Effects of Chicken Serum Metabolite Treatment on the Blood Glucose Control and Inflammatory Response in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
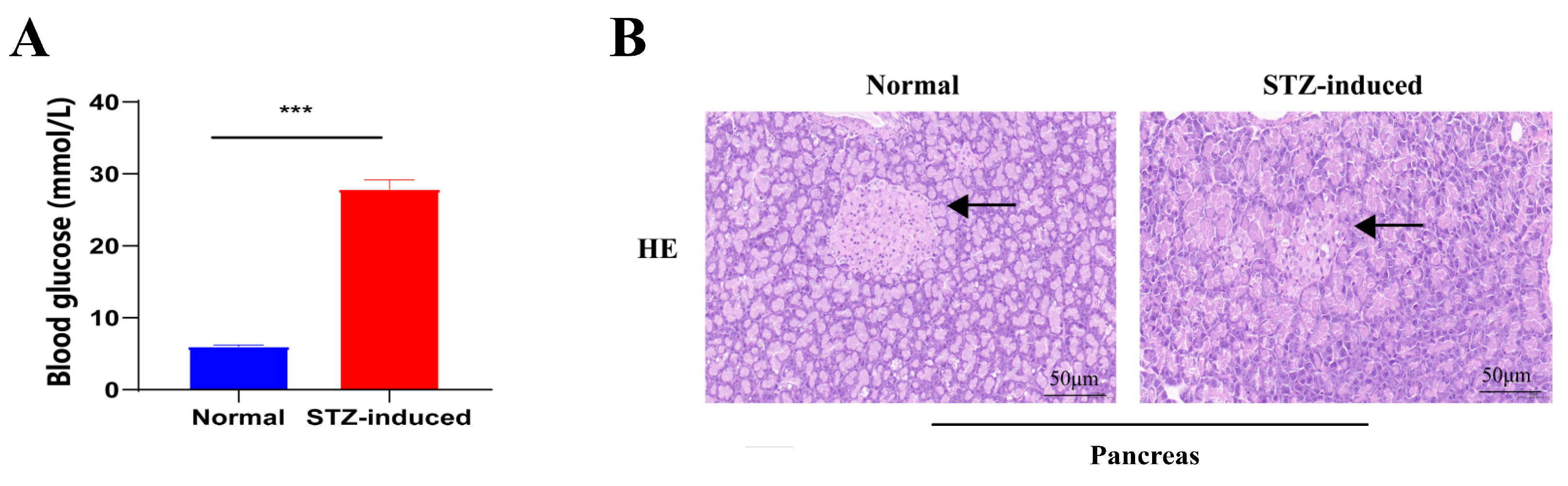
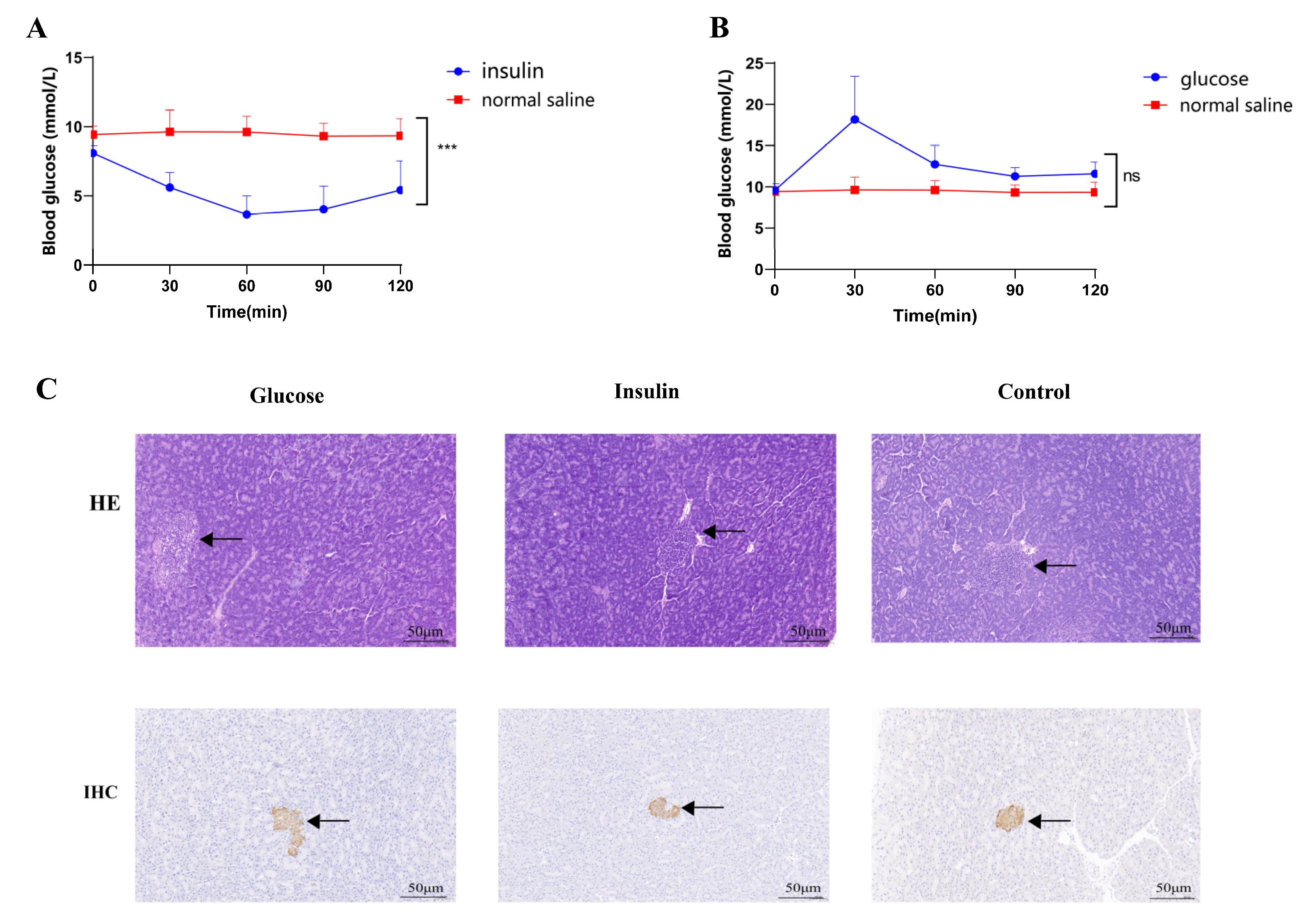
2.1. STZ-Induced T2DM Rats and Insulin/Glucose-Induced Acute Hypoglycemic/Hyperglycemic Chickens
2.2. Effects of Chicken Serum Treatment on Blood Glucose Control and Inflammatory Response
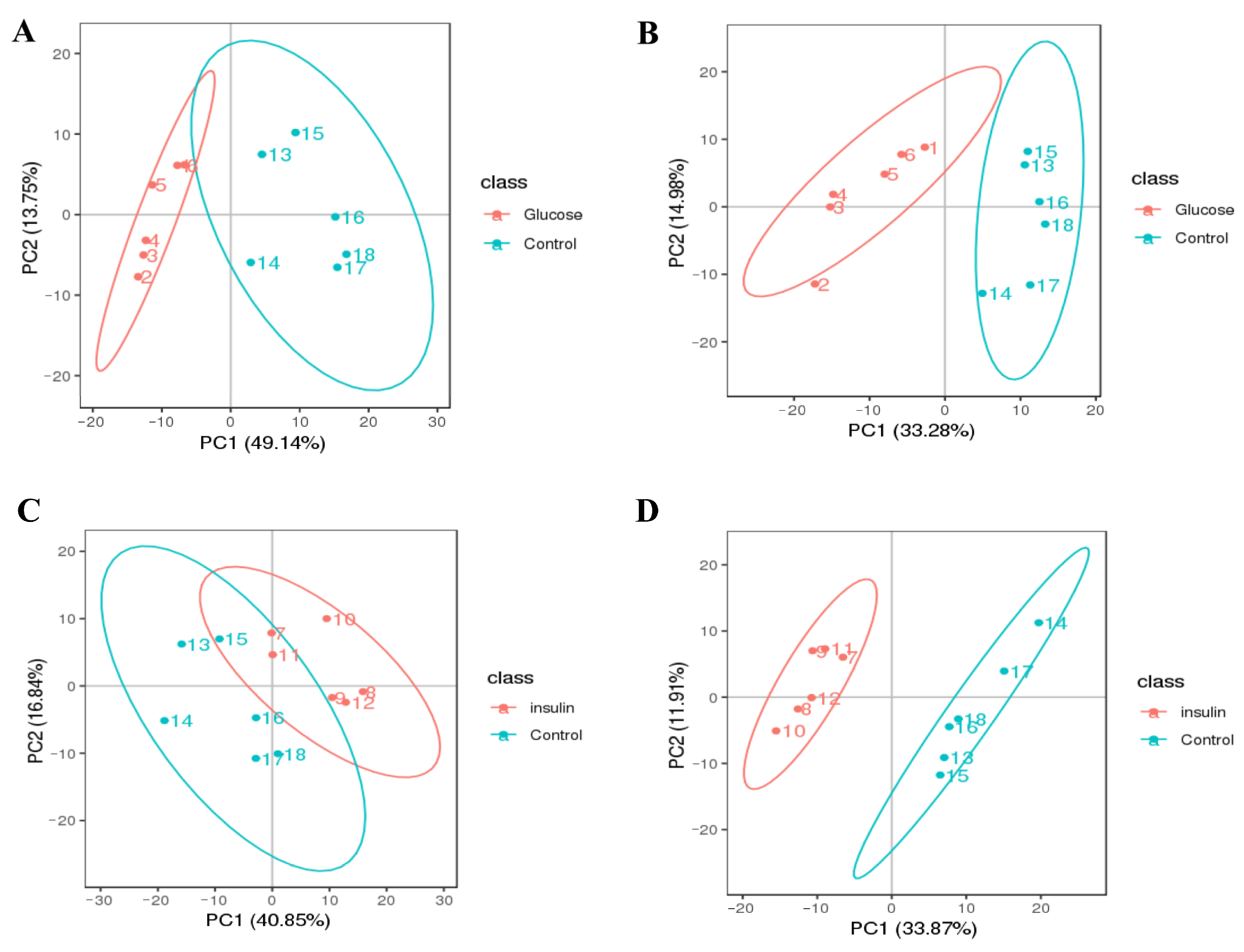
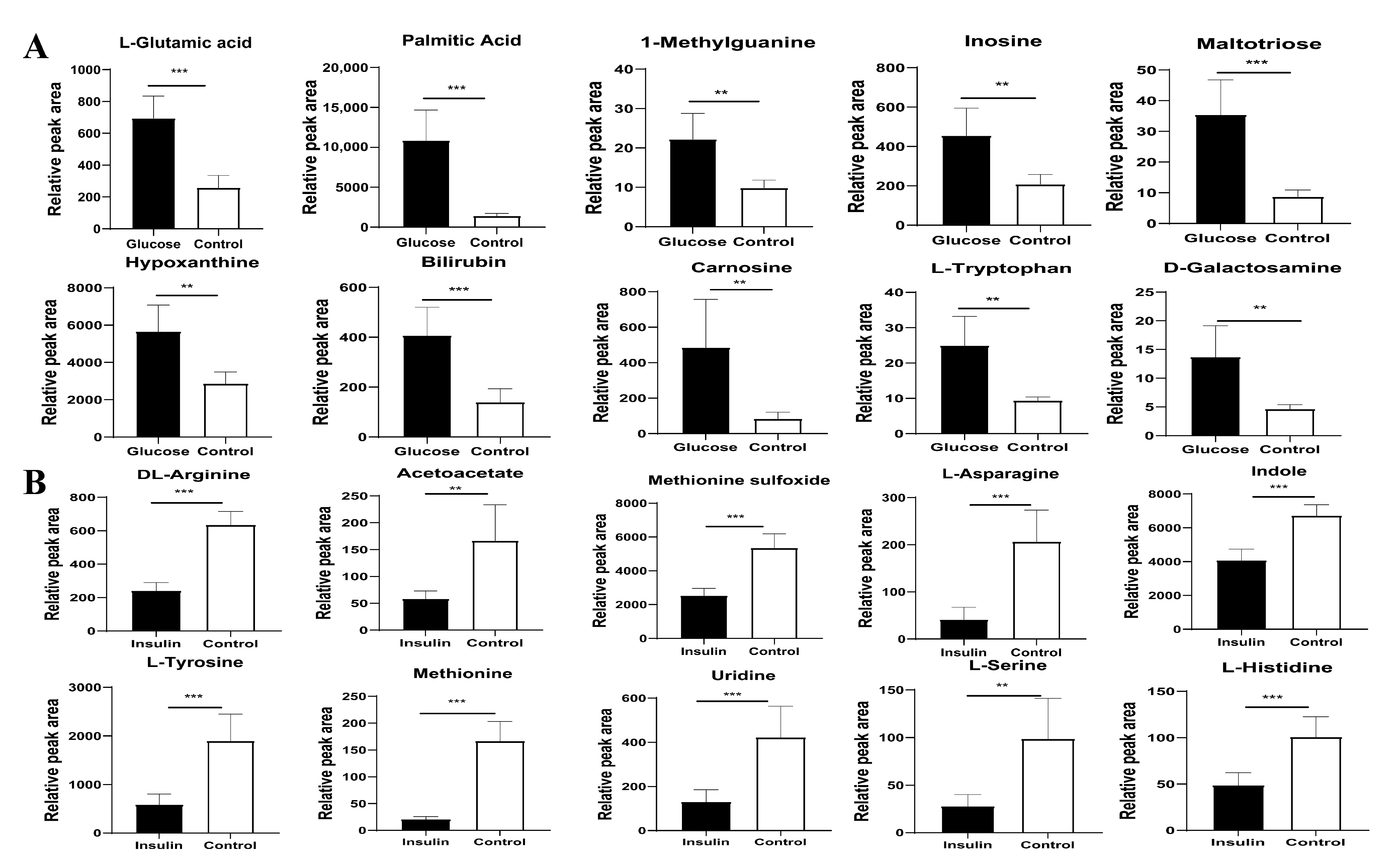
2.3. Key Metabolites Screening for Glucose Regulation in the Chicken Serum
2.4. Key Metabolites Identification for Glucose Regulation in Hyperglycemic Chickens
2.5. Effects of DL-Arginine on Blood Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity in STZ-Induced T2DM Rats
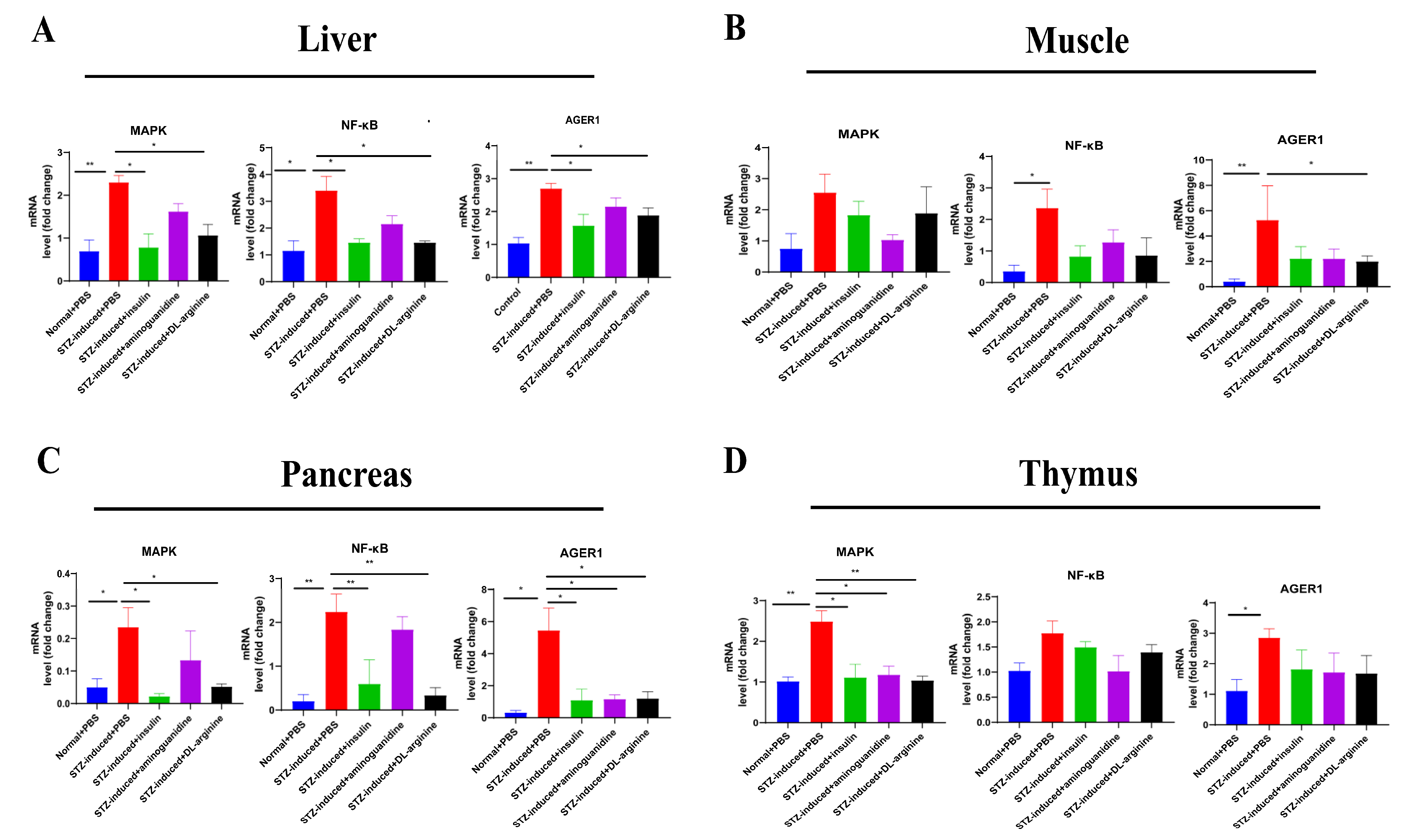
2.6. Effects of DL-Arginine on the Expression of Genes Involved in Glucose Metabolism in STZ-Induced T2DM Rats
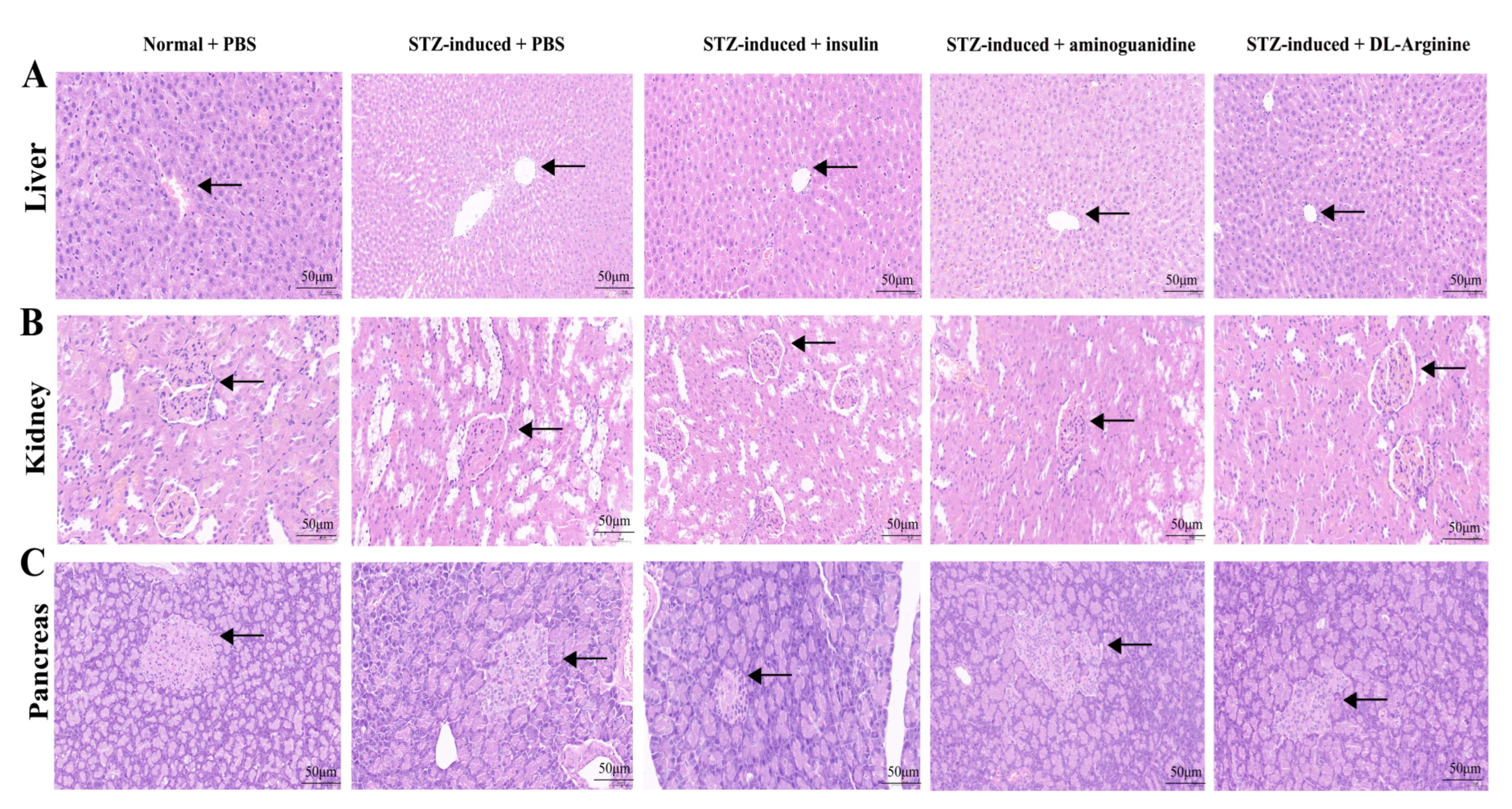
2.7. Effects of DL-Arginine on the Pathological Injury and Expression of Genes Involved in Inflammatory Response in STZ-Induced T2DM Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Experimental Animals
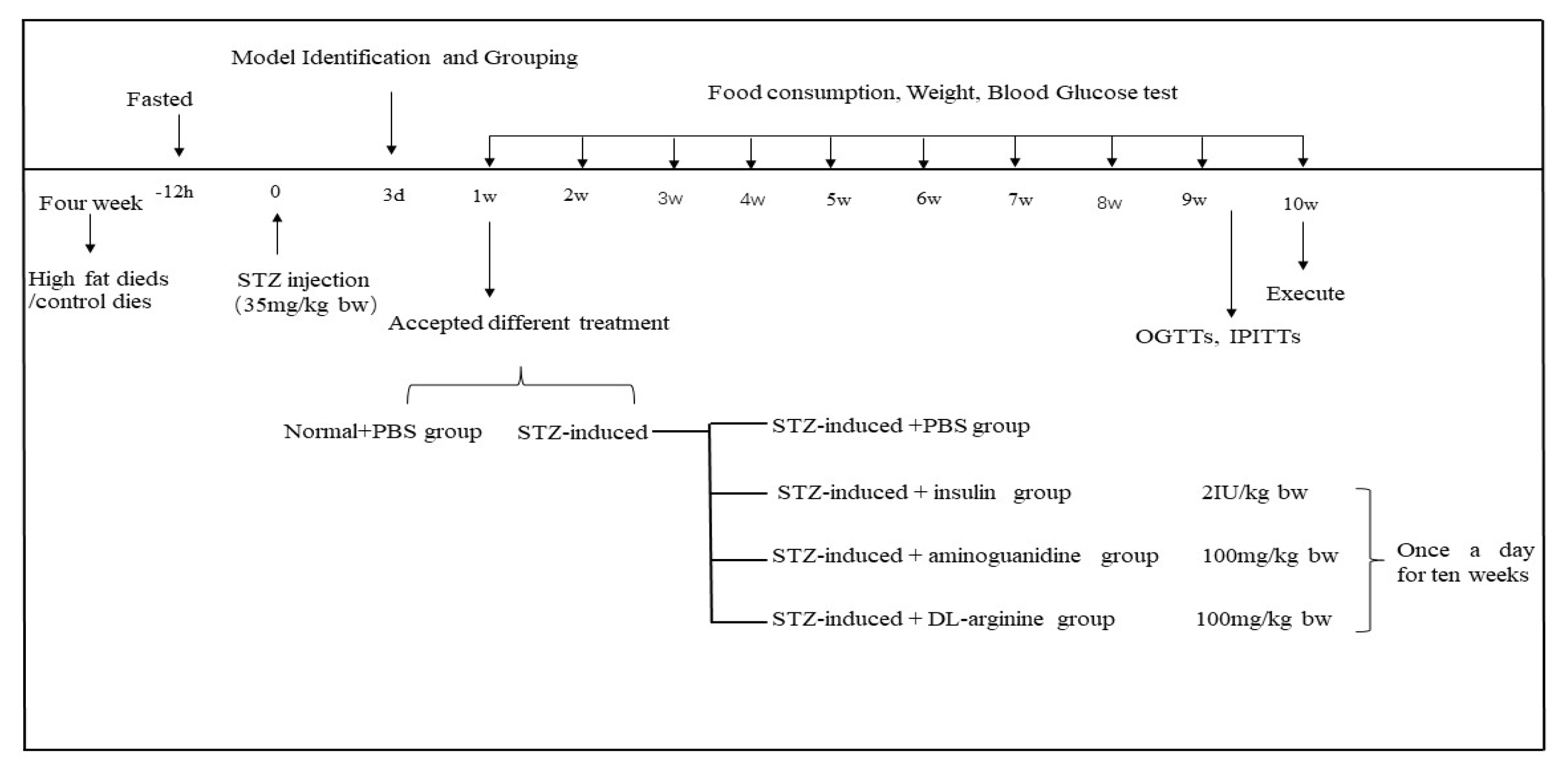
4.3. STZ-Induced T2DM Rats
4.4. Acute Hypoglycemic and Hyperglycemic Chickens Induced by Insulin/Glucose
4.5. HE Sections and Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Chicken Serum Treatment in STZ-Induced T2DM Rats
4.7. Measurement of the Serum AGEs, Fructosamine and Biochemical Blood Examination
4.8. Untargeted Metabolomics of Chicken Serum
4.8.1. Metabolite Extraction
4.8.2. UHPLC-MS/MS Analysis
4.8.3. Data Processing and Metabolite Identification
4.8.4. Data Analysis
4.9. DL-Arginine Treatment in STZ-Induced T2DM Rats
4.10. OGTTs, IPITTs
4.11. Real-Time qRT-PCR
