Neurotrophic Factors in Experimental Cerebral Acanthamoebiasis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
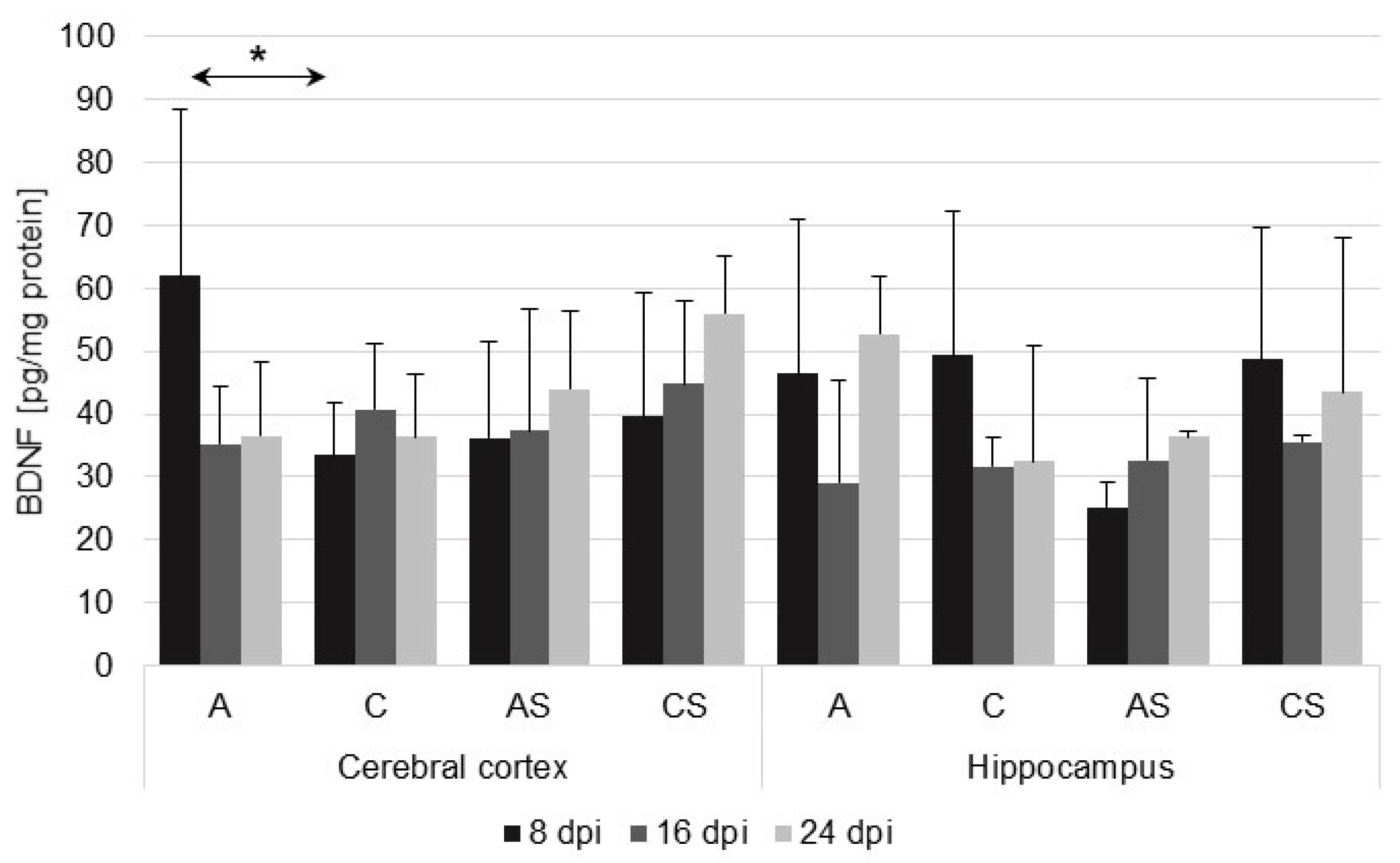
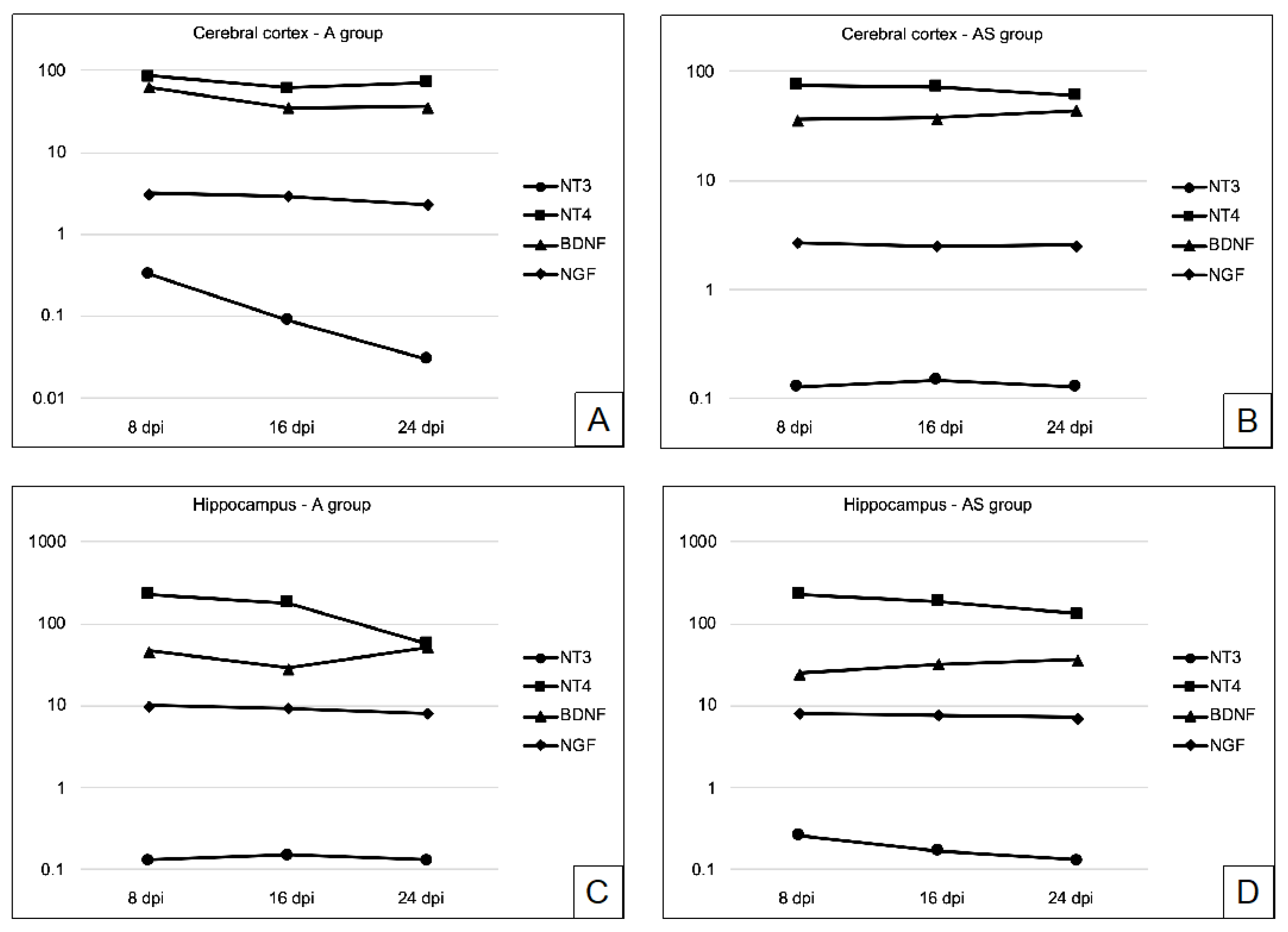
2.1. BDNF in the Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus during Acanthamoebiasis
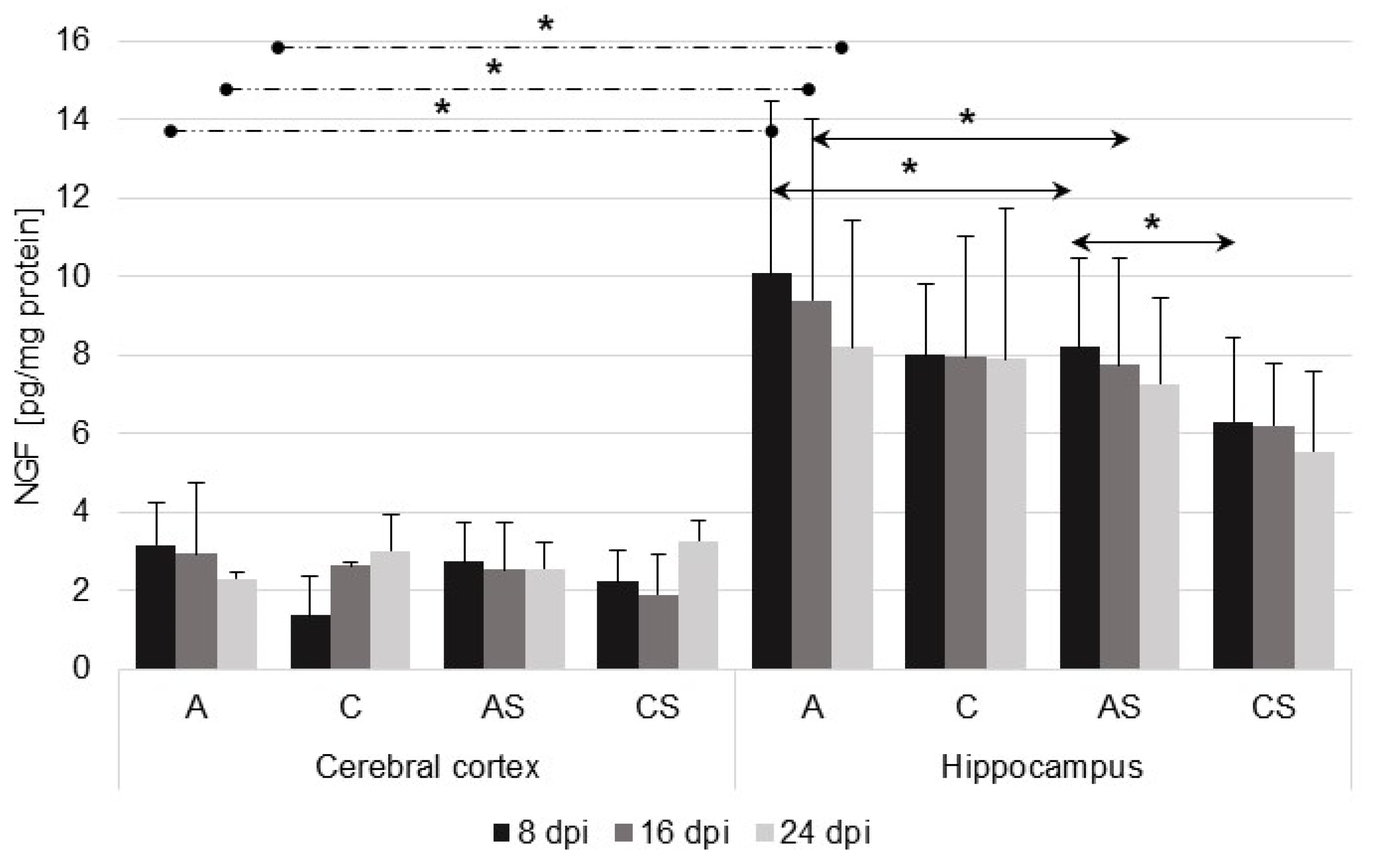
2.2. Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) in the Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus during Acanthamoebiasis
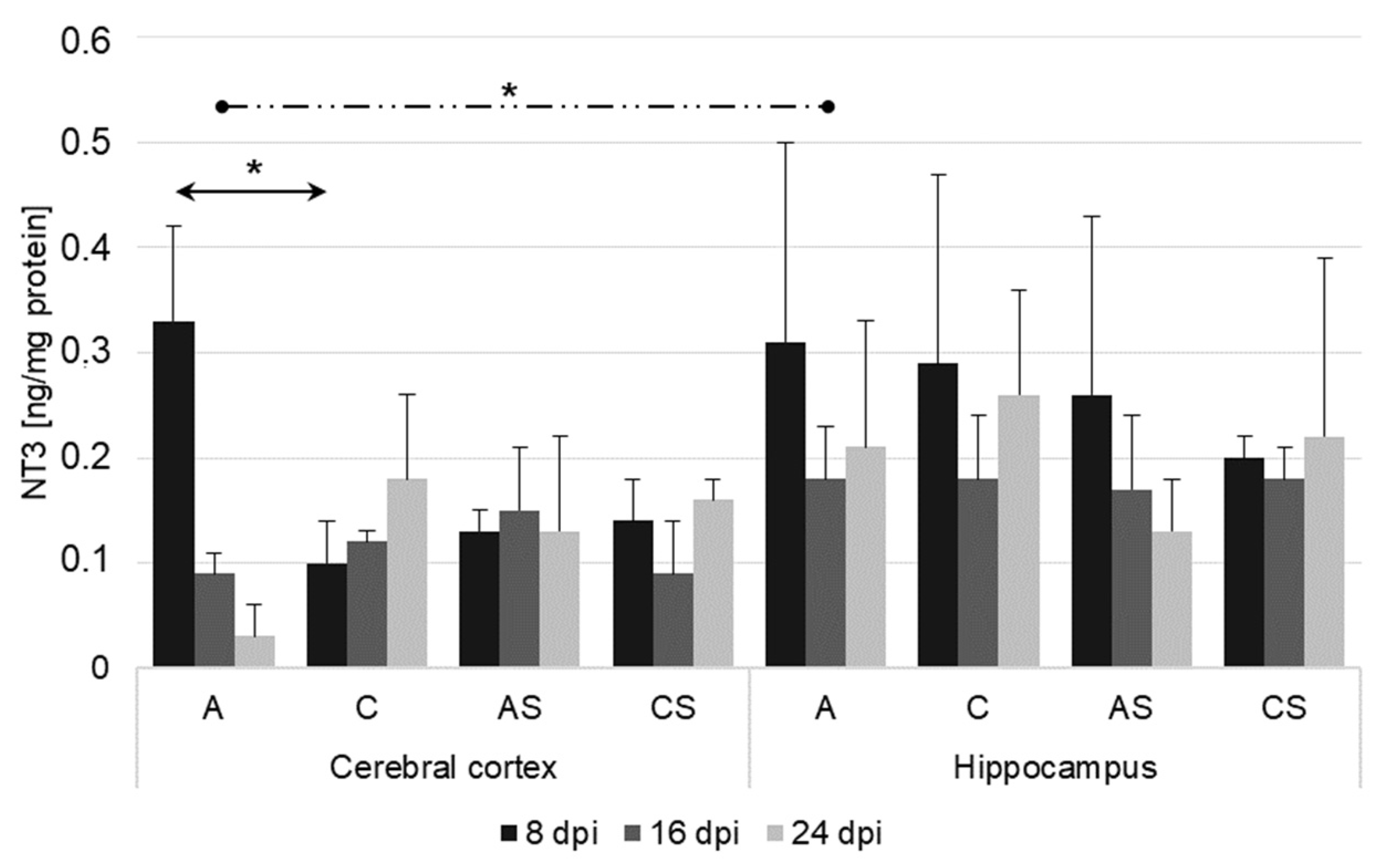
2.3. NT-3 in the Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus during Acanthamoebiasis
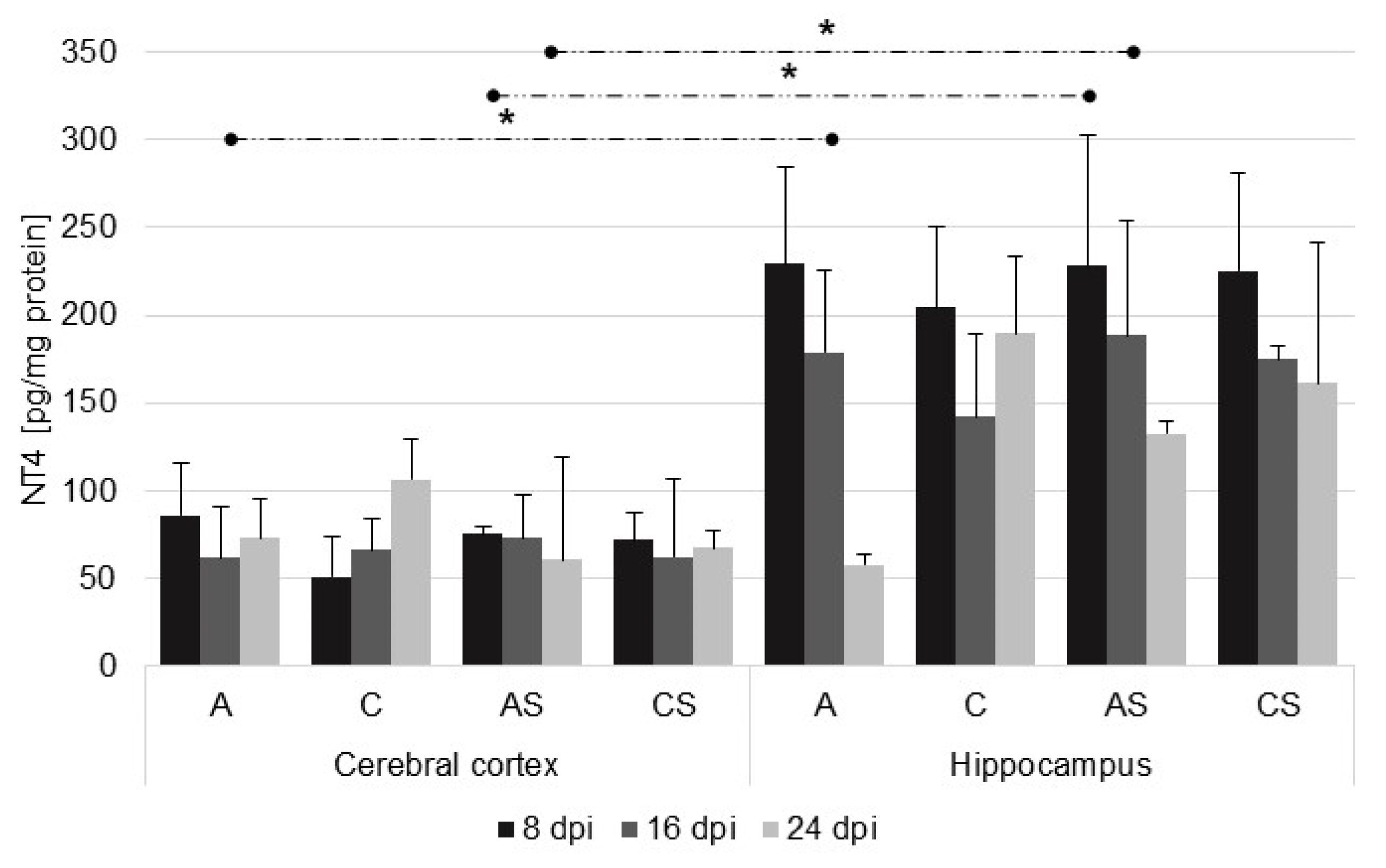
2.4. NT-4 in the Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus during Acanthamoebiasis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Model and Parasites
4.2. Sample Homogenization
4.3. Protein Assay
4.4. Determination of BDNF Concentration
4.5. Determination of NGF Concentration
4.6. Determination of NT-3 Concentration
4.7. Determination of NT-4 Concentration
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siddiqui, R.; Khan, N.A. Biology and pathogenesis of Acanthamoeba. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kot, K.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. Immunopathogenicity of Acanthamoeba spp. in the brain and lungs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 27, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvesvara, G.S. Infections with free-living amebae. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 114, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Gutowska, I.; Kolasa-Wołosiuk, A.; Kot, K.; Łanocha, A.; Metryka, E.; Wiszniewska, B.; Chlubek, D.