Regulation of Myeloid Dendritic Cells by Synthetic and Natural Compounds for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dendritic Cells
3. The Role of Dendritic Cells in Pathogenesis of RA
4. DC-Targeting Strategies for the Treatment of RA
5. Compounds with Therapeutic Efficacy/Potential for RA through DC Regulation
5.1. Synthetic Compounds
5.2. Natural Compounds
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.J.N.P.G. Primer arthritis rheumatoid. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, S.T.; Steyn, F.J.; McCombe, P.A. Gender differences in autoimmune disease. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 35, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smolen, J.S.; Steiner, G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolati, S.; Sadreddini, S.; Rostamzadeh, D.; Ahmadi, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Yousefi, M. Utilization of nanoparticle technology in rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 80, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, D.L.; Wolfe, F.; Huizinga, T.W.J. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpízar-Rodríguez, D.; Pluchino, N.; Canny, G.; Gabay, C.; Finckh, A. The role of female hormonal factors in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2016, 56, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woolf, A.D.; Pfleger, B. Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions. Bull. World Health Organ. 2003, 81, 646–656. [Google Scholar]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerurkar, L.; Siebert, S.; McInnes, I.B.; Cavanagh, J. Rheumatoid arthritis and depression: An inflammatory perspective. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 6, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokka, T.; Abelson, B.; Pincus, T. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: 2008 update. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, S35–S61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klareskog, L.; Padyukov, L.; Rönnelid, J.; Alfredsson, L. Genes, environment and immunity in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klareskog, L.; Padyukov, L.; Alfredsson, L. Smoking as a trigger for inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2007, 19, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmström, V.; Catrina, A.I.; Klareskog, L. The immunopathogenesis of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: From triggering to targeting. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 17, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-H.; Huang, N.; Chen, Y.-M.; Chen, T.-J.; Chou, P.; Lee, Y.-L.; Chou, Y.-J.; Lan, J.-L.; Lai, K.-L.; Lin, C.-H.; et al. Association between a history of periodontitis and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A nationwide, population-based, case–control study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 72, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potempa, J.; Mydel, P.; Koziel, J. The case for periodontitis in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergot, A.-S.; Giri, R.; Thomas, R. The microbiome and rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 33, 101497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, J.A.; Karlson, E.W. The Roles of Cigarette Smoking and the Lung in the Transitions Between Phases of Preclinical Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klareskog, L.; Rönnelid, J.; Lundberg, K.; Padyukov, L.; Alfredsson, L. Immunity to Citrullinated Proteins in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 651–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smolen, J.S. Insights into the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A paradigm in medicine. