Human α-Defensin-6 Neutralizes Clostridioides difficile Toxins TcdA and TcdB by Direct Binding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. α-def-6 Directly Interacts with TcdB without Affecting Its Autoprotease or Enzyme Activity
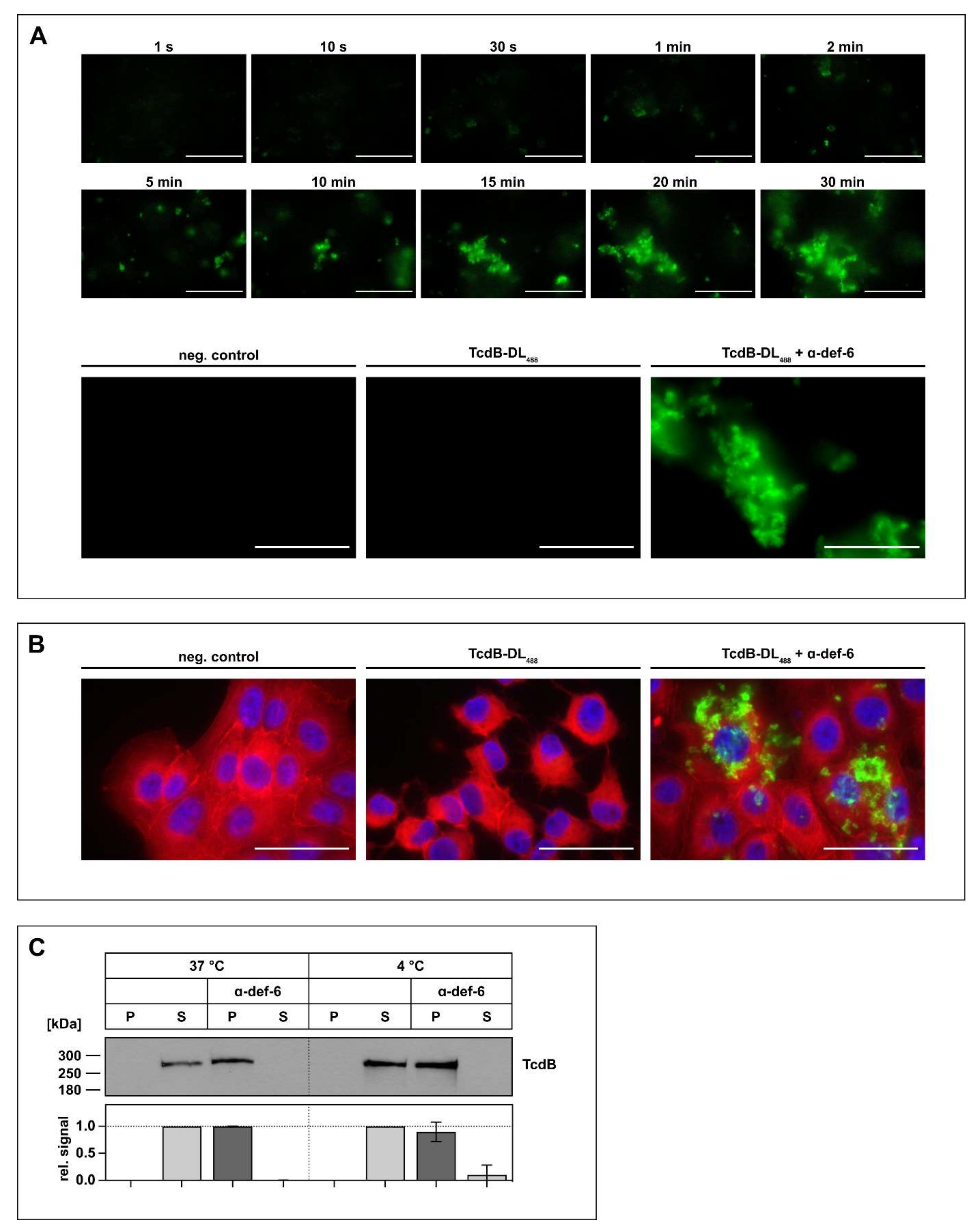
2.2. Interaction between α-def-6 and TcdB Leads to the Rapid Formation of Toxin-Inhibitor-Complexes
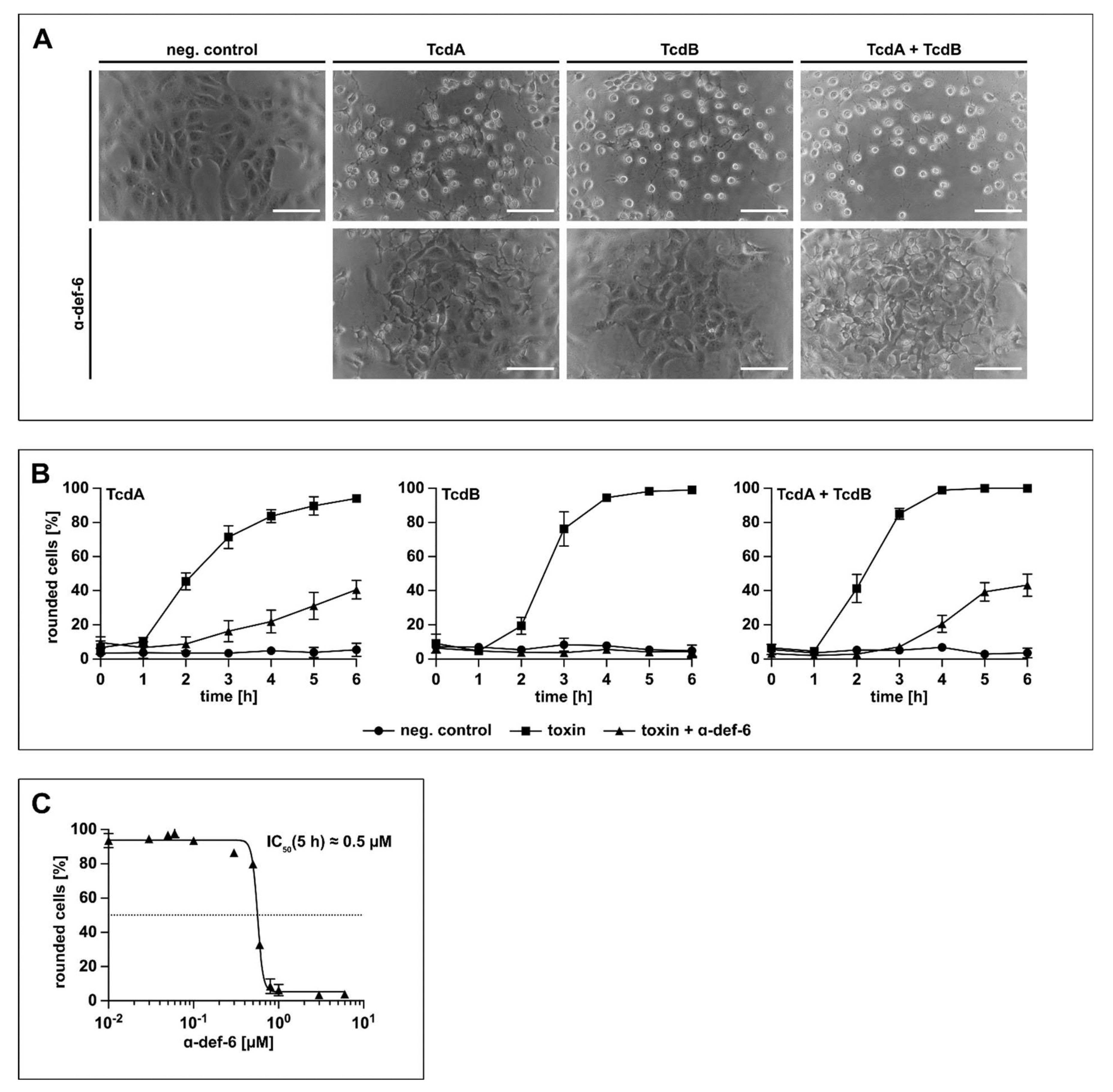
2.3. Vero Cells Are Protected from Intoxication with TcdB by α-def-6 in a Time- and Concentration-Dependent Manner
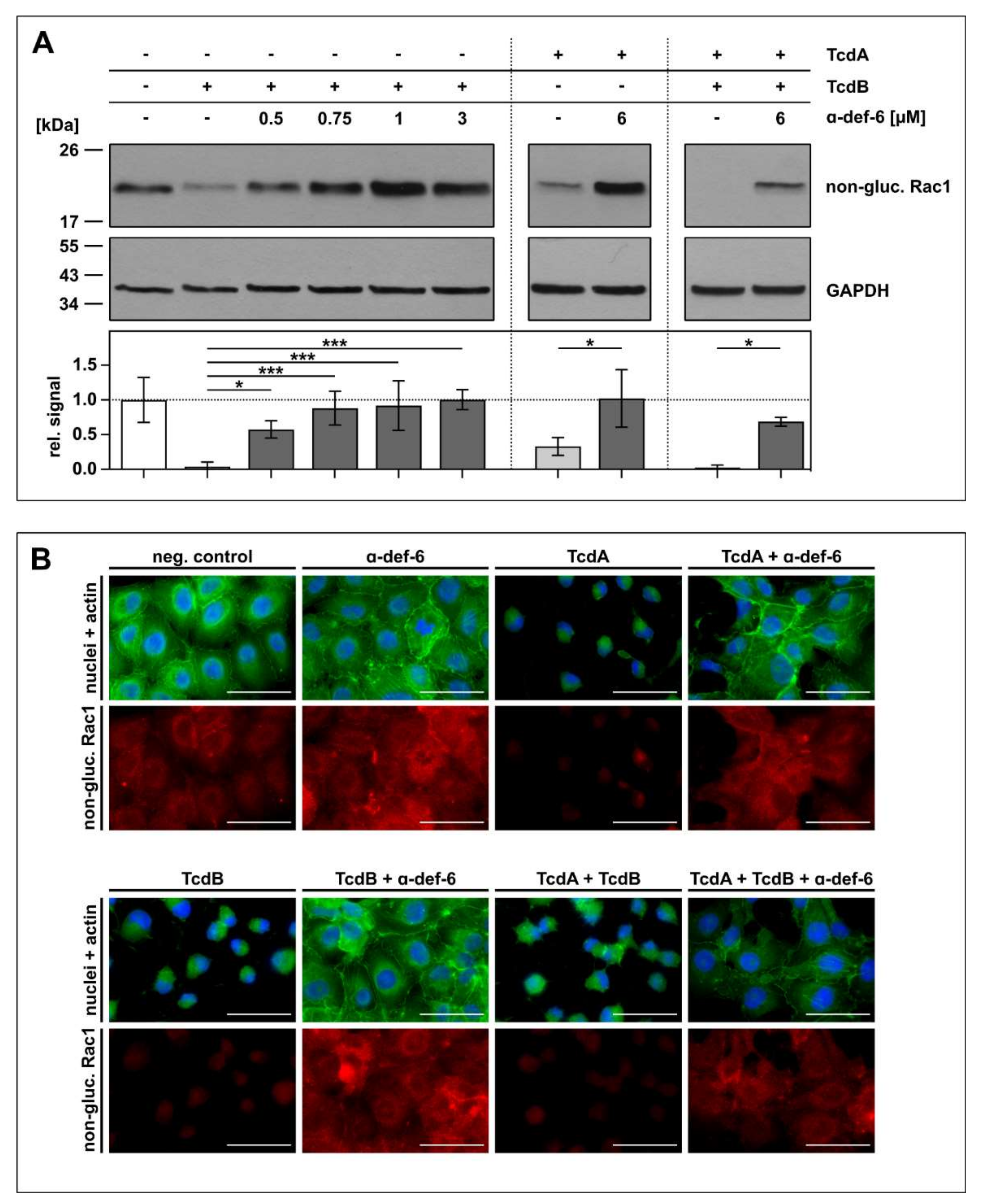
2.4. Intracellular Rac1 In Vero Cells Is Protected from Toxin-Mediated Glucosylation in the Presence of α-def-6
2.5. CaCo-2 Cells Are Protected from the Cytotoxic Effect of TcdA and TcdB in the Presence of α-def-6
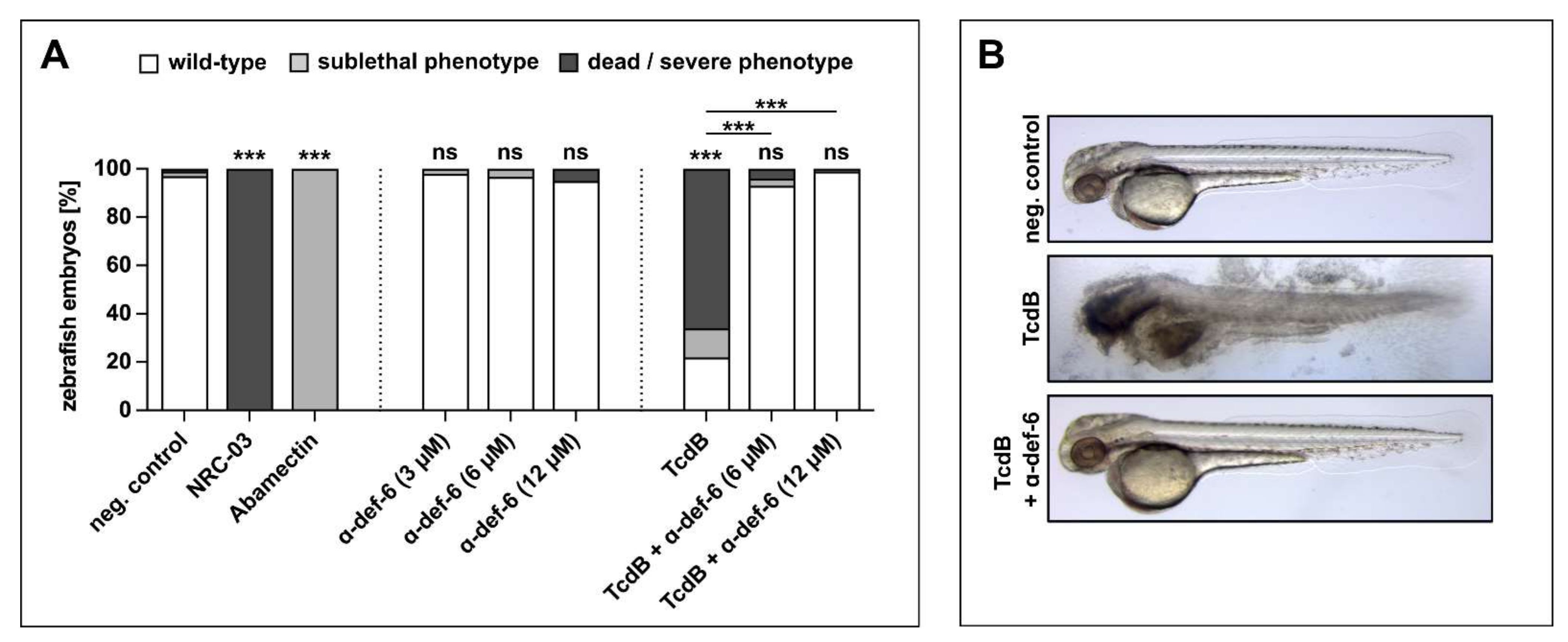
2.6. α-def-6 Reduces the Cytotoxic Effects of TcdB in an In Vivo Zebrafish Embryo System
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Cell Culture, Cytotoxicity and Cell Viability Assays
4.2.2. Biotinylation of TcdB
4.2.3. Surface Plasmon Resonance Measurements
4.2.4. In Vitro Autoprocessing of TcdB
4.2.5. In Vitro Glucosylation of Rac1 by TcdB
4.2.6. UDP-GloTM Glucosyltransferase Assay
4.2.7. Fluorochrome Labeling of TcdB
4.2.8. Aggregation of TcdB-DL488 over Time in the Absence of Cultured Cells
4.2.9. Aggregation of TcdB-DL488 in the Presence of Cultured Cells
4.2.10. Precipitation Assay with TcdB
4.2.11. Intracellular Rac1 Status after Treatment with TcdA or TcdB
4.2.12. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.2.13. Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) Measurements
4.2.14. Zebrafish Experiments
4.2.15. Reproducibility of Experiments and Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suetens, C.; Latour, K.; Kärki, T.; Ricchizzi, E.; Kinross, P.; Moro, M.L.; Jans, B.; Hopkins, S.; Hansen, S.; Lyytikäinen, O.; et al. Prevalence of Healthcare-Associated Infections, Estimated Incidence and Composite Antimicrobial Resistance Index in Acute Care Hospitals and Long-Term Care Facilities: Results from Two European Point Prevalence Surveys, 2016 to 2017. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1800516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tschudin-Sutter, S.; Kuijper, E.J.; Durovic, A.; Vehreschild, M.J.G.T.; Barbut, F.; Eckert, C.; Fitzpatrick, F.; Hell, M.; Norèn, T.; O’Driscoll, J.; et al. Guidance Document for Prevention of Clostridium Difficile Infection in Acute Healthcare Settings. