Unveiling the Toxicity of Fine and Nano-Sized Airborne Particles Generated from Industrial Thermal Spraying Processes in Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Process-Generated Fine and Nano-Sized Particle Characterisation
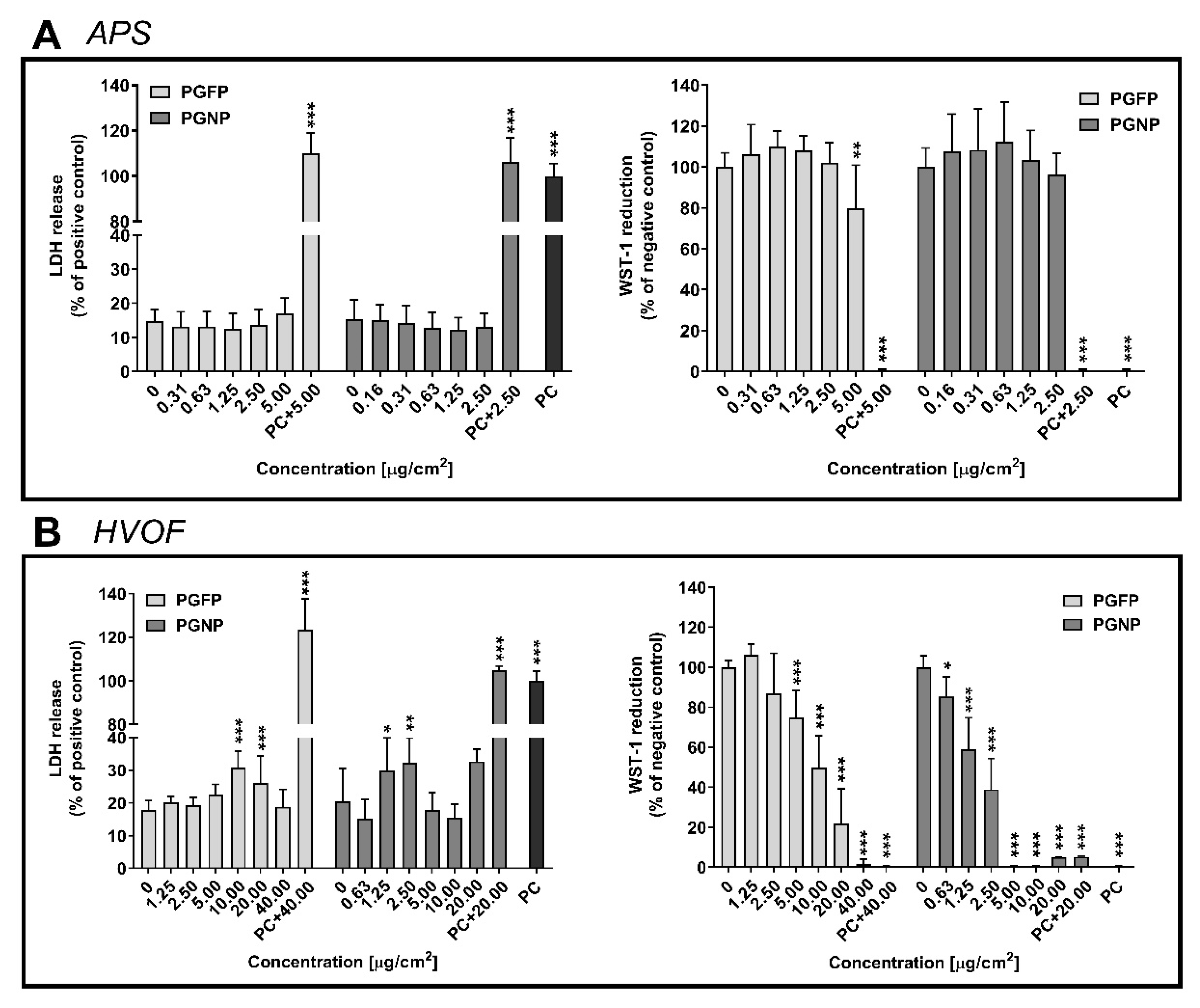
2.2. Plasma Membrane Integrity and Cell Viability
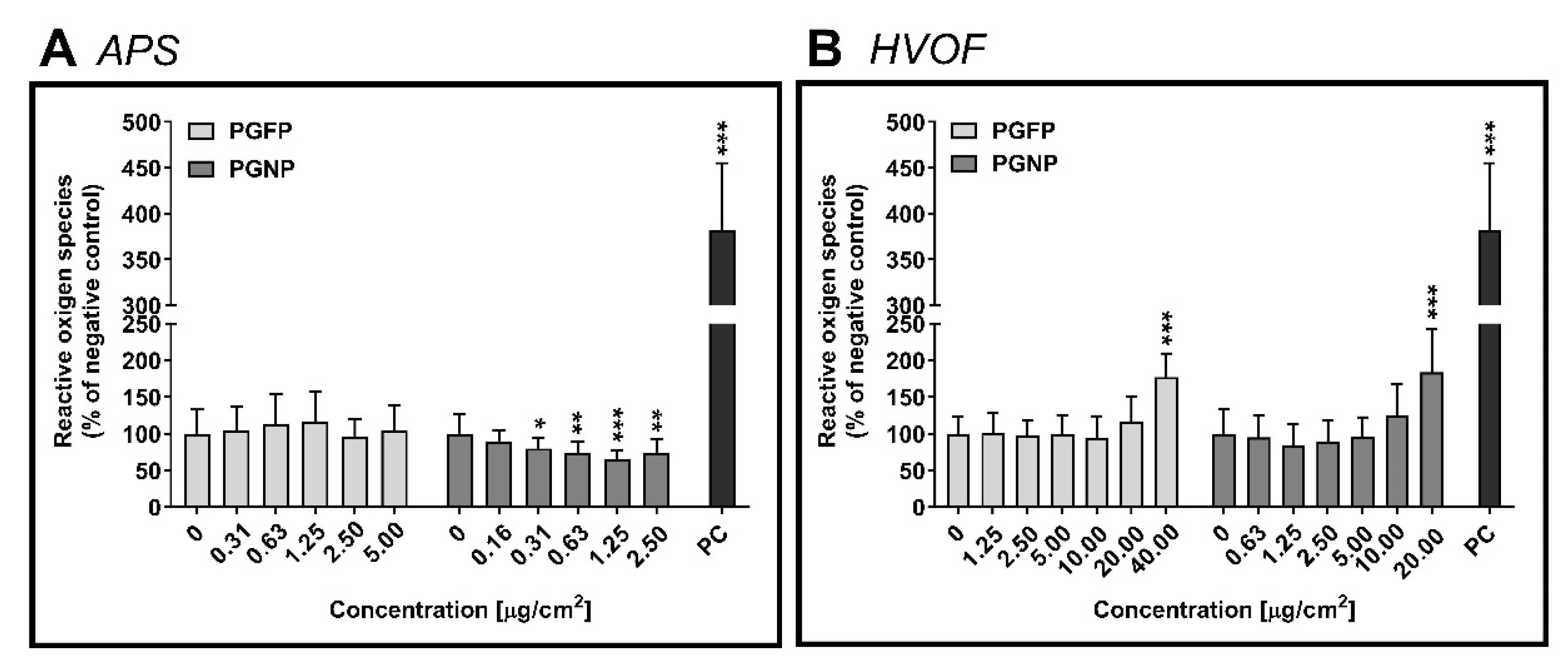
2.3. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Levels
2.4. Cellular Uptake of the (Nano)Particles
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Histone Gamma-H2AX Phosphorylation
2.7. Primary and Oxidative DNA Damage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Fine and Nano-Sized Particle Suspensions and Characterisation
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Exposure Conditions
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assessment
4.6. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Generation
4.7. Cellular Uptake, Cell Cycle and Histone Gamma-H2AX Phosphorylation Analysis by Flow Cytometry
4.8. DNA Damage Assessment
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Bessa, M.J.; Brandão, F.; Viana, M.; Gomes, J.F.; Monfort, E.; Cassee, F.R.; Fraga, S.; Teixeira, J.P. Nanoparticle exposure and hazard in the ceramic industry: An overview of potential sources, toxicity and health effects. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Salmatonidis, A.; Bezantakos, S.; Ribalta, C.; Moreno, N.; Córdoba, P.; Cassee, F.R.; Boere, J.; Fraga, S.; Teixeira, J.P.; et al. Characterizing the Chemical Profile of Incidental Ultrafine Particles for Toxicity Assessment Using an Aerosol Concentrator. Ann. Work Exp. Health 2021, 65, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribalta, C.; Koivisto, A.J.; Salmatonidis, A.; López-Lilao, A.; Monfort, E.; Viana, M. Modeling of High Nanoparticle Exposure in an Indoor Industrial Scenario with a One-Box Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salmatonidis, A.; Viana, M.; Pérez, N.; Alastuey, A.; Germán, F.; Angurel, L.A.; Sanfélix, V.; Monfort, E. Nanoparticle formation and emission during laser ablation of ceramic tiles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 126, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salmatonidis, A.; Viana, M.; Biskos, G.; Bezantakos, S. Particle size distributions and hygroscopic restructuring of ultrafine particles emitted during thermal spraying. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.S.; Maragkidou, A.; Viana, M.; Querol, X.; Hämeri, K.; de Francisco, I.; Estepa, C.; Borrell, C.; Lennikov, V.; de la Fuente, G.F. Process-generated nanoparticles from ceramic tile sintering: Emissions, exposure and environmental release. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, A.; Viana, M.; Querol, X.; Moreno, N.; De Francisco, I.; Estepa, C.; De La Fuente, G. Ultrafine and nanoparticle formation and emission mechanisms during laser processing of ceramic materials. J. Aerosol Sci. 2015, 88, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viana, M.; Fonseca, A.S.; Querol, X.; López-Lilao, A.; Carpio, P.; Salmatonidis, A.; Monfort, E. Workplace exposure and release of ultrafine particles during atmospheric plasma spraying in the ceramic industry. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmatonidis, A.; Ribalta, C.; Sanfélix, V.; Bezantakos, S.; Biskos, G.; Vulpoi, A.; Simion, S.; Monfort, E.; Viana, M. Workplace Exposure to Nanoparticles during Thermal Spraying of Ceramic Coatings. Ann. Work Exp. Health 2018, 63, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.; Viana, M.; Querol, X.; Moreno, N.; de Francisco, I.; Estepa, C.; de la Fuente, G. Workplace Exposure to Process-Generated Ultrafine and Nanoparticles in Ceramic Processes Using Laser Technology. In Indoor and Outdoor Nanoparticles; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 159–179. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, B.O. Deposition and clearance of inhaled particles. Environ. Health Perspect 1984, 55, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, M.; Kreyling, W.G. Deposition and biokinetics of inhaled nanoparticles. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, Y.-F.; Xu, Y.-H.; Shi, M.-H.; Lian, Y.-X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E69–E74. [Google Scholar]
- Schraufnagel, D.E. The health effects of ultrafine particles. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanasiou, A.; Viana, M.; Querol, X.; Moreno, T.; de Leeuw, F. Assessment of personal exposure to particulate air pollution during commuting in European cities--recommendations and policy implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, V.; Miller, M.R.; Clift, M.J.D.; Elder, A.; Mills, N.L.; Moller, P.; Schins, R.P.F.; Vogel, U.; Kreyling, W.G.; Alstrup Jensen, K.; et al. Nanomaterials Versus Ambient Ultrafine Particles: An Opportunity to Exchange Toxicology Knowledge. Environ. Health Perspect 2017, 125, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the air: A review of the effects of particulate matter air pollution on human health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamanaka, R.B.; Mutlu, G.M. Particulate Matter Air Pollution: Effects on the Cardiovascular System. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trethowan, W.N.; Burge, P.S.; Rossiter, C.E.; Harrington, J.M.; Calvert, I.A. Study of the respiratory health of employees in seven European plants that manufacture ceramic fibres. Occup. Environ. Med. 1995, 52, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaakkola, M.S.; Sripaiboonkij, P.; Jaakkola, J.J. Effects of occupational exposures and smoking on lung function in tile factory workers. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2011, 84, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, F.; Shahtaheri, S.J.; Golbabaei, F.; Barkhordari, A.; Rahimi-Froushani, A.; Khadem, M. Evaluation of Occupational Exposure of Glazers of a Ceramic Industry to Cobalt Blue Dye. Iran J. Public Health 2013, 42, 868–875. [Google Scholar]
- Bessa, M.J.; Brandão, F.; Fokkens, P.; Cassee, F.R.; Salmatonidis, A.; Viana, M.; Vulpoi, A.; Simon, S.; Monfort, E.; Teixeira, J.P.; et al. Toxicity assessment of industrial engineered and airborne process-generated nanoparticles in a 3D human airway epithelial in vitro model. Nanotoxicology 2021, 15, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cediel-Ulloa, A.; Isaxon, C.; Eriksson, A.; Primetzhofer, D.; Sortica, M.A.; Haag, L.; Derr, R.; Hendriks, G.; Löndahl, J.; Gudmundsson, A.; et al. Toxicity of stainless and mild steel particles generated from gas–metal arc welding in primary human small airway epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlovska, I.; Ramata-Stunda, A.; Martinsone, Z.; Boroduskis, M.; Patetko, L.; Martinsone, I.; Seile, A.; Vanadzins, I. In vitro impact preliminary assessment of airborne particulate from metalworking and woodworking industries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manke, A.; Wang, L.; Rojanasakul, Y. Mechanisms of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 942916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peixoto, M.S.; de Oliveira Galvão, M.F.; Batistuzzo de Medeiros, S.R. Cell death pathways of particulate matter toxicity. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jederlinic, P.J.; Abraham, J.L.; Churg, A.; Himmelstein, J.S.; Epler, G.R.; Gaensler, E.A. Pulmonary fibrosis in aluminum oxide workers. Investigation of nine workers, with pathologic examination and microanalysis in three of them. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1990, 142, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björ, O.; Damber, L.; Edström, C.; Nilsson, T. Long-term follow-up study of mortality and the incidence of cancer in a cohort of workers at a primary aluminum smelter in Sweden. Scand J. Work Environ. Health 2008, 34, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomassen, Y.; Koch, W.; Dunkhorst, W.; Ellingsen, D.G.; Skaugset, N.P.; Jordbekken, L.; Arne Drabløs, P.; Weinbruch, S. Ultrafine particles at workplaces of a primary aluminium smelter. J. Environ. Monit. 2006, 8, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, D.W.; Yoon, C.; Lee, B.S.; Kim, Y.; Chang, J.; Lee, K. Comparison of subchronic immunotoxicity of four different types of aluminum-based nanoparticles. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salnikow, K.; Zhitkovich, A. Genetic and Epigenetic Mechanisms in Metal Carcinogenesis and Cocarcinogenesis: Nickel, Arsenic, and Chromium. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halasova, E.; Adamkov, M.; Matakova, T.; Kavcova, E.; Poliacek, I.; Singliar, A. Lung cancer incidence and survival in chromium exposed individuals with respect to expression of anti-apoptotic protein survivin and tumor suppressor P53 protein. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2010, 15, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lippmann, M.; Chen, L.-C. Health effects of concentrated ambient air particulate matter (CAPs) and its components. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2009, 39, 865–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.I.; Green, F.Y.; Davies, J.C.; Murray, J. Pulmonary and systemic toxicity following exposure to nickel nanoparticles. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2010, 53, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Chung, Y.-H.; Seo, D.-S.; Choi, H.-S.; Lim, C.-H. Twenty-Eight-Day Repeated Inhalation Toxicity Study of Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticles in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 34, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, I.-S.; Baek, M.; Choi, S.-J. Comparative cytotoxicity of Al2O3, CeO2, TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles to human lung cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 3453–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Yin, L.H.; Tang, M.; Pu, Y.P. ZnO, TiO2, SiO2, and Al2O3 Nanoparticles-induced Toxic Effects on Human Fetal Lung Fibroblasts. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 661–669. [Google Scholar]
