The Pollen Donor Affects Seed Development, Taste, and Flavor Quality in ‘Hayward’ Kiwifruit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fruit-Setting Rate
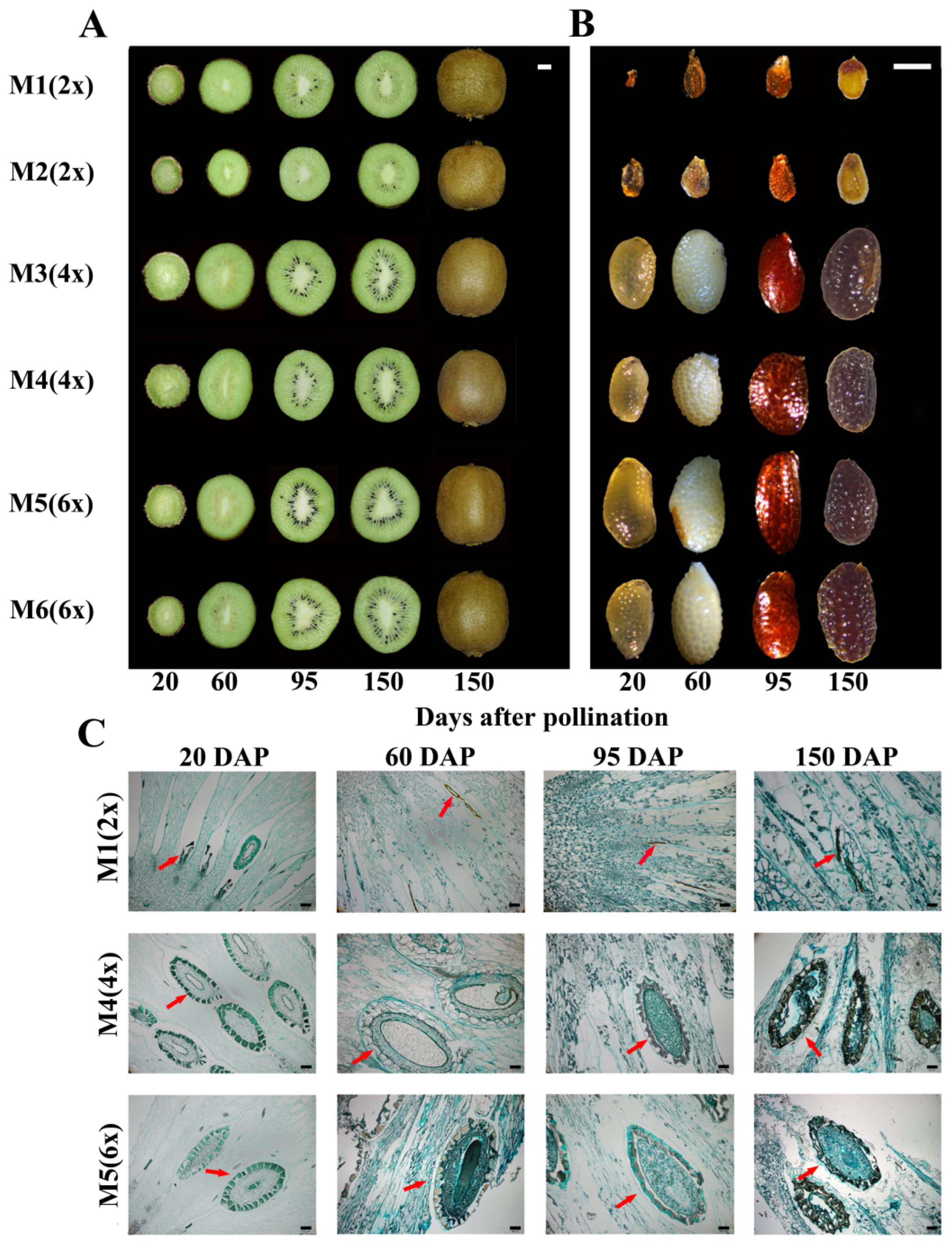
2.2. Fruit and Seeds Appearance Trait
2.3. Fruit and Seed Characteristics and Seed Histology
2.4. Fruit Soluble Solid Content (SSC), Dry Matter Content (DM), Titratable Acidity (TA), Ratio of SSC and TA (SAR), and Ascorbic Acid (ASA) Content
2.5. Sugar and Acid Components
2.6. Volatile Compound Content in the Different Pollination Schemes
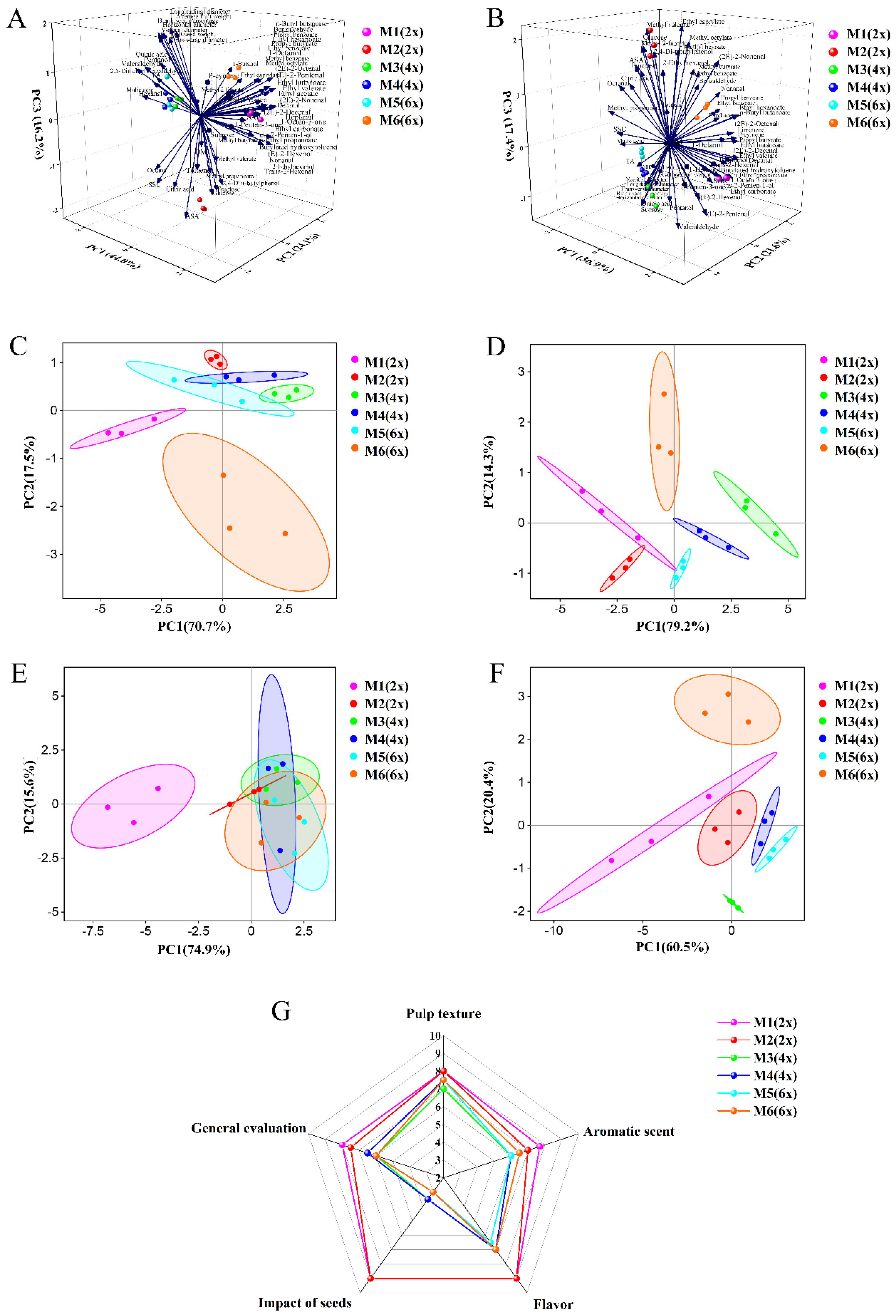
2.7. PCA of Fruit Quality and E-Tongue and E-Nose Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Pollen Preparation, Pollen Viability, and Pollination
4.3. Observation of Fruit and Seed Characteristics and Histological Analysis of Seed Development
4.4. External Evaluation of Fruit and Seed Quality
4.5. Determination of Fruit Soluble Solid Content (SSC), Dry Matter Content (DM), Titratable Acidity (TA), and Ascorbic Acid (ASA) Content
4.6. Determination of Soluble Sugars and Organic Acids in Fruits
4.7. Determination of Volatile Substance Content
4.8. E-Tongue and E-Nose Analysis
4.9. Sensory Evaluation
4.10. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pozzi, F.I.; Pratta, G.R.; Acuña, C.A.; Felitti, S.A. Xenia in bahiagrass: Gene expression at initial seed formation. Seed Sci. Res. 2018, 29, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denney, J.O. Xenia Includes Metaxenia. HortScience 1992, 27, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebel, B.R.; Trump, I.J. Xenia and Metaxenia in Apples. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1932, 18, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabir, A. Xenia and metaxenia in grapes: Differences in berry and seed characteristics of maternal grape cv. ‘Narince’ (Vitis vinifera L.) as influenced by different pollen sources. Plant Biol. 2015, 17, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, A.; McGhie, T.; Boldingh, H.; Rees, J.; Blackmore, A.; Jaksons, P.; Machin, T. The effect of pollen donor on fruit weight, seed weight and red colour development in Actinidia chinensis ‘Hort22D’. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2016, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, A.G.; Clark, C.J.; Sharrock, K.R.; de Silva, H.N.; Jaksons, P.; Wood, M.E. Choice of pollen donor affects weight but not composition of Actinidia chinensis var. chinensis ‘Zesy002’ (Gold3) kiwifruit. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2017, 46, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Jiang, Z.; He, Y.; Zhong, M.; Huang, C.; Qu, X.; Xu, X. The Comprehensive Evaluation Analysis of the Fruit Quality in Actinidia eriantha Pollinated with Different Pollen Donors Based on the Membership Function Method. Erwerbs-Obstbau 2022, 64, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, A.; Latocha, P.; Drzewiecki, J.; Hallmann, E.; Najman, K.; Leontowicz, H.; Leontowicz, M.; Lata, B. The choice of female or male parent affects some biochemical characteristics of fruit or seed of kiwiberry (Actinidia arguta). Euphytica 2019, 215, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.-Y.; Zhong, M.; Huang, C.-H.; Liao, G.-L.; Xu, X.-B. Effects of pollens from the 10 selectedActinidiamale genotypes on 4 commercial planting kiwifruit female cultivars in Southern China. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2019, 47, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, A.G.; Dunn, J.K.; Jia, Y.L. Pollen parent effects on fruit attributes of diploid Actinidia chinensis ‘Hort16A’ kiwifruit. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2013, 41, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, L.; Qian, P.; Liu, W.; Han, D.; Wu, Z. Sugar Contents and Composition in the Mature Fruit of Different Longan Cultivars. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2016, 37, 915–921. [Google Scholar]
- Gaaliche, B.; Trad, M.; Mars, M. Effect of pollination intensity, frequency and pollen source on fig (Ficus carica L.) productivity and fruit quality. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 130, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.U.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Song, K.J. Response of fruit set and quality and seed formation to ploidy levels of pollen donor in yellow-fleshed kiwifruits. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2021, 62, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, K.N. Preharvest Practices Affecting Postharvest Quality of ‘Hayward’ Kiwifruit. Ph.D. Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Seal, A.G.; Dunn, J.K.; De Silva, H.N.; McGhie, T.K.; Lunken, R.C.M. Choice of pollen parent affects red flesh colour in seedlings of diploid Actinidia chinensis (kiwifruit). N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2013, 41, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-H. Fruit Quality in Induced Polyploids of Actinidia chinensis. HortScience 2013, 48, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, V.J.; Macrae, E.A.; Young, H. Relationships between sensory properties and chemical composition of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa). J. Sci. Food Agric. 1991, 57, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, K.; Attanayake, S.; Walker, S.; Gunson, A.; Boldingh, H.; MacRae, E. Acidity and taste in kiwifruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 32, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, I.; Fukuda, T.; Shimohashi, A.; Oota, T. Sugar and Organic Acid Composition in the Fruit Juice of Different Actinidia Varieties. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2008, 14, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.C.; Boldingh, H.L.; McAtee, P.A.; Gunaseelan, K.; Luo, Z.; Atkinson, R.G.; David, K.M.; Burdon, J.N.; Schaffer, R.J. Fruit development of the diploid kiwifruit, Actinidia chinensis ’Hort16A’. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; MacRae, E.; Wohlers, M.; Marsh, K. Changes in volatile production and sensory quality of kiwifruit during fruit maturation in Actinidia deliciosa ‘Hayward’ and A. chinensis ‘Hort16A’. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2011, 59, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Liao, B.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z. Pollen donor affects the taste and aroma compounds in ‘Cuixiang’ and ‘Xuxiang’ kiwifruit. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 314, 111945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.; Paterson, V.J. Characterisation of Bound Flavour Components in kiwifruit. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1995, 68, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, C.S.; Marsh, K.B.; Winz, R.A.; Harker, R.F.; Wohlers, M.W.; White, A.; Goddard, M.R. The impact of cold storage and ethylene on volatile ester production and aroma perception in ‘Hort16A’ kiwifruit. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Kebede, B.T.; Grauwet, T.; Van Loey, A.; Hu, X.; Hendrickx, M. A multivariate approach into physicochemical, biochemical and aromatic quality changes of puree based on Hayward kiwifruit during the final phase of ripening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 117, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Gu, S.; Zhu, L.; Hong, X. Tracing internal quality and aroma of a red-fleshed kiwifruit during ripening by means of GC-MS and E-nose. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 21164–21174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, I.; Oliveira, M. Fruit production in kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) using preserved pollen. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2004, 55, ar03211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaghani, A.; Soloklui, A.A.G.; Oraguzie, N.; Zare, D. Pollen Source Influences Fruit Quality, Aril Properties, and Seed Characteristics in Pomegranate. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2017, 17, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yokoi, S.; Tezuka, T. A high maternal genome excess causes severe seed abortion leading to ovary abscission in Nicotiana interploidy-interspecific crosses. Plant Direct 2020, 4, e00257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdon, J.; Pidakala, P.; Martin, P.; Billing, D.; Boldingh, H. Fruit maturation and the soluble solids harvest index for ‘Hayward’ kiwifruit. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 213, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Liao, B.; Li, R.; Liu, Z. Changes in taste and volatile compounds and ethylene production determined the eating window of ‘Xuxiang’ and ‘Cuixiang’ kiwifruit cultivars. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 194, 112093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, T.; Dong, S. Effectiveness of lysozyme coatings and 1-MCP treatments on storage and preservation of kiwifruit. Food Chem. 2019, 288, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.Q. Effect of Pollen Xenia on the Fruit Quality of Kiwifruit, ‘Bruno’ and ‘White’. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ma, F.; Cheng, L. Metabolism of organic acids, nitrogen and amino acids in chlorotic leaves of ‘Honeycrisp’ apple (Malus domestica Borkh) with excessive accumulation of carbohydrates. Planta 2010, 232, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yong, K.; Liu, Z. 1-MCP extends the shelf life of ready-to-eat ‘Hayward’ and ‘Qihong’ kiwifruit stored at room temperature. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 289, 110437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhan, P.; Tian, H.-L.; Wang, P.; Lu, C.; Tian, P.; Zhang, Y.-Y. Insights into the Aroma Profile in Three Kiwifruit Varieties by HS-SPME-GC-MS and GC-IMS Coupled with DSA. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pollen Donors | Species | Ploidy Level | Name | Pollen Vitality (%) | Flowers-Number | Fruit Number | Fruit-Setting Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 a | A. chinensis | Diploid, 2x | M1 (2x) | 77.46 | 200 | 196 | 98.00 a |
| M2 a | A. chinensis | Diploid, 2x | M2 (2x) | 76.21 | 218 | 201 | 92.20 c |
| M3 a | A. chinensis | Tetraploid, 4x | M3 (4x) | 82.27 | 150 | 149 | 99.33 a |
| M4 b | A. chinensis | Tetraploid, 4x | M4 (4x) | 70.35 | 171 | 162 | 94.74 b |
| M5 a | A. deliciosa | Hexaploid, 6x | M5 (6x) | 76.13 | 163 | 153 | 93.87 bc |
| M6 a | A. deliciosa | Hexaploid, 6x | M6 (6x) | 82.13 | 193 | 180 | 93.26 bc |
| M7 a | A. kolomikta | Diploid, 2x | M7 (2x) | 66.33 | 154 | 38 | 24.68 f |
| M8 a | A. arguta | Tetraploid, 4x | M8 (4x) | 75.79 | 146 | 30 | 20.55 g |
| M9 b | A. melanandra | Tetraploid, 4x | M9 (4x) | 68.05 | 142 | 53 | 37.32 d |
| M10 b | A. eriantha | Tetraploid, 4x | M10 (4x) | 65.87 | 40 | 11 | 27.50 e |
| Male | Fruit | Seeds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Fruit Weight (g) | Longitudinal Diameter (mm) | Transverse Diameter (mm) | Percentage of Black Seed | Horizontal Diameter (mm) | Vertical Diameter (mm) | 1000-Seed Weight (g) | |
