Abstract
BPA is one of the most common endocrine disruptors that is widely being manufactured daily nationwide. Although scientific evidence supports claims of negative effects of BPA on humans, there is also evidence suggesting that a low level of BPA is safe. However, numerous in vivo trials contraindicate with this claim and there is a high possibility of BPA exposure could lead to obesity. It has been speculated that this does not stop with the exposed subjects only, but may also cause transgenerational effects. Direct disruption of endocrine regulation, neuroimmune and signaling pathways, as well as gut microbiata, has been identified to be interrupted by BPA exposure, leading to overweight or obesity. In these instances, cardiovascular complications are one of the primary notable clinical signs. In regard to this claim, this review paper discusses the role of BPA on obesity in the perspective of endocrine disruptions and possible cardiovascular complications that may arise due to BPA. Thus, the aim of this review is to outline the changes in gut microbiota and neuroimmune or signaling mechanisms involved in obesity in relation to BPA. To identify potentially relevant articles, a depth search was done on the databases Nature, PubMed, Wiley Online Library, and Medline & Ovid from the past 5 years. According to Boolean operator guideline, selected keywords such as (1) BPA OR environmental chemical AND fat OR LDL OR obese AND transgenerational effects or phenocopy (2) Endocrine disruptors OR chemical AND lipodystrophy AND phenocopy (3) Lipid profile OR weight changes AND cardiovascular effect (4) BPA AND neuroimmune OR gene signaling, were used as search terms. Upon screening, 11 articles were finalized to be further reviewed and data extraction tables containing information on (1) the type of animal model (2) duration and dosage of BPA exposure (3) changes in the lipid profile or weight (4) genes, signaling mechanism, or any neuroimmune signal involved, and (5) transgenerational effects were created. In toto, the study indicates there are high chances of BPA exposure affecting lipid profile and gene associated with lipolysis, leading to obesity. Therefore, this scoping review recapitulates the possible effects of BPA that may lead to obesity with the evidence of current in vivo trials. The biomarkers, safety concerns, recommended dosage, and the impact of COVID-19 on BPA are also briefly described.
1. Introduction
Bisphenol A (BPA), also known as an obesogen, is a commonly used industrial chemical for plastic-based production. Despite the fact that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) claims BPA is safe for consumers in an acceptable range (50 mcg/kg) in manufacturing, it still raises concerns among researchers [1]. Although it has been used for decades, recent discovery shows that even a small quantity of BPA exposure can interfere with normal homeostasis in the body over time. Particularly, numerous prospective clinical data and in vivo trials have proven that BPA could lead to endocrine disruptions, thereby promoting lipid accumulations, causing obesity as a commonly notable sign. The negative effect not only stops with the exposed subjects but also results in transgenerational effects. Studies claim that up to 85% of those BPA product consumers tend to be obese and at least 59% of those subjects tend to develop large waist circumference [2,3,4]. A recent study shows that cardiovascular complications such as angina, hypertension, heart attack, and peripheral artery disease are common among subjects exposed to BPA for a long time [5]. Even drinking water in a polycarbonate bottle just for two weeks can raise the BPA in urine to up to two-thirds [6]. In consideration of this claim, in the year 2010, the National Toxicology unit classified BPA as a toxic chemical while FDA went along with the decision in 2018 and declared that they did not find any evidence suggesting that BPA was safe for consumption [7]. Correspondingly, the World Health Organization (WHO) points out the negative outcome of BPA consumption and motivates deep investigations on BPA.
Bisphenol A
BPA (2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane) is a chemical that is produced from the condensation of acetone and phenol. It comprises two hydroxyphenyl groups, which are derived from bisphenols and grouped as diphenylmethane. It is insoluble in water and highly soluble in organic solvents. Exposure to extreme heat eases the release of BPA. It is the most commonly used element, particularly for plastic-based manufacturing [8]. According to the global BPA market report in 2018, BPA annual production increased by 3% and it is expected that it could reach up to 7348 kg tonnes by the year 2023. Of these, North East Asia is the highest in the list of countries that consume the most BPA [9]. This may also serve as one of the primary reasons for Asia countries to be among the fattest nations in comparison with other countries globally. BPA is also known as xenoestrogen due to its ability to imitate estrogens in the human body. This is most likely because of the similarity of phenol groups which are present in BPA and estrogen. This likeness makes the synthetic compound interfere and stimulate the estrogenic pathways. This is achieved by the binding of BPA to estrogen receptors (ER) such as ERα, and ERβ. Despite being a selective modulator for estrogen receptors, an excessive level of BPA can cause it to freely bind with androgen receptors as well [8].
Usually, subjects tend to be exposed to BPA through food, like leaching from water bottles or plastic food containers. This could be due to the slow decomposing of polymer bonds in the polycarbonates which allows the release of unpolymerized monomers to be mixed with liquids or foods. This toxicant has a very poor understanding of its toxicokinetics mechanism which makes the complete elimination of the BPA impossible from the human body [10]. However, BPA can be eliminated via urine upon conjugation in the liver within 24 h, after a half-life of at least 5.3 h. In most cases, BPA tends to accumulate in different tissues such as the placenta, lungs, kidney, and liver [11]. In these respective tissues, β-glucuronidase enzyme exists in a very high concentration. As such, this enzyme will deconjugate BPA, and make it to exist freely in its active form. Since BPA naturally possesses lipophilic affinity, it will bind to fats in a high affinity, further leading to its bioaccumulation [10] and promoting adipogenesis [11].
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
The search was done based on the protocol described in Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [12]. The search was done systematically to identify potentially relevant journals associated with BPA and obesity from the view of endocrine disruptions. For these, a few databases were selected such as Wiley Online Library, Nature, Medline & Ovid, and PubMed. Google Scholar was used as the platform to cross-check our articles to not leave out any potentially relevant articles. The article search was limited to the past five years. Boolean operator guidelines were followed to select and perform the keywords search [13]. These are as described as: (1) BPA OR environmental chemical AND fat OR LDL OR obese AND transgenerational effects or phenocopy (2) Endocrine disruptors OR chemical AND lipodystrophy AND phenocopy (3) Lipid profile OR weight changes AND cardiovascular effect (4) BPA AND neuroimmune OR gene signaling.
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
Only original articles discussing in vivo studies were included in this review. All selected articles were written in English with the presence of an abstract. The articles selection was limited from January 2017 till 15 January 2022, to give recent evidence on the selected topic. The selected articles must precisely provide all the findings. This includes (1) the type of animal model (2) duration and dosage of BPA exposure (3) changes in the lipid profile or weight or cardiovascular changes (4) genes, signaling mechanism, or any neuroimmune signal involved, and (5) transgenerational effects.
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
All review articles, theses, conference proceedings, patents, and articles written in any other language apart from English were excluded from being further reviewed. Those articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria were also excluded. Any study focusing on retrospective data with an unclear dosage or duration of BPA exposure was also excluded; this was the main reason for clinical data being excluded. Data extraction was done independently by five authors (R.N, H.B, M.D.Y, H.E, and R.H). All extracted data were compiled together and any arise disagreements were further discussed with other authors (R.R, S.H.T, and S.H) until mutual understanding was achieved. The finalized data extraction was tabulated as shown in Table 1. It contained information on (1) type of animal model (2) type of BPA exposure (3) duration of exposure and dosage of exposure, and (4) the summary of the findings. No conflict of interest was found among the authors during the data extraction.

Table 1.
BPA and obesity: in vivo study.
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search
The initial search resulted in 1252 potentially relevant articles. Upon thorough screening, 766 articles were removed owing to duplication and unmatched search contents. Another 353 articles were further removed upon screening the title and abstracts. Only titles containing BPA as the endocrine disruptors were considered to be retained. However, another 98 search results were eliminated upon confirmation as review papers, theses, dissertations, patents, copyrights, and articles discussing retrospective data based on clinical writings. Upon deep screening, 31 were finalized to be reviewed in detail. Figure 1 summarizes the screening for the literature search.
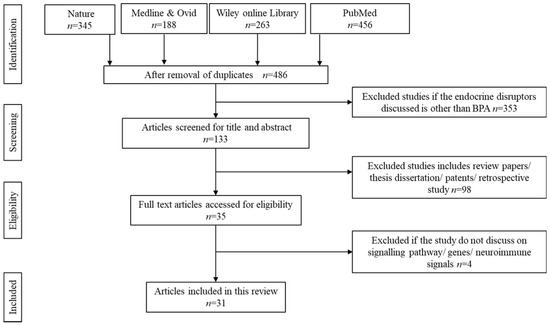
Figure 1.
Identification and screening for literature search.
3.2. BPA and Obesity
Obesity is one of the emerging health conditions worldwide, specifically in Asia. Obesity is simply defined as the abnormal accumulation of fat. However, considering body mass index, this may differ between different groups of population based on their height and weight. While lack of exercise and poor nutritional intake could be some reasons for obesity, one of the external reasons could be due to endocrine disruptions [25]. Past scientific studies have proven that endocrine disruptions could lead to obesity. This endocrine disruption mechanism in most conditions results in transgenerational effects. BPA increases the risk of obesity via altering the normal pathway of endocrine (metabolic pathway) in the adipose tissue.
BPA, an estrogenic chemical, is able to hinder the release of adiponectin by binding with estrogen receptors specifically with ERα and ERβ. By acting on adipocytes and infiltrating macrophages, BPA lowers adiponectin and elevates inflammatory cytokines [26]. In this context, the presence of inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNFα, promote inflammation in the adipose tissue, hindering lipolysis. In this case, the lipid overflow towards the oxidative tissues like skeletal muscles and liver will promote ectopic fat distribution, thereby leading to abdominal obesity [27]. Besides, certain genes responsible for lipid metabolism are downregulated in the case of BPA binding to estrogen receptors. This includes fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) and a cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) [28]. FABP4, known as a novel adipokine, is a cytoplasmic protein produced by the mature adipocytes that have the ability to bind to hydrophobic ligands [29] such as in lipid A [30]. Lipid A is an endotoxin and it is known for its ability to anchor to the hydrophobic surface of lipopolysaccharide [31]. By binding with lipid A, FABP4 enhances the accumulation of fatty acids and causes high concentration gradients with the cell membranes. This fatty acid deposition will eventually combine with the unsaturated parts of the long chain fatty acids, leading to even distribution of lipids to other organelles, [32], further preventing abnormal fat deposition. Upregulation of FABP4 in adipose tissue may reduce the transportation of free fatty acids. This prevents the breakdown of free fatty acids or β oxidation. As a result, since there is no breakdown of free fatty acids, this may accumulate inside the adipose tissue, exceeding its normal capacity. Eventually, this will overspill to other organs such as the liver. In the liver, the normal function facilitating the storage of triglycerides is interrupted, leading to toxic reactive species formation due to excessive level of lipids. In due course, lipotoxicity emerges [33].
