The Role of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists in Insulin Resistance with Concomitant Obesity Treatment in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Pathomechanism and Role of IR in PCOS
3. Role of GLP-1RAs in IR Associated with PCOS
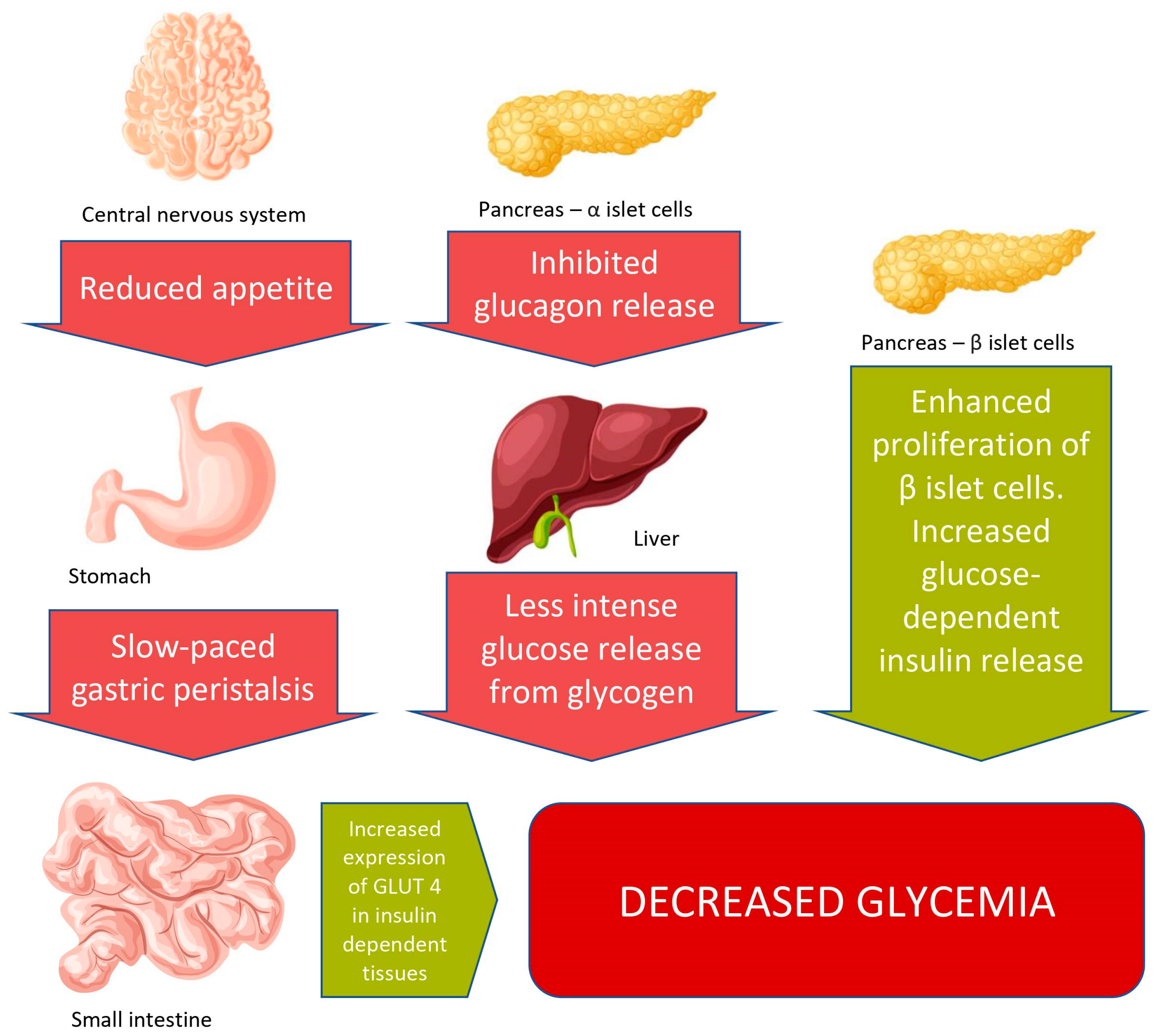
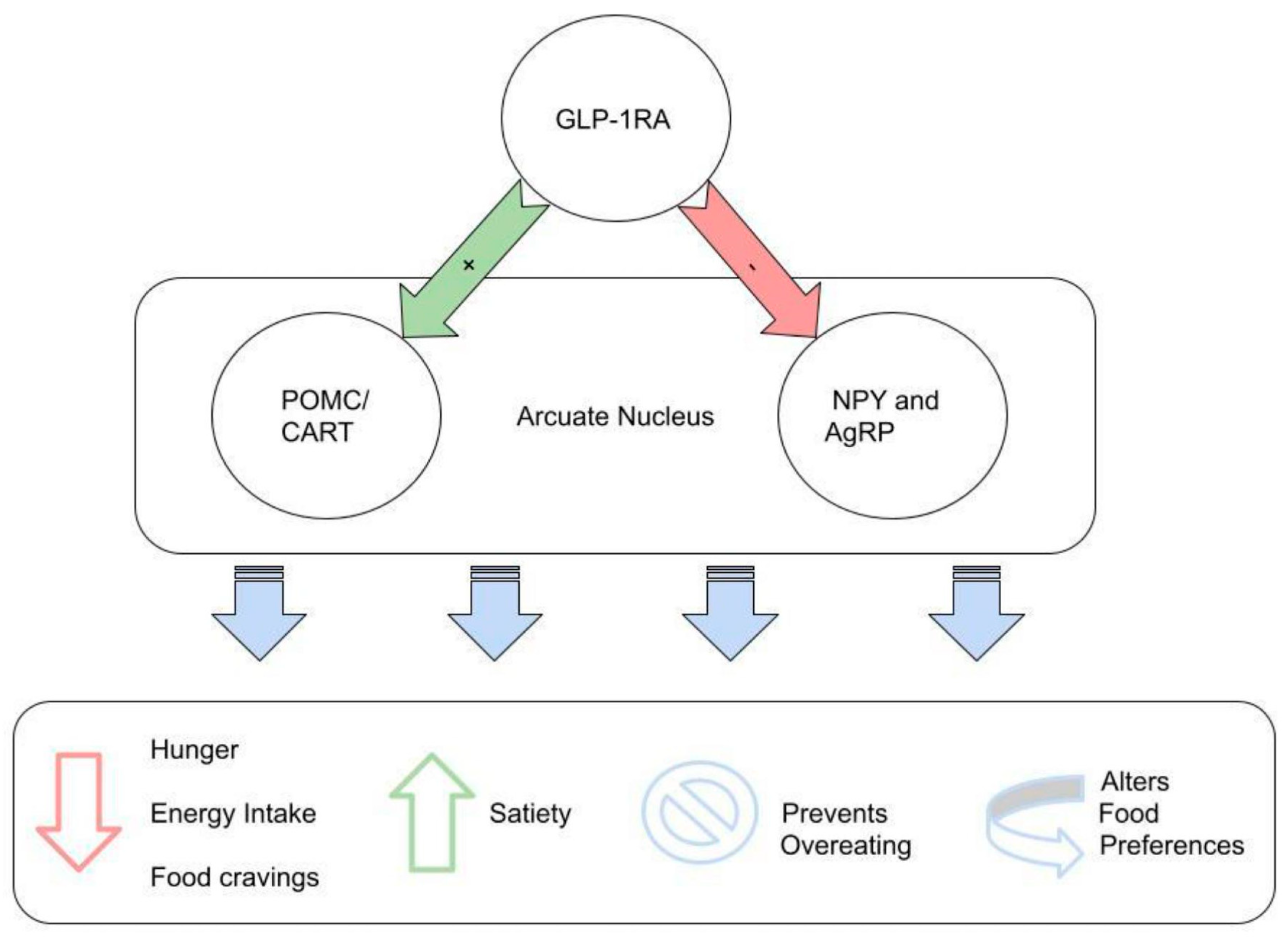
3.1. Body Weight Reduction
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of GLP-1RAs
3.3. GLP-1RAs and Reproductive System
3.4. GLP-1RAs and Oxidative Stress
3.5. GLP-1RAs Impact on Lipid Metabolism in the Context of IR
4. Discussion and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misso, M.; Costello, M.; Dokras, A.; Laven, J.; Moran, L.; Piltonen, T.; Norman, R. International Evidencebased for the Assessment and management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome; Monash University: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Miazgowski, T.; Martopullo, I.; Widecka, J.; Miazgowski, B.; Brodowska, A. National and Regional Trends in the Prevalence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome since 1990 within Europe: The Modeled Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deswal, R.; Narwal, V.; Dang, A.; Pundir, C. The Prevalence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Brief Systematic Review. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirmans, S.; Pate, K. Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, F.; Simbar, M.; Tohidi, M.; Hosseinpanah, F.; Azizi, F. The Prevalence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in a Community Sample of Iranian Population: Iranian PCOS Prevalence Study. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2011, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Goodarzi, M.O. Genetic Determinants of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Progress and Future Directions. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkin, S.S.; Phy, J.L.; Sites, C.K.; Yang, D. Environmental Determinants of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Morreale, H.F. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Definition, Aetiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, A.M.; Adamska, A.; Krentowska, A.; Łebkowska, A.; Hryniewicka, J.; Adamski, M.; Kowalska, I. Body Composition, Serum Concentrations of Androgens and Insulin Resistance in Different Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Phenotypes. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, G.; Dewailly, D.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Franks, S.; Gambineri, A.; Kelestimur, F.; Macut, D.; Micic, D.; Pasquali, R.; et al. The Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Position Statement from the European Society of Endocrinology. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 171, P1–P29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witchel, S.F.; Oberfield, S.E.; Peña, A.S. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Pathophysiology, Presentation, and Treatment with Emphasis on Adolescent Girls. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1545–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasquin Leon, L.I.; Anastasopoulou, C.; Mayrin, J.V. Polycystic Ovarian Disease; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. The Pathogenesis of Insulin Resistance: Integrating Signaling Pathways and Substrate Flux. J. Clin. Investig. Am. Soc. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ells, L.J.; Rees, K.; Brown, T.; Mead, E.; Al-Khudairy, L.; Azevedo, L.; McGeechan, G.J.; Baur, L.; Loveman, E.; Clements, H.; et al. Interventions for Treating Children and Adolescents with Overweight and Obesity: An Overview of Cochrane Reviews. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.M.W.; Gallagher, M.; Gooding, H.; Feldman, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Ludwig, D.S.; Ebbeling, C.B. A Randomized Pilot Study of Dietary Treatments for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2016, 11, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legro, R. Obesity and PCOS: Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2012, 30, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, L.J.; Brown, W.J.; McNaughton, S.A.; Joham, A.E.; Teede, H.J. Weight Management Practices Associated with PCOS and Their Relationships with Diet and Physical Activity. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 32, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Smith, C.A.; Costello, M.F.; MacMillan, F.; Moran, L.; Ee, C. Barriers and Facilitators to Weight Management in Overweight and Obese Women Living in Australia with PCOS: A Qualitative Study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whigham, L.; Butz, D.; Dashti, H.; Tonelli, M.; Johnson, L.; Cook, M.; Porter, W.; Eghbalnia, H.; Markley, J.; Lindheim, S.; et al. Metabolic Evidence of Diminished Lipid Oxidation in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Curr. Metab. 