| M1 (2x) | 69.81 ± 6.67 c | 49.73 ± 2.50 c | 51.19 ± 3.16 c | 13.95% | 0.646 ± 0.146 c | 0.972 ± 0.061 c | 0.21 e |
| M2 (2x) | 68.12 ± 6.17 c | 48.44 ± 2.01 c | 52.39 ± 2.81 c | 12.50% | 0.622 ± 0.142 c | 1.030 ± 0.182 c | 0.24 d |
| M3 (4x) | 104.94 ± 8.92 b | 57.17 ± 3.25 b | 67.11 ± 3.51 b | 100% | 1.429 ± 0.138 ab | 2.457 ± 0.133 a | 1.07 c |
| M4 (4x) | 104.68 ± 10.97 b | 56.69 ± 2.07 b | 68.75 ± 3.54 ab | 100% | 1.317 ± 0.107 b | 2.265 ± 0.178 b | 1.06 c |
| M5 (6x) | 113.53 ± 10.58 a | 57.67 ± 2.51 ab | 68.68 ± 3.31 ab | 100% | 1.394 ± 0.102 ab | 2.438 ± 0.148 a | 1.68 a |
| M6 (6x) | 120.91 ± 7.83 a | 59.24 ± 3.27 a | 69.65 ± 2.44 a | 100% | 1.464 ± 0.092 a | 2.532 ± 0.218 a | 1.54 b |
| Male | DM (%) | SSC (%) | TA (%) | SAR | ASA (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 (2x) | 20.22 ± 0.97 ab | 15.1 ± 0.88 b | 0.97 ± 0.07 b | 15.60 ± 0.47 b | 52.92 ± 2.41 bc |
| M2 (2x) | 20.98 ± 1.05 a | 17.6 ± 0.64 a | 0.94 ± 0.23 b | 18.72 ± 0.68 a | 68.91 ± 3.20 a |
| M3 (4x) | 20.35 ± 1.09 ab | 17.3 ± 0.12 a | 0.93 ± 0.00 b | 18.60 ± 0.08 a | 52.57 ± 2.00 bc |
| M4 (4x) | 19.16 ± 0.89 c | 15.5 ± 0.74 b | 1.47 ± 0.17 a | 11.09 ± 0.30 c | 51.18 ± 2.64 c |
| M5 (6x) | 20.54 ± 0.72 a | 17.0 ± 0.39 a | 1.74 ± 0.18 a | 10.03 ± 1.15 c | 56.65 ± 1.94 b |
| M6 (6x) | 19.51 ± 0.73 bc | 13.6 ± 0.11 c | 1.06 ± 0.29 b | 12.01 ± 1.02 c | 45.26 ± 0.26 d |
| Male | Fructose (mg g−1) | Glucose (mg g−1) | Sucrose (mg g−1) | Total Sugar (mg g−1) | Sweetness Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Pericarp | Inner Pericarp | Outer Pericarp | Inner Pericarp | Outer Pericarp | Inner Pericarp | Outer Pericarp | Inner Pericarp | Outer Pericarp | Inner Pericarp | |
| M1 (2x) | 21.08 ± 0.06 b | 19.15 ± 0.45 bc | 27.98 ± 0.73 cd | 26.68 ± 0.75 c | 27.30 ± 2.71 a | 20.08 ± 1.22 b | 76.36 ± 3.18 b | 65.91 ± 2.11 b | 83.78 ± 2.99 b | 72.27 ± 2.24 b |
| M2 (2x) | 25.08 ± 0.50 a | 21.86 ± 0.97 a | 38.91 ± 0.60 a | 36.06 ± 1.47 a | 18.90 ± 0.97 b | 17.67 ± 1.71 b | 82.89 ± 1.39 a | 75.61 ± 3.78 a | 90.03 ± 1.47 a | 81.19 ± 4.04 a |
| M3 (4x) | 20.98 ± 0.44 b | 19.38 ± 0.44 bc | 29.42 ± 0.63 bc | 27.09 ± 0.61 c | 20.84 ± 1.10 b | 19.98 ± 0.39 b | 72.43 ± 1.45 b | 70.11 ± 1.15 ab | 78.15 ± 2.22 b | 72.85 ± 1.54 b |
| M4 (4x) | 20.03 ± 0.62 b | 18.77 ± 0.04 c | 26.65 ± 0.82 d | 25.35 ± 0.06 c | 25.75 ± 0.52 a | 25.98 ± 1.15 a | 71.24 ± 2.09 b | 66.44 ± 1.39 b | 79.46 ± 1.63 b | 76.57 ± 1.11 ab |
| M5 (6x) | 21.30 ± 0.14 b | 20.77 ± 0.61 ab | 29.89 ± 0.19 b | 29.99 ± 0.75 b | 13.36 ± 0.94 c | 18.11 ± 0.44 b | 64.55 ± 0.66 c | 68.87 ± 1.80 ab | 71.56 ± 0.63 c | 75.45 ± 2.04 ab |
