Signal Sequence-Dependent Orientation of Signal Peptide Fragments to Exosomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cell Systems
2.2. Secretion of SEAP from HEK-Blue hTLR3 Cells after Poly(I:C) Treatment
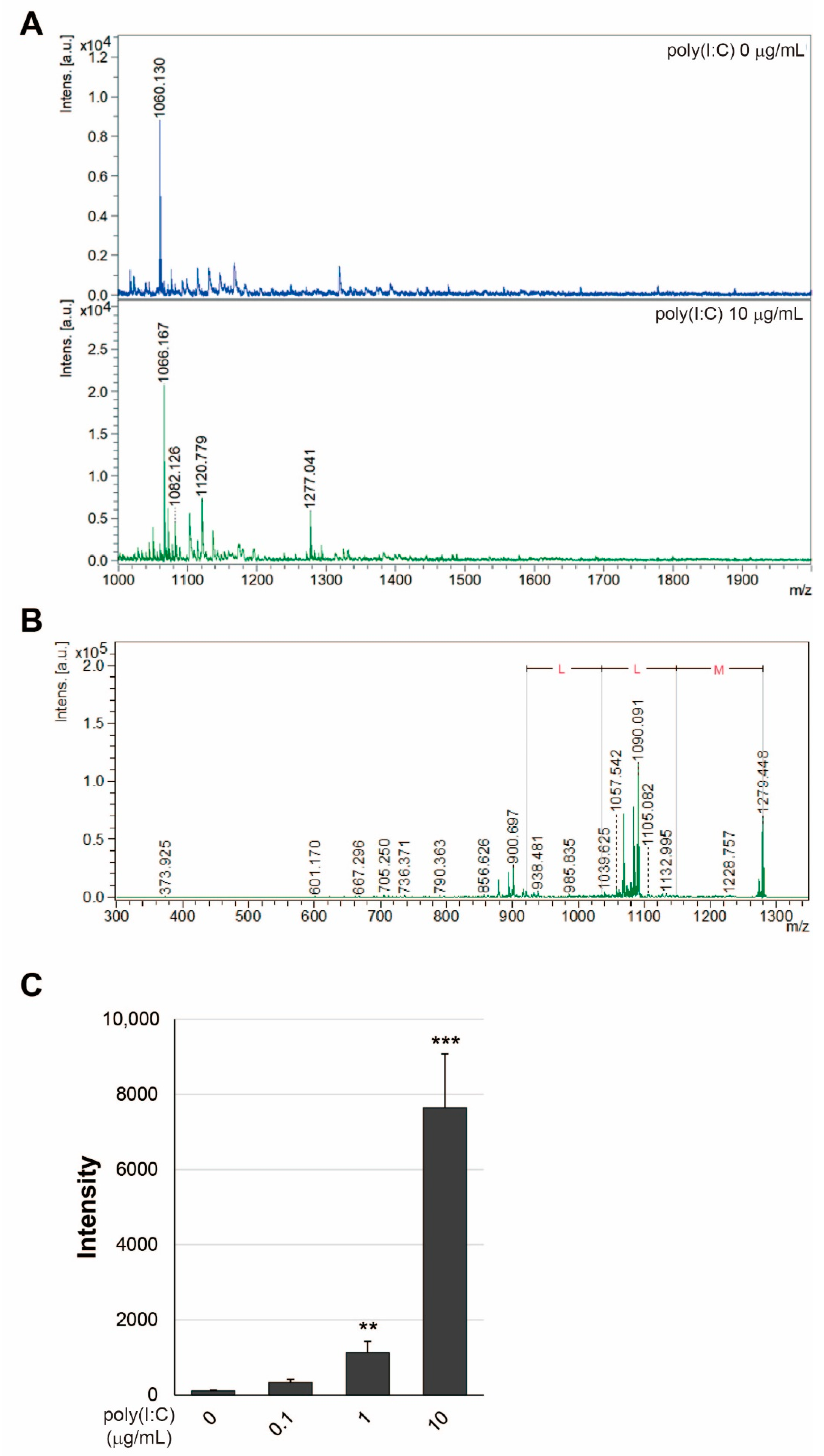
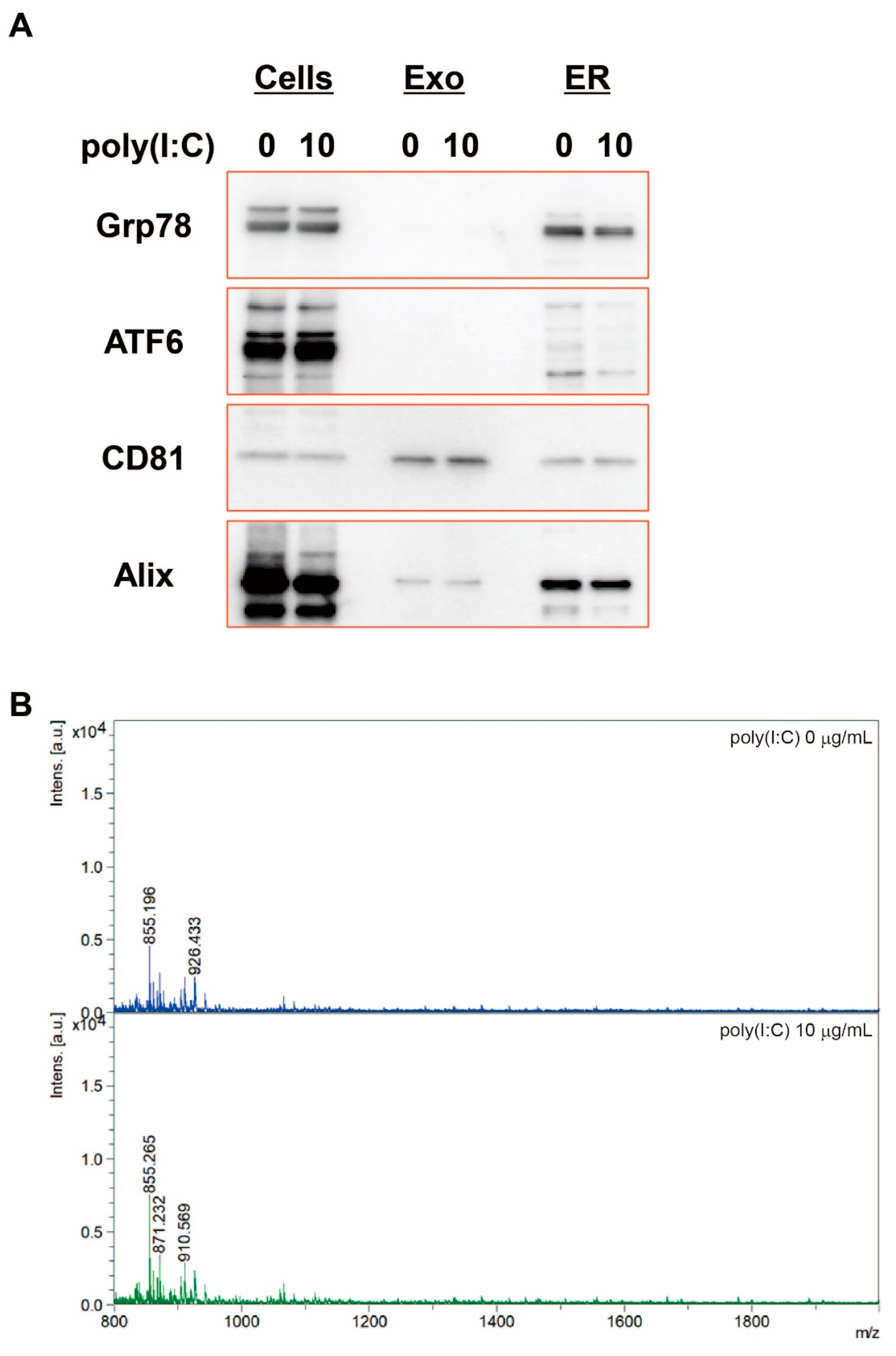
2.3. Detection of SEAP SP in Exosomes from HEK-Blue hTLR3 Cells
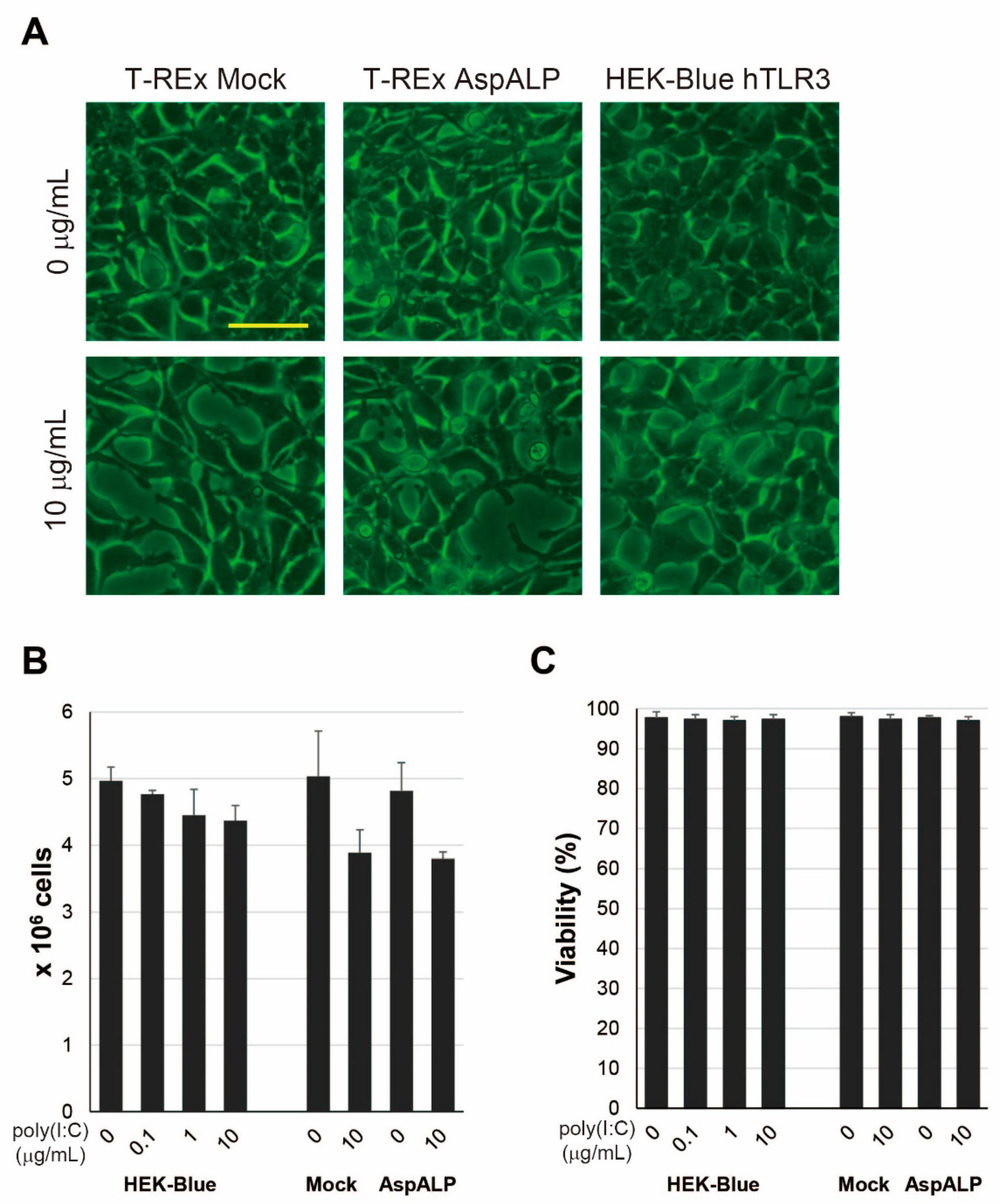
2.4. Alteration in Properties of HEK-Blue hTLR3 Cells after Poly(I:C) Treatment
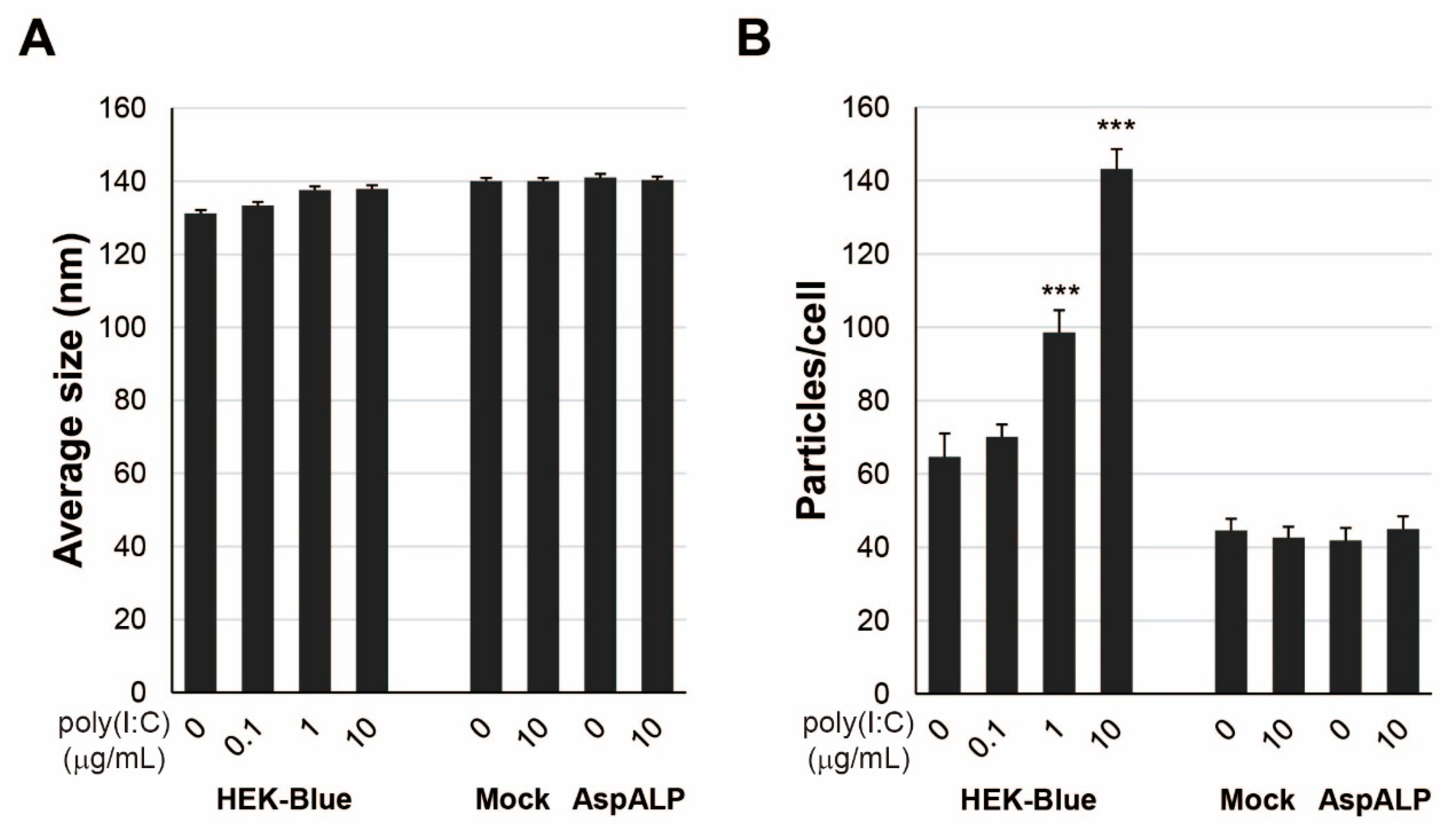
2.5. Properties of Exosomes from HEK-Blue hTLR3 Cells
2.6. Confirmation That the ER Fraction Is Not Contaminated in Exosomes
2.7. Binding of SP Fragment with CALM
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells
4.2. Isolation of Exosomes from Conditioned Medium
4.3. Measurement of SEAP Activity
4.4. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
4.5. Isolation of ER Fraction
4.6. SP Identification with MALDI-TOF MS/MS
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Calmodulin Binding Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pemberton, C.J.; Siriwardena, M.; Kleffmann, T.; Ruygrok, P.; Palmer, S.C.; Yandle, T.G.; Richards, A.M. First identification of circulating prepro-A-type natriuretic peptide (preproANP) signal peptide fragments in humans: Initial assessment as cardiovascular biomarkers. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardena, M.; Kleffmann, T.; Ruygrok, P.; Cameron, V.A.; Yandle, T.G.; Nicholls, M.G.; Richards, A.M.; Pemberton, C.J. B-type natriuretic peptide signal peptide circulates in human blood: Evaluation as a potential biomarker of cardiac ischemia. Circulation 2010, 122, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemberton, C.J.; Siriwardena, M.; Kleffmann, T.; Richards, A.M. C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) signal peptide fragments are present in the human circulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 449, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.; Chang, M.D.T. Signal peptide of eosinophil cationic protein is toxic to cells lacking signal peptide peptidase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 322, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.T.; Kao, Y.L.; Wu, C.M.; Fan, T.C.; Lai, Y.K.; Huang, K.L.; Chang, Y.S.; Tsai, J.J.; Chang, M.D.T. Signal peptide of eosinophil cationic protein upregulates transforming growth factor-alpha expression in human cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 100, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.S.; Tsai, P.W.; Wang, Y.; Fan, T.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chang, M.D.T.; Pai, T.W.; Huang, C.F.; Lan, C.Y.; Chang, H.T. Chemoattraction of macrophages by secretory molecules derived from cells expressing the signal peptide of eosinophil cationic protein. BMC Syst. Biol. 2012, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampatis, D.E.; Rutz, C.; Furkert, J.; Schmidt, A.; Wüstenhagen, D.; Kubick, S.; Tsopanoglou, N.E.; Schülein, R. The protease-activated receptor 1 possesses a functional and cleavable signal peptide which is necessary for receptor expression. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routhu, K.V.; Tsopanoglou, N.E.; Strande, J.L. Parstatin(1-26): The putative signal peptide of protease-activated receptor 1 confers potent protection from myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 332, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.F.; Ye, Y.; Xu, S.; Tao, W.; Zhao, S.; Jin, T.; Nicoll, R.A.; Shi, Y.S.; Sheng, N. Signal peptide represses GluK1 surface and synaptic trafficking through binding to amino-terminal domain. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, P.; Johnson, A.E. Signal sequence recognition and protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1994, 10, 87–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.; van Waes, M.A. The translocon: A dynamic gateway at the ER membrane. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 15, 799–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.C.; Blobel, G. Post-translational cleavage of presecretory proteins with an extract of rough microsomes from dog pancreas containing signal peptidase activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5598–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weihofen, A.; Binns, K.; Lemberg, M.K.; Ashman, K.; Martoglio, B. Identification of signal peptide peptidase, a presenilin-type aspartic protease. Science 2002, 296, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, C.; Thomas, E.C.; Merino-Trigo, A.; Teasdale, R.D.; Gleeson, P.A. Intracellular sorting and transport of proteins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2003, 83, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owji, H.; Nezafat, N.; Negahdaripour, M.; Hajiebrahimi, A.; Ghasemi, Y. A comprehensive review of signal peptides: Structure, roles, and applications. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 97, 422–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Niwa, M.; Suzuki, H.; Kobayashi, N.B.; Yoshida, T.; Sawada, M. Secretion of signal peptides via extracellular vesicles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 560, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martoglio, B.; Graf, R.; Dobberstein, B. Signal peptide fragments of preprolactin and HIV-1 p-gp160 interact with calmodulin. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 6636–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, M.; Falzone, L.; Caponnetto, A.; Gattuso, G.; Barbagallo, C.; Battaglia, R.; Mirabella, F.; Broggi, G.; Altieri, R.; Certo, F. Serum Extracellular Vesicle-Derived circHIPK3 and circSMARCA5 Are Two Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Glioblastoma Multiforme. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, M.; Jiang, H.; Xie, Y.; Jin, W.; Han, S. The Biological Roles of Exosomal Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancers. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, R.; Palini, S.; Vento, M.E.; La Ferlita, A.; Lo Faro, M.J.; Caroppo, E.; Borzì, P.; Falzone, L.; Barbagallo, D.; Ragusa, M. Identification of extracellular vesicles and characterization of miRNA expression profiles in human blastocoel fluid. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, Y.; Fang, C.; Wang, H. Exosomal circular RNA sorting mechanisms and their function in promoting or inhibiting cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 3369–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Heijne, G. Towards a comparative anatomy of N-terminal topogenic protein sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 189, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Tomiyoshi, R.; Kuroiwa, T.; Mihara, K.; Omura, T. Functions of signal and signal-anchor sequences are determined by the balance between the hydrophobic segment and the N-terminal charge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidow, H.; Nissen, P. Structural diversity of calmodulin binding to its target sites. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5551–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Hegde, R.S. A Calmodulin-Dependent Translocation Pathway for Small Secretory Proteins. Cell 2011, 147, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Peng, P.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Cao, D.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Gui, T.; Li, X. Characterization and proteomic analysis of ovarian cancer-derived exosomes. J. Proteomics 2013, 80, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthikumar, S.; Gangoda, L.; Liem, M.; Fonseka, P.; Atukorala, I.; Ozcitti, C.; Mechler, A.; Adda, C.G.; Ang, C.-S.; Mathivanan, S. Proteogenomic analysis reveals exosomes are more oncogenic than ectosomes. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15375–15396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bouteiller, O.; Merck, E.; Hasan, U.A.; Hubac, S.; Benguigui, B.; Trinchieri, G.; Bates, E.E.M.; Caux, C. Recognition of Double-stranded RNA by Human Toll-like Receptor 3 and Downstream Receptor Signaling Requires Multimerization and an Acidic pH. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38133–38145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matijevic, T.; Marjanovic, M.; Pavelic, J. Functionally active toll-like receptor 3 on human primary and metastatic cancer cells. Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 70, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Than, M.; Aldous, S.; Troughton, R.; Richards, M.; Pemberton, C.J. CNP Signal Peptide in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yao, F.; Svensjö, T.; Winkler, T.; Lu, M.; Eriksson, C.; Eriksson, E. Tetracycline repressor, tetR, rather than the tetR-mammalian cell transcription factor fusion derivatives, regulates inducible gene expression in mammalian cells. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ono, K.; Niwa, M.; Suzuki, H.; Kobayashi, N.B.; Yoshida, T.; Sawada, M. Signal Sequence-Dependent Orientation of Signal Peptide Fragments to Exosomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063137
Ono K, Niwa M, Suzuki H, Kobayashi NB, Yoshida T, Sawada M. Signal Sequence-Dependent Orientation of Signal Peptide Fragments to Exosomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(6):3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063137
Chicago/Turabian StyleOno, Kenji, Mikio Niwa, Hiromi Suzuki, Nahoko Bailey Kobayashi, Tetsuhiko Yoshida, and Makoto Sawada. 2022. "Signal Sequence-Dependent Orientation of Signal Peptide Fragments to Exosomes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 6: 3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063137
APA StyleOno, K., Niwa, M., Suzuki, H., Kobayashi, N. B., Yoshida, T., & Sawada, M. (2022). Signal Sequence-Dependent Orientation of Signal Peptide Fragments to Exosomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(6), 3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063137





