S-Acetyl-Glutathione Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating Oxidative Imbalance and Inflammation
Abstract
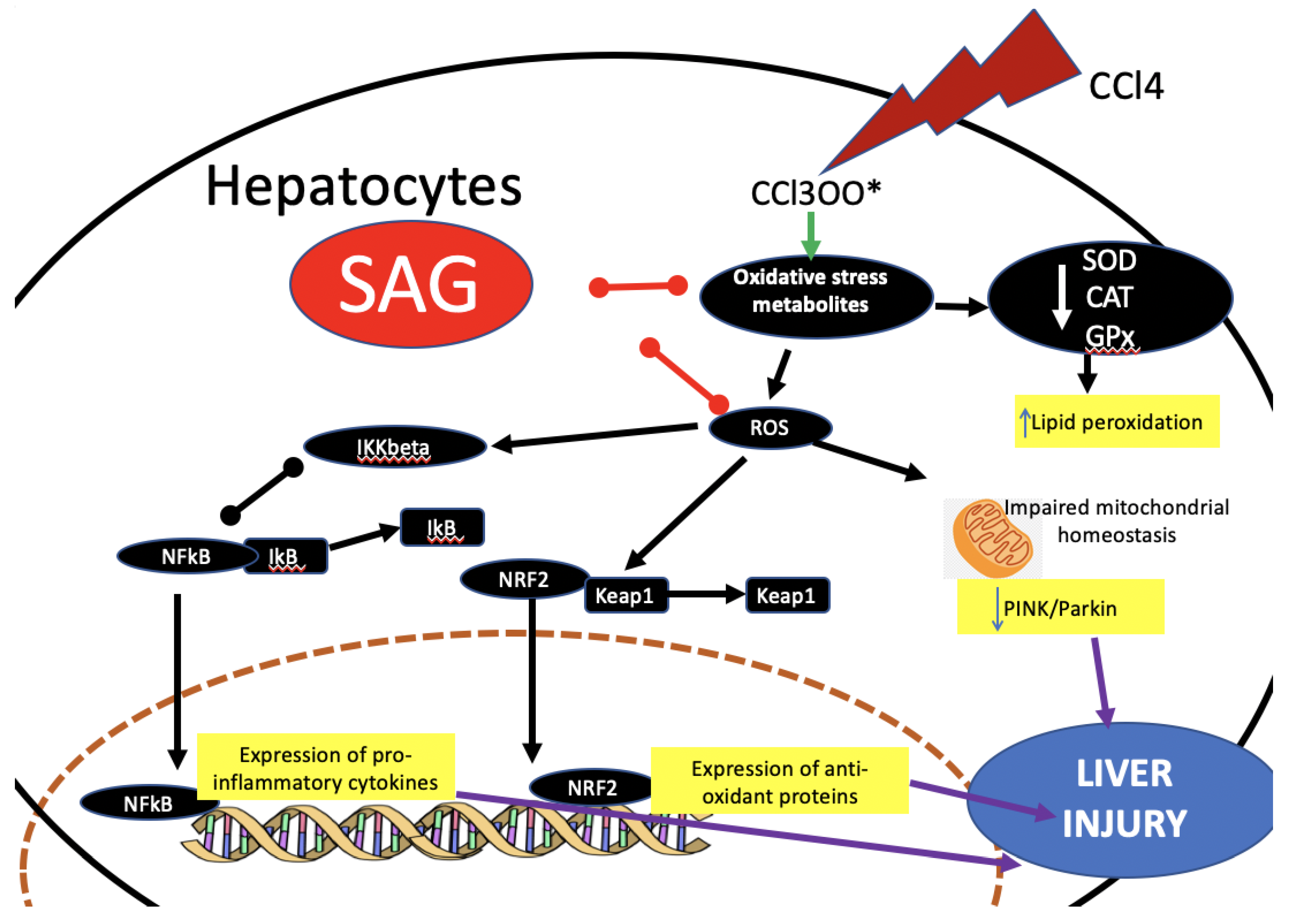
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of SAG on Cytotoxicity and Hepatoprotective Activity in Cells: Preliminary In Vitro Data
2.2. Experimental Timeline
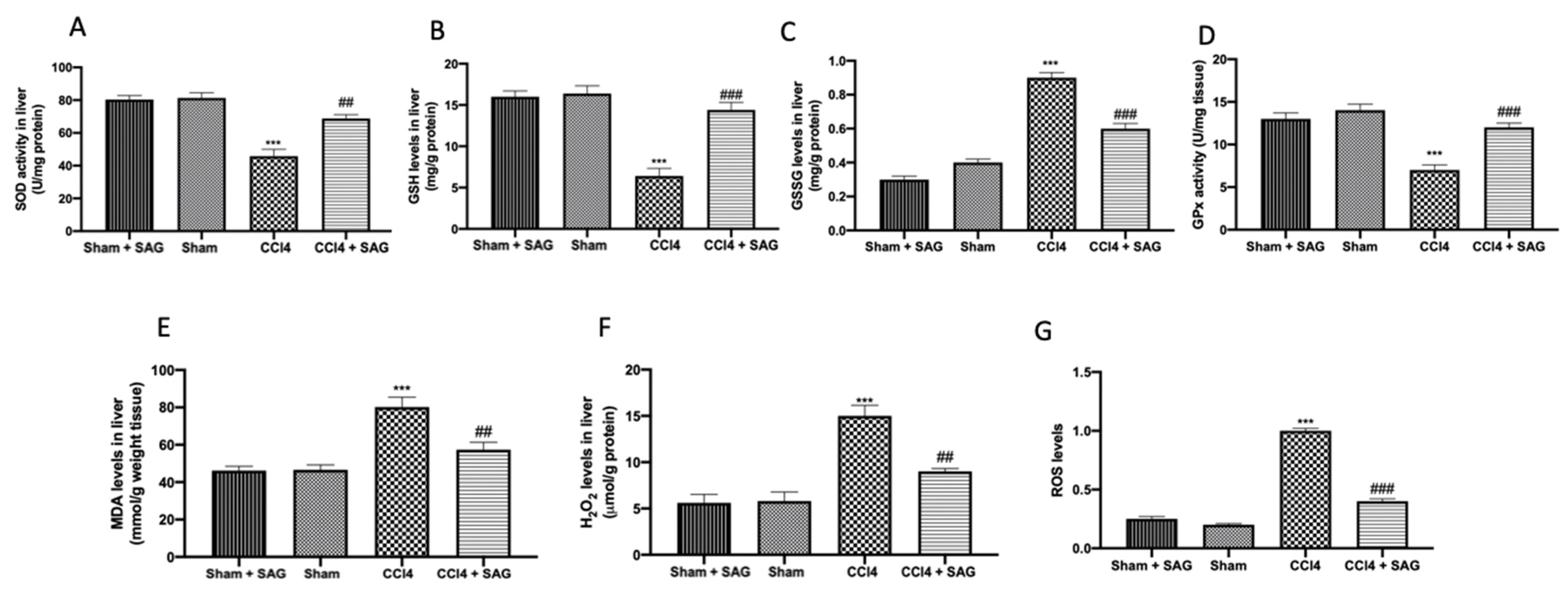
