Structural and Functional Characterization of a New Bacterial Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Involved in Fruiting Body Formation in Myxobacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of CoDPP III
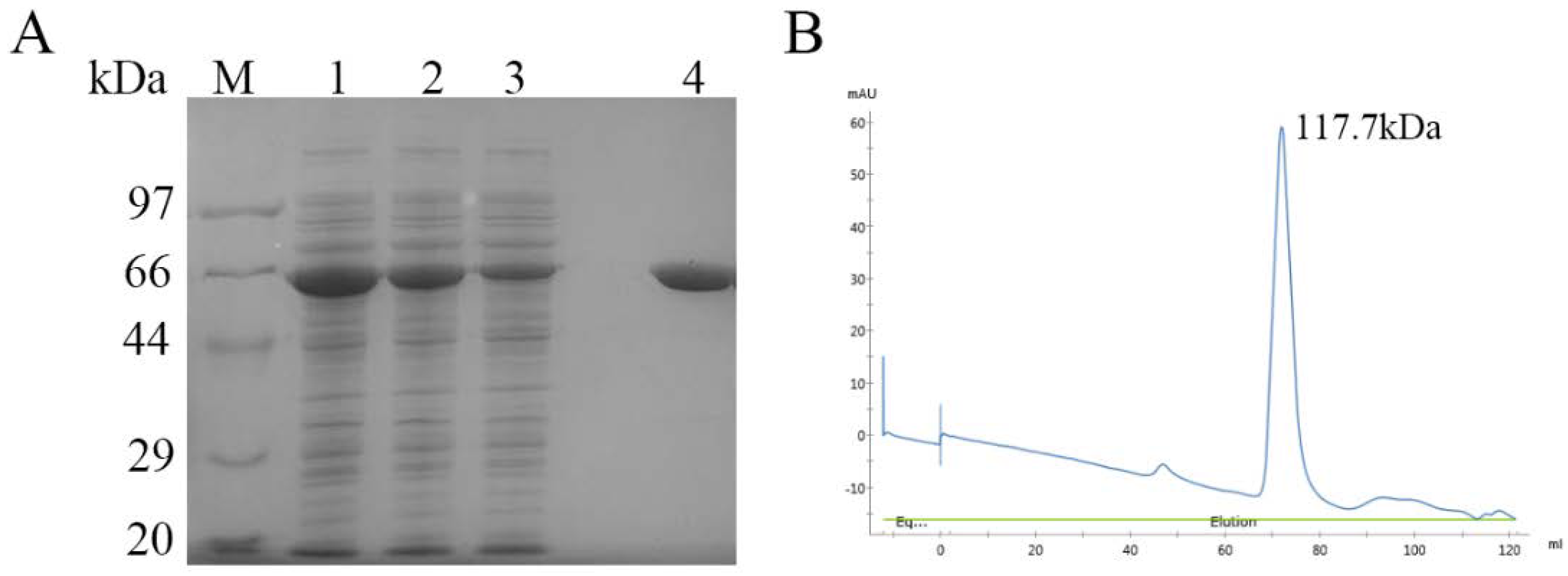
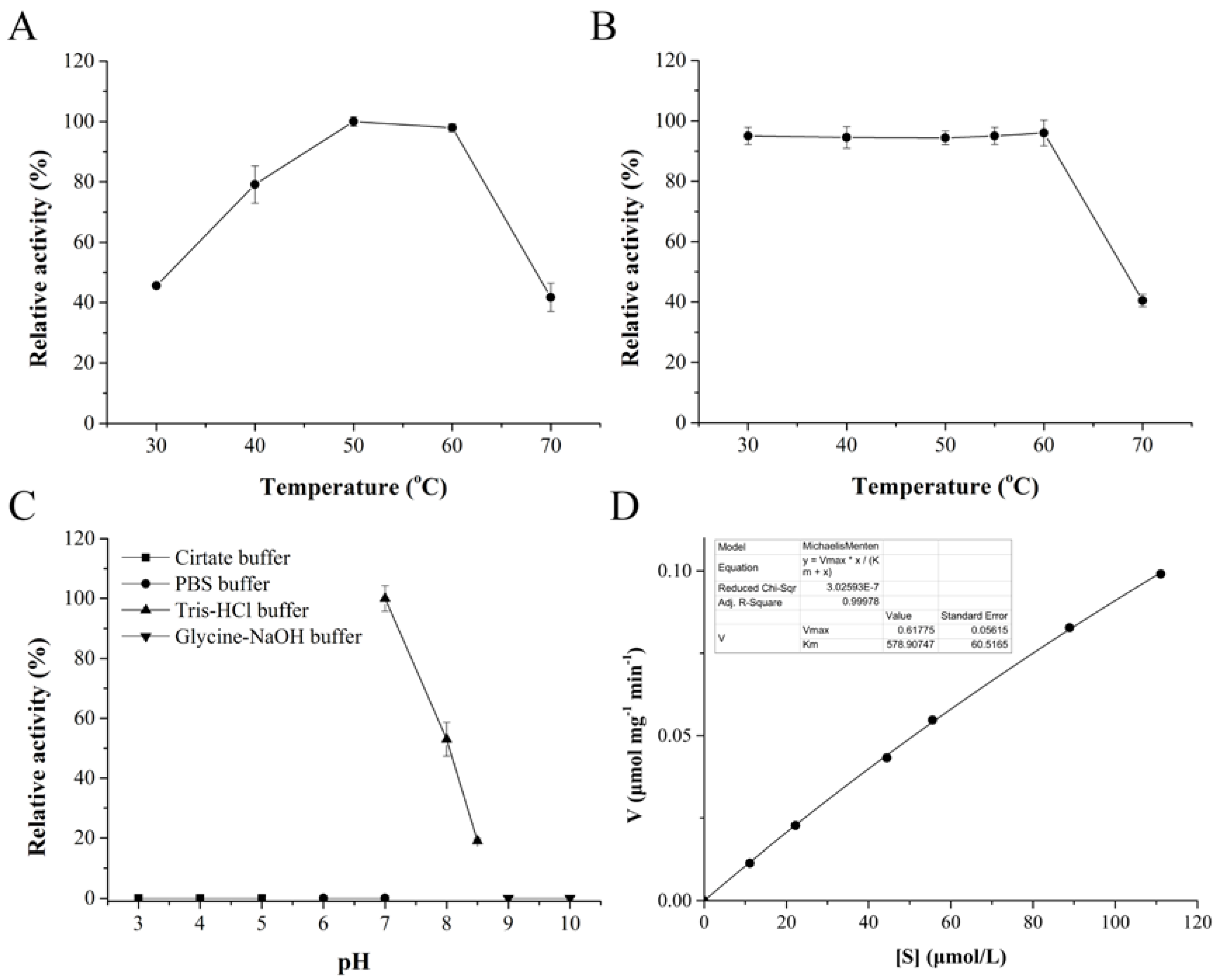
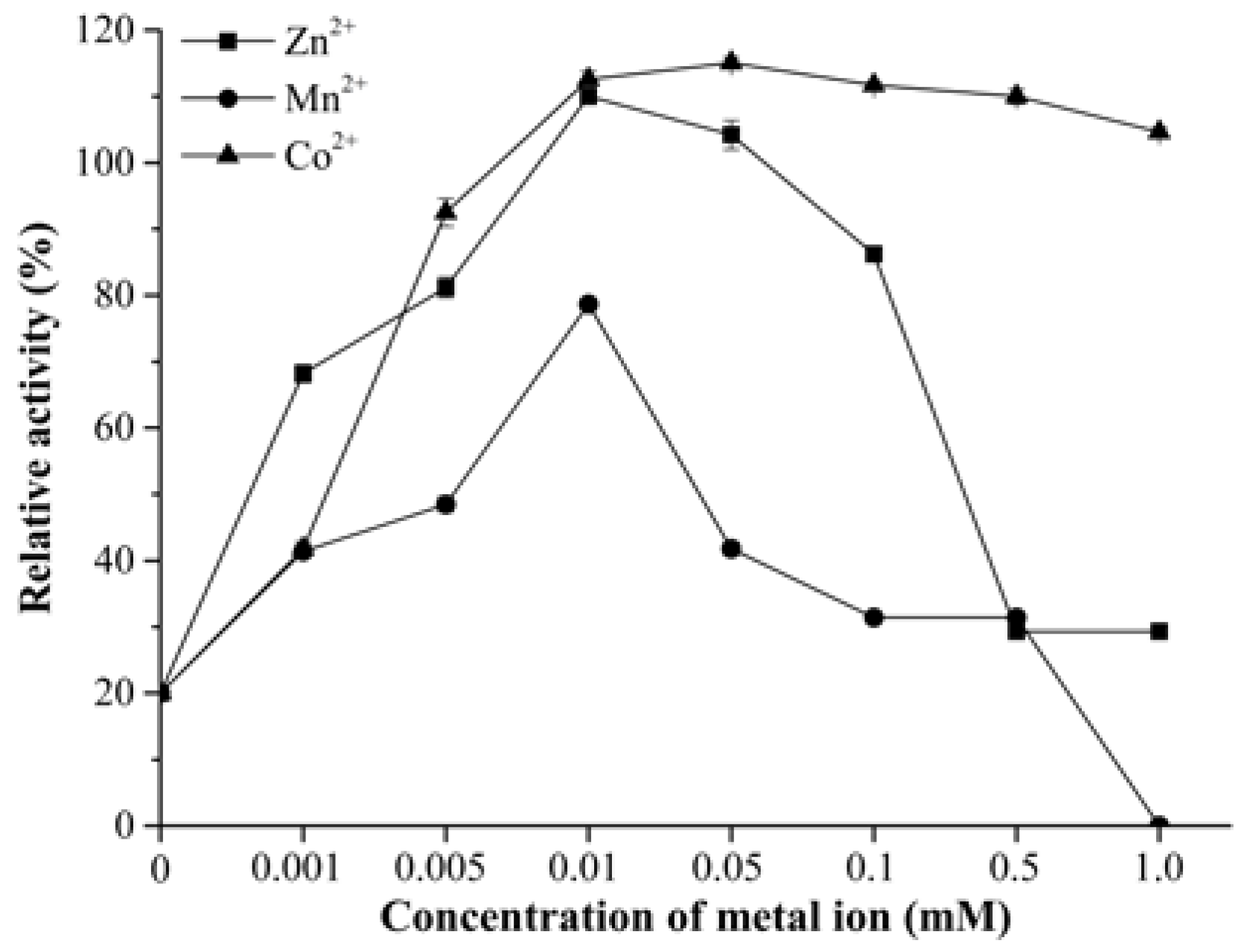
2.2. Biochemical Characterization of DPP III
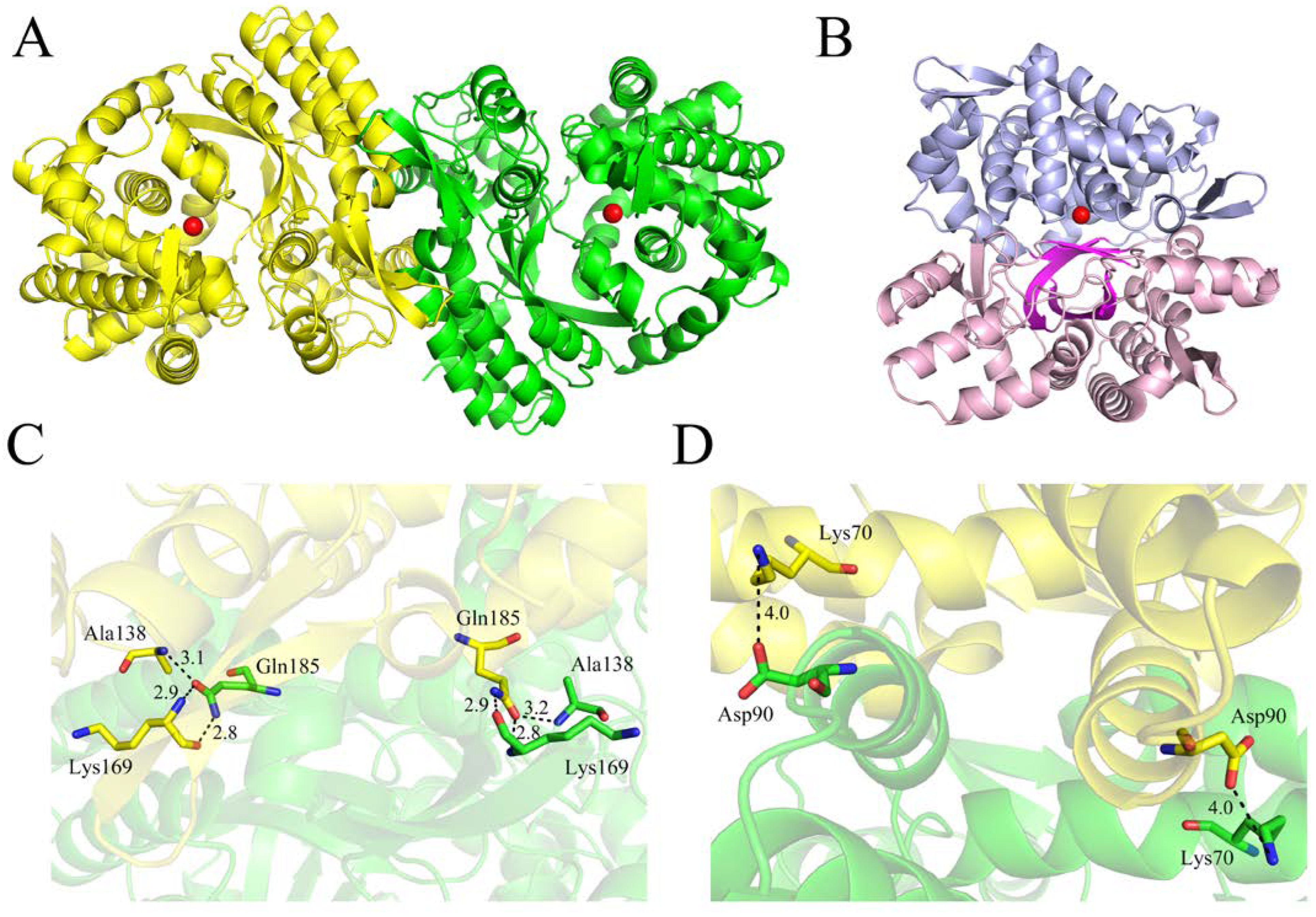
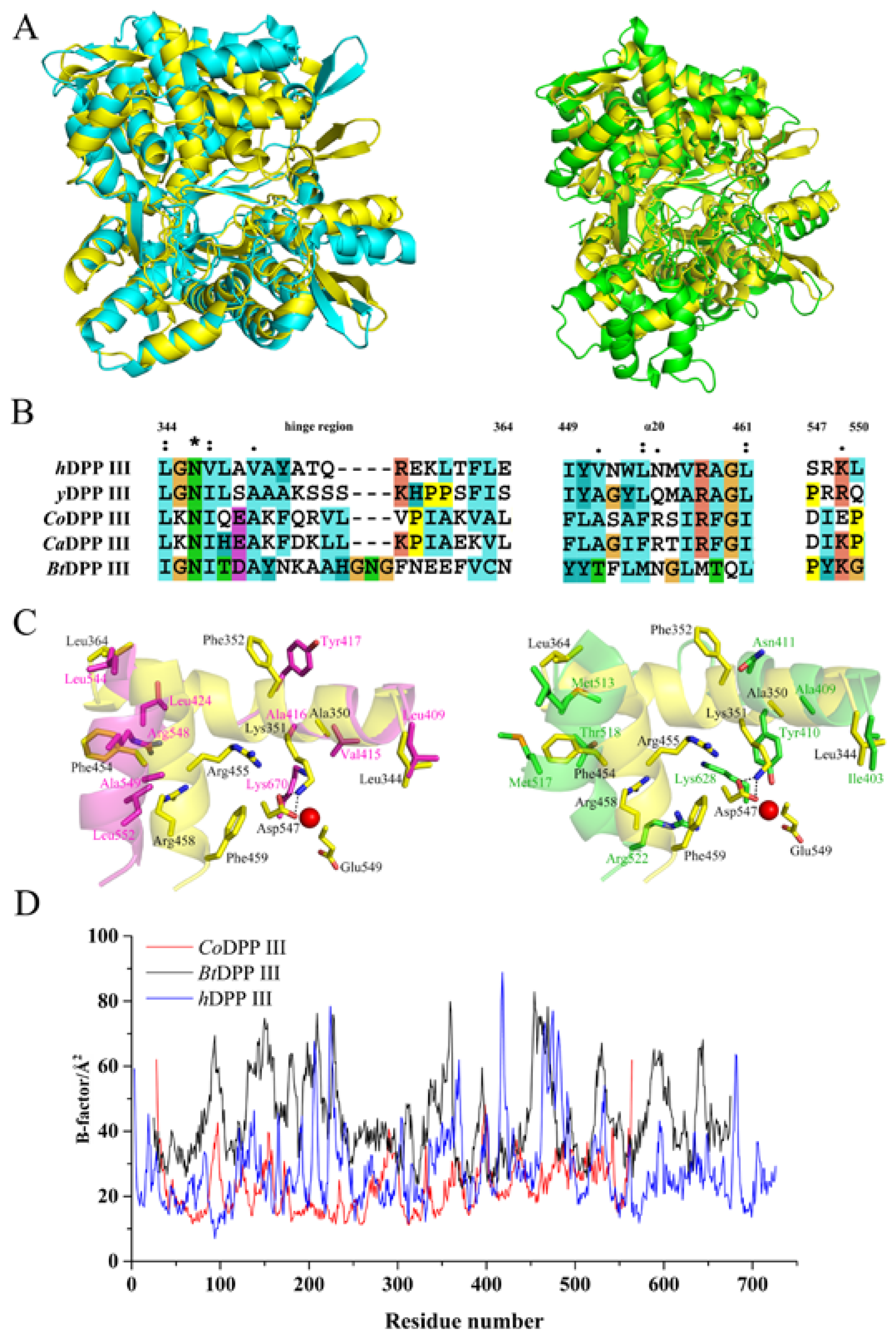
2.3. Overall Structure of CoDPP III
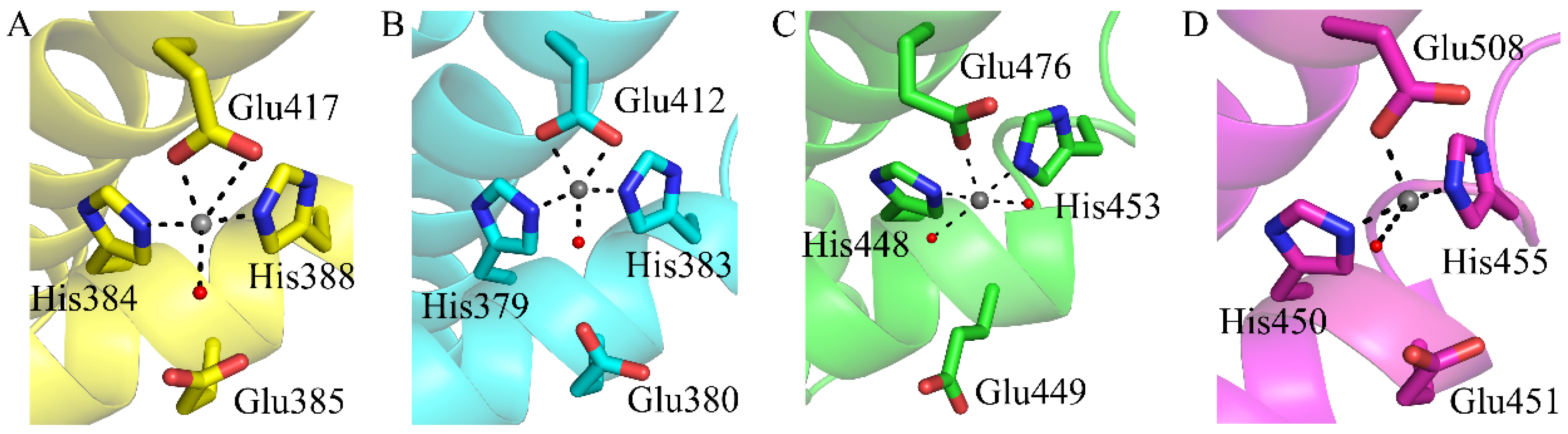
2.4. Active Site of CoDPP III
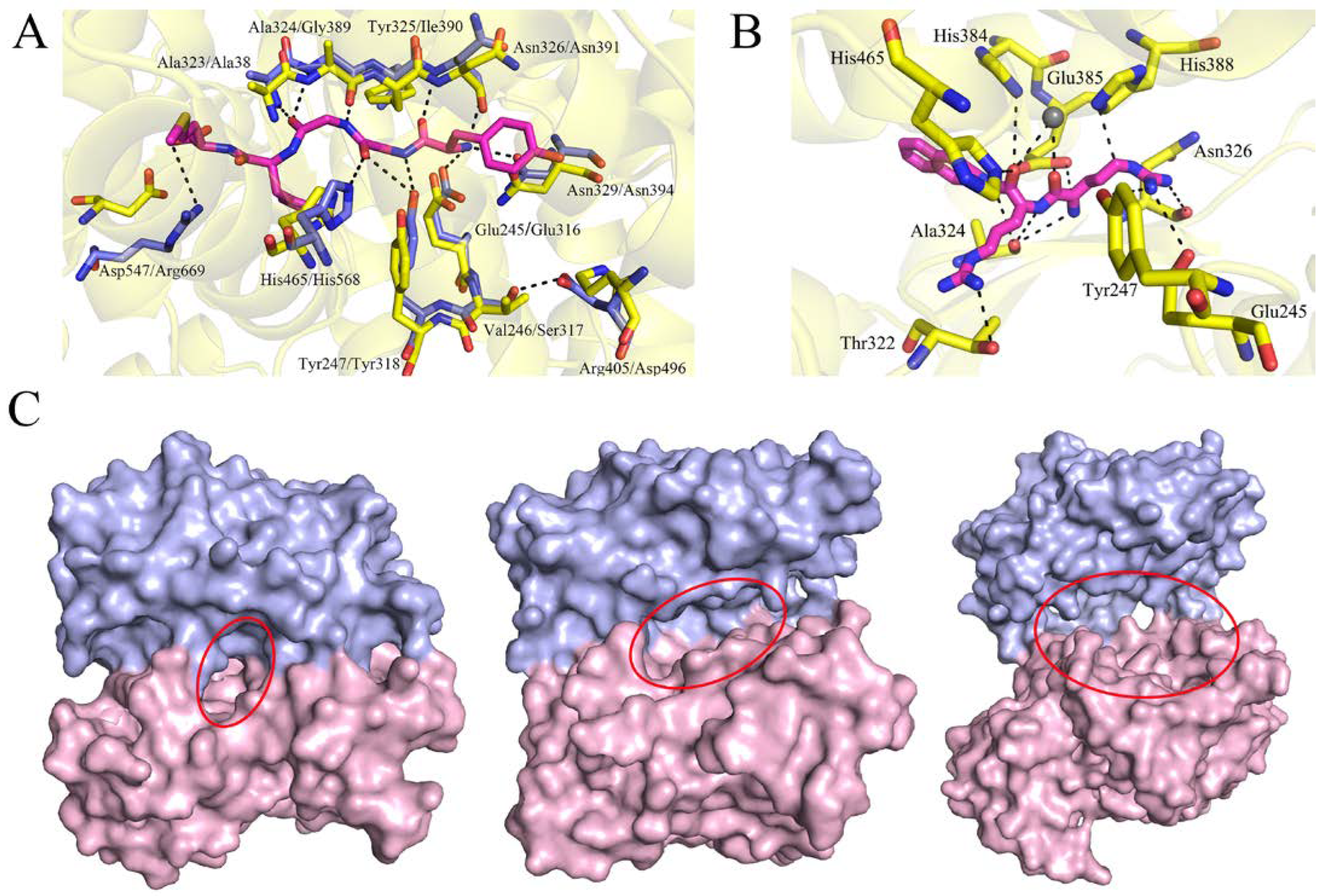
2.5. Mode of Substrate Binding
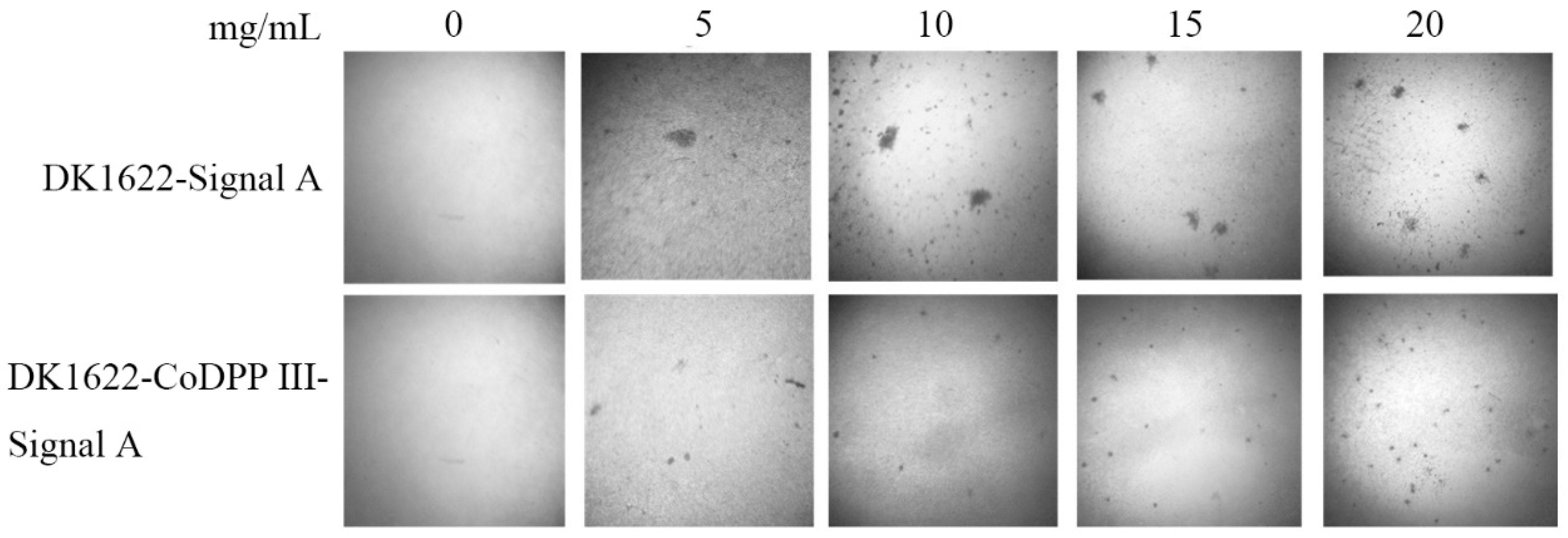
2.6. CoDPP III Promotes the Developmental Process of M. xanthus DK1622
2.7. A-Signal from DK1622-CoDPP III Restored Development in asgA Mutant
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Strains and Cultures
3.2. Gene Cloning and Sequence Analysis of CoDPP III
3.3. Protein Expression and Purification of CoDPP III
3.4. Determination of Molecular Mass
3.5. Biochemical Characterization of CoDPP III
3.6. Crystallization, Data Collection, Structure Determination, and Refinement
3.7. Molecular Docking
3.8. RT-PCR
3.9. Heterologous Expression of Codpp III in M. xanthus DK1622
3.10. Western Blot Analysis
3.11. Construction of asgA Mutant
3.12. Isolation of the A-Signal
3.13. Development Assay
3.14. Sporulation Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prajapati, S.C.; Chauhan, S.S. Dipeptidyl peptidase III: A multifaceted oligopeptide N-end cutter. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 3256–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaga, S.; Babić, D.; Osmak, M.; Sprem, M.; Abramić, M. Tumor cytosol dipeptidyl peptidase III activity is increased with histological aggressiveness of ovarian primary carcinomas. Gynecol. Oncol. 2003, 91, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, S.; Taschler, U.; Domenig, O.; Poglitsch, M.; Bourgeois, B.; Pollheimer, M.; Pusch, L.M.; Malovan, G.; Frank, S.; Madl, T.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 3 modulates the renin-angiotensin system in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 13711–13723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komeno, M.; Pang, X.; Shimizu, A.; Molla, M.R.; Yasuda-Yamahara, M.; Kume, S.; Rahman, N.I.A.; Soh, J.E.C.; Nguyen, L.K.C.; Ahmat Amin, M.K.B.; et al. Cardio- and