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. The activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMP-1, TIMP-3) in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in experimental acanthamoebiasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adalid-Peralta, L.; Sáenz, B.; Fragoso, G.; Cárdenas, G. Understanding host-parasite relationship: The immune central nervous system microenvironment and its effect on brain infections. Parasitology 2018, 145, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J. Inflammatory mediators and modulation of blood-brain barrier permeability. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2000, 20, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaliński, B.; Lażewski-Banaszak, P.; Dąbkowska, E.; Paczkowska, E.; Gołąb-Janowska, M.; Nowacki, P. The role of neurotrophic factors in regeneration of the nervous system. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2012, 46, 579–590. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Aarão, T.L.; de Sousa, J.R.; Falcão, A.S.C.; Falcão, L.F.M.; Quaresma, J.A.S. Nerve growth factor and pathogenesis of leprosy: Review and update. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, D.; Bramham, C.R. BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: A synthesis and breakdown. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobbo, B.L.; Doorduin, J.; Klein, H.C.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Bromberg, E.; de Vries, E.F.J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders: Focus on neuroinflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3295–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calabrese, F.; Rossetti, A.C.; Racagni, G.; Gass, P.; Riva, M.A.; Molteni, R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A bridge between inflammation and neuroplasticity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, S.; Li, C.; Lu, N.; Yue, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhi, X.; Zhang, D.; Yuan, Y. The serum protein levels of the tPA-BDNF pathway are implicated in depression and antidepressant treatment. