RETRACTED: Metformin and Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Metformin and the Insulin-Signaling Network
3. Metformin in Breast Cancer
3.1. Metformin and Prevention of Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality
3.2. Metformin and Breast Cancer Treatment
3.2.1. Metformin in Early-Stage Breast Cancer
3.2.2. Metformin in Metastatic Breast Cancer
3.3. Other Breast Cancer–Related Applications of Metformin
4. Metformin and Breast Cancer: A Look to the Future
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breast Cancer. Who.int. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, X.; Ren, Y.; Shan, P.F. Global, regional, and national burden and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: An analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Martin, A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Cufí, S.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A. Metformin and energy metabolism in breast cancer: From insulin physiology to tumour-initiating stem cells. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 674–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannucci, E.; Harlan, D.M.; Archer, M.C.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Habel, L.A.; Pollak, M.; Regensteiner, J.D.; Yee, D. Diabetes and cancer: A consensus report. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Varghese, S.; Büsselberg, D. Challenges and perspectives in the treatment of diabetes associated breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 70, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, I.; Sadetzki, S.; Catane, R.; Karasik, A.; Kaufman, B. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, W.; Wang, B.; Guo, A.; Mao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; He, R.; Min, Y.; Huang, Y. The effect of metformin on the clinicopathological features of breast cancer with type 2 diabetes. World J. Oncol. 2020, 11, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Kuppusamy, G. Metformin in breast cancer: Preclinical and clinical evidence. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2020, 44, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, L.D.; Mortimer, J.E.; Natarajan, R.; Dietze, E.C.; Seewaldt, V.L. Metabolic health, insulin, and breast cancer: Why oncologists should care about insulin. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biello, F.; Platini, F.; D’Avanzo, F.; Cattrini, C.; Mennitto, A.; Genestroni, S.; Martini, V.; Marzullo, P.; Aimaretti, G.; Gennari, A. Insulin/IGF axis in breast cancer: Clinical evidence and translational insights. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, C.; Irwin, M.L.; Xiao, L.; Henderson, K.D.; Smith, A.W.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Bernstein, L.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; McTiernan, A. Associations of insulin resistance and adiponectin with mortality in women with breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, D.M.; Buse, J.B.; Davidson, M.B.; Ferrannini, E.; Holman, R.R.; Sherwin, R.; Zinman, B. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: A consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: A consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J. Metformin: Historical overview. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J.; Turner, R.C. Metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, S.; Carvalho, C.; Santos, M.S.; Seiça, R.; Oliveira, C.R.; Moreira, P.I. Mechanisms of action of metformin in type 2 diabetes and associated complications: An overview. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, T.; Pafundi, P.C.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Caturano, A.; Vetrano, E.; Aprea, C.; Albanese, G.; Di Martino, A.; Ricozzi, C.; et al. Can metformin exert as an active drug on endothelial dysfunction in diabetic subjects? Biomedicines 2020, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Vetrano, E.; Rinaldi, L.; Coviello, F.; Di Martino, A.; Albanese, G.; Marfella, R.; Sardu, C.; et al. Effects of metformin in heart failure: From pathophysiological rationale to clinical evidence. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Pafundi, P.C.; Galiero, R.; Gjeloshi, K.; Masini, F.; Acierno, C.; Di Martino, A.; Albanese, G.; Alfano, M.; Rinaldi, L.; et al. Metformin: A potential therapeutic tool for rheumatologists. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Pafundi, P.C.; Morgillo, F.; Di Liello, R.; Galiero, R.; Nevola, R.; Marfella, R.; Monaco, L.; Rinaldi, L.; Adinolfi, L.E.; et al. Metformin: An old drug against old age and associated morbidities. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 160, 108025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.M.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Koklesová, L.; Líšková, A.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D. Counteracting chemoresistance with metformin in breast cancers: Targeting cancer stem cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurelac, I.; Umesh Ganesh, N.; Iorio, M.; Porcelli, A.M.; Gasparre, G. The multifaceted effects of metformin on tumor microenvironment. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 98, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, R.J.; Niraula, S.; Chang, M.C.; Done, S.J.; Ennis, M.; McCready, D.R.; Leong, W.L.; Escallon, J.M.; Reedijk, M.; Goodwin, P.J.; et al. Changes in insulin receptor signaling underlie neoadjuvant metformin administration in breast cancer: A prospective window of opportunity neoadjuvant study. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, R.; Chowdhury, T.A. Metformin in cancer. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 143, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennari, A.; Foca, F.; Zamarchi, R.; Rocca, A.; Amadori, D.; De Censi, A.; Bologna, A.; Cavanna, L.; Gianni, L.; Scaltriti, L.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) expression on circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and metastatic breast cancer outcome: Results from the TransMYME trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 181, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Juboori, S.; Vadakekolathu, J.; Idri, S.; Wagner, S.; Zafeiris, D.; Pearson, J.; Almshayakhchi, R.; Caraglia, M.; Desiderio, V.; Miles, A.K.; et al. PYK2 promotes HER2-positive breast cancer invasion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Metformin: A therapeutic opportunity in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, F.; Decoux-Poullot, A.-G.; Tanti, J.F.; Clavel, S. Energy disruptors: Rising stars in anticancer therapy? Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.K.; Arya, A.; Malecek, M.-K.; Shin, D.S.; Carneiro, B.; Chandra, S.; Kaplan, J.; Kalyan, A.; Altman, J.K.; Platanias, L.; et al. Repurposing metformin for cancer treatment: Current clinical studies. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40767–40780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Guo, Y. Metformin and its benefits for various diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Kubatka, P.; Triggle, C.R.; Büsselberg, D. Metformin: The answer to cancer in a flower? Current knowledge and future prospects of metformin as an anti-cancer agent in breast cancer. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnicki, S.; Kapral, M.; Węglarz, L. Molecular targets of metformin antitumor action. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, V.C.; Dietze, E.C.; Jovanovic-Talisman, T.; McCune, J.S.; Seewaldt, V.L. Metformin and chemoprevention: Potential for heart-healthy targeting of biologically aggressive breast cancer. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 509714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coradini, D.; Oriana, S. Impact of sex hormones dysregulation and adiposity on the outcome of postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Clin. Obes. 2021, 11, e12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.R.; Morrison, V.; Levin, D.; Mohan, M.; Forteath, C.; Beall, C.; McNeilly, A.; Balfour, D.J.; Savinko, T.; Wong, A.K.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.A.; Lim, H.-W.; Kim, Y.H.; Ho, W.Y.; Foong, Y.H.; Nelson, V.L.; Nguyen, H.C.B.; Chegireddy, K.; Kim, J.; Habertheuer, A.; et al. Distinct macrophage populations direct inflammatory versus physiological changes in adipose tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5096–E5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.R.; Brown, K.A. Obesity and breast cancer: Role of inflammation and aromatase. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 51, T51–T59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, E.D.; Jindal, S.; Wellberg, E.A.; Schedin, T.; Anderson, S.M.; Thor, A.D.; Edwards, D.P.; MacLean, P.S.; Schedin, P. Metformin inhibits stromal aromatase expression and tumor progression in a rodent model of postmenopausal breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.J.; Pritchard, K.I.; Ennis, M.; Clemons, M.; Graham, M.; Fantus, I.G. Insulin-lowering effects of metformin in women with early breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2008, 8, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahdan-Alaswad, R.; Fan, Z.; Edgerton, S.M.; Liu, B.; Deng, X.-S.; Árnadóttir, S.; Richer, J.K.; Anderson, S.M.; Thor, A.D. Glucose promotes breast cancer aggression and reduces metformin efficacy. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3759–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahdan-Alaswad, R.S.; Edgerton, S.M.; Salem, H.S.; Thor, A.D. Metformin targets glucose metabolism in triple negative breast cancer. J. Oncol. Transl. Res. 2018, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D. High glucose represses the anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effect of metformin in triple negative breast cancer cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, J.A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Cufí, S.; Corominas-Faja, B.; Joven, J.; Martín-Castillo, B.; Vazquez-Martin, A. Metformin is synthetically lethal with glucose withdrawal in cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 2782–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Sahra, I.; Laurent, K.; Giuliano, S.; Larbret, F.; Ponzio, G.; Gounon, P.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Giorgetti-Peraldi, S.; Cormont, M.; Bertolotto, C.; et al. Targeting cancer cell metabolism: The combination of metformin and 2-deoxyglucose induces p53-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wokoun, U.; Hellriegel, M.; Emons, G.; Gründker, C. Co-treatment of breast cancer cells with pharmacologic doses of 2-deoxy-D-glucose and metformin: Starving tumors. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Thaker, N.; De, A. Combined 2-deoxy glucose and metformin improves therapeutic efficacy of sodium-iodide symporter-mediated targeted radioiodine therapy in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer 2015, 7, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Huo, X.; Sun, P.; Sun, H.; Ma, X.; Ma, X.; et al. Targeting P-glycoprotein function, p53 and energy metabolism: Combination of metformin and 2-deoxyglucose reverses the multidrug resistance of MCF-7/Dox cells to doxorubicin. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8622–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Everett, R.S.; Thakker, D.R. Efficacious dose of metformin for breast cancer therapy is determined by cation transporter expression in tumours. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 2724–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Yung, E.; Pintilie, M.; Muaddi, H.; Chaib, S.; Yeung, M.; Fusciello, M.; Sykes, J.; Pitcher, B.; Hagenkort, A.; et al. MATE2 expression is associated with cancer cell response to metformin. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checkley, L.A.; Rudolph, M.C.; Wellberg, E.A.; Giles, E.; Wahdan-Alaswad, R.S.; Houck, J.A.; Edgerton, S.M.; Thor, A.D.; Schedin, P.; Anderson, S.M.; et al. Metformin accumulation correlates with organic cation transporter 2 protein expression and predicts mammary tumor regression in vivo. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Giacomini, K.M. Transporters involved in metformin pharmacokinetics and treatment response. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.; Shao, L.; Tomlinson, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.-M. Metformin transporter pharmacogenomics: Insights into drug disposition-where are we now? Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berstein, L.M.; Iyevleva, A.G.; Vasilyev, D.; Poroshina, T.E.; Imyanitov, E.N. Genetic polymorphisms potentially associated with response to metformin in postmenopausal diabetics suffering and not suffering with cancer. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3681–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, T.K.; Everett, R.S.; Thakker, D.R. Cation-selective transporters are critical to the AMPK-mediated antiproliferative effects of metformin in human breast cancer cells: Transporters in metformin effect against breast cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez, J.A.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Cufí, S.; Corominas-Faja, B.; Cuyàs, E.; Barrera, J.B.; Martín-Castillo, B.; Carretero, A.S.; Joven, J. Oncobiguanides: Paracelsus’ law and nonconventional routes for administering diabetobiguanides for cancer treatment. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Col, N.F.; Ochs, L.; Springmann, V.; Aragaki, A.K.; Chlebowski, R.T. Metformin and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis and critical literature review. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebowski, R.T.; McTiernan, A.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Manson, J.E.; Aragaki, A.K.; Rohan, T.; Ipp, E.; Kaklamani, V.G.; Vitolins, M.; Wallace, R.; et al. Diabetes, metformin, and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2844–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Satkunam, M.; Pond, G.R.; Steinberg, G.; Blandino, G.; Schünemann, H.J.; Muti, P. Association of metformin with breast cancer incidence and mortality in patients with type II diabetes: A GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S. Association between metformin therapy and breast cancer incidence and mortality: Evidence from a meta-analysis. J. Breast Cancer 2015, 18, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-M.M.; Bookwalter, D.B.; O’Brien, K.M.; Jackson, C.L.; Weinberg, C.R.; Sandler, D.P. A prospective study of type 2 diabetes, metformin use, and risk of breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Esquinas, E.; Guinó, E.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Llorca, J.; Altzibar, J.M.; Peiró-Pérez, R.; Martín, V.; Moreno-Iribas, C.; Tardón, A.; et al. Association of diabetes and diabetes treatment with incidence of breast cancer. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, S.; Sendur, M.A.N.; Altundag, K. Demographic and clinico-pathological characteristics in patients with invasive breast cancer receiving metformin. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besic, N.; Satej, N.; Ratoša, I.; Horvat, A.G.; Marinko, T.; Gazic, B.; Petric, R. Long-term use of metformin and the molecular subtype in invasive breast carcinoma patients—A retrospective study of clinical and tumor characteristics. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lega, I.C.; Fung, K.; Austin, P.C.; Lipscombe, L.L. Metformin and breast cancer stage at diagnosis: A population-based study. Curr. Oncol. 2017, 24, e85–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuyàs, E.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Alarcón, T.; Lupu, R.; Joven, J.; Menendez, J.A. Germline BRCA1 mutation reprograms breast epithelial cell metabolism towards mitochondrial-dependent biosynthesis: Evidence for metformin-based “starvation” strategies in BRCA1 carriers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52974–52992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peairs, K.S.; Barone, B.B.; Snyder, C.F.; Yeh, H.-C.; Stein, K.B.; Derr, R.L.; Brancati, F.L.; Wolff, A. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, W.R.; Hosler, A.S.; Kuliszewski, M.G.; Leinung, M.C.; Zhang, X.; Schymura, M.J.; Boscoe, F.P. Impact of preexisting type 2 diabetes mellitus and antidiabetic drugs on all-cause and cause-specific mortality among Medicaid-insured women diagnosed with breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2020, 66, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, K.; Jia, X.; Tian, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, J.; Tao, M.; Mao, Y. Metformin use is associated with better survival of breast cancer patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Oncologist 2015, 20, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Esteva, F.J.; Ensor, J.