2014, 1, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorakae, S.; Jona, E.; de Courten, B.; Lambert, G.W.; Lambert, E.A.; Phillips, S.E.; Clarke, I.J.; Teede, H.J.; Henry, B.A. Brown Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2019, 90, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domecq, J.P.; Prutsky, G.; Mullan, R.J.; Hazem, A.; Sundaresh, V.; Elamin, M.B.; Phung, O.J.; Wang, A.; Hoeger, K.; Pasquali, R.; et al. Lifestyle Modification Programs in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4655–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Effectiveness of Lifestyle Modification in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Patients with Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2022, 12, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; McBreairty, L.E.; Zello, G.A.; Pierson, R.A.; Gordon, J.J.; Serrao, S.B.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Chizen, D.R. A Pulse-Based Diet and the Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes Diet in Combination with Health Counseling and Exercise Improve Health-Related Quality of Life in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 41, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carolo, A.L.; Mendes, M.C.; Rosa e Silva, A.C.J.D.S.; Vieira, C.S.; de Sá, M.F.S.; Ferriani, R.A.; dos Reis, R.M. O Aconselhamento Nutricional Promove Mudanças Nos Hábitos Alimentares de Adolescentes Com Excesso de Peso e Obesas e Com Síndrome Dos Ovários Policísticos. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obstet. 2017, 39, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network Part of NHS Quality Improvement Scotland SIGN Management of Obesity; The Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN): Edinburgh, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, K.; Cnattingius, S.; Näslund, I.; Roos, N.; Trolle Lagerros, Y.; Granath, F.; Stephansson, O.; Neovius, M. Outcomes of Pregnancy after Bariatric Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderpoor, N.; Shorakae, S.; de Courten, B.; Misso, M.L.; Moran, L.J.; Teede, H.J. Metformin and Lifestyle Modification in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2015, 21, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, R.A.; Carmina, E.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Dokras, A.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Futterweit, W.; Lobo, R.; Norman, R.J.; Talbott, E.; Dumesic, D.A. Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk and Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Women with the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Consensus Statement by the Androgen Excess and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (AE-PCOS) Society. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2038–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devin, J.K.; Nian, H.; Celedonio, J.E.; Wright, P.; Brown, N.J. Sitagliptin Decreases Visceral Fat and Blood Glucose in Women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, Z.; Papageorgiou, M.; Deshmukh, H.; Rigby, A.S.; Qamar, U.; Abbas, J.; Khan, A.Y.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Atkin, S.L.; Sathyapalan, T. Effects of Empagliflozin on Metabolic Parameters in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2019, 90, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niafar, M.; Pourafkari, L.; Porhomayon, J.; Nader, N. A Systematic Review of GLP-1 Agonists on the Metabolic Syndrome in Women with Polycystic Ovaries. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2016, 293, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, M.P. Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance Related to White, Beige, and Brown Adipocytes. Mol. Metab. 2020, 34, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, F.; Bonora, E.; Moghetti, P. Insulin Resistance in a Large Cohort of Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Comparison between Euglycaemic-Hyperinsulinaemic Clamp and Surrogate Indexes. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 32, 2515–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghetti, P.; Tosi, F.; Bonin, C.; di Sarra, D.; Fiers, T.; Kaufman, J.M.; Giagulli, V.A.; Signori, C.; Zambotti, F.; Dall’Alda, M.; et al. Divergences in Insulin Resistance between the Different Phenotypes of the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E628–E637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, L.W.