Effect of Gene Silencing of Translation Initiation Factors eIF(iso)4G and eIF(iso)4E on Sour Cherry Rootstock Resistance to Sharka Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Creation of Vectors for Plant Transformation in Order to Silence the Genes of Translation Initiation Factors
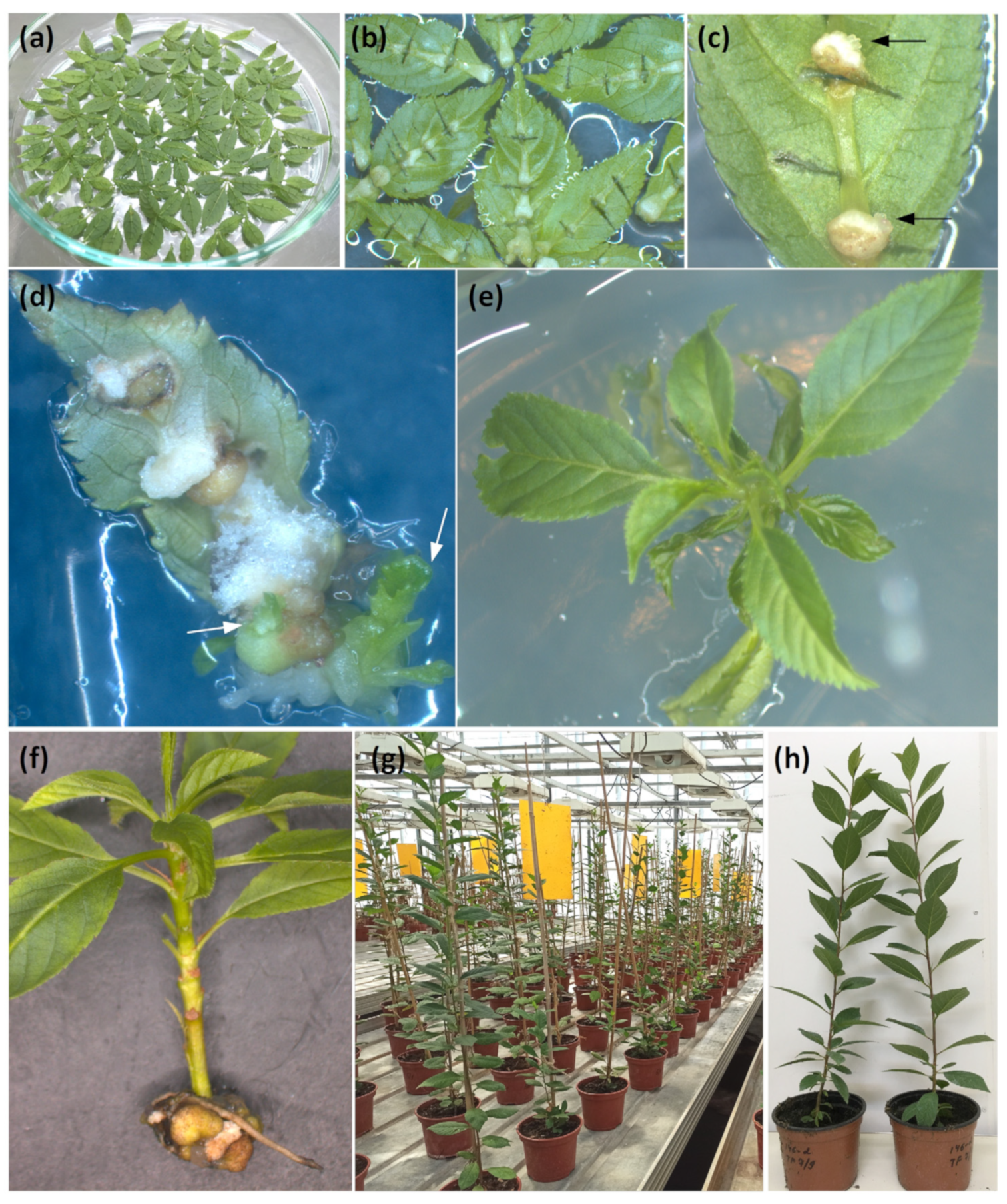
2.2. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of Clonal Rootstock and Production of Putative Transgenic Plants
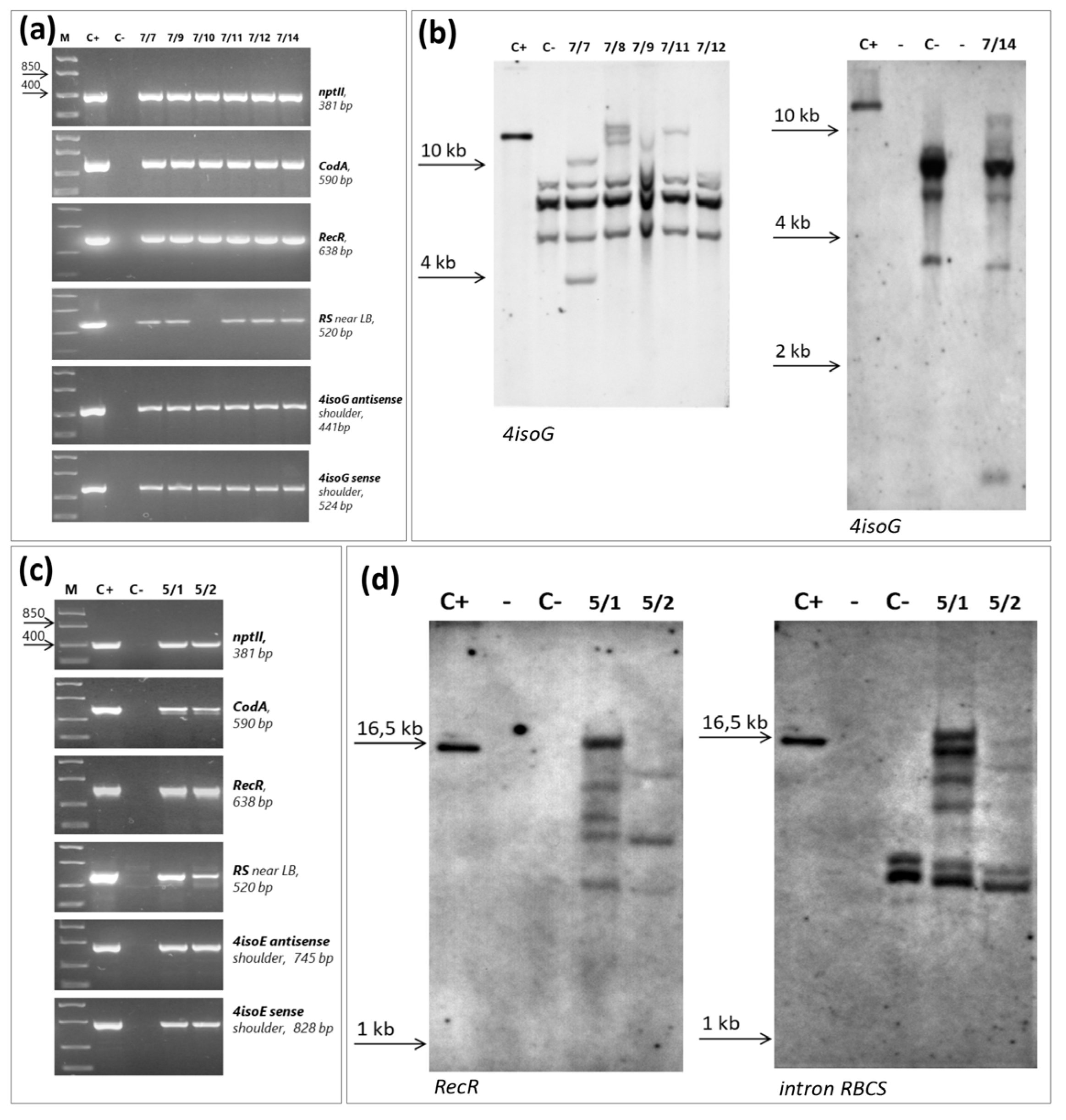
2.3. Molecular Analysis of Putative Transgenic Rootstock 146-2Plants
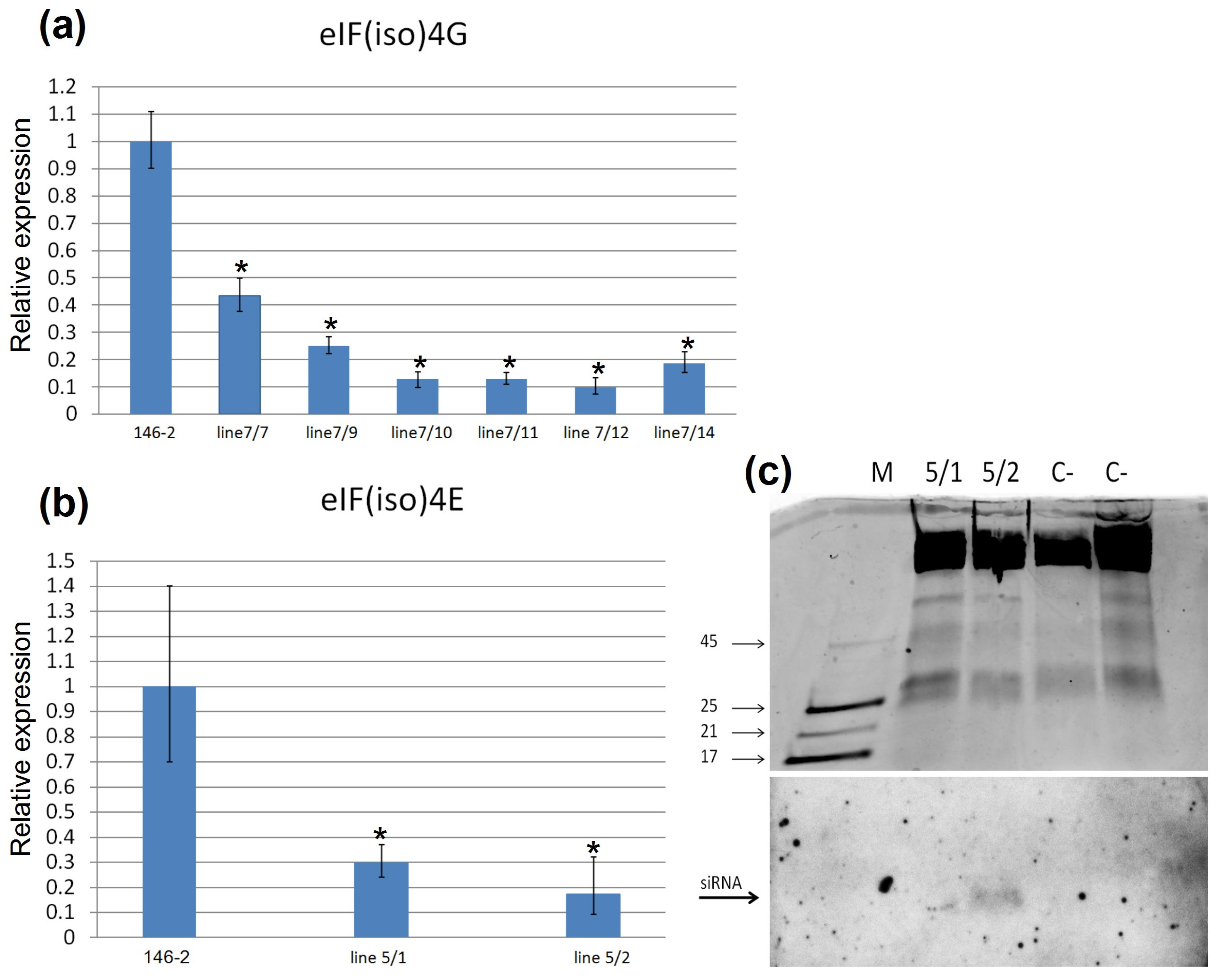
2.4. Analysis of eIF4isoG and eIF4isoE Genes Expression in Transgenic Clones of Rootstock 146-2
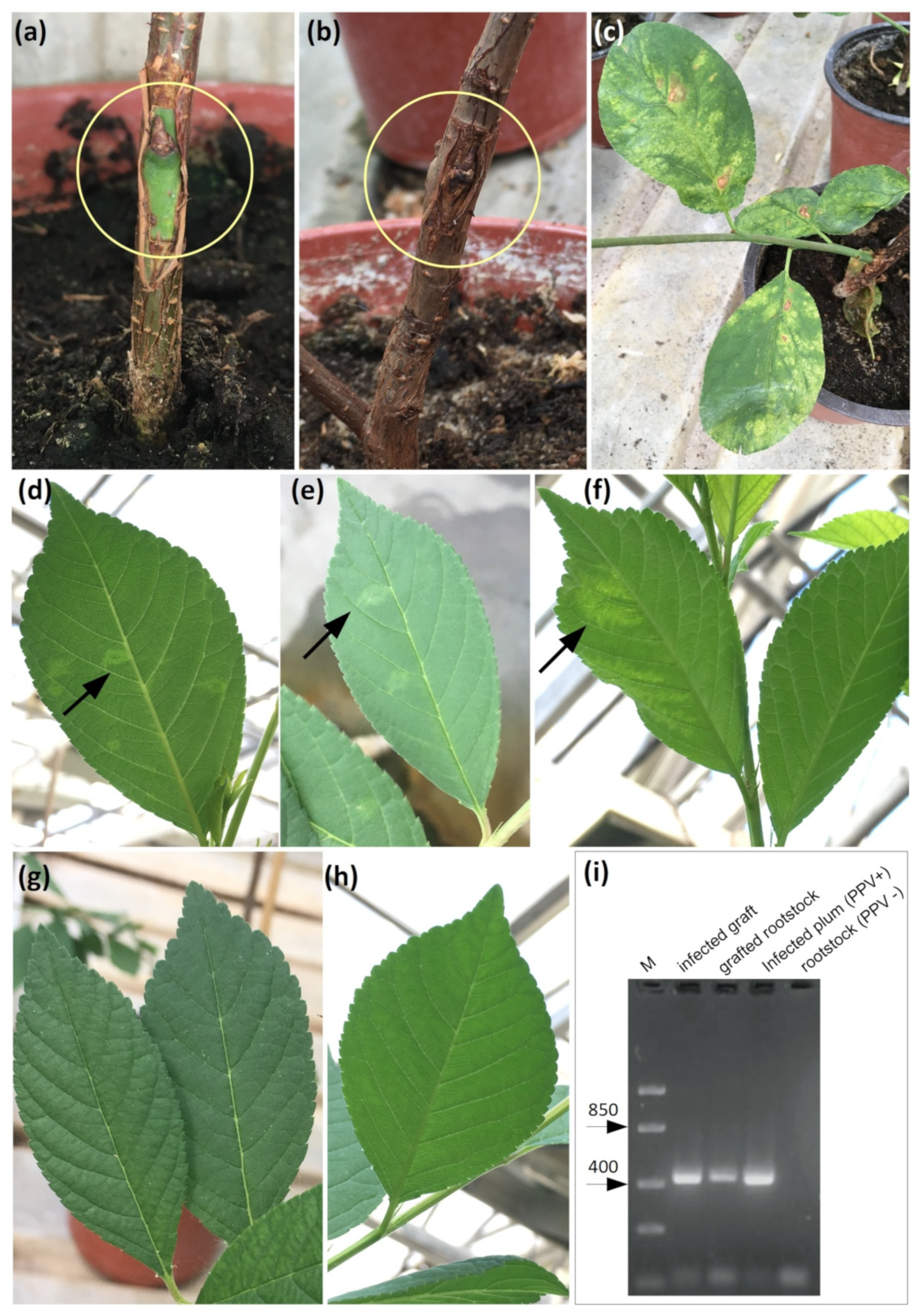
2.5. Analysis of Plant Resistance of Transgenic Rootstock 146-2 Lines to PPV
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Plasmid Construction
4.3. Agrobacterium Strain for Plant Transformation
4.4. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation and Plant Regeneration
4.5. PCR Analysis and Southern Hybridization
4.6. RNA Extraction and qPCR Assay
4.7. Northern Blot Hybridization
4.8. Grafting for Virus Inoculation
4.9. Analysis of Infected Plants
4.9.1. DAS-ELISA
4.9.2. RT-PCR Detection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Németh, M. History and importance of plum pox in stone-fruit production. EPPO Bull. 1994, 24, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambra, M.; Capote, N.; Myrta, A.; Llácer, G. Plum pox virus and the estimated costs associated with sharka disease. EPPO Bull. 2006, 36, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochor, J.; Babula, P.; Adam, V.; Krska, B.; Kizek, R. Sharka: The Past, The Present and The Future. Viruses 2012, 4, 2853–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García, J.A.; Glasa, M.; Cambra, M.; Candresse, T. Plum pox virus and sharka: A model potyvirus and a major disease. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodamilans, B.; Valli, A.; Mingot, A.; León, D.S.; Baulcombe, D.; Lopez-Moya, J.J.; García, J.A. RNA Polymerase Slippage as a Mechanism for the Production of Frameshift Gene Products in Plant Viruses of the Potyviridae Family. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6965–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gildow, F.; Damsteegt, V.; Stone, A.; Schneider, W.; Luster, D.; Levy, L. Plum Pox in North America: Identification of Aphid Vectors and a Potential Role for Fruit in Virus Spread. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 868–874. Available online: http://www.apsnet.org/phyto/ (accessed on 25 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Damsteegt, V. Plum pox virus (sharka). CABI Compend. CABI Int. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, M. Virus certification of fruit tree propagative material in western Europe. In Plant Virus Disease Control; Hadidi, A., Khetarpal, R.K., Koganezawa, H., Eds.; APS Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1998; pp. 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, M.; Martinez-Gomez, P.; Dicenta, F.; Weber, W.E. Resistance of almond cultivars to Plum pox virus (sharka). Plant Breed. 2003, 122, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marandel, G.; Salava, J.; Abbott, A.; Candresse, T.; Decroocq, V. Quantitative trait loci meta-analysis of Plum pox virus resistance in apricot (Prunusarmeniaca L.): New insights on the organization and the identification of genomic resistance factors. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, W. Hypersensitivity—A Possibility for Breeding Sharka Resistant Plum Hybrids. Acta Hortic. 1998, 472, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorza, R.; Ravelonandro, M.; Callahan, A.M.; Cordts, J.M.; Fuchs, M.; Dunez, J.; Gonsalves, D. Transgenic plums (Prunus domestica L.) express the plum pox virus coat protein gene. Plant Cell Rep. 1994, 14, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelonandro, M.; Scorza, R.; Bachelier, J.C.; Labonne, G.; Levy, L.; Damsteegt, V.; Callahan, A.M.; Dunez, J. Resistance of transgenic Prunusdomestica to plum pox virus infection. Plant Dis. 1997, 81, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hily, J.M.; Scorza, R.; Webb, K.; Ravelonandro, M. Accumulation of the long class of siRNA is associated with resistance to Plum pox virus in a transgenic woody perennial plum tree. Mol. Plant—Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hily, J.