Reported Cases and Diagnostics of Occupational Insect Allergy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
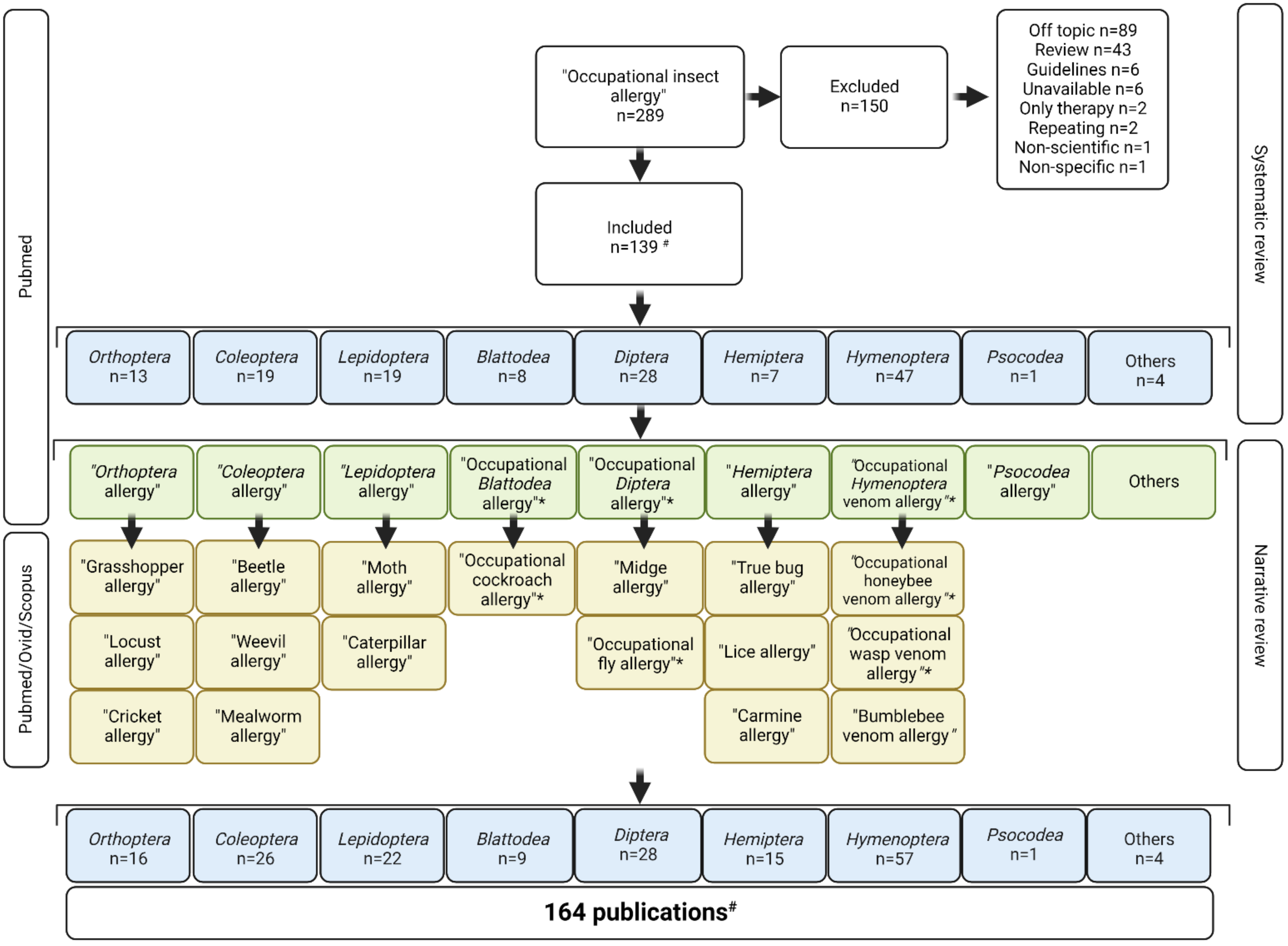
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Orthoptera
3.1.1. Grasshopper Allergy
3.1.2. Cricket Allergy
3.2. Coleoptera
3.2.1. Beetle Allergy
| Beetle Allergy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Bruchus lentis | Armentia A [37] | 2003 | 1 | Agronomist | SPT, SIC, immunoblot |
| Bruchus lentis | Armentia A [35] | 2006 | 16 | Farmers, cooks | SPT, SIC, oral provocation, sIgE |
| Bruchus pisorum | Armentia A [36] | 2020 | 6 | Farmers, agronomists | SPT, patch test, SIC, oral provocation, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Dermestidae | Brito FF [44] | 2002 | 1 | Wool worker | SPT, SIC, conjunctival provocation, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Dermestidae | Sheldon JM [43] | 1941 | 1 | Museum curator | SPT |
| Sitophilus granarius | Herling C [41] | 1995 | 66 | Bakers | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Sitophilus granarius | Lunn JA [40] | 1966 | 75 | Millworkers | SPT, SIC |
| Sitophilus granarius | Frankland AW [39] | 1964 | 2 | Laboratory | SPT |
| Sitophilus granarius | Lunn JA [38] | 1966 | 1 | Laboratory | SPT, SIC |
| Trogoderma variabile | Bernstein JA [42] | 2009 | 1 | Pet food manufacturer | Reversibility test, SPT, nasal provocation, sIgE, immunoblot |
| TenebrionidaeAllergy | |||||
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Alphitobius diaperinus | Schroeckenstein DC [45] | 1988 | 3 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, inhibition test, HRT |
| Tenebrio molitor | Bernstein DI [46] | 1983 | 5 | LFB | SPT, sIgE |
| Tenebrio molitor | Siracusa A [47] | 1994 | 14 | LFB | SPT, sIgE PEF measurements, BHR, inhibition test |
| Tenebrio molitor | Armentia A [48] | 1997 | 50 | Cereal workers | SPT, sIgE, conjunctival provocation, SIC |
| Tenebrio molitor | Bernstein J [49] | 2002 | 1 | Teacher | SPT, nasal provocation |
| Tenebrio molitor | Siracusa A [50] | 2003 | 76 | LFB | SPT, sIgE |
| Tenebrio molitor | Panzani R [51] | 2008 | 54 | Bakers | SPT, BHR |
| Tenebrio molitor, Zophobas morio | Renström A [7] | 2011 | 59 | Pet shop | sIgE, spirometry |
| Tenebrio molitor | Broekman HCHP [52] | 2017 | 4 | Breeders | SPT, sIgE, BAT, immunoblot, DBPCFC |
| Tenebrio molitor | Francis F [28] | 2019 | 31 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Tenebrio molitor | Nebbia S [53] | 2019 | 2 | Food industry | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot, BAT |
| Tenebrio molitor | Ganseman E [54] | 2022 | 1 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot, BAT, inhibition test |
| Tenebrio molitor, Alphitobius diaperinus | Schroeckenstein DC [55] | 1989 | 1 | Animal handler | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot, inhibition test |
| Tribolium confusum | Schultze-Werninghaus G [56] | 1991 | 125 | Flour | sIgE, inhibition test, immunoblot |
| Tribolium confusum | Alanko A [57] | 2000 | 1 | Flour | SPT, sIgE, SIC |
| Zophobas morio | Bregnbak D [33] | 2013 | 1 | Zoo owner | SPT |
3.2.2. Tenebrionidae Allergy
3.3. Lepidoptera
3.3.1. Moth Allergy
| Moth Allergy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Bombyx mori | Harindranath N [64] | 1985 | 243 | Silk industry | SPT, sIgE |
| Bombyx mori | Uragoda CG [63] | 1991 | 53 | Silk industry | PEF measurements, questionnaire |
| Bombyx mori | Gowda G [65] | 2014 | 120 | Silk industry | Reversibility test, SPT |
| Bombyx mori | Zuo J [66] | 2015 | 24 | Unknown | Immunoblot, inhibition test |
| Ephestia | Armentia A [59] | 2004 | 15 | Baker, farmer | SPT, SIC, sIgE, inhibition test |
| Ephestia | Panzani R [51] | 2008 | 57 | Bakers | SPT, BHR |
| Ephestia kuehniella | Mäkinen-Kiljunen S [58] | 2003 | 1 | Baker | SPT, sIgE, inhibition test, nasal provocation |
| Ephestia kuehniella | Moreno Escobosa MC [60] | 2014 | 1 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Galleria mellonella | Stevenson DD [61] | 1966 | 1 | LFB | SPT, HRT, immunoblot, SIC |
| Galleria mellonella | Siracusa A [47] | 1994 | 14 | LFB | SPT, sIgE, PEF measurements, BHR, inhibition test |
| Galleria mellonella | Siracusa A [50] | 2003 | 76 | LFB | SPT, sIgE |
| Galleria mellonella | Bregnbak D [33] | 2013 | 1 | Zoo owner | SPT |
| Lymantria dispar, Pectinophora gossypiella, Euproctis chrysorrhoea | Suarthana E [17] | 2012 | 157 | Insect breeders | sIgE |
| Orgyia pseudotsugata | Press E [62] | 1977 | 428 | Timber, forestry workers | SPT, questionnaire |
| Caterpillar Allergy | |||||
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Lymantria dispar, Orgyia pseudotsugata | Etkind P [67] | 1982 | 17 | Laboratory | Scratch test |
| Thaumetopoe pityocampa | Vega JM [68] | 1997 | 1 | Pine-forest worker | SPT, immunoblot |
| Thaumetopoe pityocampa | Vega JM [69] | 1999 | 55 | Pine-forest workers | SPT, immunoblot |
| Thaumetopoe pityocampa | Vega JM [70] | 2000 | 16 | Pine-forest workers | SPT, immunoblot |
| Thaumetopoe pityocampa | Rebollo S [71] | 2002 | 13 | Unknown | SPT, immunoblot |
| Thaumetopoe pityocampa | Vega J [72] | 2004 | 30 | Pine-forest workers | SPT, immunoblot |
| Thaumetopoe pityocampa | Morales-Cabeza C [73] | 2016 | 1 | Pine-resin worker | SPT, sIgE, BAT, immunoblot |
| Thaumetopoe pityocampa | Ricciardi L [74] | 2021 | 3 | Pine-forest workers | Questionnaire |
3.3.2. Caterpillar Allergy
3.4. Blattodea
Cockroach Allergy
3.5. Diptera
3.5.1. Fly Allergy
| Fly Allergy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Calliphora vomitoria | Pazzaglia M [99] | 2003 | 1 | LFB | SPT |
| Calliphora vomitoria | Siracusa A [50] | 2003 | 75 | LFB | SPT, sIgE |
| Ceratitis capitata | de Las Marinas MD [87] | 2014 | 2 | Production | SPT, sIgE, SIC, immunoblot, FeNO, BHR |
| Champignon flies | Cimarra M [94] | 1999 | 1 | Mushroom cultivator | SPT, conjunctival provocation, PEF measurements, immunoblot |
| Drosophila melanogaster | Colomb S [85] | 2017 | 59 | Laboratory | Questionnaire, SPT, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Drosophila melanogaster | Jones M [83] | 2017 | 286 | Laboratory | Questionnaire, sIgE |
| Drosophila melanogaster | Betancor D [86] | 2021 | 1 | Laboratory | SPT, FeNO, nasal provocation, immunoblot |
| Drosophila melanogaster | Spieksma FT [84] | 1986 | 22 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, inhibition test, SIC |
| Elk fly | Laukkanen A [95] | 2005 | 1 | Geological researcher | SPT, sIgE, inhibition test, nasal and conjunctival provocation |
| Glossina morsitans | Stevens WJ [100] | 1996 | 1 | Laboratory | sIgE |
| Lucilia caesar | Siracusa A [47] | 1994 | 14 | LFB | SPT, sIgE, PEF measurements, BHR, inhibition test |
| Lucilia cuprina | Kaufman GL [92] | 1986 | 1 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, BHR |
| Lucilia cuprina | Baldo BA [91] | 1989 | 30 | Laboratory | sIgE, immunoblot |
| Lucilia cuprina | Kaufman GL [93] | 1989 | 53 | Laboratory | Questionnaire, sIgE |
| Musca domestica | Tee RD [88] | 1985 | 1 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, inhibition test |
| Musca domestica | Wahl R [90] | 1997 | 1 | Farmer | Conjunctival provocation, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Musca domestica | Focke M [89] | 2003 | 1 | Farmer | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot, inhibition test |
| Screwworm fly | Herrmann GH [98] | 1966 | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Screwworm fly | Dille JR [97] | 1968 | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Sewer flies | Gold BL [96] | 1985 | 1 | Sewage worker | SPT, HRT, SIC |
| Midge Allergy | |||||
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Chironomid midges | Baur X [101] | 1992 | 85 | Fish food, laboratory | SPT, sIgE |
| Chironomid midges | Teranishi H [102] | 1995 | 1 | Environmental researcher | sIgE, inhibition test, immunoblot |
| Chironomid midges | Seldén AI [103] | 2013 | 8 | Sewage workers | FeNO, sIgE |
| Chironomus lewisi, Chironomus riparius | Tee RD [104] | 1985 | 26 | Unknown | SPT, sIgE, inhibition test |
| Chironomus thummi | Liebers V [105] | 1993 | 225 | Fish food | SPT, sIgE |