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Keevil, B.G.; Jayagopal, V.; Coady, A.M.; Rigby, A.S.; Atkin, S.L. Insulin Resistance Variability in Women with Anovulatory and Ovulatory Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, and Normal Controls. Horm. Metab. Res. Horm. Stoffwechs. Horm. Metab. 2011, 43, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borruel, S.; Fernández-Durán, E.; Alpañés, M.; Martí, D.; Álvarez-Blasco, F.; Luque-Ramírez, M.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F. Global Adiposity and Thickness of Intraperitoneal and Mesenteric Adipose Tissue Depots Are Increased in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannerås-Holm, L.; Leonhardt, H.; Kullberg, J.; Jennische, E.; Odén, A.; Holm, G.; Hellström, M.; Lönn, L.; Olivecrona, G.; Stener-Victorin, E.; et al. Adipose Tissue Has Aberrant Morphology and Function in PCOS: Enlarged Adipocytes and Low Serum Adiponectin, but Not Circulating Sex Steroids, Are Strongly Associated with Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E304–E311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbould, A. Chronic Testosterone Treatment Induces Selective Insulin Resistance in Subcutaneous Adipocytes of Women. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 192, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Feng, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Hua, M. Adiponectin, TNF-α and Inflammatory Cytokines and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cytokine 2016, 86, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Vatner, D.F.; Goedeke, L.; Hirabara, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; Perry, R.J.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms by Which Adiponectin Reverses High Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32584–32593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, X.; Zhong, H.; Peng, Q.; Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Qin, X.; Qin, A. Low Circulating Adiponectin Levels in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 3961–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, X. Circulating Adipokine Levels in Nonobese Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and in Nonobese Control Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 537809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabani, S.; Arab, A.; Karimi, E.; Nouri, M.; Mansourian, M. Blood Circulating Levels of Adipokines in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 28, 3032–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifarelli, V.; Beeman, S.C.; Smith, G.I.; Yoshino, J.; Morozov, D.; Beals, J.W.; Kayser, B.D.; Watrous, J.D.; Jain, M.; Patterson, B.W.; et al. Decreased Adipose Tissue Oxygenation Associates with Insulin Resistance in Individuals with Obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6688–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, F.; Sreekumaran Nair, K.; Daniels, J.K.; Basal, E.; Schimke, J.M. Hyperandrogenism Sensitizes Mononuclear Cells to Promote Glucose-Induced Inflammation in Lean Reproductive-Age Women. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, F.; Rote, N.S.; Minium, J.; Weaver, A.L.; Kirwan, J.P. Elevated Circulating Levels of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Cytokine 2010, 51, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Haeusler, R.A.; McGraw, T.E.; Accili, D. Biochemical and Cellular Properties of Insulin Receptor Signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Dunaif, A. Insulin Resistance and the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Revisited: An Update on Mechanisms and Implications. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 981–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Takaguri, A.; Ichihara, K.; Satoh, K. Inhibition of the TNF-α-Induced Serine Phosphorylation of IRS-1 at 636/639 by AICAR. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 122, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Farrokhi, F.R.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Insulin Resistance: Review of the Underlying Molecular Mechanisms. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 8152–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamska, A.; Karczewska-Kupczewska, M.; Nikołajuk, A.; Otziomek, E.; Górska, M.; Kowalska, I.; Straczkowski, M. Normal Metabolic Flexibility despite Insulin Resistance Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Endocr. J. 2013, 60, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; Allard, C.; Morford, J.J.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Molinas, A.J.; Butcher, S.M.; Fine, N.H.; Blandino-Rosano, M.; Sure, V.N.; et al. Androgen Excess in Pancreatic β Cells and Neurons Predisposes Female Mice to Type 2 Diabetes. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, A.; Recabarren, M.P.; Rojas-García, P.P.; Gutiérrez, M.; Morales, K.; Sir-Petermann, T.; Recabarren, S.E. Prenatal Testosterone Exposure Disrupts Insulin Secretion and Promotes Insulin Resistance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risal, S.; Pei, Y.; Lu, H.; Manti, M.; Fornes, R.; Pui, H.P.; Zhao, Z.; Massart, J.; Ohlsson, C.; Lindgren, E.; et al. Prenatal Androgen Exposure and Transgenerational Susceptibility to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.R.; Goyeneche, A.A.; Heber, M.F.; Abruzzese, G.A.; Ferrer, M.J.; Telleria, C.M.; Motta, A.B. Prenatal Testosterone Exposure Induces Insulin Resistance, Uterine Oxidative Stress and pro-Inflammatory Status in Rats. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2021, 519, 111045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Riopel, M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Dong, Y.; Birmingham, A.; Seo, J.B.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Wollam, J.; Hernandez-Carretero, A.; Fu, W.; et al. Adipose Tissue Macrophage-Derived Exosomal MiRNAs Can Modulate In Vivo and In Vitro Insulin Sensitivity. Cell 2017, 171, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Du, H.; Wei, S.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, M.; Hatch, G.M.; Chen, L. Adipocyte-Derived Exosomal MiR-27a Induces Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle Through Repression of PPARγ. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2171–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yu, J.; Li, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, W.; Jiang, H.; Hong, Z. MiR-27a Promotes Insulin Resistance and Mediates Glucose Metabolism by Targeting PPAR-γ-Mediated PI3K/AKT Signaling. Aging 2019, 11, 7510–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Hu, J.; Ma, J.; Cui, L.; Chen, Z.J. Differential Expression Profile of Plasma Exosomal MicroRNAs in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 2021, 115, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghetti, P.; Tosi, F. Insulin Resistance and PCOS: Chicken or Egg? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, J.E.; Jakubowicz, D.J. Decreases in Ovarian Cytochrome P450c17 Alpha Activity and Serum Free Testosterone after Reduction of Insulin Secretion in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadagan, D.; Khan, R.; Amer, S. Thecal Cell Sensitivity to Luteinizing Hormone and Insulin in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 16, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; DiVall, S.A.; Deneau, R.M.; Wolfe, A. Insulin Regulation of GnRH Gene Expression through MAP Kinase Signaling Pathways. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2005, 242, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinyua, A.W.; Doan, K.V.; Yang, D.J.; Huynh, M.K.Q.; Choi, Y.H.; Shin, D.M.; Kim, K.W. Insulin Regulates Adrenal Steroidogenesis by Stabilizing SF-1 Activity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deswal, R.; Yadav, A.; Dang, A.S. Sex Hormone Binding Globulin—An Important Biomarker for Predicting PCOS Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2018, 64, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadkarni, P.; Chepurny, O.G.; Holz, G.G. Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis by GLP-1. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2014, 121, 23–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, A.R.; Deyoung, M.B.; Lowe, C.; Parkes, D.G. GLP-1 Receptor Activated Insulin Secretion from Pancreatic β-Cells: Mechanism and Glucose Dependence. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Keyhani-Nejad, F. High Glycemic Index Metabolic Damage—A Pivotal Role of GIP and GLP-1. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.C. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) and Protective Effects in Cardiovascular Disease: A New Therapeutic Approach for Myocardial Protection. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bloemendaal, L.; ten Kulve, J.S.; la Fleur, S.E.; Ijzerman, R.G.; Diamant, M. Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 on Appetite and Body Weight: Focus on the CNS. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 221, T1–T16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, D.; Toyoda, M.; Kimura, M.; Miyauchi, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Sato, H.; Tanaka, E.; Kuriyama, Y.; Miyatake, H.; Abe, M.; et al. Effects of Liraglutide, a Human Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Analogue, on Body Weight, Body Fat Area and Body Fat-Related Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Intern. Med. 2013, 52, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, A.D. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022 Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin. Diabetes 2022, 40, 10–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.; Lee, M.H.; Yaow, C.Y.L.; Chin, Y.H.; Goh, X.L.; Ng, C.H.; Lim, A.Y.L.; Muthiah, M.D.; Khoo, C.M. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Lonardo, A.; Targher, G. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Metabolites 2021, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Atkin, S.L.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. GLP-1 Mimetics and Cognition. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Soria, M.; Carranza-Naval, M.J.; del Marco, A.; Garcia-Alloza, M. Role of Liraglutide in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölscher, C. Novel Dual GLP-1/GIP Receptor Agonists Show Neuroprotective Effects in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Models. Neuropharmacology 2018, 136, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glintborg, D.; Andersen, M. Medical Treatment and Comorbidity in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: An Updated Review. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2020, 12, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siamashvili, M.; Davis, S.N. Update on the Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, M.; Frøssing, S.; Clausen, H.V.; Kistorp, C.; Faber, J.; Skouby, S.O. Effects of Liraglutide on Ovarian Dysfunction in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2017, 35, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahal, H.; Aburima, A.; Ungvari, T.; Rigby, A.S.; Coady, A.M.; Vince, R.V.; Ajjan, R.A.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Naseem, K.M.; Atkin, S.L. The Effects of Treatment with Liraglutide on Atherothrombotic Risk in Obese Young Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Controls. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2015, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cena, H.; Chiovato, L.; Nappi, R.E. Obesity, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, and Infertility: A New Avenue for GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolism. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 105, e2695–e2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachoń, D.; Teede, H. Ovarian Function and Obesity—Interrelationship, Impact on Women’s Reproductive Lifespan and Treatment Options. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 316, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungheim, E.S.; Moley, K.H. Current Knowledge of Obesity’s Effects in the Pre-and Periconceptional Periods and Avenues for Future Research. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, L.J.; Norman, R.J.; Teede, H.J. Metabolic Risk in PCOS: Phenotype and Adiposity Impact. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulter, A.A.; Rebello, C.J.; Greenway, F.L. Centrally Acting Agents for Obesity: Past, Present, and Future. Drugs 2018, 78, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.B.; Lau, J. The Discovery and Development of Liraglutide and Semaglutide. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metabolism. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Hayes, M.R.; Skibicka, K.P. GLP-1 and Weight Loss: Unraveling the Diverse Neural Circuitry. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ard, J.; Fitch, A.; Fruh, S.; Herman, L. Weight Loss and Maintenance Related to the Mechanism of Action of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 2821–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frøssing, S.; Nylander, M.; Chabanova, E.; Frystyk, J.; Holst, J.J.; Kistorp, C.; Skouby, S.O.; Faber, J. Effect of Liraglutide on Ectopic Fat in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensterle, M.; Kravos, N.A.; Goričar, K.; Janez, A. Short-Term Effectiveness of Low Dose Liraglutide in Combination with Metformin versus High Dose Liraglutide Alone in Treatment of Obese PCOS: Randomized Trial. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2017, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensterle, M.; Kravos, N.A.; Pfeifer, M.; Kocjan, T.; Janez, A. A 12-Week Treatment with the Long-Acting Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Liraglutide Leads to Significant Weight Loss in a Subset of Obese Women with Newly Diagnosed Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Hormones 2015, 14, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensterle, M.; Kocjan, T.; Kravos, N.A.; Pfeifer, M.; Janez, A. Short-Term Intervention with Liraglutide Improved Eating Behavior in Obese Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Endocr. Res. 2015, 40, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensterle, M.; Pirš, B.; Goričar, K.; Dolžan, V.; Janež, A. Genetic Variability in GLP-1 Receptor Is Associated with Inter-Individual Differences in Weight Lowering Potential of Liraglutide in Obese Women with PCOS: A Pilot Study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensterle, M.; Salamun, V.; Kocjan, T.; Vrtacnik Bokal, E.; Janez, A. Short Term Monotherapy with GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Liraglutide or PDE 4 Inhibitor Roflumilast Is Superior to Metformin in Weight Loss in Obese PCOS Women: A Pilot Randomized Study. J. Ovarian. Res. 2015, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyapalan, T.; Atkin, S.L. Mediators of Inflammation in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Relation to Adiposity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 758656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, H.; Tateya, S.; Tamori, Y.; Kotani, K.; Hiasa, K.I.; Kitazawa, R.; Kitazawa, S.; Miyachi, H.; Maeda, S.; Egashira, K.; et al. MCP-1 Contributes to Macrophage Infiltration into Adipose Tissue, Insulin Resistance, and Hepatic Steatosis in Obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Park, M.S.; Choung, J.S.; Kim, S.S.; Oh, H.H.; Choi, C.S.; Ha, S.Y.; Kang, Y.; Kim, Y.; Jun, H.S. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Inhibits Adipose Tissue Macrophage Infiltration and Inflammation in an Obese Mouse Model of Diabetes. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Huang, T.; Chen, A.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, F.; Gu, X. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Improves Insulin Resistance in Vitro through Anti-Inflammation of Macrophages. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. Rev. Bras. Pesqui. Med. Biol. 2016, 49, e5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim Chung, L.T.; Hosaka, T.; Yoshida, M.; Harada, N.; Sakaue, H.; Sakai, T.; Nakaya, Y. Exendin-4, a GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, Directly Induces Adiponectin Expression through Protein Kinase A Pathway and Prevents Inflammatory Adipokine Expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Li, T.; An, P.; Yan, W.; Zheng, H.; Wang, B.; Mu, Y. Exendin-4 Upregulates Adiponectin Level in Adipocytes via Sirt1/Foxo-1 Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oncul, M.; Albayrak, M.; Sozer, V.; Karakus, B.; Gelisgen, R.; Karatas, S.; Simsek, G.; Uzun, H. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Endothelial Dysfunction: A Potential Role for Soluble Lectin-like Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 20, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasner, N.M.; Ido, Y.; Ruderman, N.B.; Cacicedo, J.M. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analog Liraglutide Inhibits Endothelial Cell Inflammation through a Calcium and AMPK Dependent Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, A.L.L.; Faria, L.C.; Guimarães, T.C.M.; Moreira, G.V.; Cândido, A.L.; Couto, C.A.; Reis, F.M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yao, X.Y.; Shi, R.X.; Liu, S.F.; Wang, X.Y. A Potential Link between Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Update Meta-Analysis. Reprod. Health 2018, 15, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somm, E.; Montandon, S.A.; Loizides-Mangold, U.; Gaïa, N.; Lazarevic, V.; de Vito, C.; Perroud, E.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L.; Dibner, C.; Schrenzel, J.; et al. The GLP-1R Agonist Liraglutide Limits Hepatic Lipotoxicity and Inflammatory Response in Mice Fed a Methionine-Choline Deficient Diet. Transl. Res. 2021, 227, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamun, V.; Jensterle, M.; Janez, A.; Bokal, E.V. Liraglutide Increases IVF Pregnancy Rates in Obese PCOS Women with Poor Response to First-Line Reproductive Treatments: A Pilot Randomized Study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 179, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainez, N.M.; Coss, D. Obesity, Neuroinflammation and Reproductive Function. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2719–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsanis, C.; Dermitzaki, E.; Avgoustinaki, P.; Malliaraki, N.; Mytaras, V.; Margioris, A.N. The Impact of Adipose Tissue-Derived Factors on the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal (HPG) Axis. Hormones 2015, 14, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Hayes, E.; Prizant, H.; Srivastava, R.K.; Hammes, S.R.; Sen, A. Leptin-Induced CART (Cocaine- and Amphetamine-Regulated Transcript) Is a Novel Intraovarian Mediator of Obesity-Related Infertility in Females. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Maeda, N.; Kashine, S.; Fujishima, Y.; Kozawa, J.; Hiuge-Shimizu, A.; Okita, K.; Imagawa, A.; Funahashi, T.; Shimomura, I. Short-Term Effects of Liraglutide on Visceral Fat Adiposity, Appetite, and Food Preference: A Pilot Study of Obese Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2011, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruning, J.C.; Gautam, D.; Burks, D.J.; Gillette, J.; Schubert, M.; Orban, P.C.; Klein, R.; Krone, W.; Muller-Wieland, D.; Kahn, C.R. Role of Brain Insulin Receptor in Control of Body Weight and Reproduction. Science 2000, 289, 2122–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Sun, A. The Therapeutic Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Metformin on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Protocol for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e26295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, M.A.; Deshmukh, H.; Atkin, S.; Sathyapalan, T. The Potential Role of Incretin-Based Therapies for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Narrative Review of the Current Evidence. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 12, 2042018821989238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beak, S.A.; Heath, M.M.; Small, C.J.; Morgan, D.G.A.; Ghatei, M.A.; Taylor, A.D.; Buckingham, J.C.; Bloom, S.R.; Smith, D.M. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Stimulates Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Secretion in a Rodent Hypothalamic Neuronal Cell Line. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, M.A.H.; Al-Farsi, Y.M.; Al-Khaduri, M.M.; Saleh, J.; Waly, M.I. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Is Linked to Increased Oxidative Stress in Omani Women. Int. J. Women’s Health 2018, 10, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabravolski, S.A.; Nikiforov, N.G.; Eid, A.H.; Nedosugova, L.V.; Starodubova, A.V.; Popkova, T.V.; Bezsonov, E.E.; Orekhov, A.N. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Chronic Inflammation in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, S.; Uyanikoglu, H.; Incebiyik, A.; Incebiyik, H.; Hilali, N.G.; Sabuncu, T.; Sak, E. Associations of Serum Fetuin-A and Oxidative Stress Parameters with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2018, 45, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moti, M.; Amini, L.; Ardakani, S.S.M.; Kamalzadeh, S.; Masoomikarimi, M.; Jafarisani, M. Oxidative Stress and Anti-Oxidant Defense System in Iranian Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 2015, 13, 373. [Google Scholar]
- Khashchenko, E.; Vysokikh, M.; Uvarova, E.; Krechetova, L.; Vtorushina, V.; Ivanets, T.; Volodina, M.; Tarasova, N.; Sukhanova, I.; Sukhikh, G. Activation of Systemic Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Adolescent Girls with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Combination with Metabolic Disorders and Excessive Body Weight. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repaci, A.; Gambineri, A.; Pasquali, R. The Role of Low-Grade Inflammation in the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.; Abate, N.; Chandalia, M.; Rizvi, A.A.; Giglio, R.V.; Nikolic, D.; Gammazza, A.M.; Barbagallo, I.; Isenovic, E.R.; Banach, M.; et al. Liraglutide Reduces Oxidative Stress and Restores Heme Oxygenase-1 and Ghrelin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Pilot Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambadiari, V.; Pavlidis, G.; Kousathana, F.; Varoudi, M.; Vlastos, D.; Maratou, E.; Georgiou, D.; Andreadou, I.; Parissis, J.; Triantafyllidi, H.; et al. Effects of 6-Month Treatment with the Glucagon like Peptide-1 Analogue Liraglutide on Arterial Stiffness, Left Ventricular Myocardial Deformation and Oxidative Stress in Subjects with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Cao, J.; Han, J.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, N.; He, J. Liraglutide Activates the Nrf2/HO-1 Antioxidant Pathway and Protects Brain Nerve Cells against Cerebral Ischemia in Diabetic Rats. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 3094504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; She, M.; Xu, M.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Zheng, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; et al. GLP-1 Treatment Protects Endothelial Cells from Oxidative Stress-Induced Autophagy and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Millán, E.; Martín, M.A.; Goya, L.; Lizárraga-Mollinedo, E.; Escrivá, F.; Ramos, S.; Álvarez, C. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Improves Beta-Cell Antioxidant Capacity via Extracellular Regulated Kinases Pathway and Nrf2 Translocation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sireesh, D.; Dhamodharan, U.; Ezhilarasi, K.; Vijay, V.; Ramkumar, K.M. Association of NF-E2 Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) and Inflammatory Cytokines in Recent Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Molecular Mechanisms by Which GLP-1 RA and DPP-4i Induce Insulin Sensitivity. Life Sci. 2019, 234, 116776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, C.; Lu, M.; Chen, C.; Nie, X.; Abudukerimu, B.; Zhang, K.; Ning, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; et al. The Key Role of a Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist in Body Fat Redistribution. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 240, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zong, C.; Qin, D.; Wang, Y.; Yingfeng Yang, Y.; et al. GLP-1/GLP-1R Signaling in Regulation of Adipocyte Differentiation and Lipogenesis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.; McGee, S.L. 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Display Phenotypic Characteristics of Multiple Adipocyte Lineages. Adipocyte 2015, 4, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristancho, A.G.; Lazar, M.A. Forming Functional Fat: A Growing Understanding of Adipocyte Differentiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Donelan, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, P.; Yang, L.; Ding, Y.; Tang, D.; Li, S. GLP-1 Induces the Expression of FNDC5 Derivatives That Execute Lipolytic Actions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 777026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.S.; Kakoly, N.S.; Tan, J.W.J.; Fitzgerald, G.; Bahri Khomami, M.; Joham, A.E.; Cooray, S.D.; Misso, M.L.; Norman, R.J.; Harrison, C.L.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuffer, W.A.; Trujillo, J.M. Liraglutide: A New Option for the Treatment of Obesity. Pharmacotherapy 2015, 35, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves New Drug Treatment for Chronic Weight Management, First Since 2014|FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014 (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Capehorn, M.S.; Catarig, A.M.; Furberg, J.K.; Janez, A.; Price, H.C.; Tadayon, S.; Vergès, B.; Marre, M. Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide 1.0 mg vs Once-Daily Liraglutide 1.2 mg as Add-on to 1-3 Oral Antidiabetic Drugs in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes (SUSTAIN 10). Diabetes Metab. 2020, 46, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Gabe, M.B.N.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Oxyntomodulin: Actions and Role in Diabetes. Peptides 2018, 100, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camins, A.; Ettcheto, M.; Busquets, O.; Manzine, P.R.; Castro-Torres, R.D.; Beas-Zarate, C.; Verdaguer, E.; Sureda, F.X.; Bulló, M.; Olloquequi, J.; et al. Triple GLP-1/GIP/Glucagon Receptor Agonists, a Potential Novel Treatment Strategy in Alzheimer’s Disease. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucheit, J.D.; Pamulapati, L.G.; Carter, N.; Malloy, K.; Dixon, D.L.; Sisson, E.M. Oral Semaglutide: A Review of the First Oral Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Pieber, T.R.; Hartoft-Nielsen, M.L.; Hansen, O.K.H.; Jabbour, S.; Rosenstock, J. Effect of Oral Semaglutide Compared with Placebo and Subcutaneous Semaglutide on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bednarz, K.; Kowalczyk, K.; Cwynar, M.; Czapla, D.; Czarkowski, W.; Kmita, D.; Nowak, A.; Madej, P. The Role of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists in Insulin Resistance with Concomitant Obesity Treatment in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084334
Bednarz K, Kowalczyk K, Cwynar M, Czapla D, Czarkowski W, Kmita D, Nowak A, Madej P. The Role of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists in Insulin Resistance with Concomitant Obesity Treatment in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(8):4334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084334
Chicago/Turabian StyleBednarz, Krzysztof, Karolina Kowalczyk, Marlena Cwynar, Dominika Czapla, Wiktor Czarkowski, Dominika Kmita, Artur Nowak, and Paweł Madej. 2022. "The Role of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists in Insulin Resistance with Concomitant Obesity Treatment in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 8: 4334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084334
APA StyleBednarz, K., Kowalczyk, K., Cwynar, M., Czapla, D., Czarkowski, W., Kmita, D., Nowak, A., & Madej, P. (2022). The Role of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists in Insulin Resistance with Concomitant Obesity Treatment in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(8), 4334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084334






