Heterocyclic Compounds as Synthetic Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Recent Advances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibitors
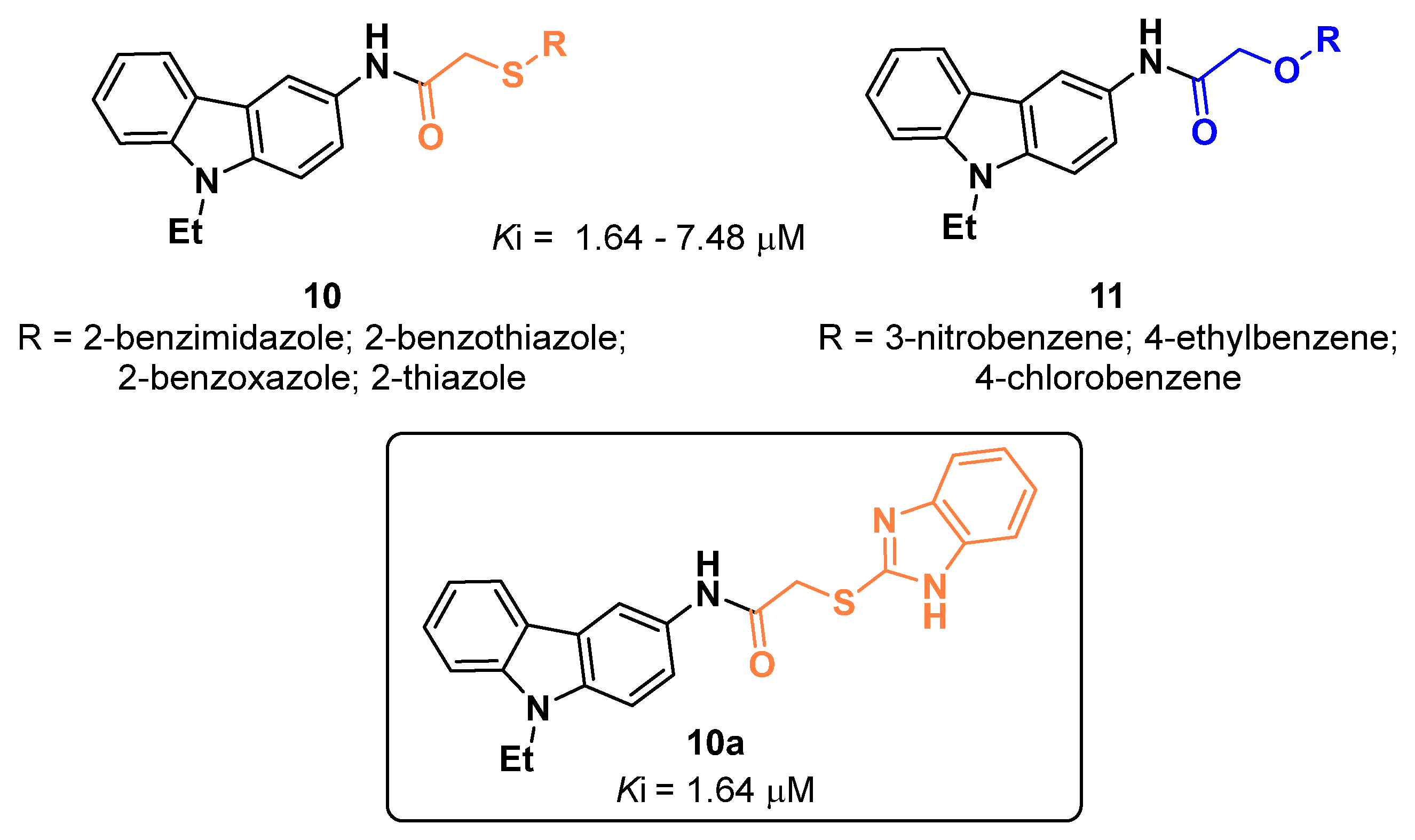
2.1. Carbazoles
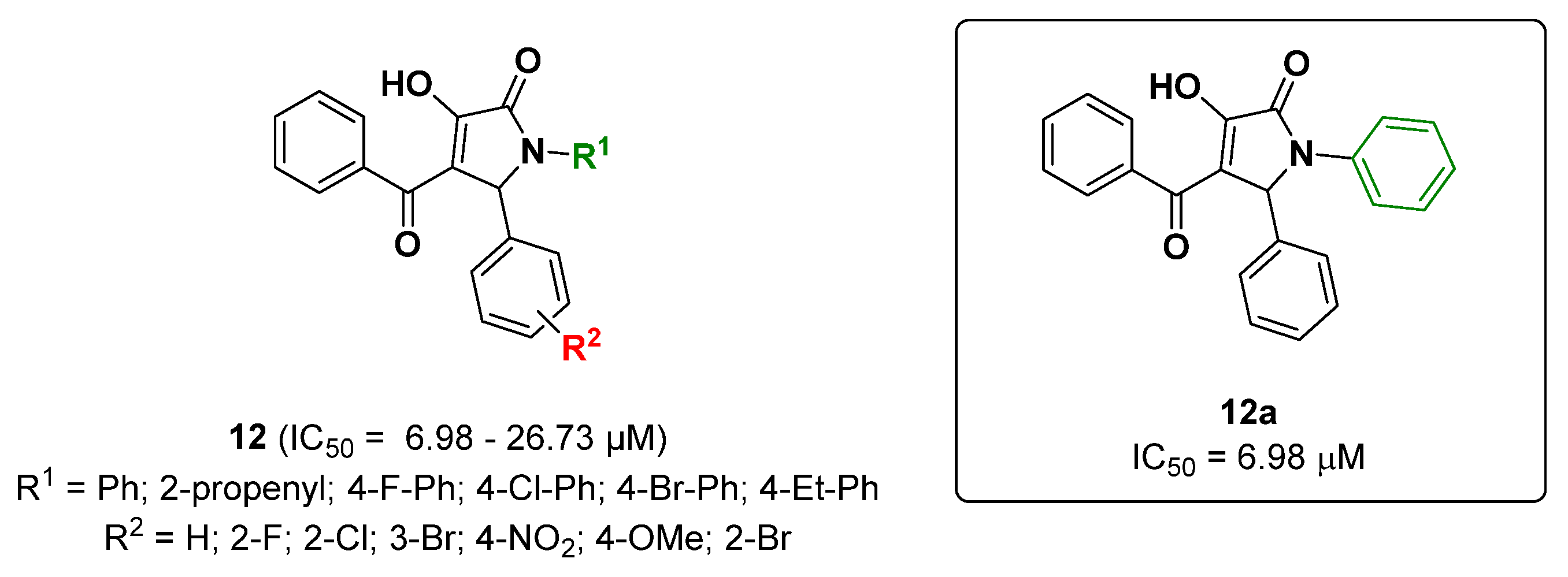
