IL-33 and IL-37: A Possible Axis in Skin and Allergic Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Interleukins: The Proteinic Network behind Immune Responses and Therapies in Generalized Inflammatory States
1.2. IL-37
1.3. IL-33
- Investigate the role of IL-33 and IL-37 and find possible connections between them.
- Focus on the role of IL-37 in cutaneous diseases and possible correlations with IL-33.
- Possible therapeutic usage of IL-37.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
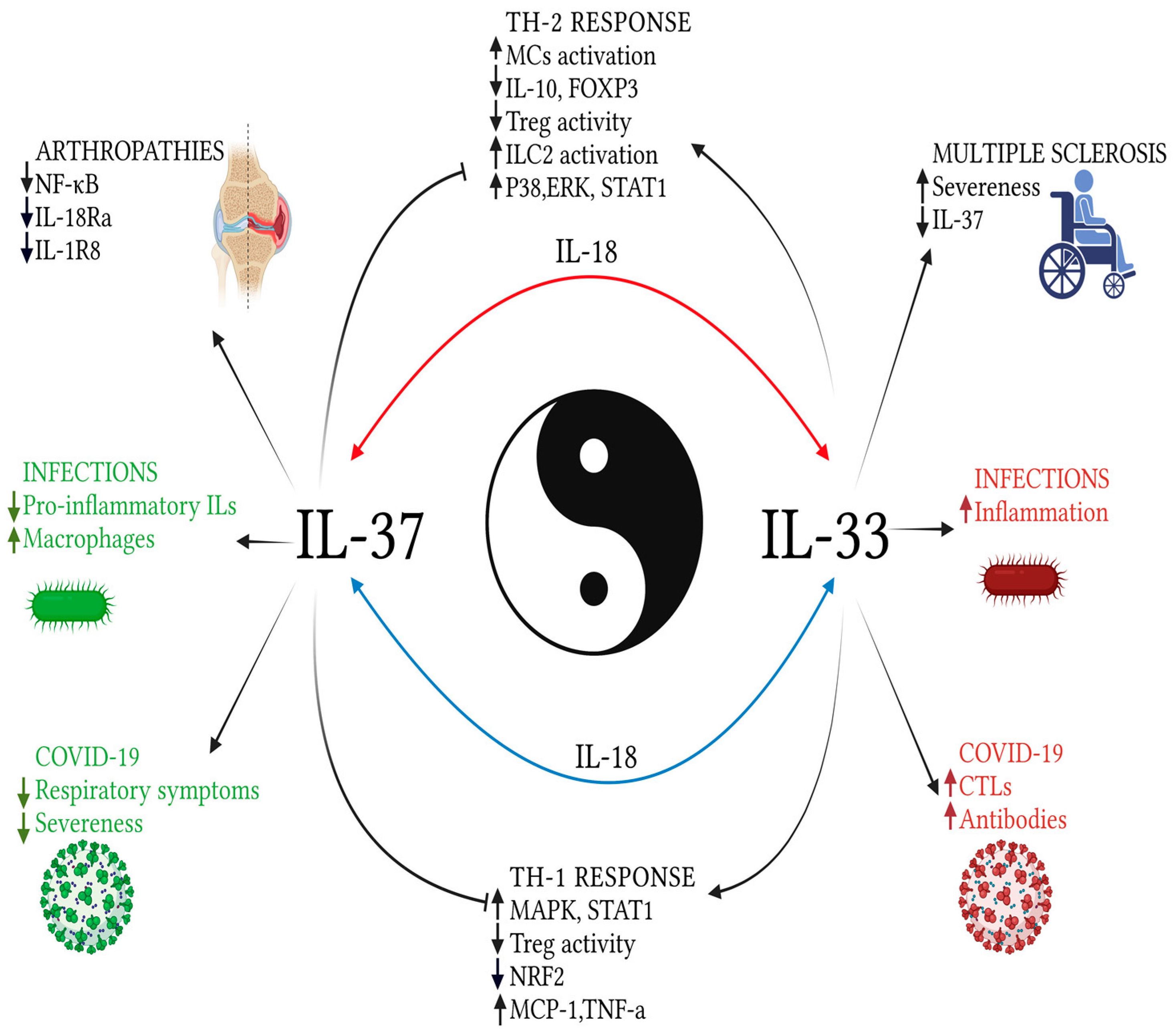
3.1. The Axis IL-33/IL-37: What We Do Know
3.2. Involvement of IL-33 and IL-37 in Clinical Conditions
3.2.1. Atopic Dermatitis and Skin Irritation
3.2.2. Allergic Contact Dermatitis
3.2.3. Psoriasis
3.2.4. Melanoma
3.2.5. Asthma
3.3. Potential Therapeutic Strategies of IL-33 and IL-37 Axis
3.4. Role of the IL-33/IL-37 Interaction in Autoimmune Diseases
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IL | interleukin |
| IL-18BP | IL-18 binding protein |
| IFN | interferon |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| IL-1R | IL-1-receptor |
| DCs | dendritic cells |
| MCs | mast cells |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| STAT1 | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinases |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| M-CSF | Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| MCP | Monocyte Chemotactic Protein |
| CCL12 | Chemokine C-C motif ligand 12 |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| VEGFR2 | Vascular-Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 |
| IgE | immunoglobulin E |
| CTL | cytotoxic T lymphocytes |
| AD | atopic dermatitis |
| Treg | T regulatory cells |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NRF2 | nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 |
| ILCs | lymphoid cells |
| MITF | melanocyte inducing transcription factor |
| TSLP | thymic stromal lymphopoietin |
| SS | systemic sclerosis |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythematosus |
| BD | Behçet’s disease |
References
- Shimizu, M.; Takei, S.; Mori, M.; Yachie, A. Pathogenic Roles and Diagnostic Utility of Interleukin-18 in Autoinflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozario, C.; Martínez-Sobrido, L.; McSorley, H.J.; Chauché, C. Could Interleukin-33 (IL-33) Govern the Outcome of an Equine Influenza Virus Infection? Learning from Other Species. Viruses 2021, 13, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchin, I.; Bourcier, M. The Role of Interleukins in the Pathogenesis of Dermatological Immune-Mediated Diseases. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 4474–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-M.; An, J. Cytokines, Inflammation, and Pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Pomi, F.; Borgia, F.; Custurone, P.; Vaccaro, M.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. Role of HMGB1 in Cutaneous Melanoma: State of the Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, M.; Irrera, N.; Cutroneo, G.; Rizzo, G.; Vaccaro, F.; Anastasi, G.; Borgia, F.; Cannavò, S.; Altavilla, D.; Squadrito, F. Differential Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase Isoforms NNOS and INOS in Patients with Non-Segmental Generalized Vitiligo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Ragoonanan, D.; Mahadeo, K.M.; Gill, J.; Gorlick, R.; Shpal, E.; Li, S. IL12 Immune Therapy Clinical Trial Review: Novel Strategies for Avoiding CRS-Associated Cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 952231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Venanzi Rullo, E.; Berretta, M.; Cacopardo, B.; Pellicanò, G.F.; Nunnari, G.; Guarneri, C. New Generation Biologics for the Treatment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. State of the Art and Considerations about the Risk of Infection. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M. Regulation of Skin Barrier Function via Competition between AHR Axis versus IL-13/IL-4-JAK-STAT6/STAT3 Axis: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdaca, G.; Greco, M.; Tonacci, A.; Negrini, S.; Borro, M.; Puppo, F.; Gangemi, S. IL-33/IL-31 Axis in Immune-Mediated and Allergic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, R.M.; Cristani, M.; Vicchio, T.M.; Alibrandi, A.; Giovinazzo, S.; Saija, A.; Campennì, A.; Trimarchi, F.; Gangemi, S. Increased Serum Interleukin-37 (IL-37) Levels Correlate with Oxidative Stress Parameters in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macleod, T.; Berekmeri, A.; Bridgewood, C.; Stacey, M.; McGonagle, D.; Wittmann, M. The Immunological Impact of IL-1 Family Cytokines on the Epidermal Barrier. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 808012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Bacchi, M.; Bertolino, M. Pharmacokinetics of IL-18 Binding Protein in Healthy Volunteers and Subjects with Rheumatoid Arthritis or Plaque Psoriasis. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 31, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.L.; Renshaw, B.R.; Garka, K.E.; Smith, D.E.; Sims, J.E. Genomic Organization of the Interleukin-1 Locus. Genomics 2002, 79, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kulk, N.; Nold, M.F.; Gräf, R.; Kim, S.-H.; Reinhardt, D.; Dinarello, C.A.; Bufler, P. The IL-1 Family Member 7b Translocates to the Nucleus and Down-Regulates Proinflammatory Cytokines. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5477–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Caraffa, A.; Kritas, S.K.; Ronconi, G.; Lessiani, G.; Toniato, E.; Theoharides, T.C. Mast Cell, pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory: Jekyll and Hyde, the Story Continues. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, M.; Cicero, F.; Mannucci, C.; Calapai, G.; Spatari, G.; Barbuzza, O.; Cannavò, S.P.; Gangemi, S. IL-33 Circulating Serum Levels Are Increased in Patients with Non-Segmental Generalized Vitiligo. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2016, 308, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalesnikoff, J.; Galli, S.J. Antiinflammatory and immunosuppressive functions of mast cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 677, 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Chowdhry, S.; Pizarro, T.T. Opposing Functions of Classic and Novel IL-1 Family Members in Gut Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.; Grimmel, J.; Goedicke, S.; Möbus, A.M.; Bulau, A.-M.; Bufler, P.; Ali, S.; Martin, M.U. Analysis of Nuclear Localization of Interleukin-1 Family Cytokines by Flow Cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 387, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Neff, C.P.; Barber, K.; Hong, J.; Luo, Y.; Azam, T.; Palmer, B.E.; Fujita, M.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A.; et al. Extracellular Forms of IL-37 Inhibit Innate Inflammation in Vitro and in Vivo but Require the IL-1 Family Decoy Receptor IL-1R8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, E.; Stojkovic, S.; Kaun, C.; Lemberger, C.E.; de Martin, R.; Rauscher, S.; Gröger, M.; Maurer, G.; Neumayer, C.; Huk, I.; et al. Interleukin-33 Stimulates GM-CSF and M-CSF Production by Human Endothelial Cells. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 116, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouchaki, E.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Dadgostar, E.; Karami, M.; Nikoueinejad, H.; Akbari, H. Correlation of Serum Levels of IL-33, IL-37, Soluble Form of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 (VEGFR2), and Circulatory Frequency of VEGFR2-Expressing Cells with Multiple Sclerosis Severity. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 16, 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, A.B.R.M.; David, M.A.; de Castro, L.F.; da Silva, R.M.; Longhi, L.N.A.; Blotta, M.H.D.S.L.; Mamoni, R.L. Differential Production of Interleukin-1 Family Cytokines (IL-1β, IL-18, IL-33 and IL-37) in Patients with Paracoccidioidomycosis: Correlation with Clinical Form and Antifungal Therapy. Med. Mycol. 2018, 56, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Amo-Aparicio, J.; Neff, C.P.; Tengesdal, I.W.; Azam, T.; Palmer, B.E.; López-Vales, R.; Bufler, P.; Dinarello, C.A. Role for Nuclear Interleukin-37 in the Suppression of Innate Immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4456–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaremi, S.; Asgarzadeh, A.; Kianfar, H.; Mohammadnia, A.; Asghariazar, V.; Safarzadeh, E. The Role of IL-1 Family of Cytokines and Receptors in Pathogenesis of COVID-19. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 923–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wu, B.; Ji, L.; Chen, P.; Li, F.; Cao, J.; Ke, Y.; Yuan, L.; Min, Z.; et al. Interleukin (IL)-1 Family Cytokines Could Differentiate Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Associated Thrombocytopenia. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, O.; Kaabachi, W.; Dhifallah, I.B.; Hamzaoui, A.; Hamzaoui, K. Elevated Expression of TSLP and IL-33 in Behçet’s Disease Skin Lesions: IL-37 Alleviate Inflammatory Effect of TSLP. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 192, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehat, M.; Talaei, R.; Dadgostar, E.; Nikoueinejad, H.; Akbari, H. Evaluating Serum Levels of IL-33, IL-36, IL-37 and Gene Expression of IL-37 in Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 17, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Tettamanti, L.; Kritas, S.K.; Gallenga, C.E.; D’Ovidio, C.; Mastrangelo, F.; Ronconi, G.; Caraffa, A.; Toniato, E.; Conti, P. IL-33 Mediates Allergy through Mast Cell Activation: Potential Inhibitory Effect of Certain Cytokines. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.E.; Kritas, S.K.; Ronconi, G.; di Emidio, P.; Conti, P. CAR-T Cell Therapy Causes Inflammation by IL-1 Which Activates Inflammatory Cytokine Mast Cells: Anti-Inflammatory Role of IL-37. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 1981–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Diaz, A.; Pavel, A.B.; Fernandes, M.; Lefferdink, R.; Erickson, T.; Canter, T.; Rangel, S.; Peng, X.; Li, R.; et al. Use of Tape Strips to Detect Immune and Barrier Abnormalities in the Skin of Children with Early-Onset Atopic Dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Sun, X.; Zhu, J.; Hon, K.-L.; Jiang, P.; Chu, I.M.-T.; Tsang, M.S.-M.; Lam, C.W.-K.; Zeng, H.; Wong, C.-K. IL-37 Ameliorating Allergic Inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis Through Regulating Microbiota and AMPK-MTOR Signaling Pathway-Modulated Autophagy Mechanism. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, G.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Matsuda-Taniguchi, T.; Takai-Yumine, A.; Takemura, M.; Yan, X.; Furue, M.; Nakahara, T. Natural Compounds Tapinarof and Galactomyces Ferment Filtrate Downregulate IL-33 Expression via the AHR/IL-37 Axis in Human Keratinocytes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 745997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berraïes, A.; Hamdi, B.; Ammar, J.; Hamzaoui, K.; Hamzaoui, A. Increased Expression of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Induced Sputum from Asthmatic Children. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 178, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ding, F.; Zhai, Y.; Tao, W.; Bi, J.; Fan, H.; Yin, N.; Wang, Z. IL-37 Is Protective in Allergic Contact Dermatitis through Mast Cell Inhibition. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Lunding, L.P.; Zissler, U.M.; Vock, C.; Webering, S.; Ehlers, J.C.; Orinska, Z.; Chaker, A.