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lessa, F.C.; Gould, C.V.; McDonald, L.C. Current Status of Clostridium Difficile Infection Epidemiology. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55 (Suppl. S2), S65–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aktories, K.; Schwan, C.; Jank, T. Clostridium Difficile Toxin Biology. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 281–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordus, S.L.; Thomas, A.K.; Lacy, D.B. Clostridioides Difficile Toxins: Mechanisms of Action and Antitoxin Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 20, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehne, S.A.; Cartman, S.T.; Heap, J.T.; Kelly, M.L.; Cockayne, A.; Minton, N.P. The Role of Toxin A and Toxin B in Clostridium Difficile Infection. Nature 2010, 467, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuehne, S.A.; Collery, M.M.; Kelly, M.L.; Cartman, S.T.; Cockayne, A.; Minton, N.P. Importance of Toxin A, Toxin B, and CDT in Virulence of an Epidemic Clostridium Difficile Strain. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Eichel-Streiber, C.; Boquet, P.; Sauerborn, M.; Thelestam, M. Large Clostridial Cytotoxins—A Family of Glycosyltransferases Modifying Small GTP-Binding Proteins. Trends Microbiol. 1996, 4, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, I.; Gerhard, R. Large Clostridial Cytotoxins. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 152, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qa’Dan, M.; Spyres, L.M.; Ballard, J.D. PH-Induced Conformational Changes in Clostridium Difficile Toxin B. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 2470–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barth, H.; Pfeifer, G.; Hofmann, F.; Maier, E.; Benz, R.; Aktories, K. Low PH-Induced Formation of Ion Channels by Clostridium Difficile Toxin B in Target Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10670–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfeifer, G.; Schirmer, J.; Leemhuis, J.; Busch, C.; Meyer, D.K.; Aktories, K.; Barth, H. Cellular Uptake of Clostridium Difficile Toxin B. Translocation of the N-Terminal Catalytic Domain into the Cytosol of