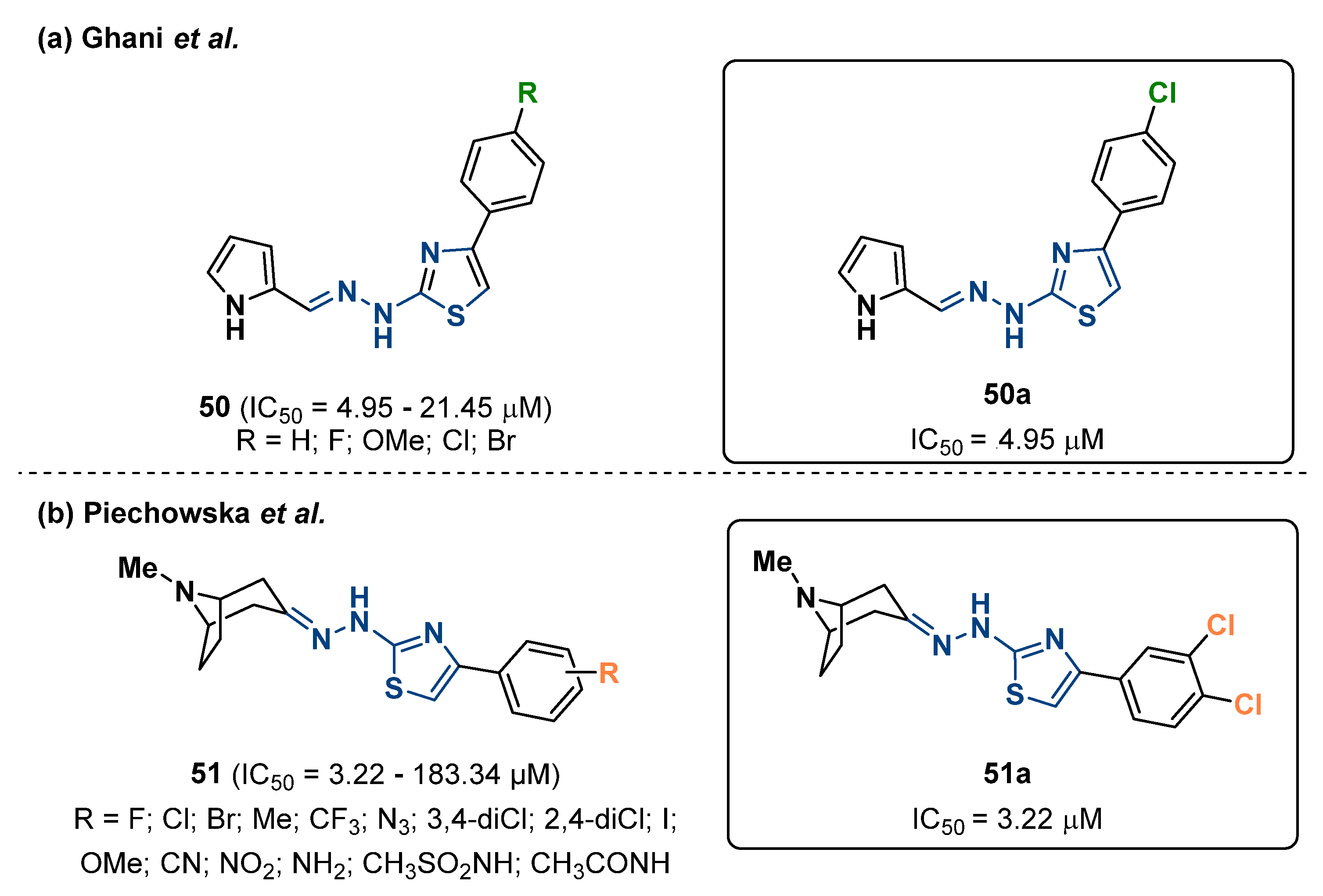
2.2. Compounds Derived from Pyrrol
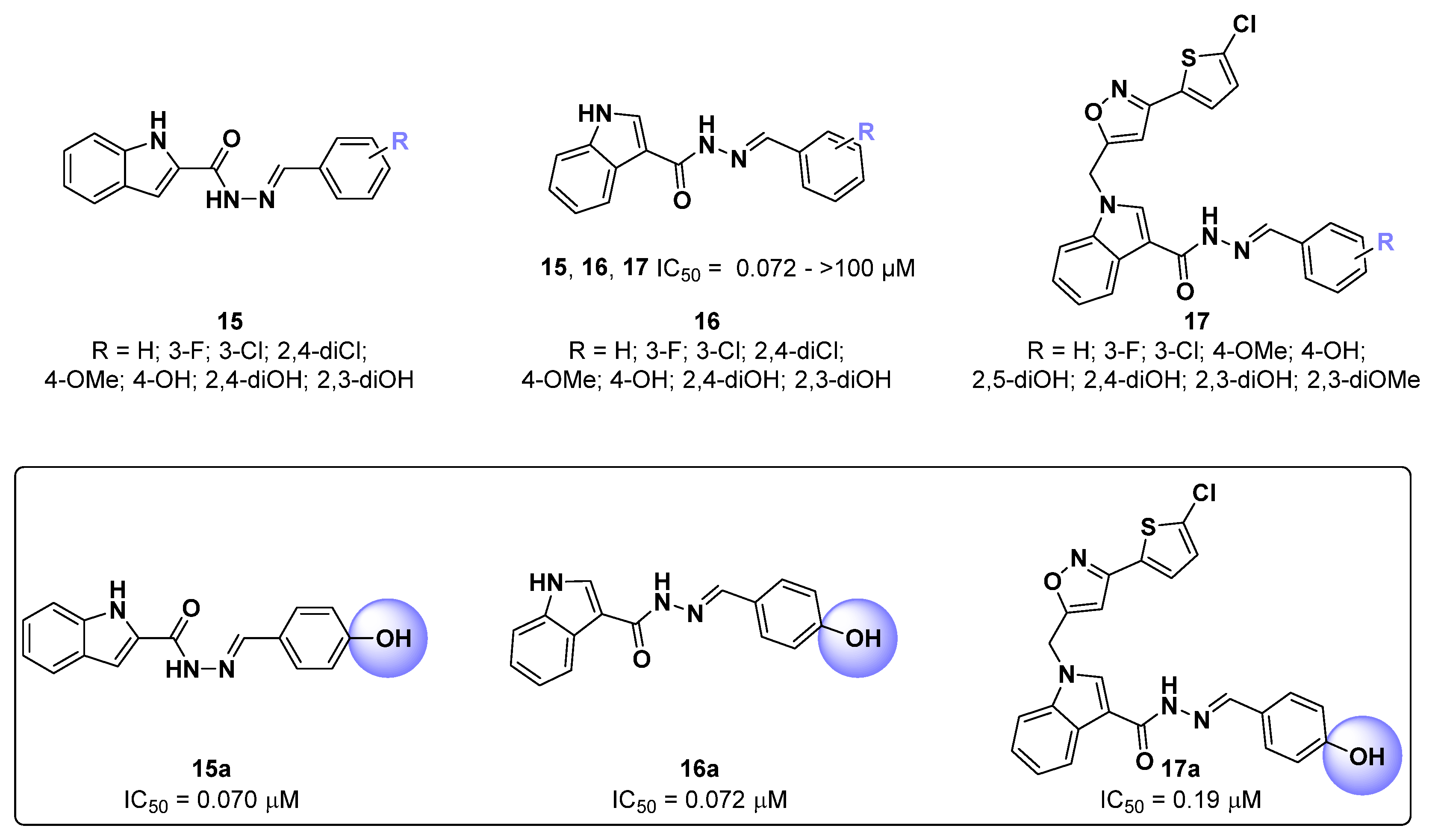
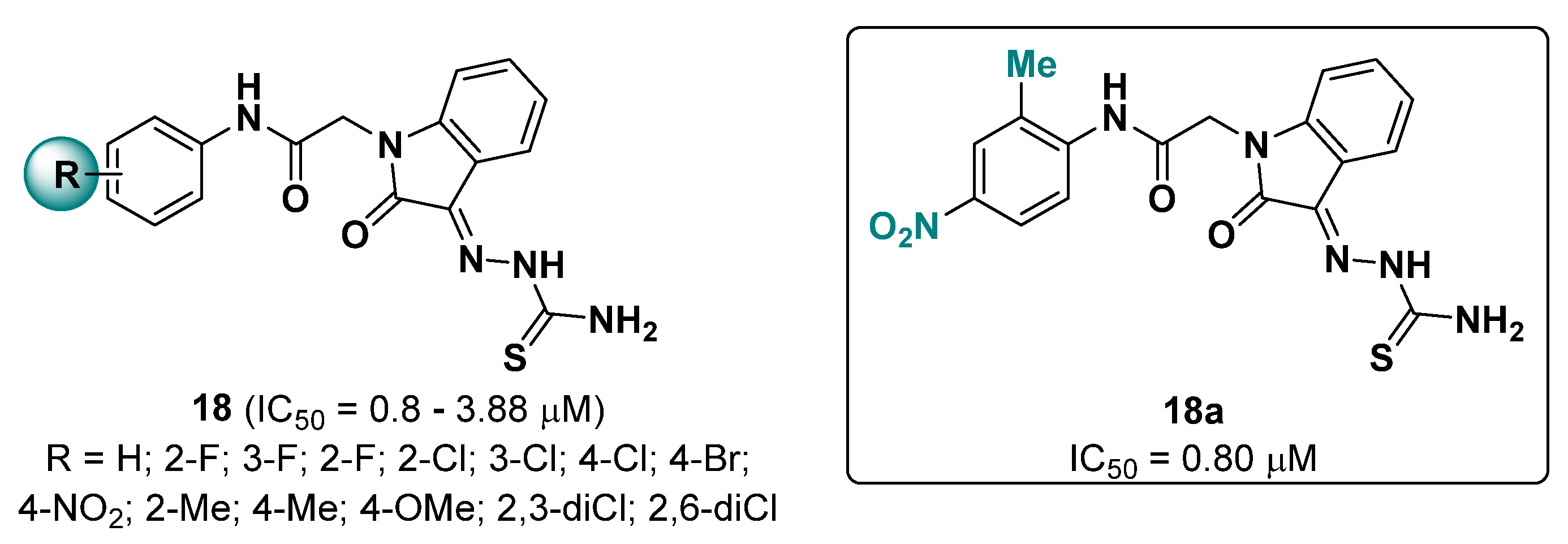
2.3. Indole Derivatives
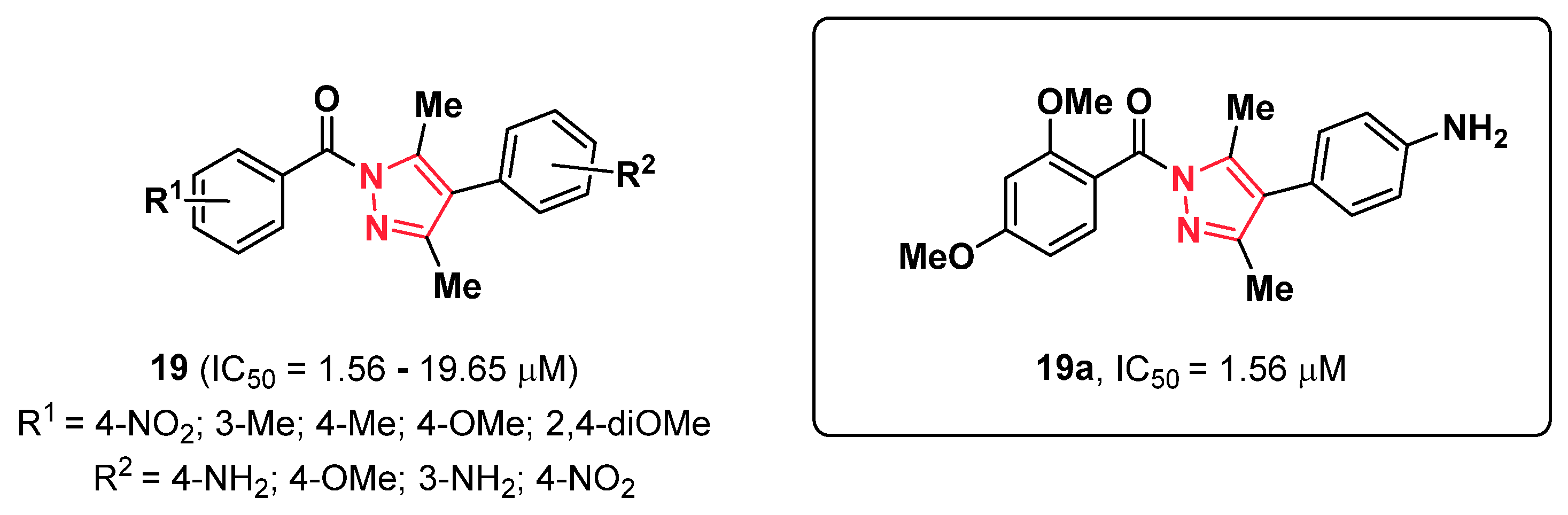
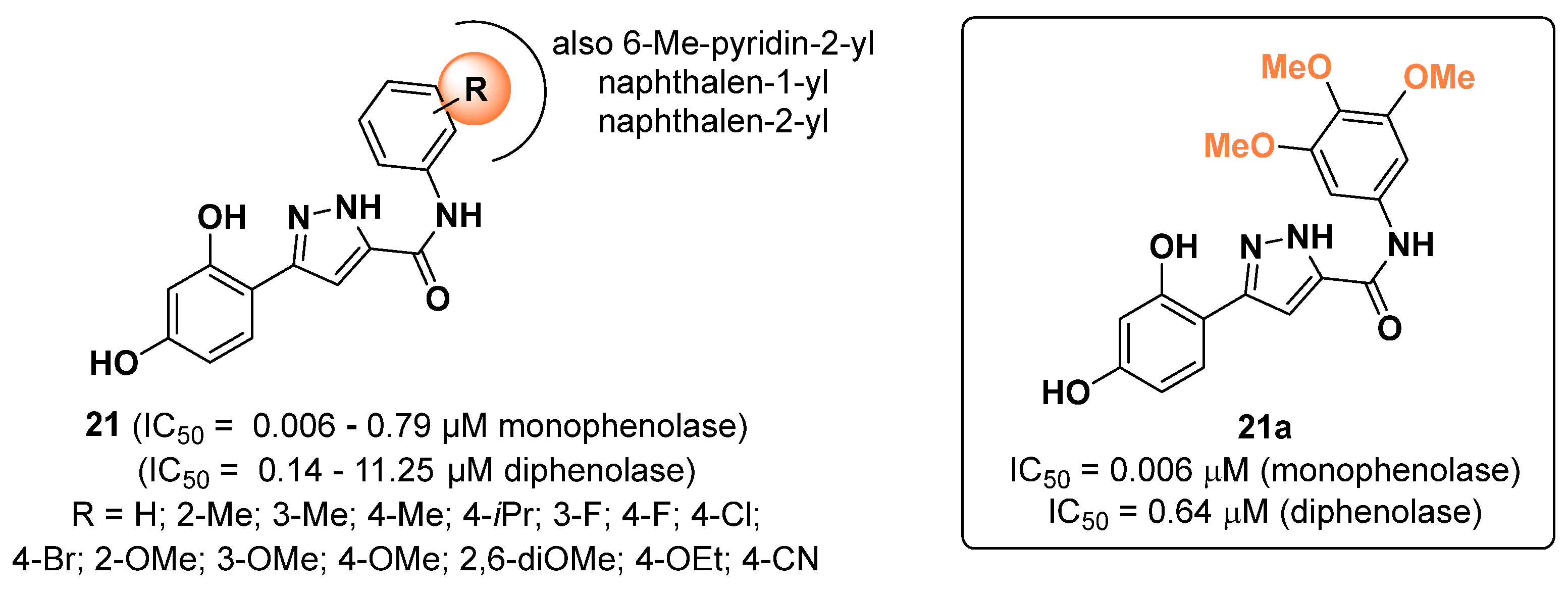
2.4. Pyrazoles