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Ladner, U.; Pap, T.; Gay, R.E.; Neidhart, M.; Gay, S. Mechanisms of Disease: The molecular and cellular basis of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2005, 1, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Buckley, C.D.; Isaacs, J.D. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis—Shaping the immunological landscape. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemble, S.; Croft, A.P. Critical Role of Synovial Tissue–Resident Macrophage and Fibroblast Subsets in the Persistence of Joint Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 715894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Hong, W.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Körner, H.; Wei, W. Ontology and Function of Fibroblast-Like and Macrophage-Like Synoviocytes: How Do They Talk to Each Other and Can They Be Targeted for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrivastava, A.K.; Pandey, A. Inflammation and rheumatoid arthritis. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 69, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.T.N. Nanotherapeutic approaches for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danks, L.; Takayanagi, H. Immunology and bone. J. Biochem. 2013, 154, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, D.; Young, J.W.; Banchereau, J. Dendritic Cells. Adv. Immunol. 1999, 72, 255–324. [Google Scholar]
- Collin, M.; Bigley, V. Human dendritic cell subsets: An update. Immunology 2018, 154, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, K.-T.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, T.-T.; Bracci, N.; Lin, C.-C. Dendritic Cells and Antiphospholipid Syndrome: An Updated Systematic Review. Life 2021, 11, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, M.; Mok, W.H.; Radford, K.J. Human dendritic cell subsets and function in health and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4309–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, I.F.; Silk, J.D.; Gileadi, U.; Salio, M.; Mathew, B.; Ritter, G.; Schmidt, R.; Harris, A.L.; Old, L.; Cerundolo, V. NKT Cells Enhance CD4+ and CD8+ T Cell Responses to Soluble Antigen In Vivo through Direct Interaction with Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 5140–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, M.J.; Crowe, N.Y.; Hayakawa, Y.; Takeda, K.; Yagita, H.; Godfrey, D. NKT cells—Conductors of tumor immunity? Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, T.Y.F.; Hwang, Y.Y.; Scanlon, S.T.; Zaghouani, H.; Garbi, N.; Fallon, P.G.; McKenzie, A.N.J. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells license dendritic cells to potentiate memory TH2 cell responses. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hawiger, D.; Inaba, K.; Dorsett, Y.; Guo, M.; Mahnke, K.; Rivera, M.; Ravetch, J.V.; Steinman, R.M.