The RAGE/DIAPH1 Signaling Axis & Implications for the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Complications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs)
1.2. The Broad Swath of AGE Receptors
1.3. RAGE Is a Multi-Ligand Receptor
1.4. Diaphanous 1 (DIAPH1) Binds to the Cytoplasmic Tail of RAGE: Studies in Cell-Based Studies and In Vivo Models
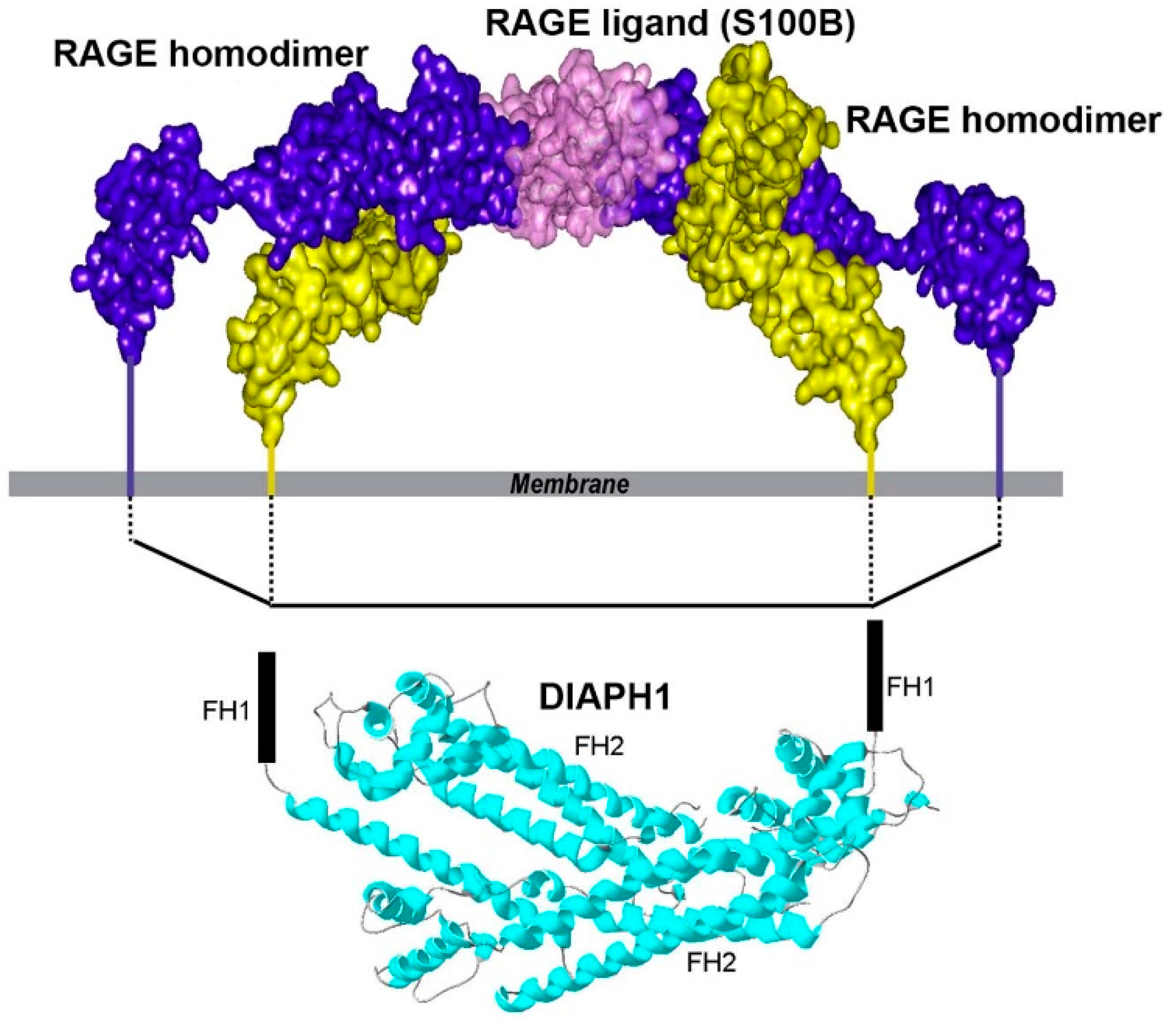
1.5. ctRAGE-DIAPH1 Interactions and Structural Biology
1.6. RAGE/DIAPH1 and Diabetic Atherosclerosis
1.6.1. Micro-RNA (miR-21-3p) and RAGE
1.6.2. Diabetes and Microcalcification: New Insights into Roles for Macrophages and Extracellular Vesicles
1.6.3. Diabetes and Regression of Atherosclerosis
1.7. RAGE/DIAPH1 and Diabetic Kidney Disease
1.7.1. HMGB1 and DKD: Studies in Mouse Models
1.7.2. Anti-RAGE Vaccination and a New Therapeutic Opportunity for DKD
1.7.3. Acute Glucose Fluctuation and Upregulation of RAGE
1.7.4. Updates on Tracking sRAGEs in DKD
1.7.5. Small Molecules Targeting the Cytoplasmic Domain of RAGE Interaction with DIAPH1
1.7.6. RAGE229 and Dampening the Inflammatory Response: Paving the Way to Identifying Biomarkers to Track RAGE-Dependent Inflammation In Vivo
1.7.7. RAGE/DIAPH1: Broad Implications for the Complications of Diabetes
1.8. Perspectives on the Therapeutic Approaches to Targeting RAGE/DIAPH1 in the Clinic: What Are the Natural Functions of RAGE/DIAPH1?