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cong, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Li, Q. NT-3 promotes oligodendrocyte proliferation and nerve function recovery after spinal cord injury by inhibiting autophagy pathway. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 247, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Shi, X.; Wang, H.; Si, C.; Liu, Q.; Du, Y. Neurotrophin-3 promotes the neuronal differentiation of BMSCs and improves cognitive function in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 629356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Kuo, L.T.; Luh, H.T. The roles of neurotrophins in traumatic brain injury. Life 2021, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, C.A.; Vieira, E.L.; Rocha, N.P.; Castro, V.M.; Oréfice, J.L.; Barichello, T.; Costa, R.A.; Oréfice, F.; Young, L.; Teixeira, A.L. Serum levels of neurotrophic factors in active toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 21, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, M.; Marín-García, P.; Pérez-Benavente, S.; Sánchez-Nogueiro, J.; Puyet, A.; Bautista, J.M.; Diez, A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the course of experimental cerebral malaria. Brain Res. 2013, 1490, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.R.; Conroy, A.L.; Hawkes, M.; Elphinstone, R.E.; Gamble, J.L.; Hayford, K.; Namasopo, S.; Opoka, R.O.; Liles, W.C.; Kain, K.C. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is associated with disease severity and clinical outcome in Ugandan children admitted to hospital with severe malaria. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portes, A.; Giestal-de-Araujo, E.; Fagundes, A.; Pandolfo, P.; de Sá Geraldo, A.; Lira, M.L.; Amaral, V.F.; Lagrota-Candido, J. Leishmania amazonensis infection induces behavioral alterations and modulates cytokine and neurotrophin production in the murine cerebral cortex. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 301, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, P.M.; Camargos, E.R.; Azevedo, A.A.; Chiari, E.; Morel, G.; Machado, C.R. Cardiac NGF and GDNF expression during Trypanosoma cruzi infection in rats. Auton. Neurosci. 2006, 130, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathina, S.; Das, U.N. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, S.C.; Stadelmann, C.; Spreer, A.; Brück, W.; Nau, R.; Gerber, J. Increased expression of BDNF and proliferation of dentate granule cells after bacterial meningitis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.C.; Huang, H.-B.; Tseng, H.-Y.H.; Lu, M.-C. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor suppressed proinflammatory cytokines secretion and enhanced MicroRNA(miR)-3168 expression in macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenone, A.; Gill, J.S.; Zacharias, D.A.; Windebank, A.J. Expression of high- and low-affinity neurotrophin receptors on human transformed B lymphocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 1996, 64, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaretti, A.; Antonelli, A.; Piastra, M.; Genovese, O.; Polidori, G.; Aloe, L. Expression of neurotrophic factors in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of children with viral and bacterial meningoencephalitis. Acta Paediatr. 2004, 93, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górnik, K.; Kuźna-Grygiel, W. Histological studies of selected organs of mice experimentally infected with Acanthamoeba spp. Folia Morphol. 