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Dendritic Cells Induce Peripheral T Cell Unresponsiveness under Steady State Conditions in Vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worbs, T.; Hammerschmidt, S.I.; Förster, R. Dendritic cell migration in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmi, H.; Akira, S. TLR Signalling and the Function of Dendritic Cells. Mech. Epithel. Def. 2005, 86, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerboni, S.; Gentili, M.; Manel, N. Diversity of Pathogen Sensors in Dendritic Cells. Adv. Immunol. 2013, 120, 211–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, M.G.; Silva, Z.; Ligeiro, D.; Seixas, E.; Crespo, H.; Carrascal, M.A.; Silva, M.; Piteira, A.R.; Paixão, P.; Lau, J.T.; et al. The phagocytic capacity and immunological potency of human dendritic cells is improved by α2,6-sialic acid deficiency. Immunology 2013, 138, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchereau, J.; Briere, F.; Caux, C.; Davoust, J.; Lebecque, S.; Liu, Y.-J.; Pulendran, B.; Palucka, K. Immunobiology of Dendritic Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 767–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheib, N.; Tiemann, J.; Becker, C.; Probst, H.C.; Raker, V.K.; Steinbrink, K. The Dendritic Cell Dilemma in the Skin: Between Tolerance and Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, A.; de Mingo Pulido, Á.; Ruffell, B. Dendritic Cells and Their Role in Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, K.L.; Ahmed, M.; Das, S.; Gopal, R.; Horne, W.; Connell, T.D.; Moynihan, K.D.; Kolls, J.K.; Irvine, D.J.; Artyomov, M.N.; et al. Targeting dendritic cells to accelerate T-cell activation overcomes a bottleneck in tuberculosis vaccine efficacy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jongbloed, S.L.; Lebre, M.C.; Fraser, A.R.; Gracie, J.A.; Sturrock, R.D.; Tak, P.P.; McInnes, I.B. Enumeration and phenotypical analysis of distinct dendritic cell subsets in psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 8, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohnmacht, C.; Pullner, A.; King, S.B.; Drexler, I.; Meier, S.; Brocker, T.; Voehringer, D. Constitutive ablation of dendritic cells breaks self-tolerance of CD4 T cells and results in spontaneous fatal autoimmunity. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, B.P.; Conacher, M.; Hunter, D.; McInnes, I.B.; Liew, F.Y.; Brewer, J.M. A Novel Dendritic Cell-Induced Model of Erosive Inflammatory Arthritis: Distinct Roles for Dendritic Cells in T Cell Activation and Induction of Local Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 7071–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geem, D.; Harusato, A.; Flannigan, K.; Denning, T.L. Harnessing Regulatory T Cells for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, T.P.W.; Lai, R.; Dabbagh, L.; Wallace, T.M.; De Gara, C.J. Survival in rectal cancer is predicted by T cell infiltration of tumour-associated lymphoid nodules. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 161, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmester, G.R.; Feist, E.; Dörner, T. Emerging cell and cytokine targets in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 10, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuto, O.; Di Bartolo, V.; Michel, F.M. Tailoring T-cell receptor signals by proximal negative feedback mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingren, A.G.; Parra, E.; Varga, M.; Kalland, T.; Sjogren, H.-O.; Hedlund, G.; Dohlsten, M. T Cell Activation Pathways: B7, LFA-3, and ICAM-1 Shape Unique T Cell Profiles. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 37, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, A. Autoreactive T cells in type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2881–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentcheva-Hoang, T.; Egen, J.G.; Wojnoonski, K.; Allison, J.P. B7-1 and B7-2 Selectively Recruit CTLA-4 and CD28 to the Immunological Synapse. Immunity 2004, 21, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogel, I.; Kasran, A.; Cremer, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Boon, L.; Van Gool, S.W.; Ceuppens, J.L. CD28/CTLA-4/B7 costimulatory pathway blockade affects regulatory T-cell function in autoimmunity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.B.; Langridge, W.H.R. The function of myeloid dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutzky, V.; Hannawi, S.; Thomas, R. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Dendritic cells. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebre, M.C.; Jongbloed, S.L.; Tas, S.W.; Smeets, T.J.; McInnes, I.B.; Tak, P.P. Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovium Contains Two Subsets of CD83−DC-LAMP− Dendritic Cells with Distinct Cytokine Profiles. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, G.; Lebecque, S.; Miossec, P. Anatomic Localization of Immature and Mature Dendritic Cells in an Ectopic Lymphoid Organ: Correlation with Selective Chemokine Expression in Rheumatoid Synovium. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5333–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakey, R.L.; Morgan, T.G.; Rowan, A.D.; Isaacs, J.D.; Cawston, T.E.; Hilkens, C.M.U. A novel paradigm for dendritic cells as effectors of cartilage destruction. Rheumatology 2008, 48, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jongbloed, S.L.; Benson, R.A.; Nickdel, M.B.; Garside, P.; McInnes, I.B.; Brewer, J.M. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells regulate breach of self-tolerance in autoimmune arthritis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenink, M.H.; Han, W.; Toes, R.E.M.; Radstake, T.R.D.J. Dendritic Cells and their Potential Implication in Pathology and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 188, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škoberne, M.; Beignon, A.-S.; Larsson, M.; Bhardwaj, N. Apoptotic Cells at the Crossroads of Tolerance and Immunity. Role Apoptosis Infect. 2005, 289, 259–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, A.E.; Thomson, A.W. Tolerogenic dendritic cells and the quest for transplant tolerance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, S.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, N.-C.; Choi, H.-J.; Song, J.-Y.; Seo, H.G.; Choi, J.; Jung, S.Y.; Kang, S.; Choi, Y.-S.; et al. Rosiglitazone-mediated dendritic cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 115, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.E.; Swan, D.J.; Wong, O.Y.; Buck, M.; Eltherington, O.; Harry, R.A.; Patterson, A.M.; Pratt, A.G.; Reynolds, G.; Doran, J.-P.; et al. Tolerogenic dendritic cells generated with dexamethasone and vitamin D3 regulate rheumatoid arthritis CD4+ T cells partly via transforming growth factor-β1. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 187, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benham, H.; Nel, H.J.; Law, S.C.; Mehdi, A.M.; Street, S.; Ramnoruth, N.; Pahau, H.; Lee, B.T.; Ng, J.; Brunck, M.E.G.; et al. Citrullinated peptide dendritic cell immunotherapy in HLA risk genotype–positive rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 290ra87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amir, M.; Campbell, S.; Kamenecka, T.M.; Solt, L.A. Pharmacological modulation and genetic deletion of REV-ERBα and REV-ERBβ regulates dendritic cell development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shen, J.; Liu, L.; Lu, X.; Xue, J. Vasoactive intestinal peptide-induced tolerogenic dendritic cells attenuated arthritis in experimental collagen-induced arthritic mice. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Van Lieshout, A.W.T.; Van Riel, P.L.C.M.; Berg, W.B.V.D.; Adema, G.J. Dendritic cells, Fc receptors, and Toll-like receptors: Potential allies in the battle against rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okano, T.; Saegusa, J.; Nishimura, K.; Takahashi, S.; Sendo, S.; Ueda, Y.; Morinobu, A. 3-bromopyruvate ameliorate autoimmune arthritis by modulating Th17/Treg cell differentiation and suppressing dendritic cell activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep42412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Li, X.; Luo, X.; He, J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Han, Y.; Jie, H.; Zhuang, J.; Li, Y.; et al. The mechanisms of hydroxychloroquine in rheumatoid arthritis treatment: Inhibition of dendritic cell functions via Toll like receptor 9 signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matasić, R.; Dietz, A.; Vuk-Pavlović, S. Maturation of human dendritic cells as sulfasalazine target. Croat. Med. J. 2001, 42, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Luo, J.; Yan, C.; Hao, R.; Zhao, X.; Jia, R.; He, J.; Xu, D.; Miao, M.; Li, X. Methotrexate, combined with cyclophosphamide attenuates murine collagen induced arthritis by modulating the expression level of Breg and DCs. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 90, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldinucci, A.; Biagioli, T.; Manuelli, C.; Repice, A.M.; Massacesi, L.; Ballerini, C. Modulating dendritic cells (DC) from immunogenic to tolerogenic responses: A novel mechanism of AZA/6-MP. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 218, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandaru, M.; Pasham, V.; Yang, W.; Bobbala, D.; Rotte, A.; Lang, F. Effect of Azathioprine on Na+/H+Exchanger Activity in Dendritic Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, B.M.; Zeyda, M.; Stuhlmeier, K.; Grisar, J.; Smolen, J.S.; Watschinger, B.; Stulnig, T.M.; Hörl, W.H.; Zlabinger, G.J.; Säemann, M.D. The active metabolite of leflunomide, A77 1726, interferes with dendritic cell function. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 7, R694–R703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldwin, H.M.; Ito-Ihara, T.; Isaacs, J.D.; Hilkens, C.M.U. Tumour necrosis factor alpha blockade impairs dendritic cell survival and function in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 69, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richez, C.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Dumoulin, C.; Dehais, J.; Moreau, J.-F.; Blanco, P. Myeloid dendritic cells correlate with clinical response whereas plasmacytoid dendritic cells impact autoantibody development in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with infliximab. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; He, Y.; Han, J.; Zhuang, J.; He, J.; Sun, E. Not only anti-inflammation, etanercept abrogates collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting dendritic cell migration and maturation. Central Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 44, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres-Ejarque, R.; Ale, H.B.; Grys, K.; Tosi, I.; Solanky, S.; Ainali, C.; Catak, Z.; Sreeneebus, H.; Saklatvala, J.; Dand, N.; et al. Enhanced NF-κB signaling in type-2 dendritic cells at baseline predicts non-response to adalimumab in psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richez, C.; Barnetche, T.; Khoryati, L.; Duffau, P.; Kostine, M.; Contin-Bordes, C.; Blanco, P.; Schaeverbeke, T. Tocilizumab Treatment Decreases Circulating Myeloid Dendritic Cells and Monocytes, 2 Components of the Myeloid Lineage. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalder, R.; Zhang, B.; Wrobel, L.J.; Boehncke, W.; Brembilla, N.C. The Janus Kinase inhibitor tofacitinib impacts human dendritic cell differentiation and favours M1 macrophage development. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 29, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, S.; Nakayamada, S.; Sakata, K.; Kitanaga, Y.; Ma, X.; Lee, S.; Ishii, A.; Yamagata, K.; Nakano, K.; Tanaka, Y. Janus Kinase Inhibitor Baricitinib Modulates Human Innate and Adaptive Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbongue, J.C.; Nieves, H.A.; Torrez, T.W.; Langridge, W.H.R. The Role of Dendritic Cell Maturation in the Induction of Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Feng, P.; Yin, Y.; Bushley, K.; Spatafora, J.W.; Wang, C. Cyclosporine Biosynthesis in Tolypocladium inflatum Benefits Fungal Adaptation to the Environment. mBio 2018, 9, e01211-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawaya, A.; Costa, Y.D.; Mazzafera, P. Unraveling the Biosynthesis of Pilocarpine in Pilocarpus microphyllus. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Jie, H.; He, Y.; Han, J.; He, J.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, E. Apigenin, a potent suppressor of dendritic cell maturation and migration, protects against collagen-induced arthritis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 20, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, C.H.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-C.; Lehman, C.W.; Wang, S.-P.; Chen, D.-Y.; Tsai, S.-W.; Lin, C.-C. Atractylodin Suppresses Dendritic Cell Maturation and Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in a Mouse Model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6773–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Jiao, Q.; Ding, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, R.; Shan, L.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Berberine induces dendritic cell apoptosis and has therapeutic potential for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 63, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Li, S.; Lin, W.-Y.; Lehman, C.W.; Bracci, N.R.; Tsai, S.-W. Alleviation of Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Crotonoside through Modulation of Dendritic Cell Differentiation and Activation. Plants 2020, 9, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L. Insights into the modulatory role of cyclosporine A and its research advances in acute inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 93, 107420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.-Y.; Yan, M.; Kim, S.B.; Ravikumar, S.; Kwon, S.-R.; Vanarsa, K.; Kim, H.