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/overweight-obesity#:~:text=Adults,-Age%2Dadjusted%20percentage&text=the%20above%20table-,Nearly%201%20in%203%20adults%20(30.7%25)%20are%20overweight.,obesity%20(including%20severe%20obesity) (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/diabetes-statistics (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Giacco, F.; Brownlee, M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maillard, L.C. Action des acides aminés sur les sucres: Formation des mél-anoidines par voie méthodique. Comptes R. Acad. Sci. 1912, 154, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, H.H.; Ramasamy, R.; Schmidt, A.M. Advanced Glycation End Products: Building on the Concept of the “Common Soil” in Metabolic Disease. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqz006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briceno Noriega, D.; Zenker, H.E.; Croes, C.A.; Ewaz, A.; Ruinemans-Koerts, J.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; van Neerven, R.J.J.; Teodorowicz, M. Receptor Mediated Effects of Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) on Innate and Adaptative Immunity: Relevance for Food Allergy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Dietary advanced glycation end-products: Perspectives linking food processing with health implications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2559–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, M.; Hellwig, M.; Henle, T.; Vieths, S. Influence of the Maillard Reaction on the Allergenicity of Food Proteins and the Development of Allergic Inflammation. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislinger, T.; Fu, C.; Huber, B.; Qu, W.; Taguchi, A.; Du Yan, S.; Hofmann, M.; Yan, S.F.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Stern, D.; et al. N(epsilon)-(carboxymethyl)lysine adducts of proteins are ligands for receptor for advanced glycation end products that activate cell signaling pathways and modulate gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31740–31749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.; Reverdatto, S.; Frolov, A.; Hoffmann, R.; Burz, D.S.; Shekhtman, A. Structural Basis for Pattern Recognition by the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE). J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27255–27269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Manigrasso, M.; Scalabrin, M.; Rai, V.; Reverdatto, S.; Burz, D.S.; Fabris, D.; Schmidt, A.M.; Shekhtman, A. Change in the Molecular Dimension of a RAGE-Ligand Complex Triggers RAGE Signaling. Structure 2016, 24, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, J.; Li, L.; Liu, N.; Liang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Chen, X. Effects of Nε-carboxymethyl-Lysine on ERS-mediated apoptosis in diabetic atherosclerosis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 172, e478–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, M.W.; Hedegaard, R.V.; Andersen, J.M.; de Courten, B.; Bügel, S.; Nielsen, J.; Skibsted, L.H.; Dragsted, L.O. Advanced glycation endproducts in food and their effects on health. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassara, H.; Cai, W.; Tripp, E.; Pyzik, R.; Yee, K.; Goldberg, L.; Tansman, L.; Chen, X.; Mani, V.; Fayad, Z.A.; et al. Oral AGE restriction ameliorates insulin resistance in obese individuals with the metabolic syndrome: A randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkens, A.M.A.; Houben, A.J.; Niessen, P.M.; Wijckmans, N.; de Goei, E.; Van den Eynde, M.D.G.; Scheijen, J.L.J.M.; Waarenburg, M.; Mari, A.; Berendschot, T.T.J.M.; et al. A 4-week high-AGE diet does not impair glucose metabolism and vascular function in obese individuals. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e156950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senatus, L.; MacLean, M.; Arivazhagan, L.; Egaña-Gorroño, L.; López-Díez, R.; Manigrasso, M.B.; Ruiz, H.H.; Vasquez, C.; Wilson, R.; Shekhtman, A.; et al. Inflammation Meets Metabolism: Roles for the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products Axis in Cardiovascular Disease. Immunometabolism 2021, 3, e210024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egaña-Gorroño, L.; López-Díez, R.; Yepuri, G.; Ramirez, L.S.; Reverdatto, S.; Gugger, P.F.; Shekhtman, A.; Ramasamy, R.; Schmidt, A.M. Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) and Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: Insights From Human Subjects and Animal Models. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; He, J.C.; Cai, W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; Vlassara, H. Advanced glycation endproduct (AGE) receptor 1 is a negative regulator of the inflammatory response to AGE in mesangial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11767–11772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stitt, A.W.; Li, Y.M.; Gardiner, T.A.; Bucala, R.; Archer, D.B.; Vlassara, H. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) co-localize with AGE receptors in the retinal vasculature of diabetic and of AGE-infused rats. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 523–531. [Google Scholar]