2.3. Effects of SAG on Oxidative Stress Induced by CCl4 Chronic Exposure
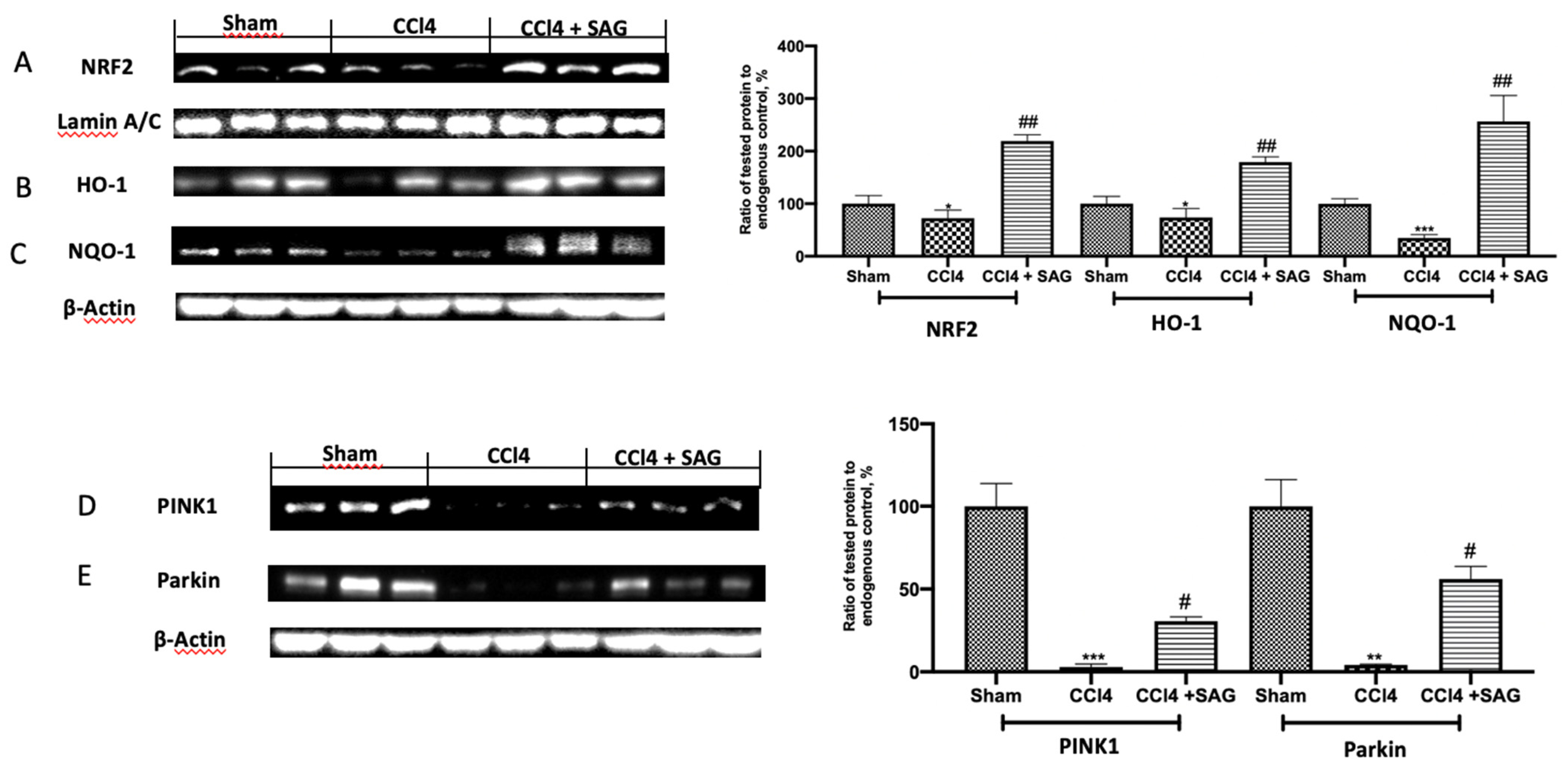
2.4. Effects of SAG on Mitophagy Impairments Induced by CCl4 Chronic Exposure
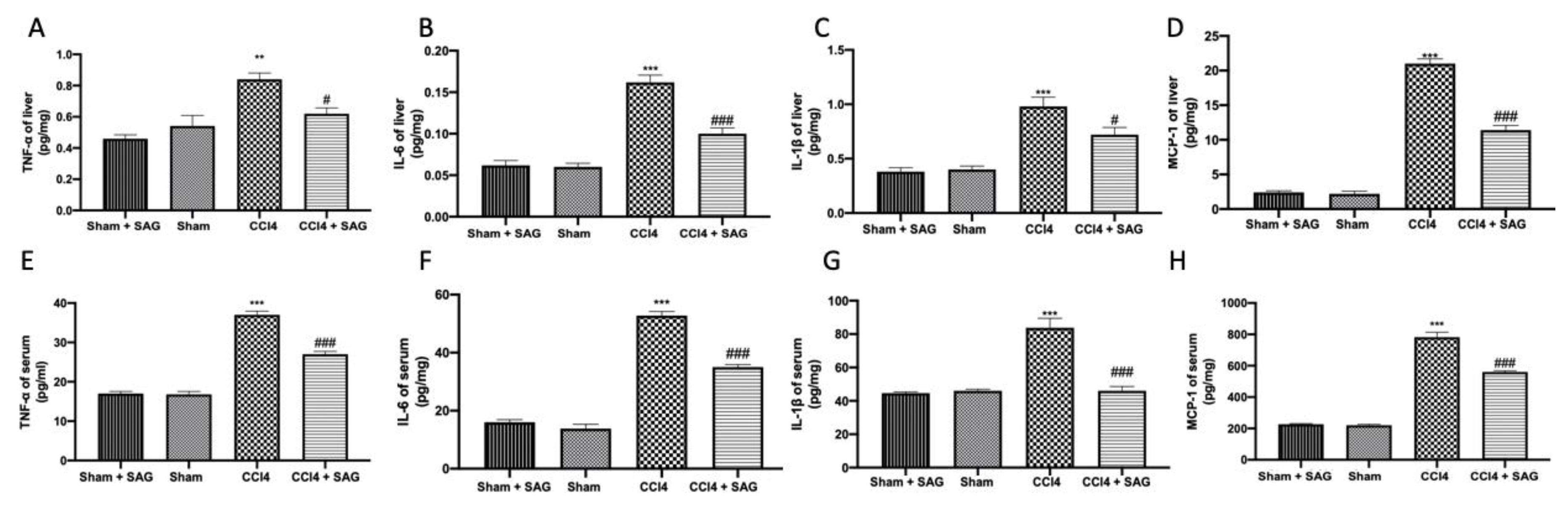
2.5. Effects of SAG on Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Secretion Induced by CCl4 Chronic Exposure