Aside from this, FABP4 is closely associated with a gene known as proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (PCSK1), that encodes proprotein convertase PC1/3. Downregulation of FABP4 will result in the reduction of PCSK1, thereby leading to the deficiency of PC1/3 [28]. Since the primary role of PC1/3 is in the initial step of insulin biosynthesis, the deficiency of PC1/3 could impair the proteolytic cleavage of proinsulin [34]. Excessive levels of proinsulin will stimulate hyperphagia, causing expansion of fat cells mass and accumulation of lipids. This is because insulin possesses the ability to inhibit lipolysis [35]. Conversely, CD36 is an important regulator for CD36 is one of the long chain fatty acids in the plasma membrane of the adipose tissue. As such, over expression of CD36 can cause flux to the long chain fatty acids, leading to visceral obesity [36].
3.3. BPA, Obesity and Neuroimmune Signals
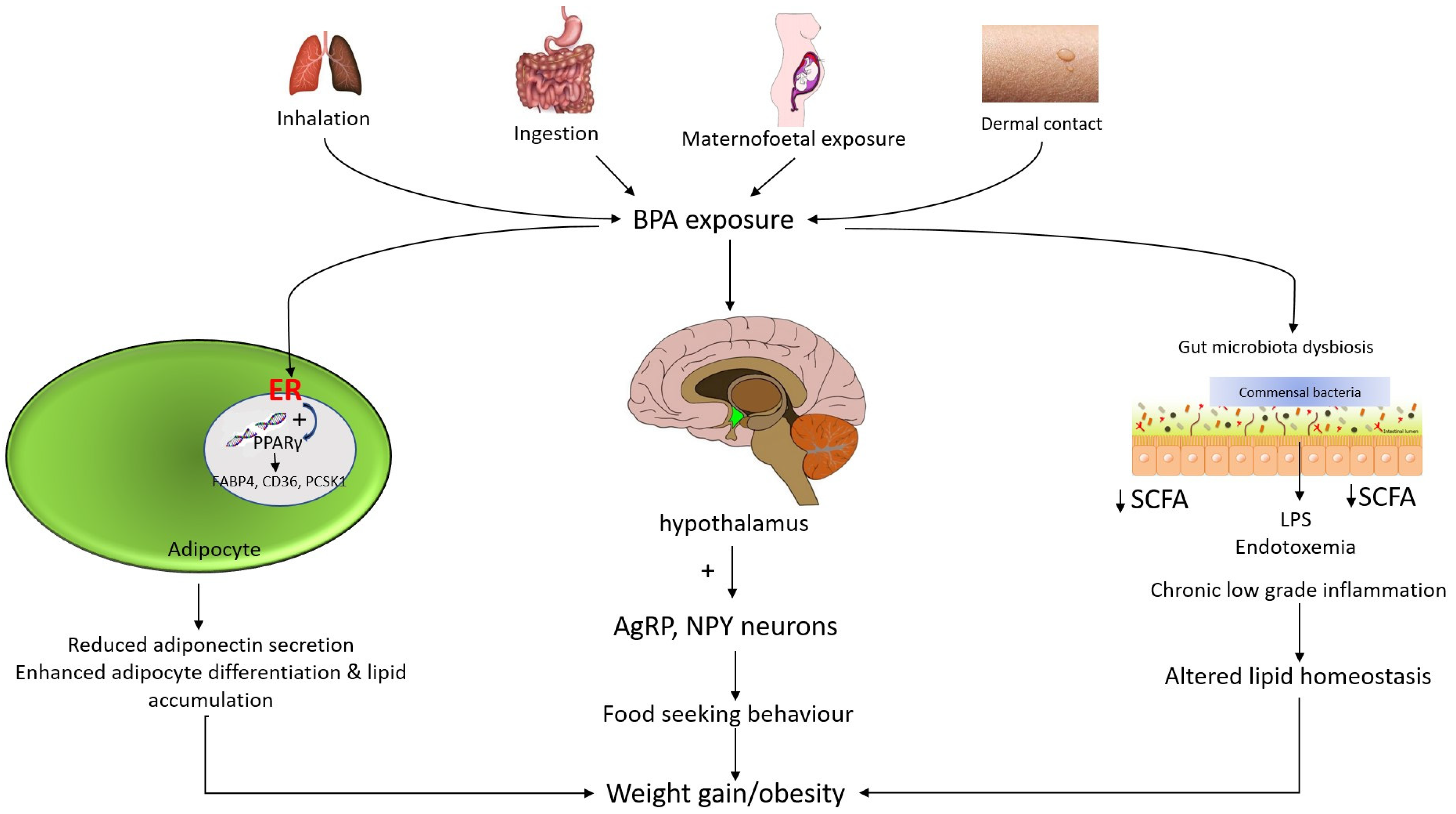
BPA ingestions result in endocrine disruptions and cause an interruption in neuroimmune signals in the central nervous system (CNS), in association with obesity. Exposure to BPA could affect the hypothalamic circuitry in CNS which is proven to stimulate the expression of Agouti related peptide (AgRP) and neuropeptide Y (NPY). In contrast, the level of proopiomelanocortin (POMC) will be reduced [37]. AgRP is an orexigenic peptide that becomes over-activated in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. AgRP neurons comprise a few downstream neuronal pathways which become suppressed by the AgRP neuron activation. The downstream neuronal signals are the appetite regulator or suppressor. For instance, an activated AgRP neuron will block the action of anorexigenic neurons (appetite suppressing neurons) at the nucleus of the paraventricular thalamus. Thereby, a hunger-like response pattern is triggered in the insular cortex [38]. In contrast, AgRP neurons have been found to control appetite by hindering the action of anorexigenic neurons in the parabrachial nucleus (PBN) that produces calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) by the photostimulation formed by AgRP axonal fibers. Parabrachial CGRP is responsible for controlling satiety. Inhibition of CGRP neurons may increase food intake and frequency while decreasing sensitivity to the anorexic effects of meal-related satiety peptides in a compensatory way [39]. Apart from that, AgRP neurons induce hunger via projecting to the downstream signaling pathway namely in the lateral hypothalamus, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, and thalamic and hypothalamic nucleus in the paraventricular [38]. Figure 2 illustrates the potential molecular and mechanistic links between BPA and obesity.
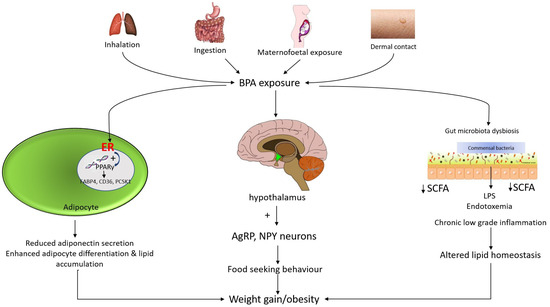
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of bisphenol A and associated obesity. Mechanism of BPA-induced weight gain may be due to its estrogenic activity. BPA binds to estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ) and subsequently induces a perturbation in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) signaling. BPA increases the number and size of adipocytes by regulating the expression of genes such as fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4), cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (PCSK1). In addition, the estrogenic effect of BPA inhibits adiponectin secretion. Meanwhile, in utero and adult exposure to BPA affect the hypothalamic Agouti-related peptide (AgRP) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) neurons. These potent neuropeptides have a stimulating effect on the appetite. BPA that accumulates in the gut may contribute to gut bacterial dysbiosis. BPA exposure reduces gut small chain fatty acid (SCFA) and increases systemic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels, leading to chronic low-grade inflammation and subsequently altered lipid homeostasis.
BPA can cause the arcuate nucleus’ cell bodies to generate excessive levels of NPY, which is subsequently transmitted and deposited into the paraventricular nucleus. There, it stimulates the outflow of efferent impulses in the paraventricular nucleus, resulting in an increase in hunger [40]. In these, Y1 receptors, also known as lipid modulators, are responsible for NPY’s appetite-stimulating effect [41]. NPY can also trigger lipogenic enzymes in the adipose tissues, which contributes to obesity development. As a result, NPY stimulates and controls the formation of adipose tissue in a direct manner. Pre-adipocyte proliferation has been linked to the excessive expression of the local NPY in the visceral. Thus, through the stimulation of the Y1 receptor, this adipose tissue tends to grow in size [42]. Furthermore, triggering of the Y2 receptor in the NPY might result in the formation and accumulation of adipose tissue. The Y2 receptor ligand, also known as gut-derived hormone peptide YY (PYY), is produced postprandially from L cells into the distal intestine [42].
3.4. Signaling Pathway of BPA in Obesity
Studies have proven that BPA could stimulate genes associated with lipid metabolism in humans via the deactivation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha (PPARα) signaling pathway. This may further trigger the expression of CD36, and FABP4 in the adipose tissue. PPARα is an important element in the catabolism of fatty acids and this process occurs via the expression of genes related to oxidation of the mitochondrial and peroxisomal fatty acids. Conversely, when PPARα is suppressed, lipids tend to accumulate in the hepatocytes, further aggravating obesity. Alternatively, BPA could prompt adipocytes dysfunction by acting directly on PPARγ. Generally, PPARγ is known for its prime modulation activity on adipogenesis, specifically isoform PPARγ2 which is present abundantly in adipose tissue. Upon stimulation, PPARγ will further activate its downstream signaling molecules such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, lipoprotein lipase, CD36, and aquaporin 7, leading to excessive adipocyte differentiation, thereby interfering in the lipid metabolism process [43]. Studies show that phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase promoter activation could lead to the development of lipodystrophy, due to the extreme level of lipid droplets in the brown adipose tissue [44] while the high level of lipoprotein lipase may induce assimilation of triglycerides [45].
Besides, BPA disrupts the metabolism of lipid by increasing sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1). SREBP1 is an essential transcription factor that regulates fatty acid metabolism via the modulation of genes responsible for lipolysis and lipogenesis such as FAS and SCD. Primarily, SREBP1 exists in the inactive form binding to the endoplasmic reticulum together with SREBP cleavage activating protein (SCAP), forming a coatamer protein II vesicles. This will then enter the Golgi apparatus to become the mature form of n-SREBP-1 from p-SREBP-1. The matured form will then enter the nucleus and actively bind with sterol regulatory elements and activate targeted genes [46]. In the case of increased levels of sterol in the cellular region, SREBP is hindered from entering the nucleus. Thus, the targeted genes are not activated, leading to accumulations of lipids in the liver [47]. Anyhow, BPA stimulates the adipogenic signaling pathway by inducing the overexpression of CEBPA. CEBPA is known for its role in adipose tissue differentiation and its overexpression will eventually stimulate its downstream pathway involving hexokinase 2, CD36, and lipoprotein lipase [48].
In fact, lipid profile is greatly altered with BPA exposure. Experiments by Santangeli et al. (2018) prove that zebrafish exposed to BPA show decreased level of DGAT2 [18]. DGAT2 gene is responsible for β oxidation and synthesis of triglycerides, and changes in the DGAT2 level inversely correlate with the changes in the size of the fat cells [49]. Comparatively, Pu et al. (2017) witnessed sex-specific gene alteration in subjects exposed to BPA. They discovered that BPA could extensively upregulate estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1) and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) genes in female preadipocytes compared to the male preadipocytes. In this case, ESR1 is also known as a regulator of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA). VEGFA functions predominantly in the regulation of angiogenesis of adipose tissue. As such, over expression of ESR1 and GR increase adipogenic differentiation [20]. This claim was further proved by Caporossi et al. (2015) who witnessed a similar outcome, which may be quoted as females being more susceptible to health effects such as obesity compared to males due to BPA exposure [50]. Furthermore, CB1 could also be one of the targets of BPA in association with obesity development. It has been hypothesized that CB1 upregulation could stimulate the appetite, cause lipids to stock up together, and inhibit lipolysis by compromising the action of PPARα.