2005, 64, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Numakawa, T.; Suzuki, S.; Kumamaru, E.; Adachi, N.; Richards, M.; Kunugi, H. BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocciti, V. What is the role of brain derived neurotrophic factor in multiple sclerosis neuroinflammation? Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, R.R.; Boggs, A.; Leider, D.; Kraemer, P.; Brown, R.; Scheff, S.W.; Seroogy, K.B. Effects of exercise following lateral fluid percussion brain injury in rats. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 1998, 12, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzniewska, B.; Rejmak, E.; Malik, A.R.; Jaworski, J.; Kaczmarek, L.; Kalita, K. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression in neurons via the serum response factor/c-Fos pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, J.; Peng, W.; Chen, W. Neurotrophin-3 accelerates reendothelialization through inducing EPC mobilization and homing. Open Life Sci. 2020, 15, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagappan, G.; Zaitsev, E.; Senatorov, V.V., Jr.; Yang, J.; Hempstead, B.L.; Lu, B. Control of extracellular cleavage of ProBDNF by high frequency neuronal activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kot, K.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Ptak, M.; Roszkowska, P.; Kram, A. Histological changes in the kidneys and heart in experimental Acanthamoebiasis in immunocompetent and immunosuppressed hosts. Folia Biol. 2021, 69, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.P.; Nishiyama, N. Neurotrophic factor gene expression in astrocytes during development and following injury. Brain Res. Bull. 1994, 35, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnerbauer, M.; Rothhammer, V. Protective functions of reactive astrocytes following central nervous system insult. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 573256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnone, G.; De Benedetti, F.; Bracci-Laudiero, L. NGF and its receptors in the regulation of inflammatory response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlfeld, R. Neurotrophic cross-talk between the nervous and immune systems: Relevance for repair strategies in multiple sclerosis? J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 265, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.X.; Song, J.; Huang, X.; HuiLin, G. Granulomatous amoebic encephalitis presenting as a solitary mass lesion. Radiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massilamany, C.; Marciano-Cabral, F.; da Rocha-Azevedo, B.; Jamerson, M.; Gangaplara, A.; Steffen, D.; Zabad, R.; Illes, Z.; Sobel, R.A.; Reddy, J. SJL mice infected with Acanthamoeba castellanii develop central nervous system autoimmunity through the generation of cross-reactive T cells for myelin antigens. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardner, J.; Ghorpade, A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1: The TIMPed balance of matrix metalloproteinases in the central nervous system. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 74, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noga, O.; Hanf, G.; Görges, D.; Dinh, Q.T.; Groneberg, D.A.; Suttorp, N.; Kunkel, G. Regulation of NGF and BDNF by dexamethasone and theophylline in human peripheral eosinophils in allergics and non-allergics. Regul. Pept. 2005, 132, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, G.A.; Dencoff, J.E.; Correa, N., Jr.; Reiners, M.; Ford, C.C. Effect of steroids on CSF matrix metalloproteinases in multiple sclerosis: Relation to blood-brain barrier injury. Neurology 1996, 46, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, C.F. Neurotrophin-4: The odd one out in the neurotrophin family. Neurochem. Res. 1996, 21, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.Y.; Kim, M.W.; Bang, M.S.; Kim, M. Increased expression of neurotrophin 4 following focal cerebral ischemia in adult rat brain with treadmill exercise. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e52461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thoenen, H. Neurotrophins and neuronal plasticity. Science 1995, 270, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, Y.; Kira, R.; Takahata, Y.; Gondo, K.; Mizuno, Y.; Aoki, T.; Hara, T. Neurotrophin-4 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in cerebrospinal fluid from meningitis/encephalitis patients. Pediatr. Neurol. 2002, 27, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.T.; Li, L.Y.; Zou, X.L.; Song, X.B.; Hu, Y.L.; Feng, Z.T.; Wang, T.T. Immunohistochemical distribution of NGF, BDNF, NT-3, and NT-4 in adult rhesus monkey brains. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Kot, K.; Gutowska, I.; Kolasa-Wołosiuk, A.; Chlubek, D.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. Expression and activity of COX-1 and COX-2 in Acanthamoeba sp.-infected lungs according to the host immunological status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Markowitz, S.M.; Sobieski, T.; Martinez, A.J.; Duma, R.J. Experimental Acanthamoeba infections in mice pretreated with methylprednisolone or tetracycline. Am. J. Pathol. 1978, 92, 733–744. [Google Scholar]
- Derda, M.; Wojtkowiak-Giera, A.; Kolasa-Wołosiuk, A.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Hadaś, E.; Jagodziński, P.P.; Wandurska-Nowak, E. Acanthamoeba infection in lungs of mice expressed by toll-like receptors (TLR2 and TLR4). Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 165, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanocha, N.