Abstract
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a group of lung illnesses characterized by severe inflammation, with no treatment. The fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme is an integral membrane protein responsible for the hydrolysis of the main endocannabinoids, such as anandamide (AEA). In pre-clinical pain and inflammation models, increasing the endogenous levels of AEA and other bioactive fatty acid amides (FAAs) via genetic deletion or the pharmacological inhibition of FAAH produces many analgesic benefits in several different experimental models. To date, nobody has investigated the role of FAAH inhibition on an ALI mouse model. Mice were subjected to a carrageenan injection and treated orally 1 h after with the FAAH inhibitor URB878 dissolved in a vehicle consisting of 10% PEG-400, 10% Tween-80 and 80% saline at different doses: The inhibition of FAAH activity was able to counteract not only the CAR-induced histological alteration, but also the cascade of related inflammatory events. URB878 clears the way for further studies based on FAAH inhibition in acute lung pathologies.
1. Introduction
Acute lung injury (ALI) or its more severe form acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a group of lung illnesses characterized by a severe inflammatory process that causes severe hypoxia, hypercapnia, diffuse infiltration, and poor pulmonary compliance [1].
The inflammatory process causes alveolar and interstitial edema, impaired alveolar fluid clearance, reduction in surfactant synthesis and function, and lung fibrosis, depending on whether it starts from the alveolar or microvascular side. The persistence of inflammatory mediators (mainly of neutrophilic origin) in the bronchoalveolar lavage prevents the resolution of the inflammatory process in the lungs [2]. Systemic inflammation is triggered by the release of inflammatory mediators from injured lung tissue, and it can lead to multiple organ failure, which is the leading cause of mortality in ARDS patients. In patients with ALI and ARDS, the intensivist may need to raise their standards to overcome a hypoxia crisis and treat specific pathologies that arise during disease progress. Recruitment movements, prone positioning, nitric oxide inhalation, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) are all options for resolving a hypoxic crisis [2,3,4,5,6].
Despite significant advances in understanding the biology and pathophysiology of ALI over the past decades, there is still no effective therapy strategy for these disorders [7].
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is an integral membrane protein responsible for the hydrolysis of the endocannabinoid N-arachidonoylethanolamide (anandamide, AEA) and other related amidated signaling lipids, such as palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), N-oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and linoleoylethanolamide (LEA) [8]. In pre-clinical pain and inflammation models, increasing endogenous levels of AEA and other bioactive fatty acid amides (FAAs) via genetic deletion or the pharmacological inhibition of FAAH produced many analgesic benefits in several different experimental models [8,9,10,11,12,13,14].
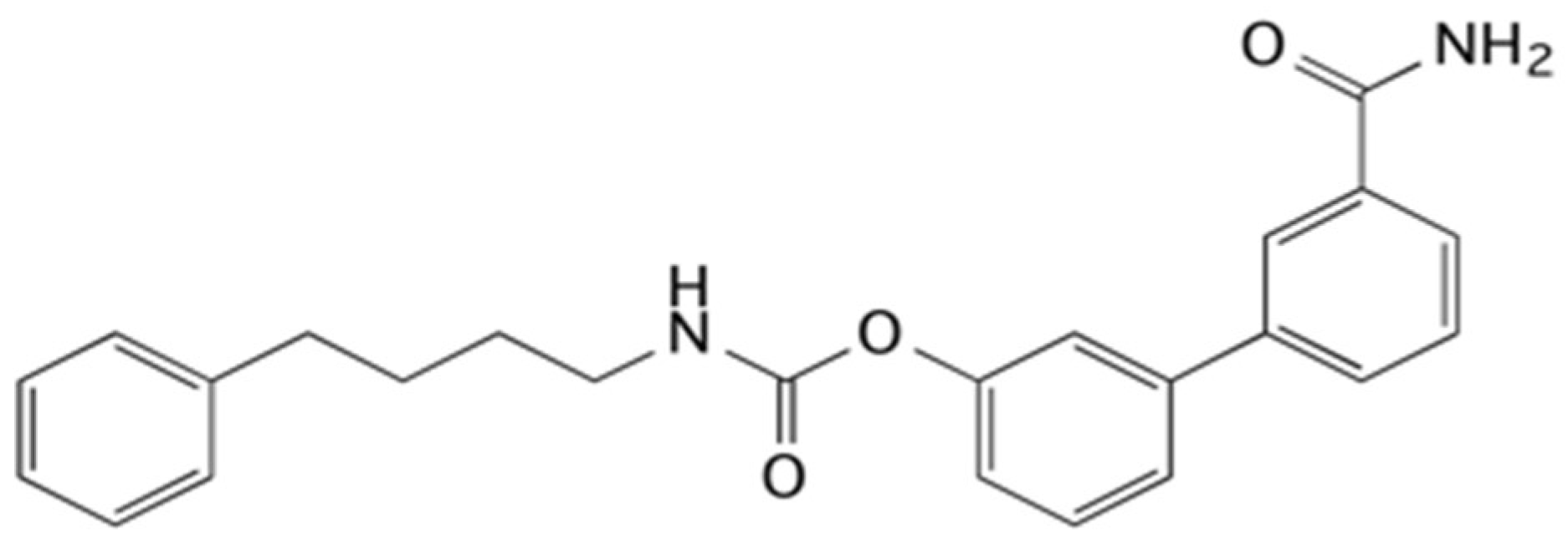
The inhibition of FAAH has been shown to be useful in different experimental models, such as cisplatin- and nicotine-induced vomiting in Suncus murinus [15], naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal [16], gaping elicited by a lithium-paired context in the rat [17] or chronic cerebral hypoperfusion [18]. Additionally, URB597, the FAAH inhibitor most used as a pharmacological tool [19], has also shown its beneficial effects on other pathologies, such as anxiety and depression [20,21,22,23], neuropathic pain [24], 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson’s model [25], stress [26,27], hypertension [28,29,30,31,32,33,34], and lung problems [35,36,37]. Particular attention is mainly due to the fact that the inhibition of FAAH showed no adverse cardiovascular or gastrointestinal hemorrhaging as is commonly seen with cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors [38,39] and, for this reason, it has become an alternative therapeutic strategy for inflammation-related diseases. In this scenario, the interest in FAAH inhibitors is always very current and worthy of further study. In particular, it was decided to use 4-phenylbutylcarbamic acid 3′-carbamoylbiphenyl-3-yl ester (URB878, Figure 1), an in vitro very potent FAAH inhibitor (IC50 = 0.33 ± 0.03 nM) [40] able to increase the knowledge of N-substituted biphenylcarbamic acid FAAH inhibitors [41,42].
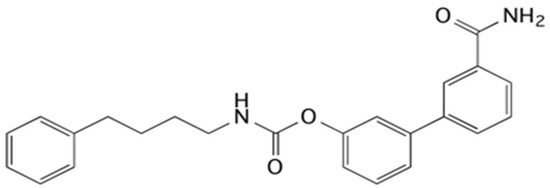
Figure 1.
Structural formula of the FAAH inhibitor URB878.
URB878 is a structural analog of the pharmacological tool URB597, but differs from it by the N-substituent, which is 4-phenylbutyl in the case of URB878 compared to a cyclohexyl for URB597. The characteristics of the substituents are similar as they are both lipophilic, but the first has an arylalkyl moiety able to improve the interaction with the hydrophobic chain. URB878 has never been studied using in vitro models other than FAAH and in vivo, but the authors chose to use it because they consider it worthy of further study due to its excellent inhibitory capacity. Moreover, it can be considered that the molecule has structural characteristics to be considered selective towards off-targets because they are very similar to those of other FAAH inhibitory carbamates of the URB series, which have shown selectivity, as reported with URB597 and URB937 [19,40,43,44].
The injection of carrageenan (CAR) into the pleural space has been widely used to investigate the pathophysiology of acute inflammation in pleurisy and to assess the role of mediators involved in cellular damage.
It is a consolidated experimental model that leads to lung injury, local inflammation, infiltration by polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs), mast cell degranulation, the migration and accumulation of pleural exudate, the production of cytokines, oxidative/nitrosative stress and lipid peroxidation with consequences in DNA damage.
The aim of this study is to investigate, for the first time, the role of FAAH inhibition in acute lung injury. To this end, a new pharmacological tool is used, the sub-nanomolar FAAH inhibitor URB878.