Along with other studies, Tian et al. (2021) noticed a decreased level of G-protein coupled receptor 55 (gpr55) and fatty acid amide hydrolase in zebrafish subjected to BPA in the static water system [51]. The gpr55 gene may bind to CB1 and lysophosphatidylinositol, an endogenous ligand, with high affinity in order to activate its downstream signaling pathway. The expression of lipogenic genes in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue will be stimulated as a result of this binding [52]. Meanwhile, decreased level of fatty acid amide hydrolase was able to enhance the system signaling of endocannabinoids, thus triggering the frequency of hunger [53]. Apart from this, the decrease of zinc α 2 glycoprotein (ZAG), hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), and elevation of TLR4 and NF-κB are some other indications of BPA interference with lipid profile [24]. ZAG protein plays an important role in the mobilization of adipose tissue, thereby modulating lipid metabolism to maintain body weight. Reduced ZAG levels, on the other hand, are linked to lipogenesis activation and lipolysis inhibition, as well as hepatic fat storage and dyslipidemia [24].
Into the bargain, BPA induced reduction of HSL, causing the lipolysis to be inhibited as well. HSL’s major function is to facilitate the hydrolysis of diacylglycerol and triacylglycerol. HSL is usually phosphorylated during the hydrolysis process by extracellular-regulated kinase and protein kinase A. Thus, the lipolytic enzyme is activated, which improves the conversion of HSLs into lipid droplets. In this context, more of its hydrophobic surface is exposed, making lipid droplet adhesion to the substrate easier. In short, this mechanism promotes lipolysis. Disruption or a reduction in HSL levels, on the other hand, interferes with the metabolic phenotypes and slows down lipolysis [54]. Increased level of TLR4 and NF-κB is another signaling pathway manifested in obesity induction due to BPA exposure [24]. TLR4 elevation has been shown to stimulate downstream pathway proteins such as IKK-NF-B and JNK via the MyD88 and non-MyD88 routes. Some agonists, including lipopeptides, lipopolysaccharides, saturated fatty acids, and oxidised low-density lipoprotein, eventually bind to TLR and cause adipose tissue to expand. Such expansion of adipose tissue causes the monocyte chemotactic protein-1, inflammatory factors, and free fatty acids to be released, resulting in obesity [55].
3.5. BPA and Dysregulation of Gut Microbiome
BPA has been shown to cause intestinal dysbiosis in obese people through interference with estrogen receptors. Microbiome acts as substrates for xenobiotics, microbial metabolites, and also for estrogen molecules. In this instance, estrogen does play an important role in bacterial colonization in the gut. This is because, estrogen can stimulate the formation of mucous in the intestine which may further allow beneficial bacteria to populate in the gut, thereby enhancing the integrity of the gut lumen [51]. Alternatively, estrogen has the potential to selectively allow the growth of bacteria in the gut [56], and this effect is commonly observable during BPA exposure. BPA exposure during pregnancy, in particular, promotes the evolution of obesity phenotypes in rats by disrupting the gut flora. Investigations in SD rats reveal that changes in normal gut flora promote lipogenesis by compromising gut–brain integrity, as reported in Table 1. The lower amount of IgA and development of pIgR support this theory [15,19]. IgA regulates gut homeostasis by maintaining the permeability of the gut barrier, which is critical for gut homeostasis. In reality, the abundance of beneficial bacteria in the gut has an impact on the establishment of the gut barrier [19]. Bifdobacterium spp. are vital for reducing total cholesterol [57], pro-inflammatory cytokines in adipose tissues, and maintaining a regular lipid metabolism process [58]. Obese subjects exposed to BPA had lower levels of Bifdobacterium spp [59], Firmicutes phylum, specifically Clostridium butyricum, Clostridium Cluster XIV, Clostridium butyricum, and Clostridium Cluster XIVa [19]. Butyrate, a key component in the expression of the leptin gene, is produced by Firmicutes [60]. As a result, a lower amount of Firmicutes lowers the leptin levels and raises appetites. Clostridium spp., on the other hand, regulates lipid metabolism, inhibits lipid buildup in the liver, and reduces the formation of short-chain fatty acids [61]. Because BPA reduces Clostridium spp, it has the inverse effect in the gut. Particularly, the level of Firmicutes often is related to leucocytes DNA methylation in the genes responsible for lipid metabolism and obesity in pregnant mothers [62].
On the flip side, sex-dependent BPA exposure results in differences in gut microbial composition. Male offspring, for example, have an abundance of Bacteroides, Mollicutes, Prevotellaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae, Akkermansia, Methanobrevibacter, and Sutterella, whereas female offspring have an abundance of Lachnobacterium spp. and Prevotella spp. Both genders’ perinatal were exposed to the same dose (50 mg/kg) and the same period of BPA in this study [63]. This implies that BPA causes sex-dependent microbial dysregulation. This assertion is backed up by research conducted by Wu et al. in 2020, who observe the similar effects of BPA on male and female obesity phenotypic development [64]. Succinctly, the pro-inflammatory gut microbiome is commonly observed in female subjects while the anti-inflammatory microbiome is seen in male subjects exposed to BPA [59]. Conversely, In contrast, both genders of progeny have higher levels of CKC4 protein, which increases triglyceride accumulation in the muscle [65]. Another study found that BPA promotes Proteobacteria colonization and reduction of phylum Tenericutes [59]. Proteobacteria overgrowth indicates gut dysbiosis, which might indicate increased inflammation [66] and permeability in the colon [67] as well as increased fat storage [68].
Simultaneously, prenatal BPA exposure raises lipopolysaccharide levels and lowers the variety of gut bacteria and metabolites such as short chain fatty acids in progeny. Reddivari et al. (2017) observe that BPA exposure of 200 µg/kg/day triggers inflammation in the liver and intestine and increased the systemic lipopolysaccharides via gut microbiome dysregulation. An elevated level of Methanobrevibacter is seen in prenatal exposure to BPA, which is closely associated with a high level of energy intake and weight gain. To add, some of the short chain fatty acid-producing bacteria such as Ruminococcaceae, Odoribacter spp., and Oscillospira spp. are drastically reduced in BPA-exposed subjects [69]. Short chain fatty acids play a vital role in lipid homeostatic and prevent diet-induced obesity via the releasing of anorectic hormones and by raising the energy expenditure [70]. Adult Canis familiaris exposed with BPA for 2 weeks exhibited a high level of Bacteroides ovatus, Ruminococcus spp., and Cetobacterium somerae along with a reduction in beneficial microbes such as Flexispira spp and Bacteroides spp. This normal shift of bacteria in the gut may lead to leaky gut, causing harmful microbes metabolites to cross the blood–brain barrier, further enhancing the development of disease [62].
3.6. BPA and Transgenerational Effects of Obesity
BPA, a reprotoxicant, increases the risk of sperm and ova cell malformation in those who are exposed to it. Tail impairment, sperm hook curvature, poor sperm morphology, follicle cell loss in the primordial, and cell loss in the stroma are just a few examples of data supporting this claim. This type of anomaly can be handed on through the F1 lineages [16]. This is because BPA has the ability to induce obesity to be passed down through the generations through epigenetic transgenerational inheritance. As indicated in Table 1, all researchers agree that BPA exposure may be passed down from the male and female germlines to the progeny. The epiphenotype’s effects can be carried down up to F5 generations [71]. Figure 3 shows the inheritance pattern of obesity from F0 generation up to the offspring. The transgenerational effects occur mainly due to DNA methylation of the CpG dinucleotides [72] which is closely associated with genomic imprinting [73]. This imprinting is permanently programmed and unable to be reversed or reprogrammed after fertilization which eases the transmission of defected genes to the offspring [74]. Those genes can be either inherited from the maternal or paternal side. Exposure to 50 μg/kg/day in the long term has been proven to decrease lysine and histone acetylation of H3K9, H3K27, and H4K12. Conversely, the level of deacetylase Sirt1 is increased, which in turn enhances the binding of ERβ to caveolin 1. This is one of the mechanisms of epigenetic inheritance in the offspring due to BPA exposure [73].
BPA may change and rearrange transcription factors in the germline during embryo development, resulting in the demethylation of DNA in the genome. Demethylated DNA permits transcription factors to connect to it readily, which should not happen. This binding will eventually prevent DNA from being remethylated, resulting in the alterations being maintained in the adult germline. The CTCF motif is found in area 107 in sperm, which is where this activity normally takes place [75]. This is due to the presence of progenitors and mature adipocytes in the CTCF locus [71]. This defect might then be passed on to the embryo during fertilisation, resulting in the persistence of transcriptional alterations during the embryogenesis stage. Upregulation of genes that cause deformity, notably in cell physiology, liver morphology, and fat tissue morphology, will eventually be passed on to the progeny. Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of the changed phenotypes is partly attributable to germline-mediated epimutations [76]. Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (Gdnf) and estrogen-related receptor alpha (Esrra) are the most typically differentially methylation genes linked to adult onset obesity [74].
Conversely, if identical transcription factor alterations are present in the oocytes, the obesity epiphenotype can be handed down through the maternal germline. If both the male and female are exposed to BPA, a faulty transcription factor is found in both the sperm and the oocytes, making it easier for the transgenerational impact to be passed on to the progeny. In such instances, FTO sites will be triggered, and its binding sites will be exposed, allowing BPA to bind to these receptors in the chromatin area of primordial germ cells. This generally happens after the DNA has previously been demethylated. As a result, DNA remethylation is inhibited, throughout the gestation period or after E13.5 when the germline is developing [71]. Furthermore, some research suggests that BPA-dependent FTO enhancers are located in the ARC area of the hypothalamus, which is implicated in hunger regulation [71]. Another possible explanation for obesity’s transgenerational impact might be BPA’s activation of the intronic enhancer of FTO. As a result, the amount of m6A is lowered, and this chromatin-associated eRNA will persist until the intergenic enhancer fertilization process is completed. The intergenic enhancer interacts with the FTO promoter and its intronic enhancer during this phase, resulting in FTO activation during the preimplantation stage. As a result, the progeny will be actively transferred in the continuance of gene expression [71,77].