Eukaryotic Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44535–44541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reineke, J.; Tenzer, S.; Rupnik, M.; Koschinski, A.; Hasselmayer, O.; Schrattenholz, A.; Schild, H.; von Eichel-Streiber, C. Autocatalytic Cleavage of Clostridium Difficile Toxin B. Nature 2007, 446, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egerer, M.; Giesemann, T.; Jank, T.; Satchell, K.J.F.; Aktories, K. Auto-Catalytic Cleavage of Clostridium Difficile Toxins A and B Depends on Cysteine Protease Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 25314–25321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Just, I.; Selzer, J.; Wilm, M.; von Eichel-Streiber, C.; Mann, M.; Aktories, K. Glucosylation of Rho Proteins by Clostridium Difficile Toxin B. Nature 1995, 375, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Just, I.; Wilm, M.; Selzer, J.; Rex, G.; von Eichel-Streiber, C.; Mann, M.; Aktories, K. The Enterotoxin from Clostridium Difficile (ToxA) Monoglucosylates the Rho Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 13932–13936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etienne-Manneville, S.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases in Cell Biology. Nature 2002, 420, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, G.; Pothoulakis, C.; LaMont, J.T.; Madara, J.L. Clostridium Difficile Toxin A Perturbs Cytoskeletal Structure and Tight Junction Permeability of Cultured Human Intestinal Epithelial Monolayers. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, G.; Koutsouris, A.; Pothoulakis, C.; LaMont, J.T.; Madara, J.L. Clostridium Difficile Toxin B Disrupts the Barrier Function of T84 Monolayers. Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Lavergne, V.; Skinner, A.M.; Gonzales-Luna, A.J.; Garey, K.W.; Kelly, C.P.; Wilcox, M.H. Clinical Practice Guideline by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA): 2021 Focused Update Guidelines on Management of Clostridioides Difficile Infection in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1029–e1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, M.H.; Gerding, D.N.; Poxton, I.R.; Kelly, C.; Nathan, R.; Birch, T.; Cornely, O.A.; Rahav, G.; Bouza, E.; Lee, C.; et al. Bezlotoxumab for Prevention of Recurrent Clostridium Difficile Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, L.D.; Kroh, H.K.; Hsieh, E.; Yang, X.; Beaumont, M.; Sheth, P.R.; DiNunzio, E.; Rutherford, S.A.; Ohi, M.D.; Ermakov, G.; et al. Epitopes and Mechanism of Action of the Clostridium Difficile Toxin A-Neutralizing Antibody Actoxumab. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 1030–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G. Human Antimicrobial Peptides and Proteins. Pharmaceuticals 2014, 7, 545–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giesemann, T.; Guttenberg, G.; Aktories, K. Human α-Defensins Inhibit Clostridium Difficile Toxin B. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Ückert, A.K.; Landenberger, M.; Papatheodorou, P.; Hoffmann-Richter, C.; Mittler, A.-K.; Ziener, U.; Hägele, M.; Schwan, C.; Müller, M.; et al. Human Peptide α-Defensin-1 Interferes with Clostridioides Difficile Toxins TcdA, TcdB, and CDT. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 6244–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korbmacher, M.; Fischer, S.; Landenberger, M.; Papatheodorou, P.; Aktories, K.; Barth, H. Human α-Defensin-5 Efficiently Neutralizes Clostridioides Difficile Toxins TcdA, TcdB, and CDT. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairatana, P.; Nolan, E.M. Human α-Defensin 6: A Small Peptide That Self-Assembles and Protects the Host by Entangling Microbes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, S.; Popoff, M.R.; Barth, H. Human Alpha-Defensin-1 Protects Cells from Intoxication with Clostridium Perfringens Iota Toxin. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, fty022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jank, T.; Ziegler, M.O.P.; Schulz, G.E.; Aktories, K. Inhibition of the Glucosyltransferase Activity of Clostridial Rho/Ras-Glucosylating Toxins by Castanospermine. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donta, S.T.; Sullivan, N.; Wilkins, T.D. Differential Effects of Clostridium Difficile Toxins on Tissue-Cultured Cells. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1982, 15, 1157–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamm, E.E.; Voth, D.E.; Ballard, J.D. Identification of Clostridium Difficile Toxin B Cardiotoxicity Using a Zebrafish Embryo Model of Intoxication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14176–14181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Masi, A.; Leboffe, L.; Polticelli, F.; Tonon, F.; Zennaro, C.; Caterino, M.; Stano, P.; Fischer, S.; Hägele, M.; Müller, M.; et al. Human Serum Albumin Is an Essential Component of the Host Defense Mechanism against Clostridium Difficile Intoxication. