebrafish causes female-to-male sex reversal through abnormal gonadal proliferation and differentiation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 433, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, Y.; Vestergaard, M.C.; Takagi, M. Damage in brain development by morpholino knockdown of zebrafish dax1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 113, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Peng, G. nr0b1 (DAX1) loss of function in zebrafish causes hypothalamic defects via abnormal progenitor proliferation and differentiation. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 21, S1673–S8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.J.; Lee, M.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, C.F. Development of gonadal tissue and aromatase function in the protogynous orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Zool. Stud. 2011, 50, 693–704. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Lin, H. The mRNA expression of P450 aromatase, gonadotropin beta-subunits and FTZ-F1 in the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus Coioides) during 17α-methyltestosterone-induced precocious sex change. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2007, 74, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.L.; Schimmer, B.P. Steroidogenic factor 1: A key determinant of endocrine development and function. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, M.; Balasubramanian, S. Expression analysis and localization of wt1, ad4bp/sf-1 and gata4 in the testis of catfish, Clarias batrachus: Impact of wt1-esiRNA silencing. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 431, 164–176. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, M.M. Estradiol and the developing brain. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 91–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.J.; Wu, G.C.; Dufour, S.; Chang, C.F. Activation of the brain-pituitary-gonadotropic axis in the black porgy Acanthopagrus schlegelii during gonadal differentiation and testis development and effect of estradiol treatment. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 281, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, J.S.; Kim, B.M.; Lee, C.J.; Yoon, Y.D.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, J.S. Bisphenol A modulates expression of sex differentiation genes in the self-fertilizing fish, Kryptolebias marmoratus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 104, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdic, G.; Sharpe, R.M.; Saunders, P.T. Maternal oestrogen/xenoestrogen exposure alters expression of steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1/Ad4BP) in the fetal rat testis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1997, 127, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, J.A. Regulation of progesterone production in the rabbit corpus luteum. Biol. Reprod. 1989, 40, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.J.; Fan-Chiang, Y.C.; Dufour, S.; Chang, C.F. Activation of brain steroidogenesis and neurogenesis during the gonadal differentiation in protandrous black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Dev. Neurobiol. 2016, 76, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, G.; Aruna, A.; Chang, C.F. Neuropeptide Arginine Vasotocin Positively Affects Neurosteroidogenesis in the Early Brain of Grouper, Epinephelus coioides. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 9, 718–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, A.; Lin, C.J.; Nagarajan, G.; Chang, C.F. Neurohypophysial Hormones Associated with Osmotic Challenges in the Brain and Pituitary of the Euryhaline Black Porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Cells 2021, 10, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, A.; Nagarajan, G.; Chang, C.F. Involvement of corticotrophin-releasing hormone and corticosteroid receptors in the brain-pituitary-gill of tilapia during the course of seawater acclimation. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 24, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruna, A.; Nagarajan, G.; Chang, C.F. The acute salinity changes activate the dual pathways of endocrine responses in the brain and pituitary of tilapia. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 211, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruna, A.; Wang, T.P.; Cao, J.C.; Lan, D.S.; Nagarajan, G.; Chang, C.F. Differential expression of hypothalamic and gill-crh system with osmotic stress in the euryhaline black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 768122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Gene | Orientation | Nucleotide Sequence | Usage | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| star | Forward | 5′-TCAGCACAGGGCTTCATCACTAT-3′ | q-PCR | |
| Reverse | 5′-TGCAAAAATGCCTGAGCAAAG-3′ | q-PCR | ||
| Sense | 5′-CGGCATATGAGGAACATGACAG-3′ | In-situ | GU929702 | |
| Anti Sense | 5′-CCACCTGCGTCTGAGAGAG-3′ | In-situ | ||
| sf-1 | Forward | 5′-TCGGCTTCGTGAAAAACGT-3′ | q-PCR | |
| Reverse | 5′-CTCCTGGGCATGGCTCAA-3′ | q-PCR | ||
| Sense | 5′-GCTGCAAGGGGTTCTTCAAG-3′ | In-situ | JQ320496 | |
| Anti Sense | 5′-CGGGGTACTCTGACTTGATG-3′ | In-situ | ||
| dax-1 | Forward | 5′-TGAAGAAGTGCTGGAGTGTAGATATCA-3′ | q-PCR | |
| Reverse | 5′-CCCTCCACATCTGGGTTGAA-3′ | q-PCR | ||
| Sense | 5′-CTCGGCGGTGCTGGTGAAGAC-3′ | In-situ | GU929703 | |
| Anti Sense | 5′-GCCGGACGTGCTCGTTGAGAG-3′ | In-situ | ||
| β-actin | Forward | 5′-AGGGAGAAGATGACCCAGATCA-3′ | q-PCR | AY510710 |
| Reverse | 5′-GGGACAGCACAGCCTGCAT-3′ | q-PCR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagarajan, G.; Aruna, A.; Alkhamis, Y.A.; Mathew, R.T.; Chang, C.-F. Expression and Transcript Localization of star, sf-1, and dax-1 in the Early Brain of the Orange-Spotted Grouper Epinephelus coioides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052614
Nagarajan G, Aruna A, Alkhamis YA, Mathew RT, Chang C-F. Expression and Transcript Localization of star, sf-1, and dax-1 in the Early Brain of the Orange-Spotted Grouper Epinephelus coioides. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(5):2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052614
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagarajan, Ganesan, Adimoolam Aruna, Yousef Ahmed Alkhamis, Roshmon Thomas Mathew, and Ching-Fong Chang. 2022. "Expression and Transcript Localization of star, sf-1, and dax-1 in the Early Brain of the Orange-Spotted Grouper Epinephelus coioides" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 5: 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052614
APA StyleNagarajan, G., Aruna, A., Alkhamis, Y. A., Mathew, R. T., & Chang, C.-F. (2022). Expression and Transcript Localization of star, sf-1, and dax-1 in the Early Brain of the Orange-Spotted Grouper Epinephelus coioides. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(5), 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052614