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Lee, M.-H.; Yeung, S.-C.J. Metformin and thiazolidinediones are associated with improved breast cancer-specific survival of diabetic women with HER2+ breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.H.; Satkunam, M.; Pond, G.R.; Blandino, G. Clinical pathological characteristics and prognostic analysis of 1013 breast cancer patients with diabetes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 137, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong, B.A.; Pharmer, L.A.; Oskar, S.; Eaton, A.; Stempel, M.; Patil, S.; King, T.A. The effect of metformin on breast cancer outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-J.; Yuan, J.; Bi, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. The effect of metformin on biomarkers and survivals for breast cancer- a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 141, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Han, J.; Yang, B.R.; Jang, M.-J.; Kim, M.; Lee, D.-W.; Kim, T.-Y.; Im, S.-A.; Lee, H.-B.; Moon, H.-G.; et al. Association of insulin, metformin, and statin with mortality in breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 53, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lega, I.C.; Austin, P.C.; Gruneir, A.; Goodwin, P.J.; Rochon, P.A.; Lipscombe, L.L. Association between metformin therapy and mortality after breast cancer: A population-based study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3018–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, P.J.; Bazelier, M.T.; Vestergaard, P.; Leufkens, H.G.; Schmidt, M.K.; De Vries, F.; De Bruin, M.L. Use of metformin and survival of diabetic women with breast cancer. Curr. Drug Saf. 2013, 8, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kwon, H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.B.; Park, H.S.; Sohn, G.; Lee, Y.; Koh, B.S.; Yu, J.H.; et al. Metformin increases survival in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-positive breast cancer patients with diabetes. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Hirsch, H.A.; Struhl, K. Metformin decreases the dose of chemotherapy for prolonging tumor remission in mouse xenografts involving multiple cancer cell types. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3196–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, G.Z.; Dias, M.M.; Ropelle, E.R.; Osório-Costa, F.; Rossato, F.A.; Vercesi, A.E.; Saad, M.J.; Carvalheira, J.B. Metformin amplifies chemotherapy-induced AMPK activation and antitumoral growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3993–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, E.; Samuel, S.M.; Líšková, A.; Samec, M.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D. Targeting glucose metabolism to overcome resistance to anticancer chemotherapy in breast cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.A.; Iliopoulos, D.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Struhl, K. Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells, and acts together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong remission. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7507–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Choi, J.; Kim, A. Anti-cancer effect of metformin by suppressing signaling pathway of HER2 and HER3 in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Tumour. Biol. 2016, 37, 5811–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Martin, A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Menendez, J. The antidiabetic drug metformin suppresses HER2 (erbB-2) oncoprotein overexpression via inhibition of the mTOR effector p70S6K1 in human breast carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Martín, A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; del Barco, S.; Martín-Castillo, B.; Menéndez, J.A. mTOR inhibitors and the anti-diabetic biguanide metformin: New insights into the molecular management of breast cancer resistance to the HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor lapatinib (Tykerb). Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2009, 11, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cufí, S.; Corominas-Faja, B.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Dorca, J.; Barrera, J.B.; Martín-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A. Metformin-induced preferential killing of breast cancer initiating CD44+CD24−/low cells is sufficient to overcome primary resistance to trastuzumab in HER2+ human breast cancer xenografts. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Martin, A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Del Barco, S.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A. The anti-diabetic drug metformin suppresses self-renewal and proliferation of trastuzumab-resistant tumor-initiating breast cancer stem cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 126, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannella, V.E.; Dal Pra, A.; Muaddi, H.; McKee, T.D.; Stapleton, S.; Sykes, J.; Glicksman, R.; Chaib, S.; Zamiara, P.; Milosevic, M.; et al. Reprogramming metabolism with metformin improves tumor oxygenation and radiotherapy response. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6741–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Maity, A. Molecular pathways: A novel approach to targeting hypoxia and improving radiotherapy efficacy via reduction in oxygen demand. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.L.; Kolozsvary, A.; Isrow, D.M.; Al Feghali, K.; Lapanowski, K.; Jenrow, K.A.; Kim, J.H. A novel mechanism of high dose radiation sensitization by metformin. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.W.; Lee, H.; Dings, R.P.M.; Williams, B.; Powers, J.; Dos Santos, T.; Choi, B.-H.; Park, H.J. Metformin kills and radiosensitizes cancer cells and preferentially kills cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jenrow, K.A.; Brown, S.L. Novel biological strategies to enhance the radiation therapeutic ratio. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2018, 36, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Gao, C.; Guo, M.; Law, B.Y.K.; Xu, Y. Effects of metformin treatment on radiotherapy efficacy in patients with cancer and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 4881–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioce, M.; Valerio, M.; Casadei, L.; Pulito, C.; Sacconi, A.; Mori, F.; Biagioni, F.; Manetti, C.; Muti, P.; Strano, S.; et al. Metformin-induced metabolic reprogramming of chemoresistant ALDHbright breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4129–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, B.; Azmi, A.S.; Ali, S.; Zaiem, F.; Sarkar, F.H. Metformin may function as anti-cancer agent via targeting cancer stem cells: The potential biological significance of tumor-associated miRNAs in breast and pancreatic cancers. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; et al. Metformin suppresses triple-negative breast cancer stem cells by targeting KLF5 for degradation. Cell Discov. 2017, 3, 17010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Meng, X. Hyperglycemia and chemoresistance in breast cancer: From cellular mechanisms to treatment response. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 628359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanni, B.; Puntoni, M.; Cazzaniga, M.; Pruneri, G.; Serrano, D.; Guerrieri-Gonzaga, A.; Trabacca, M.S.; Viale, G.; Bruzzi, P.; DeCensi, A.; et al. Dual effect of metformin on breast cancer proliferation in a randomized presurgical trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2593–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinsky, K.; Zheng, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Du, X.; Mundi, P.; Yang, J.; Refice, S.; Feldman, S.M.; Taback, B.; Connolly, E.; et al. Proteomic modulation in breast tumors after metformin exposure: Results from a “window of opportunity” trial. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 19, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, S.; Dowling, R.; Ennis, M.; Chang, M.C.; Done, S.; Hood, N.; Escallon, J.; Leong, W.L.; McCready, D.R.; Reedijk, M.; et al. Metformin in early breast cancer: A prospective window of opportunity neoadjuvant study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadad, S.; Iwamoto, T.; Jordan, L.; Purdie, C.; Bray, S.; Baker, L.; Jellema, G.; Deharo, S.; Hardie, G.; Pusztai, L.; et al. Evidence for biological effects of metformin in operable breast cancer: A pre-operative, window-of-opportunity, randomized trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 128, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukioki, T.; Shien, T.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Kajihara, Y.; Hatono, M.; Kawada, K.; Kochi, M.; Iwamoto, T.; Ikeda, H.; et al. Influences of preoperative metformin on immunological factors in early breast cancer. Cancer Chem. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiralerspong, S.; Palla, S.L.; Giordano, S.H.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Liedtke, C.; Barnett, C.M.; Hsu, L.; Hung, M.-C.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3297–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Castillo, B.; Pernas, S.; Dorca, J.; Alvarez, I.; Martínez, S.; Pérez-Garcia, J.M.; Batista-López, N.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, C.A.; Amillano, K.; Domínguez, S.; et al. A phase 2 trial of neoadjuvant metformin in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy in women with early HER2-positive breast cancer: The METTEN study. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35687–35704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bonet, E.; Buxó, M.; Cuyàs, E.; Pernas, S.; Dorca, J.; Álvarez, I.; Martínez, S.; Pérez-Garcia, J.M.; Batista-López, N.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, C.A.; et al. Neoadjuvant metformin added to systemic therapy decreases the proliferative capacity of residual breast cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Galeana, P.; Muñoz-Montaño, W.; Lara-Medina, F.; Alvarado-Miranda, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, V.; Villarreal-Garza, C.; Quintero, R.M.; Porras-Reyes, F.; Bargallo-Rocha, E.; Del Carmen, I.; et al. Ki67 changes identify worse outcomes in residual breast cancer tumors after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncologist 2018, 23, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, E.; Horimoto, Y.; Arakawa, A.; Himuro, T.; Senuma, K.; Nakai, K.; Saito, M. Differences in Ki67 expressions between pre- and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy specimens might predict early recurrence of breast cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 63, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, S.; Hernadez-Aya, L.F.; Lei, X.