2.6. Effects of SAG on TL4/NFkB Signaling Activation Induced by CCl4 Chronic Exposure
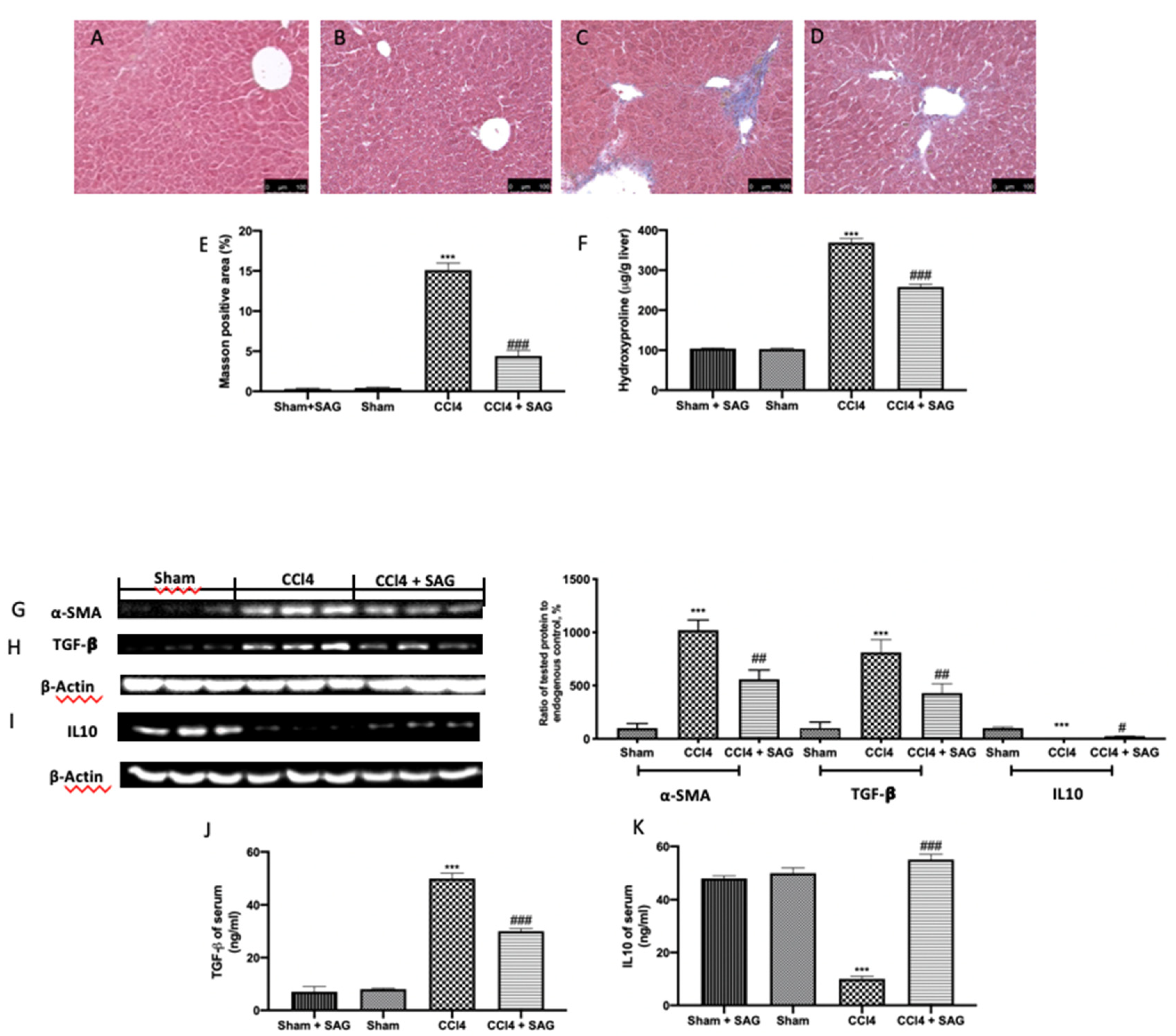
2.7. Effects of SAG on Liver Fibrosis Induced by CCl4 Chronic Exposure
2.8. Effects of SAG on Histopathological Alterations and Liver Function Induced by CCl4 Chronic Exposure
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Culture of Hepatocytes
4.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.3. Activities of ALT and AST in Cell Supernatants
4.4. Animals
4.5. Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema (Preliminary Data)
4.6. Experimental Groups
- Sham + SAG: mice were injected intraperitoneally with olive oil twice a week and were treated orally for 8 weeks with SAG (30 mg/kg) (Merk, CAS n 3054-47-5, AMBH95E07091) dissolved in saline.
- Sham: mice were injected intraperitoneally with olive oil twice a week.
- CCl4: mice were intraperitoneally injected with CCl4 1 mL/kg (diluted at 1:10 in olive oil) twice a week for 8 consecutive weeks to induce liver fibrosis [11].
- SAG: mice were administered with CCl4 to induce liver fibrosis as vehicle group and were treated orally for 8 weeks with SAG (30 mg/kg) dissolved in saline.