-M.; Ravelonandro, M.; Damsteegt, V.; Bassett, C.; Petri, C.; Liu, Z.; Scorza, R. Plum Pox Virus Coat Protein Gene Intron-hairpin-RNA (ihpRNA) Constructs Provide Resistance to Plum Pox Virus in Nicotiana benthamiana and Prunus domestica. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2007, 132, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Tian, L.; Brown DC, W.; Svircev, A.M.; Stobbs, L.W.; Sanfaçon, H. Generation of efficient resistance to Plum pox virus (PPV) in Nicotianabenthamiana and Prunusdomestica expressing triple-intron-spanned double-hairpin RNAs simultaneously targeting 5′ and 3′ conserved genomic regions of PPV. Acta Hortic. 2013, 1063, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ravelonandro, M.; Scorza, R.; Michel, H.J.; Briard, P. The efficiency of RNA interference for conferring stable resistance to plum pox virus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2014, 118, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, T.; Pushin, A.; Miroshnichenko, D.; Dolgov, S. Generation of Transgenic Rootstock Plum ((Prunus pumila L. × P. salicinaLindl.) × (P. cerasiferaEhrh.)) Using Hairpin-RNA Construct for Resistance to the Plum pox virus. Agronomy 2018, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sidorova, T.; Mikhailov, R.; Pushin, A.; Miroshnichenko, D.; Dolgov, S. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of Russian Commercial Plum cv. “Startovaya” (Prunus domestica L.) With Virus-Derived Hairpin RNA Construct Confers Durable Resistance to PPV Infection in Mature Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, O.; García, J.A.; Gorris, M.T.; Domínguez, E.; Cambra, M. Generation and characterisation of functional recombinant antibody fragments against RNA replicase NIb from plum pox virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, M.; Esteban, O.; García, J.A.; Peña, L.; Cambra, M. Resistance to Plumpox virus in plants expressing cytosolic and nuclear single-chain antibodies against the viral RNA Nib replicase. Plant Pathol. 