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Litton, J.K.; Hsu, L.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. Effect of Metformin on Survival Outcomes in Diabetic Patientswith Triple Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer 2012, 118, 1202–12011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenblick, A.; Agbor-Tarh, D.D.; Bradbury, I.I.; Di Cosimo, S.; Azim, H.A., Jr.; Fumagalli, D.; Sarp, S.S.; Wolff, A.; Andersson, M.M.; Kroep, J.; et al. Impact of diabetes, insulin, and metformin use on the outcome of patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive primary breast cancer: Analysis from the ALTTO phase III randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.J.; Parulekar, W.R.; Gelmon, K.A.; Shepherd, L.E.; Ligibel, J.A.; Hershman, D.L.; Rastogi, P.; Mayer, I.A.; Hobday, T.J.; Lemieux, J.; et al. Effect of metformin vs. placebo on and metabolic factors in NCIC CTG MA.32. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, I.; E Chen, B.; Lohmann, A.E.; Ennis, M.; Ligibel, J.; Shepherd, L.; Hershman, D.L.; Whelan, T.; Stambolic, V.; Mayer, I.; et al. The effect of metformin vs. placebo on sex hormones in Canadian cancer trials group MA.32. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P. CCTGMA.32, A Phase III Randomized Double-Blind Placebo Controlled Adjuvant Trial of Metformin (MET) vs. Placebo (PLAC) in Early Breast Cancer (BC): Results of the Primary Efficacy Analysis (Clinical Trials.gov NCT01101438); San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nanni, O.; Amadori, D.; De Censi, A.; Rocca, A.; Freschi, A.; Bologna, A.; Gianni, L.; Rosetti, F.; Amaducci, L.; Cavanna, L.; et al. Metformin plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in the first-line treatment of HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. The MYME randomized, phase 2 clinical trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 174, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, I.; Lohmann, A.E.; Ennis, M.; Dowling, R.J.O.; Cescon, D.; Elser, C.; Potvin, K.R.; Haq, R.; Hamm, C.; Chang, M.C.; et al. A phase II randomized clinical trial of the effect of metformin versus placebo on progression-free survival in women with metastatic breast cancer receiving standard chemotherapy. Breast 2019, 48, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, Y.-K.I.; Du, X.; Rayannavar, V.; Hopkins, B.; Shaw, J.; Bessler, E.; Thomas, T.; Pires, M.M.; Keniry, M.; Parsons, R.; et al. Metformin and erlotinib synergize to inhibit basal breast cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 10503–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenn, K.; Maurer, M.; Lee, S.M.; Crew, K.D.; Trivedi, M.S.; Accordino, M.K.; Hershman, D.L.; Kalinsky, K. Phase 1 study of erlotinib and metformin in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Turner, N.C. Targeting the PI3-kinase pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, X.; Guo, J.; Sun, T.; Li, X.; Yao, L.; Dong, H.; Xu, Y. Metabolic reprogramming in triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Cao, J.; Tao, Z.; Li, T.; Wang, B.; et al. A randomized phase II study of aromatase inhibitors plus metformin in pre-treated postmenopausal patients with hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 84224–84236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Campone, M.; Piccart, M.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Rugo, H.S.; Sahmoud, T.; Noguchi, S.; Gnant, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Lebrun, F.; et al. Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, C.; Esteva, F.; Patel, M.M.; Raghavendra, A.S.; Ueno, N.T.; Moulder, S.L.; Hess, K.R.; Shroff, G.S.; Hodge, S.; Koenig, K.H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the combination of metformin, everolimus and exemestane in overweight and obese postmenopausal patients with metastatic, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, a phase II study. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Pauli, C.; Du, X.; Wang, D.G.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Amadiume, S.C.; Goncalves, M.D.; Hodakoski, C.; Lundquist, M.R.; et al. Publisher Correction: Suppression of insulin feedback enhances the efficacy of PI3K inhibitors. Nature 2018, 560, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnery, S.E.; Mayer, I.A. Management of toxicity to isoform α-specific PI3K inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, x21–x26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Kyriakides, S.; Ohno, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Poortmans, P.; Rubio, I.T.; Zackrisson, S.; Senkus, E.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Early breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1194–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee on Gynecologic Practice. Committee Opinion No. 601: Tamoxifen and uterine cancer. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 123, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, J.V., Jr.; Chia, V.M. Maturitas Endometrial hyperplasia and the risk of progression to carcinoma. Maturitas 2009, 63, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauwen, S.; Depreeuw, J.; Coenegrachts, L.; Hermans, E.; Lambrechts, D.; Amant, F. Dual blockade of PI3K/AKT/mTOR (NVP-BEZ235) and Ras/Raf/MEK (AZD6244) pathways synergistically inhibit growth of primary endometrioid endometrial carcinoma cultures, whereas NVP-BEZ235 reduces tumor growth in the corresponding xenograft models. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 138, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Feng, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, X.; Wan, Q.; Cai, D. Metformin is associated with reduced cell proliferation in human endometrial cancer by inbibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2018, 34, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.R.; Robinson, P.J.; Jane, F.; White, S.; Brown, K.A.; Piessens, S.; Edwards, A.; Mcneilage, J.; Woinarski, J.; Chipman, M.; et al. The benefits of adding metformin to tamoxifen to protect the endometrium-A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 89, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, H.C.F.; Unger, J.M.; Phillips, K.-A.; Boyle, F.; Hitre, E.; Porter, D.; Francis, P.; Goldstein, L.J.; Gomez, H.; Vallejos, C.; et al. Goserelin for ovarian protection during breast-cancer adjuvant chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.-R.; Jin, H.; Gao, K.; Twamley, E.W.; Ou, J.-J.; Shao, P.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.-F.; Davis, J.M.; Chan, P.K.; et al. Metformin for treatment of antipsychotic-induced amenorrhea and weight gain in women with first-episode schizophrenia, a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Du, D.; Chen, Q.; Wu, M.; Wu, T.; Wen, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Metformin prevents murine ovarian aging. Aging 2019, 11, 3785–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, P.; Ren, W.; Cui, P.; Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Y.; et al. Metformin intervention against ovarian toxicity during chemotherapy for early breast cancer: Study protocol for a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Maturitas 2020, 137, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieli-Conwright, C.M.; Wong, L.; Waliany, S.; Bernstein, L.; Salehian, B.; Mortimer, J.E. An observational study to examine changes in metabolic syndrome components in patients with breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy: Metabolic Syndrome, Chemotherapy, and Cancer. Cancer 2016, 122, 2646–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosio, M.; Urpilainen, E.; Hautakoski, A.; Marttila, M.; Arffman, M.; Sund, R.; Ahtikoski, A.; Puistola, U.; Läärä, E.; Karihtala, P.; et al. Association of antidiabetic medication and statins with survival from ductal and lobular breast carcinoma in women with type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lim, W.; Kim, E.-K.; Kim, M.-K.; Paik, N.-S.; Jeong, S.-S.; Yoon, J.-H.; Park, C.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, L.S.; et al. Phase II randomized trial of neoadjuvant metformin plus letrozole versus placebo plus letrozole for estrogen receptor positive postmenopausal breast cancer (METEOR). BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egormin, P.A.; Bershtein, L.M.; Zabezhinskii, M.A.; Piskunova, T.S.; Popovich, I.G.; Semenchenko, A.V. Metformin decelerates aging and development of mammary tumors in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 139, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, V.N.; Berstein, L.M.; Egormin, P.A.; Piskunova, T.S.; Popovich, I.G.; Zabezhinski, M.A.; Kovalenko, I.G.; Poroshina, T.E.; Semenchenko, A.V.; Provinciali, M.; et al. Effect of metformin on life span and on the development of spontaneous mammary tumors in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2005, 40, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, S.R.; Cheng, W.-C.; Liu, D.; Gaude, E.; Haider, S.; Metcalf, T.; Patel, N.; Teoh, E.J.; Gleeson, F.; Bradley, K.; et al. Integrated pharmacodynamic analysis identifies two metabolic adaptation pathways to metformin in breast cancer. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 679–688.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyàs, E.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Buxó, M.; Pernas, S.; Dorca, J.; Álvarez, I.; Martínez, S.; Pérez-Garcia, J.M.; Batista-López, N.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, C.A.; et al. Metformin induces a fasting- and antifolate-mimicking modification of systemic host metabolism in breast cancer patients. Aging 2019, 11, 2874–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdura, S.; Cuyàs, E.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A. Metformin as an archetype immuno-metabolic adjuvant for cancer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1633235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
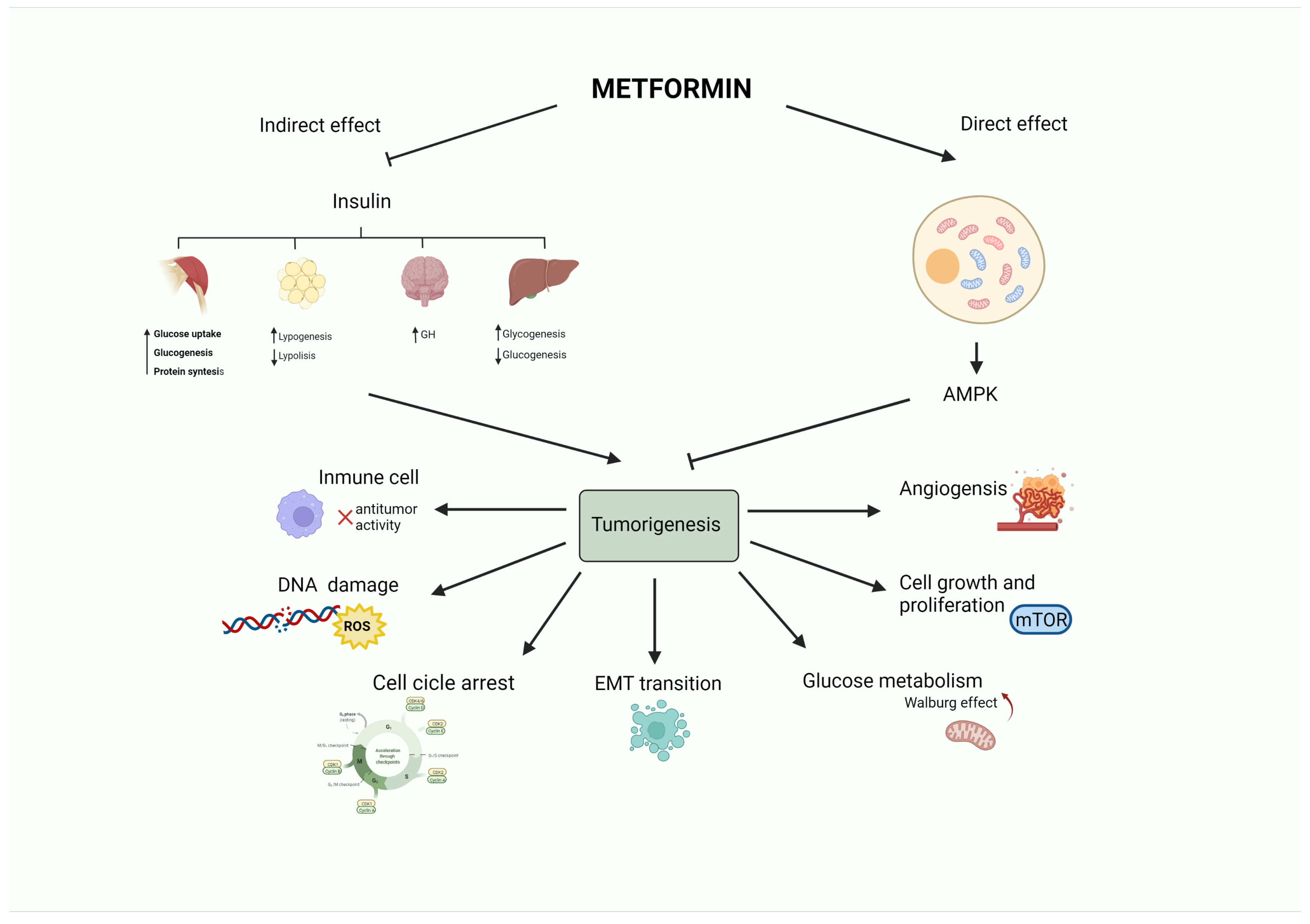
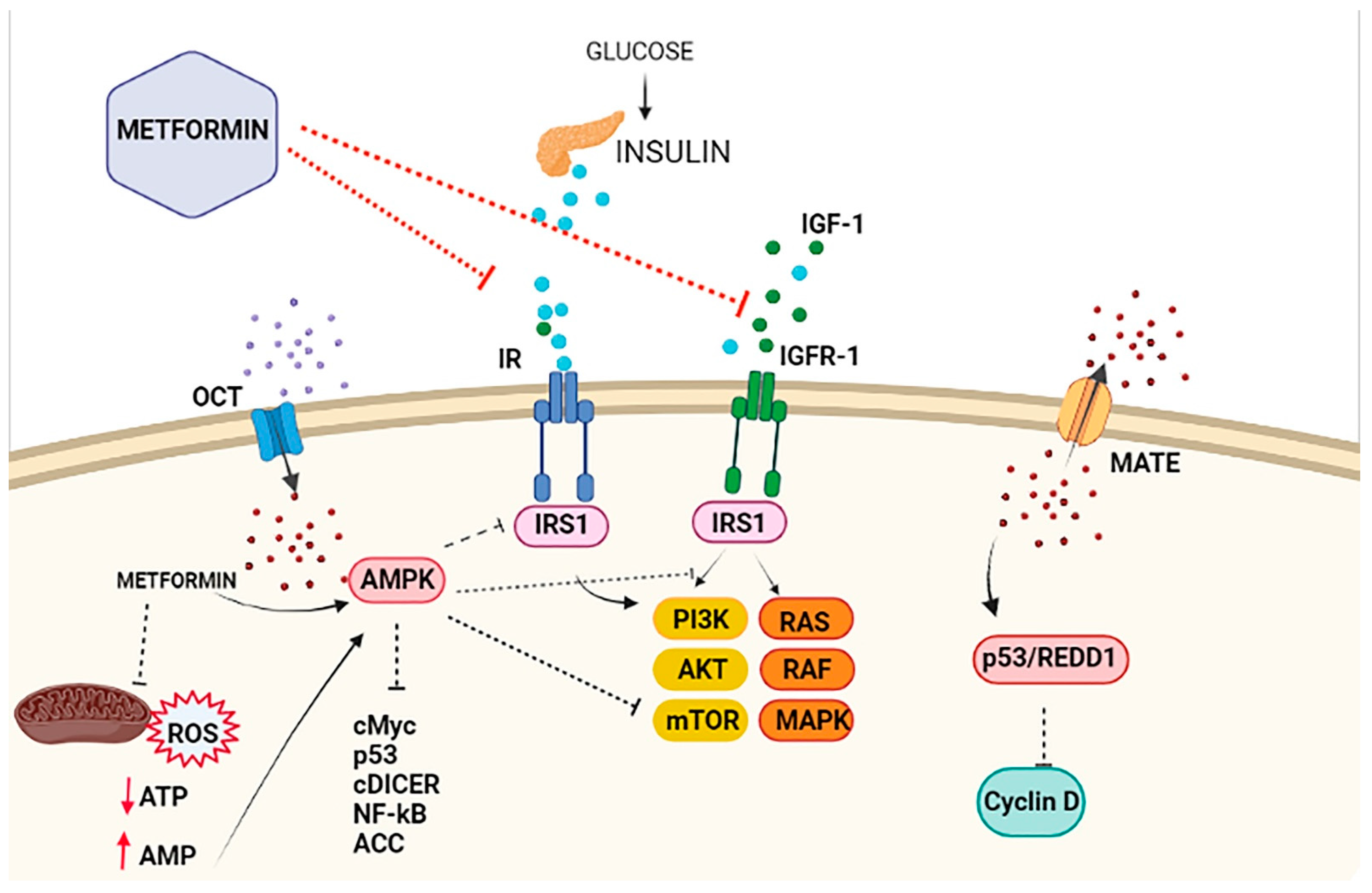
| Study Design/Type and Reference | Observations |
|---|---|
| Meta-analysis 7 studies No participant number provided [57] | Metformin may have a protective effect on breast cancer risk among postmenopausal women with diabetes. This association was stronger with longer metformin use (>3 years). |
| Cohort Study 68,019 women of the Women’s Health Initiative clinical trial population [58] | Diabetic women receiving metformin had lower incidence of invasive breast cancer, whereas women with diabetes receiving other antidiabetic drugs presented a slightly higher incidence. |
| Meta-analysis 12 studies 16,230 participants [59] | No significant association was found between metformin exposure and breast cancer incidence. |
| Meta-analysis 11 studies 838,333 participants [60] | Metformin did not reduce breast cancer incidence. |
| Case-control; The Sister Study 44,451 women with type 2 diabetes and diagnosed with breast cancer [61] | Metformin use was related to increased risk of ER-negative breast cancer |
| Study Design/Type and Reference | Observations |