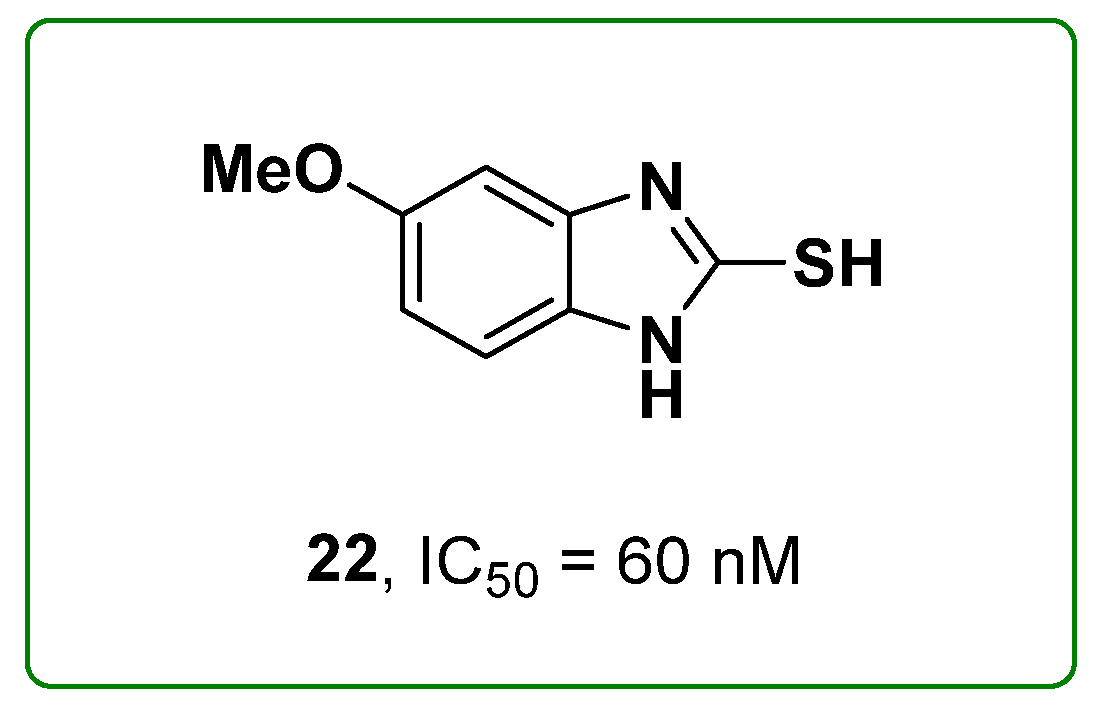
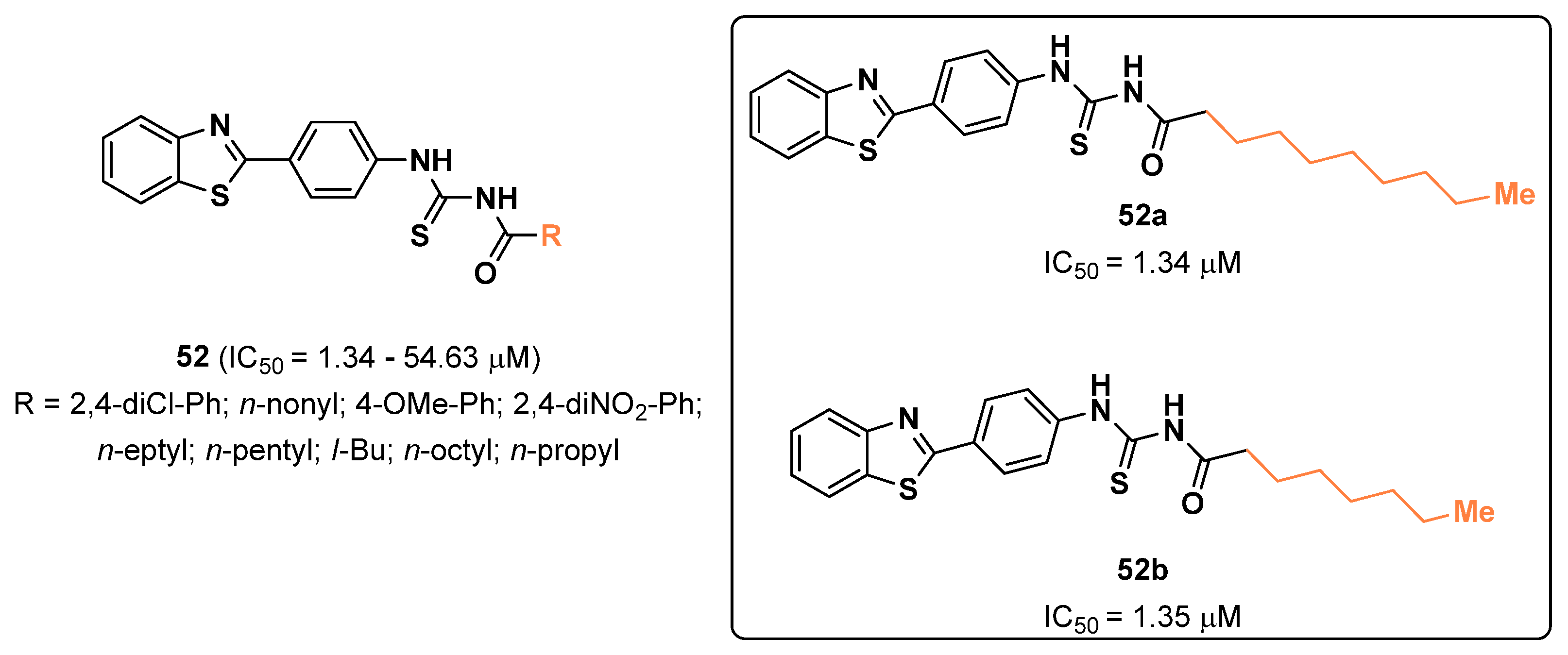
2.5. Benzimidazoles
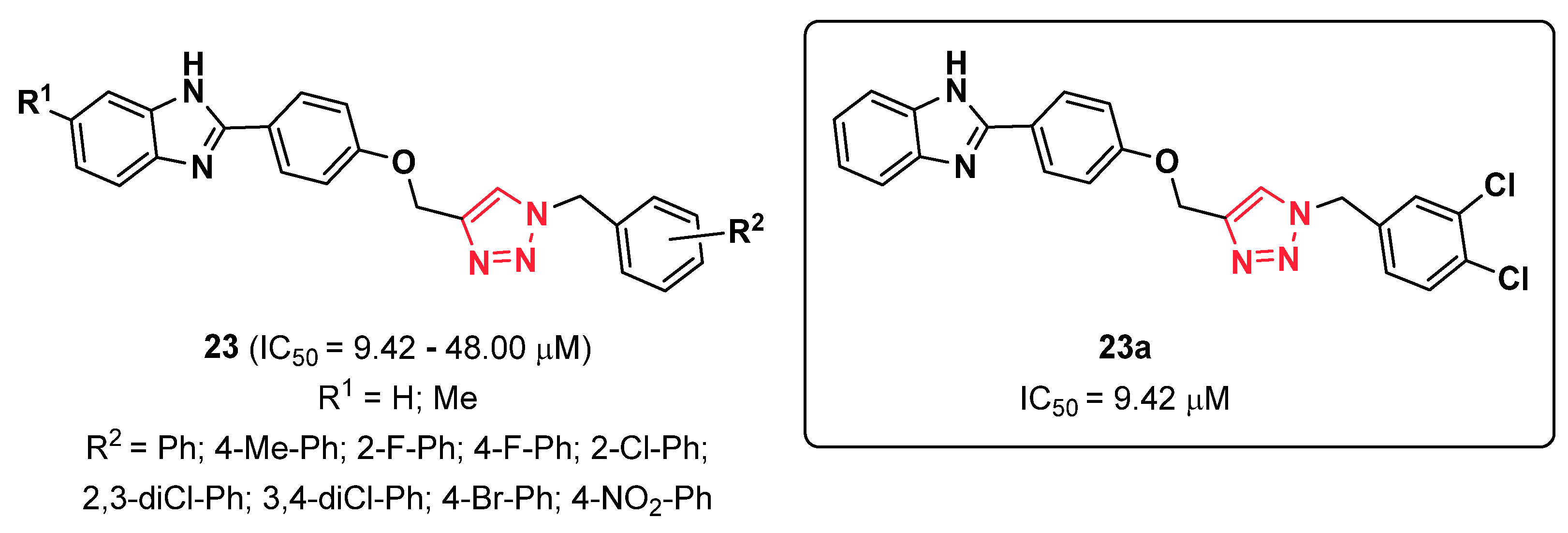
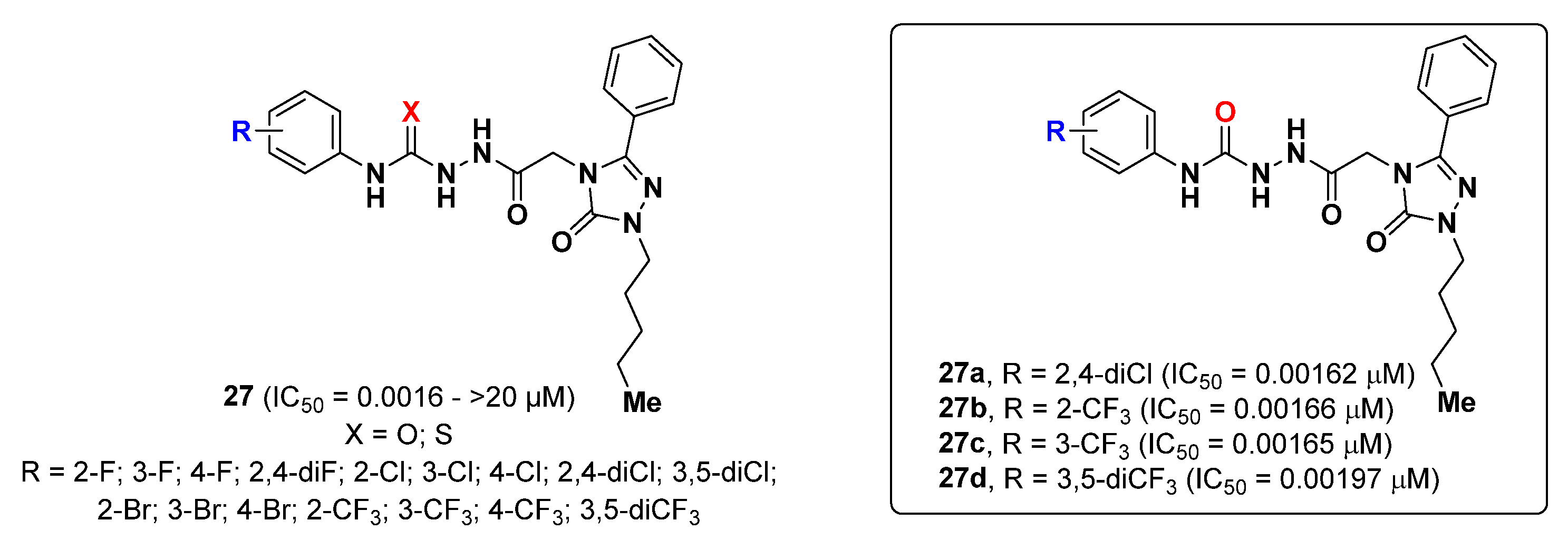
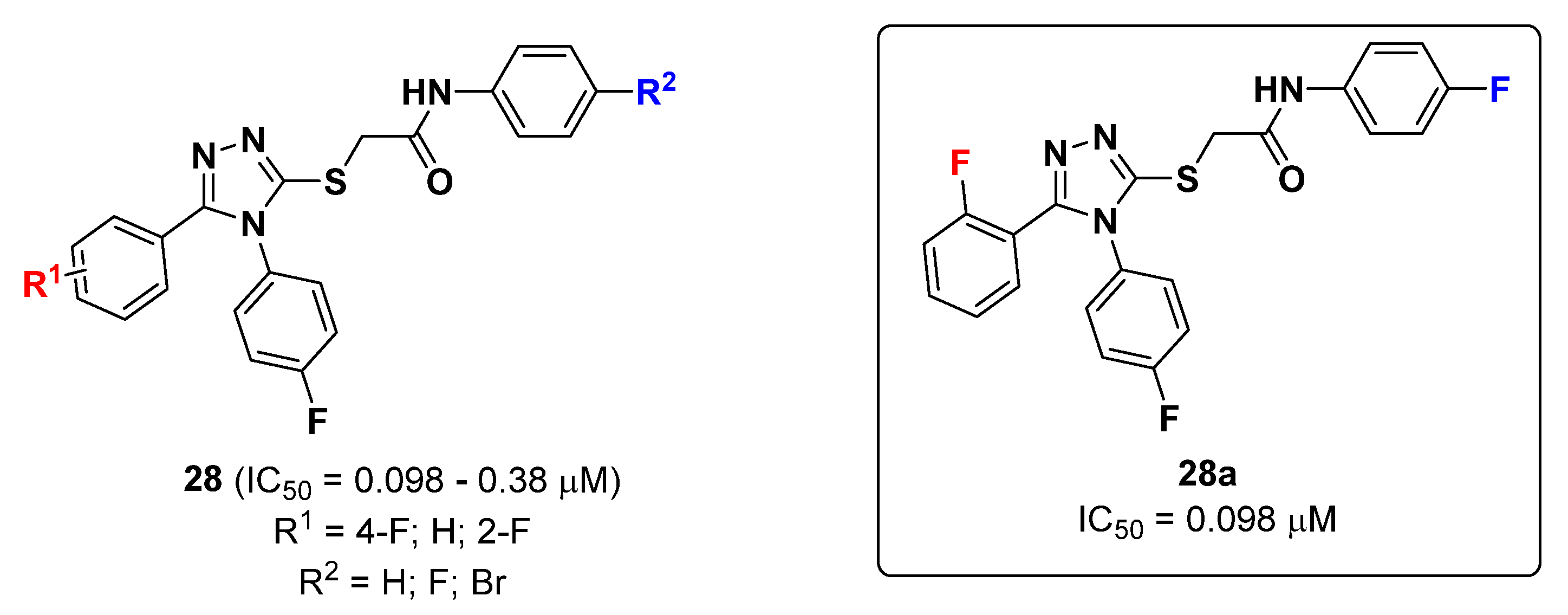
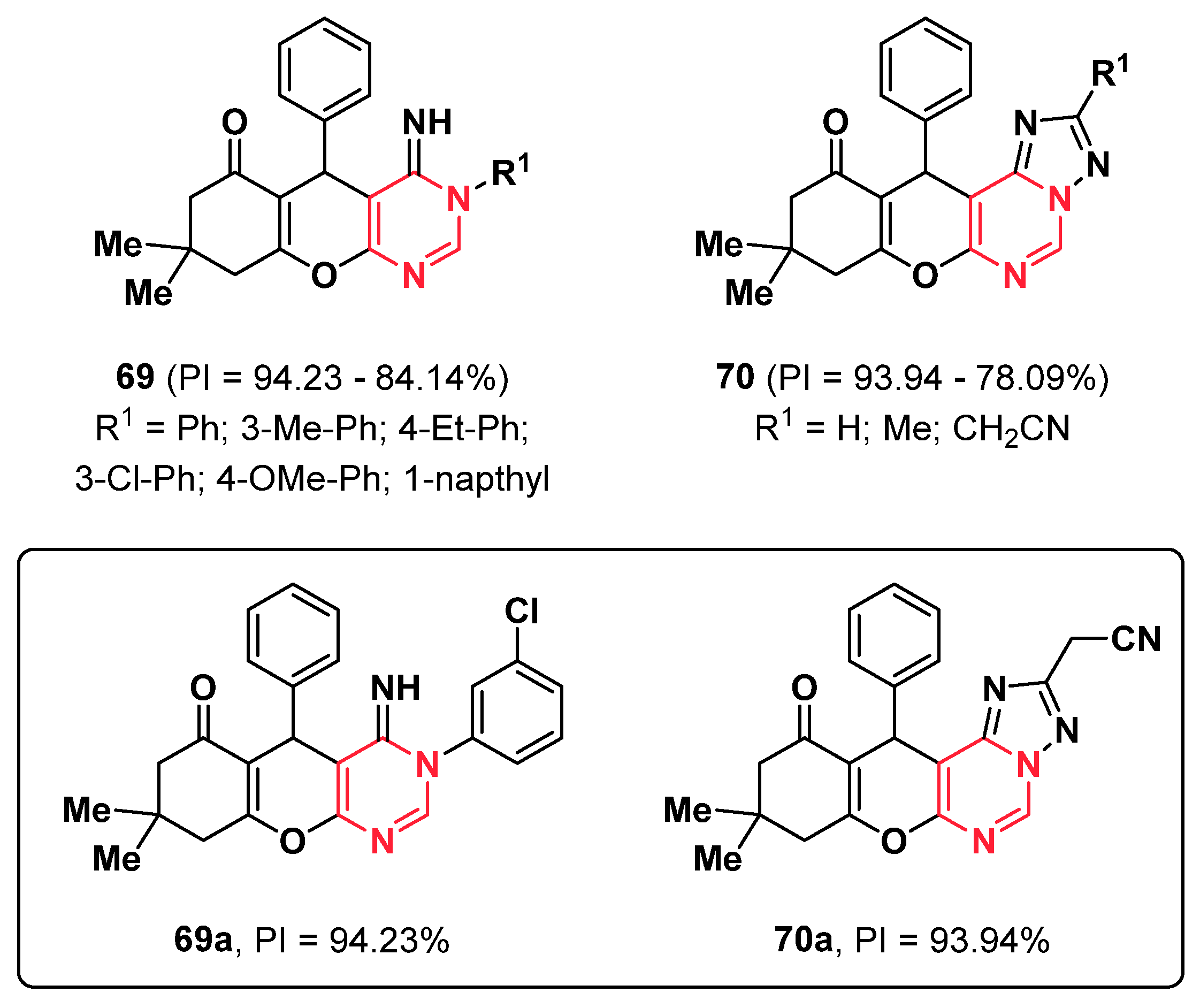