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B.; Lang, N.J.; et al. IL-37 Regulates Allergic Inflammation by Counterbalancing Pro-inflammatory IL-1 and IL-33. Allergy 2022, 77, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, F.; Custurone, P.; Li Pomi, F.; Cordiano, R.; Alessandrello, C.; Gangemi, S. IL-31: State of the Art for an Inflammation-Oriented Interleukin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Dilisio, M.F.; Samadi, F.; Agrawal, D.K. Counteractive Effects of IL-33 and IL-37 on Inflammation in Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, Y.; Okajima, A.; Sakamoto, N.; Hashimoto, A.; Tanabe, R.; Kawajiri, A.; Kawabe, T.; Ishii, N. IL-33-ILC2 Axis Promotes Anti-Tumor CD8+ T Cell Responses via OX40 Signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 637, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Shi, R.; Wu, Y.; Hakimah Binti Ismail, I. Contribution of IL-33/ILC2-Mediated Th2 Cytokines during the Progression of Minimal Change Disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 114, 109493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanik-Kułak, P.; Michalska-Jakubus, M.; Kowal, M.; Krasowska, D. Serum Levels of Selected IL-1 Family Cytokines in Patients with Morphea. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, P.; Gallenga, C.E.; Caraffa, A.; Ronconi, G.; Kritas, S.K. Impact of Mast Cells in Fibromyalgia and Low-grade Chronic Inflammation: Can IL-37 Play a Role? Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, J.R.; Prudente, R.L.; Dias Junior, L.B.; Oliveira Carneiro, F.R.; Sotto, M.N.; Simões Quaresma, J.A. IL-37 and Leprosy: A Novel Cytokine Involved in the Host Response to Mycobacterium leprae Infection. Cytokine 2018, 106, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Ye, J.; Shi, H.; Yin, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Interleukin-37 Is Increased in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease and Associated with Disease Activity. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wen, X.; Hao, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; He, G.; Jiang, X. The Role of IL-37 in Skin and Connective Tissue Diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutet, M.-A.; Nerviani, A.; Pitzalis, C. IL-36, IL-37, and IL-38 Cytokines in Skin and Joint Inflammation: A Comprehensive Review of Their Therapeutic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gemperline, D.C.; Turner, M.J.; Oldach, J.; Molignano, J.; Sims, J.T.; Stayrook, K.R. Transcriptomic Analysis of Healthy and Atopic Dermatitis Samples Reveals the Role of IL-37 in Human Skin. Immunohorizons 2021, 5, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Baek, A.R.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, A.S.; Kim, D.J.; Chin, S.S.; Park, S.W. IL-37 Attenuates Lung Fibrosis by Inducing Autophagy and Regulating TGF-Β1 Production in Mice. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. An IL-1 Family Member Requires Caspase-1 Processing and Signals through the ST2 Receptor. Immunity 2005, 23, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Yin, H.; Gu, C.; Fang, X.; Zhu, R.; Yu, T.; Mi, W.; et al. A Dysregulated Sebum–Microbial Metabolite–IL-33 Axis Initiates Skin Inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20212397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossius, A.H.; Berents, T.L.; Sætre, F.; Nilsen, H.R.; Bradley, M.; Asad, S.; Haraldsen, G.; Sundnes, O.; Holm, J. Early Transcriptional Changes after UVB Treatment in Atopic Dermatitis Include Inverse Regulation of IL-36γ and IL-37. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rønholt, K.; Nielsen, A.L.-L.; Johansen, C.; Vestergaard, C.; Fauerbye, A.; López-Vales, R.; Dinarello, C.A.; Iversen, L. IL-37 Expression Is Downregulated in Lesional Psoriasis Skin. Immunohorizons 2020, 4, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Gallenga, C.E.; Ronconi, G.; Caraffa, A.; Kritas, S.K. Activation of Mast Cells Mediates Inflammatory Response in Psoriasis: Potential New Therapeutic Approach with IL-37. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Fu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Huang, J.; et al. Establishment and Validation of Evaluation Models for Post-Inflammatory Pigmentation Abnormalities. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Pregliasco, F.E.; Bellomo, R.G.; Gallenga, C.E.; Caraffa, A.; Kritas, S.K.; Lauritano, D.; Ronconi, G. Mast Cell Cytokines IL-1, IL-33, and IL-36 Mediate Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis: A Novel Therapeutic Approach with the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines IL-37, IL-38, and IL-1Ra. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Kou, L.; Yin, P.; Jing, Y. Excessive Activation of IL-33/ST2 in Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Promotes Invasion and Metastasis in Ovarian Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 23, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, E.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, N.; McKenzie, A.N.J. Emerging Roles for IL-25 and IL-33 in Colorectal Cancer Tumorigenesis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 981479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, J.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; Wan, G.; Sun, J.; Pan, C. Increased Expression of ST2 on Regulatory T Cells Is Associated with Cancer Associated Fibroblast-Derived IL-33 in Laryngeal Cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 237, 154023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Jin, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, L.; Qi, G.; Yang, J. The Role of IL-33/ST2 Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment and Treg Immunotherapy. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.S.; Scott, I.C.; Majithiya, J.B.; Rapley, L.; Kemp, B.P.; England, E.; Rees, D.G.; Overed-Sayer, C.L.; Woods, J.; Bond, N.J.; et al. Oxidation of the Alarmin IL-33 Regulates ST2-Dependent Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, I.C.; Majithiya, J.B.; Sanden, C.; Thornton, P.; Sanders, P.N.; Moore, T.; Guscott, M.; Corkill, D.J.; Erjefält, J.S.; Cohen, E.S. Interleukin-33 Is Activated by Allergen- and Necrosis-Associated Proteolytic Activities to Regulate Its Alarmin Activity during Epithelial Damage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ming, B.; Wu, T.; Gao, R.; Hu, P.; Tang, J.; Zhong, J.; Zheng, F.; Dong, L. IL-33/ST2 Axis Contributes to the Dermal Fibrosis of Systemic Sclerosis via Promoting Fibroblasts Activation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2022, 107, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, L.; Sangers, T.; Greveling, K.; Prens, E.; Haedersdal, M.; van Doorn, M. Efficacy and Tolerability of Intralesional Bleomycin in Dermatology: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Komine, M.; Tsuda, H.; Oshio, T.; Ohtsuki, M. Interleukin-33 Is Expressed in the Lesional Epidermis in Herpes Virus Infection but Not in Verruca vulgaris. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 855–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, F.; Giuffrida, R.; Coppola, M.; Princiotta, R.; Vaccaro, M.; Guarneri, F.; Cannavò, S.P. Efficacy and Safety of Conventional versus Daylight Photodynamic Therapy in Children Affected by Multiple Facial Flat Warts. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 31, 101819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, K.; Moens, U.; Policastro, B.; Johnsen, J.I.; Koljonen, V.; Sihto, H.; Lui, W.