2. Results
2.1. URB878 Reduces CAR-Induced Lung Injury
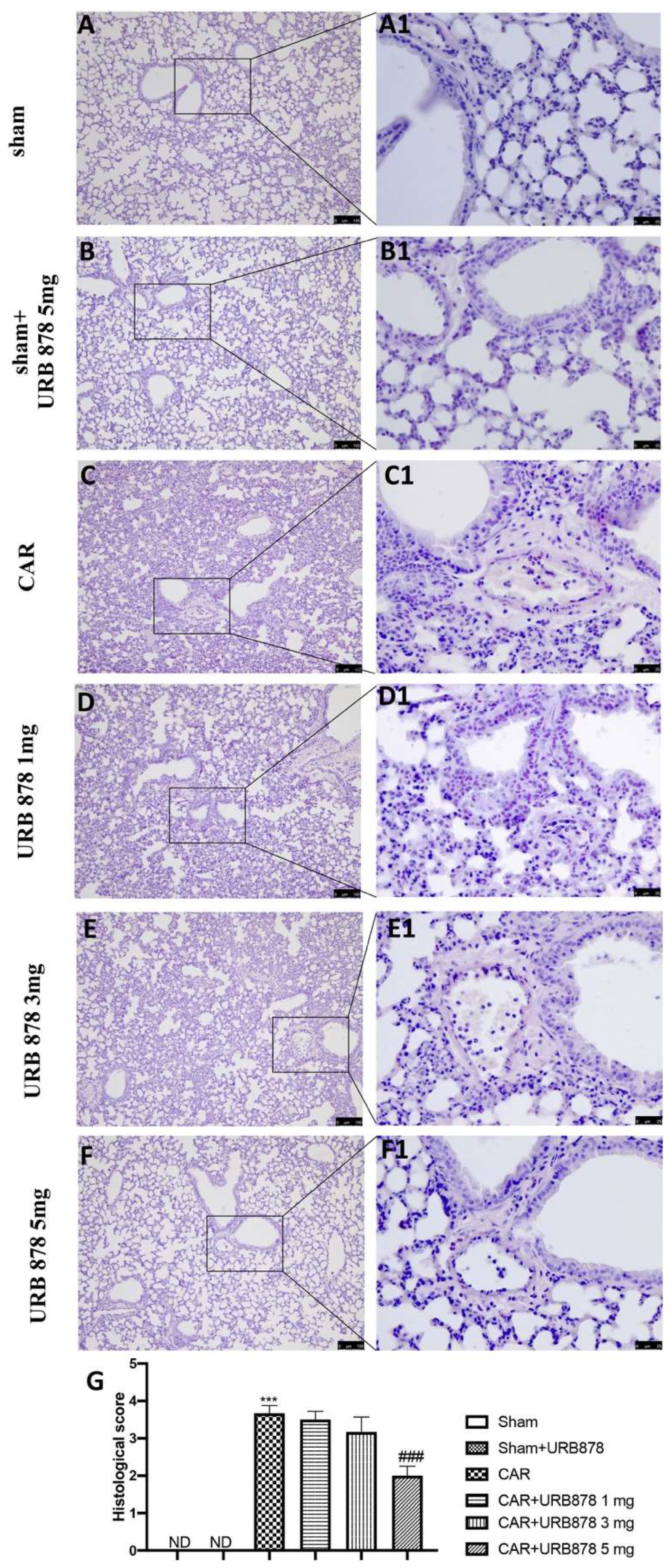
The injection of CAR into the pleural cavity was characterized by significant tissue injury and infiltration of neutrophils (PMNs) and edema (Figure 2C,C1; see histological score Figure 2G), compared to sham animals (Figure 2A,A1; see histological score Figure 2G) or to sham animals treated with URB878 at the higher dose (Figure 2B,B1; see histological score Figure 2G). URB878 at the doses of 1 mg/Kg (Figure 2D,D1; see histological score Figure 2G) and 3 mg/Kg (Figure 2E,E1; see histological score Figure 2G) did not show any significant decrease in the inflammatory state. On the other hand, the use of a high dose, that is, 5 mg/kg (Figure 2F,F1; see histological score Figure 2G), showed a significant reduction in the degree of CAR-induced injury.

Figure 2.
Inhibitions of CAR-induced lung injury by URB878. Sham (A,A1); Sham+URB878 5 mg/kg (B,B1); CAR (C,C1); CAR+URB878 1 mg/kg (D,D1); CAR+URB878 3 mg/kg (E,E1); CAR+URB878 5 mg/kg (F,F1); Histological score (G). ND: not detectable. Scale bar for (A–F) was 100 μm; Scale bar for (A1–F1) was 25 μm; Values are means ± SEM of 6 mice for all groups. Photos shown are representative of the results obtained. See manuscript for further details. *** p < 0.001 vs. sham; ### p < 0.001 vs. CAR.
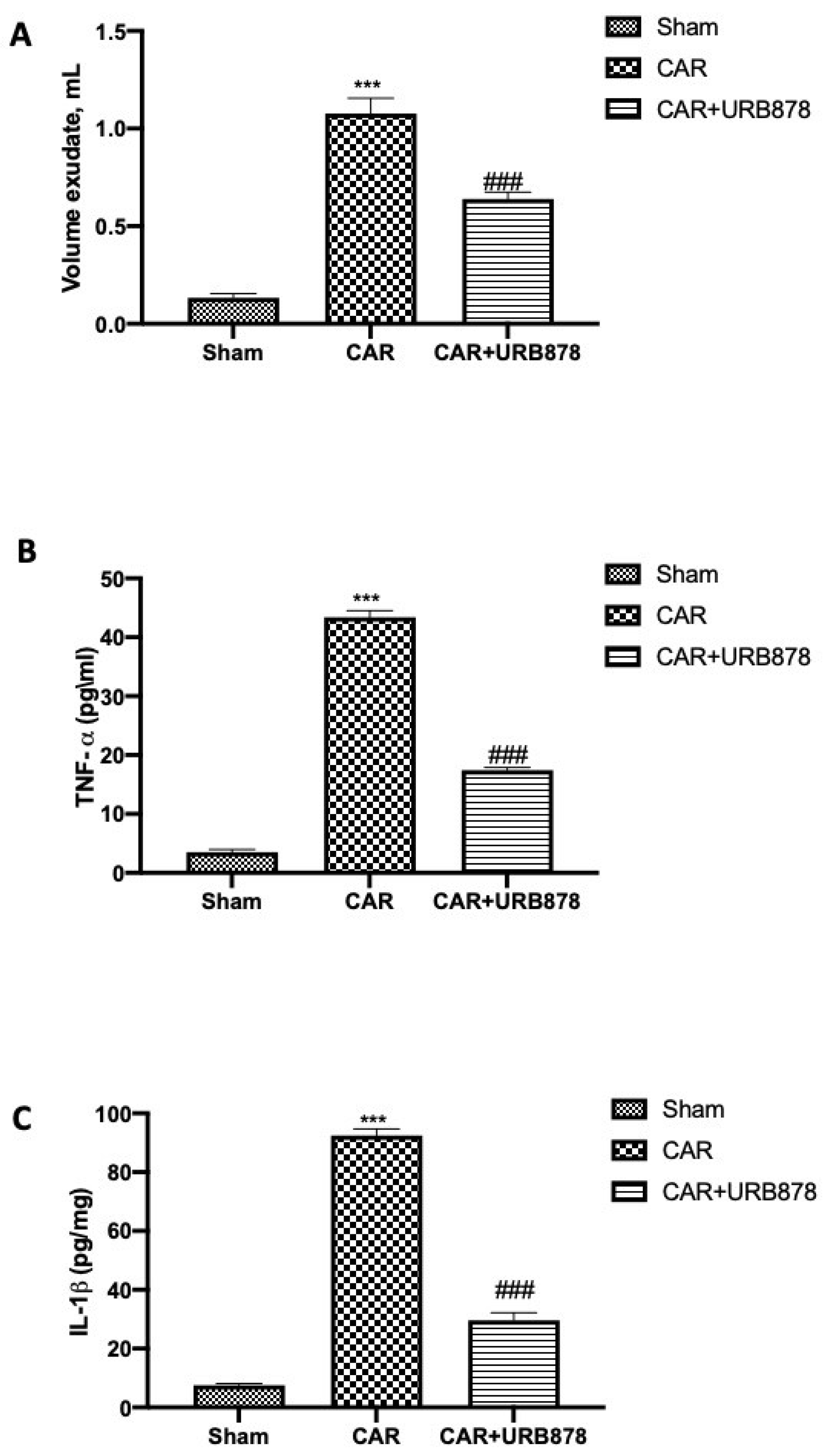
Additionally, the injection of CAR stimulated an acute inflammatory response characterized by the accumulation of exudates (Figure 3A) rich in pro-inflammatory cytokine content, such as TNF-α (Figure 3B) and IL-1β (Figure 3C). URB878 at a dose of 5 mg/kg was able to significantly reduce exudate formation as well as pro-inflammatory cytokine production.
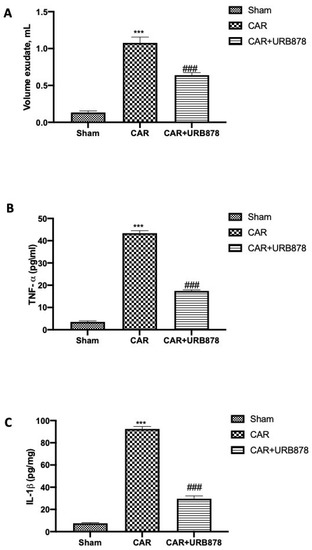
Figure 3.
URB878 administration decreases exudate volumes and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Volume exudates (A); TNF-α (B) and IL-1β (C). URB878 was used at a dose of 5 mg/kg. See manuscript for further details. Values are means ± SEM of 6 mice for all groups. *** p < 0.001 vs. sham; ### p < 0.001 vs. CAR.