2.6. Triazoles
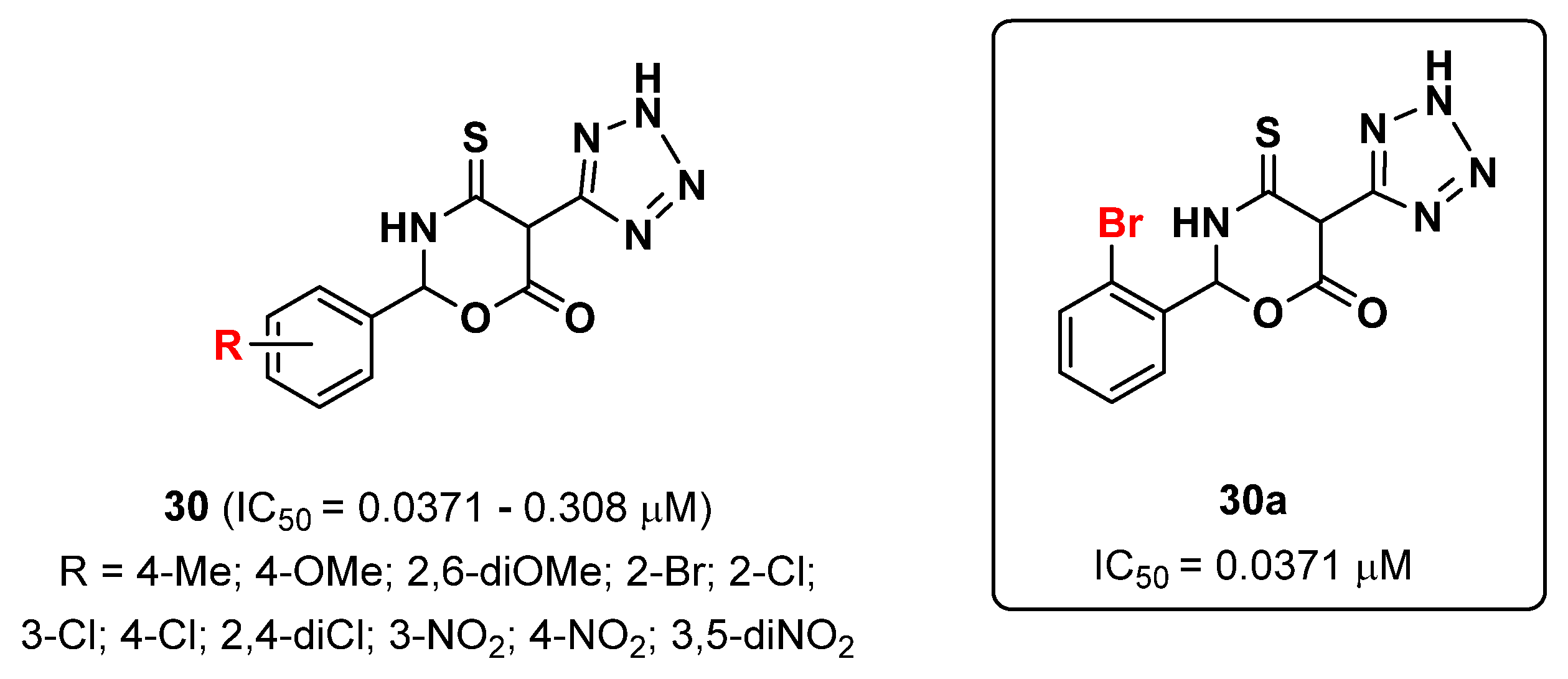
2.7. Tetrazoles
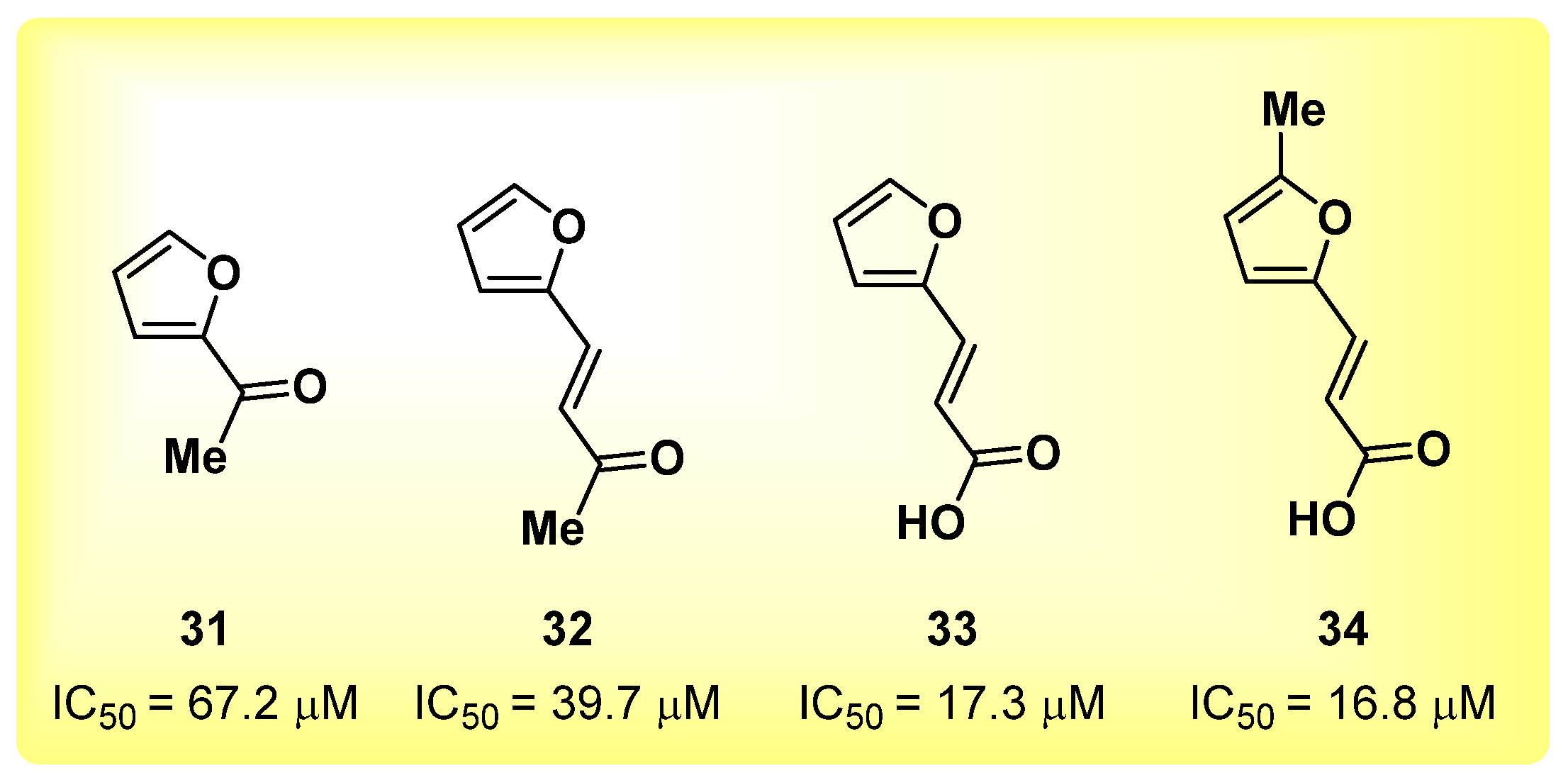
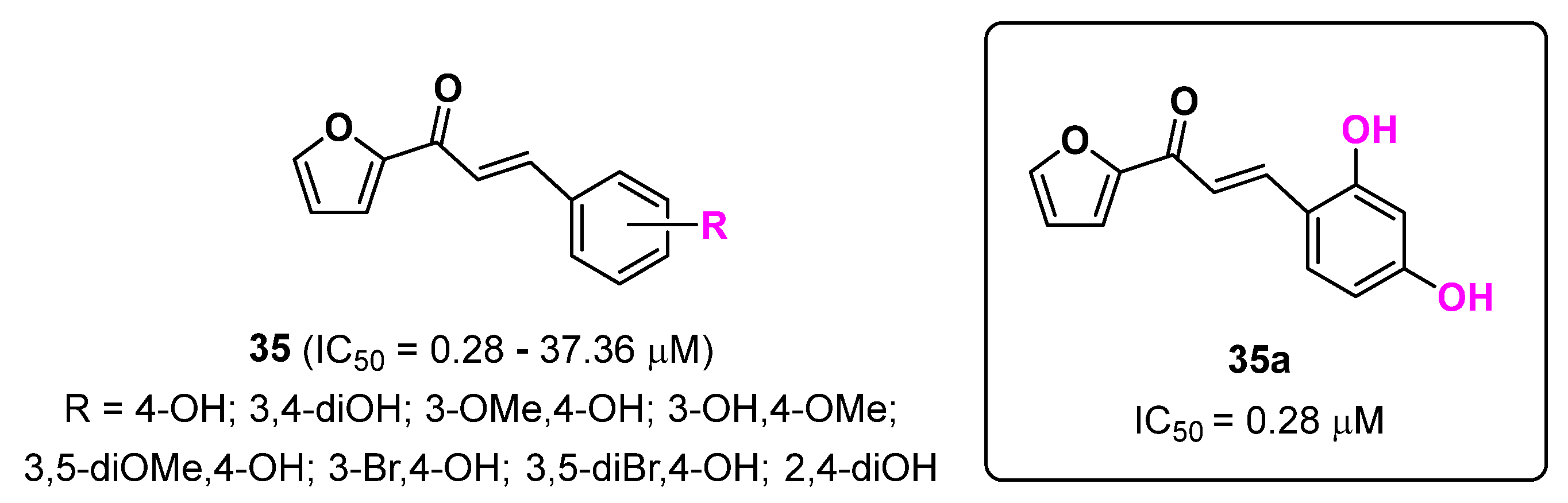
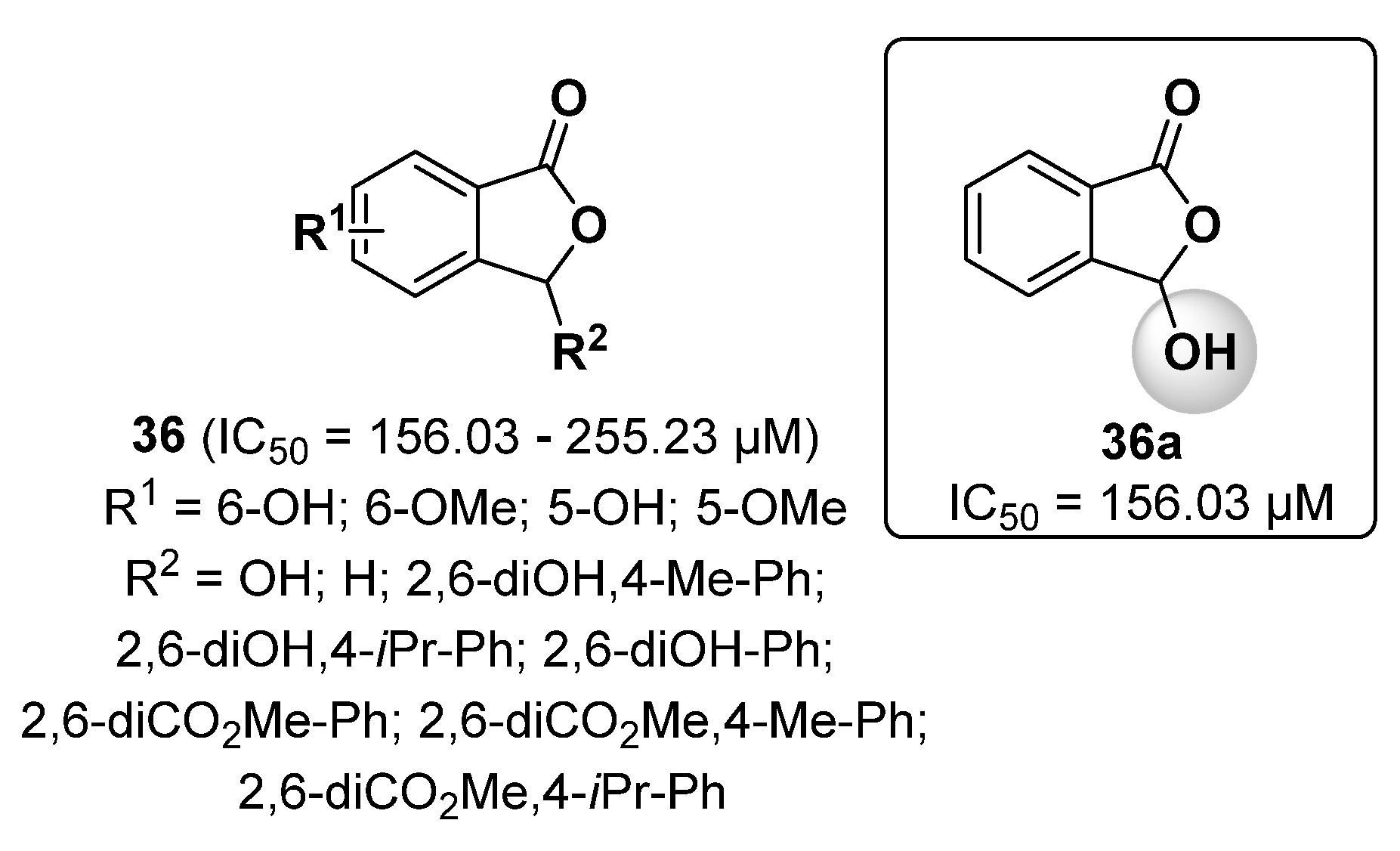
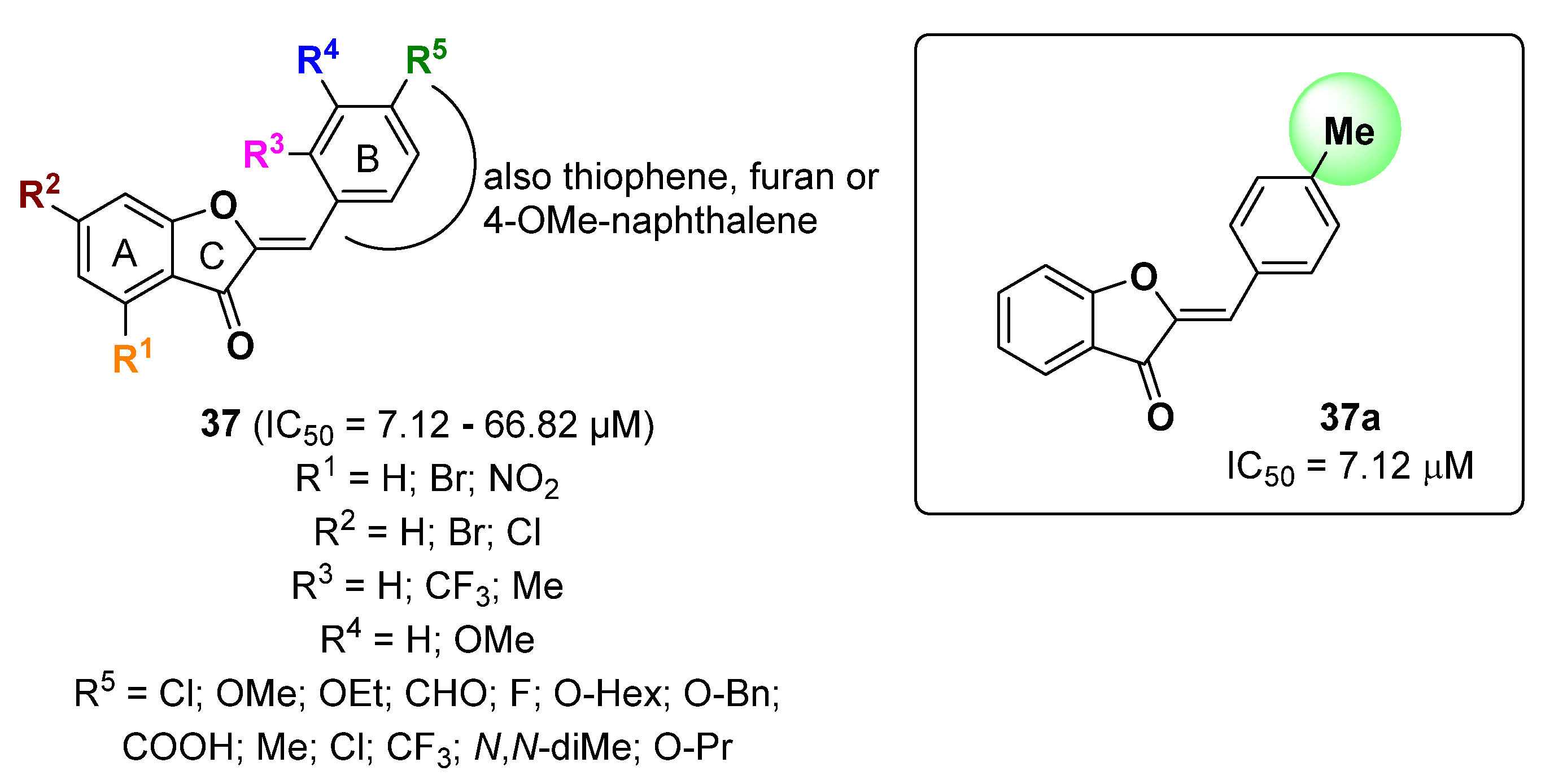
2.8. Furan Derivatives