| Chironomus thummi | Galindo PA [106] | 1999 | 4 | Fish food | SPT, sIgE, conjunctival and nasal provocation, immunoblot |
| Chironomus thummi | Meseguer Arce J [107] | 2013 | 8 | Fish food | SPT, PEF measurements, BHR, nasal provocation, sIgE, immunoblot, inhibition test |
| Chironomus: thummi, annularius, tentans and tepperi | Baur X [108] | 1982 | 99 | Fish food | SPT, sIgE, inhibition test, SIC |
3.5.2. Midge Allergy
3.6. Hemiptera
3.6.1. True Bug Allergy
3.6.2. Lice Allergy
| True Bug Allergy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Eurygaster | Armentia A [59] | 2004 | 15 | Stored grain | SPT, SIC, sIgE, inhibition test |
| Eurygaster | Panzani R [51] | 2008 | 57 | Bakers | SPT, BHR |
| Macrolophus caliginosus | Lindström I [110] | 2017 | 2 | Greenhouse workers | SPT, sIgE, SIC, reversibility test |
| Macrolophus pygmaeus | Suojalehto H [109] | 2021 | 117 | Greenhouse workers | sIgE, FeNO |
| MetopopIax ditomoides, Microplax albofasciato | García Lázaro MA [111] | 1997 | 1 | Water bottling | SPT, conjunctival provocation, BHR, PEF measurements, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Whitefly | Campion KM [125] | 2012 | 26 | Insect breeders | sIgE |
| Lice Allergy | |||||
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Dactylopius coccus | Burge PS [113] | 1979 | 2 | Dye factory, Cosmetics blender | SIC |
| Dactylopius coccus | Park GR [112] | 1981 | 1 | Soldier | None |
| Dactylopius coccus | Quirce S [116] | 1993 | 9 | Dye factory | SPT, sIgE, inhibition tests, SIC, oral provocation |
| Dactylopius coccus | Acero S [120] | 1998 | 1 | Spice warehouse | SPT, SIC, immunoblot |
| Dactylopius coccus | Lizaso MT [115] | 2000 | 3 | Dye factory | SPT, SIC, immunoblot |
| Dactylopius coccus | Añíbarro B [119] | 2003 | 2 | Butchers | SPT, SIC, immunoblot |
| Dactylopius coccus | Tabar-Purroy AI [114] | 2003 | 2 | Dye factory | SPT, SIC, immunoblot |
| Dactylopius coccus | Ferrer A [118] | 2005 | 1 | Butcher | SPT, SIC, immunoblot, sIgE, inhibition test |
| Dactylopius coccus | Cox CE [117] | 2012 | 1 | Screen printer | SPT, sIgE, BAT |
3.7. Hymenoptera
3.7.1. General Hymenoptera Venom Allergy
3.7.2. Honey Bee Venom Allergy
3.7.3. Bumblebee Venom Allergy
| General Hymenoptera Venom Allergy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Encarsia | Campion KM [125] | 2012 | 26 | Insect breeders | sIgE |
| Hymenoptera | Kahan E [131] | 1997 | 500 | General | Questionnaire |
| Hymenoptera | Ono T [129] | 1998 | 118 | Pest-control operators | Questionnaire, sIgE |
| Hymenoptera | Incorvaia C [163] | 2004 | 112 | Forest workers | Questionnaire |
| Hymenoptera | Turbyville JC [164] | 2013 | 3 | Soldiers | Retrospective analysis |
| Hymenoptera | Paolocci G [132] | 2014 | 181 | General | Questionnaire |
| Hymenoptera | Voss JD [165] | 2016 | 23 | Soldiers | Retrospective analysis |
| Hymenoptera | Toletone A [126] | 2017 | 104 | Outdoor workers | Questionnaire |
| Hymenoptera | Ricciardi L [130] | 2018 | 341 | Forestry workers | Questionnaire |
| Honey bee Venom Allergy | |||||
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Honey bee | Light WC [140] | 1975 | 34 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | Müller U [142] | 1977 | 57 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | Bousquet J [166] | 1982 | 250 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire, sIgE |
| Honey bee | Kemeny DM [167] | 1983 | 11 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | Nordvall SL [141] | 1983 | 37 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | Reisman RE [151] | 1983 | 2 | Honey production | SPT, sIgE, inhibition |
| Honey bee | Bousquet J [137] | 1984 | 176 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire, SPT, sIgE |
| Honey bee | Lomnitzer R [168] | 1986 | 15 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | Khan RH [169] | 1991 | 14 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | Annila IT [170] | 1997 | 78 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | García-Robaina JC [171] | 1997 | 242 | Beekeepers | SPT, sIgE |
| Honey bee | Kalyoncu AF [172] | 1997 | 786 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire, sIgE |
| Honey bee | Yee CJ [146] | 1997 | 78 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | Eich-Wanger C [144] | 1998 | 62 | Beekeepers | SPT, sIgE |
| Honey bee | Manso EC [173] | 1998 | 59 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | Annila IT [139] | 2000 | 6 | Beekeepers | SPT, HRT |
| Honey bee | Garrido-Fernandez SG [149] | 2004 | 3 | Beekeepers | Patch test, sIgE |
| Honey bee | Rudeschko O [150] | 2004 | 1 | Beekeeper | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot, inhibition test |
| Honey bee | Celikel S [133] | 2006 | 494 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire |
| Honey bee | Kalogeromitros D [138] | 2006 | 35 | Beekeepers | SPT, sIgE |
| Honey bee | Meiler F [174] | 2008 | 10 | Beekeepers | sIgE, cytokine production, T cell response |
| Honey bee | Münstedt K [134] | 2008 | 1053 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire |
| Honey bee | Münstedt K [148] | 2010 | 73 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire |
| Honey bee | Richter AG [175] | 2011 | 852 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire |
| Honey bee | Varga EM [145] | 2013 | 10 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | von Moos S [176] | 2013 | 96 | Outdoor workers, beekeepers | Questionnaire |
| Honey bee | Celiksoy MH [177] | 2014 | 301 | Beekeepers | sIgE, cytokine production, T cell response |
| Honey bee | Gómez Torrijos E [153] | 2016 | 2 | Pharmacy laboratory | SPT, sIgE, BHR, SIC |
| Honey bee | Guan K [143] | 2016 | 54 | Beekeepers | SPT, sIgE |
| Honey bee | Li LS [152] | 2016 | 1 | Royal jelly factory | SPT, sIgE, PEF measurements, inhibition test, immunoblot |
| Honey bee | Matysiak J [178] | 2016 | 30 | Beekeepers | sIgE |
| Honey bee | Boonpiyathad T [179] | 2017 | 15 | Beekeepers | B cell characterization |
| Honey bee | Carballo I [180] | 2017 | 158 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire, sIgE |
| Honey bee | Ediger D [181] | 2018 | 242 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire |
| Honey bee | Demirkale ZH [135] | 2020 | 69 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire |
| Honey bee, wasp | Annila IT [136] | 1996 | 191 | Beekeepers | Questionnaire |
| Bumblebee Venom Allergy | |||||
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Bombus terrestris, Bombus pennsylvanicus | Hoffman DR [156] | 2001 | 6 | Bumblebee farm | sIgE, SPT, inhibition test |
| Bumblebee | Josef P [157] | 1993 | 1 | Bumblebee farm | SPT, sIgE |
| Bumblebee | Kochuyt A [155] | 1993 | 5 | Bumblebee farm | SPT, sIgE |
| Bumblebee | de Groot H [161] | 1995 | 6 | Bumblebee farm, greenhouse worker | SPT, sIgE, sting challenge, inhibition test |
| Bumblebee | Stapel SO [159] | 1998 | 6 | Bumblebee farm | sIgE, inhibition test, immunoblot |
| Bumblebee | de Jong NW [162] | 1999 | 11 | Bumblebee farm, greenhouse worker | SPT, sIgE |
| Bumblebee | Stern A [158] | 2000 | 2 | Biologists | SPT, sIgE, sting challenge |
| Bumblebee | Roll A [160] | 2005 | 1 | Biologist | SPT, sIgE, inhibition test |
| Bumblebee | Lindström I [154] | 2022 | 121 | Greenhouse workers | sIgE |
| Wasp Venom Allergy | |||||
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Hornet and paper wasp | Hayashi Y [182] | 2014 | 1353 | Forest workers, electrical facility field workers | Questionnaire, sIgE |
| Wasp | Pérez-Pimiento A [183] | 2007 | 98 | Unknown | Retrospective analysis |
| Yellow jacket wasp | Shimizu T [128] | 1995 | 323 | Forestry workers | Questionnaire, sIgE |
3.7.4. Wasp Venom Allergy
3.8. Psocoptera and Others
| Psocoptera Allergy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Psocoptera | Veraldi S [184] | 2019 | 1 | Book shop | SPT |
| Others | |||||
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Liposcelis decolor | Marco G [185] | 2016 | 1 | Carpenter, exposed to barley | SPT, immunoblot, BHR |
| Caddis fly | Warrington RJ [187] | 2003 | 105 | Hydroelectric power plant | SPT |
| Caddis fly | Miedinger D [188] | 2010 | 1 | Hydroelectric power plant | SIC |