reno-protective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase III in diabetic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Shimizu, A.; Kurita, S.; Zankov, D.P.; Takeuchi, K.; Yasuda-Yamahara, M.; Kume, S.; Ishida, T.; Ogita, H. Novel Therapeutic Role for Dipeptidyl Peptidase III in the Treatment of Hypertension. Hypertension 2016, 68, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matić, S.; Tomašić Paić, A.; Sobočanec, S.; Pinterić, M.; Pipalović, G.; Martinčić, M.; Matovina, M.; Tomić, S. Interdisciplinary Study of the Effects of Dipeptidyl-Peptidase III Cancer Mutations on the KEAP1-NRF2 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.A.; Jain, M.; Chauhan, S.S. Ets-1/Elk-1 is a critical mediator of dipeptidyl-peptidase III transcription in human glioblastoma cells. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 1861–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karačić, Z.; Šupljika, F.; Tomić, A.; Brkljačić, L.; Paić, A.T.; Ćehić, M.; Tomić, S. Neuropeptides, substrates and inhibitors of human dipeptidyl peptidase III, experimental and computational study—A new substrate identified. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramić, M.; Agić, D. Survey of Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Inhibitors: From Small Molecules of Microbial or Synthetic Origin to Aprotinin. Molecules 2022, 27, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agić, D.; Karnaš, M.; Šubarić, D.; Lončarić, M.; Tomić, S.; Karačić, Z.; Bešlo, D.; Rastija, V.; Molnar, M.; Popović, B.M.; et al. Coumarin Derivatives Act as Novel Inhibitors of Human Dipeptidyl Peptidase III: Combined In Vitro and In Silico Study. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kurosawa, H.; Nishimura, K.; Hazato, T. Identification of dipeptidyl peptidase III in human neutrophils. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, J.; Iwamoto, H.; Nagao, I.; Enmyo, K.; Sugao, H.; Kanemitu, N.; Ikeda, K.; Takeda, M.; Inoue, M.; Ikeda, T.; et al. Characterization of the metal-substituted dipeptidyl peptidase III (rat liver). Biochemistry 2001, 40, 11860–11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocco, C.; Gillibert-Duplantier, J.; Neaud, V.; Fukasawa, K.M.; Claverol, S.; Bonneu, M.; Puiroux, J. Identification and characterization of two dipeptidyl-peptidase III isoforms in Drosophila melanogaster. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanda, S.; Singh, H.; Singh, J.; Singh, T.P. Functional characterization and specific effects of various peptides on enzymatic activity of a DPP-III homologue from goat brain. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2008, 23, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hromić-Jahjefendić, A.; Jajčanin Jozić, N.; Kazazić, S.; Grabar Branilović, M.; Karačić, Z.; Schrittwieser, J.H.; Das, K.M.P.; Tomin, M.; Oberer, M.; Gruber, K.; et al. A novel Porphyromonas gingivalis enzyme: An atypical dipeptidyl peptidase III with an ARM repeat domain. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karačić, Z.; Vukelić, B.; Ho, G.H.; Jozić, I.; Sučec, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B.; Kozlović, M.; Brenner, S.E.; Ludwig-Müller, J.; Abramić, M. A novel plant enzyme with dual activity: An atypical Nudix hydrolase and a dipeptidyl peptidase III. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.E.; Fleischmann, R.D.; DeBoy, R.T.; Paulsen, I.T.; Fouts, D.E.; Eisen, J.A.; Daugherty, S.C.; Dodson, R.J.; Durkin, A.S.; Gwinn, M.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the oral pathogenic Bacterium porphyromonas gingivalis strain W83. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 5591–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karačić, Z.; Ban, Ž.; Macheroux, P.J.C.T.i.P.; Research, P. A novel member of the dipeptidyl peptidase III family from Armillariella tabescens. Curr. Top. Pept. Protein Res. 2017, 18, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- de Vries, L.E.; Sanchez, M.I.; Groborz, K.; Kuppens, L.; Poreba, M.; Lehmann, C.; Nevins, N.; Withers-Martinez, C.; Hirst, D.J.; Yuan, F.; et al. Characterization of P. falciparum dipeptidyl aminopeptidase 3 specificity identifies differences in amino acid preferences between peptide-based substrates and covalent inhibitors. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 3998–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J.; Thomas, P.D.; Huang, X.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D624–D632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabljić, I.; Tomin, M.; Matovina, M.; Sučec, I.; Tomašić Paić, A.; Tomić, A.; Abramić, M.; Tomić, S. The first dipeptidyl peptidase III from a thermophile: Structural basis for thermal stability and reduced activity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baral, P.K.; Jajcanin-Jozić, N.; Deller, S.; Macheroux, P.; Abramić, M.; Gruber, K. The first structure of dipeptidyl-peptidase III provides insight into the catalytic mechanism and mode of substrate binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 22316–22324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, G.A.; Dobrovetsky, E.; Viertlmayr, R.; Dong, A.; Binter, A.; Abramic, M.; Macheroux, P.