- Pugliese, G.; Pricci, F.; Iacobini, C.; Leto, G.; Amadio, L.; Barsotti, P.; Frigeri, L.; Hsu, D.K.; Vlassara, H.; Liu, F.T.; et al. Accelerated diabetic glomerulopathy in galectin-3/AGE receptor 3 knockout mice. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Kurihara, Y.; Takeya, M.; Kamada, N.; Kataoka, M.; Jishage, K.; Ueda, O.; Sakaguchi, H.; Higashi, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. A role for macrophage scavenger receptors in atherosclerosis and susceptibility to infection. Nature 1997, 386, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, H.; Lyu, J.; Imachi, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Sato, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Saheki, T.; Seo, K.; Salimah, J.B.; Iwama, H.; et al. AGEs inhibit scavenger receptor class B type I gene expression via Smad1 in HUVECs. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2021, 66, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Li, W.; Silverstein, R.L. Advanced glycation end products induce a prothrombotic phenotype in mice via interaction with platelet CD36. Blood 2012, 119, 6136–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hodgkinson, C.P.; Laxton, R.C.; Patel, K.; Ye, S. Advanced glycation end-product of low density lipoprotein activates the toll-like 4 receptor pathway implications for diabetic atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Beijnum, J.R.; Buurman, W.A.; Griffioen, A.W. Convergence and amplification of toll-like receptor (TLR) and receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) signaling pathways via high mobility group B1 (HMGB1). Angiogenesis 2008, 11, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Sharma, E.; Sehgal, A.; Kaur, I.; Kumar, A.; Arora, R.; Pal, G.; Kakkar, M.; Kumar, R.; Bungau, S. Expatiating the molecular approaches of HMGB1 in diabetes mellitus: Highlighting signalling pathways via RAGE and TLRs. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grevers, L.C.; de Vries, T.J.; Vogl, T.; Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Sloetjes, A.W.; Leenen, P.J.; Roth, J.; Everts, V.; van den Berg, W.B.; van Lent, P.L. S100A8 enhances osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro through activation of Toll-like receptor 4: Implications for bone destruction in murine antigen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclerc, E.; Fritz, G.; Vetter, S.W.; Heizmann, C.W. Binding of S100 proteins to RAGE: An update. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burstein, A.H.; Sabbagh, M.; Andrews, R.; Valcarce, C.; Dunn, I.; Altstiel, L. Development of Azeliragon, an Oral Small Molecule Antagonist of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts, for the Potential Slowing of Loss of Cognition in Mild Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 5, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Vianna, M.; Gerlach, M.; Brett, J.; Ryan, J.; Kao, J.; Esposito, C.; Hegarty, H.; Hurley, W.; Clauss, M.; et al. Isolation and characterization of two binding proteins for advanced glycosylation end products from bovine lung which are present on the endothelial cell surface. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 14987–14997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.A.; Drury, S.; Fu, C.; Qu, W.; Taguchi, A.; Lu, Y.; Avila, C.; Kambham, N.; Bierhaus, A.; Nawroth, P.; et al. RAGE mediates a novel proinflammatory axis: A central cell surface receptor for S100/calgranulin polypeptides. Cell 1999, 97, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hori, O.; Brett, J.; Slattery, T.; Cao, R.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.X.; Nagashima, M.; Lundh, E.R.; Vijay, S.; Nitecki, D.; et al. The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a cellular binding site for amphoterin. Mediation of neurite outgrowth and co-expression of rage and amphoterin in the developing nervous system. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25752–25761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taguchi, A.; Blood, D.C.; del Toro, G.; Canet, A.; Lee, D.C.; Qu, W.; Tanji, N.; Lu, Y.; Lalla, E.; Fu, C.; et al. Blockade of RAGE-amphoterin signalling suppresses tumour growth and metastases. Nature 2000, 405, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.D.; Chen, X.; Fu, J.; Chen, M.; Zhu, H.; Roher, A.; Slattery, T.; Zhao, L.; Nagashima, M.; Morser, J.; et al. RAGE and amyloid-beta peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 1996, 382, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedini, A.; Cao, P.; Plesner, A.; Zhang, J.; He, M.; Derk, J.; Patil, S.A.; Rosario, R.; Lonier, J.; Song, F.; et al. RAGE binds preamyloid IAPP intermediates and mediates pancreatic β cell proteotoxicity. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 682–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chavakis, T.; Bierhaus, A.; Al-Fakhri, N.; Schneider, D.; Witte, S.; Linn, T.; Nagashima, M.; Morser, J.; Arnold, B.; Preissner, K.T.; et al. The pattern recognition receptor (RAGE) is a counterreceptor for leukocyte integrins: A novel pathway for inflammatory cell recruitment. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Rai, V.; Hudson, B.I.; Song, F.; Schmidt, A.M.; Barile, G.R. RAGE binds C1q and enhances C1q-mediated phagocytosis. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 274, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, V.; Touré, F.; Chitayat, S.; Pei, R.; Song, F.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Rosario, R.; Ramasamy, R.; Chazin, W.J.; et al. Lysophosphatidic acid targets vascular and oncogenic pathways via RAGE signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Kubo, H.; Morimoto, K.; Fujino, N.; Suzuki, T.; Takahasi, T.; Yamada, M.; Yamaya, M.; Maekawa, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products binds to phosphatidylserine and assists in the clearance of apoptotic cells. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertheloot, D.; Naumovski, A.L.; Langhoff, P.; Horvath, G.L.; Jin, T.; Xiao, T.S.; Garbi, N.; Agrawal, S.; Kolbeck, R.; Latz, E. RAGE Enhances TLR Responses through Binding and Internalization of RNA. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4118–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirois, C.M.; Jin, T.; Miller, A.L.; Bertheloot, D.; Nakamura, H.; Horvath, G.L.; Mian, A.; Jiang, J.; Schrum, J.; Bossaller, L.; et al. RAGE is a nucleic acid receptor that promotes inflammatory responses to DNA. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2447–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hudson, B.I.; Kalea, A.Z.; Del Mar Arriero, M.; Harja, E.; Boulanger, E.; D’Agati, V.; Schmidt, A.M. Interaction of the RAGE cytoplasmic domain with diaphanous-1 is required for ligand-stimulated cellular migration through activation of Rac1 and Cdc42. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34457–34468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strieder-Barboza, C.; Baker, N.A.; Flesher, C.G.; Karmakar, M.; Neeley, C.K.; Polsinelli, D.; Dimick, J.B.; Finks, J.F.; Ghaferi, A.A.; Varban, O.A.; et al. Advanced glycation end-products regulate extracellular matrix-adipocyte metabolic crosstalk in diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touré, F.; Fritz, G.; Li, Q.; Rai, V.; Daffu, G.; Zou, Y.S.; Rosario, R.; Ramasamy, R.; Alberts, A.S.; Yan, S.F.; et al. Formin mDia1 mediates vascular remodeling via integration of oxidative and signal transduction pathways. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Weng, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Guo, X. Mdia1 is Crucial for Advanced Glycation End Product-Induced Endothelial Hyperpermeability. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, K.M.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Li, Q.; Quadri, N.; Thiagarajan, D.; Sreejit, G.; Wang, L.; Zirpoli, H.; Aranda, J.F.; Alberts, A.S.; et al. The Formin, DIAPH1, is a Key Modulator of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. EBioMedicine 2017, 26, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manigrasso, M.B.; Friedman, R.A.; Ramasamy, R.; D’Agati, V.; Schmidt, A.M. Deletion of the formin Diaph1 protects from structural and functional abnormalities in the murine diabetic kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1601–F1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, V.; Gaeta, G.; Lombardi, A.; Nastri, F.; Maglio, O.; Isernia, C.; Saviano, M. Discovering protein secondary structures: Classification and description of isolated alpha-turns. Biopolymers 1996, 38, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Maldonado, A.Y.; Burz, D.S.; Reverdatto, S.; Schmidt, A.M.; Shekhtman, A. Signal Transduction in Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 5133–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Smith, E.A. Diaphanous-1 affects the nanoscale clustering and lateral diffusion of receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE). Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, L.; Raman, K.G.; Lee, K.J.; Lu, Y.; Ferran, L.J., Jr.; Chow, W.S.; Stern, D.; Schmidt, A.M. Suppression of accelerated diabetic atherosclerosis by the soluble receptor for advanced glycation endproducts. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciarelli, L.G.; Wendt, T.; Qu, W.; Lu, Y.; Lalla, E.; Rong, L.L.; Goova, M.T.; Moser, B.; Kislinger, T.; Lee, D.C.; et al. RAGE blockade stabilizes established atherosclerosis in diabetic apolipoprotein E-null mice. Circulation 2002, 106, 2827–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro-Paavonen, A.; Watson, A.M.; Li, J.; Paavonen, K.; Koitka, A.; Calkin, A.C.; Barit, D.; Coughlan, M.T.; Drew, B.G.; Lancaster, G.I.; et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) deficiency attenuates the development of atherosclerosis in diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koulis, C.; Kanellakis, P.; Pickering, R.J.; Tsorotes, D.; Murphy, A.J.; Gray, S.P.; Thomas, M.C.