2.2. URB878 Inhibits CAR-Induced Mast Cell Degranulation, PMN Infiltration and MPO Production
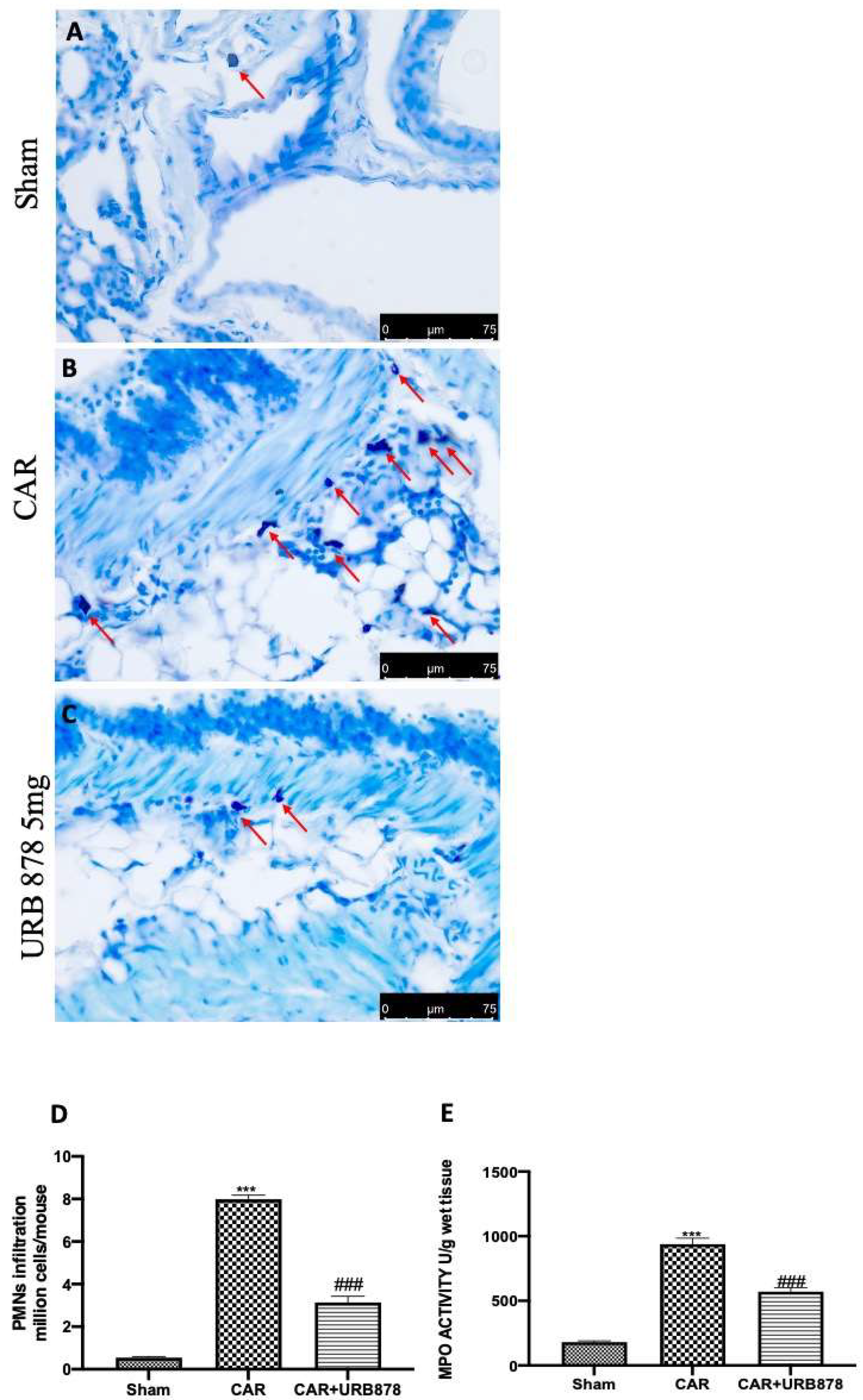
Lung edema, epithelial and endothelial injury are strongly connected with a significant influx of mast cells, PMNs, and leukocytes into the interstitium and broncheoalveolar space, which alters lung health [45,46,47]. After the CAR injection, we found a significantly increase in mast cell degranulation, PMN infiltration and MPO levels (Figure 4B,D,E), compared to sham animals (Figure 4A,D,E). On the other hand, the inhibition of FAAH with 5 mg/kg of URB878 significantly decreased all these parameters (Figure 4C–E).
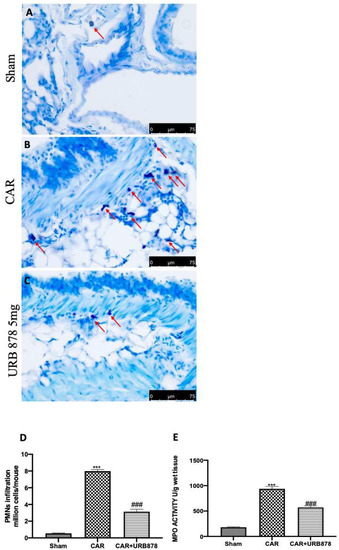
Figure 4.
URB878 administration decreases cell infiltration. Sham (A); CAR (B); CAR+URB878 5 mg/kg (C); PMN infiltration (D); MPO levels (E). Mast cells were indicated with red arrow. Scale bar for (A–C) was 75 μm; Values are means ± SEM of 6 mice for all groups. Values are means ± SEM of 6 mice for all groups. Photos shown are representative of the results obtained. See manuscript for further details. *** p < 0.001 vs. sham; ### p < 0.001 vs. CAR.
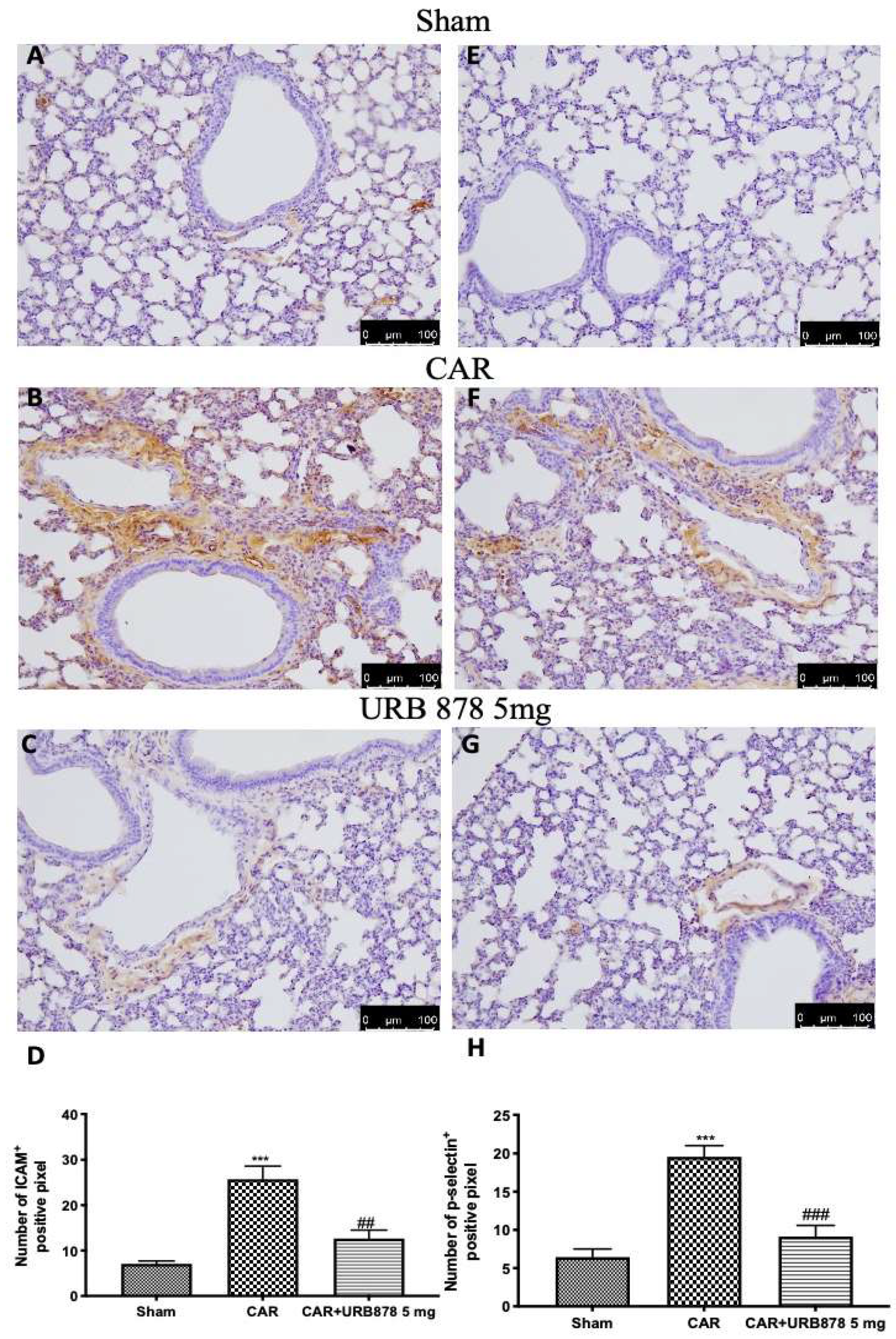
2.3. URB878 Reduces the Expressions of the Adhesion Molecules ICAM and P-Selectin
The intensity of ICAM and P-selectin staining significantly increases in lung tissue slices taken from CAR-treated animals (Figure 5B,F; see Figure 5D and Figure 5H, respectively) compared to sham groups (Figure 5A,E; see Figure 5D and Figure 5H, respectively). URB878 at a dose of 5 mg/kg significantly decreases both stainings (Figure 5C,G; see Figure 5D and Figure 5H, respectively).
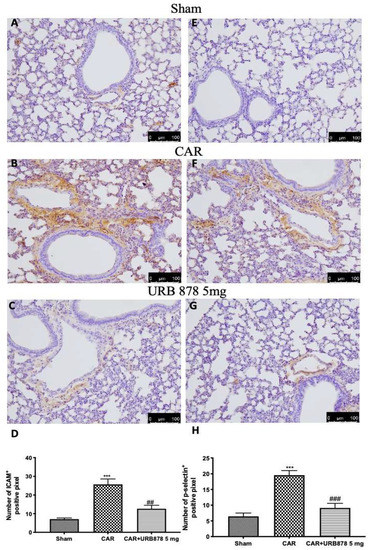
Figure 5.
