A Single Episode of Cortical Spreading Depolarization Increases mRNA Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines, Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Pannexin-1 Channels in the Cerebral Cortex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
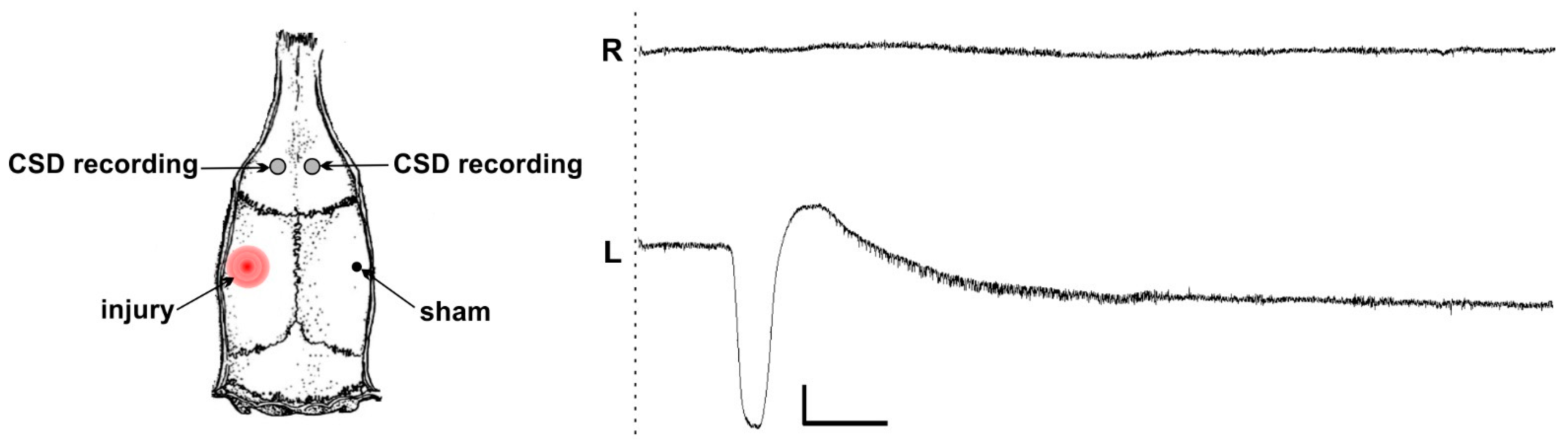
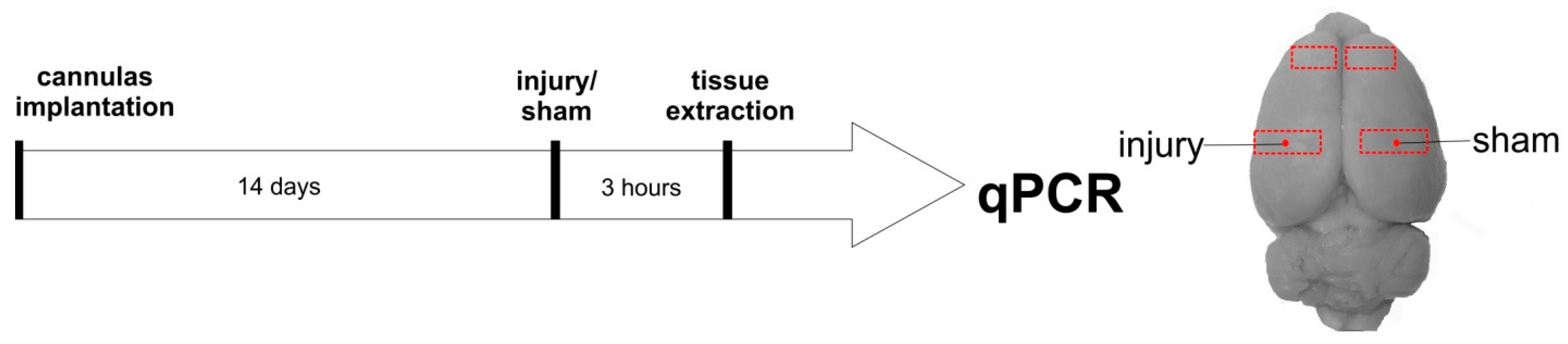
2.2. Stereotaxic Surgery
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, and qPCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSD | cortical spreading depolarization |
| Il1b | interleukin-1beta |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| Il6 | interleukin-6 |
| CGRP | calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| Panx1 | pannexin-1 |
| TGFb | transforming growth factor beta |
References
- Huber-Lang, M.; Lambris, J.; Ward, P.A. Innate immune responses to trauma. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthos, D.N.; Sandkühler, J. Neurogenic neuroinflammation: Inflammatory CNS reactions in response to neuronal activity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetta, I.; Riolo, R.; Todaro, F.; Tuttolomondo, A. New Insights on Metabolic and Genetic Basis of Migraine: Novel Impact on Management and Therapeutical Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.M.; Ashina, M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and migraine with aura: A systematic review. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, L.N.; Eftekhari, S.; Wang, M.; Charles, A.C.; Russo, A.F. Cortical spreading depression as a site of origin for migraine: Role of CGRP. Cephalalgia 2018, 39, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdener, E.; Kaya, Z.; Dalkara, T. Parenchymal neuroinflammatory signaling and dural neurogenic inflammation in migraine. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursun, O.; Yemisci, M.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.; Karatas, H. Migraine and neuroinflammation: The inflammasome perspective. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, M.; Kotan, D.; Çiftçi, G.G.; Çiftçi, I.H.; Cikriklar, H.I. Serum levels of endocan, claudin-5 and cytokines in migraine. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 930–936. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, R.H.; Gollion, C.; Amin, F.M.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Hadjikhani, N.; Ashina, M. Imaging the inflammatory phenotype in migraine. J. Headache Pain 2022, 23, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D. Association of serum levels of calcitonin gene-related peptide and cytokines during migraine attacks. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2019, 22, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jander, S.; Schroeter, M.; Peters, O.; Witte, O.W.; Stoll, G. Cortical Spreading Depression Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Gene Expression in the Rat Brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takizawa, T.; Qin, T.; Lopes de Morais, A.; Sugimoto, K.; Chung, J.Y.; Morsett, L.; Mulder, I.; Fischer, P.; Suzuki, T.; Anzabi, M.; et al. Non-invasively triggered spreading depolarizations induce a rapid pro-inflammatory response in cerebral cortex. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 40, 1117–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbach, A.; Bruehl, C.; Witte, O.W. Microarray-based long-term detection of genes differentially expressed after cortical spreading depression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatas, H.; Erdener, S.E.; Gursoy-Ozdemir, Y.; Lule, S.; Eren-Koçak, E.; Sen, Z.D.; Dalkara, T. Spreading depression triggers headache by activating neuronal Panx1 channels. Science 2013, 339, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Levy, D.; Noseda, R.; Kainz, V.; Jakubowski, M.; Burstein, R. Activation of Meningeal Nociceptors by Cortical Spreading Depression: Implications for Migraine with Aura. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8807–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Velagapudi, R.; Terrando, N. Neuroinflammation after surgery: From mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquens, A.; Needham, E.J.; Zanier, E.R.; Degos, V.; Gressens, P.; Menon, D. Neuro-Inflammation Modulation and Post-Traumatic Brain Injury Lesions: From Bench to Bed-Side. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.S.; Johnson, T.; Kuipers, H.M.; Kristensen, D.; Siersma, V.D.; Vila, P.; Jolles, J.; Papaioannou, A.; Abildstrom, H.; Silverstein, J.H.; et al. Does anaesthesia cause postoperative cognitive dysfunction? A randomised study of regional versus general anaesthesia in 438 elderly patients. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2003, 47, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartings, J.A.; Andaluz, N.; Bullock, M.R.; Hinzman, J.M.; Mathern, B.; Pahl, C.; Puccio, A.; Shutter, L.; Strong, A.J.; Vagal, A.; et al. Prognostic Value of Spreading Depolarizations in Patients With Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenfeld, A.; McVige, J.; Knievel, K. Post-traumatic headache: Pathophysiology and management—A review. J. Concussion 2022, 6, 20597002221093478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, H.; Eigenbrodt, A.K.; Seifert, T.; Sinclair, A.J.; Scher, A.I.; Schytz, H.W.; Lee, M.J.; De Icco, R.; Finkel, A.G.; Ashina, M. Post-traumatic headache attributed to traumatic brain injury: Classification, clinical characteristics, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagraoui, M.; Latoche, J.R.; Cartwright, N.G.; Sukumar, G.; Dalgard, C.L.; Schaefer, B.C. Controlled Cortical Impact and Craniotomy Induce Strikingly Similar Profiles of Inflammatory Gene Expression, but with Distinct Kinetics. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, C.L.; Huber, B.R.; Peskind, E. Traumatic brain injury, neuroinflammation, and post-traumatic headaches. Headache 2013, 53, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhuri, R.; Cui, L.; Yong, C.; Bowyer, S.; Klein, R.M.; Welch, K.M.A.; Berman, N.E.J. Cortical spreading depression and gene regulation: Relevance to migraine. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 51, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martami, F.; Jahromi, S.R.; Togha, M.; Ghorbani, Z.; Seifishahpar, M.; Saidpour, A. The serum level of inflammatory markers in chronic and episodic migraine: A case-control study. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-C.; Kainz, V.; Burstein, R.; Levy, D. Tumor necrosis factor-α induces sensitization of meningeal nociceptors mediated via local COX and p38 MAP kinase actions. Pain 2011, 152, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, E.J.; Schmidt, T.W.; Firm, C.S.; Russo, A.; Durham, P.L. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide expression and secretion from rat trigeminal ganglion neurons. J. Neurochem. 2005, 96, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, F.; Lütz, W.; Eitner, A.; Leuchtweis, J.; Lehmenkühler, A.; Schaible, H.-G. Tumor necrosis factor reduces the amplitude of rat cortical spreading depressionin vivo. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.K.; Patil, C.S.; Jackson, M.F. Pannexin-1 in the CNS: Emerging concepts in health and disease. J. Neurochem. 2020, 154, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, D.; Maturana, C.; Pelissier, T.; Hernández, A.; Constandil, L. Interactions of pannexin 1 with NMDA and P2X7 receptors in central nervous system pathologies: Possible role on chronic pain. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 101, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-P.; Qin, T.; Seidel, J.L.; Zheng, Y.; Eikermann, M.; Ferrari, M.D.; Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.V.D.