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A.; Cooper, M.E.; Allen, T.J. Role of bone-marrow- and non-bone-marrow-derived receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) in a mouse model of diabetes-associated atherosclerosis. Clin. Sci. 2014, 127, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Yu, M.; Zhao, J.; Mei, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Yu, M.; Liu, F.; Chen, G. miR-21-3p regulates AGE/RAGE signalling and improves diabetic atherosclerosis. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2020, 38, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, R.; Katsuki, S.; Travers, R.; Romero, D.C.; Becker-Greene, D.; Passos, L.S.A.; Higashi, H.; Blaser, M.C.; Sukhova, G.K.; Buttigieg, J.; et al. S100A9-RAGE Axis Accelerates Formation of Macrophage-Mediated Extracellular Vesicle Microcalcification in Diabetes Mellitus. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1838–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration; Baigent, C.; Blackwell, L.; Emberson, J.; Holland, L.E.; Reith, C.; Bhala, N.; Peto, R.; Barnes, E.H.; Keech, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: A meta-analysis of data from 170,000 participants in 26 randomised trials. Lancet 2010, 376, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiro, T.; Kimura, T.; Morimoto, T.; Miyauchi, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Yamagishi, M.; Ozaki, Y.; Kimura, K.; Saito, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; et al. Diabetes mellitus is a major negative determinant of coronary plaque regression during statin therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome—Serial intravascular ultrasound observations from the Japan Assessment of Pitavastatin and Atorvastatin in Acute Coronary Syndrome Trial (the JAPAN-ACS Trial). Circ. J. 2010, 74, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Distel, E.; Barrett, T.J.; Chung, K.; Girgis, N.M.; Parathath, S.; Essau, C.C.; Murphy, A.J.; Moore, K.J.; Fisher, E.A. miR33 inhibition overcomes deleterious effects of diabetes mellitus on atherosclerosis plaque regression in mice. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaudreault, N.; Kumar, N.; Olivas, V.R.; Eberlé, D.; Stephens, K.; Raffai, R.L. Hyperglycemia impairs atherosclerosis regression in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagareddy, P.R.; Murphy, A.J.; Stirzaker, R.A.; Hu, Y.; Yu, S.; Miller, R.G.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Distel, E.; Westerterp, M.; Huang, L.S.; et al. Hyperglycemia promotes myelopoiesis and impairs the resolution of atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parathath, S.; Grauer, L.; Huang, L.S.; Sanson, M.; Distel, E.; Goldberg, I.J.; Fisher, E.A. Diabetes adversely affects macrophages during atherosclerotic plaque regression in mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feig, J.E.; Parathath, S.; Rong, J.X.; Mick, S.L.; Vengrenyuk, Y.; Grauer, L.; Young, S.G.; Fisher, E.A. Reversal of hyperlipidemia with a genetic switch favorably affects the content and inflammatory state of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation 2011, 123, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrett, T.J.; Distel, E.; Murphy, A.J.; Hu, J.; Garshick, M.S.; Ogando, Y.; Liu, J.; Vaisar, T.; Heinecke, J.W.; Berger, J.S.; et al. Apolipoprotein AI) Promotes Atherosclerosis Regression in Diabetic Mice by Suppressing Myelopoiesis and Plaque Inflammation. Circulation 2019, 140, 1170–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senatus, L.; López-Díez, R.; Egaña-Gorroño, L.; Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Daffu, G.; Li, Q.; Rahman, K.; Vengrenyuk, Y.; Barrett, T.J.; et al. RAGE impairs murine diabetic atherosclerosis regression and implicates IRF7 in macrophage inflammation and cholesterol metabolism. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e137289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanji, N.; Markowitz, G.S.; Fu, C.; Kislinger, T.; Taguchi, A.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Stern, D.; Schmidt, A.M.; D’Agati, V.D. Expression of advanced glycation end products and their cellular receptor RAGE in diabetic nephropathy and nondiabetic renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Kato, I.; Doi, T.; Yonekura, H.; Ohashi, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yamagishi, S.; Sakurai, S.; Takasawa, S.; et al. Development and prevention of advanced diabetic nephropathy in RAGE-overexpressing mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, T.M.; Tanji, N.; Guo, J.; Kislinger, T.R.; Qu, W.; Lu, Y.; Bucciarelli, L.G.; Rong, L.L.; Moser, B.; Markowitz, G.S.; et al. RAGE drives the development of glomerulosclerosis and implicates podocyte activation in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myint, K.M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Doi, T.; Kato, I.; Harashima, A.; Yonekura, H.; Watanabe, T.; Shinohara, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Tsuneyama, K.; et al. RAGE control of diabetic nephropathy in a mouse model: Effects of RAGE gene disruption and administration of low-molecular weight heparin. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2510–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiniger, N.; Lau, K.; McCalla, D.; Eby, B.; Cheng, B.; Lu, Y.; Qu, W.; Quadri, N.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Furmansky, M.; et al. Deletion of the receptor for advanced glycation end products reduces glomerulosclerosis and preserves renal function in the diabetic OVE26 mouse. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flyvbjerg, A.; Denner, L.; Schrijvers, B.F.; Tilton, R.G.; Mogensen, T.H.; Paludan, S.R.; Rasch, R. Long-term renal effects of a neutralizing RAGE antibody in obese type 2 diabetic mice. Diabetes 2004, 53, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, L.J.; Denner, L.; Schrijvers, B.F.; Tilton, R.G.; Rasch, R.; Flyvbjerg, A. Renal effects of a neutralising RAGE-antibody in long-term streptozotocin-diabetic mice. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 188, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaida, Y.; Fukami, K.; Matsui, T.; Higashimoto, Y.; Nishino, Y.; Obara, N.; Nakayama, Y.; Ando, R.; Toyonaga, M.; Ueda, S.; et al. DNA aptamer raised against AGEs blocks the progression of experimental diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3241–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sotokawauchi, A.; Matsui, T.; Higashimoto, Y.; Nishino, Y.; Koga, Y.; Yagi, M.; Yamagishi, S.I. DNA aptamer raised against receptor for advanced glycation end products suppresses renal tubular damage and improves insulin resistance in diabetic mice. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2021, 18, 1479164121990533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesch, G.; Sourris, K.C.; Summers, S.A.; McCarthy, D.; Ward, M.S.; Borg, D.J.; Gallo, L.A.; Fotheringham, A.K.; Pettit, A.R.; Yap, F.Y.; et al. Deletion of bone-marrow-derived receptor for AGEs (RAGE) improves renal function in an experimental mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.S.; Gamboni-Robertson, F.; He, Q.; Svetkauskaite, D.; Kim, J.Y.; Strassheim, D.; Sohn, J.W.; Yamada, S.; Maruyama, I.; Banerjee, A.; et al. High mobility group box 1 protein interacts with multiple Toll-like receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, C917–C924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira-Machado, J.A.; Volpe, C.M.d.O.; Veloso, C.A.; Chaves, M.M. HMGB1, TLR and RAGE: A functional tripod that leads to diabetic inflammation. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, J.; Kwan, T.; Stribos, E.G.D.; Messchendorp, A.L.; Loh, Y.W.; Wang, X.; Paul, M.; Cunningham, E.C.; Habib, M.; et al. Blockade of HMGB1 Attenuates Diabetic Nephropathy in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azegami, T.; Nakayama, T.; Hayashi, K.; Hishikawa, A.; Yoshimoto, N.; Nakamichi, R.; Itoh, H. Vaccination Against Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products Attenuates the Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapanis, M.; James, S.; Craig, M.E.; O’Neal, D.; Ekinci, E.I. Complications of diabetes and metrics of glycaemic management derived from continuous glucose monitoring. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, dgac034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Fang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, H. Acute glucose fluctuation promotes RAGE expression via reactive oxygen species-mediated NF-κB activation in rat podocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, M.C.; Kraakman, M.J.; Tikellis, C.; Lee, M.K.S.; Hanssen, N.M.J.; Kammoun, H.L.; Pickering, R.J.; Dragoljevic, D.; Al-Sharea, A.; Barrett, T.J.; et al. Transient Intermittent Hyperglycemia Accelerates Atherosclerosis by Promoting Myelopoiesis. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbeke, M.; De Bruyne, S.; De Buyzere, M.; Lapauw, B.; Speeckaert, R.; Petrovic, M.; Delanghe, J.R.; Speeckaert, M.M. The role of soluble receptor for advanced glycation end-products (sRAGE) in the general population and patients with diabetes mellitus with a focus on renal function and overall outcome. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2021, 58, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.; Dhar, I.; Zhou, Q.; Elmoselhi, H.; Shoker, M.; Shoker, A. AGEs/sRAGE, a novel risk factor in the pathogenesis of end-stage renal disease. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2016, 423, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, P.; Caldiroli, L.; Dozio, E.; Rigolini, R.; Giubbilini, P.; Romanelli, M.M.C.; Messa, P.; Vettoretti, S. AGEs and sRAGE Variations at Different Timepoints in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manigrasso, M.B.; Pan, J.; Rai, V.; Zhang, J.; Reverdatto, S.; Quadri, N.; DeVita, R.J.; Ramasamy, R.; Shekhtman, A.; Schmidt, A.M. Small Molecule Inhibition of Ligand-Stimulated RAGE-DIAPH1 Signal Transduction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manigrasso Michaele, B.; Rabbani, P.; Egaña-Gorroño, L.; Quadri, N.; Frye, L.; Zhou, B.; Reverdatto, S.; Ramirez Lisa, S.; Dansereau, S.; Pan, J.; et al. Small-molecule antagonism of the interaction of the RAGE cytoplasmic domain with DIAPH1 reduces diabetic complications in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabf7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucciarelli, L.G.