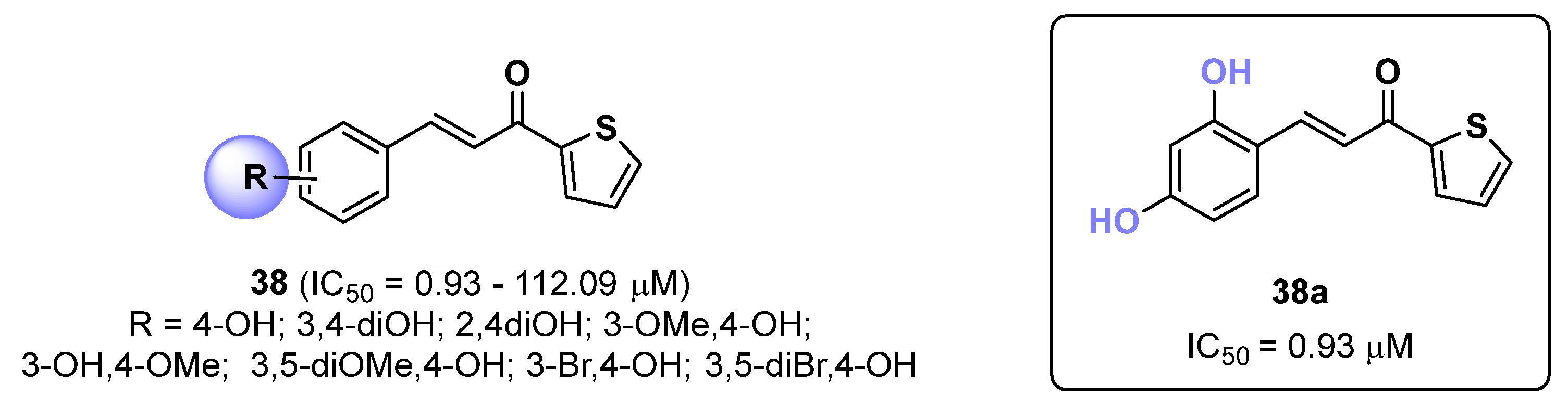
2.9. Thiophene Derivatives
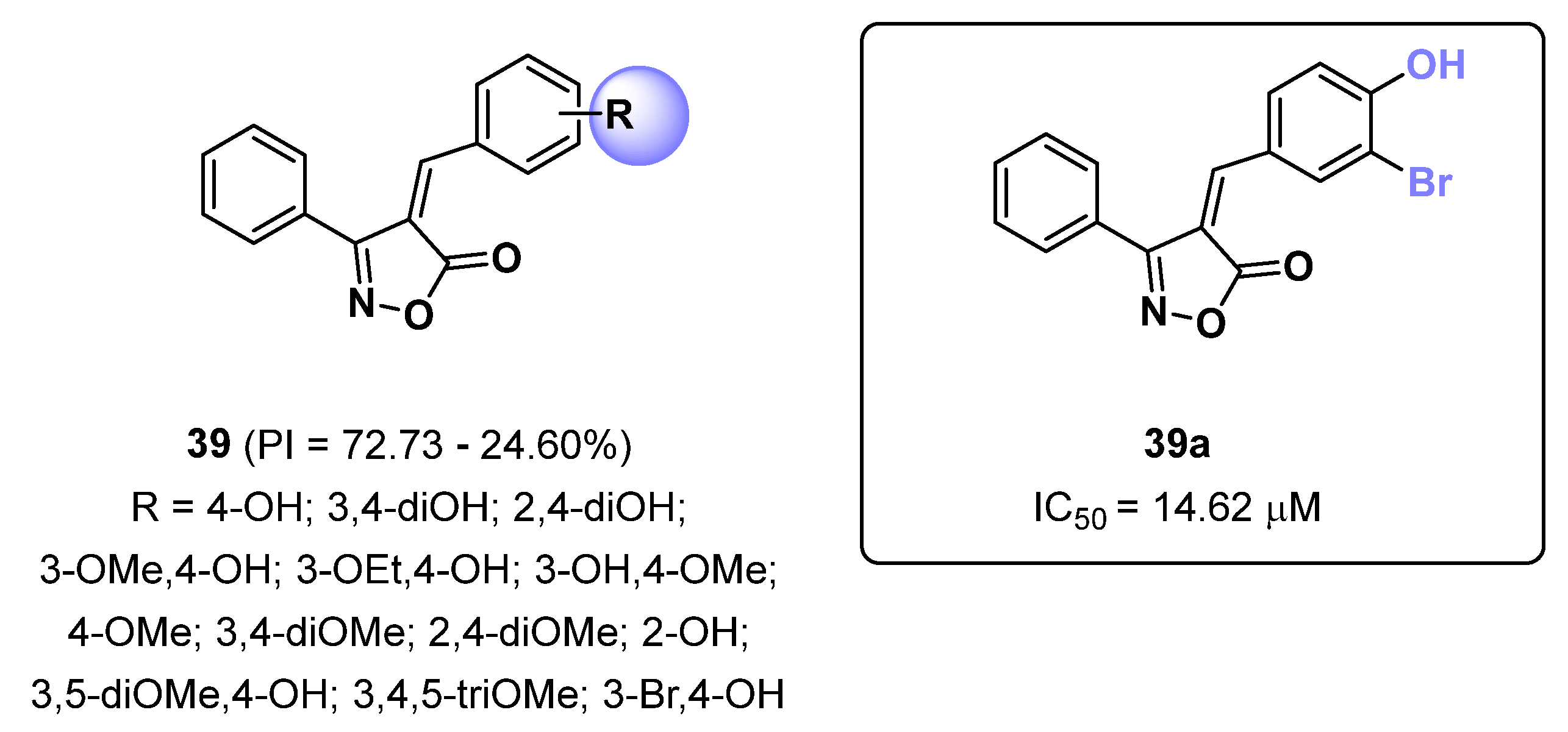
2.10. Isoxazoles
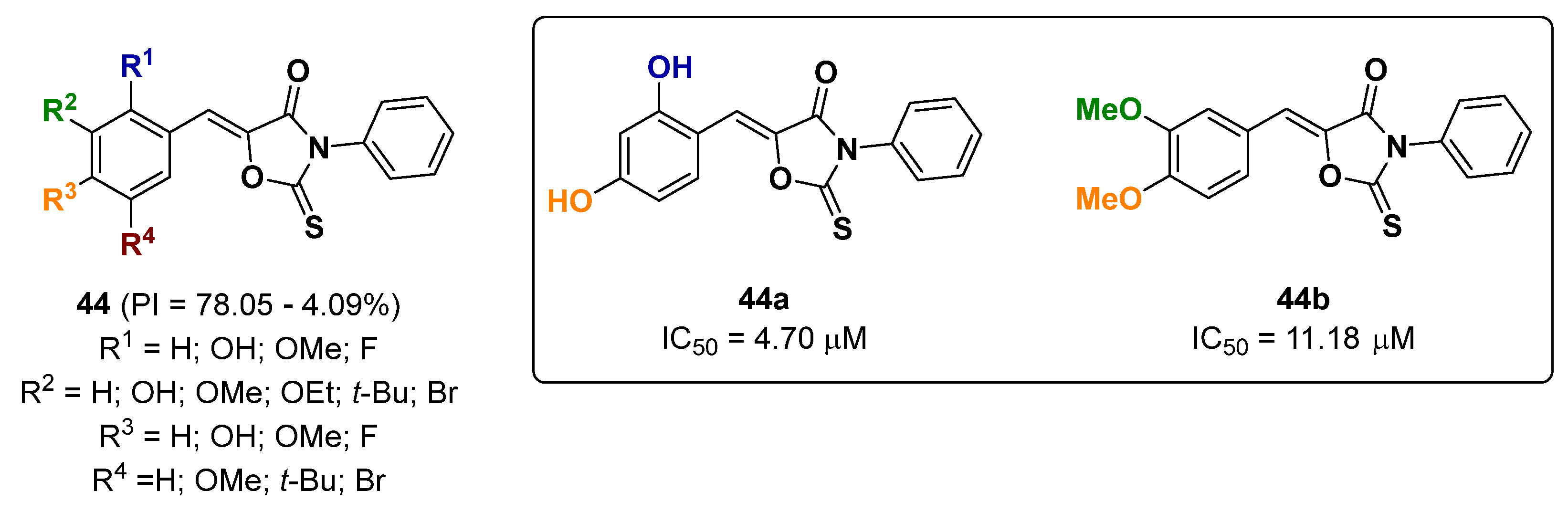
2.11. Oxazolines
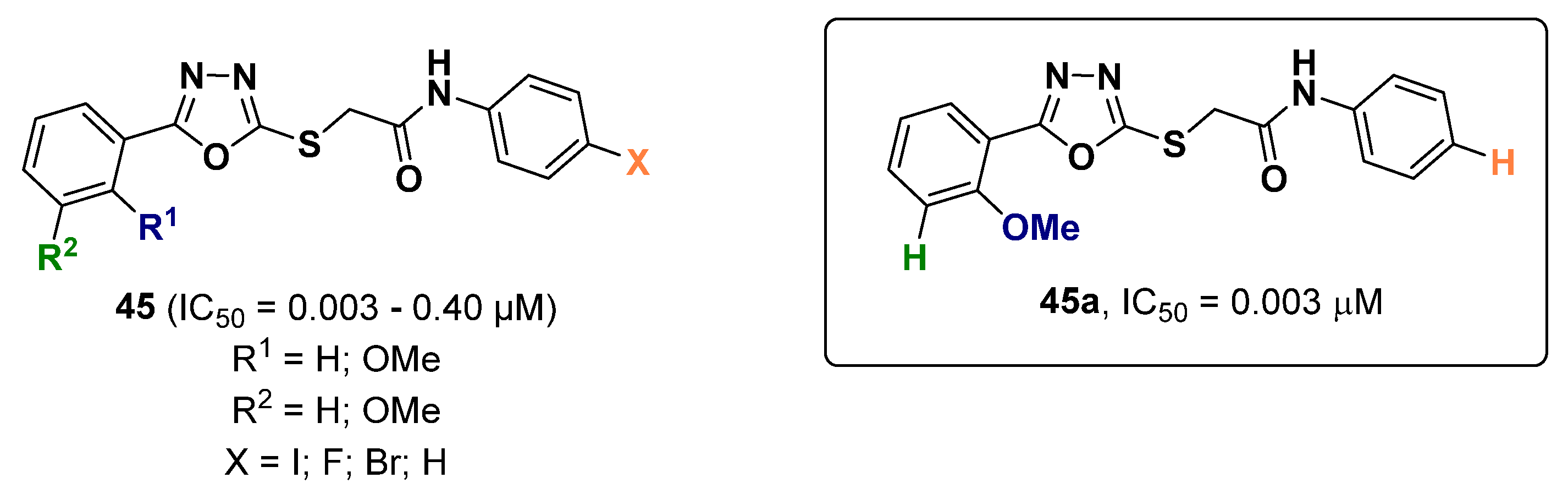
2.12. Oxadiazoles
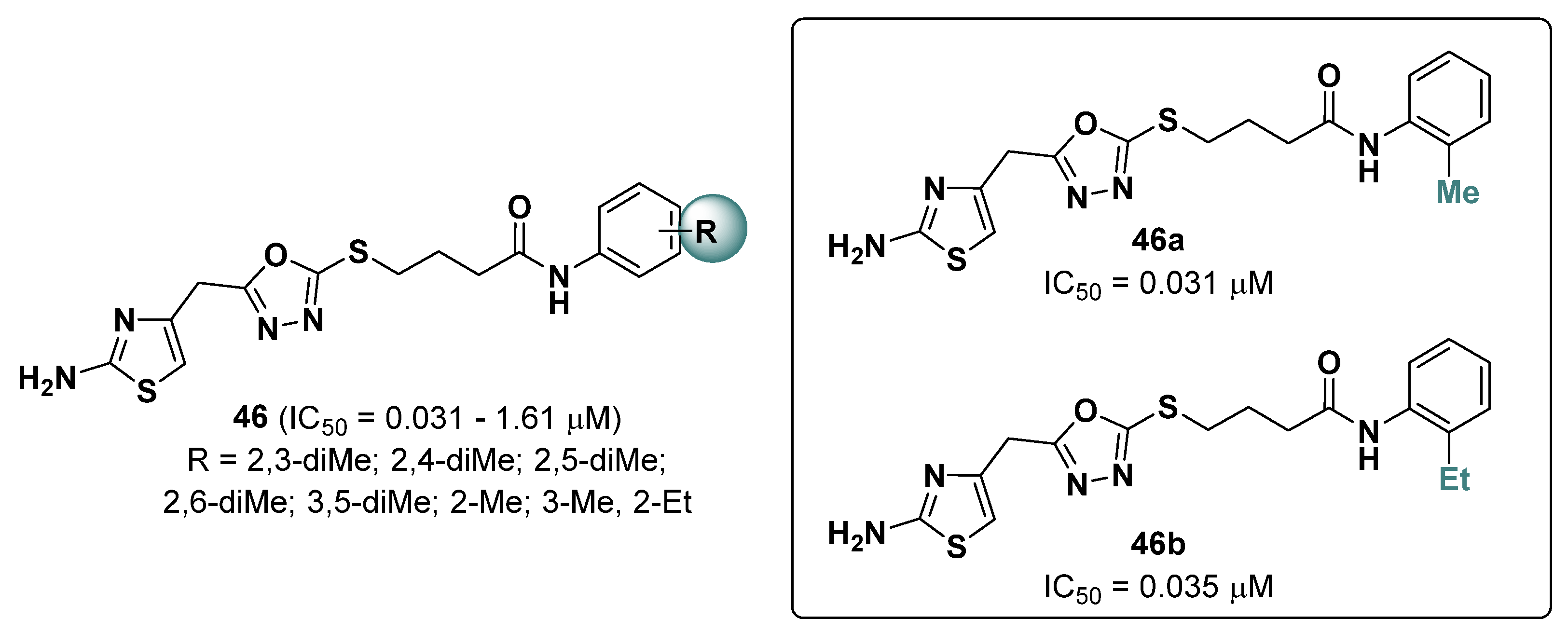