- Ivask, A.; Titma, T.; Visnapuu, M.; Vija, H.; Kakinen, A.; Sihtmae, M.; Pokhrel, S.; Madler, L.; Heinlaan, M.; Kisand, V. Toxicity of 11 metal oxide nanoparticles to three mammalian cell types in vitro. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1914–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaousi, A.; Jones, E.; Case, C.P. The in vitro genotoxicity of orthopaedic ceramic (Al2O3) and metal (CoCr alloy) particles. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 2010, 697, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Chromium, nickel and welding. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1990, 49, 677. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, J.P.; Wise, S.S.; Little, J.E. The cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of particulate and soluble hexavalent chromium in human lung cells. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 2002, 517, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kusaka, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sato, K.; Mo, Y.; Kluz, T.; Donaldson, K. Comparative toxicity of standard nickel and ultrafine nickel in lung after intratracheal instillation. J. Occup. Health 2003, 45, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morimoto, Y.; Hirohashi, M.; Ogami, A.; Oyabu, T.; Myojo, T.; Hashiba, M.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Kambara, T.; Lee, B.W.; Kuroda, E. Pulmonary toxicity following an intratracheal instillation of nickel oxide nanoparticle agglomerates. J. Occup. Health 2011, 53, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Åkerlund, E.; Cappellini, F.; Di Bucchianico, S.; Islam, S.; Skoglund, S.; Derr, R.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Hendriks, G.; Karlsson, H.L. Genotoxic and mutagenic properties of Ni and NiO nanoparticles investigated by comet assay, γ-H2AX staining, Hprt mutation assay and ToxTracker reporter cell lines. Environ. Mol. Mutagen 2018, 59, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roedel, E.Q.; Cafasso, D.E.; Lee, K.W.M.; Pierce, L.M. Pulmonary toxicity after exposure to military-relevant heavy metal tungsten alloy particles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 259, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.; Armknecht, S.; Johnston, T.; Zhitkovich, A. Undetectable role of oxidative DNA damage in cell cycle, cytotoxic and clastogenic effects of Cr(VI) in human lung cells with restored ascorbate levels. Mutagenesis 2012, 27, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeLoughery, Z.; Luczak, M.W.; Ortega-Atienza, S.; Zhitkovich, A. DNA Double-Strand Breaks by Cr(VI) Are Targeted to Euchromatin and Cause ATR-Dependent Phosphorylation of Histone H2AX and Its Ubiquitination. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 143, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Leonard, S.S.; Wang, S.; Vallyathan, V.; Castranova, V.; Shi, X. Cr (VI) induces cell growth arrest through hydrogen peroxide-mediated reactions. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 222, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; He, G.; Gong, W.; Wen, W.; Sun, W.; Ning, B.; Huang, S.; Wu, K.; Huang, C.; Wu, M.; et al. Effects of nickel on cyclin expression, cell cycle progression and cell proliferation in human pulmonary cells. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1720–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Mo, L.; Zhang, Q. Nickel nanoparticle-induced cell transformation: Involvement of DNA damage and DNA repair defect through HIF-1α/miR-210/Rad52 pathway. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Dai, X. The relationship between DNA single-stranded damage response and double-stranded damage response. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, K.J.; O’Connell, M.J. Cell cycle regulation by checkpoints. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1170, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mjelle, R.; Hegre, S.A.; Aas, P.A.; Slupphaug, G.; Drabløs, F.; Saetrom, P.; Krokan, H.E. Cell cycle regulation of human DNA repair and chromatin remodeling genes. DNA Repair 2015, 30, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Podhorecka, M.; Skladanowski, A.; Bozko, P. H2AX Phosphorylation: Its Role in DNA Damage Response and Cancer Therapy. J. Nucleic Acids 2010, 2010, 920161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacroix, G.; Koch, W.; Ritter, D.; Gutleb, A.C.; Larsen, S.T.; Loret, T.; Zanetti, F.; Constant, S.; Chortarea, S.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; et al. Air–Liquid Interface In vitro Models for Respiratory Toxicology Research: Consensus Workshop and Recommendations. Appl. Vitr. Toxicol. 2018, 4, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loret, T.; Peyret, E.; Dubreuil, M.; Aguerre-Chariol, O.; Bressot, C.; le Bihan, O.; Amodeo, T.; Trouiller, B.; Braun, A.; Egles, C.; et al. Air-liquid interface exposure to aerosols of poorly soluble nanomaterials induces different biological activation levels compared to exposure to suspensions. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frieke Kuper, C.; Gröllers-Mulderij, M.; Maarschalkerweerd, T.; Meulendijks, N.M.M.; Reus, A.; van Acker, F.; Zondervan-van den Beuken, E.K.; Wouters, M.E.L.; Bijlsma, S.; Kooter, I.M. Toxicity assessment of aggregated/agglomerated cerium oxide nanoparticles in an in vitro 3D airway model: The influence of mucociliary clearance. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, I.; Uboldi, C.; Bernard, E.; Sobrido, M.S.; Dine, S.; Hagège, A.; Vrel, D.; Herlin, N.; Rose, J.; Orsière, T.; et al. Toxicological Assessment of ITER-Like Tungsten Nanoparticles Using an In vitro 3D Human Airway Epithelium Model. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Jaques, P.A.; Chang, M.; Froines, J.R.; Sioutas, C. Versatile aerosol concentration enrichment system (VACES) for simultaneous in vivo and in vitro evaluation of toxic effects of ultrafine, fine and coarse ambient particles Part I: Development and laboratory characterization. J. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 1281–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, M.J.; Brandão, F.; Fokkens, P.H.B.; Leseman, D.; Boere, A.J.F.; Cassee, F.R.; Salmatonidis, A.; Viana, M.; Vulpoi, A.; Simon, S.; et al. In vitro Toxicity of Industrially Relevant Engineered Nanoparticles in Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells: Air-Liquid Interface versus Submerged Cultures. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NanoToxclass Standard Operation Procedure—Preparation of Nanoparticle Suspensions by Cup Horn Sonication. Available online: https://www.nanopartikel.info/files/projekte/NanoToxClass/NanoToxClassSOP_Dispersion_by_cup_horn_sonication_V2.0.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Paur, H.-R.; Cassee, F.R.; Teeguarden, J.; Fissan, H.; Diabate, S.; Aufderheide, M.; Kreyling, W.G.; Hänninen, O.; Kasper, G.; Riediker, M. In-vitro cell exposure studies for the assessment of nanoparticle toxicity in the lung—A dialog between aerosol science and biology. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 668–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Toyooka, T.; Ibuki, Y. Simple and easy method to evaluate uptake potential of nanoparticles in mammalian cells using a flow cytometric light scatter analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3018–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosário, F.; Bessa, M.J.; Brandão, F.; Costa, C.; Lopes, C.B.; Estrada, A.C.; Tavares, D.S.; Teixeira, J.P.; Reis, A.T. Unravelling the Potential Cytotoxic Effects of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles and Metal(Loid) Mixtures on A549 Human Cell Line. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B.; Pásaro, E.; Méndez, J. Evaluation of okadaic acid-induced genotoxicity in human cells using the micronucleus test and γH2AX analysis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2011, 74, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, P.; Azqueta, A.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Koppen, G.; Bonassi, S.; Milić, M.; Gajski, G.; Costa, S.; Teixeira, J.P.; Costa Pereira, C.; et al. Minimum Information for Reporting on the Comet Assay (MIRCA): Recommendations for describing comet assay procedures and results. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3817–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, M.J.; Brandao, F.; Querido, M.M.; Costa, C.; Pereira, C.C.; Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B.; Carriere, M.; Teixeira, J.P.; Fraga, S. Optimization of the harvesting and freezing conditions of human cell lines for DNA damage analysis by the alkaline comet assay. Mutat. Res. 2019, 845, 402994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Stock Suspension Concentration (mg/mL) | Stock Suspension Concentration (Number of Particles/mL) | Hydrodynamic Size (nm) | Oxidative Potential (A.U.) * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APS | PGFP | 0.068 | 8.49 × 108 | 244 ± 120 | 3291 |
| PGNP | 0.034 | 4.21 × 108 | 410 ± 162 | 5319 | |
| HVOF | PGFP | 1.069 | 9.72 × 108 | 247 ± 116 | 9893 |
| PGNP | 0.140 | 15.86 × 108 | 236 ± 86 | 12833 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bessa, M.J.; Brandão, F.; Fokkens, P.H.B.; Leseman, D.L.A.C.; Boere, A.J.F.; Cassee, F.R.; Salmatonidis, A.; Viana, M.; Monfort, E.; Fraga, S.; et al. Unveiling the Toxicity of Fine and Nano-Sized Airborne Particles Generated from Industrial Thermal Spraying Processes in Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084278
Bessa MJ, Brandão F, Fokkens PHB, Leseman DLAC, Boere AJF, Cassee FR, Salmatonidis A, Viana M, Monfort E, Fraga S, et al. Unveiling the Toxicity of Fine and Nano-Sized Airborne Particles Generated from Industrial Thermal Spraying Processes in Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(8):4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084278
Chicago/Turabian StyleBessa, Maria João, Fátima Brandão, Paul H. B. Fokkens, Daan L. A. C. Leseman, A. John F. Boere, Flemming R. Cassee, Apostolos Salmatonidis, Mar Viana, Eliseo Monfort, Sónia Fraga, and et al. 2022. "Unveiling the Toxicity of Fine and Nano-Sized Airborne Particles Generated from Industrial Thermal Spraying Processes in Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 8: 4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084278
APA StyleBessa, M. J., Brandão, F., Fokkens, P. H. B., Leseman, D. L. A. C., Boere, A. J. F., Cassee, F. R., Salmatonidis, A., Viana, M., Monfort, E., Fraga, S., & Teixeira, J. P. (2022). Unveiling the Toxicity of Fine and Nano-Sized Airborne Particles Generated from Industrial Thermal Spraying Processes in Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(8), 4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084278