URB878 administration decreases ICAM and P-selectin expression. Sham (A); CAR (B); CAR+URB878 5 mg/kg (C); graphical analysis (D) for ICAM. Sham (E); CAR (F); CAR+URB878 5 mg/kg (G); graphical analysis (H) for P-selectin. Scale bar for (A–C) and (E–G) was 100 μm; Values are means ± SEM of 6 mice for all groups. Photos shown are representative of the results obtained. See manuscript for further details. *** p < 0.001 vs. sham; ## p < 0.01 vs. CAR; ### p < 0.001 vs. CAR.
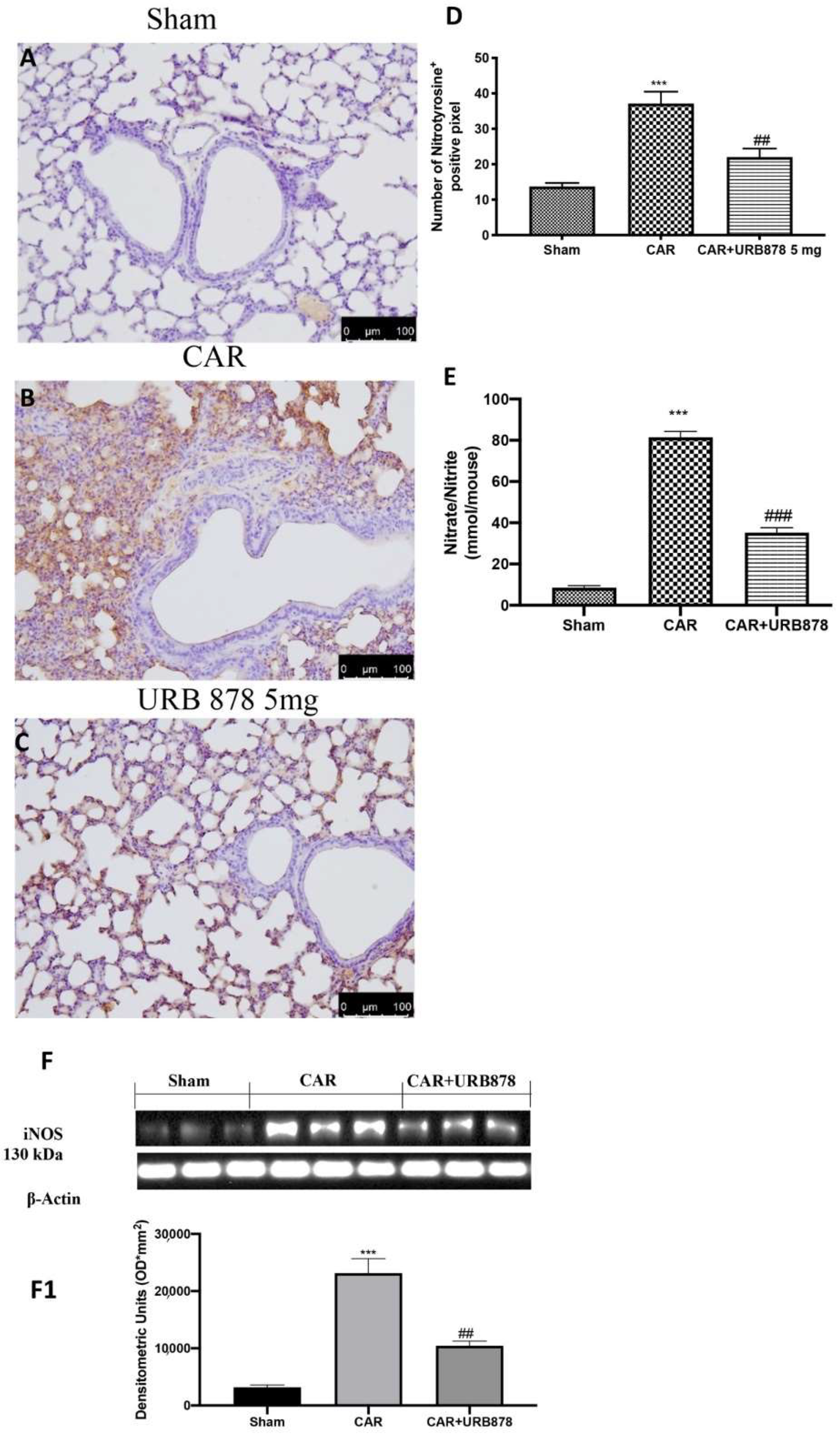
2.4. Effect of URB878 Administration on CAR-Induced Nitrosative Stress
By Western blots, immunohistochemistry and nitrite/nitrate analyses, we investigated the effects of FAAH inhibition on nitrosative stress. We found that, after the CAR injection, there was a significant increase in nitrotyrosine (Figure 6B,D), iNOS (Figure 6F; see densitometric analysis Figure 6F1) and nitrite/nitrate levels (Figure 6E), compared to the sham group (Figure 6A; see Figure 6D for nitrotyrosine expression; Figure 6F for densitometric analysis; Figure 6F1 for iNOS activity; Figure 6E for nitrite/nitrate levels). As assumed, the inhibition of FAAH by URB878 protects the lung against nitrosative stress, decreasing free radical production (Figure 6C; see Figure 6D for nitrotyrosine expression; Figure 6F for densitometric analysis; Figure 6F1 for iNOS activity; Figure 6E for nitrite/nitrate levels).

Figure 6.
Effect of URB878 on nitrosative stress. Sham (A); CAR (B); CAR+URB878 5 mg/kg (C); graphical analysis (D) for nitrotyrosine. Nitrite/nitrate levels (E); Western Blot for iNOS expression (F); densitometric analysis (F1); Scale bar for (A–C) was 100 μm; Values are means ± SEM of 6 mice for all groups. Photos shown are representative of the results obtained. See manuscript for further details. *** p < 0.001 vs. sham; ## p < 0.01 vs. CAR; ### p < 0.001 vs. CAR.
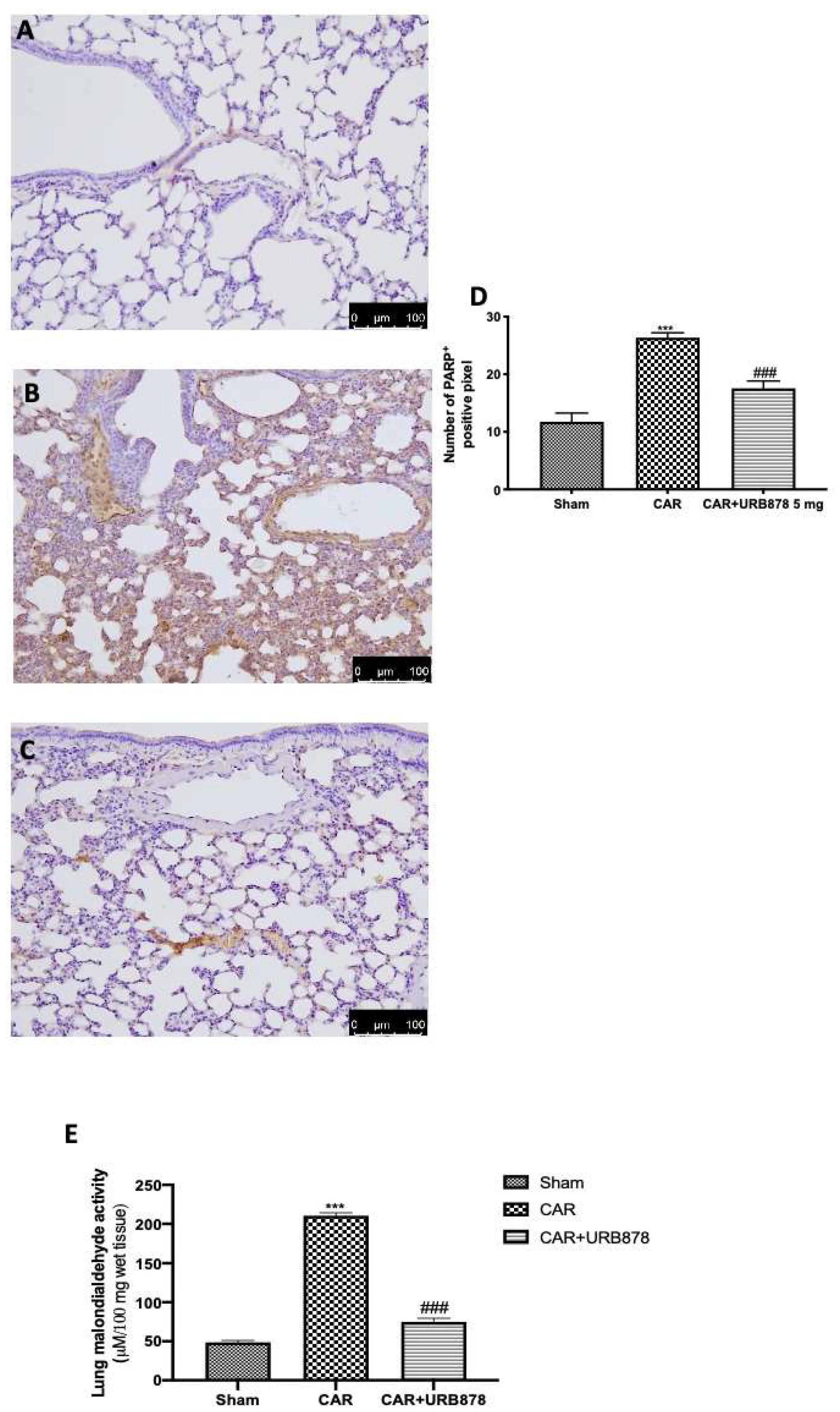
2.5. FAAH Inihibition Reduces DNA Damage and Lipid Peroxidation
Immunohistochemical analysis of lung tissue collected from CAR-treated mice showed an increased in PARP positive cells (Figure 7B,D) compared to the sham group (Figure 7A,D). URB878 at a dose of 5 mg/kg was able to significantly decrease PARP expression (Figure 7C,D). Additionally, we evaluated lipid peroxidation by MDA activity, and we found that CAR injection in the pleural cavity significantly increased lipid peroxidation compared to the sham group (Figure 7E). On the other hand, URB878 at a dose of 5 mg/kg significantly decreased lipid peroxidation levels.