2011, 60, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopan, J.; Lv, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J. Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factors Shape RNA Viruses Resistance in Plants. Hortic. Plant J. 2020, 6, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopan, J.; Mou, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Ma, W.; Walsh, J.A.; Hu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B-beta (eIF2B beta), a new class of plant virus resistance gene. Plant J. 2017, 90, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, A.M.; Gosalvez, B.; Sempere, R.N.; Burgos, L.; Aranda, M.A.; Truniger, V. Melon RNA interference (RNAi) lines silenced for Cm-eIF4E show broad virus resistance. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, D.; Timerbaev, V.; Okuneva, A.; Klementyeva, A.; Sidorova, T.; Pushin, A.; Dolgov, S. Enhancement of resistance to PVY in intragenic marker-free potato plants by RNAi-mediated silencing of eIF4E translation initiation factors. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 140, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, J.; Cruz, L.; Trick, H.; Fellers, J. RNAi-Mediated Silencing of Endogenous Wheat Genes EIF(Iso)4E-2 and EIF4G Induce Resistance to Multiple RNA Viruses in Transgenic Wheat. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 2642–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, J.; Brumin, M.; Wolf, D.; Leibman, D.; Klap, C.; Pearlsman, M.; Sherman, A.; Arazi, T.; Gal-On, A. Development of broad virus resistance in non-transgenic cucumber using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyott, D.E.; Sheehan, E.; Molnar, A. Engineering of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated potyvirus resistance in transgene-free Arabidopsis plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moury, B.; Lebaron, C.; Szadkowski, M.; Ben Khalifa, M.; Girardot, G.; Bi, B.A.B.; Koné, D.; Nitiema, L.W.; Fakhfakh, H.; Gallois, J.