On the other hand, BPA is able to modify and increase the expression of mRNA in the DNA methyltransferases, histone methyltransferases, and their downstream proteins in the neonatal germ cells on prenatal exposure with BPA [78]. This epigenome alteration is further supported by the studies done by Alonso-Magdalena et al. (2016) that show that inheritance of TNFRSF12A, ESRRA, FGF19, WNT10B, GDNF, ENOPH1, ATF3, NCAM2, NTF3, PITX3, and DPYSL2 as evidence of obesity development in the offspring [79]. Another commonly observed epigenetic pattern is the alteration in IGF2 methylation in the male germline, which results in β-cell dysfunction and impaired glucose tolerance in the offspring [80]. Impaired glucose tolerance enhances the downregulation of Pdx1, causing the miR-338 to be upregulated. This will be eventually passed down to the offspring and Chang et al. (2016) observe a suppression in Pdx1 expression, causing deacetylation of histone type 3 and 4 in the F1 generation. This process happens through the methylation action of H3K9 and the demethylation action of H3K4 [81]. Since glucose metabolism plays a vital role in spermatogenesis, impaired glucose tolerance greatly affects the normal function and structure of the sperm. In female subjects, stromal cell loss due to the increased level of oxidative stress, and the decreased level of SOD, GSH, or GPx may further enhance the transmission of the defects through reproductive organs [16].
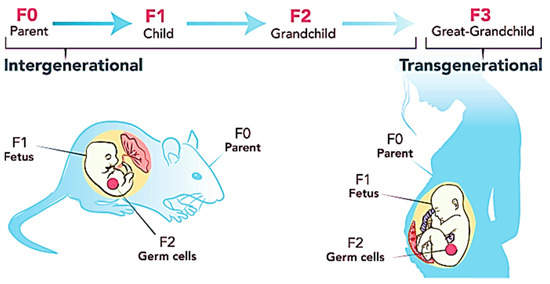
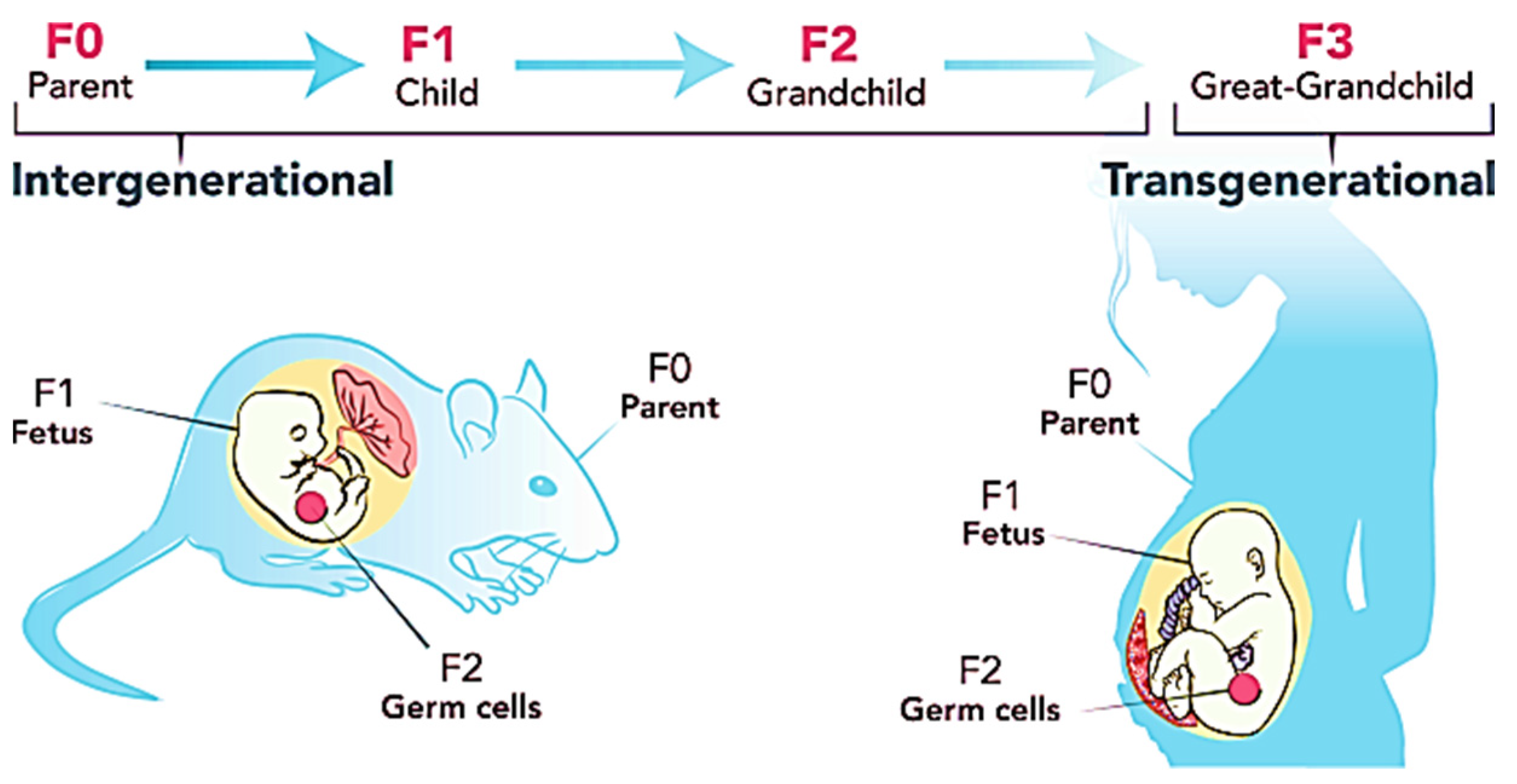
Figure 3.
Transgenerational inheritance pattern of obesity. Figure reused under the permission granted by http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ (accessed on 21 February 2022) [82].
Figure 3.
Transgenerational inheritance pattern of obesity. Figure reused under the permission granted by http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ (accessed on 21 February 2022) [82].
Another study shows that BPA exposure in prenatal interferes with miRNA expression, causing 15 related genes to insulin signaling to be affected. As a result, resistance towards insulin rises, leading to reduced hepatic glycogen storage in the F1 generation. Simultaneously, hepatic DNA methylation will be reduced due to the activation and overexpression of DNA methyltransferase 3B mRNA. As such, the synthesizing of glycogen will be hindered as a cause of hypermethylation of hepatic glucokinase [83]. Junge et al. (2018) notice prenatal BPA exposure alters methylation at CpG sites at the mesoderm-specific transcript gene. This mesoderm-specific transcript gene encodes for α/β hydrolase an obesity-associated gene in the paternal and possesses the isoform imprinting that can be transmitted to the offspring [84].
3.7. BPA and Cardiovascular Complications
Obesity develops when NPY and AgRP levels rise as a result of prolonged or frequent BPA exposure. In response to this assertion, in the event of BPA exposure, the activation of the same neurons contributes to cardiac disease. As one of the key regulators of the heart, NPY can directly interact with cardiac nerves. NPY, on the other hand, has the capacity to act as both a cardiac stressor and a depressant. This effect is primarily influenced by the ligand concentration, receptor expression, and the presence of adrenergic and DPP4 activity in the heart. Alike in obesity, the pathogenesis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathies, hypertension, myocardial ischemia, heart failure, and atherosclerosis is closely associated with Y1 and Y2 receptors. NPY affects protein degradation, cardiac contraction, and cardiomyocyte proliferation via the autocrine or paracrine mechanism [85]. In contrast, Y2 receptors are responsible for the enhancement of Ito postsynaptic stimulus, inhibition of presynaptic neurotransmitter release and reduction of Ito in cardiomyocytes [86]. BPA could trigger the expression of NPY via the sympathetic nerve. Because an increase in NPY merely reflects an increase in the density of sympathetic nerve terminals. Sympathetic nerves link to the parasympathetic nerves via the Y2 receptor on the surface of parasympathetic nerves. As a result, the release of acetylcholine is suppressed, preventing the heart from relaxing, resulting in bradycardia and coronary artery spasm. Overexpression of NPY stimulates angiogenesis in blood vessels by stimulating the release of VEGF and enhancing the process of mitogenesis or vasoconstriction in endothelial cells, resulting in decreased coronary blood flow and cardia output [85], endothelial dysfunction, increased peripheral resistance, and the formation of local vascular stenosis. On the other hand, the release of VEGF does contribute to plaque rupture and hemorrhage [87]. Table 2 summarizes the effect of BPA on cardiovascular disease.
On the contrary, NPY possesses the characteristics to stop the effect of anti-angiogenic agents in cardiac such as endostatin and angiostatin [88] thereby preventing the revascularization of ischemic tissue [86] and the thickening of the intimal tissue in the heart [87]. Furthermore, NPY increases the release of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 in heart tissue under specific clinical conditions. As a result, there is an imbalance of interaction in sympatho-vagal, cardiac contraction, and remodeling, which leads to endothelium dysfunction, uncontrolled angiogenesis, and proliferation in cardiac tissue. As a result, the risk of cardiac arrhythmias, hypertrophy, ischemia, and even heart failure increases [85]. According to studies, NPY inhibits the activity of adenylate cyclase, N-type Ca2+, and nicotinic cholinergic currents in the heart, and triggers the synthesis of inositol phosphates and the activation or inhibition of inwardly rectifying K+ [89]. NPY may also activate the MAPK/ERK, PI3K/Akt, and Gq molecular pathways, causing Ca2+ to be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum via inositol triphosphate. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase is activated as a result of the increase in intracellular Ca2+. This is followed by increased PKC activation via diacylglycerol [85], which leads to cardiac hypertrophy or failure [90]. From the context of AgRP, AgRP increases hunger by acting directly on the CNS, hence weight gain is a typical clinical manifestation. According to studies, this results in a persistent drop in mean arterial pressure and heart rate. Although the underlying molecular mechanism is unknown, scientists believe it is connected to MC3/4R, an AgRP antagonist found in the hypothalamus. It is speculated that the antagonism action of AgRP could potentially inhibit the sympathetic activity in adipose tissue in addition to the stimulation of pressor and tachycardiac in heart due to chronic central MC3/4R activation [91].

Table 2.
BPA and cardiovascular disease.
Table 2.