-O.; Sveinbjørnsson, B. The Merkel Cell Polyomavirus T-Antigens and IL-33/ST2-IL1RAcP Axis: Possible Role in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaSilva-Arnold, S.C.; Thyagarajan, A.; Seymour, L.J.; Yi, Q.; Bradish, J.R.; Al-Hassani, M.; Zhou, H.; Perdue, N.J.; Nemeth, V.; Krbanjevic, A.; et al. Phenotyping Acute and Chronic Atopic Dermatitis-like Lesions in Stat6VT Mice Identifies a Role for IL-33 in Disease Pathogenesis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2018, 310, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.J.; Frezza, V.; Davidovich, P.; Najda, Z.; Clancy, D.M. IL-1 Family Cytokines Serve as “Activity Recognition Receptors” for Aberrant Protease Activity Indicative of Danger. Cytokine 2022, 157, 155935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, S.; Huth, L.; Marquardt, Y.; Cheremkhina, M.; Heise, R.; Baron, J.M. MMP-3 Plays a Major Role in Calcium Pantothenate-Promoted Wound Healing after Fractional Ablative Laser Treatment. Lasers Med. Sci. 2022, 37, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, W.-J.; Yao, H.; Li, T.-M. Therapeutic Effects of Interleukin-37 and Induced Cardiosphere on Treating Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 88, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Ji, L.; Wen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, D.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; et al. IL-37 Inhibits the Production of Inflammatory Cytokines in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Its Correlation with Disease Activity. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elazeem, R.I.; Abdelnabi, H.H.; Hegab, D.S.; Mohamed, W.S.; Ameen, T.E. Serum Interleukin-33 (IL-33) in Children with Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cross-Sectional Study. Egypt. J. Immunol. 2022, 29, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.-C.; Li, H.-M.; Wang, J.-B.; Leng, R.-X.; Wang, D.-G.; Ye, D.-Q. Elevated Plasma Interleukin-37 Levels in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Lupus 2016, 25, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakerian, L.; Kolahdooz, H.; Garousi, M.; Keyvani, V.; Kamal Kheder, R.; Abdulsattar Faraj, T.; Yazdanpanah, E.; Esmaeili, S.-A. IL-33/ST2 Axis in Autoimmune Disease. Cytokine 2022, 158, 156015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ben Dhifallah, I.; Borhani-Haghighi, A.; Hamzaoui, A.; Hamzaoui, K. Decreased Level of IL-37 Correlates Negatively with Inflammatory Cytokines in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Neuro-Behcet’s Disease. Iran. J. Immunol. 2019, 16, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wang, C.; Kijlstra, A.; Zhou, X.; Yang, P. A Possible Role for Interleukin 37 in the Pathogenesis of Behcet’s Disease. Curr. Mol. Med. 2014, 14, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouali, E.; Kaabachi, W.; Hamzaoui, A.; Hamzaoui, K. Interleukin-37 Expression Is Decreased in Behçet’s Disease and Is Associated with Inflammation. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 167, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Year | Cytokine or Axis | Disease | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-33/IL-37 Axis | ||||
| Lopetuso et al. [19] | 2013 | IL-33 and IL-37 | Gut diseases | IL-33 as a prototypic alarmin: - passively released upon cellular damage, stress, or necrosis - innate immune response signaling - physiological inflammation - gut homeostasis - a tool for tumor cells to create an ideal growth environment (IL-33/ST2 axis in tumor progression) IL-37 potential role in antibody production, B-cell activation, and colon tumorigenesis |
| Ross et al. [20] | 2013 | IL-33 and IL-37 | - | IL-33 induces pro-inflammatory immune responses when released from destroyed cells IL-37 downregulates reactions in macrophages to limit the immune response |
| Li et al. [21] | 2015 | IL-37 | Inflammation | IL-37 binds IL-18R for anti-inflammatory purposes |
| Montanari et al. [22] | 2016 | IL-33 | Atherosclerosis | Endothelial cells as targets for IL-33 to exert its pro-inflammatory effects via GM-CSF and M-CSF production |