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Hwang, Y.C.; Kaneko, M.; Song, F.; Sell, D.R.; Strauch, C.; Monnier, V.M.; Yan, S.F.; Schmidt, A.M.; et al. RAGE and modulation of ischemic injury in the diabetic myocardium. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoporis, J.N.; Hatziagelaki, E.; Gupta, S.; Izhar, S.; Salpeas, V.; Tsiavou, A.; Rigopoulos, A.G.; Triantafyllis, A.S.; Marshall, J.C.; Parker, T.G.; et al. Circulating Ligands of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products and the Soluble Form of the Receptor Modulate Cardiovascular Cell Apoptosis in Diabetes. Molecules 2020, 25, 5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozio, E.; Vianello, E.; Briganti, S.; Lamont, J.; Tacchini, L.; Schmitz, G.; Corsi Romanelli, M.M. Expression of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products in Epicardial Fat: Link with Tissue Thickness and Local Insulin Resistance in Coronary Artery Disease. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2327341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, G.R.; Pachydaki, S.I.; Tari, S.R.; Lee, S.E.; Donmoyer, C.M.; Ma, W.; Rong, L.L.; Buciarelli, L.G.; Wendt, T.; Hörig, H.; et al. The RAGE axis in early diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 2916–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McVicar, C.M.; Ward, M.; Colhoun, L.M.; Guduric-Fuchs, J.; Bierhaus, A.; Fleming, T.; Schlotterer, A.; Kolibabka, M.; Hammes, H.P.; Chen, M.; et al. Role of the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) in retinal vasodegenerative pathology during diabetes in mice. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Yi, W.; He, C.; Hu, Y.; et al. Extensive Sub-RPE Complement Deposition in a Nonhuman Primate Model of Early-Stage Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.A.; Hong, Y.H.; Moon, M.K.; Koo, B.K.; Kim, T.W. Up-regulation of the receptor for advanced glycation end products in the skin biopsy specimens of patients with severe diabetic neuropathy. J. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 10, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bierhaus, A.; Haslbeck, K.M.; Humpert, P.M.; Liliensiek, B.; Dehmer, T.; Morcos, M.; Sayed, A.A.; Andrassy, M.; Schiekofer, S.; Schneider, J.G.; et al. Loss of pain perception in diabetes is dependent on a receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakur, V.; Sadanandan, J.; Chattopadhyay, M. High-Mobility Group Box 1 Protein Signaling in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, M.N.; Farah, A.I.; Al-Qirim, T.M. The cardiovascular complications of diabetes: A striking link through protein glycation. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 58, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhipa, A.S.; Borse, S.P.; Baksi, R.; Lalotra, S.; Nivsarkar, M. Targeting receptors of advanced glycation end products (RAGE): Preventing diabetes induced cancer and diabetic complications. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Hurtado del Pozo, C.; Rosario, R.; Zou, Y.S.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Xu, X.; Patel, P.R.; Benoit, V.M.; Yan, S.F.; Li, H.; et al. RAGE regulates the metabolic and inflammatory response to high-fat feeding in mice. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1948–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurtado Del Pozo, C.; Ruiz, H.H.; Arivazhagan, L.; Aranda, J.F.; Shim, C.; Daya, P.; Derk, J.; MacLean, M.; He, M.; Frye, L.; et al. A Receptor of the Immunoglobulin Superfamily Regulates Adaptive Thermogenesis. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 773–791.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Hasu, M.; Popov, D.; Zhang, J.H.; Chen, J.; Yan, S.D.; Brett, J.; Cao, R.; Kuwabara, K.; Costache, G.; et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (AGEs) has a central role in vessel wall interactions and gene activation in response to circulating AGE proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8807–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musumeci, D.; Roviello, G.N.; Montesarchio, D. An overview on HMGB1 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents in HMGB1-related pathologies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, H.J.; Fages, C.; Kuja-Panula, J.; Ridley, A.J.; Rauvala, H. Receptor for advanced glycation end products-binding COOH-terminal motif of amphoterin inhibits invasive migration and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4805–4811. [Google Scholar]