BPA and cardiovascular disease.
| Author | Subjects | Type of Exposure | Duration of Exposure | Dosage | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apaydin et al., 2019 [92] | Adult male albino rats | Oral gavage | 28 days | 130 mg/kg/bw/day |
|
| Bruno et al., 2019 [93] | 5 week old adult female balb/c mice | Drinking water | 2 weeks | 2.5, 25, and 250 µg/L |
|
| Reventun et al., 2020 [94] | 8 weeks old male wild-type CD1 mice | Drinking water | 16 weeks | 4 × 10−7 M |
|
| Bahey et al., 2019 [95] | Adult male Wistar rats | Intraperitoneal injection | 3 weeks | 1.2 mg/kg/day |
|
| Brown et al., 2019 [96] | 3rd generation homozygous TG(ERE:GFP)Casper Danio rerio zebrafish | Water in a static system | 6 h post fertilization to 5 days of post fertilization | 25 and 1000 μg/L |
|
| Friques et al., 2020 [97] | 3 weeks old male Wistar rats | Oral gavage | 60 days | 100 μg/kg/day |
|
| Amin, 2019 [98] | Adult Wistar rats | Subcutaneous injection | 6 days | 30 mg/kg/day |
|
| Makowska et al., 2021 [99] | 8 weeks old female juvenile pigs mixture of Piétrain and Duroc breed | Capsules | 28 days | 0.05 mg/kg/day |
|
| Lombó et al., 2019 [100] | 4 months old wild type Danio rerio zebrafish | Water in a static system | 24 h post fertilization | 2000 and 4000 μg/L |
|
| Valokola et al., 2018 [101] | Adult male Wistar rats | Oral gavage | 4 weeks | 10, 25, and 50 mg/kg |
|
| Rameshrad et al., 2018 [102] | Male albino Wistar rats | Oral gavage | 2 months | 35 mg/kg/day |
|
| Eweda et al., 2019 [103] | Adult male Wister albino rats | Oral | 6 weeks | 30 mg/kg |
|
| Khodayar et al., 2018 [104] | 6 weeks old male Wistar rats | Oral | 30 days | 50 mg/kg |
|
| Sivashanmugam et al., 2017 [105] | 12 to 14 weeks old male albino Wistar rats | Oral | 30 days | 10,100, and 400 mg BPA/kg |
|
| Kasneci et al., 2017 [106] | C57bl/6n mice | Drinking water | 22 days | 25 ng/ml |
|
| Prudencio et al., 2021 [107] | 3 to 4 months old female Sprague Dawley rats | Not specified | Not specified | 0.0–100 µM |
|
| Oluranti et al., 2021 [108] | Wistar rats | Oral | 28 days | 25, and 50 mg/kg |
|
| Rasdi et al., 2020 [109] | 6 to 8 weeks old female Sprague Dawley rats | Drinking water | Pregnancy day 2 up to 21 days | 0.05 and 0.2 mg/ml |
|
| Gear et al., 2017 [110] | Female Sprague Dawley rats | Oral gavage | 6 months | 2.5, 25, 250, 2500, and 25,000 μg/kg/day |
|
| Vanani et al., 2020 [111] | 8 to 10 weeks old male Wistar rats | Intragastric intubation | 14 days | 250 mg/kg |
|
4. BPA Interaction with Specific Receptors in Obesity
Generally, the binding of BPA to estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ) in obesity is well known. Recent investigations prove that BPA binds with estrogen receptors with a force of 42 van der Waals, leading to the activation of different pathways which contribute to obesity. The similar features in adipogenic transcription and interaction of BPA with estrogen receptors further ease the development of obesity [112]. However, recent studies have disclosed different receptors such as androgen receptor, GPR30, glucocorticoid receptor, and estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRγ) have been hypothesized linked to obesity in association with BPA action.
4.1. Androgen Receptor
BPA has the potential to bind with androgen receptors which can suppress the expression of androgen. In other words, BPA disrupts the activation of androgen and exhibits anti-androgenic effects [113]. The secretion of testosterone, a most common form of androgen determines the pattern of fat distribution in a sex-dependent manner [114]. The reduced level of testosterone in males increases central adiposity. Basically, adipocytes contain a very concentrated amount of aromatase. Aromatase is an estrogen synthetase that transforms testosterone into oestradiol. Thus, free androgen levels in the circulatory system will be increased. Simultaneously, oestrogen will suppress the luteinizing hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone via the action of hypothalamo-pituitary axis. Resultantly, the production of testosterone will be further reduced. This low level of testosterones enhances adiposity through negative feedback of hypogonadal obesity cycle in males [115].
4.2. GPR30
BPA’s lipophilic features ease the binding of BPA to GPR30 and stimulate the overexpression of GPR30 in fat cells. This is because GPR30 is known as a membrane protein which has the ability to bind with estrogen and activates its intracellular signaling pathway [116]. In such a case, the adiponectin levels will be lowered, preventing lipolysis as discussed earlier. However, the activation of GPR30 could be due to the increased expression of FAS and phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in mature adipocytes. This will eventually activate its downstream signaling molecules such as GPR30, in mature adipocytes [117], thereby increasing the rate of proliferation in the adipocyte cells and secretion of cytokines by adipocytes [118]. As a result, the mass of the fat cell will increase, subsequently contributing to obesity over time [119].
4.3. Glucocorticoid Receptor
BPA is able to bind with glucocorticoid receptors and exhibit against action. As such, upon binding the downstream molecules of glucocorticoids such as CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ) will be stimulated followed by C/EBPα and PPARγ transcription factor pathway. Since C/EBPβ plays a pivotal role in preadipocyte differentiation, the activation of C/EBPβ will eventually stimulate adipogenesis and lead to over-accumulation of fats [120].
4.4. Estrogen-Related Receptor Gamma (ERRγ)
Study shows that BPA could bind with ERRγ with a high affinity due to the presence of a crystalized shaped ligand-binding domain in the ERRγ. A nanomolar concentration of as low as 5.6 BPA is enough to bind and stimulate the transcriptional activity of ERRγ. ERRγ is responsible to modulate the expression of Pck1, a glucogenesis gene [121]. In this context, a knock-out of Pck1 will result in suppressed glyceroneogenesis activity and decreased level of re-esterification process in fatty acid. As a consequence of this, lipodystrophy emerges [122]. This might be the primary underlying reason for ERRγ as the major element in contributing to infants’ obesity [121].
5. BPA Exposure and Adverse Perinatal, Childhood, and Adult Cardiovascular Health Outcomes
There is a growing body of evidence indicating a relationship between early exposure to BPA with the development and progression of cardiovascular disease throughout a human’s life. Prolong exposure of adults to BPA has been associated with cardiovascular and hypertension disease. Higher urinary BPA was significantly found in patients diagnosed with cardiovascular disease like angina, coronary heart attack and heart attack. Higher BPA concentrations (>0.00048 μg/mL) are positively associated with coronary heart disease [123]. BPA has been shown to have long term effects. A 10-year prospective study in the United Kingdom done by Melzer et al. (2010) found higher BPA exposure, reflected in higher urinary concentrations of BPA, is consistently associated with a higher incidence of coronary heart disease [124]. Besides that, high levels of urine BPA are also shown to be linked to a higher prevalence of peripheral artery disease in adults. Hypertension is well known as a significant risk factor for CV diseases. Studies have proven that individuals diagnosed with hypertension are found to have increased total urinary BPA. BPA exposure also can cause a decrease in heart rate variability (HRV). Decreased HRV together with increased blood pressure is reported to increase the chance of developing cardiovascular disease [125,126]. A recent study done by Kataria et al. (2017) reveals that BPA exposure can induce an oxidant stress-induced injury to the endothelium and may lead to its dysfunction [127].
A study done by Kubo et al. (2004) proposes that BPA promoted HIF-1alpha (hypoxia-inducible factor) degradation in the presence of cobalt and prevents the induction of erythropoietin which responds to hypoxia. Disturbance in the development of the respiratory system could cause infants to experience intermittent hypoxia [128]. Hypoxia is believed to be responsible for the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases like stroke and myocardial infarction. Other than that, it is also suggested that BPA exposure during pregnancy may alter the fetal epigenome, altering the shape and function of the fetal heart, potentially leading to a variety of cardiovascular diseases in children and adults [123]. The placenta has a huge and important role in fetal development and growth. It is considered a chief regulator of nutrient and oxygen supply to the growing embryo during gestation. Any disturbance or changes in the structural and functional of the placenta may cause adverse health outcomes to the neonate. BPA has been associated with the changes at the molecular level, especially in the placental micro-RNA expression, DNA methylation, and genomic imprinting [129].
6. Biomarkers
The detection of biomarkers is essential in the clinical setting to prevent any unwanted adverse effects and biomarkers are an excellent diagnostic tool to rule out the causative element and the underlying mechanism of a particular condition. Physicians usually focus on changes in hormone levels such as testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and cortisol to access the enzymatic activity in subjects exposed to BPA. This is because changes in such hormones are indicative of homeostatic interruption. For instance, extreme levels of cortisol are indicative of interference of BPA in the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, while AST, ALT, and lactate dehydrogenase are indicators for liver damage in an attempt to remove BPA metabolites [130]. Different biomarkers than the abovementioned biomarkers serve as an ideal diagnostic tool if the subjects refer to hospitals with any underlying conditions such as subjects exposed with BPA with ovarian cancer; the presence of keratin 4 genes is vital to confirm the diagnosis [130]. However, visfatin, resistin, leptin, or haptoglobin are ideal biomarkers for adiposity. Specifically for BPA-associated obesity, C-reactive protein, Von Willebrand factor, or sialic acids are good predictors and biochemical parameters that are necessary for clinical diagnostics [131].
Apart from this, there are few biomarkers that indicate BPA exposure in humans. In regard to this statement, sugar metabolism is considered to be the most effective procedure in determining the exogenous BPA exposure while metabolomics is known for its sensitiveness in determining health hazards risk due to BPA. For instance, from a metabolomics perspective, excessive levels of lactate and choline have been proven to be closely linked to BPA exposure. The presence of lactate and choline can be detected even less than 1 mg/L or 25µg/kg/day of BPA exposure. This applies to prenatal BPA exposures too [132]. Lactate and choline can be measured via blood plasma in normal subjects while in fetuses, it can be detected through amniotic fluid or scalp [133]. Urine is another method of biomarker detection for BPA exposure. In urine, different forms of BPA can be measured. This includes unconjugated BPA, BPA glucuronide, total BPA, or even BPA sulfates. This method is considered to be ideal since BPA is a hydrophilic chemical with semivolatile properties, urine contains the highest concentration of metabolites with a minimal risk of external contamination, and the BPA content can be detected in the range of ng/mL [134].
Other than this, 8OHdG, 8-isoprostane, and MDA can be spotted in the urine that results from oxidative stress due to BPA [135]. The presence of 8OHdG, a marker for oxidative stress, induces DNA damage while 8-isoprostane is an indicator for lipid peroxidation due to the BPA toxicokinetics mechanism [136]. The transgenerational effects biomarker for BPA can be detected via the expression of the Kisspeptin gene in the placenta. Since BPA is also known for its reprotoxicant characteristics, it could affect the hypothalamic pituitary gonadal axis, and lead to obvious transgenerational effects [135]. DNA methylation of BDNF in region IV, a neurotrophin that is present in the brain which affects neurocognitive developments can be spotted in blood. Studies show that downregulation of BDNF in offspring is one of the notable clinical signs observed in prenatal fetuses exposed to BPA [137]. 3-nitrotyrosine is another common biomarker that can be noticed in BPA-exposed subjects. 3-nitrotyrosine is said to be raised in the plasma of pregnant mothers and umbilical cord due to nitrosative stress. Similar effects were witnessed in rodents and pregnant sheep exposed to BPA [138].
7. Safety Concerns and Dosage
In consideration of BPA side effects, some nations, such as Canada, France, and the European Union, have outright prohibited the use of BPA in favor of bisphenol S and bisphenol F [139]. According to the FDA in 2014, a dosage of 50 mcg/kg/day, which is equivalent to 23 mcg/pound/bw, is considered safe. However, animals exposed to a dose similar to or lower than this (10 mcg/kg) had adverse effects [140]. According to the toxicological research report, the active form of BPA is undetectable in fetuses up to 8 h [141]. In toto, the daily consumption of BPA is deemed to be tolerated at 10% of total body weight, or 0.05 mg/kg [142].