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braun, E.J.; Sweazea, K.L. Glucose regulation in birds. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 151, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, D.J.; Flückiger, R.; Austad, S.N. Comparative biology of aging in birds: An update. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D. Birds as pathology-free models of type II diabetes. Austin Endocrinol. Diabetes Case Rep. 2017, 2, 1007. [Google Scholar]
- Beuchat, C.A.; Chong, C.R. Hyperglycemia in hummingbirds and its consequences for hemoglobin glycation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1998, 120, 3409–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.; Portner, H.O. Temperature, metabolic power and the evolution of endothermy. Biol. Rev. 2010, 85, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.; Rothery, P. Scaling of body temperature in mammals and birds. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, T. Evaluation of Protein Glycation and Antioxidant Levels in Birds of Prey; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sessa, L.; Gatti, E.; Zeni, F.; Antonelli, A.; Catucci, A.; Koch, M.; Pompilio, G.; Fritz, G.; Raucci, A.; Bianchi, M.E. The receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) is only present in mammals and belongs to a family of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuck, J.; Borges, C.R.; Braun, E.J.; Sweazea, K.L. Chicken albumin exhibits natural resistance to glycation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 203, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Schaffer, S.W.; Azuma, J. The potential usefulness of taurine on diabetes mellitus and its complications. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franconi, F.; Loizzo, A.; Ghirlanda, G.; Seghieri, G. Taurine supplementation and diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007, 9, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, I.; Dhar, A.; Wu, L.; Desai, K. Arginine attenuates methylglyoxal- and high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress by an endothelial nitricoxide synthase-independent mechanism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 342, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuradha, C.V. Aminoacid support in the prevention of diabetes and diabetic complications. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2009, 10, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldyrev, A.A.; Aldini, G.; Derave, W. Physiology and path-ophysiology of carnosine. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1803–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hipkiss, A.R. Carnosine and its possible roles in nutrition and health. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2009, 57, 87–154. [Google Scholar]
- Cheah, I.K.; Halliwell, B. Ergothioneine: Antioxidant potential, physiological function and role in disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, N.; Thornalley, P.J. Emerging role of thiamine therapy for prevention and treatment of early-stage diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalaf, A.; Kleefstra, N.; Groenier, K.H.; Bilo, H.J.; Gans, R.O.; Heeringa, P.; Scheijen, J.L.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Navis, G.J.; Bakker, S.J. Effect of benfotiamine on advanced glycation endproducts and markers of endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voziyan, P.A.; Hudson, B.G. Pyridoxamine: The many virtues of a Maillard reaction inhibitor. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornalley, P.J. Use of aminoguanidine (Pimagedine) to prevent the formation of advanced glycation end products. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 419, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwergold, B.S.; Miller, C.B. Potential of birds to serve as pathology-free models of type 2 diabetes, part 2: Do high levels of carbonyl-scavenging amino acids (e.g., taurine) and low concentrations of methylglyoxal limit the production of advanced glycation end-products? Rejuvenation Res. 2014, 17, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, L.D.; Galluccio, E.; Villa, V.; Fontana, B.; Spadoni, S.; Piatti, P.M. Decreased diabetes risk over 9 year after 18-month oral L-arginine treatment in middle-aged subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and metabolic syndrome (extension evaluation of L-arginine study). Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2805–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Han, M.; Rezaei, A.; Li, D.; Wu, G.; Ma, X. L-Arginine Modulates Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Obesity and Diabetes. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatti, P.M.; Monti, L.D.; Valsecchi, G.; Magni, F.; Setola, E.; Marchesi, F.; Galli-Kienle, M.; Pozza, G.; Alberti, K.G. Long-term oral L-arginine administration improves peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Xie, D.; Lu, M.; Li, P.; Lv, H.; Yang, C.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Characterization of white tea metabolome: Comparison against green and black tea by a nontargeted metabolomics approach. Food Res. Int. 2017, 96, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haspel, J.A.; Chettimada, S.; Shaik, R.S.; Chu, J.H.; Raby, B.A.; Cernadas, M.; Carey, V.; Process, V.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Ifedigbo, E.; et al. Circadian rhythm reprogramming during lung inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, D. Metabonomic analysis of the therapeutic effect of Zhibai Dihuang Pill in treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yuan, H.; Xu, E.; Liu, J. Toxicology of paraquat and pharmacology of the protective effect of 5-hydroxy-1-methylhydantoin on lung injury caused by paraquat based on metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Jin, Y.X.; Shen, W.; Neng, J.