- Shishibori, T.; Oyama, Y.; Matsushita, O.; Yamashita, K.; Furuichi, H.; Okabe, A.; Maeta, H.; Hata, Y.; Kobayashi, R. Three distinct anti-allergic drugs, amlexanox, cromolyn and tranilast, bind to S100A12 and S100A13 of the S100 protein family. Biochem. J. 1999, 338 Pt 3, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, T.; Ramachandran, V.; Gomez, S.B.; Schmidt, A.M.; Logsdon, C.D. S100P-derived RAGE antagonistic peptide reduces tumor growth and metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4356–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Zhu, W.; He, F.; Li, Z.; Cai, N.; Wang, H.H. An Aptamer-Based Antagonist against the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products (RAGE) Blocks Development of Colorectal Cancer. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9958051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, S.I.; Matsui, T. Therapeutic Potential of DNA-aptamers Raised Against AGE-RAGE Axis in Diabetes-related Complications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2802–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Akirav, E.M.; Chen, W.; Henegariu, O.; Moser, B.; Desai, D.; Shen, J.M.; Webster, J.C.; Andrews, R.C.; Mjalli, A.M.; et al. RAGE ligation affects T cell activation and controls T cell differentiation. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4272–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burstein, A.H.; Grimes, I.; Galasko, D.R.; Aisen, P.S.; Sabbagh, M.; Mjalli, A.M. Effect of TTP488 in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deane, R.; Singh, I.; Sagare, A.P.; Bell, R.D.; Ross, N.T.; LaRue, B.; Love, R.; Perry, S.; Paquette, N.; Deane, R.J.; et al. A multimodal RAGE-specific inhibitor reduces amyloid β-mediated brain disorder in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1377–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeong, M.S.; Jang, S.B. Molecular Characteristics of RAGE and Advances in Small-Molecule Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Egan, J.; Vasan, S.; Jyothirmayi, G.N.; Masurekar, M.R.; Lopez, S.; Williams, C.; Torres, R.L.; Wagle, D.; Ulrich, P.; et al. An advanced glycation endproduct cross-link breaker can reverse age-related increases in myocardial stiffness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2809–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brownlee, M.; Vlassara, H.; Kooney, A.; Ulrich, P.; Cerami, A. Aminoguanidine prevents diabetes-induced arterial wall protein cross-linking. Science 1986, 232, 1629–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridharan, V.V.; Generoso, J.S.; Collodel, A.; Dominguini, D.; Faller, C.J.; Tardin, F.; Bhatti, G.S.; Petronilho, F.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Barichello, T. Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) Mediates Cognitive Impairment Triggered by Pneumococcal Meningitis. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, G.C.; Borget, M.Y.; Bernier, S.; Garneau, D.; da Silva Duarte, A.J.; Dumais, N. RAGE and CCR7 mediate the transmigration of Zika-infected monocytes through the blood-brain barrier. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayaka, S.A.; McClellan, S.A.; Peng, X.; Barrett, R.P.; Francis, R.; Hazlett, L.D. HMGB1 Antagonist, Box A, Reduces TLR4, RAGE, and Inflammatory Cytokines in the Cornea of P. aeruginosa-Infected Mice. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 34, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zoelen, M.A.; Schouten, M.; de Vos, A.F.; Florquin, S.; Meijers, J.C.; Nawroth, P.P.; Bierhaus, A.; van der Poll, T. The receptor for advanced glycation end products impairs host defense in pneumococcal pneumonia. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4349–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jessop, F.; Schwarz, B.; Scott, D.; Roberts, L.M.; Bohrnsen, E.; Hoidal, J.R.; Bosio, C.M. Impairing RAGE signaling promotes survival and limits disease pathogenesis following SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e155896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ligand/Ligand Family | Reference |
|---|---|
| AGEs (advanced glycation end-products) | [30] |
| S100A12, S100B (+other S100/calgranulins) | [31] |
| HMGB1 (Amphoterin) | [32,33] |
| Amyloid beta-peptide | [34] |
| Islet amyloid polypeptide | [35] |
| Mac-1 | [36] |
| C1q | [37] |
| Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) | [38] |
| Phosphatidylserine (PS) | [39] |
| RNA, DNA | [40,41] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramasamy, R.; Shekhtman, A.; Schmidt, A.M. The RAGE/DIAPH1 Signaling Axis & Implications for the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094579
Ramasamy R, Shekhtman A, Schmidt AM. The RAGE/DIAPH1 Signaling Axis & Implications for the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Complications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094579
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamasamy, Ravichandran, Alexander Shekhtman, and Ann Marie Schmidt. 2022. "The RAGE/DIAPH1 Signaling Axis & Implications for the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Complications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094579
APA StyleRamasamy, R., Shekhtman, A., & Schmidt, A. M. (2022). The RAGE/DIAPH1 Signaling Axis & Implications for the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Complications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094579