| Caddis fly | Kraut A [186] | 1994 | 28 | Hydroelectric power plant | Questionnaire, SPT, sIgE, PEF measurements |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kogevinas, M.; Zock, J.-P.; Jarvis, D.; Kromhout, H.; Lillienberg, L.; Plana, E.; Radon, K.; Torén, K.; Alliksoo, A.; Benke, G.; et al. Exposure to substances in the workplace and new-onset asthma: An international prospective population-based study (ECRHS-II). Lancet 2007, 370, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quirce, S.; Sastre, J. Occupational asthma: Clinical phenotypes, biomarkers, and management. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2019, 25, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gans, M.D.; Gavrilova, T. Understanding the immunology of asthma: Pathophysiology, biomarkers, and treatments for asthma endotypes. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 36, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.E. Asthma: Defining of the persistent adult phenotypes. Lancet 2006, 368, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, B.; Pini, C. Does occupational exposure to insects lead to species-specific sensitization? Allergy 2003, 58, 868–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukutomi, Y.; Kawakami, Y. Respiratory sensitization to insect allergens: Species, components and clinical symptoms. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renström, A.; Olsson, M.; Hedrén, M.; Johansson, S.G.O.; Van Hage, M. Pet shop workers: Exposure, sensitization, and work-related symptoms. Allergy 2011, 66, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, T.E. Occupational inhalant allergy to arthropods. Clin. Rev. Allergy 1990, 8, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moruzzo, R.; Mancini, S.; Guidi, A. Edible Insects and Sustainable Development Goals. Insects 2021, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; van Itterbeeck, J.; Heetkamp, M.J.W.; Brand, H.V.D.; van Loon, J.J.A.; van Huis, A. An exploration on greenhouse gas and ammonia production by insect species suitable for animal or human consumption. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, A.C.; Miller, A.C.; Miller, M.E.; Xiao, H.; Wu, X. Potential health benefits of edible insects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3499–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, C.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, C.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of frozen and dried formulations from migratory locust (Locusta migratoria) as a Novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, C.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of frozen and dried formulations from whole house crickets (Acheta domesticus) as a Novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06779. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsui, H.-C.; Ronsmans, S.; Hoet, P.H.; Nemery, B.; Vanoirbeek, J.A. Is Occupational Asthma Caused by Low-Molecular-Weight Chemicals Associated with Contact Dermatitis? A Retrospective Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 2346–2354.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenplas, O.; Lantin, A.-C.; D’Alpaos, V.; Larbanois, A.; Hoet, P.; Vandeweerdt, M.; Thimpont, J.; Speybroeck, N. Time trends in occupational asthma in Belgium. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suarthana, E.; Shen, A.; Henneberger, P.K.; Kreiss, K.; Leppla, N.C.; Bueller, D.; Lewis, D.M.; Bledsoe, T.A.; Janotka, E.; Petsonk, E.L. Post-hire asthma among insect-rearing workers. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 54, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankland, A.W. Locust sensitivity. Ann. Allergy 1953, 11, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Burge, P.S.; Edge, G.; O’Brien, I.M.; Harries, M.G.; Hawkins, R.; Pepys, J. Occupational asthma in a research centre breeding locusts. Clin. Allergy 1980, 10, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, R.D.; Gordon, D.J.; Hawkins, E.R.; Nunn, A.J.; Lacey, J.; Venables, K.M.; Cooter, R.J.; McCaffery, A.R.; Taylor, A.J.N. Occupational allergy to locusts: An investigation of the sources of the allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1988, 81, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopata, A.L.; Fenemore, B.; Jeebhay, M.F.; Gäde, G.; Potter, P.C. Occupational allergy in laboratory workers caused by the African migratory grasshopper Locusta migratoria. Allergy 2005, 60, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauschenberg, R.; Bauer, A.; Beissert, S.; Spornraft-Ragaller, P. Occupational immediate-type allergy to locusts in a zookeeper. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2015, 13, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, H.; Wang, C.; Ni, M.; Yu, D.; Zhang, L.; Kang, L. Hexamerin-2 Protein of Locust as a Novel Allergen in Occupational Allergy. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrgovic, I.; Messerschmidt, A.; Kaufmann, R.; Valesky, E. Occupational immediate-type reactions to locusts—A possible cross-reactivity between desert locusts. JAAD Case Rep. 2018, 4, 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soparkar, G.R.; Patel, P.C.; Cockcroft, D.W. Inhalant atopic sensitivity to grasshoppers in research laboratories. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1993, 92 Pt 1, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, B.E. Contact urticaria to locusts. Br. J. Dermatol. 1988, 118, 707–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartra, J.; Carnes, J.; Muñoz-Cano, R.; Bissinger, I.; Picado, C.; Valero, A.L. Occupational asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis caused by cricket allergy. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 18, 141–142. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, F.; Doyen, V.; Debaugnies, F.; Mazzucchelli, G.; Caparros, R.; Alabi, T.; Blecker, C.; Haubruge, E.; Corazza, F. Limited cross reactivity among arginine kinase allergens from mealworm and cricket edible insects. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linares, T.; Hernandez, D.; Bartolome, B. Occupational rhinitis and asthma due to crickets. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 100, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Las Marinas, M.D.; Cerdá, J.C.; López-Matas, M.A.; González-Ruiz, A.; Martorell, C.; Felix, R.; Alvariño, M.; Carnés, J. Hexamerin-like protein 2, a cricket allergen involved in occupational and food allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2021, 51, 858–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagenstose, A.H.; Mathews, K.P.; Homburger, H.A.; Saaveard-Delgado, A.P. Inhalant allergy due to crickets. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1980, 65, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Roberts, J.; Fishwick, D.; Tate, P.; Rawbone, R.; Stagg, S.; Barber, C.M.; Adisesh, A. Respiratory symptoms in insect breeders. Occup. Med. 2011, 61, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bregnbak, D.; Friis, U.F.; Zachariae, C.; Menné, T.; Johansen, J.D. Protein contact dermatitis caused by worms and insects used to feed exotic birds. Contact Dermat. 2014, 70, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Hoang, J.A.; Kothari, A.; Eiwegger, T.; Vadas, P. Shellfish allergy is a risk factor for cricket anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 2396–2398.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armentia, A.; Lombardero, M.; Blanco, C.; Fernandez, S.; Sanchez-Monge, R. Allergic hypersensitivity to the lentil pest Bruchus lentis. Allergy 2006, 61, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentia, A.; Alvarez, R.; Moreno-González, V.; Martín, B.; Fernández, S.; Martín, S.; Moro, A.; Vega, J.M.; Barrios, A.; Castillo, M.; et al. Occupational airborne contact urticaria, anaphylaxis and asthma in farmers and agronomists due to Bruchus pisorum. Contact Dermat. 2020, 83, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentia, A.; Lombardero, M.; Barber, D.; Castrodeza, J.; Calderon, S.; Martin-Gil, F.J.; Callejo, A.M. Occupational asthma in an agronomist caused by the lentil pest Bruchus lentis. Allergy 2003, 58, 1200–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, J.A.; Hughes, D.T.D. Pulmonary hypersensitivity to the grain weevil. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1967, 24, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Frankland, A.W.; Lunn, J.A. Asthma caused by the grain weevil. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1965, 22, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lunn, J.A. Millworkers’ asthma: Allergic responses to the grain weevil (Sitophilus granarius). Br. J. Ind. Med. 1966, 23, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herling, C.; Svendsen, U.; Schou, C. Identification of important allergenic proteins in extracts of the granary weevil (Sitophilus granarius). Allergy 1995, 50, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Morgan, M.S.; Ghosh, D.; Arlian, L. Respiratory sensitization of a worker to the warehouse beetle Trogoderma variabile: An index case report. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, J.; Johnston, J. Hypersensitivity to beetles (Coleoptera): Report of a case. J. Allergy 1941, 12, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, F.F.; Mur, P.; Barber, D.; Lombardero, M.; Galindo, P.A.; Gomez, E.; Borja, J. Occupational rhinoconjunctivitis and asthma in a wool worker caused by Dermestidae spp. Allergy 2002, 57, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeckenstein, D.C.; Meier-Davis, S.; Graziano, F.M.; Falomo, A.; Bush, R.K. Occupational sensitivity to Alphitobius diaperinus (Panzer) (lesser mealworm). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1988, 82, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, D.I.; Gallagher, J.S.; Bernstein, I.L. Mealworm asthma: Clinical and immunologic studies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1983, 72 Pt 1, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, A.; Bettini, P.; Bacoccoli, R.; Severini, C.; Verga, A.; Abbritti, G. Asthma caused by live fish bait. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 93, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentia, A.; Martinez, A.; Castrodeza, R.; Martínez, J.; Jimeno, A.; Méndez, J.; Stolle, R. Occupational allergic disease in cereal workers by stored grain pests. J. Asthma 1997, 34, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Bernstein, I.L. A novel case of mealworm-induced occupational rhinitis in a school teacher. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2002, 23, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa, A.; Marcucci, F.; Spinozzi, F.; Marabini, A.; Pettinari, L.; Pace, M.L.; Tacconi, C. Prevalence of occupational allergy due to live fish bait. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzani, R.; Armentia, A.; Lobo, R.; Postigo, I.; Martinez, J.; Arranz, M.L.; Martíin-Gil, F.J.; Fernandez, J.C. Tolerance mechanisms in response to antigens responsible for baker’s asthma in different exposed people. J. Asthma 2008, 45, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekman, H.C.; Knulst, A.C.; Jager, C.F.D.H.; van Bilsen, J.H.; Raymakers, F.M.; Kruizinga, A.G.; Gaspari, M.; Gabriele, C.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.; Houben, G.F.; et al. Primary respiratory and food allergy to mealworm. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 600–603.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nebbia, S.; Lamberti, C.; Giorgis, V.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Manfredi, M.; Marengo, E.; Pessione, E.; Schiavone, A.; Boita, M.; Brussino, L.; et al. The cockroach allergen-like protein is involved in primary respiratory and food allergy to yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor). Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganseman, E.; Ieven, T.; Frans, G.; Coorevits, L.; Pörtner, N.; Martens, E.; Bullens, D.M.; Schrijvers, R.; Breynaert, C.; Proost, P. Alpha-amylase as the culprit in an occupational mealworm allergy case. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 992195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeckenstein, D.C.; Meier-Davis, S.; Bush, R.K. Occupational sensitivity to Tenebrio molitor Linnaeus (yellow mealworm). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 86, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze-Werninghaus, G.; Zachgo, W.; Rotermund, H.; Wiewrodt, R.; Merget, R.; Wahl, R.; Burow, G.; Zur Strassen, R. Tribolium confusum (confused flour beetle, rice flour beetle)—An occupational allergen in bakers: Demonstration of IgE antibodies. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1991, 94, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanko, K.; Tuomi, T.; Vanhanen, M.; Pajari-Backas, M.; Kanerva, L.; Havu, K.; Saarinen, K.; Bruynzeel, D.P. Occupational IgE-mediated allergy to Tribolium confusum (confused flour beetle). Allergy 2000, 55, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinen-Kiljunen, S.; Mussalo-Rauhamaa, H.; Petman, L.; Rinne, J.; Haahtela, T. A baker’s occupational allergy to flour moth (Ephestia kuehniella). Allergy 2001, 56, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentia, A.; Lombardero, M.; Martinez, C.; Barber, D.; Vega, J.M.; Callejo, A. Occupational asthma due to grain pests Eurygaster and Ephestia. J. Asthma 2004, 41, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobosa, M.C.M.; Zavala, B.B.; López, J.A. Occupational allergy to Ephestia kuehniella in the biological control industry. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 24, 459–460. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, D.D.; Mathews, K.P. Occupational asthma following inhalation of moth particles. J. Allergy 1967, 39, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Press, E.; Googins, J.A.; Poareo, H.; Jones, K. Health hazards to timber and forestry workers from the Douglas fir tussock moth. Arch. Environ. Health 1977, 32, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uragoda, C.G.; Wijekoon, P.N.B. Asthma in silk workers. J. Soc. Occup. Med. 1991, 41, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harindranath, N.; Prakash, O.; Rao, P.V.S. Prevalence of occupational asthma in silk filatures. Ann. Allergy 1985, 55, 511–515. [Google Scholar]
- Gowda, G.; Sarkar, N.; Ashwathnarayana, A.G.; Narayanaswamy, H.; Nagaraj, C.; Vijayeendra, A.M.; Shivalingaiah, A.H.; Shah, A. A study on occupational asthma among workers of silk filatures in South India. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 18, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, J.; Lei, M.; Yang, R.; Liu, Z. Bom m 9 from Bombyx mori is a novel protein related to asthma. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 59, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etkind, P.H.; Odell, T.M.; Canada, A.T.; Sharma, S.K.; Finn, A.M.; Tuthill, R. The gypsy moth caterpillar: A significant new occupational and public health problem. J. Occup. Med. 1982, 24, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.M.; Moneo, I.; Armentia, A.; López-Rico, R.; Curiel, G.; Bartolomé, B.; Fernández, A. Anaphylaxis to a pine caterpillar. Allergy 1997, 52, 1244–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.M.; Moneo, I.; Armentia, A.; Fernández, A.; La Fuente, D.; Sánchez, P.; Sanchís, M. Allergy to the pine processionary caterpillar (Thaumetopoea pityocampa). Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.M.; Moneo, I.; Armentia, A.; De La Fuente, R.; Fernández, A. Pine processionary caterpillar as a new cause of immunologic contact urticaria. Contact Dermat. 2000, 43, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo, S.; Moneo, I.; Vega, J.; Herrera, I.; Caballero, M. Pine processionary caterpillar allergenicity increases during larval development. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 128, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, J.; Vega, J.M.; Moneo, I.; Armentia, A.; Caballero, M.L.; Miranda, A. Occupational immunologic contact urticaria from pine processionary caterpillar (Thaumetopoea pityocampa): Experience in 30 cases. Contact Dermat. 