-L. Knock-out mutation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E2 (eIF4E2) confers resistance to pepper veinal mottle virus in tomato. Virology 2020, 539, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.A.; Lin, Z.D.; Moll, T.; Chauhan, R.D.; Hayden, L.; Renninger, K.; Beyene, G.; Taylor, N.J.; Carrington, J.C.; Staskawicz, B.J.; et al. Simultaneous CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of cassava eIF4E isoforms nCBP-1 and nCBP-2 reduces cassava brown streak disease symptom severity and incidence. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, N.T.; Tran, H.T.; Bui, T.P.; Nguyen, G.T.; Van Nguyen, D.; Ta, D.T.; Trinh, D.D.; Molnar, A.; Pham, N.B.; Chu, H.H.; et al. Simultaneously induced mutations in eIF4E genes by CRISPR/Cas9 enhance PVY resistance in tobacco. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilardi, V.; Etavazza, M. Biotechnological strategies and tools for Plum pox virus resistance: Trans-, intra-, cis-genesis, and beyond. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kohalmi, S.E.; Svircev, A.; Wang, A.; Sanfaçon, H.; Tian, L. Silencing of the Host Factor eIF(iso)4E Gene Confers Plum Pox Virus Resistance in Plum. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e50627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubio, J.; Sánchez, E.; Tricon, D.; Montes, C.; Eyquard, J.-P.; Chague, A.; Aguirre, C.; Prieto, H.; Decroocq, V. Silencing of one copy of the translation initiation factor eIFiso4G in Japanese plum (Prunus salicina) impacts susceptibility to Plum pox virus (PPV) and small RNA production. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 440-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaart, J.G.; Krens, F.A.; Pelgrom, K.T.B.; Mendes, O.; Rouwendal, G.J.A. Effective production of marker-free transgenic strawberry plants using inducible site-specific recombination and a bifunctional selectable marker gene. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2004, 2, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robaglia, C.; Caranta, C. Translation initiation factors: A weak link in plant RNA virus infection. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicaise, V.; Gallois, J.