8. Conclusions
In conclusion, this review summarizes the underlying mechanism of BPA in obesity. Exposure to BPA enhance adipogenesis, lipid dysregulation, and adipose tissue inflammation, thereby increasing the risk of obesity and the presence of a high concentration of BPA in serum and urinary are the evidence for this. The articles included in the reviews specify that BPA could induce transgenerational effects in obesity and can last up to F5 generation. Due to similar pathway involvement in BPA, cardiovascular complications in obesity are also one of the most notable signs. However, the effect can be sex-dependent. The usage of BPA is impossible to be banned completely. However, it is highly recommended to use alternatives such as BPS.
9. Future Directions
The literature search in this study is limited to animals and the evidence of BPA exposure and obesity is still something in which the conclusions concerning human health effects are debatable. There is no definite safe dosage that has been suggested for humans except on the basis of animal study evidence. As such, the association between BPA and obesity in humans is still lacking. There is a high possibility that the conclusion drawn from animal studies could not be valid to be practiced for humans. As such, there must be more studies focusing on BPA exposure in humans that must be done in the future. In this way, the undiscovered underlying mechanism can be studied and the issue of the global obesity epidemic can be prevented by the modification of the genes involved. Perhaps in the future, we can focus on the effects of BPA in each stage of the fetus development up to birth in association with obesity. This research gap will surely give insights to researchers to develop a more reliable intervention for obesity in the future. In due course, there is a clear need for studies focusing on pre-intervention to reverse obesity. Future research should focus on the alternative method for BPA usage or limit the leakage of BPA from manufactured products. In prioritizing global health, policies should be constructed to prohibit the usage of BPA in food containers, particularly in baby feeding bottles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.N., M.D.Y., Y.Y.K., H.E. and H.B.; methodology, R.N.; software, H.B.; validation, H.B. and F.O.; formal analysis, R.N.; investigation, R.N., R.R. and S.H.T.; resources, H.B.; data curation, F.O.; writing—original draft preparation, R.N.; writing—review and editing, R.N., M.D.Y., Y.Y.K., H.E. and S.H.; visualization, H.B., H.E. and S.H.; supervision, H.B., M.D.Y., Y.Y.K., F.O., R.R. and S.H.T.; project administration, F.O.; funding acquisition, F.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Long Term Research Grant Scheme-Malaysia Research University Network (Grant No. 630018-14001) under Ministry of Higher Education.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aungst, J. 2014 Updated Safety Assessment of Bisphenol A (BPA) for Use in Food Contact Applications. 2014. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/90124/download (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Kandaraki, E.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Livadas, S.; Palioura, E.; Economou, F.; Koutsilieris, M.; Palimeri, S.; Panidis, D.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E. Endocrine disruptors and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Elevated serum levels of bisphenol A in women with PCOS. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E480–E484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingaiah, S.; Meeker, J.D.; Pearson, K.R.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Petrozza, J.; Hauser, R. Temporal variability and predictors of urinary bisphenol A concentrations in men and women. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, M.; Chen, B.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; et al. Urinary Bisphenol A (BPA) Concentration Associates with Obesity and Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E223–E227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, H.S. Impact of Bisphenol A on the Cardiovascular System—Epidemiological and Experimental Evidence and Molecular Mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carwile, J.L.; Luu, H.T.; Bassett, L.S.; Driscoll, D.A.; Yuan, C.; Chang, J.Y.; Ye, X.; Calafat, A.M.; Michels, K.B. Polycarbonate Bottle Use and Urinary Bisphenol A Concentrations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO; UN and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Toxicological and Health Aspects of Bisphenol A, Ottawa, Canada. 2010. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44624/97892141564274_eng.pdf;sequence=1 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Matuszczak, E.; Komarowska, M.D.; Debek, W.; Hermanowicz, A. The Impact of Bisphenol A on Fertility, Reproductive System, and Development: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 4068717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L. Global Bisphenol A Market Report 2018: Analysis 2013–2017 & Forecasts 2018–2023; Transparncy Market Research: Dublin, Ireland, 2018; Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/global-bisphenol-a-market-report-2018-analysis-2013-2017--forecasts-2018-2023-300757673.html (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Genuis, S.J.; Beesoon, S.; Birkholz, D.; Lobo, R.A. Human Excretion of Bisphenol A: Blood, Urine, and Sweat (BUS) Study. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 185731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lee, H.K.; Kong, A.P.S.; Lim, L.L.; Cai, Z.; Chung, A.C.K. Early-life exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals associates with childhood obesity. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 23, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA Extension Statement for Reporting of Systematic Reviews Incorporating Network Meta-analyses of Health Care Interventions: Checklist and Explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naomi, R.; Bahari, H.; Yazid, M.D.; Othman, F.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Hussain, M.K. Potential Effects of Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas) in Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia—A Systematic Review in Diabetic Retinopathy Context. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Ferrini, M.G.; Jellyman, J.K.; Han, G.; Ross, M.G. In vivo and in vitro bisphenol A exposure effects on adiposity. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2018, 9, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, M.K.; Tain, Y.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Hsu, W.H.; Yeh, Y.T.; Chang, S.K.C.; Liao, J.X.; Hou, C.Y. Resveratrol Butyrate Esters Inhibit Obesity Caused by Perinatal Exposure to Bisphenol A in Female Offspring Rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabeer, S.; Afjal, M.A.; Ahmad, S.; Fatima, M.; Habib, H.; Parvez, S.; Raisuddin, S. Transgenerational effect of parental obesity and chronic parental bisphenol A exposure on hormonal profile and reproductive organs of preadolescent Wistar rats of F1 generation: A one-generation study. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A.; Shioda, K.; Mitsunaga, S.; Yawata, S.; Angle, B.M.; Nagel, S.C.; vom Saal, F.S.; Shioda, T. Prenatal Exposure to Bisphenol A Disrupts Naturally Occurring Bimodal DNA Methylation at Proximal Promoter of fggy, an Obesity-Relevant Gene Encoding a Carbohydrate Kinase, in Gonadal White Adipose Tissues of CD-1 Mice. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangeli, S.; Notarstefano, V.; Maradonna, F.; Giorgini, E.; Gioacchini, G.; Forner-Piquer, I.; Habibi, H.R.; Carnevali, O. Effects of diethylene glycol dibenzoate and Bisphenol A on the lipid metabolism of Danio rerio. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaisé, Y.; Menard, S.; Cartier, C.; Gaultier, E.; Lasserre, F.; Lencina, C.; Harkat, C.; Geoffre, N.; Lakhal, L.; Castan, I.; et al. Gut dysbiosis and impairment of immune system homeostasis in perinatally-exposed mice to Bisphenol A precede obese phenotype development. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Gingrich, J.D.; Steibel, J.P.; Veiga-Lopez, A. Sex-Specific Modulation of Fetal Adipogenesis by Gestational Bisphenol A and Bisphenol S Exposure. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3844–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoker, C.; Andreoli, M.F.; Kass, L.; Bosquiazzo, V.L.; Rossetti, M.F.; Canesini, G.; Luque, E.H.; Ramos, J.G. Perinatal exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) impairs neuroendocrine mechanisms regulating food intake and kisspetin system in adult male rats. Evidences of metabolic disruptor hypothesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 499, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neier, K.; Marchlewicz, E.M.; Bedrosian, L.D.; Dolinoy, D.C.; Harris, C. Characterization of the mouse white adipose tissue redox environment and associations with perinatal environmental exposures to bisphenol A and high-fat diets. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 66, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Yan, S.; Meng, Z.; Huang, S.; Sun, W.; Jia, M.; Teng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. New insights into bisphenols induced obesity in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Activation of cannabinoid receptor CB1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Jia, Y.; Wu, F.; Meng, Y.; Sun, Q.; Jia, L. Combined Exposure to Fructose and Bisphenol A Exacerbates Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Liver of Developmental Male Rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindel, J.J.; Newbold, R.; Schug, T.T. Endocrine disruptors and obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Jonathan, N.; Hugo, E.R.; Brandebourg, T.D. Effects of bisphenol A on adipokine release from human adipose tissue: Implications for the metabolic syndrome. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouwborst, I.; Bowser, S.M.; Goossens, G.H.; Blaak, E.E. Ectopic Fat Accumulation in Distinct Insulin Resistant Phenotypes; Targets for Personalized Nutritional Interventions. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menale, C.; Piccolo, M.T.; Cirillo, G.; Calogero, R.A.; Papparella, A.; Mita, L.; Del Giudice, E.M.; Diano, N.; Crispi, S.; Mita, D.G. Bisphenol A effects on gene expression in adipocytes from children: Association with metabolic disorders. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 54, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisgin, A.A.; Cetinel, S.; Zuvin, M.; Kosar, A.; Kutlu, O. Therapeutic nanoparticles and their targeted delivery applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogero, M.M.; Calder, P.C. Obesity, inflammation, toll-like receptor 4 and fatty acids. Nutrients 2018, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Reynolds, C.M.; Trent, M.S.; Bishop, R.E. Lipid a modification systems in gram-negative bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 295–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Liu, Z.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, C. FABP4 reversed the regulation of leptin on mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation in mice adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Escoté, X.; Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Miranda, M.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Pérez-Pérez, R.; Peral, B.; Cardona, F.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; et al. FABP4 Dynamics in Obesity: Discrepancies in Adipose Tissue and Liver Expression Regarding Circulating Plasma Levels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larder, R.; Lim, C.T.; Coll, A.P. Genetic aspects of human obesity. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2014; Volume 124, pp. 93–106. [Google Scholar]