2004, 50, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Cabeza, C.; Prieto-García, A.; Acero, S.; Bartolomé-Zavala, B.; Morgado, J.M.; Matito, A.; Sánchez-Muñoz, L.; Alvarez-Twose, I. Systemic mastocytosis presenting as occupational IgE-mediated anaphylaxis to pine processionary caterpillar. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 117, 333–334.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardi, L.; Giorgianni, C.; Briguglio, G.; Gangemi, S.; Spatari, G. Processionary caterpillar reactions in Southern Italy forestry workers: Description of three cases. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2021, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstat-Korzenny, E.; Yudovich, A.; Morgenstern-Kaplan, D. Lepidopterism: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pomés, A.; Mueller, G.A.; Randall, T.A.; Chapman, M.D.; Arruda, L.K. New Insights into Cockroach Allergens. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschunke, E. Contact urticaria, dermatitis and asthma from cockroaches (Periplaneta americana). Contact Dermat. 1978, 4, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, D.; Bernstein, D.; Gallagher, J.; Arlian, L. Cockroach sensitization in laboratory workers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1987, 80, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, M.; Baur, X. Cockroach infestation on seagoing ships. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2008, 63, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, M.; Latza, U.; Baur, X. Occupational health risks due to shipboard cockroaches. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2008, 81, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marraccini, P.; Previdi, M.; Cantone, L.; Varin, E.; Salimbeni, R.; Todaro, A.; Panciera, D.; Costamagna, P. The possible role of cockroaches in baker’s asthma. Med. Lav. 2007, 98, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanerva, L.; Tarvainen, K.; Tupasela, O.; Kaarsalo, K.; Estlander, T. Occupational allergic contact urticaria caused by cockroach (Blaberus giganteus). Contact Dermat. 1995, 33, 445–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.; Blair, S.; MacNeill, S.; Welch, J.; Hole, A.; Baxter, P.; Cullinan, P. Occupational allergy to fruit flies. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 74, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spieksma, F.T.; Vooren, P.H.; Kramps, J.A.; Dijkman, J.H. Respiratory allergy to laboratory fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1986, 77 Pt 1, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomb, S.; Bourrain, J.L.; Leduc, V.; Burmester, T.; Marin, G.; Lesage, F.-X.; Dhivert-Donnadieu, H.; Demoly, P. Identification of the larval serum proteins as major fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) occupational allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1153–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancor, D.; López-Matas, M.A.; González-Ruiz, A.; Martín-López, L.; Carnés, J.; Fernández-Nieto, M.D.M. Sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein and alcohol dehydrogenase, new occupational allergens in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2021, 51, 1387–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De las Marinas, M.D.; Félix, R.; Martorell, C.; Cerda, J.C.; Bartolomé, B.; Martorell, A. Occupational asthma caused by exposure to Ceratitis capitata (Mediterranean fruit fly). J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 24, 194–196. [Google Scholar]
- Tee, R.D.; Gordon, D.J.; Lacey, J.; Nunn, A.; Brown, M.; Taylor, A.J. Occupational allergy to the common house fly. (Musca domestica): Use of immunologic response to identify atmospheric allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1985, 76, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focke, M.; Hemmer, W.; Wohrl, S.; Gotz, M.; Jarisch, R.; Kofler, H. Specific sensitization to the common housefly (Musca domestica) not related to insect panallergy. Allergy 2003, 58, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, R.; Fraedrich, J. Occupational allergy to the housefly (Musca domestica). Allergy 1997, 52, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, B.A.; Bellas, T.E.; Tovey, E.; Kaufman, G.L. Occupational allergy in an entomological research centre. II. Identification of IgE-binding proteins from developmental stages of the blowfly Lucilia cuprina and other species of adult flies. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1989, 19, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, G.L.; Baldo, B.A.; Tovey, E.; Bellas, T.E.; Gandevia, B.H. Inhalant allergy following occupational exposure to blowflies. Clin. Allergy 1986, 16, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, G.L.; Gandevia, B.H.; Bellas, T.E.; Tovey, E.R.; Baldo, B.A. Occupational allergy in an entomological research centre. I. Clinical aspects of reactions to the sheep blowfly Lucilia cuprina. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1989, 46, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cimarra, M.; Martínez-Cócera, C.; Chamorro, M.; Cabrera, M.; Robledo, T.; Alonso, A.; Castellano, A.; Bartolome, J.; Lombardero, M. Occupational asthma caused by champignon flies. Allergy 1999, 54, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukkanen, A.; Ruoppi, P.; Mäkinen-Kiljunen, S. Deer ked-induced occupational allergic rhinoconjunctivitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005, 94, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, B.L.; Mathews, K.P.; Burge, H.A. Occupational asthma caused by sewer flies. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 131, 949–952. [Google Scholar]
- Dille, J.R.; Gibbons, H.L.; Spikes, G.A. Allergicproblems in screwworm fly eradication program personnel. Aerosp. Med. 1968, 39, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, G.H. Allergy to screwworm fly dust. A new occupational disease. Tex. Med. 1966, 62, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Pazzaglia, M.; Tullo, S.; Tosti, A. Occupational protein contact dermatitis due to Calliphora vomitoria larvae (maggots) bred as fishing bait. Contact Dermat. 2003, 48, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.J.; Abbeele, J.V.D.; Bridts, C.H. Anaphylactic reaction after bites by Glossina morsitans (tsetse fly) in a laboratory worker. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 700–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, X.; Liebers, V. Insect hemoglobins (Chi tI) of the diptera family Chironomidae are relevant environmental, occupational, and hobby-related allergens. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1992, 64, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teranishi, H.; Kawai, K.; Murakami, G.; Miyao, M.; Kasuya, M. Occupational allergy to adult chironomid midges among environmental researchers. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1995, 106, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seldén, A.I.; Calo, A.; Mölleby, G.; Hultgren, O. Chironomid midge sensitization in sewage workers: Case study. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2013, 27, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tee, R.D.; Cranston, P.S.; Dewair, M.; Prelicz, H.; Baur, X.; Kay, A.B. Evidence for haemoglobins as common allergenic determinants in IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to chironomids (non-biting midges). Clin. Allergy 1985, 15, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebers, V.; Hoernstein, M.; Baur, X. Humoral immune response to the insect allergen Chi t I in aquarists and fish-food factory workers. Allergy 1993, 48, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, P.A.; Lombardero, M.; Mur, P.; Feo, F.; Gómez, E.; Borja, J.; García, R.; Barber, D. Patterns of immunoglobulin E sensitization to chironomids in exposed and unexposed subjects. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 9, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Arce, J.M.; Villajos, I.M.S.-G.; Iraola, V.; Carnes, J.; Caldas, E.F. Occupational allergy to aquarium fish food: Red midge larva, freshwater shrimp, and earthworm. A clinical and immunological study. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 23, 462–470. [Google Scholar]