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Ayata, C.; Eikermann-Haerter, K. Inhibition of the P2X7–PANX1 complex suppresses spreading depolarization and neuroinflammation. Brain 2017, 140, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tye, A.E.; Zhao, J.; Ma, D.; Raddant, A.C.; Bu, F.; Spector, B.L.; Winslow, N.K.; Wang, M.; Russo, A.F. Induction of calcitonin gene-related peptide expression in rats by cortical spreading depression. Cephalalgia 2016, 39, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Edvinsson, L.; Ekman, R. Vasoactive peptide release in the extracerebral circulation of humans during migraine headache. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 28, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, L.V.; Kuznetsova, G.D.; Coenen, A.M. Unilateral cortical spreading depression induced by sound in rats. Brain Res. 2009, 1286, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samotaeva, I.; Tillmanns, N.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Vinogradova, L. Intracortical microinjections may cause spreading depression and suppress absence seizures. Neuroscience 2013, 230, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradova, L.V.; Rysakova, M.P.; Pavlova, I.V. Small damage of brain parenchyma reliably triggers spreading depolarization. Neurol. Res. 2020, 42, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, M.P.; Medvedeva, T.M.; Pavlova, I.V.; Vinogradova, L.V. Region-Specific Vulnerability of the Amygdala to Inju-ry-Induced Spreading Depolarization. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilborg, A.; Passarelli, M.; Steitz, J.A. Calcium signaling and transcription: Elongation, DoGs, and eRNAs. Recept. Clin. Investig. 2016, 3, e1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Forward | Reverse | Tanneling, °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calca | AGT TCT CCC CTT TCC TGG TTG TC | CCA GTA GGC GAG CTT CTT CTT CA | 65 |
| Panx1 | CAC CGA GCC CAA GTT CAA GG | GGC CCA GCA GTA AGA GTC CA | 64 |
| Il1b | TCT GTG ACT CGT GGG ATG AT | CAC TTG TTG GCT TAT GTT CTG TC | 61 |
| Tnf | GTC CAA CTC CGG GCT CAG AAT | ACT CCC CCG ATC CAC TCA G | 65 |
| Il6 | GCC ACT GCC TTC CCT ACT TCA C | GAC AGT GCA TCA TCG CTG TTC ATA C | 63 |
| Tgfb | GCG CCT GCA GAG ATT CAA GTC AAC | TCA GGC GTA TCA GTG GGG GTC A | 65 |
| Ywhaz | TTG AGC AGA AGA CGG AAG GT | GAA GCA TTG GGG ATC AAG AA | 63 |
| Osbp | TCC GGG AGA CTT TAC CTT CAC TT | GTG TCA CCC TCT TAT CAA CCA CC | 63 |
| Hprt1 | CGT CGT GAT TAG TGA TGA TGA AC | CAA GTC TTT CAG TCC TGT CCA TAA | 65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volobueva, M.N.; Suleymanova, E.M.; Smirnova, M.P.; Bolshakov, A.P.; Vinogradova, L.V. A Single Episode of Cortical Spreading Depolarization Increases mRNA Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines, Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Pannexin-1 Channels in the Cerebral Cortex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010085
Volobueva MN, Suleymanova EM, Smirnova MP, Bolshakov AP, Vinogradova LV. A Single Episode of Cortical Spreading Depolarization Increases mRNA Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines, Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Pannexin-1 Channels in the Cerebral Cortex. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolobueva, Maria N., Elena M. Suleymanova, Maria P. Smirnova, Alexey P. Bolshakov, and Lyudmila V. Vinogradova. 2023. "A Single Episode of Cortical Spreading Depolarization Increases mRNA Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines, Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Pannexin-1 Channels in the Cerebral Cortex" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010085
APA StyleVolobueva, M. N., Suleymanova, E. M., Smirnova, M. P., Bolshakov, A. P., & Vinogradova, L. V. (2023). A Single Episode of Cortical Spreading Depolarization Increases mRNA Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines, Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Pannexin-1 Channels in the Cerebral Cortex. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010085