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.J.; Fu, Z.W. Low dose streptozotocin (STZ) combined with high energy intake can effectively induce type 2 diabetes through altering the related gene expression. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, H.W.; Ho, Y.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Hsieh, Y.L. SEPT9 Upregulation in Satellite Glial Cells Associated with Diabetic Polyneuropathy in a Type 2 Diabetes-like Rat Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.A.; Fall, T.; Pasko, D.; Barker, A.; Sharp, S.J.; Arriola, L.; Balkau, B.; Barricarte, A.; Barroso, I.; Boeing, H.; et al. Common genetic variants highlight the role of insulin resistance and body fat distribution in type 2 diabetes, independent of obesity. Diabetes 2014, 63, 4378–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Buey, G.; Núñez-Córdoba, J.M.; Llavero-Valero, M.; Gargallo, J.; Salvador, J.; Escalada, J. Is HOMA-IR a potential screening test for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults with type 2 diabetes? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 41, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobgen, W.S.; Fried, S.K.; Fu, W.J.; Meininger, C.J.; Wu, G. Regulatory role for the arginine-nitric oxide pathway in metabolism of energy substrates. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2006, 17, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Bazer, F.W.; Davis, T.A.; Kim, S.W.; Li, P.; Marc Rhoads, J.; Carey Satterfield, M.; Smith, S.B.; Spencer, T.E.; Yin, Y. Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Ren, J.; Tang, L.; Gong, J.; Lin, Y.; Fang, H.; Su, D. Hesperetin, a Promising Treatment Option for Diabetes and Related Complications: A Literature Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8582–8592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, A.; Szahidewicz-Krupska, E.; Mazur, G.; Doroszko, A. Insulin Resistance and Endothelial Dysfunction Constitute a Common Therapeutic Target in Cardiometabolic Disorders. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 3634948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, J.D.; Balderas, F.L. Inhibition by L-arginine and spermidine of hemoglobin glycation and lipid peroxidation in rats with induced diabetes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2006, 60, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leturque, A.; Brot-Laroche, E.; Le Gall, M. GLUT2 Mutations, Translocation, and Receptor Function in Diet Sugar Managing. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E985–E992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Famurewa, A.C.; Tang, J.; Olatunde, O.O.; Olatunji, O.J. Hyperoside attenuates neuroinflammation, cognitive impairment and oxidative stress via suppressing TNF-α/NF-κB/caspase-3 signaling in type 2 diabetes rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.A.; Reza, M.I.; Shafiq, M.; Kumariya, S.; Singh, P.; Husain, A.; Hanif, K.; Gayen, J.R. Naringin ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus-induced steatohepatitis by inhibiting RAGE/NF-κB mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-H.; Ou, H.-C.; Day, C.-H.; Chen, H.-I.; Pai, P.-Y.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chen, R.J.; Chang, R.L.; PadmaViswanadha, V.; Hsieh, D.J.-Y.; et al. Deep sea minerals ameliorate diabetic-induced inflammation via inhibition of TNFα signaling pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melloul, D. Role of NF-kappaB in beta-cell death. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldor, R.; Yeffet, A.; Baum, K.; Doviner, V.; Amar, D.; Ben-Neriah, Y.; Christofori, G.; Peled, A.; Carel, J.C.; Boitard, C.; et al. Conditional and specific NF-kappaB blockade protects pancreatic beta cells from diabetogenic agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5072–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Abraham, N.G.; Vanella, L.; Zhang, Y.; Inaba, M.; Hosaka, N.; Hoshino, S.; Shi, M.; Ambrosini, Y.M.; Gershwin, M.E.; et al. Successful modulation of type 2 diabetes in db/db mice with intra-bone marrow--bone marrow transplantation plus concurrent thymic transplantation. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 35, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H.; Striker, G.E. AGE restriction in diabetes mellitus: A paradigm shift. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.J.; Meszaros, K.; Entes, L.J.; Claypool, M.D.; Pinkett, J.G.; Gadbois, T.M.; Reaven, G.M. A New Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes: The Fat-Fed, Streptozotocin-Treated Rat. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2000, 49, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Smith, C.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Uritboonthai, W.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Siuzdak, G. Solvent-dependent metabolite distribution, clustering, and protein extraction for serum profiling with mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barri, T.; Dragsted, L.O. UPLC-ESI-QTOF/MS and multivariate data analysis for blood plasma and serum metabolomics: Effect of experimental artefacts and anticoagulant. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 768, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps; R Package Version 1.2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package ‘Corrplot’: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix; Version 