4.7. Analysis of Biochemical Indicators
4.8. Determination of Myeloperoxidase Activity
4.9. ELISA
4.10. Histopathological Examination
4.11. Western Blot Analysis
4.12. Statistical Evaluation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. Liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, G.; Parola, M. Oxidative damage and fibrogenesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.G.; Cai, H.; Landmesser, U.; Griendling, K.K. Interactions of angiotensin II with NAD (P) H oxidase, oxidant stress and cardiovascular disease. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2003, 4, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoguchi, T.; Sonta, T.; Tsubouchi, H.; Etoh, T.; Kakimoto, M.; Sonoda, N.; Sato, N.; Sekiguchi, N.; Kobayashi, K.; Sumimoto, H. Protein kinase C–dependent increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in vascular tissues of diabetes: Role of vascular NAD (P) H oxidase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, S227–S232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, K.K. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a common phenotype in aging and cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1019, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholten, D.; Trebicka, J.; Liedtke, C.; Weiskirchen, R. The carbon tetrachloride model in mice. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindryckx, F.; Colle, I.; Van Vlierberghe, H. Experimental mouse models for hepatocellular carcinoma research. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2009, 90, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaisako, K.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, M.; Cong, M.; Moore-Morris, T.J.; Park, T.J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Paik, Y.H.; et al. Origin of myofibroblasts in the fibrotic liver in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3297–E3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halliwell, B. Oxidants and human disease: Some new concepts. FASEB J. 1987, 1, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosek, P.; Nakano, M. Hepatoprotective effect of rooibos tea (Aspalathus linearis) on CCl 4-induced liver damage in rats. Physiol. Res. 2003, 52, 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, P.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Dai, Y.; He, Q. Breviscapine ameliorates CCl4induced liver injury in mice through inhibiting inflammatory apoptotic response and ROS generation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sies, H. Strategies of antioxidant defense. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 215, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, C.S. Role of oxidative stress and antioxidant therapy in alcoholic and nonalcoholic liver diseases. Adv. Pharmacol. 1997, 38, 601–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cervinkova, Z.; Drahota, Z. Enteral administration of lipid emulsions protects liver cytochrome c oxidase from hepatotoxic action of thioacetamide. Physiol. Res. 1998, 47, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.C. Regulation of hepatic glutathione synthesis: Current concepts and controversies. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meister, A.; Anderson, M.E. Glutathione. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1983, 52, 711–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.-U.; Cinatl, J.; Dauletbaev, N.; Buxbaum, S.; Treusch, G.; Cinatl, J.; Gerein, V.; Doerr, H.W. Effects of S-acetylglutathione in cell and animal model of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 194, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, S.; Francioso, A.; Cavallaro, R.A.; d’Erme, M.; Putignano, P.; Miraglia, N.; Mosca, L. Clinical Nutrition & Dietetics. Clin. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 4, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, A.; Miners, J.O.; Mackenzie, P.I. The UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: Their role in drug metabolism and detoxification. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Gao, D.; Liu, W.; Wei, H.; Lin, J.M. Imitation of drug metabolism in human liver and cytotoxicity assay using a microfluidic device coupled to mass spectrometric detection. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, S.; Stahl, S.; Paul, N.; Barber, J.; Kenna, J.G. In Vitro inhibition of the bile salt export pump correlates with risk of cholestatic drug-induced liver injury in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyendyk, J.P.; Kassel, K.M.; Allen, K.; Guo, G.L.; Li, G.; Cantor, G.H.; Copple, B.L. Fibrinogen deficiency increases liver injury and early growth response-1 (Egr-1) expression in a model of chronic xenobiotic-induced cholestasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 178, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videla, L.A.; Rodrigo, R.; Orellana, M.; Fernandez, V.; Tapia, G.; Quinones, L.; Varela, N.; Contreras, J.; Lazarte, R.; Csendes, A.; et al. Oxidative stress-related parameters in the liver of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Clin. Sci. 2004, 106, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casalena, G.; Daehn, I.; Bottinger, E. Transforming growth factor-beta, bioenergetics, and mitochondria in renal disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2012, 32, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubli, D.A.; Gustafsson, A.B. Mitochondria and mitophagy: The yin and yang of cell death control. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czaja, M.J.; Ding, W.X.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Friedman, S.L.; Kim, J.S.; Komatsu, M.; Lemasters, J.J.; Lemoine, A.; Lin, J.D.; Ou, J.H.; et al. Functions of autophagy in normal and diseased liver. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1131–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serviddio, G.; Bellanti, F.; Stanca, E.; Lunetti, P.; Blonda, M.; Tamborra, R.; Siculella, L.; Vendemiale, G.; Capobianco, L.; Giudetti, A.M. Silybin exerts antioxidant effects and induces mitochondrial biogenesis in liver of rat with secondary biliary cirrhosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Kwon, Y.; Choe, S.Y.; Hong, S.M.; Yoo, H.; Goto, T.; Kawada, T.; Choi, H.S.; Joe, Y.; Chung, H.T.; et al. Quercetin reduces obesity-induced hepatosteatosis by enhancing mitochondrial oxidative metabolism via heme oxygenase-1. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalheri, H.; Both, C.; Martins, M. The Interplay between Environmental Filtering and Spatial Processes in Structuring Communities: The Case of Neotropical Snake Communities. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poling, J.; Gajawada, P.; Richter, M.; Lorchner, H.; Polyakova, V.; Kostin, S.; Shin, J.; Boettger, T.; Walther, T.; Rees, W.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the oncostatin M receptor-beta prevents inflammatory heart failure. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2014, 109, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpechcinski, A.; Chorostowska-Wynimko, J.; Struniawski, R.; Kupis, W.; Rudzinski, P.; Langfort, R.; Puscinska, E.; Bielen, P.; Sliwinski, P.; Orlowski, T. Cell-free DNA levels in plasma of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and inflammatory lung disease. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Dong, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, G.; Dang, X.; Lu, X.; Jia, M. Chlorogenic acid reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Toxicology 2013, 303, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.T.; Bian, C.; Yuan, J.C.; Chu, W.H.; Xiang, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, C.S.; Feng, H.; Lin, J.K. Curcumin attenuates acute inflammatory injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in experimental traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; He, M.; Qiang, L. Exercise Therapy Downregulates the Overexpression of TLR4, TLR2, MyD88 and NF-kappaB after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 4, 3718–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z.G. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, H.Y.; Ma, X. Tamoxifen reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells, apoptosis and inhibits IKK/NF-kB pathway after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.S. Regulation of cell death and autophagy by IKK and NF-kappaB: Critical mechanisms in immune function and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; Campolo, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Fusco, R.; Pugliatti, P.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Protective Effects of Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA-um) in Myocardial Ischaemia and Reperfusion Injury in vivo. Shock 2016, 46, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide (PEA-um((R))) in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Cirmi, S.; Gugliandolo, E.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Navarra, M. A flavonoid-rich extract of orange juice reduced oxidative stress in an experimental model of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 30, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Yeo, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.C. Protection of rat hepatocytes exposed to CCl4 in-vitro by cynandione A, a biacetophenone from Cynanchum wilfordii. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 52, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Fernandes, T.; de Avila, R.I.; de Moura, S.S.; de Almeida Ribeiro, G.; Naves, M.M.V.; Valadares, M.C. Campomanesia adamantium (Myrtaceae) fruits protect HEPG2 cells against carbon tetrachloride-induced toxicity. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boone, L.; Meyer, D.; Cusick, P.; Ennulat, D.; Bolliger, A.P.; Everds, N.; Meador, V.; Elliott, G.; Honor, D.; Bounous, D. Selection and interpretation of clinical pathology indicators of hepatic injury in preclinical studies. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 34, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; D’Amico, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; Scuto, M.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; et al. Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts Counteract Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in an Acute Experimental Model of Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Fusco, R.; et al. The Methyl Ester of 2-Cyano-3,12-Dioxooleana-1,9-Dien-28-Oic Acid Reduces Endometrial Lesions Development by Modulating the NFkB and Nrf2 Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Biochemical Evaluation of the Antioxidant Effects of Hydroxytyrosol on Pancreatitis-Associated Gut Injury. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Chakraborty, A.K.; Dey, P.; Kar, P.; Guha, P.; Sen, S.; Kumar, A.; Sen, A.; Chaudhuri, T.K. Amelioration of CCl4 induced liver injury in swiss albino mice by antioxidant rich leaf extract of Croton bonplandianus Baill. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Cordaro, M.; D’Amico, R.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Smeriglio, A.; Mandalari, G.; et al. The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Anacardium occidentale L. Cashew Nuts in a Mouse Model of Colitis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Sun, P.; Yi, R.; Han, X.; Zhao, X. Raw Bowl Tea (Tuocha) Polyphenol Prevention of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Intestinal Function in Mice. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; Crupi, R.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. PEA/Polydatin: Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Approach to Counteract DNBS-Induced Colitis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; D’Amico, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Fusco, R.; Di Paola, R.; Schievano, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of a new micronized formulation of the ALIAmide palmitoylglucosamine in preclinical models of inflammation and osteoarthritis pain. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saber, S.; Mahmoud, A.A.A.; Helal, N.S.; El-Ahwany, E.; Abdelghany, R.H. Renin-angiotensin system inhibition ameliorates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice through the inactivation of nuclear transcription factor kappa B. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 96, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Paracetamol, a New Association to Relieve Hyperalgesia and Pain in a Sciatic Nerve Injury Model in Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uesugi, T.; Froh, M.; Arteel, G.E.; Bradford, B.U.; Thurman, R.G. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in the mechanism of early alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Hepatology 2011, 34, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallagangula, K.S.; Nagaraj, S.K.; Venkataswamy, L.; Chandrappa, M. Liver fibrosis: A compilation on the biomarkers status and their significance during disease progression. Future Sci. OA 2018, 4, FSO250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, T.H.; Shiau, C.W.; Jao, P.; Yang, N.J.; Tai, W.T.; Liu, C.J.; Tseng, T.C.; Yang, H.C.; Liu, C.H.; Huang, K.W.; et al. Src-homology protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 agonist, SC-43, reduces liver fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. The Role of Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts on an Experimental Model of Painful Degenerative Joint Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Scuto, M.; Cordaro, M.; D’Amico, R.; Evangelista, M.; Peli, A.; Peritore, A.F.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. Formyl Peptide Receptor 1 Signaling in Acute Inflammation and Neural Differentiation Induced by Traumatic Brain Injury. Biology 2020, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Scuto, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Modulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome through Formyl Peptide Receptor 1 (Fpr-1) Pathway as a New Therapeutic Target in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esposito, E.; Campolo, M.; Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Franco, D.; Filippone, A.; Peritore, A.F.; Cuzzocrea, S. Protective Effects of Xyloglucan in Association with the Polysaccharide Gelose in an Experimental Model of Gastroenteritis and Urinary Tract Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Adelmidrol: A New Promising Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Tool in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Paola, R.; Modafferi, S.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; D’Amico, R.; Ontario, M.L.; Interdonato, L.; Salinaro, A.T.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. S-Acetyl-Glutathione Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating Oxidative Imbalance and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084429
Di Paola R, Modafferi S, Siracusa R, Cordaro M, D’Amico R, Ontario ML, Interdonato L, Salinaro AT, Fusco R, Impellizzeri D, et al. S-Acetyl-Glutathione Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating Oxidative Imbalance and Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(8):4429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084429
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Paola, Rosanna, Sergio Modafferi, Rosalba Siracusa, Marika Cordaro, Ramona D’Amico, Maria Laura Ontario, Livia Interdonato, Angela Trovato Salinaro, Roberta Fusco, Daniela Impellizzeri, and et al. 2022. "S-Acetyl-Glutathione Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating Oxidative Imbalance and Inflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 8: 4429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084429
APA StyleDi Paola, R., Modafferi, S., Siracusa, R., Cordaro, M., D’Amico, R., Ontario, M. L., Interdonato, L., Salinaro, A. T., Fusco, R., Impellizzeri, D., Calabrese, V., & Cuzzocrea, S. (2022). S-Acetyl-Glutathione Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating Oxidative Imbalance and Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(8), 4429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084429