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Gruber, K. Entropy-driven binding of opioid peptides induces a large domain motion in human dipeptidyl peptidase III. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6525–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabljić, I.; Meštrović, N.; Vukelić, B.; Macheroux, P.; Gruber, K.; Luić, M.; Abramić, M. Crystal structure of dipeptidyl peptidase III from the human gut symbiont Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, A.; González, M.; Tomić, S. The large scale conformational change of the human DPP III-substrate prefers the “closed” form. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Reithofer, V.; Reisinger, M.; Wallner, S.; Pavkov-Keller, T.; Macheroux, P.; Gruber, K. Substrate complexes of human dipeptidyl peptidase III reveal the mechanism of enzyme inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agić, D.; Brkić, H.; Kazazić, S.; Tomić, A.; Abramić, M. Aprotinin interacts with substrate-binding site of human dipeptidyl peptidase III. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 3596–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, B.W. Structural basis of the action of thermolysin and related zinc peptidases. Acc. Chem. Res. 1988, 21, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukelić, B.; Salopek-Sondi, B.; Špoljarić, J.; Sabljić, I.; Meštrović, N.; Agić, D.; Abramić, M. Reactive cysteine in the active-site motif of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron dipeptidyl peptidase III is a regulatory residue for enzyme activity. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Jodha, D.; Singh, J.; Dhanda, S. Purification, kinetic and functional characterization of membrane bound dipeptidyl peptidase-III from NCDC 252: A probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, Z.; Luo, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, B.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; et al. A predatory myxobacterium controls cucumber Fusarium wilt by regulating the soil microbial community. Microbiome 2020, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitworth, D.E. Myxobacteria: Physiology and Regulation. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretl, D.J.; Kirby, J.R. Molecular Mechanisms of Signaling in Myxococcus xanthus Development. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 3805–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuspa, A.; Plamann, L.; Kaiser, D. Identification of heat-stable A-factor from Myxococcus xanthus. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 3319–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensign, J.C.; Wolfe, R.S. Lysis of Bacterial Cell Walls by an Enzyme Isolated from a Myxobacter. J. Bacteriol. 1965, 90, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensign, J.C.; Wolfe, R.S. Characterization of a small proteolytic enzyme which lyses bacterial cell walls. J. Bacteriol. 1966, 91, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingard, M.; Matsueda, G.; Wolfe, R.S. Myxobacter AL-1 protease II: Specific peptide bond cleavage on the amino side of lysine. J. Bacteriol. 1972, 112, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnosspelius, G. Purification and properties of an extracellular protease from Myxococcus virescens. J. Bacteriol. 1978, 133, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, F.; Guespin-Michel, J.F. Production of an extracellular milk-clotting activity during development in Myxococcus xanthus. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 5136–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poza, M.; Sieiro, C.; Carreira, L.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Villa, T.G. Production and characterization of the milk-clotting protease of Myxococcus xanthus strain 422. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, F.; Ye, X.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Cui, Z. AmyM, a Novel Maltohexaose-Forming α-Amylase from Corallococcus sp. strain EGB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajcanin-Jozić, N.; Deller, S.; Pavkov, T.; Macheroux, P.; Abramić, M. Identification of the reactive cysteine residues in yeast dipeptidyl peptidase III. Biochimie 2010, 92, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, K.R. The isolation and some properties of dipeptidyl peptidases II and III from porcine spleen. Int. J. Biochem. 