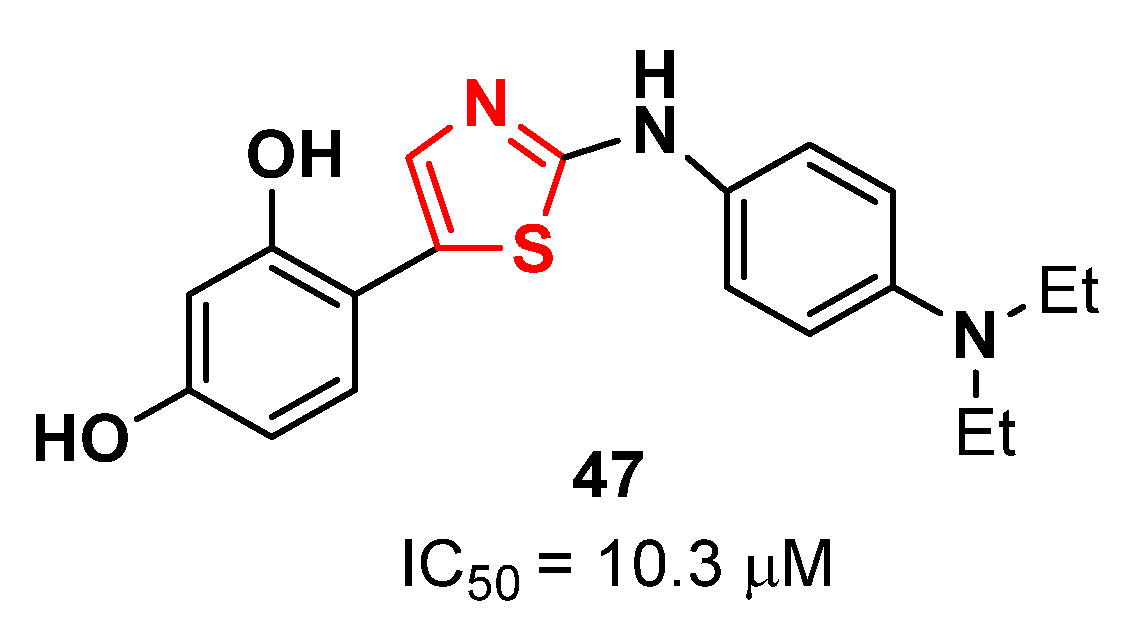
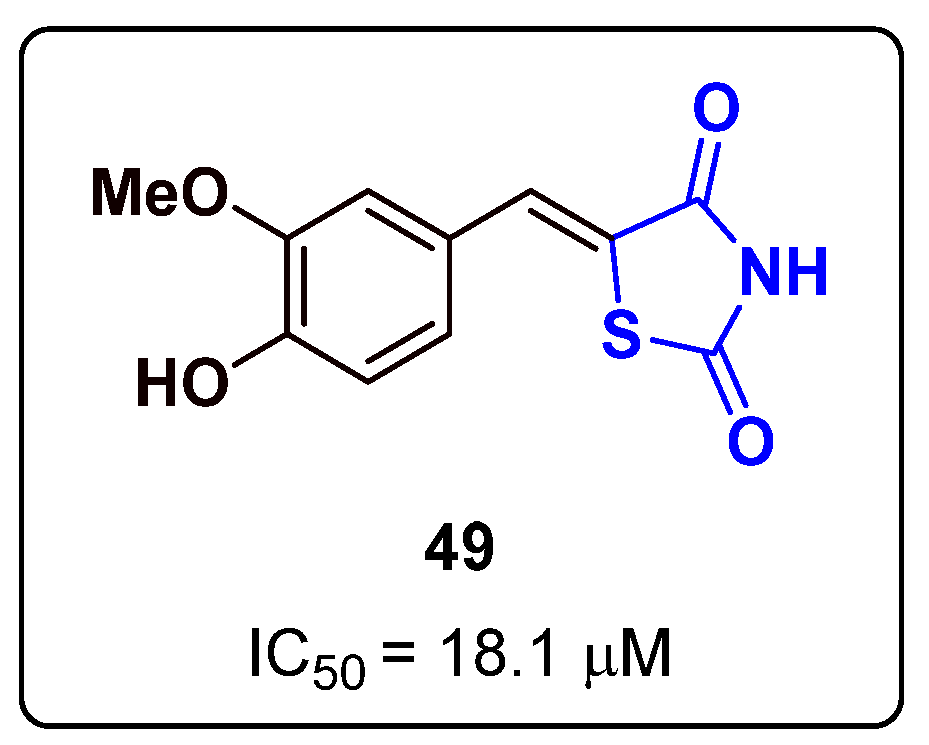
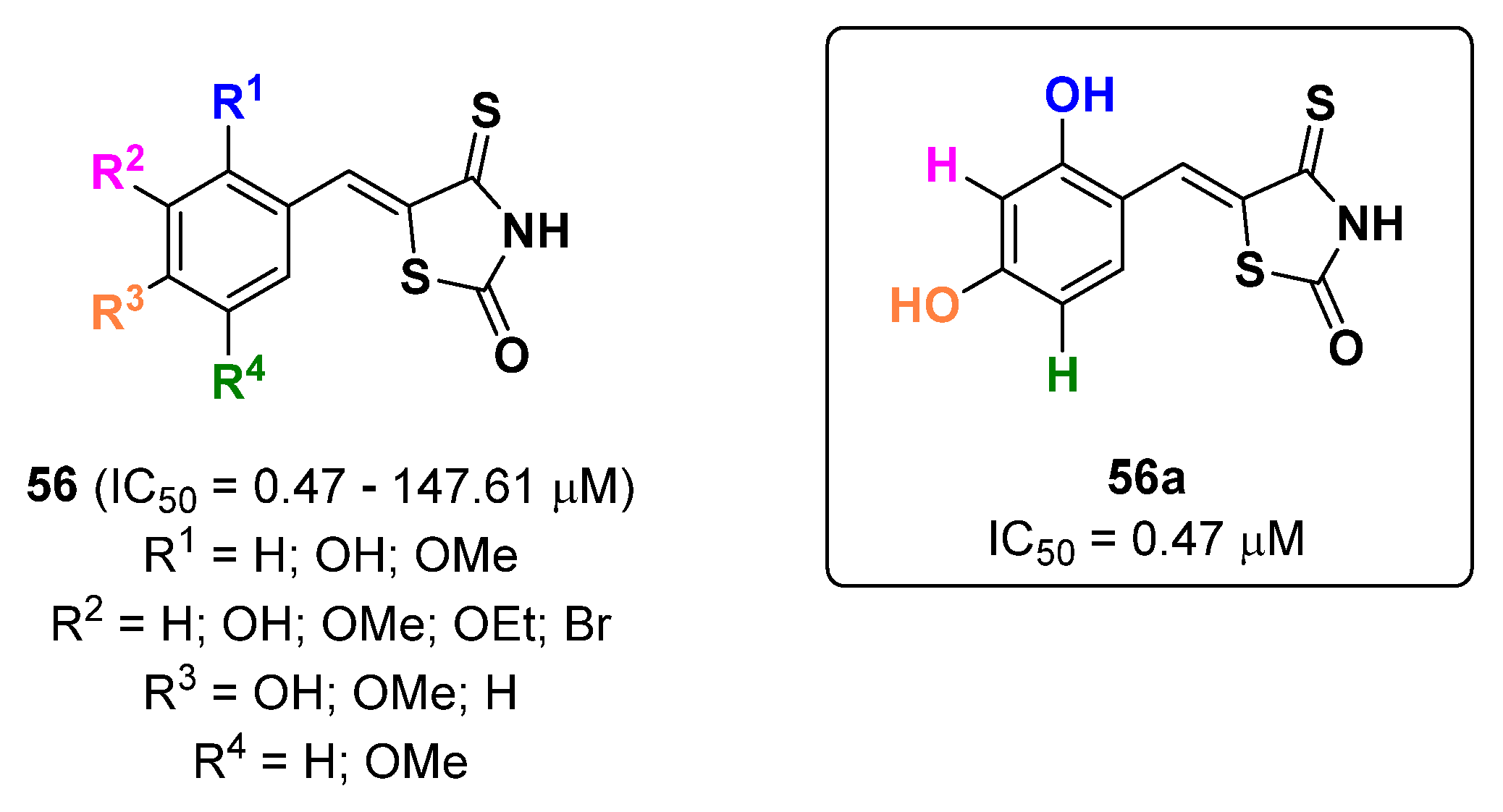
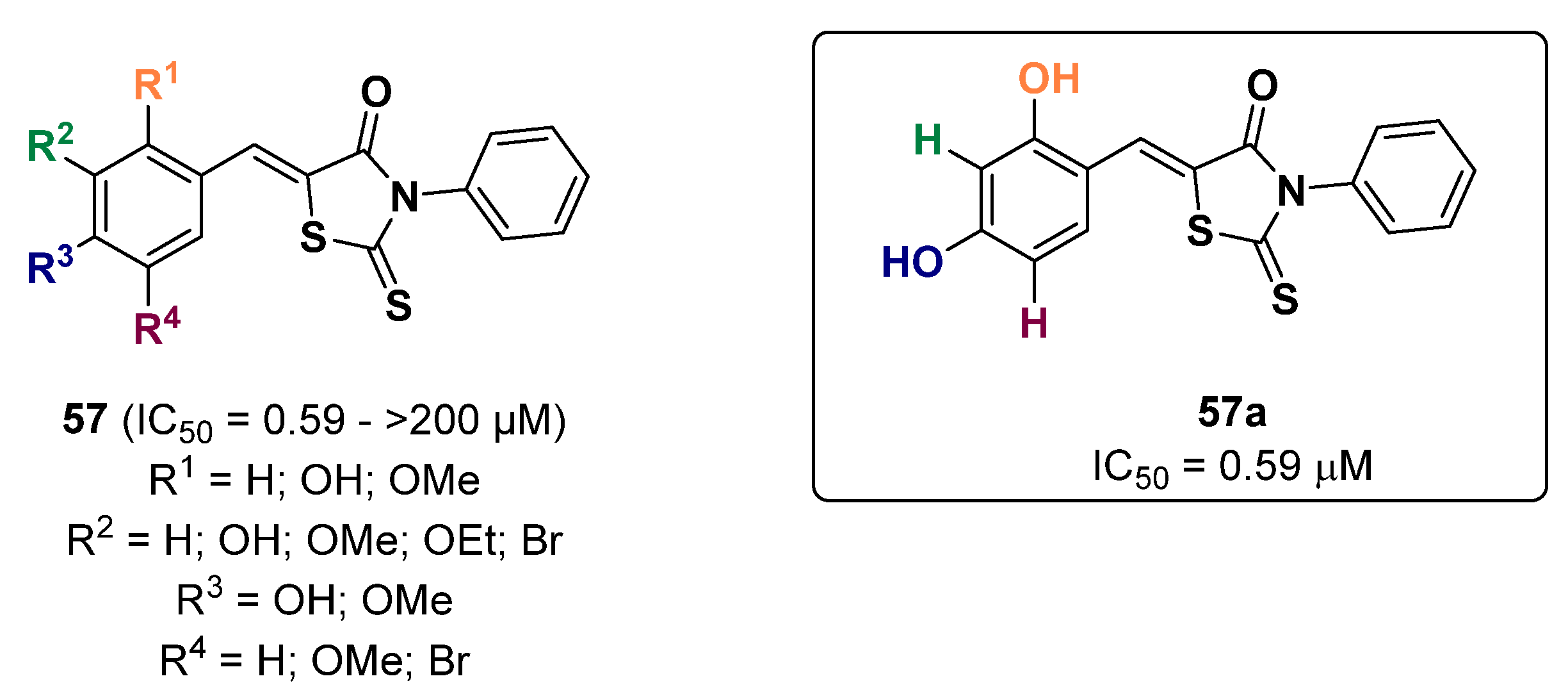
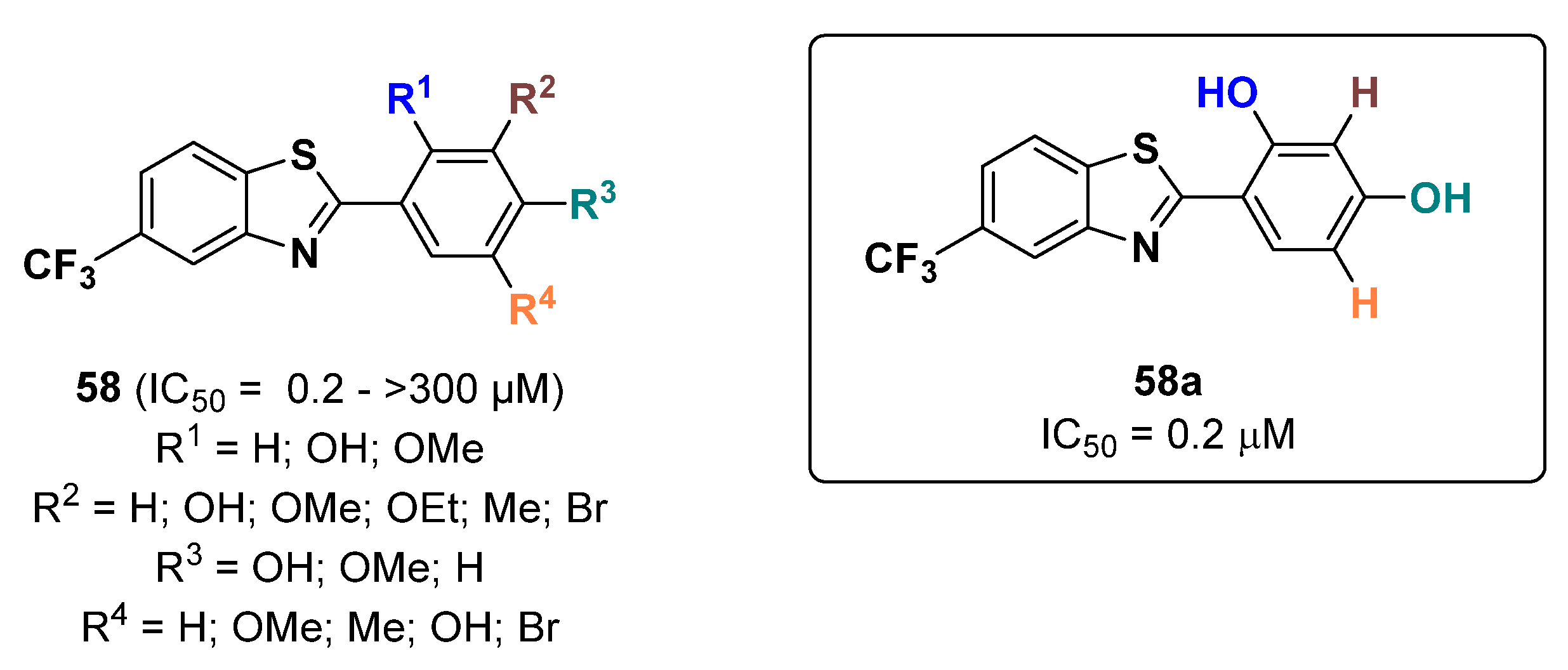
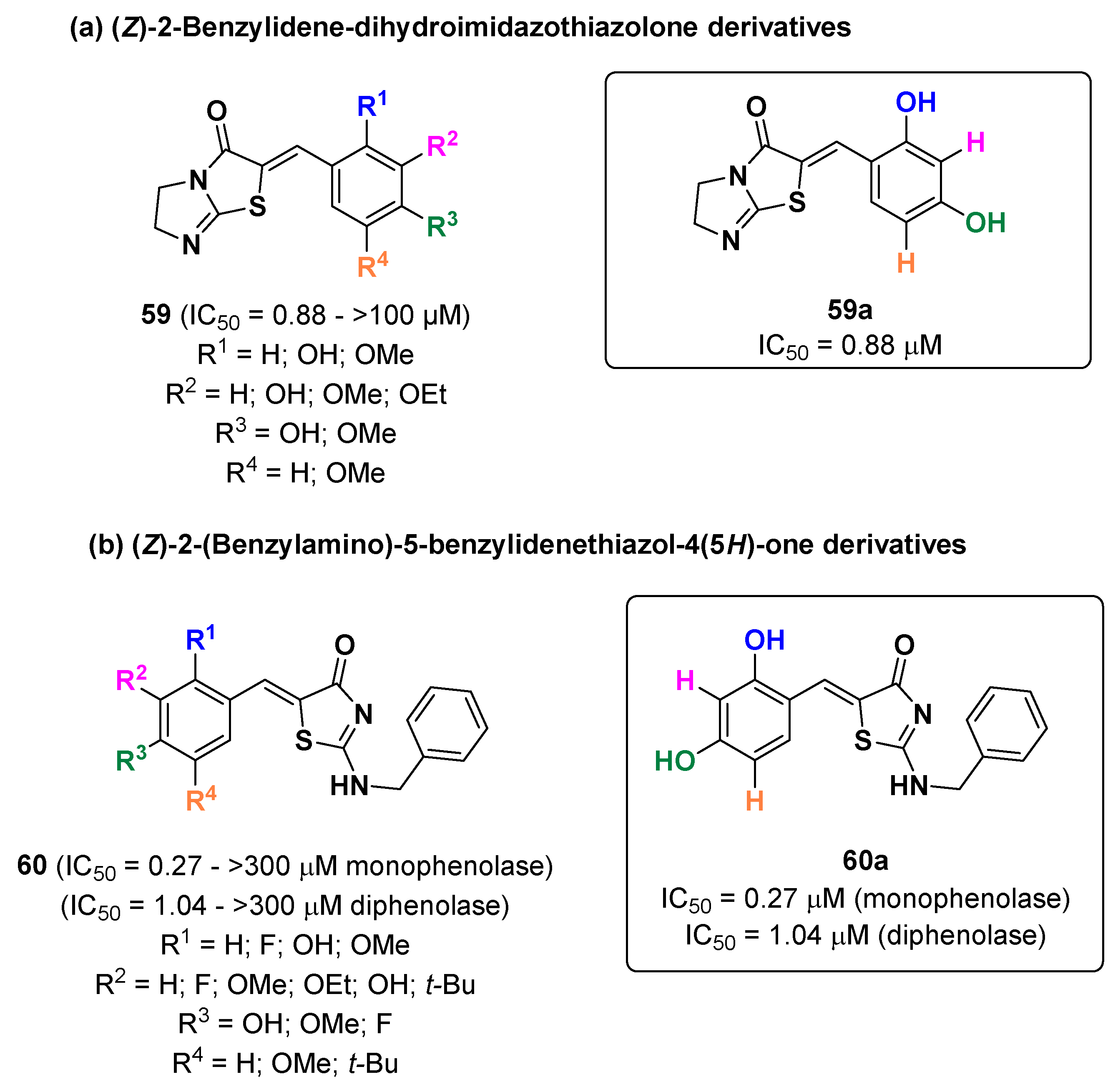
2.13. Thiazoles