- Erion, K.A.; Corkey, B.E. Hyperinsulinemia: A Cause of Obesity? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonen, A.; Tandon, N.N.; Glatz, J.F.C.; Luiken, J.J.F.P.; Heigenhauser, G.J.F. The fatty acid transporter FAT/CD36 is upregulated in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissues in human obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L.; Curtis, K.S. Estrogen disruptors and neuroimmune signaling in obesity: Focus on bisphenol A. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 19, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essner, R.A.; Smith, A.G.; Jamnik, A.A.; Ryba, A.R.; Trutner, Z.D.; Carter, M.E. AgRP Neurons Can Increase Food Intake during Conditions of Appetite Suppression and Inhibit Anorexigenic Parabrachial Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.A.; Bowen, A.J.; Schwartz, M.W.; Palmiter, R.D. Parabrachial CGRP Neurons Control Meal Termination. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokot, F.; Ficek, R. Effects of Neuropeptide Y on Appetite. Miner. Electrolyte Metab. 1999, 25, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Antwi, D.A. Brain regulation of appetite and satiety. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 37, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, Q.; Ou, C.; Chen, M. A Promising Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases: Neuropeptide Y Receptors in Humans. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stienstra, R.; Duval, C.; Müller, M.; Kersten, S. PPARs, Obesity, and Inflammation. PPAR Res. 2007, 2007, 95974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franckhauser, S.; Muñ Oz, S.; Elias, I.; Ferre, T.; Bosch, F. Adipose Overexpression of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase Leads to High Susceptibility to Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance and Obesity. Diabetes 2006, 55, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Eckel, R.H. Lipoprotein lipase: From gene to obesity. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, T.; He, J.; Jia, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z. Bisphenol A disturbed the lipid metabolism mediated by sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 in rare minnow Gobiocypris rarus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 207, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Shyy, J.Y.J. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 is negatively modulated by PKA phosphorylation. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, L.E.; Orho-Melander, M.; William-Olsson, L.; Sjöholm, K.; Sjöströ, L.; Groop, L.; Carlsson, B.; Carlsson, L.M.S.; Olsson, B. CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein (C/EBP) in Adipose Tissue Regulates Genes in Lipid and Glucose Metabolism and a Genetic Variation in C/EBP Is Associated with Serum Levels of Triglycerides. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4880–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo Hou, X.; Moser, S.; Sarr, M.G.; Thompson, G.B.; Que, F.G.; Jensen, M.D. Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase Activity in Humans. Obesity 2009, 17, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporossi, L.; Papaleo, B. Exposure to Bisphenol a and Gender Differences: From Rodents to Humans Evidences and Hypothesis about the Health Effects. J. Xenobiotics 2015, 5, 5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaliannan, K.; Robertson, R.C.; Murphy, K.; Stanton, C.; Kang, C.; Wang, B.; Hao, L.; Bhan, A.K.; Kang, J.X. Estrogen-mediated gut microbiome alterations influence sexual dimorphism in metabolic syndrome in mice. Microbiome 2018, 6, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, A.; Lee, J.H.; Wu, C.S.; Wei, Q.; Pradhan, G.; Yafi, M.; Lu, H.C.; Sun, Y. Deletion of G-protein-coupled receptor 55 promotes obesity by reducing physical activity. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 40, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipe, J.C.; Waalen, J.; Gerber, A.; Beutler, E. Overweight and obesity associated with a missense polymorphism in fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiloulis, T.; Watt, M.J. Exercise and the Regulation of Adipose Tissue Metabolism, 1st ed.; Bouchard, C., Ed.; Elsevier: Victoria, Australia, 2015; Volume 135, ISBN 9780128039915. [Google Scholar]
- Jialal, I.; Kaur, H.; Devaraj, S. Toll-like receptor status in obesity and metabolic syndrome: A translational perspective. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, H.; Debelius, J.W.; Knight, R.; Koren, O. Microbial endocrinology: The interplay between the microbiota and the endocrine system. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.-N.; Yu, Q.-F.; Fu, N.; Liu, X.-W.; Lu, F.-G. Effects of four Bifidobacteria on obesity in high-fat diet induced rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.M.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, D.K.; Kim, J.R.; Cha, M.K.; Lee, S.W.; Lim, H.T.; Kim, K.J.; Ha, N.J. Antiobesity and lipid-lowering effects of Bifidobacterium spp. in high fat diet-induced obese rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajer, N.; Du, C.Y.; Checkcinco, C.; Blumberg, B. Obesogens: How They Are Identified and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Their Action. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio: A relevant marker of gut dysbiosis in obese patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.Q. Clostridium Butyricum CGMCC0313.1 Modulates Lipid Profile, Insulin Resistance and Colon Homeostasis in Obese Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, C.S. Gut dysbiosis in animals due to environmental chemical exposures. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javurek, A.B.; Spollen, W.G.; Johnson, S.A.; Bivens, N.J.; Bromert, K.H.; Givan, S.A.; Rosenfeld, C.S. Effects of exposure to bisphenol A and ethinyl estradiol on the gut microbiota of parents and their offspring in a rodent model. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, M.; Liu, A.; Wu, C.; Li, D.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, B.; Du, J.; Gao, X.; Hong, Y. Bisphenol A and the Risk of Obesity a Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis of the Epidemiological Evidence. Dose-Response 2020, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, F.; Wu, J.; Du, Z.Y.; Zhang, M. Influence of endogenous and exogenous estrogenic endocrine on intestinal microbiota in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.-P.; Chung, Y.-T.; Li, R.; Wan, H.-T.; Wong, C.K.C. Bisphenol A alters gut microbiome: Comparative metagenomics analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massier, L.; Chakaroun, R.; Tabei, S.; Crane, A.; Didt, K.D.; Fallmann, J.; Von Bergen, M.; Haange, S.B.; Heyne, H.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Adipose tissue derived bacteria are associated with inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Gut 2020, 69, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez-Ontiveros, Y.; Páez, S.; Monteagudo, C.; Rivas, A. Endocrine disruptors in food: Impact on gut microbiota and metabolic diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddivari, L.; Veeramachaneni, D.N.R.; Walters, W.A.; Lozupone, C.; Palmer, J.; Hewage, M.K.K.; Bhatnagar, R.; Amir, A.; Kennett, M.J.; Knight, R.; et al. Perinatal Bisphenol A Exposure Induces Chronic Inflammation in Rabbit Offspring via Modulation of Gut Bacteria and Their Metabolites. mSystems 2017, 2, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, E.S.; Preston, T.; Frost, G.; Morrison, D.J. Role of Gut Microbiota-Generated Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2018, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corces, V.G.; Jung, Y.H.; Bixler, B.J.; Ruiz, D.; Wang, H.-L.V.; Linsenbaum, H.; Xiang, J.-F.; Shafik, A.M.; Jin, P. Transgenerational inheritance of BPA-induced obesity correlates with transmission of new CTCF sites in the Fto gene. bioRxiv 2020, 1, 114585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, I.; Fiory, F.; Perruolo, G.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P.; Oriente, F. Potential mechanisms of bisphenol a (BPA) contributing to human disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zuo, X.; He, D.; Ding, S.; Xu, F.; Yang, H.; Jin, X.; Fan, Y.; Ying, L.; Tian, C.; et al. Long-term exposure to a “safe” dose of bisphenol A reduced protein acetylation in adult rat testes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 9, 40337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikkam, M.; Tracey, R.; Guerrero-Bosagna, C.; Skinner, M.K. Plastics Derived Endocrine Disruptors (BPA, DEHP and DBP) Induce Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Obesity, Reproductive Disease and Sperm Epimutations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champroux, A.; Cocquet, J.; Henry-Berger, J.; Drevet, J.R.; Kocer, A. A decade of exploring the mammalian sperm epigenome: Paternal epigenetic and transgenerational inheritance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.J. Physiological aspects of female fertility: Role of the environment, modern lifestyle, and genetics. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 873–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, C.; Moir, L.; McMurray, F.; Girard, C.; Banks, G.T.; Teboul, L.; Wells, S.; Brüning, J.C.; Nolan, P.M.; Ashcroft, F.M.; et al. Overexpression of Fto leads to increased food intake and results in obesity. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Whorton, A.E.; Sekulovski, N.; Maclean, J.A.; Hayashi, K. Prenatal Exposure to Bisphenol A, E, and S Induces Transgenerational Effects on Male Reproductive Functions in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 172, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Magdalena, P.; Rivera, F.J.; Guerrero-Bosagna, C. Bisphenol-A and metabolic diseases: Epigenetic, developmental and transgenerational basis. Environ. Epigenet. 2016, 2, dvw022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariati, F.; Carbone, L.; Conforti, A.; Bagnulo, F.; Peluso, S.R.; Carotenuto, C.; Buonfantino, C.; Alviggi, E.; Alviggi, C.; Strina, I. Bisphenol A-Induced Epigenetic Changes and Its Effects on the Male Reproductive System. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Wang, D.; Xia, W.; Pan, X.; Huo, W.; Xu, S.; Li, Y. Epigenetic disruption and glucose homeostasis changes following low-dose maternal bisphenol A exposure. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, C.V.; Landon, R.; Kahn, L.G.; Enlow, M.B.; Peterson, A.K.; Bastain, T.; Braun, J.; Comstock, S.S.; Duarte, C.S.; Hipwell, A.; et al. Exploring the evidence for epigenetic regulation of environmental influences on child health across generations. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xia, W.; Wang, D.Q.; Wan, Y.J.; Xu, B.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, S.Q. Hepatic DNA methylation modifications in early development of rats resulting from perinatal BPA exposure contribute to insulin resistance in adulthood. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, K.M.; Leppert, B.; Jahreis, S.; Wissenbach, D.K.; Feltens, R.; Grützmann, K.; Thürmann, L.; Bauer, T.; Ishaque, N.; Schick, M.; et al. MEST mediates the impact of prenatal bisphenol A exposure on long-term body weight development. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.M.J.; Green, P.; Tapoulal, N.; Lewandowski, A.J.; Leeson, P.; Herring, N. The Role of Neuropeptide Y in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, A.E.G.; Sharkey, K.A.; Giles, W.R. Neuropeptide Y Modulates L-Type Ca2+ Current during Heart Development. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 891–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Shi, Y.C.; Wang, C.M.; Lin, S.; He, H.F. Regulation of neuropeptide Y in body microenvironments and its potential application in therapies: A review. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robich, M.P.; Matyal, R.; Chu, L.M.; Feng, J.; Xu, S.H.; Laham, R.J.; Hess, P.E.; Bianchi, C.; Sellke, F.W. Effects of Neuropeptide Y on collateral development in a swine model of chronic myocardial ischemia. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 49, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, S.; Balasubramaniam, A. Inhibitory and stimulatory effects of neuropeptide Y(17-36) on rat cardiac adenylate cyclase activity. Structure-function studies. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 4680–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.M.; Cummings, E.; Pantos, C.; Singh, J. Protein kinase C and cardiac dysfunction: A review. Heart Fail. Rev. 2017, 22, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallam, L.S.; Kuo, J.J.; Da Silva, A.A.; Hall, J.E. Cardiovascular, Renal, and Metabolic Responses to Chronic Central Administration of Agouti-Related Peptide. Hypertension 2004, 44, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydin, F.G.; Aslanturk, A.; Uzunhisarcikli, M.; Bas, H.; Kalender, S.; Kalender, Y. Histopathological and biochemical studies on the effect of curcumin and taurine against bisphenol A toxicity in male rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12302–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, K.A.; Mathews, J.E.; Yang, A.L.; Frisancho, J.A.; Scott, A.J.; Greyner, H.D.; Molina, F.A.; Greenaway, M.S.; Cooper, G.M.; Bucek, A.; et al. BPA Alters Estrogen Receptor Expression in the Heart After Viral Infection Activating Cardiac Mast Cells and T Cells Leading to Perimyocarditis and Fibrosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reventun, P.; Sanchez-Esteban, S.; Cook, A.; Cuadrado, I.; Roza, C.; Moreno-Gomez-Toledano, R.; Muñoz, C.; Zaragoza, C.; Bosch, R.J.; Saura, M. Bisphenol A induces coronary endothelial cell necroptosis by activating RIP3/CamKII dependent pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahey, N.G.; Elaziz, H.O.A.; Gadalla, K.K.E. Potential Toxic Effect of Bisphenol A on the Cardiac Muscle of Adult Rat and the Possible Protective Effect of Omega-3: A Histological and Immunohistochemical Study. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2019, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.R.; Green, J.M.; Moreman, J.; Gunnarsson, L.M.; Mourabit, S.; Ball, J.; Winter, M.J.; Trznadel, M.; Correia, A.; Hacker, C.; et al. Cardiovascular Effects and Molecular Mechanisms of Bisphenol A and Its Metabolite MBP in Zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friques, A.G.F.; Santos, F.D.N.; Angeli, D.B.; Silva, F.A.C.; Dias, A.T.; Aires, R.; Leal, M.A.S.; Nogueira, B.V.; Amorim, F.G.; Campagnaro, B.P.; et al. Bisphenol A contamination in infant rats: Molecular, structural, and physiological cardiovascular changes and the protective role of kefir. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 75, 108254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, D.M. Role of copeptin as a novel biomarker of bisphenol A toxic effects on cardiac tissues: Biochemical, histological, immunohistological, and genotoxic study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 36037–36047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Gonkowski, S.; Licata, P.; Crupi, R.; Gugliandolo, E. Changes Caused by Low Doses of Bisphenol A (BPA) in the Neuro-Chemistry of Nerves Located in the Porcine Heart. Animals 2021, 11, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombó, M.; González-Rojo, S.; Fernández-Díez, C.; Herráez, M.P. Cardiogenesis impairment promoted by bisphenol A exposure is successfully counteracted by epigallocatechin gallate. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valokola, M.G.; Karimi, G.; Razavi, B.M.; Kianfar, M.; Jafarian, A.H.; Jaafari, M.R.; Imenshahidi, M. The protective activity of nanomicelle curcumin in bisphenol A-induced cardiotoxicity following subacute exposure in rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshrad, M.; Imenshahidi, M.; Razavi, B.M.; Iranshahi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Bisphenol A vascular toxicity: Protective effect of Vitis vinifera (grape) seed extract and resveratrol. Phyther. Res. 2018, 32, 2396–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eweda, S.M.; Newairy, A.S.A.; Abdou, H.M.; Gaber, A.S. Bisphenol A-induced oxidative damage in the hepatic and cardiac tissues of rats: The modulatory role of sesame lignans. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayar, M.J.; Kalantari, H.; Mahdavinia, M.; Khorsandi, L.; Alboghobeish, S.; Samimi, A.; Alizadeh, S.; Zeidooni, L. Protective effect of naringin against BPA-induced cardiotoxicity through prevention of oxidative stress in male Wistar rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 43, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivashanmugam, P.; Mullainadhan, V.; Karundevi, B. Dose-dependent effect of Bisphenol-A on insulin signaling molecules in cardiac muscle of adult male rat. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 266, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasneci, A.; Lee, J.S.; Yun, T.J.; Shang, J.; Lampen, S.; Gomolin, T.; Cheong, C.C.; Chalifour, L.E. From the Cover: Lifelong Exposure of C57bl/6n Male Mice to Bisphenol A or Bisphenol S Reduces Recovery from a Myocardial Infarction. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 159, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudencio, T.M.; Swift, L.M.; Guerrelli, D.; Cooper, B.; Reilly, M.; Ciccarelli, N.; Sheng, J.; Jaimes, R.; Posnack, N.G. Bisphenol S and Bisphenol F Are Less Disruptive to Cardiac Electrophysiology, as Compared With Bisphenol A. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 183, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluranti, O.I.; Alabi, B.A.; Michael, O.S.; Ojo, A.O.; Fatokun, B.P. Rutin prevents cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation induced by bisphenol A and dibutyl phthalate exposure via NRF-2/NF-κB pathway. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasdi, Z.; Kamaludin, R.; Ab Rahim, S.; Syed, A.; Fuad, S.B.; Othman, M.H.D.; Siran, R.; Nor, N.S.M.; Hasani, N.A.H.; Kadir, S.H.S.A. The impacts of intrauterine Bisphenol A exposure on pregnancy and expression of miRNAs related to heart development and diseases in animal model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gear, R.; Kendziorski, J.A.; Belcher, S.M. Effects of bisphenol A on incidence and severity of cardiac lesions in the NCTR-Sprague-Dawley rat: A CLARITY-BPA study. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 275, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanani, A.R.; Mahdavinia, M.; Shirani, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Dehghani, M.A. Protective effects of quercetin against oxidative stress induced by bisphenol-A in rat cardiac mitochondria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15093–15102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfosse, V.; Grimaldi, M.; Pons, J.L.; Boulahtouf, A.; Le Maire, A.; Cavailles, V.; Labesse, G.; Bourguet, W.; Balaguer, P. Structural and mechanistic insights into bisphenols action provide guidelines for risk assessment and discovery of bisphenol A substitutes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2012, 109, 14930–14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Tan, H.; Shi, W.; Zhang, X.; Wei, S.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H. Molecular Initiating Events of Bisphenols on Androgen Receptor-Mediated Pathways Provide Guidelines for in Silico Screening and Design of Substitute Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, R. Obesity and androgens: Facts and perspectives. Fertil. Steril. 2006, 85, 1319–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.M.; Jones, T.H. Testosterone and obesity. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 581–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.; Dong, J. Binding and activation of the seven-transmembrane estrogen receptor GPR30 by environmental estrogens: A potential novel mechanism of endocrine disruption. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 102, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Luo, J.; Moore, W.; Alkhalidy, H.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhen, W.; Wang, Y.; Clegg, D.J.; Xu, B.; et al. GPR30 regulates diet-induced adiposity in female mice and adipogenesis in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, F.A.; Barchetta, I.; Porzia, A.; Mainiero, F.; Costantino, C.; Bertoccini, L.; Ceccarelli, V.; Morini, S.; Baroni, M.G.; Lenzi, A.; et al. Circulating IL-8 levels are increased in patients with type 2 diabetes and associated with worse inflammatory and cardiometabolic profile. Acta Diabetol. 2017, 54, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, I.; Oriente, F.; D’esposito, V.; Liguoro, D.; Liguoro, P.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Cabaro, S.; D’andrea, F.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P.; et al. Low-dose bisphenol-a regulates inflammatory cytokines through GPR30 in mammary adipose cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 63, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.G.; Boudreau, A.; Atlas, E. Bisphenol A induces differentiation of human preadipocytes in the absence of glucocorticoid and is inhibited by an estrogen-receptor antagonist. Nutr. Diabetes 2013, 4, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohmé, M.; Prud’Homme, S.M.; Boulahtouf, A.; Samarut, E.; Brunet, F.; Bernard, L.; Bourguet, W.; Gibert, Y.; Balaguer, P.; Laudet, V. Estrogen-related receptor γ is an in vivo receptor of bisphenol A. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 3124–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, E.G.; Harvey, B.J.; Forest, C. PCK1 and PCK2 as candidate diabetes and obesity genes. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 48, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, S.; Rahman, A.A.; Kadir, S.H.S.A.; Nor, N.S.M. Bisphenol A and its effects on the systemic organs of children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 3111–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, D.; Rice, N.E.; Lewis, C.; Henley, W.E.; Galloway, T.S. Association of Urinary Bisphenol A Concentration with Heart Disease: Evidence from NHANES 2003/06. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, A.; Teppala, S. Urinary bisphenol A and hypertension in a multiethnic sample of US adults. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 481641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, Y.H.; Park, H.Y.; Hong, Y.C. Associations of bisphenol A exposure with heart rate variability and blood pressure. Hypertensionaha 2012, 60, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, A.; Levine, D.; Wertenteil, S.; Vento, S.; Xue, J.; Rajendiran, K.; Kannan, K.; Thurman, J.M.; Morrison, D.; Brody, R.; et al. Exposure to bisphenols and phthalates and association with oxidant stress, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction in children. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, T.; Maezawa, N.; Osada, M.; Katsumura, S.; Funae, Y.; Imaoka, S. Bisphenol A, an environmental endocrine-disrupting chemical, inhibits hypoxic response via degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha): Structural requirement of bisphenol A for degradation of HIF-1alpha. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, P.; Fossati, S.; Warembourg, C.; Casas, M.; Clemente, D.B.P.; Garcia-Esteban, R.; Nawrot, T.S.; Vrijheid, M. Prenatal exposure to phthalates and phenols and preclinical vascular health during early adolescence. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 240, 113909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujalance-reyes, F.; Molina-López, A.M.; Ayala-soldado, N.; Lora-benitez, A.; Mora-Medina, R.; Moyano-Salvago, R. Analysis of Indirect Biomarkers of Effect after Exposure to Low Doses of Bisphenol A in a Study of Successive Generations of Mice. Animals 2022, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bermejo, M.; Mas-Pérez, I.; Murillo-Llorente, M.T. The Role of the Bisphenol A in Diabetes and Obesity. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Rang, O.; Liu, F.; Xia, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Xu, S. A systematic review of metabolomics biomarkers for Bisphenol A exposure. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, A.G.; MacOnes, G.A.; Smyser, C.D.; López, J.D.; Inder, T.E.; Mathur, A.M. Umbilical Artery Lactate Correlates with Brain Lactate in Term Infants. Am. J. Perinatol. 2017, 34, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, P.; Fan, A.M. Bisphenol A Biomarkers and Biomonitoring, 2nd ed.; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128146552. [Google Scholar]
- Mustieles, V.; D’Cruz, S.C.; Couderq, S.; Rodríguez-Carrillo, A.; Fini, J.B.; Hofer, T.; Steffensen, I.L.; Dirven, H.; Barouki, R.; Olea, N.; et al. Bisphenol A and its analogues: A comprehensive review to identify and prioritize effect biomarkers for human biomonitoring. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffensen, I.L.; Dirven, H.; Couderq, S.; David, A.; D’cruz, S.C.; Fernández, M.F.; Mustieles, V.; Rodríguez-Carillo, A.; Hofer, T. Bisphenols and oxidative stress biomarkers— associations found in human studies, evaluation of methods used, and strengths and weaknesses of the biomarkers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, G.L.; Lite, C.; Subhashree, K.D.; Santosh, W.; Barathi, S. Prenatal bisphenol-A exposure altered exploratory and anxiety-like behaviour and induced non-monotonic, sex-specific changes in the cortical expression of CYP19A1, BDNF and intracellular signaling proteins in F1 rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 142, 111442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga-Lopez, A.; Pennathur, S.; Kannan, K.; Patisaul, H.B.; Dolinoy, D.C.; Zeng, L.; Padmanabhan, V. Impact of gestational bisphenol A on oxidative stress and free fatty acids: Human association and interspecies animal testing studies. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.K. Concern about the Safety of Bisphenol A Substitutes. Diabetes Metab. J. 2019, 43, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petre, A. What Is BPA and Why Is It Bad for You? Healthline. 2018. Available online: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/what-is-bpa#bottom-line (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- EPA. Bisphenol A (BPA) Action Plan Summary; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Bolognesi, C.; Castle, L.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Engel, K.-H.; Fowler, P.; Franz, R.; Grob, K.; Gürtler, R.; Husøy, T.; Mennes, W.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).