| M6 (6x) | 20.52 ± 0.11 b | 18.83 ± 0.01 c | 27.24 ± 0.09 d | 26.10 ± 0.06 c | 13.14 ± 0.44 c | 13.30 ± 0.91 c | 60.91 ± 0.41 c | 58.22 ± 0.98 c | 68.12 ± 0.44 c | 64.51 ± 0.97 c |
| Malic acid (mg g−1) | Citric acid (mg g−1) | Quinic acid (mg g−1) | Total acid (mg g−1) | Sweet/acid ratio | ||||||
| Outer pericarp | Inner pericarp | Outer pericarp | Inner pericarp | Outer pericarp | Inner pericarp | Outer pericarp | Inner pericarp | Outer pericarp | Inner pericarp | |
| M1 (2x) | 4.25 ± 0.15 c | 5.22 ± 0.41 c | 38.79 ± 0.53 b | 50.21 ± 0.16 bc | 32.26 ± 1.14 bc | 19.29 ± 0.21 bc | 75.30 ± 1.78 b | 74.71 ± 0.78 bc | 1.11 ± 0.04 a | 0.97 ± 0.03 b |
| M2 (2x) | 6.84 ± 0.16 b | 5.87 ± 0.21 c | 47.79 ± 0.50 a | 44.48 ± 0.29 c | 28.91 ± 0.29 c | 18.21 ± 3.30 c | 83.55 ± 0.36 ab | 68.56 ± 3.55 c | 1.08 ± 0.01 a | 1.18 ± 0.02 a |
| M3 (4x) | 6.78 ± 0.62 b | 7.28 ± 0.04 b | 42.70 ± 3.03 ab | 61.24 ± 1.95 a | 33.51 ± 2.51 bc | 23.58 ± 0.77 ab | 83.00 ± 4.25 ab | 92.10 ± 2.71 a | 0.87 ± 0.03 bc | 0.79 ± 0.01 c |
| M4 (4x) | 9.15 ± 1.21 a | 10.54 ± 0.76 a | 41.94 ± 2.40 ab | 57.96 ± 0.51 ab | 40.80 ± 1.55 a | 25.28 ± 0.51 a | 91.89 ± 7.07 a | 93.79 ± 0.90 a | 0.95 ± 0.05 b | 0.82 ± 0.01 c |
| M5 (6x) | 9.21 ± 0.33 a | 8.17 ± 0.52 b | 41.98 ± 0.36 ab | 50.74 ± 1.76 bc | 37.22 ± 1.99 ab | 21.14 ± 0.46 abc | 88.41 ± 3.11 ab | 80.06 ± 1.81 b | 0.81 ± 0.02 c | 0.94 ± 0.02 b |
| M6 (6x) | 6.80 ± 0.02 b | 5.66 ± 0.37 c | 39.51 ± 2.37 b | 54.50 ± 5.36 ab | 32.43 ± 0.89 bc | 20.14 ± 0.16 bc | 78.74 ± 3.63 ab | 80.30 ± 5.40 b | 0.89 ± 0.03 bc | 0.81 ± 0.06 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, Y.; Hong, W.; Liu, H.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. The Pollen Donor Affects Seed Development, Taste, and Flavor Quality in ‘Hayward’ Kiwifruit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8876. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108876
Chai Y, Hong W, Liu H, Shi X, Liu Y, Liu Z. The Pollen Donor Affects Seed Development, Taste, and Flavor Quality in ‘Hayward’ Kiwifruit. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8876. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108876
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Yanan, Weijin Hong, Hang Liu, Xia Shi, Yanfei Liu, and Zhande Liu. 2023. "The Pollen Donor Affects Seed Development, Taste, and Flavor Quality in ‘Hayward’ Kiwifruit" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8876. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108876
APA StyleChai, Y., Hong, W., Liu, H., Shi, X., Liu, Y., & Liu, Z. (2023). The Pollen Donor Affects Seed Development, Taste, and Flavor Quality in ‘Hayward’ Kiwifruit. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8876. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108876