| Kouchaki et al. [23] | 2017 | Axis IL-33/IL-37 | Multiple sclerosis | IL-33 as a predictor of severe forms of multiple sclerosis Levels of IL-37 correlate to disease severity and balance inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway and IL-1R8 and IL-18R α receptors |
| Alves et al. [24] | 2018 | Axis IL-33/IL-37 | Paracoccidioidomycosis | - IL-33 release by cells - De novo production of IL-33 - Enhancement of Th2 cells and IgE production by B cells |
| Li et al. [25] | 2019 | IL-37 | - | IL-37 suppresses innate inflammation |
| Makaremi et al. [26] | 2022 | IL-33 and IL-37 | COVID | IL-33 can stimulate antiviral CTL activity and antibody production. Lower levels of IL-37 are associated with a higher risk of disease to COVID-19 |
| Zhan et al. [27] | 2021 | IL-33 and IL-37 | LES | Platelet count and IL-37 levels are correlated in patients affected by immune thrombocytopenia. IL-1β, IL-18, IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ, IL-33, and IL-37 as biomarkers in the diagnosis of immune thrombocytopenia in LES |
| Conti et al. [16] | 2017 | IL-37 | - | In stimulated DCs: - inhibits GM-CSF, M-CSF production - reduces inflammatory response in RA - downregulates CC chemokines and in neutrophils CXC chemokines - interfere with the TLR4 signaling pathway |
| Cutaneous diseases | ||||
| Kacem et al. [28] | 2018 | Axis IL-33/IL-37 | Behcet skin lesions |
|
| Sehat et al. [29] | 2018 | IL-33 and IL-37 | PSO | IL-33 levels correlate with the severity of the disease and IL-37 levels, a compensatory response |
| Tettamanti et al. [30] | 2018 | Axis IL-33/IL-37 | AD | IL-33 activates MCs and ILC2, driving allergic inflammatory reactions in AD |
| Caraffa et al. [31] | 2019 | IL-37 | Melanoma | Up-regulation of IL-37 RNA in tumors produces a defensive mechanism in the body of the host |
| Guttman-Yassky et al. [32] | 2019 | IL-33 and IL-37 | AD |
|
| Hou et al. [33] | 2020 | IL-37 | AD | IL-37b suppresses innate immunity by reducing the infiltration of eosinophils and induction of Foxp3+ Treg cells |
| Tsuji et al. [34] | 2022 | Axis IL-33/IL-37 | AD/PSO | - IL-37 downregulates IL-33 in keratinocytes: - IL-33 activates ILC2 and induces itching by stimulating nerves - IL-33 enhances the transcription of psoriasis-factors in keratinocytes in an autocrine mechanism - IL-37 reduces the activation of pro-inflammatory signaling mediators (p38, ERK, and STAT1) |
| Allergic diseases | ||||
| Berraïes A et al. [35] | 2016 | Asthma | - IL-33 induces TSLP production by epithelial cells of the airway tract - IL-37 suppresses TSLP production by bronchial epithelium cells | |
| Li et al. [36] | 2020 | IL-37 | DAC | - IL-37 alleviates inflammation in contact dermatitis via up-regulation of IκB expression and down-regulation of of NF-κB p65, NF-κB p65, and STAT3 - Smad3 is involved in the IL-37 cascade |
| Schröder et al. [37] | 2022 | IL-37 | Asthma | IL-37 efficacy in dampening IL-33 effects is comparable to use of corticosteroids |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borgia, F.; Custurone, P.; Li Pomi, F.; Vaccaro, M.; Alessandrello, C.; Gangemi, S. IL-33 and IL-37: A Possible Axis in Skin and Allergic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010372
Borgia F, Custurone P, Li Pomi F, Vaccaro M, Alessandrello C, Gangemi S. IL-33 and IL-37: A Possible Axis in Skin and Allergic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010372
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorgia, Francesco, Paolo Custurone, Federica Li Pomi, Mario Vaccaro, Clara Alessandrello, and Sebastiano Gangemi. 2023. "IL-33 and IL-37: A Possible Axis in Skin and Allergic Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010372
APA StyleBorgia, F., Custurone, P., Li Pomi, F., Vaccaro, M., Alessandrello, C., & Gangemi, S. (2023). IL-33 and IL-37: A Possible Axis in Skin and Allergic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010372