-Y.; Davis, L.S.; Mohan, C. Green Tea Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Suppresses Autoimmune Arthritis Through Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase Expressing Dendritic Cells and the Nuclear Factor, Erythroid 2-Like 2 Antioxidant Pathway. J. Inflamm. 2015, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-R.; Chen, D.-Y.; Chu, C.-L.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.-K.; Wu, C.-L.; Lin, C.-C. Naringenin inhibits dendritic cell maturation and has therapeutic effects in a murine model of collagen-induced arthritis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1467–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.-Y.; Chang, Y.; Sun, X.-J.; Wei, F.; Wu, Y.-J.; Dai, X.; Xu, S.; Wu, H.-X.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.-Z.; et al. Regulatory effects of paeoniflorin-6′-O-benzene sulfonate (CP-25) on dendritic cells maturation and activation via PGE2-EP4 signaling in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Xiao, L.; Ouyang, G.; Shen, Y.; Huo, R.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, B.; et al. Total glucosides of paeony inhibits Th1/Th17 cells via decreasing dendritic cells activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 280, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

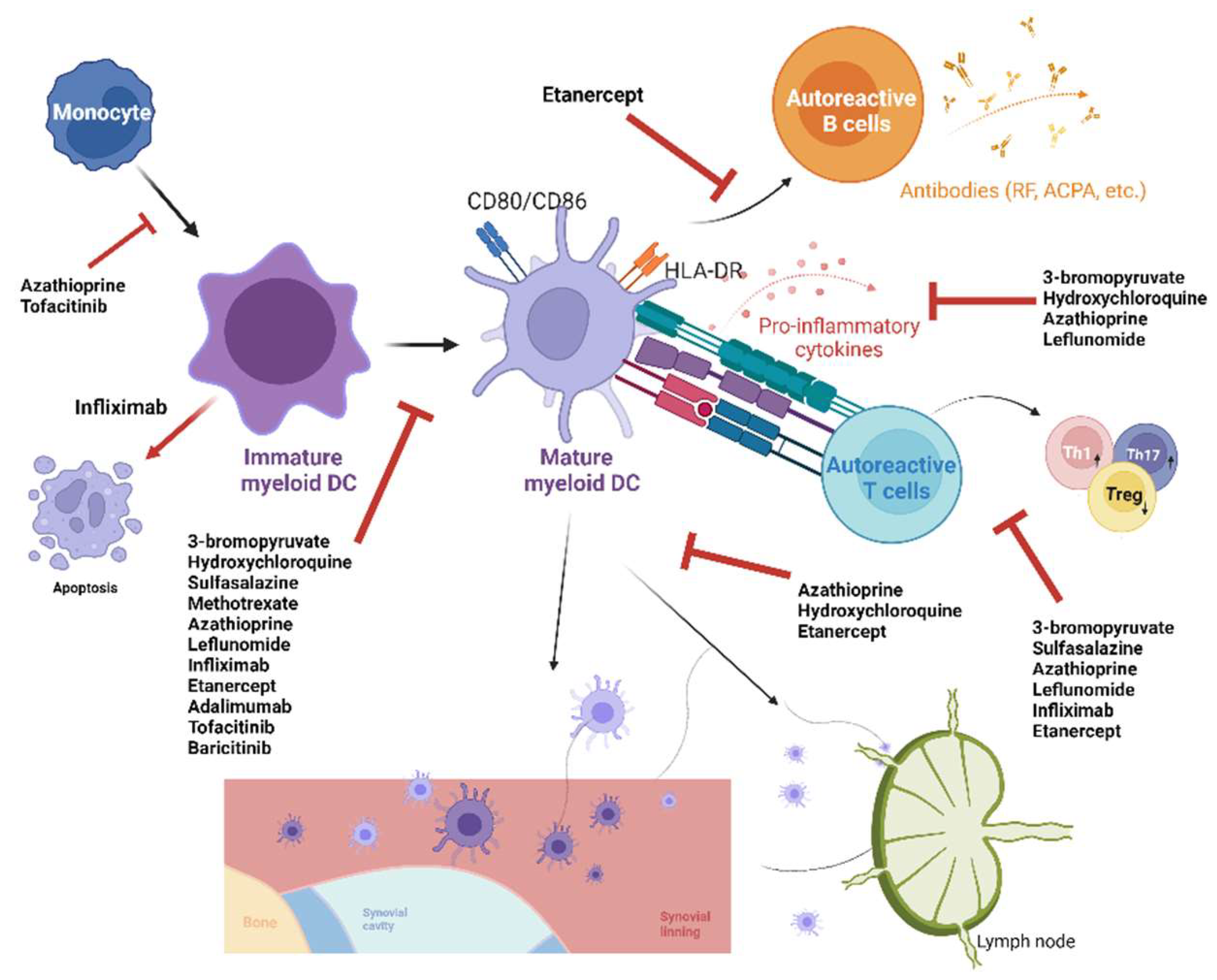
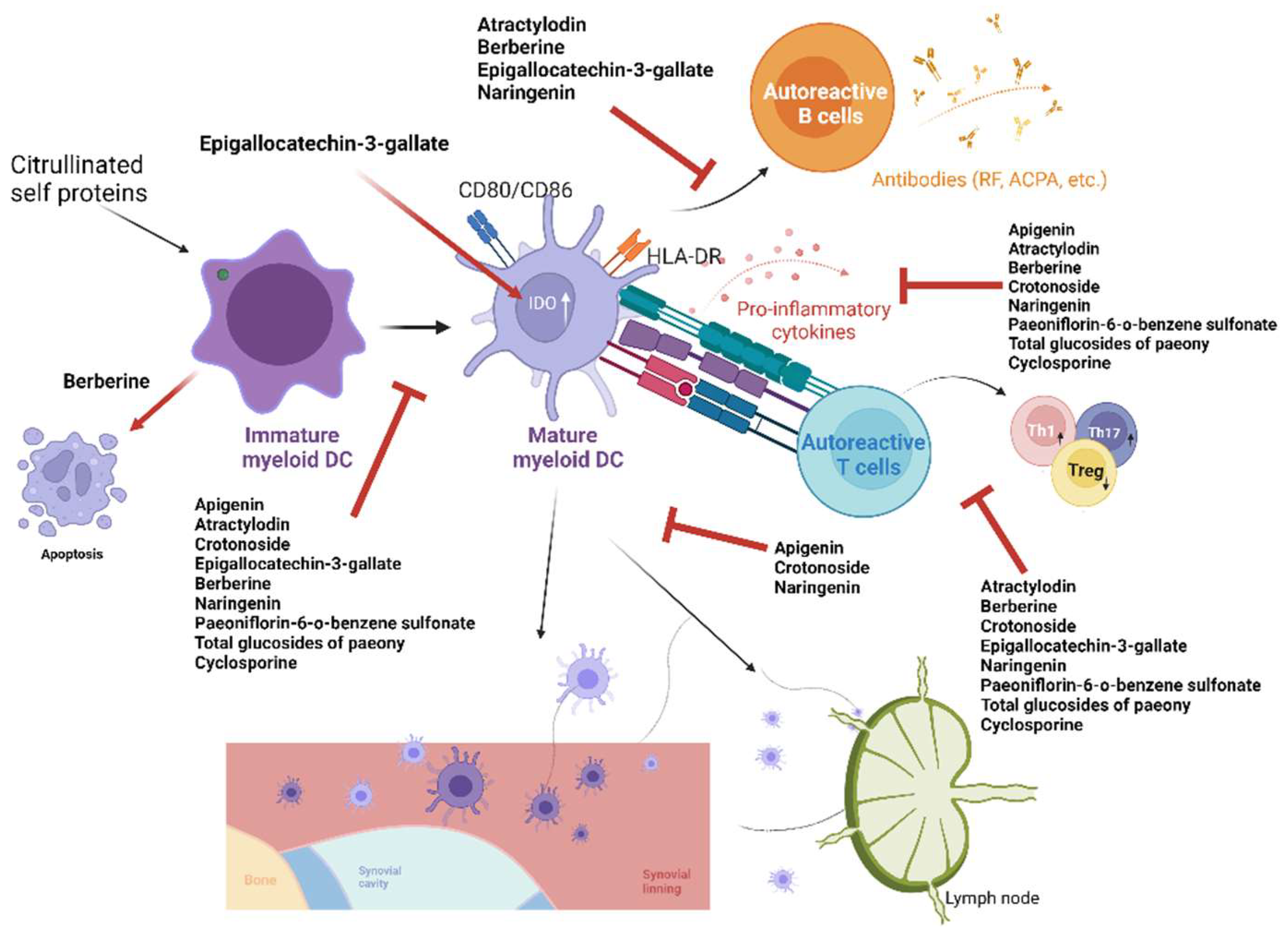
| Synthetic Compounds | In Vitro Effect on DCs | In Vivo/Ex Vivo Effect on DCs | Reference Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-bromopyruvate | Suppressed maturation and secretion of inflammatory cytokines of BMDCs | Suppressed downstream Th17 response and increased Treg response | [70] |
| Conventional DMARDs | |||
| Hydroxychloroquine | Suppressed maturation, migration, secretion of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood DCs, and maturation and migration of BMDCs | Decreased number of DCs and their maturation in lymph node of mice | [71] |
| Sulfasalazine | Suppressed maturation of moDCs and downstream T-cell proliferation | N.A. | [72] |
| Methotrexate | N.A. | Suppressed maturation of lymph node and splenic DCs in mice | [73] |
| Azathioprine | Suppressed differentiation, activation, migration, and secretion of inflammatory cytokines of moDCs and downstream T-cell proliferation | N.A. | [74,75] |
| Leflunomide | Suppressed maturation and secretion of inflammatory cytokines of moDCs and downstream T-cell proliferation | N.A. | [76] |
| Biologic DMARDs | |||
| Infliximab (an anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody) | Increased moDC apoptosis, suppressed maturation of mDCs, and downstream T-cell proliferation and Th1 response while increasing Treg response | Increased blood DCs | [77,78] |
| Etanercept (a TNF-α receptor fusion protein) | Suppressed maturation and migration of BMDCs | Reduced number and suppressed maturation and migration of lymph node DCs and downstream T- and B-cell proliferation in mice | [79] |
| Adalimumab (an anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody) | Suppressed maturation of moDCs | N.A. | [80] |
| Tocilizumab (an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody) | N.A. | Decreased blood DCs | [81] |
| Targeted synthetic DMARDs | |||
| Tofacitinib | Suppressed differentiation, activation, and maturation of moDCs | N.A. | [82,83] |
| Baricitinib | Suppressed maturation of moDCs | N.A. | [83] |