Figure 7.
Effect of URB878 on PARP expression and MDA levels. Sham (A); CAR (B); CAR+URB878 5 mg/kg (C); graphical analysis (D) for PARP. Malondialdehyde activity levels (E); Scale bar for (A–C) was 100 μm; Values are means ± SEM of 6 mice for all groups. Photos shown are representative of the results obtained. See manuscript for further details. *** p < 0.001 vs. sham; ### p < 0.001 vs. CAR.
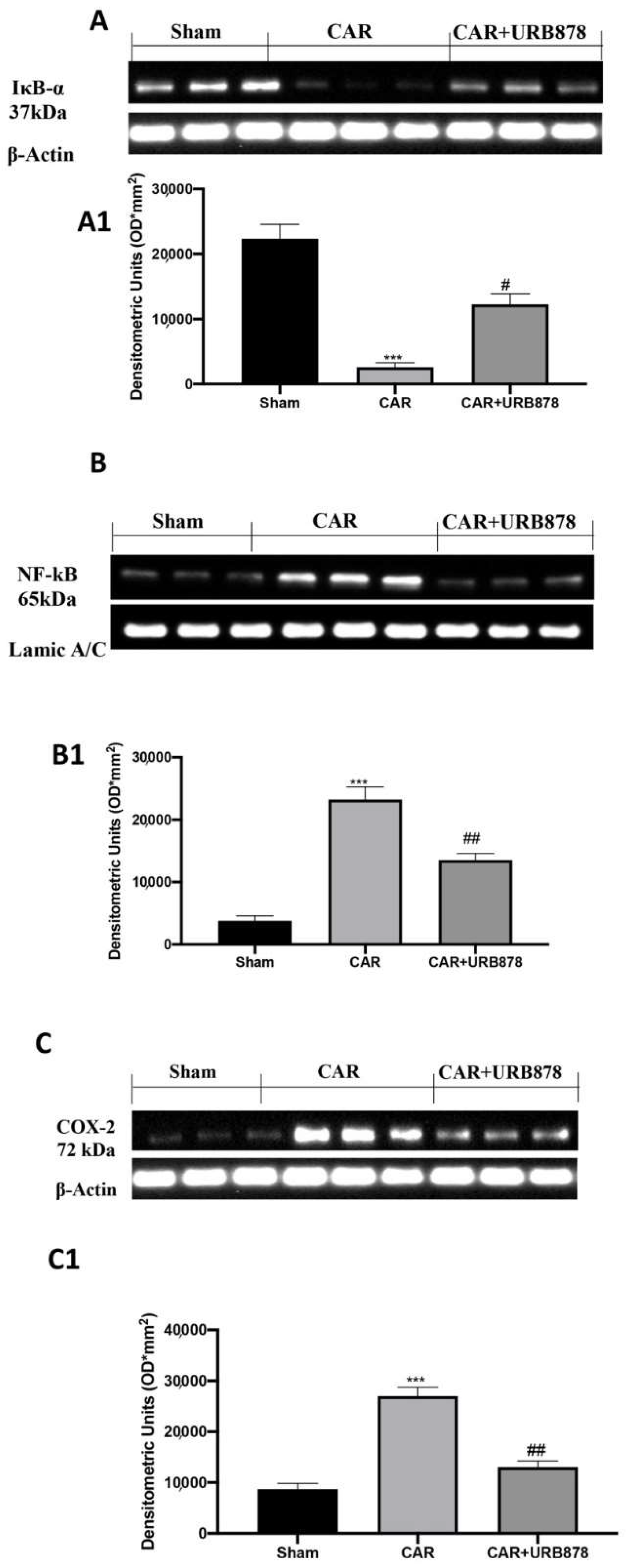
2.6. URB878 Reduces CAR-Induced Lung Inflammation
At the end of the experiment, which lasted 4 h, the lungs were processed using Western blots. The basal expression of IkB-α was significantly decreased in the lung samples obtained from CAR-injected mice, compared to the sham group (Figure 8A; see densitometric analysis in Figure 8A1). URB878 at a dose of 5 mg/kg prevented CAR-induced IkB-α degradation. Moreover, CAR increased NF-kB levels in the nuclear fractions compared with the sham-treated mice URB878 at a dose of 5 mg/kg, whose administration significantly reduced the levels of NF-kB (Figure 8B; see densitometric analysis in Figure 8B1). Furthermore, we investigated the levels of COX-2 expression following URB878 treatment and found that, after CAR injection, there was a significantly increase in lung tissue. After the treatment, COX-2 expression was reported have reached physiological levels (Figure 8C; see densitometric analysis in Figure 8C1).

Figure 8.
Western Blot and relative densitometric analysis for IkB-α (A,A1) NF-kB (B,B1) and Cox-2 (C,C1). Values are means ± SEM of 6 mice for all groups. See manuscript for further details. *** p < 0.001 vs. sham; # p < 0.05 vs. CAR; ## p < 0.01 vs. CAR.
3. Discussion and Conclusions
FAAH is a member of a broad serine hydrolase family that hydrolyze NAEs, such as AEA, PEA, and OEA, and this action is known as an entourage effect. The increased levels of NAEs due to the genetic or pharmacological inhibition of FAAH have been related to have extensive beneficial effects in both acute and chronic situations [48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56]. As a result, further research into FAAH inhibitors is needed, as well as the investigation of molecular pathways involved in the inflammatory response.
The hyperactivation of the immune system is typically linked to ALI, resulting in pulmonary inflammation, pulmonary edema, alveolar destruction, and, in severe cases, respiratory failure [57,58]. There is a significant rate of death linked with ALI/ARDS because no pharmaceutical medications have been licensed by the FDA to treat it. Animal models of ALI have greatly aided our understanding of the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of the ALI and ARDS clinical syndromes. One of the most used models to reproduce ALI damage is pleurisy obtained with an injection of carrageenan into the pleural space [59,60,61]. To date, despite the numerous studies carried out with FAAH inhibitors or with the use of genetically modified animals, no one has evaluated the role of FAAH in an experimental model of carrageenan-induced ALI.
The infiltration of inflammatory cells and rupture of the alveolar–capillary barrier histologically characterize the acute phase of ALI, resulting in a proteinaceous exudate that floods the alveolar passages, impairing gas exchange and precipitating respiratory failure [62,63]. In our study, we found that, with the inhibition of the FAAH enzyme, the entire histological damage decreases in a dose-dependent manner. The production of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β, is required for lung neutrophil recruitment and subsequent lung damage. TNF-α and IL-1β are two of the first cytokines generated by alveolar macrophages during the inflammatory phase of lung damage [64,65]. These cytokines, as well as other proinflammatory compounds, initiate, amplify, and perpetuate the inflammatory response during acute lung injury [66,67,68,69,70]. The inhibition of FAAH enzyme by URB878 at the dose of 5 mg/kg significantly decreases both cytokines release as well as the volume of exudates. Transepithelial cellular migration is an important feature of ALI, as well as the degranulation of mast cells [71,71,72]. Our study demonstrates, for the first time, that the stabilization of MCs and neutrophils from degranulation and migration by the inhibition of FAAH could attenuate inflammatory response. Inflammatory processes are aided by P-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). ALI is related, through the increase in leukocyte adherence, to the endothelium of the vascular wall [73]. FAAH inhibition significantly reduces the expression of both molecules. Different isoforms of nitric oxide synthases (NOS) and nitrosative stress determinants play essential roles in the pathogenesis of ALI-induced pulmonary dysfunction [74]. In our study, and according to the literature, we found a significant increase in nitrite and nitrate levels as well as in iNOS and nitrotyrosine expression. FAAH inhibition attenuated this increase, bringing expressions back to physiological levels. In addition, the injection of CAR into the pleural cavity triggers other cytotoxic effects, including DNA damage as well as lipid peroxidation [75]. In our study, we found that FAAH inhibition by URB878 at the dose of 5 mg/kg was able to reduce PARP activation as well as lipid peroxidation. Pulmonary expression of these mediators, especially TNF-α and IL-1β, has been linked to the nuclear translocation of the transcription factor NF-κB [76,77]. A lot of stimuli can cause IκBα phosphorylation, with the consequent nuclear translocation of the NF-κB subunit p65, which leads to a transcription of multiple proinflammatory genes, chemokines, and adhesion molecules [78,79]. In our study, we found a significant increase in NF-κB activation as well as in COX-2 compared to the sham group. On the other hand, FAAH inhibition significantly decrease the activation on this pathway.
In conclusion, our findings confirm the protective effect of FAAH in the development of CAR-induced pleurisy by inhibiting NF-κB activation, as well as the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. These actions could explain why neutrophil migration, as well as nitrosative stress, decreases during inflammatory response. The findings of this study, taken combined, add to our understanding of the FAAH modulation in the pathophysiology of inflammation and support its therapeutic potential for lung inflammatory diseases.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
CD1 mice (25–30 g, Envigo, Milan, Italy) were employed. The University of Messina Review Board for animal care (OPBA) approved the study (Prot. Num. 266/2021-PR). All animal experiments agree with the new Italian regulations (D.Lgs 2014/26), E.U. regulations (E.U. Directive 2010/63) and the ARRIVE guidelines. ALI was made as previously described by Di Paola et al. [80].