- Baur, X.; Dewair, M.; Fruhmann, G.; Aschauer, H.; Pfletschinger, J.; Braunitzer, G. Hypersensitivity to chironomids (non-biting midges): Localization of the antigenic determinants within certain polypeptide sequences of hemoglobins (erythrocruorins) of Chironomus thummi thummi (Diptera). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1982, 69 Pt 1, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suojalehto, H.; Hölttä, P.; Suomela, S.; Savinko, T.; Lindström, I.; Suuronen, K. High Prevalence of Sensitization to Mites and Insects in Greenhouses Using Biologic Pest Control. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 4130–4137.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, I.; Karvonen, H.; Suuronen, K.; Suojalehto, H. Occupational asthma from biological pest control in greenhouses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 692–694.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, M.A.G.; Muela, R.A.; Irigoyen, J.A.; Higuero, N.C.; Alguacil, P.V.; De Gregorio, A.M.; Senent, C.J. Occupational asthma caused by hypersensitivity to ground bugs. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 99, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.R. Anaphylactic shock resulting from casualty simulation. A case report. J. R. Army Med. Corps 1981, 127, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge, P.S.; O’Brien, I.M.; Harries, M.G.; Pepys, J. Occupational asthma due to inhaled carmine. Clin. Allergy 1979, 9, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabar-Purroy, A.I.; Alvarez-Puebla, M.J.; Acero-Sainz, S.; García-Figueroa, B.E.; Echechipía-Madoz, S.; Olaguibel-Rivera, J.M.; Quirce-Gancedo, S. Carmine (E-120)-induced occupational asthma revisited. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizaso, M.; Moneo, I.; García, B.; Acero, S.; Quirce, S.; Tabar, A. Identification of allergens involved in occupational asthma due to carmine dye. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000, 84, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirce, S.; Cuevas, M.; Olaguibel, J.; Tabar, A. Occupational asthma and immunologic responses induced by inhaled carmine among employees at a factory making natural dyes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 93 Pt 1, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.E.; Ebo, D. Carmine red (E-120)-induced occupational respiratory allergy in a screen-printing worker: A case report. B-ENT 2012, 8, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, Ð.; Marco, F.M.; Andreu, C.; Sempere, J.M. Occupational asthma to carmine in a butcher. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 138, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Añíbarro, B.; Seoane, J.; Vila, C.; Múgica, V.; Lombardero, M. Occupational asthma induced by inhaled carmine among butchers. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2003, 16, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Acero, S.; Tabar, A.I.; Alvarez, M.J.; García, B.E.; Olaguibe, J.M.; Moneo, I. Occupational asthma and food allergy due to carmine. Allergy 1998, 53, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgiya, Y.; Arakawa, F.; Akiyama, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Sakai, S.; Ito, S.; Yamakawa, Y.; Ohgiya, S.; Ikezawa, Z.; et al. Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of a major 38-kd cochineal allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1157–1162.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganseman, E.; Ieven, T.; Frans, G.; Denorme, P.; Coorevits, L.; Van Hoeyveld, E.; Martens, E.; Bullens, D.; Schrijvers, R.; Breynaert, C.; et al. Diagnosis of carmine allergy using carminic acid solves interference of house dust mite and crustacean cross-reactivity. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2022, 52, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osumi, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Sugimoto, N.; Suzukawa, M.; Arai, H.; Akiyama, H.; Nagase, H.; Ohta, K. Allergy to carminic acid. Asia Pac. Allergy 2019, 9, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, N.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakase, Y.; Nagase, H.; Akiyama, H.; Ohta, K. The basophil activation test identified carminic acid as an allergen inducing anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2013, 1, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campion, K.M. Respiratory symptoms in insect breeders. Occup. Med. 2012, 62, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toletone, A.; Voltolini, S.; Passalacqua, G.; Dini, G.; Bignardi, D.; Minale, P.; Massa, E.; Signori, A.; Troise, C.; Durando, P. Hymenoptera venom allergy in outdoor workers: Occupational exposure, clinical features and effects of allergen immunotherapy. Hum. Vaccine Immunother. 2017, 13, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Annila, I. Bee venom allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 1682–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Hori, T.; Tokuyama, K.; Morikawa, A.; Kuroume, T. Clinical and immunologic surveys of Hymenoptera hypersensitivity in Japanese forestry workers. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1995, 74, 495–500. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, T.; Yoshida, M.; Nakazono, N. Hymenoptera stings and serum venom-specific IgE in Japanese Pest-control operators. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 1998, 2, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricciardi, L.; Papia, F.; Cataldo, G.; Giorgianni, M.; Spatari, G.; Gangemi, S. Hymenoptera sting reactions in southern Italy forestry workers: Our experience compared to reported data. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2018, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahan, E.; Ben-Moshe, R.; Derazne, E.; Tamir, R. The impact of Hymenoptera venom allergy on occupational activities. Occup. Med. 1997, 47, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paolocci, G.; Folletti, I.; Torén, K.; Muzi, G.; Murgia, N. Hymenoptera venom allergy: Work disability and occupational impact of venom immunotherapy. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Celikel, S.; Karakaya, G.; Yurtsever, N.; Sorkun, K.; Kalyoncu, A. Bee and bee products allergy in Turkish beekeepers: Determination of risk factors for systemic reactions. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2006, 34, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münstedt, K.; Hellner, M.; Winter, D.; Von Georgi, R. Allergy to bee venom in beekeepers in Germany. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 18, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demirkale, Z.H.; Yücel, E.; Çimen, S.S.; Süleyman, A.; Özdemir, C.; Kara, A.; Tamay, Z. Venom allergy and knowledge about anaphylaxis among beekeepers and their families. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2020, 48, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annila, I.T.; Karjalainen, E.S.; Annila, P.A.; Kuusisto, P.A. Bee and wasp sting reactions in current beekeepers. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996, 77, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousquet, J.; Menardo, J.; Aznar, R.; Robinetlevy, M.; Michel, F. Clinical and immunologic survey in beekeepers in relation to their sensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1984, 73, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogeromitros, D.; Makris, M.; Gregoriou, S.; Papaioannou, D.; Katoulis, A.; Stavrianeas, N.G. Pattern of sensitization to honeybee venom in beekeepers: A 5-year prospective study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2006, 27, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annila, I.; Saarinen, J.V.; Nieminen, M.M.; Moilanen, E.; Hahtola, P.; Harvima, I.T. Bee venom induces high histamine or high leukotriene C4 release in skin of sensitized beekeepers. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2000, 10, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Light, W.C.; Reisman, R.E.; Wypych, J.I.; Arbesman, C.E. Clinical and immunological studies of beekeepers. Clin. Allergy 1975, 5, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordvall, S.L.; Uhlin, T.; Einarsson, R.; Johansson, S.G.O.; Öhman, S. Bee keepers’ IgG and IgE antibody responses to bee venom studied by means of crossed radioimmunoelectrophoresis. Clin. Allergy 1984, 14, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, U.; Spiess, J.; Roth, A. Serological investigations in hymenoptera sting allergy: IgE and haemagglutinating antibodies against bee venom in patients with bee sting allergy, bee keepers and non-allergic blood donors. Clin. Allergy 1977, 7, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, K.; Li, L.S.; Yin, J. Use of sIgE/T-IgE in Predicting Systemic Reactions: Retrospective Analysis of 54 Honeybee Venom Allergy Cases in North China. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 2091–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eich-Wanger, C.; Müller, U.R. Bee sting allergy in beekeepers. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1998, 28, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, E.M.; Kausar, F.; Aberer, W.; Zach, M.; Eber, E.; Durham, S.R.; Shamji, M.H. Tolerant beekeepers display venom-specific functional IgG4 antibodies in the absence of specific IgE. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1419–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, C.J.; Morato-Castro, F.F.; Palma, M.S.; Malaspina, O.; Neto, R.S.A.; Costa-Manso, E.; Croce, J. Acquired immunity to Africanized honeybee (Apis mellifera) venom in Brazilian beekeepers. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 1997, 7, 583–587. [Google Scholar]
- Zahirović, A.; Luzar, J.; Molek, P.; Kruljec, N.; Lunder, M. Bee Venom Immunotherapy: Current Status and Future Directions. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 58, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münstedt, K.; Wrobel, D.; Kalder, M. Efficacy of venom immunotherapy in beekeepers. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 20, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, S.G.; Aleman, E.A.; Figueroa, B.E.G.; Fagoaga, E.G.; Rivera, J.M.O.; Purroy, A.I.T. Direct and airborne contact dermatitis from propolis in beekeepers. Contact Dermat. 2004, 50, 320–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudeschko, O.; Machnik, A.; Dörfelt, H.; Kaatz, H.-H.; Schlott, B.; Kinne, R.W. A novel inhalation allergen present in the working environment of beekeepers. Allergy 2004, 59, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisman, R.E.; Hale, R.; Wypych, J.I. Allergy to honeybee body components: Distinction from bee venom sensitivity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1983, 71 Pt 1, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-S.; Guan, K. Occupational Asthma Caused by Inhalable Royal Jelly and Its Cross-reactivity with Honeybee Venom. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 2888–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrijos, E.G.; Diaz, Y.M.; Segade, J.M.B.; Brito, J.F.F.; Arias, T.A.; Bonilla, P.A.G.; Fernandez, A.L.; Rodríguez, R.G. Occupational allergic respiratory disease due to royal jelly. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 117, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindström, I.; Hölttä, P.; Suuronen, K.; Suomela, S.; Suojalehto, H. High prevalence of sensitization to bumblebee venom among greenhouse workers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochuyt, A.M.; Van Hoeyveld, E.; Stevens, E.A.M. Occupational allergy to bumble bee venom. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1993, 23, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.R.; El-Choufani, S.E.; Smith, M.M.; de Groot, H. Occupational allergy to bumblebees: Allergens of Bombus terrestris. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josef, P. Occupational allergy to bumble bee venom. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1993, 23, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.; Müllner, G.; Wüthrich, B. Successful treatment of occupational allergy to bumblebee venom after failure with honeybee venom extract. Allergy 2000, 55, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapel, S.O.; de Raadt, J.W.-L.; Toorenenbergen, A.W.; Groot, H. Allergy to bumblebee venom. II. IgE cross-reactivity between bumblebee and honeybee venom. Allergy 1998, 53, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, A.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P. Ultrarush immunotherapy in a patient with occupational allergy to bumblebee venom (Bombus terrestris). J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 15, 305–307. [Google Scholar]
- De Groot, H.; de Graaf-in ‘t Veld, C.; van Wijk, R.G. Allergy to bumblebee venom. I. Occupational anaphylaxis to bumblebee venom: Diagnosis and treatment. Allergy 1995, 50, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, N.W.; De Groot, H.; Vermeulen, A.M. Allergy to bumblebee venom. III. Immunotherapy follow-up study (safety and efficacy) in patients with occupational bumblebee-venom anaphylaxis. Allergy 1999, 54, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incorvaia, C.; Senna, G.; Mauro, M.; Bonadonna, P.; Marconi, I.; Asero, R.; Nitti, F. Prevalence of allergic reactions to Hymenoptera stings in northern Italy. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 36, 372–374. [Google Scholar]
- Turbyville, J.C.; Dunford, J.C.; Nelson, M.R. Hymenoptera of Afghanistan and the central command area of operations: Assessing the threat to deployed U.S. service members with insect venom hypersensitivity. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2013, 34, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, W.; Voss, J.D.; Kugblenu, R.; Salter, K.; Johnson, L. Case series of 23 deaths from Hymenoptera stings among United States Air Force populations. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2016, 48, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bousquet, J.; Coulomb, Y.; Robinet-Levy, M.; Michel, F.B. Clinical and immunological surveys in bee keepers. Clin. Allergy 1982, 12, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemeny, D.; Mackenziemills, M.; Harries, M.; Youlten, L.; Lessof, M. Antibodies to purified bee venom proteins and peptides. II. A detailed study of changes in IgE and IgG antibodies to individual bee venom antigens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1983, 72, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomnitzer, R.; Rabson, A.R. Lack of responsiveness of beekeeper mononuclear cells to in vitro stimulation with pure bee venom. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1986, 78 Pt 1, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Szewczuk, M.; Day, J. Bee venom anti-idiotypic antibody is associated with protection in beekeepers and bee sting-sensitive patients receiving immunotherapy against allergic reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1991, 88, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annila, I.T.; Annila, P.A.; Mörsky, P. Risk assessment in determining systemic reactivity to honeybee stings in beekeepers. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997, 78, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Robaina, J.C.; De La Torre-Morín, F.; Vazquez-Moncholi, C.; Fierro, J.; Bonnet-Moreno, C. The natural history of Apis-specific IgG and IgG4 in beekeepers. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1997, 27, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyoncu, A.F.; Demir, A.U.; Özcan, Ü.; Özkuyumcu, C.; Şahin, A.A.; Bariş, Y.I. Bee and wasp venom allergy in Turkey. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997, 78, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manso, E.C.; Morato-Castro, F.F.; Yee, C.J.; Croce, M.; Palma, M.S.; Croce, J. Honeybee venom specific IgG subclass antibodies in Brazilian beekeepers and in patients allergic to bee stings. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 1998, 8, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meiler, F.; Zumkehr, J.; Klunker, S.; Rückert, B.