1991, 23, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodha, D.; Attri, P.; Khaket, T.P.; Singh, J. Isolation, purification and biochemical characterization of dipeptidyl peptidase-III from germinated Vigna radiata seeds. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoljarić, J.; Salopek-Sondi, B.; Makarević, J.; Vukelić, B.; Agić, D.; Simaga, S.; Jajcanin-Jozić, N.; Abramić, M. Absolutely conserved tryptophan in M49 family of peptidases contributes to catalysis and binding of competitive inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2009, 37, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Xie, C.; Yao, D.; Zhou, C.Z.; Liu, J. Crystal structures of Aflatoxin-oxidase from Armillariella tabescens reveal a dual activity enzyme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 494, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramić, M.; Schleuder, D.; Dolovcak, L.; Schröder, W.; Strupat, K.; Sagi, D.; Peter-Katalini, J.; Vitale, L. Human and rat dipeptidyl peptidase III: Biochemical and mass spectrometric arguments for similarities and differences. Biol. Chem. 2000, 381, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajčanin-Jozić, N.; Abramić, M. Hydrolysis of dipeptide derivatives reveals the diversity in the M49 family. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomin, M.; Tomić, S. Dynamic properties of dipeptidyl peptidase III from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and the structural basis for its substrate specificity—A computational study. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, Q.; Qu, G.; Feng, Y.; Reetz, M.T. Utility of B-Factors in Protein Science: Interpreting Rigidity, Flexibility, and Internal Motion and Engineering Thermostability. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 1626–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, A.; Abramić, M.; Spoljarić, J.; Agić, D.; Smith, D.M.; Tomić, S. Human dipeptidyl peptidase III: Insights into ligand binding from a combined experimental and computational approach. J. Mol. Recognit. JMR 2011, 24, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomić, A.; Tomić, S. Hunting the human DPP III active conformation: Combined thermodynamic and QM/MM calculations. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 15503–15514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramić, M.; Karačić, Z.; Šemanjski, M.; Vukelić, B.; Jajčanin-Jozić, N. Aspartate 496 from the subsite S2 drives specificity of human dipeptidyl peptidase III. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, D. Signaling in myxobacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 58, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konovalova, A.; Wegener-Feldbrügge, S.; Søgaard-Andersen, L. Two intercellular signals required for fruiting body formation in Myxococcus xanthus act sequentially but non-hierarchically. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 86, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielkopf, C.L.; Bauer, W.; Urbatsch, I.L. Bradford Assay for Determining Protein Concentration. Cold Spring Harbor Protoc. 2020, 2020, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, F.A.; Saleta, M.E.; Pagliuca, R.J.; Eleotério, M.A.; Reis, R.D.; Fonseca Júnior, J.; Meyer, B.; Bittar, E.M.; Souza-Neto, N.M.; Granado, E. XDS: A flexible beamline for X-ray diffraction and spectroscopy at the Brazilian synchrotron. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2016, 23, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagin, A.A.; Steiner, R.A.; Lebedev, A.A.; Potterton, L.; McNicholas, S.; Long, F.; Murshudov, G.N. REFMAC5 dictionary: Organization of prior chemical knowledge and guidelines for its use. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; Version 2.0; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Leng, X.; Zhu, W.; Jin, J.; Mao, X. Evidence that a chaperone-usher-like pathway of Myxococcus xanthus functions in spore coat formation. Microbiology 2011, 157, 1886–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.P.; Yue, X.J.; Han, K.; Li, Z.F.; Zheng, L.S.; Yi, X.N.; Wang, H.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Li, Y.Z. Allopatric integrations selectively change host transcriptomes, leading to varied expression efficiencies of exotic genes in Myxococcus xanthus. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Schramm, A.; Jagadeesan, S.; Higgs, P.I. Two-component systems and regulation of developmental progression in Myxococcus xanthus. Methods Enzymol. 2010, 471, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Km/μM | Kcat/s−1 | Kcat/Km/mM−1 s−1 | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtND | 3.25 ± 1.12 | 0.002 ± 0.0001 | 0.615 | [16] |
| PpND | 10.63 ± 1.72 | 0.014 ± 0.003 | 1.289 | [16] |
| hDPP III | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 20.5 ± 1.2 | 9318.2 | [48] |
| yDPP III | 12.0 ± 1.7 | 0.18 ± 0.06 | 15.0 | [48] |