4.2. Experimental Design and Groups
Briefly, mice were anaesthetized and saline (0.1 mL) or saline containing 2% λ carrageenan (0.1 mL) was injected into the pleural cavity.
Mice were casually distributed into the following groups:
- (1)
- CAR: mice were subjected to the CAR injection described above, and treated with saline solution;
- (2)
- CAR+URB878: mice were subjected to the CAR injection described above, and treated orally 1 h after with URB878 dissolved in a vehicle consisting of 10% PEG-400, 10% Tween-80 and 80% saline at different doses;
- (3)
- Sham groups: animals were subjected to an injection of saline solution;
- (4)
- Sham groups+URB878: animals were subjected to URB878 treatment at different doses (data not shown) (in our results, there were not significant difference observed between Sham and Sham+URB878).
After four hours, the animals were killed, and the lungs were conserved for further study. Doses were chosen based on a dose–response study carried out in our lab. URB878 at the doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg did not show any advantage in CAR-induced lung inflammation. For this reason, we conducted our experiment only with the dose of 5 mg/kg.
4.3. Exudate and Leukocytes Count
The measure of exudates and count of leukocytes was performed as previously described [81]. Briefly, at the end of the experiment, the chest was opened, and the pleural cavity washed with 1 mL of saline solution containing heparin and indomethacin. The exudate and washing solution were removed by aspiration and the total volume measured.
The leukocytes in the exudate were suspended in phosphate-buffer saline (PBS) and, after blue toluidine staining, counted with an optical microscope in a Burker’s chamber.
4.4. Western Blot Analysis of Cytosolic and Nuclear Extracts
Extracts of the cytosol and nucleus were prepared, as previously mentioned [82,83,84,85,86]. The following primary antibodies were used: anti-iNOS (1:500, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, #sc-7271, Dallas, TX, USA), anti-Cox-2 (1:500, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, #sc-19999), anti-FAAH (1:500, Sigma-Aldrich Corp., Milan, Italy), anti-Iκbα (1:500, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, #sc-1643), and anti-nfκb (1:500, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, #sc8414) in 1 × PBS, 5% w/v non-fat dried milk, and 0.1% Tween 20, at 4 °C overnight [87,88,89,90]. For the cytosolic fraction, Western blots were also explored with antibody against β-actin protein (1:500, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA). The same methods were used for nuclear fraction with lamin A/C (1:500, Sigma-Aldrich Corp., Milan, Italy) [91,92]. Signals were examined with an enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) detection system reagent, according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Thermo, Monza, Italy). The relative expression of the protein bands was quantified by densitometry with BIORAD ChemiDocTM XRS+ software (Hercules, CA, USA) [83,87,93,94,95].
4.5. Evaluation of Tissue Lipid Peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation were assessed with the consolidated method of malonaldehyde, as previously described, and expressed as μM MDA/mg of proteins [96].
4.6. Cytokine and Nitrite/Nitrate Measurement
TNF-α, IL-1β and nitrite/nitrate concentration were measured in the exudates using ELISA kits (R & D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions, and expressed as pg/mL, or with a Griess reaction assay kit and expressed as mmol/mouse [80,93,94,96,97,98,99,100,101].
4.7. Histopathological Evaluation with Hematoxylin/Eosin and Toluidine Blue
The lung tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) for architecture alterations and toluidine blue for mast cell degranulation, and analyzed using a light microscopy (Leica DM6, Milan, Italy) associated with an Imaging system (LasX Navigator, Milan, Italy). The degree of inflammation was evaluated according to a score from normal (0) to severe (4), as previously described [83,87,102].
4.8. Immunohistochemical Localization of Nitrotyrosine, Poly(ADP-ribose), ICAM and P-Selectin
At the end of the experiments, lung tissues were incubated with anti-ICAM-1 murine polyclonal antibody (1/100 in PBS, v/v, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-P-selectin murine polyclonal antibody (1/100 in PBS, v/v, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-PAR murine polyclonal antibody (1/100 in PBS, v/v, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and anti-nitrotyrosine rabbit polyclonal antibody (1:200 in PBS, v/v, Millipore), as previously described [72,88,103,104,105,106,107,108]. Immunohistochemical images were collected using (Leica DM6, Milan, Italy) associated with an Imaging system (LasX Navigator, Milan, Italy). The digital images were opened in ImageJ, followed by deconvolution using the color deconvolution plug-in. When the IHC profiler plug-in is selected, it automatically plots a histogram profile of the deconvoluted DAB image, and a corresponding scoring log is displayed. The histogram profile corresponds to the positive pixel intensity value obtained from the computer program. All immunohistochemical analyses were carried out by two observers blinded to the treatment [72,88,103,104,105,106,107,108,109].
4.9. Materials
Unless otherwise stated, all compounds were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
4.10. Statistical Evaluation
In this study, the data are expressed as the average ± SEM and represent at least 3 experiments carried out in different days. For in vivo studies, N represents the number of animals used. The number of animals used for in vivo studies was carried out by G*Power 3.1 software (Die Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Düsseldorf, Germany). Data were analyzed by an experienced histopathologist, and all the studies were performed without knowledge of the treatments. The results were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post hoc test for multiple comparisons. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
4.11. Synthesis of URB878
The FAAH inhibitor URB878 was synthesized as previously reported [40]. Briefly, to a stirred solution of 3′-carbamoylbiphenyl-3-ol in toluene, 4-phenylbutylisocyanate was added (twice) and the reaction was refluxed for 8 h, then cooled and concentrated. The residue was purified by column chromatography and recrystallization from ethanol was performed to obtain the desired final compound.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C.; Data curation, A.F.P.; Investigation, T.G.; Methodology, R.D., R.C., E.G. and R.S.; Project administration, S.C. and R.D.P.; Supervision, T.G.; Validation, R.F. and D.I.; Writing—original draft, M.C.; Writing—review and editing, A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The University of Messina Review Board for animal care (OPBA) approved the study (Prot.Num. 266/2021-PR). All animal experiments agree with the new Italian regulations (D.Lgs 2014/26), E.U. regulations (E.U. Directive 2010/63) and the ARRIVE guidelines.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rubenfeld, G.D.; Caldwell, E.; Peabody, E.; Weaver, J.; Martin, D.P.; Neff, M.; Stern, E.J.; Hudson, L.D. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaller, M.; Richter, T. Acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Emerg. Trauma Shock 2010, 3, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasso, S.; Mascia, L.; Del Turco, M.; Malacarne, P.; Giunta, F.; Brochard, L.; Slutsky, A.S.; Marco Ranieri, V. Effects of recruiting maneuvers in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome ventilated with protective ventilatory strategy. Anesthesiology 2002, 96, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, I.; Leiner, T.; Mikor, A.; Szakmany, T.; Bogar, L.; Molnar, Z. Hemodynamic and respiratory changes during lung recruitment and descending optimal positive end-expiratory pressure titration in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care. Med. 2007, 35, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bein, T.; Kuhr, L.P.; Bele, S.; Ploner, F.; Keyl, C.; Taeger, K. Lung recruitment maneuver in patients with cerebral injury: Effects on intracranial pressure and cerebral metabolism. Intensive. Care. Med. 2002, 28, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, N.C.; Guldner, A.; Beda, A.; Rentzsch, I.; Uhlig, C.; Dittrich, S.; Spieth, P.M.; Wiedemann, B.; Kasper, M.; Koch, T.; et al. Higher levels of spontaneous breathing reduce lung injury in experimental moderate acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care. Med. 2014, 42, e702–e715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Xiu, Y.; Zhou, P.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y. A New Use for an Old Drug: Carmofur Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Inhibition of FAAH and NAAA Activities. Front. Pharm. 2019, 10, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortley, M.A.; Adcock, J.J.; Dubuis, E.D.; Maher, S.A.; Bonvini, S.J.; Delescluse, I.; Kinloch, R.; McMurray, G.; Perros-Huguet, C.; Papakosta, M.; et al. Targeting fatty acid amide hydrolase as a therapeutic strategy for antitussive therapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpelli, R.; Sasso, O.; Piomelli, D. A Double Whammy: Targeting Both Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) and Cyclooxygenase (COX) To Treat Pain and Inflammation. Chemmedchem 2016, 11, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dider, S.; Ji, J.D.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, L. Molecular mechanisms involved in the side effects of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors: A structural phenomics approach to proteome-wide cellular off-target deconvolution and disease association. Npj Syst. Biol. Appl. 2016, 2, 16023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, R.S.; Pryce, G.; Cabranes, A.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.; Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V.; Cravatt, B.F.; Michael, G.J.; Giovannoni, G.; Elphick, M.R.; et al. Fatty acid amide hydrolase as a target for neuroprotection. Mult. Scler. J. 2011, 17, S431. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, K.; Johnson, D.S.; Cravatt, B.F. Fatty acid amide hydrolase as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of pain and CNS disorders. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 763–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosburg, J.E.; Kinsey, S.G.; Lichtman, A.H. Targeting Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) to Treat Pain and Inflammation. Aaps J. 2009, 11, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccarrone, M. Fatty acid amide hydrolase: A potential target for next generation therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, L.A.; Limebeer, C.L.; Rock, E.M.; Litt, D.L.; Kwiatkowska, M.; Piomelli, D. The FAAH inhibitor URB-597 interferes with cisplatin- and nicotine-induced vomiting in the Suncus murinus (house musk shrew). Physiol. Behav. 2009, 97, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manwell, L.A.; Satvat, E.; Lang, S.T.; Allen, C.P.; Leri, F.; Parker, L.A. FAAH inhibitor, URB-597, promotes extinction and CB(1) antagonist, SR141716, inhibits extinction of conditioned aversion produced by naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal, but not extinction of conditioned preference produced by morphine in rats. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 94, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, E.M.; Limebeer, C.L.; Mechoulam, R.; Piomelli, D.; Parker, L.A. The effect of cannabidiol and URB597 on conditioned gaping (a model of nausea) elicited by a lithium-paired context in the rat. Psychopharmacology 2008, 196, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Su, S.