0.92; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Sun, Y.; Shi, H.; Yin, S.; Ji, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, P.; Shi, Y.; Mao, F.; Yan, Y.; et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Alleviate Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Reversing Peripheral Insulin Resistance and Relieving β-Cell Destruction. ACS Nano. 2018, 12, 7613–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


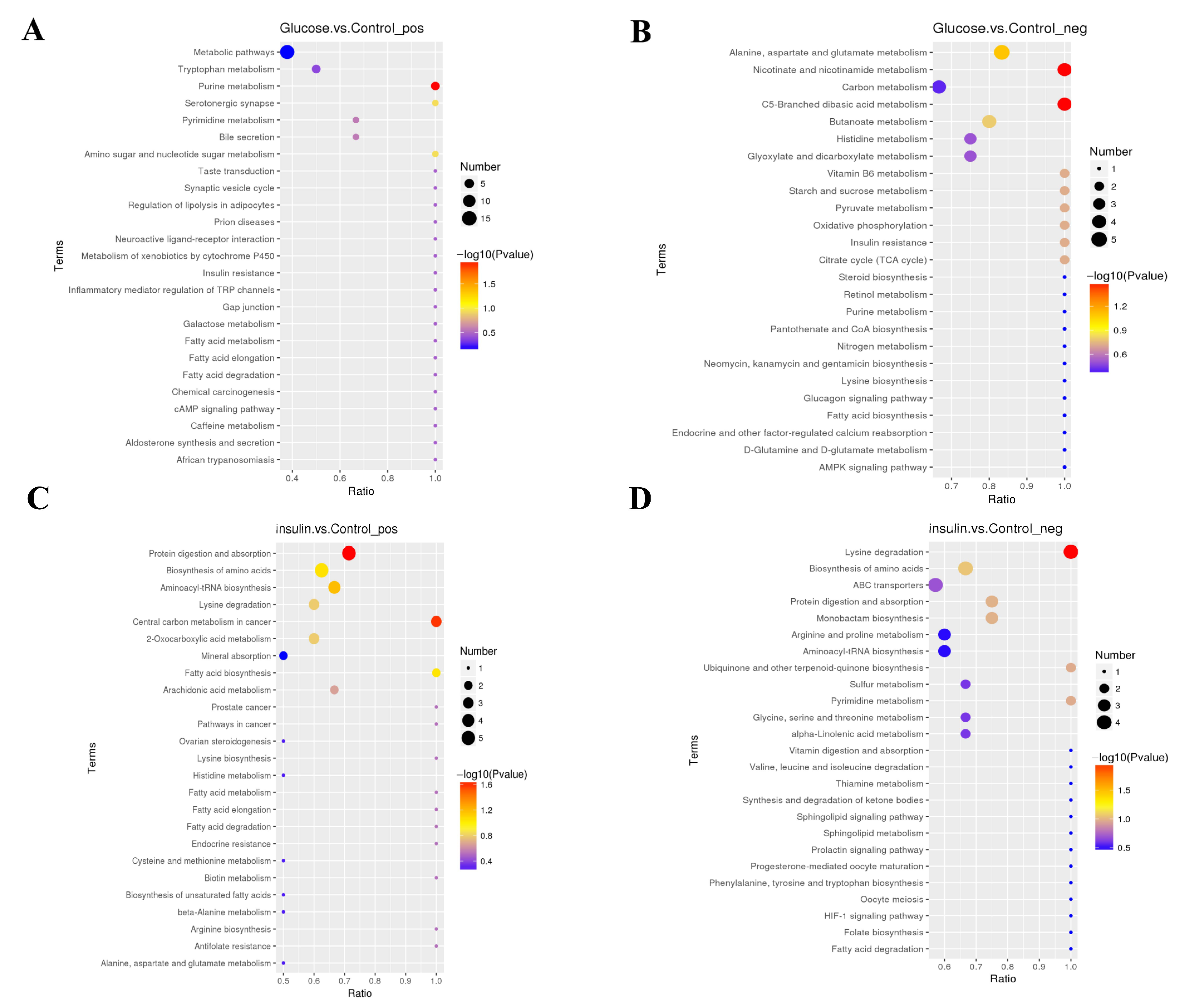



| Compared Samples | Num. of Total Ident. | Num. of Total Sig. | Num. of Sig. Up | Num. of Sig. Down |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose. vs. Control_ pos | 429 | 124 | 84 | 40 |
| Glucose. vs. Control_ neg | 295 | 125 | 96 | 29 |
| insulin. vs. Control_ pos | 429 | 118 | 73 | 45 |
| insulin. vs. Control_ neg | 295 | 79 | 33 | 46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Xu, Q. Effects of Chicken Serum Metabolite Treatment on the Blood Glucose Control and Inflammatory Response in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010523
Hu X, Liu X, Guo Y, Li Y, Cao Z, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Chen G, Xu Q. Effects of Chicken Serum Metabolite Treatment on the Blood Glucose Control and Inflammatory Response in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010523
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xuan, Xueming Liu, Yujiao Guo, Yi Li, Zhengfeng Cao, Yu Zhang, Yang Zhang, Guohong Chen, and Qi Xu. 2023. "Effects of Chicken Serum Metabolite Treatment on the Blood Glucose Control and Inflammatory Response in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010523
APA StyleHu, X., Liu, X., Guo, Y., Li, Y., Cao, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Chen, G., & Xu, Q. (2023). Effects of Chicken Serum Metabolite Treatment on the Blood Glucose Control and Inflammatory Response in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010523