| BtDPP III | 2.5 ± 0.9 | 5.0 ± 2.9 | 2000 | [29] |
| PgDPP III | 0.97 ± 0.16 | 0.75 ± 0.13 | 773.2 | [15] |
| CaDPP III | 35.2 ± 2.0 | 3.07 ± 0.04 | 87.3 | [21] |
| PaDPP III | 9.0 | 0.0292 | 3.2 | [30] |
| CoDPP III | 578.91 ± 60.52 | 1.34 ± 0.06 | 2.31 |
| Se-CoDPPIII | |
|---|---|
| Data collection | |
| Space group | P212121 |
| Resolution [Å] | 25.0–1.90 (1.97–1.90) |
| Unit-cell | |
| a/b/c [Å] | 58.14/77.85/228.29 |
| α/β/γ (°) | 90.00/90.00/90.00 |
| Unique reflections | 82,558 (7990) |
| Redundancy | 4.3 (4.3) |
| Completeness [%] | 99.7 (98.2) |
| average I/σ(I) | 24.2 (9.6) |
| Rmerge [%] | 6.7 (20.2) |
| Refinement | |
| Number of molecules in a.u. | 2 |
| No. of reflections | 78,400 (5879) |
| Rwork (95% of data) | 0.173 (0.210) |
| Rfree (5% of data) | 0.223 (0.260) |
| R.m.s.d. bonds [Å] | 0.010 |
| R.m.s.d. angles [º] | 1.515 |
| No. of non-H atoms/average B-factors [Å2] | |
| Protein | 8302/24.74 |
| Water | 934/31.81 |
| Ligand | 2/29.34 |
| Ramachandran plot | |
| Most favored [%] | 97.56 |
| Allowed [%] | 2.35 |
| Disallowed [%] | 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.-B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.-F.; Li, Z.-K.; Liu, W.-D.; Cui, Z.-L.; Huang, Y. Structural and Functional Characterization of a New Bacterial Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Involved in Fruiting Body Formation in Myxobacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010631
Chen S-B, Zhang H, Chen S, Ye X-F, Li Z-K, Liu W-D, Cui Z-L, Huang Y. Structural and Functional Characterization of a New Bacterial Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Involved in Fruiting Body Formation in Myxobacteria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010631
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Si-Bo, Han Zhang, Si Chen, Xian-Feng Ye, Zhou-Kun Li, Wei-Dong Liu, Zhong-Li Cui, and Yan Huang. 2023. "Structural and Functional Characterization of a New Bacterial Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Involved in Fruiting Body Formation in Myxobacteria" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010631
APA StyleChen, S.-B., Zhang, H., Chen, S., Ye, X.-F., Li, Z.-K., Liu, W.-D., Cui, Z.-L., & Huang, Y. (2023). Structural and Functional Characterization of a New Bacterial Dipeptidyl Peptidase III Involved in Fruiting Body Formation in Myxobacteria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010631