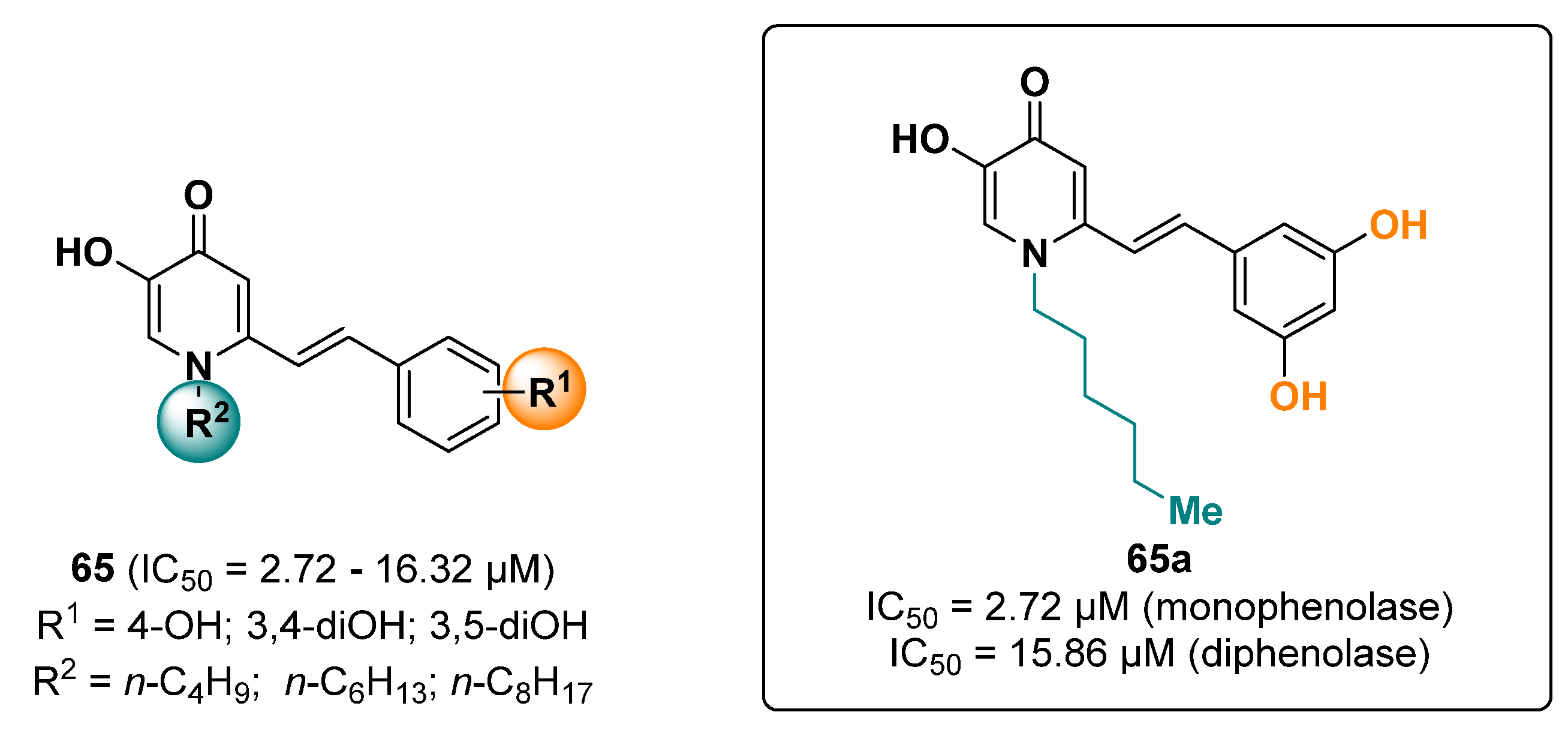
2.14. Hydroxypyridinones
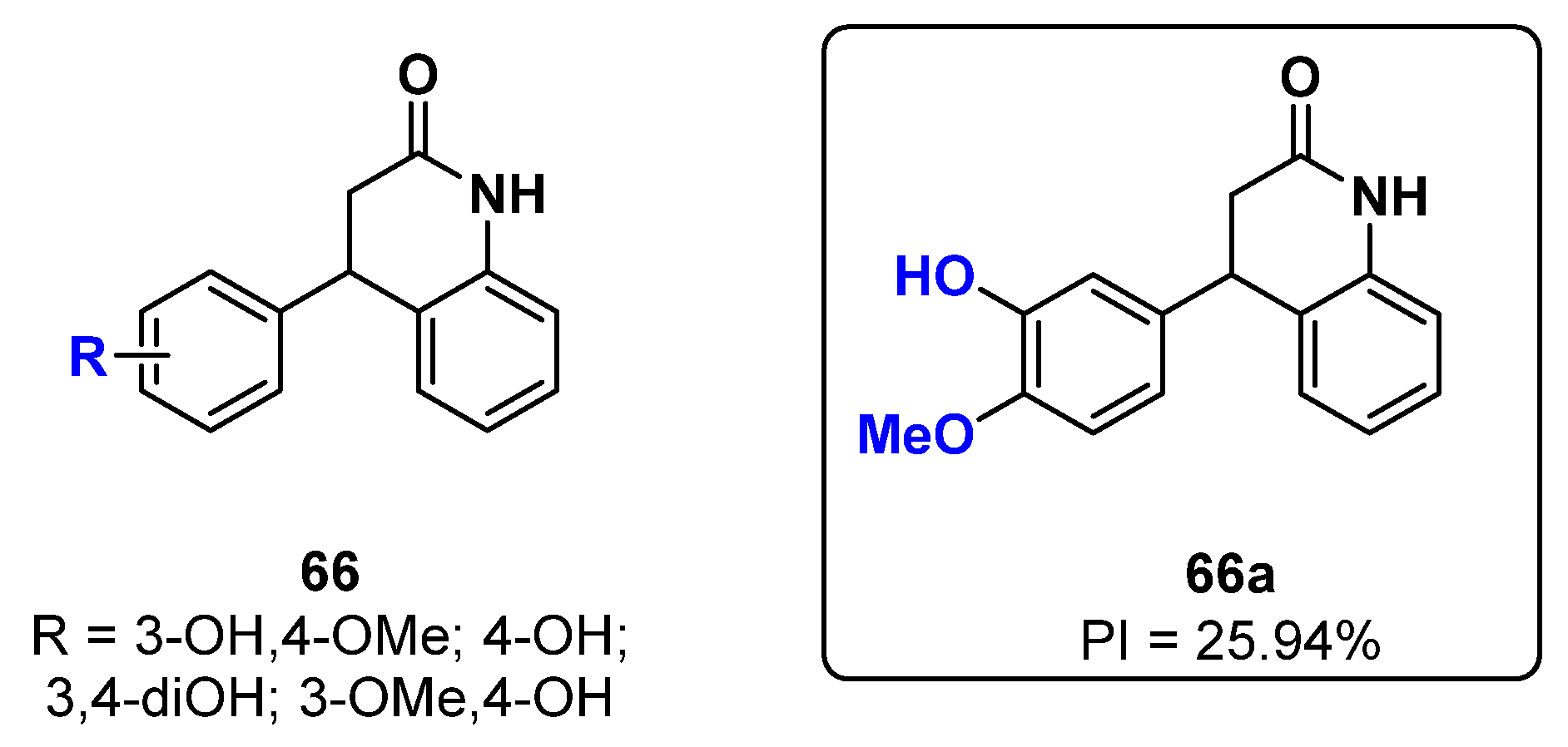
2.15. Quinoline Derivatives
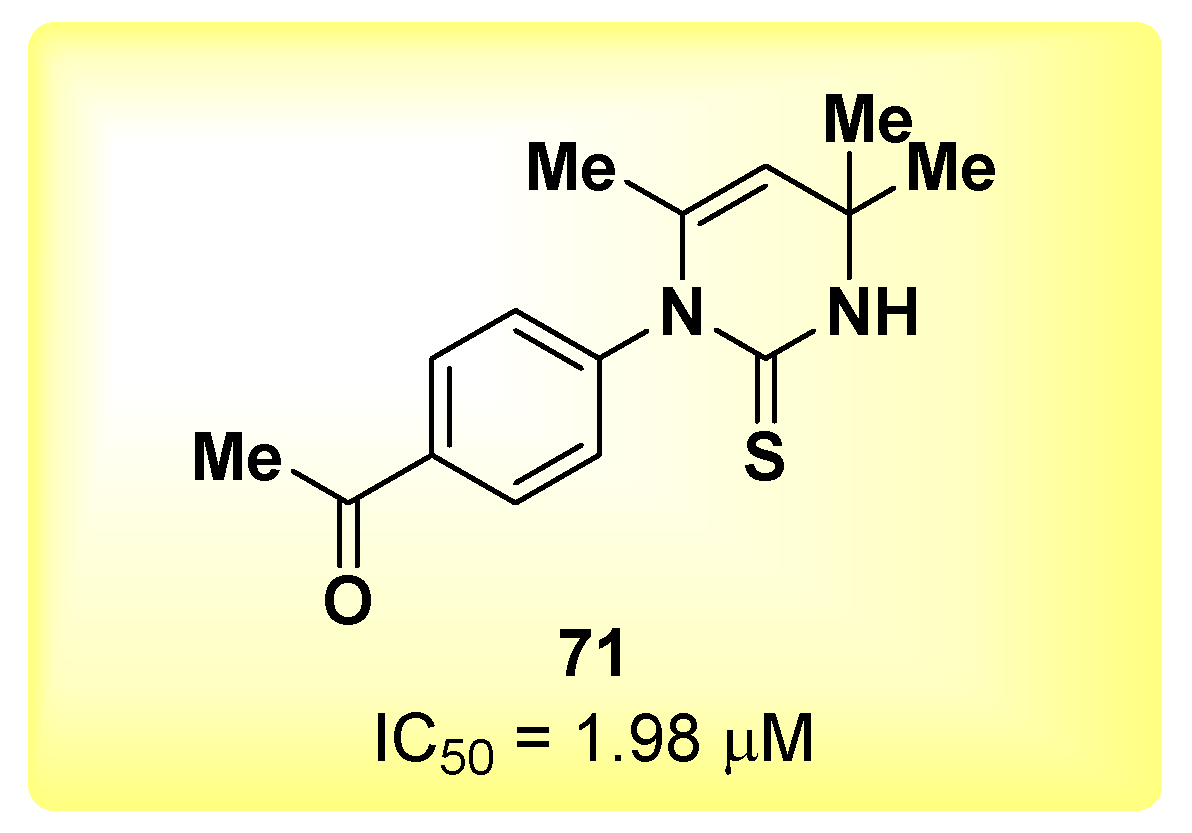
2.16. Pyrimidine-Based Derivatives
2.17. Oxoquinazoline Derivatives