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M. In vivo switch to IL-10-secreting T regulatory cells in high dose allergen exposure. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2887–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richter, A.G.; Nightingale, P.; Huissoon, A.P.; Krishna, M.T. Risk factors for systemic reactions to bee venom in British beekeepers. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 106, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Moos, S.; Graf, N.; Johansen, P.; Müllner, G.; Kündig, T.M.; Senti, G. Risk assessment of Hymenoptera re-sting frequency: Implications for decision-making in venom immunotherapy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 160, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Çelıksoy, M.H.; Sancak, R.; Söğüt, A.; Güner, Ş.N.; Korkmaz, A. Characteristics of venom allergic reactions in Turkish beekeepers and alternative treatment modalities. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 4, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matysiak, J.; Breborowicz, A.; Kycler, Z.; Derezinski, P.; Kokot, Z.J. Immune and clinical response to honeybee venom in beekeepers. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2016, 23, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boonpiyathad, T.; Meyer, N.; Moniuszko, M.; Sokolowska, M.; Eljaszewicz, A.; Wirz, O.F.; Tomasiak-Lozowska, M.M.; Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, A.; Ruxrungtham, K.; van de Veen, W. High-dose bee venom exposure induces similar tolerogenic B-cell responses in allergic patients and healthy beekeepers. Allergy 2017, 72, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, I.; Carballada, F.; Nuñez-Orjales, R.; Martín-Lázaro, J.; Vidal, C.; Gonzalez-Quintela, A. Total and Honeybee Venom-Specific Serum IgG4 and IgE in Beekeepers. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 27, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediger, D.; Terzioglu, K.; Öztürk, R.T. Venom allergy, risk factors for systemic reactions and the knowledge levels among Turkish beekeepers. Asia Pac. Allergy 2018, 8, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabè, M.; Hirata, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Sugiyama, K.; Fukushima, Y.; Fukuda, T. Epidemiologic investigation of hornet and paper wasp stings in forest workers and electrical facility field workers in Japan. Allergol. Int. 2014, 63, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pimiento, A.; Prieto-Lastra, L.; Rodríguez-Cabreros, M.; Reaño-Martos, M.; García-Cubero, Á.; García-Loria, J. Work-related anaphylaxis to wasp sting. Occup. Med. 2007, 57, 602–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veraldi, S.; Brena, M.; Süss, L. Occupational allergy to Psocoptera species. Contact Dermat. 2019, 81, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco, G.; Pelta, R.; Carnes, J.; Iraola, V.; Zambrano, G.; Baeza, M.L. Occupational allergic asthma induced by Liposcelis decolor. Allergol. Int. 2016, 65, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kraut, A.; Sloan, J.; Silviu-Dan, F.; Peng, Z.; Gagnon, D.; Warrington, R. Occupational allergy after exposure to caddis flies at a hydroelectric power plant. Occup. Environ. Med. 1994, 51, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warrington, R.; Whitman, C.; Warrington, S.M. Cytokine synthesis in occupational allergy to caddisflies in hydroelectric plant workers. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 132, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedinger, D.; Cartier, A.; Lehrer, S.B.; Labrecque, M. Occupational asthma to caddis flies (Phryganeiae). Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 67, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Shah, D.; Payal, A.R. Healthy Worker Effect Phenomenon: Revisited with Emphasis on Statistical Methods—A Review. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 21, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, A.J. Standardized mortality ratios and the “healthy worker effect”: Scratching beneath the surface. J. Occup. Med. 1976, 18, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moual, N.; Kauffmann, F.; Eisen, E.A.; Kennedy, S.M. The healthy worker effect in asthma: Work may cause asthma, but asthma may also influence work. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.G. Exposure-response in occupational allergy. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 8, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Grasshopper Allergy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Locusta migratoria | Lopata AL [21] | 2005 | 10 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, inhibition test, immunoblot |
| Locusta migratoria | Rauschenberg R [22] | 2015 | 1 | Zookeeper | SPT, sIgE |
| Locusta migratoria | Wang Y [23] | 2022 | 57 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot, inhibition test |
| Locusta migratoria, Schistocerca gregaria | Frankland AW [18] | 1953 | 34 | Laboratory | SPT |
| Locusta migratoria, Schistocerca gregaria | Burge PS [19] | 1980 | 119 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE |
| Locusta migratoria, Schistocerca gregaria | Tee RD [20] | 1988 | 35 | Laboratory | SPT, immunoblot, sIgE, inhibition test |
| Locusta migratoria, Schistocerca gregaria | Hrgovic I [24] | 2018 | 1 | Zookeeper | SPT, sIgE |
| Melanoplus sanguinipes | Soparkar GR [25] | 1993 | 17 | Laboratory | SPT, SIC |
| Undefined | Monk BE [26] | 1988 | 3 | Laboratory | Unknown |
| Cricket Allergy | |||||
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Acheta campestris | Bartra J [27] | 2008 | 1 | Pet store | SPT, nasal provocation, immunoblot |
| Acheta domesticus | Francis F [28] | 2019 | 31 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Acheta domesticus, Gryllus campestris, Gryllus bimaculatus | Linares T [29] | 2008 | 1 | Cricket breeder | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot, SIC |
| Gryllus assimilis, Gryllus bimaculatus, Gryllodes sigillatus, Acheta domesticus | de Las Marinas MD [30] | 2021 | 2 | Cricket breeders | SPT, sIgE, immunoblot |
| Undefined | Bagenstose AH [31] | 1980 | 2 | Laboratory | SPT, SIC, sIgE, HRT |
| Undefined | Harris-Roberts J [32] | 2011 | 32 | Cricket breeders | PEF measurements, sIgE |
| Undefined | Bregnbak D [33] | 2013 | 1 | Zoo owner | SPT |
| Cockroach Allergy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | 1st Author | Year | #Cases | Occupation | Diagnostics |
| Blaberus giganteus | Kanerva L [82] | 1995 | 1 | Animal care | SPT, sIgE |
| Blatella germanica | Oldenburg M [80] | 2008 | 145 | Seamen | Questionnaire, SPT, sIgE, spirometry |
| Blatella germanica, Periplaneta americana | Steinberg DR [78] | 1987 | 6 | Laboratory | SPT, sIgE, nasal provocation, inhibition test |
| Blatta orientalis | Armentia A [48] | 1997 | 50 | Cereal workers | SPT, sIgE, SIC, conjunctival provocation |
| Blatta orientalis | Panzani R [51] | 2008 | 54 | Bakers | SPT, BHR |
| Periplaneta americana | Zschunke E [77] | 1978 | 4 | Laboratory | Open patch test |
| Undefined | Marraccini P [81] | 2007 | 1 | Baker | SPT, sIgE, BHR, SIC |
| Undefined | Oldenburg M [79] | 2008 | 6 | Seamen | Questionnaire |
| Undefined | Bregnbak D [33] | 2013 | 1 | Zoo owner | SPT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ganseman, E.; Gouwy, M.; Bullens, D.M.A.; Breynaert, C.; Schrijvers, R.; Proost, P. Reported Cases and Diagnostics of Occupational Insect Allergy: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010086
Ganseman E, Gouwy M, Bullens DMA, Breynaert C, Schrijvers R, Proost P. Reported Cases and Diagnostics of Occupational Insect Allergy: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010086
Chicago/Turabian StyleGanseman, Eva, Mieke Gouwy, Dominique M. A. Bullens, Christine Breynaert, Rik Schrijvers, and Paul Proost. 2023. "Reported Cases and Diagnostics of Occupational Insect Allergy: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010086
APA StyleGanseman, E., Gouwy, M., Bullens, D. M. A., Breynaert, C., Schrijvers, R., & Proost, P. (2023). Reported Cases and Diagnostics of Occupational Insect Allergy: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010086