-L.; Chafiai, F.; Allen, L.M.; Schurdi-Levraud, V.; Browning, K.S.; Candresse, T.; Caranta, C.; Le Gall, O.; German-Retana, S. Coordinated and selective recruitment of eIF4E and eIF4G factors for potyvirus infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lellis, A.; Kasschau, K.; Whitham, S.; Carrington, J. Loss-of-susceptibility mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana reveal an essential role for eIF(iso)4E during potyvirus infection. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, M.; Nakahara, K.; Yoshii, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Uyeda, I. Selective involvement of members of the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E family in the infection of Arabidopsis thaliana by potyviruses. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.; Johansen, E.; Eyers, S.; Thomas, C.L.; Noel Ellis, T.H.; Maule, A.J. The potyvirus recessive resistance gene, sbm1, identifies a novel role for translation initiation factor eIF4E in cell-to-cell trafficking. Plant. J. 2004, 40, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combe, J.P.; Petracek, M.E.; van Eldik, G.; Meulewaeter, F.; Twell, D. Translation initiation factors eIF4E and eIFiso4E are required for polysome formation and regulate plant growth in tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 57, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanblaere, T.; Szankowski, I.; Schaart, J.; Schouten, H.; Flachowsky, H.; Broggini, G.A.; Gessler, C. The development of a cisgenic apple plant. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 154, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righetti, L.; Djennane, S.; Berthelot, P.; Cournol, R.; Wilmot, N.; Loridon, K.; Vergne, E.; Chevreau, E. Elimination of the nptII marker gene in transgenic apple and pear with a chemically inducible R/Rs recombinase. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2014, 117, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krens, F.A.; Schaart, J.G.; Van Der Burgh, A.M.; Tinnenbroek-Capel, I.E.M.; Groenwold, R.; Kodde, L.P.; Broggini, G.A.L.; Gessler, C.; Schouten, H.J. Cisgenic apple trees; development, characterization, and performance. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 27, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Timerbaev, V.; Pushin, A.; Dolgov, S. Production of marker-free tomato plants expressing the supersweet protein thaumatin II gene under the control of predominantly fruit-specific promoters. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 139, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timerbaev, V.; Mitiouchkina, T.; Pushin, A.; Dolgov, S. Production of Marker-Free Apple Plants Expressing the Supersweet Protein Gene Driven by Plant Promoter. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourenets, L.; Dolgov, S. Adventitious shoot regeneration from leaf explants of two apricot rootstocks. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1139, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourenets, L.; Pushin, A.; Dolgov, S. Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of 146-2 Russian apricot and plum rootstock with the gfpgene. Acta Hortic. 2020, 1282, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, C.; Burgos, L. Transformation of fruit trees. Useful breeding tool or continued future prospect? Transgenic Res. 2005, 14, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bioassays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, J.A.; Kuniyuki, A.H. In Vitro Propagation of Paradox Walnut Rootstocks. Hort. Sci. 1984, 19, 507–509. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235909861_In_vitro_propagation_of_Paradox_Walnut_root_stock (accessed on 25 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Quoirin, M.; Lepoivre, P. Improved medium for in vitro culture of Prunus spp. Acta Hortic. 1977, 78, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrander, J.; Kempe, T.; Messing, J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene 1983, 26, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo, G.R.; Stein, P.A.; Ludwig, R.A. A DNA transformation-competent Arabidopsis genomic library in Agro-bacterium. Nat. Biotechnol. 1991, 9, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellaporta, S.L.; Wood, J.; Hicks, J.B. A plant DNA minipreparation: Version II. Plant. Mol. Biol. Rep. 1983, 1, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, L.; Fonseca, B.; González, S.; Baeza-Yates, R.; Cambiazo, V.; Campos, R.; Gonzalez, M.; Orellana, A.; Retamales, J.; Silva, H. A Rapid and Efficient Method for Purifying High Quality Total RNA from Peaches (Prunus persica) for Functional Genomics Analyses. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menzel, W.; Jelkmann, W.; Maiss, E. Detection of four apple viruses by multiplex RT-PCR assays with coamplification of plant mRNA as internal control. J. Virol. Methods 2002, 99, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. The single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction: Twenty-something years on. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, T.; Miroshnichenko, D.; Kirov, I.; Pushin, A.; Dolgov, S. Effect of Grafting on Viral Resistance of Non-transgenic Plum Scion Combined With Transgenic PPV-Resistant Rootstock. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 621954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mourenets, L.; Pushin, A.; Timerbaev, V.; Khmelnitskaya, T.; Gribkov, E.; Andreev, N.; Dolgov, S. Effect of Gene Silencing of Translation Initiation Factors eIF(iso)4G and eIF(iso)4E on Sour Cherry Rootstock Resistance to Sharka Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010360
Mourenets L, Pushin A, Timerbaev V, Khmelnitskaya T, Gribkov E, Andreev N, Dolgov S. Effect of Gene Silencing of Translation Initiation Factors eIF(iso)4G and eIF(iso)4E on Sour Cherry Rootstock Resistance to Sharka Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010360
Chicago/Turabian StyleMourenets, Lilia, Alexander Pushin, Vadim Timerbaev, Tatyana Khmelnitskaya, Eduard Gribkov, Nikita Andreev, and Sergey Dolgov. 2023. "Effect of Gene Silencing of Translation Initiation Factors eIF(iso)4G and eIF(iso)4E on Sour Cherry Rootstock Resistance to Sharka Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010360
APA StyleMourenets, L., Pushin, A., Timerbaev, V., Khmelnitskaya, T., Gribkov, E., Andreev, N., & Dolgov, S. (2023). Effect of Gene Silencing of Translation Initiation Factors eIF(iso)4G and eIF(iso)4E on Sour Cherry Rootstock Resistance to Sharka Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010360