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guh, A.Y.; Mu, Y.; Winston, L.G.; Johnston, H.; Olson, D.; Farley, M.M.; Wilson, L.E.; Holzbauer, S.M.; Phipps, E.C.; Dumyati, G.K.; et al. Trends in U.S. Burden of Clostridioides Difficile Infection and Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, W.K.; Lyras, D.; Lacy, D.B.; Wilcox, M.H.; Kuijper, E.J. Clostridium Difficile Infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Gajendran, N.; Mittrücker, H.-W.; Weiwad, M.; Song, Y.-H.; Hurwitz, R.; Wilmanns, M.; Fischer, G.; Kaufmann, S.H.E. Human α-Defensins Neutralize Anthrax Lethal Toxin and Protect against Its Fatal Consequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4830–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Slavinskaya, Z.; Merrill, A.R.; Kaufmann, S.H.E. Human α-Defensins Neutralize Toxins of the Mono-ADP-Ribosyltransferase Family. Biochem. J. 2006, 399, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T.; Selsted, M.E.; Szklarek, D.; Harwig, S.S.; Daher, K.; Bainton, D.F.; Lehrer, R.I. Defensins. Natural Peptide Antibiotics of Human Neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 1985, 76, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T. Defensins: Antimicrobial Peptides of Innate Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, K.; Contreras, R. Human Antimicrobial Peptides: Defensins, Cathelicidins and Histatins. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevins, C.; Martin-Porter, E.; Ganz, T. Defensins and Innate Host Defence of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Gut 1999, 45, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, R.I.; Lu, W. α-Defensins in Human Innate Immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 245, 84–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, T.; Lehrer, R.I. Defensins. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1994, 6, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.C.; Bevins, C.L. Paneth Cells: Maestros of the Small Intestinal Crypts. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, E.M.; Bevins, C.L.; Ghosh, D.; Ganz, T. The Multifaceted Paneth Cell. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, N.H.; Hung, K.; Haribhai, D.; Chu, H.; Karlsson-Sjöberg, J.; Amir, E.; Teggatz, P.; Barman, M.; Hayward, M.; Eastwood, D.; et al. Enteric Defensins Are Essential Regulators of Intestinal Microbial Ecology. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericksen, B.; Wu, Z.; Lu, W.; Lehrer, R.I. Antibacterial Activity and Specificity of the Six Human {alpha}-Defensins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szyk, A.; Wu, Z.; Tucker, K.; Yang, D.; Lu, W.; Lubkowski, J. Crystal Structures of Human Alpha-Defensins HNP4, HD5, and HD6. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 2749–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Pazgier, M.; Jung, G.; Nuccio, S.-P.; Castillo, P.A.; de Jong, M.F.; Winter, M.G.; Winter, S.E.; Wehkamp, J.; Shen, B.; et al. Human α-Defensin 6 Promotes Mucosal Innate Immunity through Self-Assembled Peptide Nanonets. Science 2012, 337, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chairatana, P.; Nolan, E.M. Molecular Basis for Self-Assembly of a Human Host-Defense Peptide That Entraps Bacterial Pathogens. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13267–13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Kill Bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashova, E.; Quintyn, R.; Seveau, S.; Lu, W.; Wysocki, V.H.; Kudryashov, D.S. Human Defensins Facilitate Local Unfolding of Thermodynamically Unstable Regions of Bacterial Protein Toxins. Immunity 2014, 41, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kudryashova, E.; Seveau, S.M.; Kudryashov, D.S. Targeting and Inactivation of Bacterial Toxins by Human Defensins. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 1069–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryashova, E.; Koneru, P.C.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Strömstedt, A.A.; Lu, W.; Kudryashov, D.S. Thermodynamic Instability of Viral Proteins Is a Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern Targeted by Human Defensins. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryashova, E.; Zani, A.; Vilmen, G.; Sharma, A.; Lu, W.; Yount, J.S.; Kudryashov, D.S. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Human Defensin HNP1 and Retrocyclin RC-101. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 434, 167225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, A.; Marin, M.; Honnen, W.; Ramasamy, S.; Porter, E.; Subbian, S.; Pinter, A.; Melikyan, G.B.; Lu, W.; et al. Human Defensins Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Blocking Viral Entry. Viruses 2021, 13, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonon, F.; Di Bella, S.; Grassi, G.; Luzzati, R.; Ascenzi, P.; di Masi, A.; Zennaro, C. Extra-Intestinal Effects of C. Difficile Toxin A and B: An In Vivo Study Using the Zebrafish Embryo Model. Cells 2020, 9, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Eichel-Streiber, C.; Harperath, U.; Bosse, D.; Hadding, U. Purification of Two High Molecular Weight Toxins of Clostridium Difficile Which Are Antigenically Related. Microb. Pathog. 1987, 2, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heber, S.; Barthold, L.; Baier, J.; Papatheodorou, P.; Fois, G.; Frick, M.; Barth, H.; Fischer, S. Inhibition of Clostridioides Difficile Toxins TcdA and TcdB by Ambroxol. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 809595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morash, M.G.; Douglas, S.E.; Robotham, A.; Ridley, C.M.; Gallant, J.W.; Soanes, K.H. The Zebrafish Embryo as a Tool for Screening and Characterizing Pleurocidin Host-Defense Peptides as Anti-Cancer Agents. Dis. Models Mech. 2011, 4, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raftery, T.D.; Isales, G.M.; Yozzo, K.L.; Volz, D.C. High-Content Screening Assay for Identification of Chemicals Impacting Spontaneous Activity in Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barthold, L.; Heber, S.; Schmidt, C.Q.; Gradl, M.; Weidinger, G.; Barth, H.; Fischer, S. Human α-Defensin-6 Neutralizes Clostridioides difficile Toxins TcdA and TcdB by Direct Binding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094509
Barthold L, Heber S, Schmidt CQ, Gradl M, Weidinger G, Barth H, Fischer S. Human α-Defensin-6 Neutralizes Clostridioides difficile Toxins TcdA and TcdB by Direct Binding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094509
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarthold, Lara, Sebastian Heber, Christoph Q. Schmidt, Marion Gradl, Gilbert Weidinger, Holger Barth, and Stephan Fischer. 2022. "Human α-Defensin-6 Neutralizes Clostridioides difficile Toxins TcdA and TcdB by Direct Binding" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094509
APA StyleBarthold, L., Heber, S., Schmidt, C. Q., Gradl, M., Weidinger, G., Barth, H., & Fischer, S. (2022). Human α-Defensin-6 Neutralizes Clostridioides difficile Toxins TcdA and TcdB by Direct Binding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094509