| Compounds | Source | Animal Models of RA | In Vitro Effect on DCs | In Vivo Effect on DCs | Reference Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apigenin | Matricaria chamomilla | CIA in mice | Suppressed maturation, migration, and secretion of inflammatory cytokines in BMDCs | Suppressed number and maturation of lymph node DCs | [87] |
| Atractylodin | Atractylodis rhizoma | CIA in mice | Suppressed maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide of BMDCs, and downstream T-cell proliferation | Suppressed splenic DC maturation and downstream anti-CII antibody production and splenic Th1/Th17 responses | [88] |
| Berberine | Berberis spp. and Coptis spp. | CIA in mice | Induced apoptosis and suppressed maturation of BMDCs | Induced apoptosis and suppressed maturation of splenic and lymph node DCs with suppressed anti-CII antibody production, and downstream collagen-specific T-cell proliferation and Th1 and Th17 responses | [89] |
| Crotonoside | Croton tiglium | CIA in mice | Suppressed differentiation, maturation, production of inflammatory cytokines in BMDCs, and downstream T-cell activation and Th1/Th17 responses | Suppressed DC infiltration of joint, splenic DC maturation, and downstream Th1 and Th17 responses | [90] |
| Cyclosporine | Tolypocladium inflatum | N.A. | Suppressed maturation and secretion of inflammatory cytokines of BMDCs and downstream T-cell response | N.A. | [91] |
| Epigallocatechin-3-gallate | Camellia sinensis (green tea) | CIA in mice | Increased IDO expression in splenic DCs and downstream Treg response | Increased IDO-producing lymph node DCs, downstream Treg response, and suppressed anti-CII antibody production | [92] |
| Naringenin | Citrus spp. | CIA in mice | Suppressed maturation, migration, and secretion of inflammatory cytokines in BMDCs and downstream T-cell proliferation | Suppressed anti-CII antibody production and downstream Th1 and Th17 responses in the spleen | [93] |
| Paeoniflorin-6′-O-benzene sulfonate (CP-25) | Paeonia | Adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats | Suppressed maturation and secretion of inflammatory cytokines of BMDCs and downstream T-cell proliferation | Suppressed maturation of peripheral blood DCs in patients | [94] |
| Total glucosides of paeony | Paeonia spp. | CIA in mice | Suppressed maturation, production of inflammatory cytokines of BMDCs, and downstream Th1/Th17 responses | Suppressed splenic DC maturation, secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and downstream Th1 and Th17 responses | [95] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umbreen, H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, K.-T.; Lin, C.-C. Regulation of Myeloid Dendritic Cells by Synthetic and Natural Compounds for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010238
Umbreen H, Zhang X, Tang K-T, Lin C-C. Regulation of Myeloid Dendritic Cells by Synthetic and Natural Compounds for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010238
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmbreen, Hira, Xiang Zhang, Kuo-Tung Tang, and Chi-Chien Lin. 2023. "Regulation of Myeloid Dendritic Cells by Synthetic and Natural Compounds for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010238
APA StyleUmbreen, H., Zhang, X., Tang, K.-T., & Lin, C.-C. (2023). Regulation of Myeloid Dendritic Cells by Synthetic and Natural Compounds for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010238