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Maciejewska, A.; Sawczuk, M.; Wilk, A.; Kuźna-Grygiel, W. The occurrence Acanthamoeba (free living amoeba) in environmental and respiratory samples in Poland. Acta Protozool. 2009, 48, 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Gutowska, I.; Kot, K.; Metryka, E.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.I. Relationship between antioxidant defense in Acanthamoeba spp. infected lungs and host immunological status. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 193, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culbertson, C.G.; Ensminger, P.W.; Overton, W.M. The isolation of additional strains ff pathogenic Hartmanella sp. (Acanthamoeba): Proposed culture method for application to biological material. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1965, 43, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Kot, K.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Kapczuk, P.; Łanocha, A.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.I. Neurotrophic Factors in Experimental Cerebral Acanthamoebiasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094931
Łanocha-Arendarczyk N, Kot K, Baranowska-Bosiacka I, Kapczuk P, Łanocha A, Kosik-Bogacka DI. Neurotrophic Factors in Experimental Cerebral Acanthamoebiasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094931
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁanocha-Arendarczyk, Natalia, Karolina Kot, Irena Baranowska-Bosiacka, Patrycja Kapczuk, Aleksandra Łanocha, and Danuta Izabela Kosik-Bogacka. 2022. "Neurotrophic Factors in Experimental Cerebral Acanthamoebiasis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094931
APA StyleŁanocha-Arendarczyk, N., Kot, K., Baranowska-Bosiacka, I., Kapczuk, P., Łanocha, A., & Kosik-Bogacka, D. I. (2022). Neurotrophic Factors in Experimental Cerebral Acanthamoebiasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094931