|---|---|
| Case-control. Ontario database of 2361 patients with breast cancer diagnosis and metformin treatment [75] | 9% reduction in breast cancer–specific mortality per additional year of cumulative metformin use |
| Case-control. Danish register of 1058 patients with breast cancer and history of metformin prescription [76] | Reduction in overall mortality in diabetic patients with metformin, but no breast cancer–specific mortality. Unexpectedly, significant increase in both overall and breast cancer–specific mortality was observed after discontinuation of metformin in these patients |
| Case-control. Asan Medical Center’s breast database of 7353 patients with resected breast cancer and metformin treatment [77] | Patients had significantly better overall and cancer-specific survival |
| Meta-analysis 11 studies 838,333 participants [60] | Metformin decreased breast cancer all-cause mortality |
| Meta-analysis 11 studies 6387 participants [59] | Metformin showed a 45% risk reduction for all-cause mortality in breast cancer patients |
| Case-control. Seoul National University Hospital 919 surgically resected breast cancer cases in treatment with metformin, insulin, or metformin plus insulin [74] | Insulin was associated with worse survival, but the co-administration of insulin and metformin attenuated this detrimental effect. Both effects were more apparent in patients with ER-negative disease |
| Study Designation | Phase | Intervention | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| METTEN study | II | Neoadjuvant treatment in HER-2 positive BC (weekly paclitaxel + trastuzumab followed by 4 cycles of 3-weekly FEC + trastuzumab) plus metformin (850 mg bid)/pbo | pCR in metformin 65.5%, (95% CI: 47.3–80.1) vs control arm 58.6%, (95% CI: 40.7–74.5) |
| N = 84 | OR 1.34 [95% CI: 0.46–3.89], p = 0.589 | ||
| NCIC MA.32 | III | Adjuvant treatment with Metformin (850 mg bid)/pbo for 5 years in non-diabetic population. | ER positive/HER-2 negative patients DFS (HR = 1.01; 95% CI, 0.84–1.21) OS (HR = 1.1; 95% CI, 0.86–1.41) |
| (NCT01101438) | ER negative/HER-2 negative patients DFS (HR = 1.01; 95% CI, 0.79–1.3) OS (HR = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.64–1.23) | ||
| N = 3649 | HER-2 positive regardless ER status DFS (HR = 0.64; 95% CI, 0.43–0.95) OS (HR = 0.53; 95% CI, 0.3–0.98) | ||
| MYME trial | II | Chemotherapy regimen in metastatic BC with 8 cycles of non-pegylated liposomal doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide plus metformin 1000 mg bid/control | PFS 9.4 m. (95% CI 7.8–10.4) in metformin vs. 9.9 m. control arm (95% CI 7.4–11.5 p = 0.651) |
| (NCT01885013) | OS 34.4 m. (95% CI 19.3–37.2) metformin vs. 26.8 m. control arm (95% CI 19.4–37.9) HR 0.81, 95% CI 0.50–1.30, p = 0.382 | ||
| N = 126 | No difference in metformin effects (OS and PFS) in HOMA <2.5 and ≥2.5 | ||
| NCT01310231 | II | Chemotherapy regimen in metastatic setting (anthracyclines, platinum, taxanes or capecitabine) plus metformin 850 mg bid | PFS 5.4 m metformin vs. 6.3 m control arm. HR 1.2 (95% CI 0.63–2.31). |
| N = 40 | OS 20.2 m metformin vs. 24.2 m. control arm HR 1.68 (95% CI 0.79–3.55). |
| Study Designation | Phase | N | Clinical Setting | Study Medication | End Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04559308 (Recruiting) | II | 80 | Neoadjuvancy | 4 cycles of EC followed by weekly paclitaxel plus metformin (1000 mg bis)/control | Clinical benefit rate (tumor size) |
| NCT04387630 (Recruiting) | II/III | 120 | Neoadjuvancy | Neoadjuvant treatment as physician’s choice plus metformin (from 850 mg–2550 mg/day)/pbo | Clinical response rate T-cell cytotoxic markers |
| NCT01589367 (Completed) | II | 208 | Neoadjuvancy | Letrozole plus metformin (1000 mg bis)/pbo up to 24 weeks prior to surgery | Clinical response rate |
| NCT01929811 (Active, not recruiting) | II | 92 | Neoadjuvancy | TEC plus metformin(500 mg/day)/control | pCR |
| NCT04248998 (Recruiting) | II | 90 | Neoadjuvancy in TN breast cancer | 4 cycles of AC followed by weekly paclitaxel + FMD +metformin (850 mg bis)/pbo | pCR |
| NCT02488564 (Completed) | II | 49 | Neoadjuvancy in HER-2 positive breast cancer | Liposomal doxorubicin in combination with Docetaxel and Trastuzumab plus Metformin (1000 mg bis) | pCR |
| NCT05023967 (Recruiting) | II | 120 | Localized BC not tributary to neoadjuvant treatment | Fast for ≥16 h plus metformin (1500 mg/day) vs. observation for 4–6 weeks prior to surgery | Ki67 levels Incidence of adjacent DCIS Toxicity |
| NCT04143282 (Completed) | II | 250 | Metastatic breast cancer | Standard chemotherapy plus metformin (1000 mg bis) | Radiologic response rate OS, DFS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cejuela, M.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A.; Pernas, S. RETRACTED: Metformin and Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052705
Cejuela M, Martin-Castillo B, Menendez JA, Pernas S. RETRACTED: Metformin and Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(5):2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052705
Chicago/Turabian StyleCejuela, Mónica, Begoña Martin-Castillo, Javier A. Menendez, and Sonia Pernas. 2022. "RETRACTED: Metformin and Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 5: 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052705
APA StyleCejuela, M., Martin-Castillo, B., Menendez, J. A., & Pernas, S. (2022). RETRACTED: Metformin and Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(5), 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052705