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wu, Y.F.; Wang, D.P.; Lin, Q.; Hai, J. Cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 and fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 may protect against cognitive impairment in rats of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via PI3K/AKT signaling. Behav. Brain. Res. 2016, 313, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piomelli, D.; Tarzia, G.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Compton, T.R.; Dasse, O.; Monaghan, E.P.; Parrott, J.A.; Putman, D. Pharmacological profile of the selective FAAH inhibitor KDS-4103 (URB597). CNS Drug. Rev. 2006, 12, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, M.; Rivara, S.; Lodola, A.; Plazzi, P.V.; Tarzia, G.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Piersanti, G.; Kathuria, S.; Piomelli, D. Cyclohexylcarbamic acid 3’–or 4’-substituted biphenyl-3-yl esters as fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors: Synthesis, quantitative structure-activity relationships, and molecular modeling studies. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 4998–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, S.; Gaetani, S.; Fegley, D.; Valino, F.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Tarzia, G.; La Rana, G.; Calignano, A.; et al. Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, G.; Bambico, F.R.; Mangieri, R.; Bortolato, M.; Campolongo, P.; Solinas, M.; Cassano, T.; Morgese, M.G.; Debonnel, G.; Duranti, A.; et al. Antidepressant-like activity and modulation of brain monoaminergic transmission by blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18620–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambico, F.R.; Duranti, A.; Nobrega, J.N.; Gobbi, G. The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 modulates serotonin-dependent emotional behaviour, and serotonin1A and serotonin2A/C activity in the hippocampus. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Loverme, J.; La Rana, G.; Compton, T.R.; Parrott, J.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Tarzia, G.; Calignano, A.; et al. The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 (cyclohexylcarbamic acid 3′-carbamoylbiphenyl-3-yl ester) reduces neuropathic pain after oral administration in mice. J. Pharm. Exp. 2007, 322, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Ghiri, M.; Shahini, F.; Zarrindast, M.R. The effect of URB597, exercise or their combination on the performance of 6-OHDA mouse model of Parkinson disease in the elevated plus maze, tail suspension test and step-down task. Metab. Brain. Dis. 2021, 36, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alteba, S.; Mizrachi Zer-Aviv, T.; Tenenhaus, A.; Ben David, G.; Adelman, J.; Hillard, C.J.; Doron, R.; Akirav, I. Antidepressant-like effects of URB597 and JZL184 in male and female rats exposed to early life stress. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 39, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedse, G.; Colangeli, R.; Lavecchia, A.M.; Romano, A.; Altieri, F.; Cifani, C.; Cassano, T.; Gaetani, S. Role of the basolateral amygdala in mediating the effects of the fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 on HPA axis response to stress. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska-Kuczko, M.; Kozlowska, H.; Kloza, M.; Harasim-Symbor, E.; Biernacki, M.; Kasacka, I.; Malinowska, B. Beneficial Changes in Rat Vascular Endocannabinoid System in Primary Hypertension and under Treatment with Chronic Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase by URB597. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska-Kuczko, M.; Kozlowska, H.; Kloza, M.; Karpinska, O.; Toczek, M.; Harasim, E.; Kasacka, I.; Malinowska, B. Protective role of cannabinoid CB1 receptors and vascular effects of chronic administration of FAAH inhibitor URB597 in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Life Sci. 2016, 151, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biernacki, M.; Ambrozewicz, E.; Gegotek, A.; Toczek, M.; Bielawska, K.; Skrzydlewska, E. Redox system and phospholipid metabolism in the kidney of hypertensive rats after FAAH inhibitor URB597 administration. Redox. Biol. 2018, 15, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biernacki, M.; Ambrozewicz, E.; Gegotek, A.; Toczek, M.; Skrzydlewska, E. Long-term administration of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor (URB597) to rats with spontaneous hypertension disturbs liver redox balance and phospholipid metabolism. Adv. Med. Sci. 2019, 64, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biernacki, M.; Baranowska-Kuczko, M.; Niklinska, G.N.; Skrzydlewska, E. The FAAH Inhibitor URB597 Modulates Lipid Mediators in the Brain of Rats with Spontaneous Hypertension. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, M.; Luczaj, W.; Gegotek, A.; Toczek, M.; Bielawska, K.; Skrzydlewska, E. Crosstalk between liver antioxidant and the endocannabinoid systems after chronic administration of the FAAH inhibitor, URB597, to hypertensive rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 301, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biernacki, M.; Luczaj, W.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Ambrozewicz, E.; Toczek, M.; Skrzydlewska, E. The Effect of Long-Term Administration of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Inhibitor URB597 on Oxidative Metabolism in the Heart of Rats with Primary and Secondary Hypertension. Molecules 2018, 23, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, D.; Matthey, M.; Bindila, L.; Lerner, R.; Lutz, B.; Zimmer, A.; Fleischmann, B.K. Endocannabinoid anandamide mediates hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18710–18715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, K.; Ramer, R.; Dithmer, S.; Ivanov, I.; Merkord, J.; Hinz, B. Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors confer anti-invasive and antimetastatic effects on lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15047–15064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, J.; Sneh, A.; Shilo, K.; Nasser, M.W.; Ganju, R.K. FAAH inhibition enhances anandamide mediated anti-tumorigenic effects in non-small cell lung cancer by downregulating the EGF/EGFR pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2475–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, G.; Lin, D.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Y. Potential analgesic effects of a novel N-acylethanolamine acid amidase inhibitor F96 through PPAR-α. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Li, Y.; Ke, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Yu, H.; Huang, R.; Lu, C.; Qiu, Y. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of oxazolidone derivatives as highly potent N-acylethanolamine acid amidase (NAAA) inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12455–12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapper, J.R.; Vacondio, F.; King, A.R.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Silva, C.; Sanchini, S.; Tarzia, G.; Mor, M.; Piomelli, D. A second generation of carbamate-based fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors with improved activity in vivo. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacondio, F.; Silva, C.; Lodola, A.; Carmi, C.; Rivara, S.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Sanchini, S.; Clapper, J.R.; Piomelli, D.; et al. Biphenyl-3-yl alkylcarbamates as fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitors: Steric effects of N-alkyl chain on rat plasma and liver stability. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4466–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, M.; Lodola, A.; Rivara, S.; Vacondio, F.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Sanchini, S.; Piersanti, G.; Clapper, J.R.; King, A.R.; et al. Synthesis and quantitative structure-activity relationship of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors: Modulation at the N-portion of biphenyl-3-yl alkylcarbamates. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3487–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tarzia, G.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Piersanti, G.; Mor, M.; Rivara, S.; Plazzi, P.V.; Park, C.; Kathuria, S.; Piomelli, D. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of alkylcarbamic acid aryl esters, a new class of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vozella, V.; Ahmed, F.; Choobchian, P.; Merrill, C.B.; Zibardi, C.; Tarzia, G.; Mor, M.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Rivara, S.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety studies on URB937, a peripherally restricted fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor, in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virk, H.; Arthur, G.; Bradding, P. Mast cells and their activation in lung disease. Transl. Res. 2016, 174, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, E. Neutrophils and acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, S195–S199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, J.; Soehnlein, O. Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, K.; Uyama, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Ueda, N. Endocannabinoids and related N-acylethanolamines: Biological activities and metabolism. Inflamm. Regen. 2018, 38, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Z.; Baik, D.; Schey, R. The role of cannabinoids in regulation of nausea and vomiting, and visceral pain. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 17, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, K.A.; Darmani, N.A.; Parker, L.A. Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 722, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, L.A.; Rock, E.M.; Limebeer, C.L. Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, D.R.; Kendall, D.A.; Chapman, V. Inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase produces PPAR-alpha-mediated analgesia in a rat model of inflammatory pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolato, M.; Mangieri, R.A.; Fu, J.; Kim, J.H.; Arguello, O.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Tarzia, G.; Piomelli, D. Antidepressant-like activity of the fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 in a rat model of chronic mild stress. Biol. Psychiatry. 2007, 62, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celorrio, M.; Fernandez-Suarez, D.; Rojo-Bustamante, E.; Echeverry-Alzate, V.; Ramirez, M.J.; Hillard, C.J.; Lopez-Moreno, J.A.; Maldonado, R.; Oyarzabal, J.; Franco, R.; et al. Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition for the symptomatic relief of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 57, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, P.; Wen, J.; Tanaka, M.; Zhang, Y. Therapeutic Effect of a Novel Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Inhibitor PF04457845 in the Repetitive Closed Head Injury Mouse Model. J. Neurotrauma. 2019, 36, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchantchou, F.; Tucker, L.B.; Fu, A.H.; Bluett, R.J.; McCabe, J.T.; Patel, S.; Zhang, Y. The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor PF-3845 promotes neuronal survival, attenuates inflammation and improves functional recovery in mice with traumatic brain injury. Neuropharmacology 2014, 85, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, G.P. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2018, 20, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, E.; Brodie, D.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA 2018, 319, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentsch, A.B.; Ward, P.A. Regulation of experimental lung inflammation. Respir. Physiol. 2001, 128, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvemini, D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Bourdon, D.M.; Stern, M.K.; Currie, M.G.; Manning, P.T. Evidence of peroxynitrite involvement in the carrageenan-induced rat paw edema. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 303, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, E.; Di Paola, R.; Viviani, B.; Genovese, T.; Mazzon, E.; Lucchi, L.; Marinovich, M.; Galli, C.L.; Cuzzocrea, S. Increased carrageenan-induced acute lung inflammation in old rats. Immunology 2005, 115, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidot, D.M.; Folkesson, H.G.; Jain, L.; Sznajder, J.I.; Pittet, J.F.; Matthay, M.A. Integrating acute lung injury and regulation of alveolar fluid clearance. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L301–L306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfanos, S.E.; Mavrommati, I.; Korovesi, I.; Roussos, C. Pulmonary endothelium in acute lung injury: From basic science to the critically ill. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 1702–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Takayasu, T.; Kimura, A.; Hayashi, T.; Kakimoto, N.; Miyashita, T.; Kondo, T. Gene expression of cytokines and growth factors in the lungs after paraquat administration in mice. Leg. Med. 2006, 8, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirshahrokhi, K.; Bohlooli, S. Effect of methylsulfonylmethane on paraquat-induced acute lung and liver injury in mice. Inflammation 2013, 36, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Wang, H.D.; Lu, D.X.; Qi, R.B.; Wang, Y.P.; Yan, Y.X.; Fu, Y.M. Berberine inhibits cytosolic phospholipase A2 and protects against LPS-induced lung injury and lethality independent of the alpha2-adrenergic receptor in mice. Shock 2008, 29, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, J.; Kawakatsu, H.; Gartland, B.; Pespeni, M.; Sheppard, D.; Matthay, M.A.; Canessa, C.M.; Pittet, J.F. Interleukin-1beta decreases expression of the epithelial sodium channel alpha-subunit in alveolar epithelial cells via a p38 MAPK-dependent signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18579–18589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.; Roux, J.; Kawakatsu, H.; Su, G.; Dagenais, A.; Berthiaume, Y.; Howard, M.; Canessa, C.M.; Fang, X.; Sheppard, D.; et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 decreases expression of the epithelial sodium channel alphaENaC and alveolar epithelial vectorial sodium and fluid transport via an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 43939–43950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hybertson, B.M.; Lee, Y.M.; Cho, H.G.; Cho, O.J.; Repine, J.E. Alveolar type II cell abnormalities and peroxide formation in lungs of rats given IL-1 intratracheally. Inflammation 2000, 24, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Hybertson, B.M.; Cho, H.G.; Terada, L.S.; Cho, O.; Repine, A.J.; Repine, J.E. Platelet-activating factor contributes to acute lung leak in rats given interleukin-1 intratracheally. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L75–L80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Mallampalli, R.K. The acute respiratory distress syndrome: From mechanism to translation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 855–860, Correction in J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; Crupi, R.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Management of Acute Lung Injury: Palmitoylethanolamide as a New Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, W.; Hu, D.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, W.; Chen, C. Resveratrol efficiently improves pulmonary function via stabilizing mast cells in a rat intestinal injury model. Life Sci. 2017, 185, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Connelly, R.; Traber, D.L.; Hamahata, A.; Nakano, Y.; Esechie, A.; Jonkam, C.; von Borzyskowski, S.; Traber, L.D.; Schmalstieg, F.C.; et al. Time course of nitric oxide synthases, nitrosative stress, and poly(ADP ribosylation) in an ovine sepsis model. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talero, E.; Di Paola, R.; Mazzon, E.; Esposito, E.; Motilva, V.; Cuzzocrea, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of adrenomedullin on acute lung injury induced by Carrageenan in mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 717851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentsch, A.B.; Ward, P.A. Activation and regulation of NFkappaB during acute inflammation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1999, 37, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawiger, J. Innate immunity and inflammation: A transcriptional paradigm. Immunol. Res. 2001, 23, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxford, T.; Ghosh, G. A structural guide to proteins of the NF-kappaB signaling module. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, R.; Mazzon, E.; Muia, C.; Genovese, T.; Menegazzi, M.; Zaffini, R.; Suzuki, H.; Cuzzocrea, S. Green tea polyphenol extract attenuates lung injury in experimental model of carrageenan-induced pleurisy in mice. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Biundo, F.; Campolo, M.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Inhibition of inflammasome activation improves lung acute injury induced by carrageenan in a mouse model of pleurisy. FASEB. J. 2017, 31, 3497–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordaro, M.; Paterniti, I.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. KU0063794, a Dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 Inhibitor, Reduces Neural Tissue Damage and Locomotor Impairment After Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2415–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Petrosino, S.; Cuzzocrea, S. Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Co-UltraPEALut in a Mouse Model of Vascular Dementia. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campolo, M.; Esposito, E.; Ahmad, A.; Di Paola, R.; Paterniti, I.; Cordaro, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Wallace, J.L.; Cuzzocrea, S. Hydrogen sulfide-releasing cyclooxygenase inhibitor ATB-346 enhances motor function and reduces cortical lesion volume following traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterniti, I.; Di Paola, R.; Campolo, M.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Tremolada, G.; Maestroni, A.; Bandello, F.; Esposito, E.; et al. Palmitoylethanolamide treatment reduces retinal inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 769, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Impellizzeri, D.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Adelmidrol, a Palmitoylethanolamide Analogue, as a New Pharmacological Treatment for the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; Campolo, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Fusco, R.; Pugliatti, P.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Protective Effects of Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA-um) in Myocardial Ischaemia and Reperfusion Injury in VIVO. Shock 2016, 46, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide (PEA-um((R))) in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.; Impellizzeri, D.; Bruschetta, G.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. A new co-micronized composite containing palmitoylethanolamide and polydatin shows superior oral efficacy compared to their association in a rat paw model of carrageenan-induced inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 782, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Crupi, R.; Pascali, J.; Alfonsi, D.; Marcolongo, G.; Cuzzocrea, S. 2-pentadecyl-2-oxazoline: Identification in coffee, synthesis and activity in a rat model of carrageenan-induced hindpaw inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 108, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Absence of formyl peptide receptor 1 causes endometriotic lesion regression in a mouse model of surgically-induced endometriosis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 31355–31366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Effect of PEA-OXA on neuropathic pain and functional recovery after sciatic nerve crush. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. The Role of Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts on an Experimental Model of Painful Degenerative Joint Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Cordaro, M.; D’Amico, R.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Smeriglio, A.; Mandalari, G.; et al. The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Anacardium occidentale L. Cashew Nuts in a Mouse Model of Colitis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Britti, D.; Morittu, V.M.; Evangelista, M.; Cuzzocrea, S. Adelmidrol, in combination with hyaluronic acid, displays increased anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects against monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Arthritis. Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, R.; Crisafulli, C.; Mazzon, E.; Genovese, T.; Paterniti, I.; Bramanti, P.; Cuzzocrea, S. Effect of PD98059, a selective MAPK3/MAPK1 inhibitor, on acute lung injury in mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Wu, S.; Xie, W.; He, H. Ketamine ameliorates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in experimental traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2 pathway. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiang, J. Tenacissoside H Promotes Neurological Recovery of Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Injury in Mice by Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative stress via TrkB Pathway. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 48, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.D.; Huang, Y.H.; Lai, C.S.W.; Dong, C.M.; Ho, L.C.; Wu, E.X.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.M.; Chung, S.K.; Sham, P.C.; et al. Chemotherapy-Induced Cognitive Impairment Is Associated with Cytokine Dysregulation and Disruptions in Neuroplasticity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Liang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yin, X.; Yang, H.; Zhi, Y.; Ying, G.; Zou, J.; Chen, L.; Yao, X.; et al. Astaxanthin protects cognitive function of vascular dementia. Behav. Brain. Funct. 2020, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Paracetamol, a New Association to Relieve Hyperalgesia and Pain in a Sciatic Nerve Injury Model in Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amicoa, R.; Monacob, F.; Fuscoa, R.; Peritorea, A.F.; Genovesea, T.; Impellizzeria, D.; Crupic, R.; Interdonatoa, L.; Sforzaa, A.M.; Gugliandoloc, E. Exposure to Atrazine Induces Lung Inflammation through Nrf2-HO1 and Beclin 1/LC3 Pathways. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 55, 413–427. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, E.; Fagone, E.; Gili, E.; Fruciano, M.; Iemmolo, M.; Pistorio, M.P.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Vancheri, C. Preventive and therapeutic effects of thymosin beta4 N-terminal fragment Ac-SDKP in the bleomycin model of pulmonary fibrosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33841–33854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; D’Amico, R.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts Modulate the Nrf2 and NLRP3 Pathways in Pancreas and Lung after Induction of Acute Pancreatitis by Cerulein. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Scuto, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Modulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome through Formyl Peptide Receptor 1 (Fpr-1) Pathway as a New Therapeutic Target in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Adelmidrol: A New Promising Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Tool in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma Translocation 1 Inhibitor as a Novel Therapeutic Tool for Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Talero, E.; Siracusa, R.; Alcaide, A.; Cordaro, M.; Maria Zubelia, J.; Bruschetta, G.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Protective effect of polyphenols in an inflammatory process associated with experimental pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, S.; Gokulan, R.; Dongre, H.; Vaidya, M.; Chaukar, D.; Prabhash, K.; Ingle, A.; Joshi, S.; Dange, P.; Joshi, S.; et al. Prognostic role of Oct4, CD44 and c-Myc in radio-chemo-resistant oral cancer patients and their tumourigenic potential in immunodeficient mice. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).