Acute T-Cell-Driven Inflammation Requires the Endoglycosidase Heparanase-1 from Multiple Cell Types
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antigen-Specific T cell Transfer Model for Studying the Role of HS Degradation in T-Cell-Mediated Inflammation
2.2. HPSE-1 Drives T-Cell-Mediated Inflammatory Responses
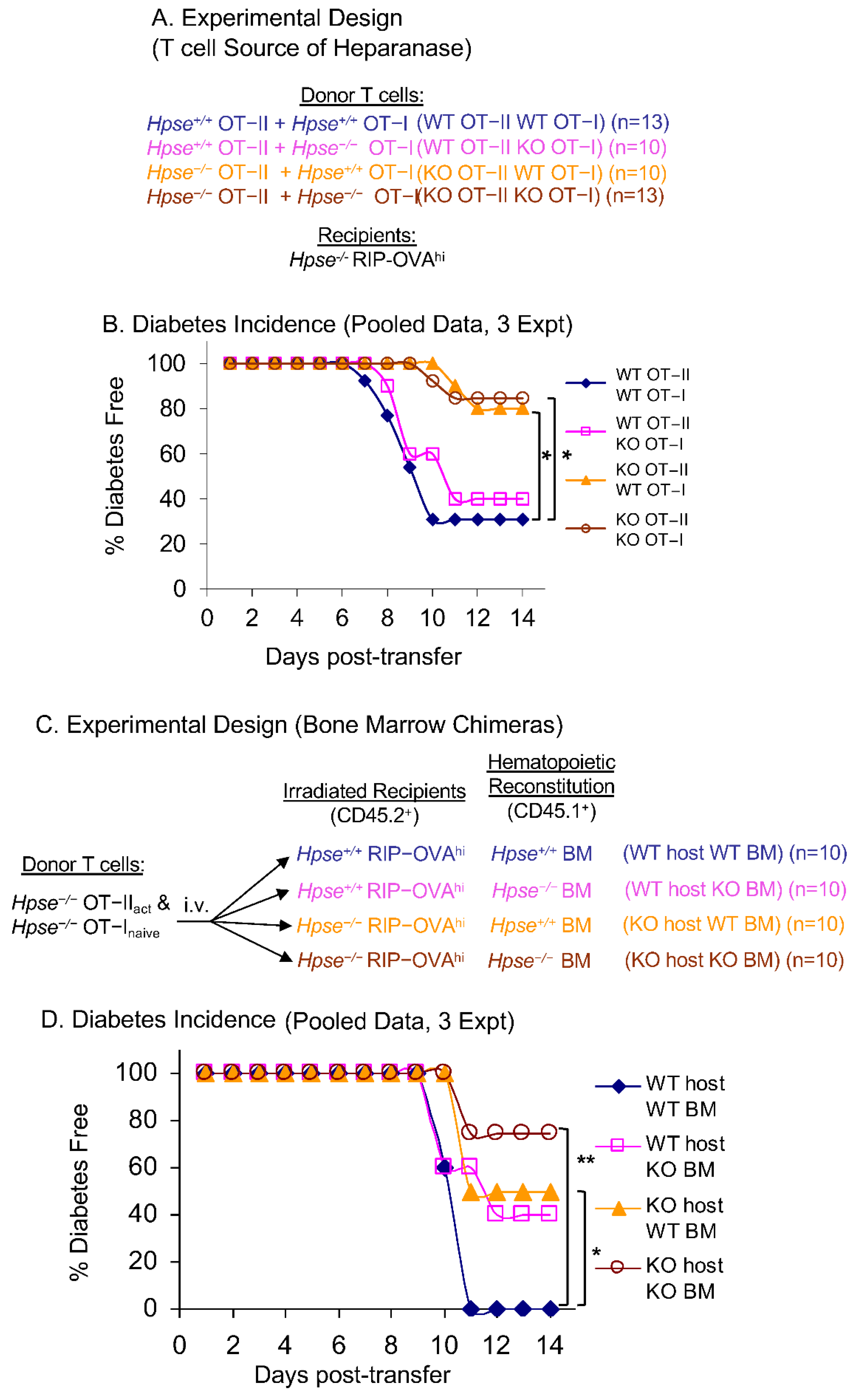
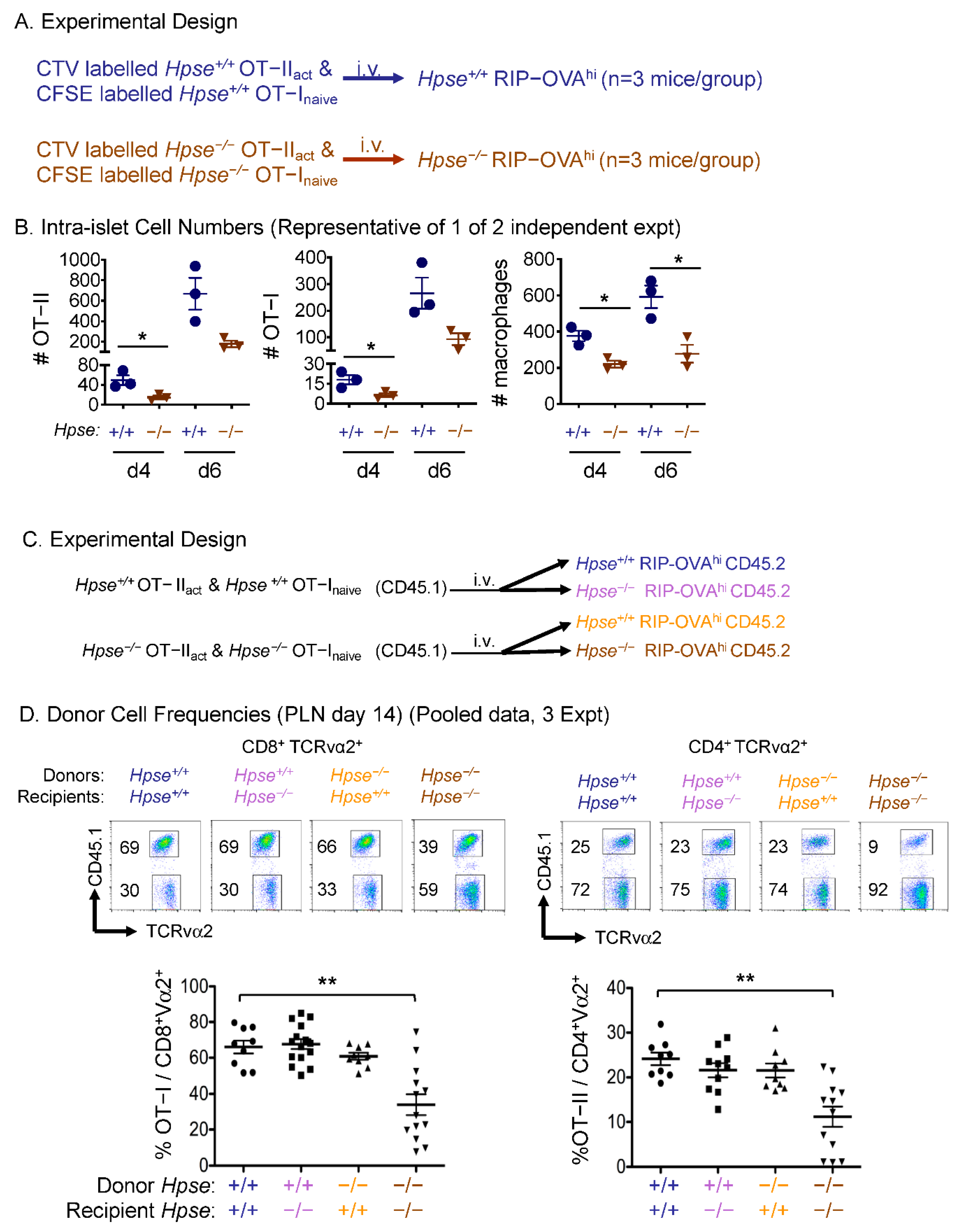
2.3. HPSE-1 from Antigen-Specific CD4+ T Cells Collaborates with Host HPSE-1 from Other Sources to Enable Islet Infiltration
2.4. HPSE-1 Drives T Cell Infiltration of Peripheral Tissues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Diabetes Induction
4.3. Bone Marrow Chimeras
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. Pancreatic Islet Histology, Inflammation, and HS Staining
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hastie, E.L.; Sherwood, D.R. A new front in cell invasion: The invadopodial membrane. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 95, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, L.C.; Lohmer, L.L.; Hagedorn, E.J.; Sherwood, D.R. Traversing the basement membrane in vivo: A diversity of strategies. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 204, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korpos, E.; Wu, C.; Song, J.; Hallmann, R.; Sorokin, L. Role of the extracellular matrix in lymphocyte migration. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madri, J.A.; Graesser, D. Cell migration in the immune system: The evolving inter-related roles of adhesion molecules and proteinases. Dev. Immunol. 2000, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parish, C.R. The role of heparan sulphate in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart, J.; Pulkoski-Gross, A.; Cao, J. Targeting matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: Bringing new life to old ideas. Genes Dis. 2015, 2, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wieczorek, E.; Jablonska, E.; Wasowicz, W.; Reszka, E. Matrix metalloproteinases and genetic mouse models in cancer research: A mini-review. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoler-Barak, L.; Petrovich, E.; Aychek, T.; Gurevich, I.; Tal, O.; Hatzav, M.; Ilan, N.; Feigelson, S.W.; Shakhar, G.; Vlodavsky, I.; et al. Heparanase of murine effector lymphocytes and neutrophils is not required for their diapedesis into sites of inflammation. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2010–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, G.M.; Li, M.; Davey, G.M.; Allison, J.; Flavell, R.A.; Carbone, F.R.; Heath, W.R. Helper requirements for generation of effector ctl to islet beta cell antigens. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5420–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phares, T.W.; Stohlman, S.A.; Hwang, M.; Min, B.; Hinton, D.R.; Bergmann, C.C. CD4 T cells promote CD8 T cell immunity at the priming and effector site during viral encephalitis. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2416–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swain, S.L.; McKinstry, K.K.; Strutt, T.M. Expanding roles for CD4(+) T cells in immunity to viruses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeonovic, C.J.; Popp, S.K.; Starrs, L.M.; Brown, D.J.; Ziolkowski, A.F.; Ludwig, B.; Bornstein, S.R.; Wilson, J.D.; Pugliese, A.; Kay, T.W.H.; et al. Loss of intra-islet heparan sulfate is a highly sensitive marker of type 1 diabetes progression in humans. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziolkowski, A.F.; Popp, S.K.; Freeman, C.; Parish, C.R.; Simeonovic, C.J. Heparan sulfate and heparanase play key roles in mouse beta cell survival and autoimmune diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parish, C.R.; Freeman, C.; Ziolkowski, A.F.; He, Y.Q.; Sutcliffe, E.L.; Zafar, A.; Rao, S.; Simeonovic, C.J. Unexpected new roles for heparanase in type 1 diabetes and immune gene regulation. Matrix Biol. 2013, 32, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonovic, C.J.; Popp, S.K.; Brown, D.J.; Li, F.J.; Lafferty, A.R.A.; Freeman, C.; Parish, C.R. Heparanase and type 1 diabetes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1221, 607–630. [Google Scholar]
- Simeonovic, C.J.; Ziolkowski, A.F.; Wu, Z.; Choong, F.J.; Freeman, C.; Parish, C.R. Heparanase and autoimmune diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, J.E.; Dorling, J. Differential staining of acid glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) by alcian blue in salt solutions. Histochemie 1965, 5, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zcharia, E.; Jia, J.; Zhang, X.; Baraz, L.; Lindahl, U.; Peretz, T.; Vlodavsky, I.; Li, J.P. Newly generated heparanase knock-out mice unravel co-regulation of heparanase and matrix metalloproteinases. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randall, K.L.; Lambe, T.; Johnson, A.L.; Treanor, B.; Kucharska, E.; Domaschenz, H.; Whittle, B.; Tze, L.E.; Enders, A.; Crockford, T.L.; et al. Dock8 mutations cripple B cell immunological synapses, germinal centers and long-lived antibody production. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Os, R.; Sheridan, T.M.; Robinson, S.; Drukteinis, D.; Ferrara, J.L.; Mauch, P.M. Immunogenicity of Ly5 (CD45)-antigens hampers long-term engraftment following minimal conditioning in a murine bone marrow transplantation model. Stem Cells 2001, 19, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, B.J.; Parish, C.R. New and improved methods for measuring lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and in vivo using CFSE-like fluorescent dyes. J. Immunol. Methods 2012, 379, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, J.J.; Sparer, T.E.; Karlstad, M.D.; Burke, S.J. Pancreatic islet inflammation: An emerging role for chemokines. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 59, R33–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vlodavsky, I.; Friedmann, Y. Molecular properties and involvement of heparanase in cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkin, P.; Doctrow, S.; Klagsbrun, M.; Svahn, C.M.; Folkman, J.; Vlodavsky, I. Basic fibroblast growth factor binds to subendothelial extracellular matrix and is released by heparitinase and heparin-like molecules. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilan, N.; Elkin, M.; Vlodavsky, I. Regulation, function and clinical significance of heparanase in cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 2018–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edovitsky, E.; Lerner, I.; Zcharia, E.; Peretz, T.; Vlodavsky, I.; Elkin, M. Role of endothelial heparanase in delayed-type hypersensitivity. Blood 2006, 107, 3609–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Tan, Y.X.; Osterholm, C.; Zhang, X.; Hedin, U.; Vlodavsky, I.; Li, J.P. Heparanase expression upregulates platelet adhesion activity and thrombogenicity. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39486–39496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeman, C.; Parish, C.R. Human platelet heparanase: Purification, characterization and catalytic activity. Biochem J. 1998, 330 Pt 3, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurts, C.; Sutherland, R.M.; Davey, G.; Li, M.; Lew, A.M.; Blanas, E.; Carbone, F.R.; Miller, J.F.; Heath, W.R. CD8 T cell ignorance or tolerance to islet antigens depends on antigen dose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12703–12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnden, M.J.; Allison, J.; Heath, W.R.; Carbone, F.R. Defective tcr expression in transgenic mice constructed using cDNA-based alpha- and beta-chain genes under the control of heterologous regulatory elements. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1998, 76, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogquist, K.A.; Jameson, S.C.; Heath, W.R.; Howard, J.L.; Bevan, M.J.; Carbone, F.R. T cell receptor antagonist peptides induce positive selection. Cell 1994, 76, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, B.J.; Warren, H.S.; Parish, C.R. Monitoring lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and in vivo with the intracellular fluorescent dye carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, B.J.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Ranasinghe, C.; Parish, C.R. The use of fluorescent target arrays for assessment of T cell responses in vivo. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 88, e51627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Sweet, R.A.; Hoyne, G.F.; Simeonovic, C.J.; Parish, C.R. Acute T-Cell-Driven Inflammation Requires the Endoglycosidase Heparanase-1 from Multiple Cell Types. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094625
Wu Z, Sweet RA, Hoyne GF, Simeonovic CJ, Parish CR. Acute T-Cell-Driven Inflammation Requires the Endoglycosidase Heparanase-1 from Multiple Cell Types. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094625
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zuopeng, Rebecca A. Sweet, Gerard F. Hoyne, Charmaine J. Simeonovic, and Christopher R. Parish. 2022. "Acute T-Cell-Driven Inflammation Requires the Endoglycosidase Heparanase-1 from Multiple Cell Types" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094625
APA StyleWu, Z., Sweet, R. A., Hoyne, G. F., Simeonovic, C. J., & Parish, C. R. (2022). Acute T-Cell-Driven Inflammation Requires the Endoglycosidase Heparanase-1 from Multiple Cell Types. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094625