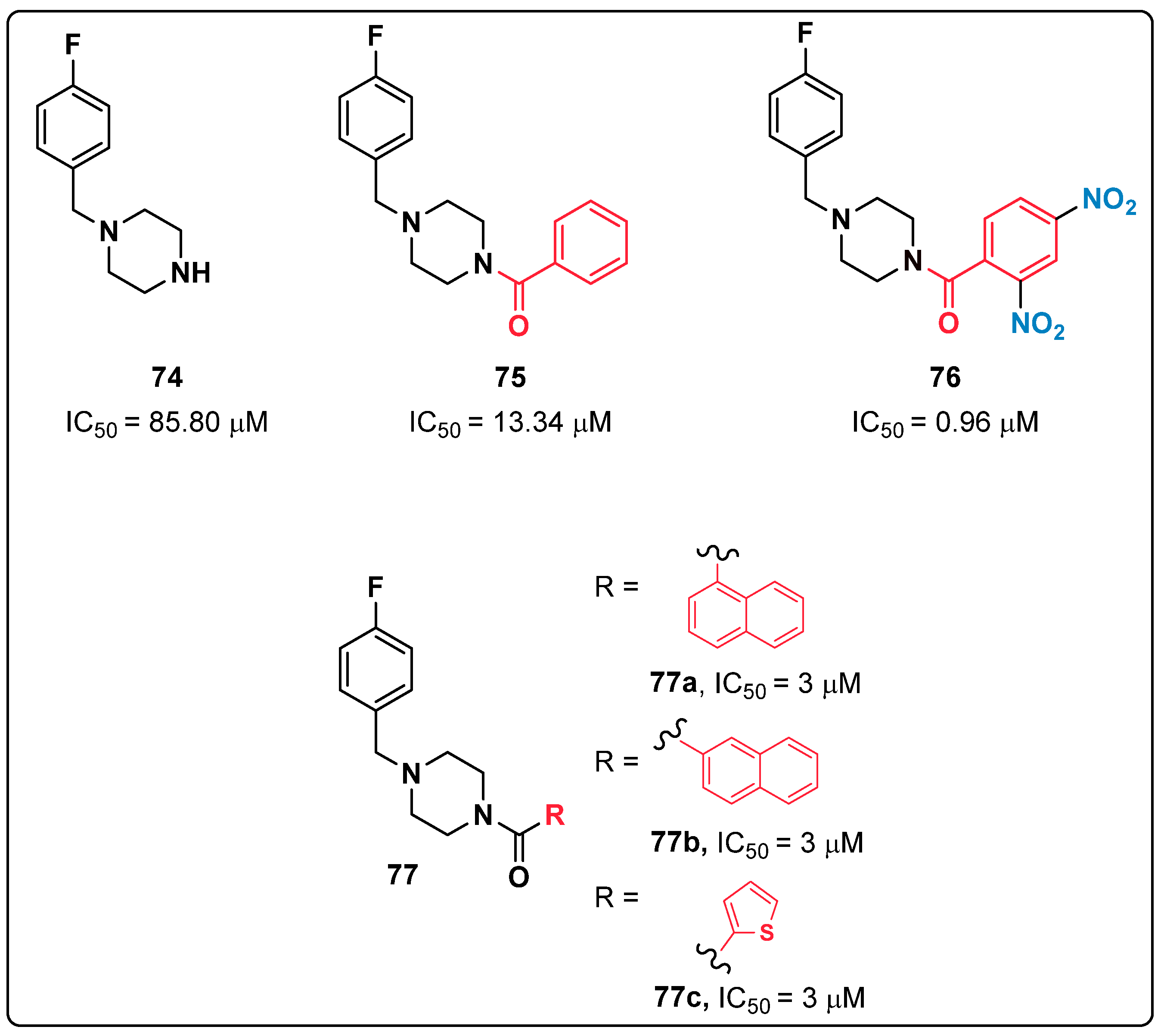
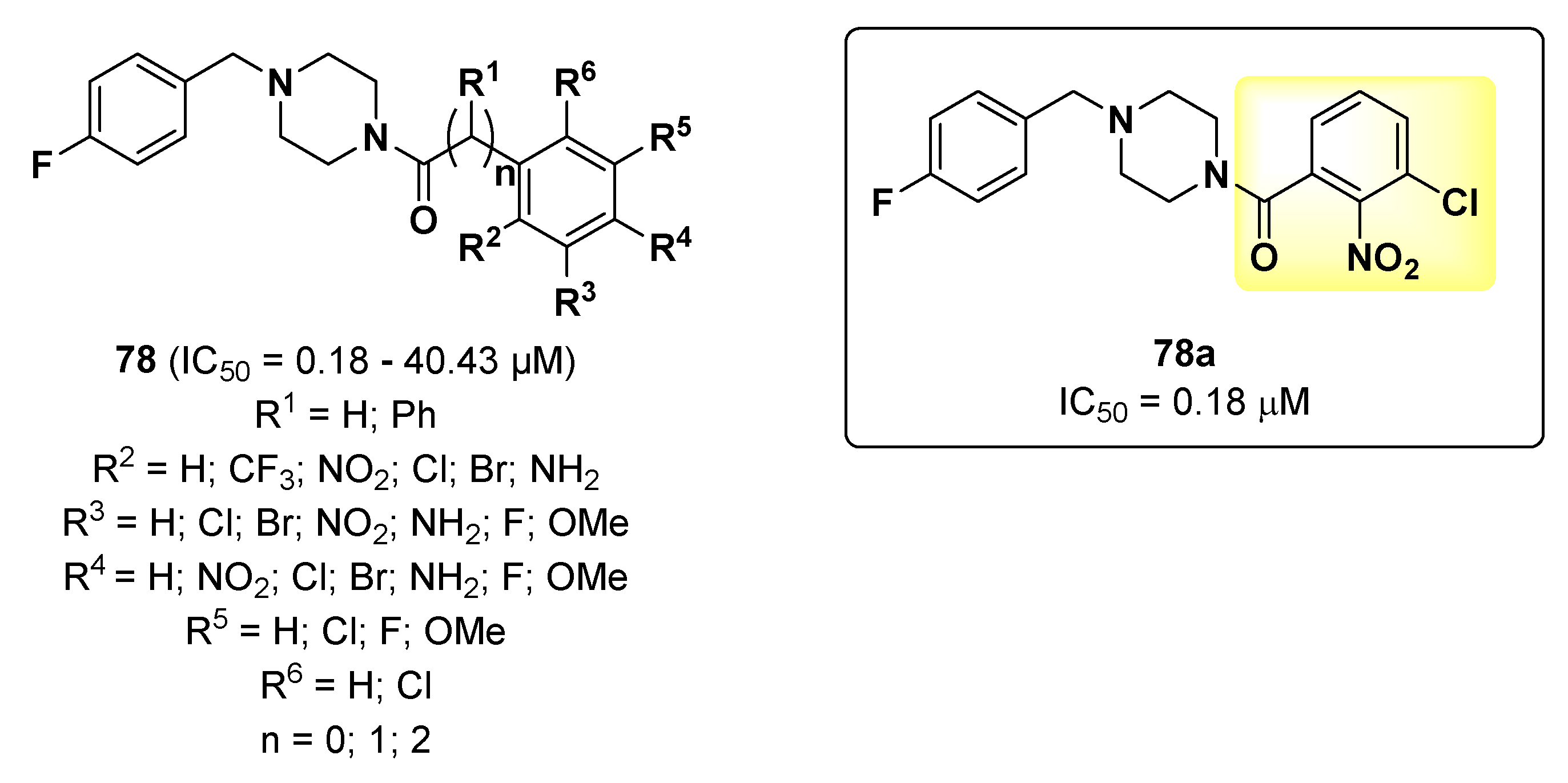
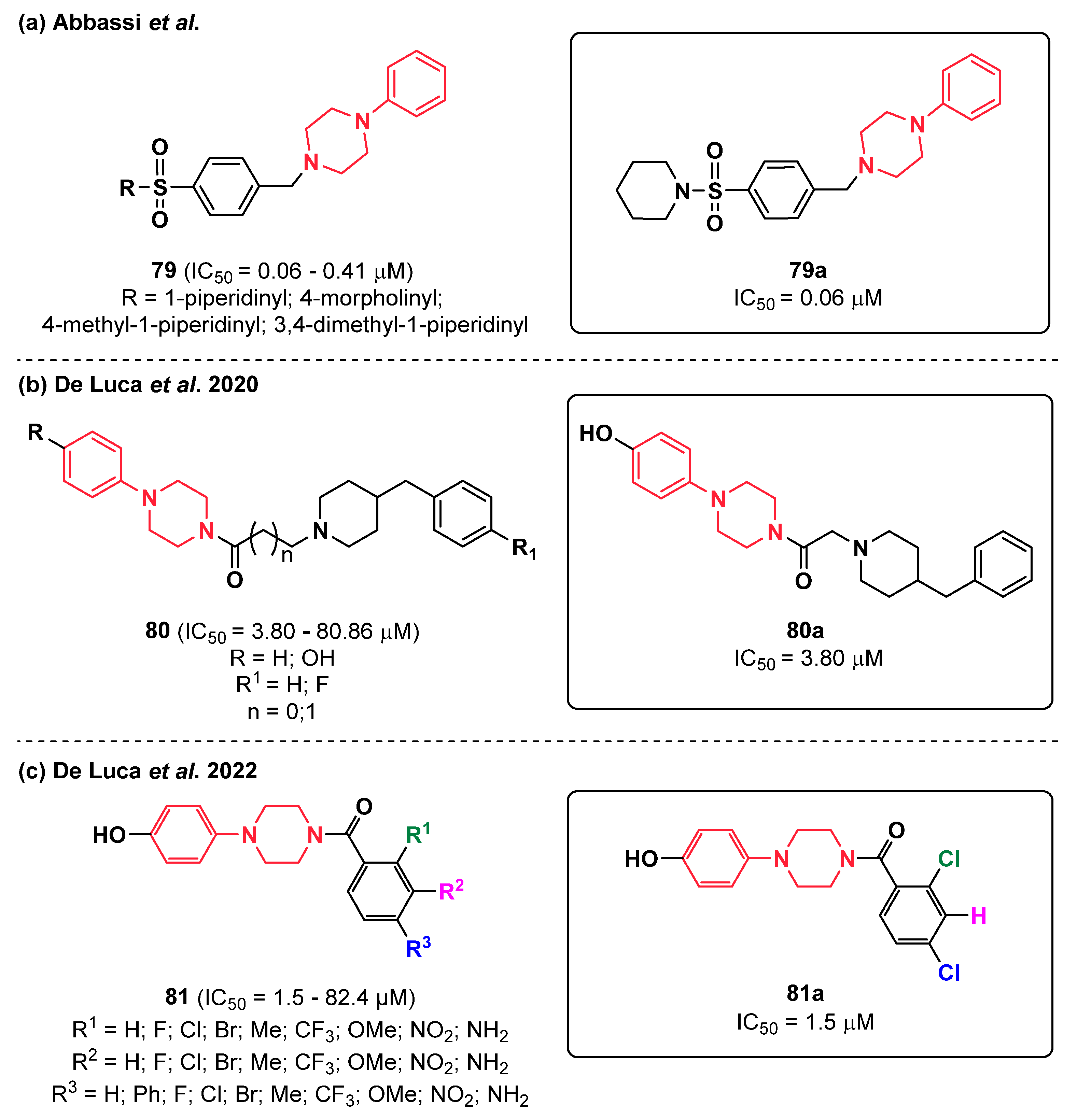
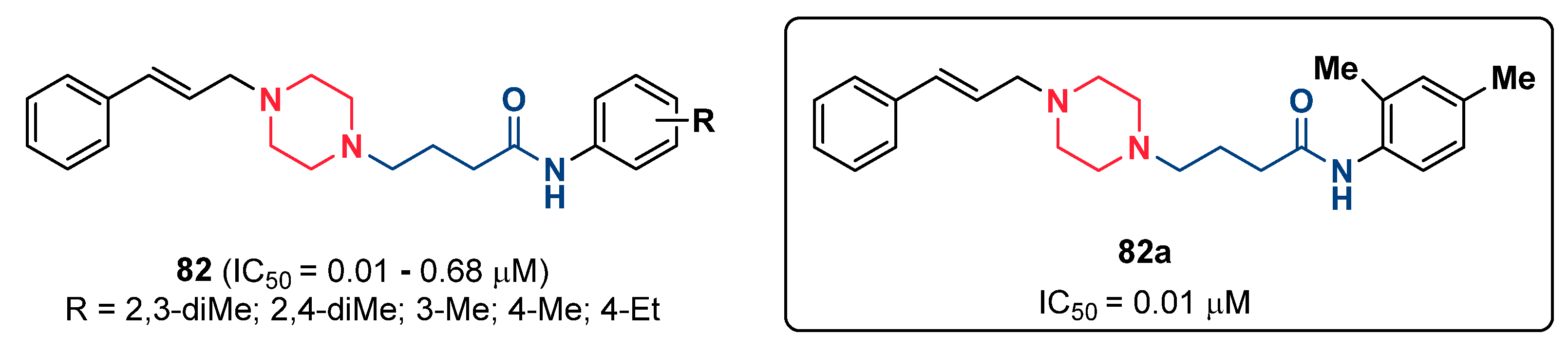
2.18. Piperazines
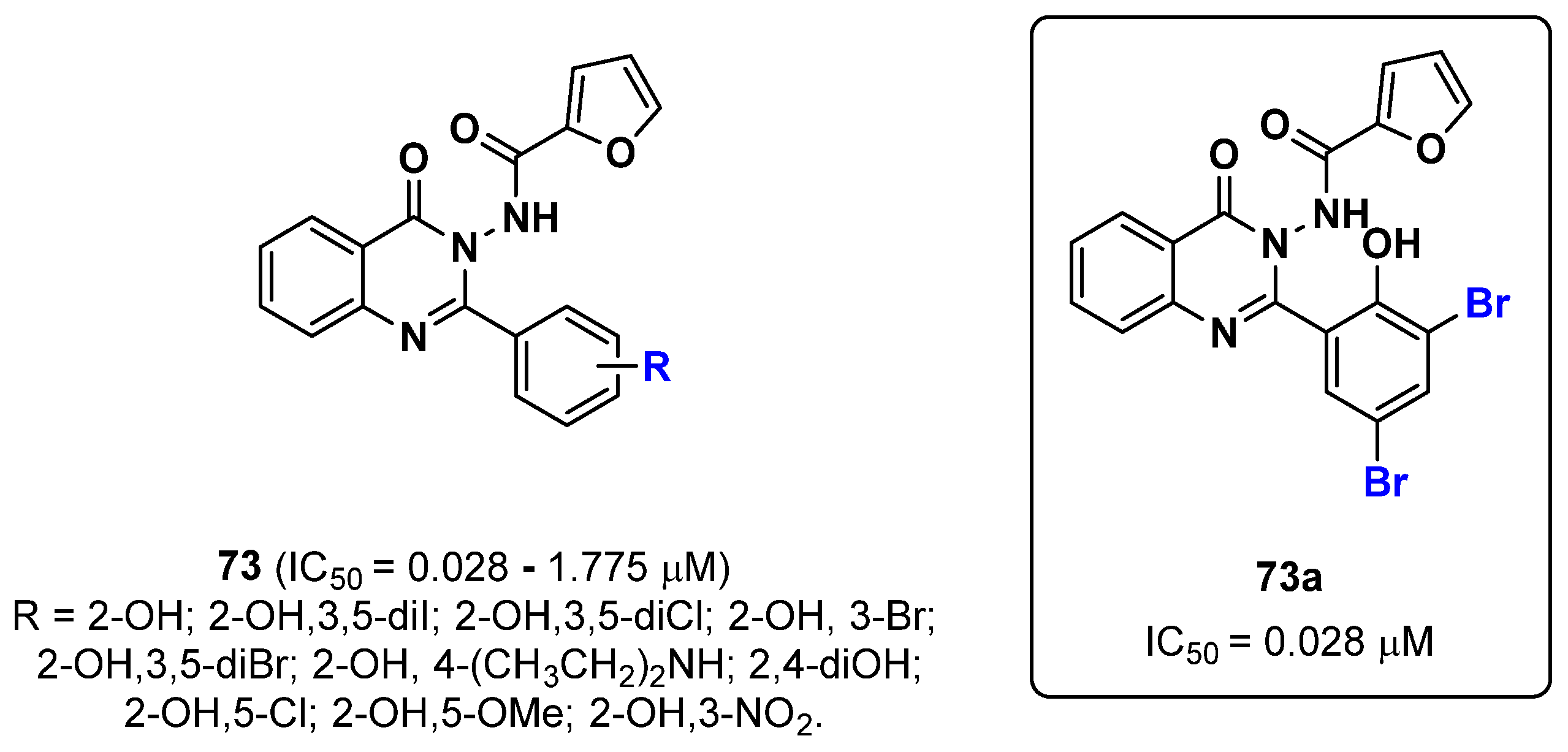
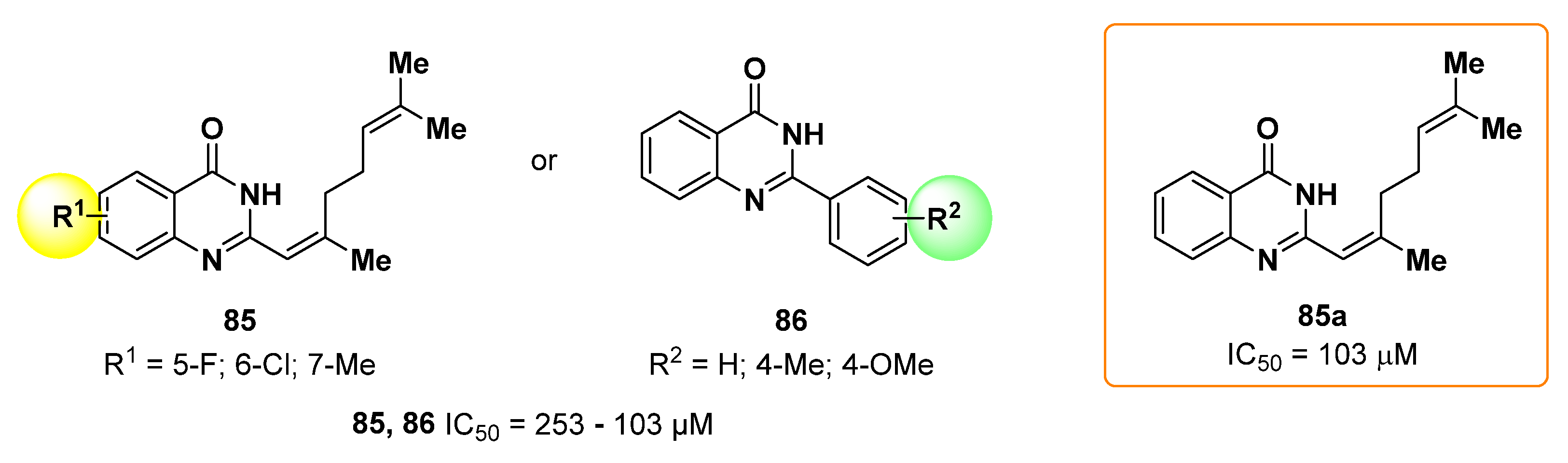
2.19. Quinazolines
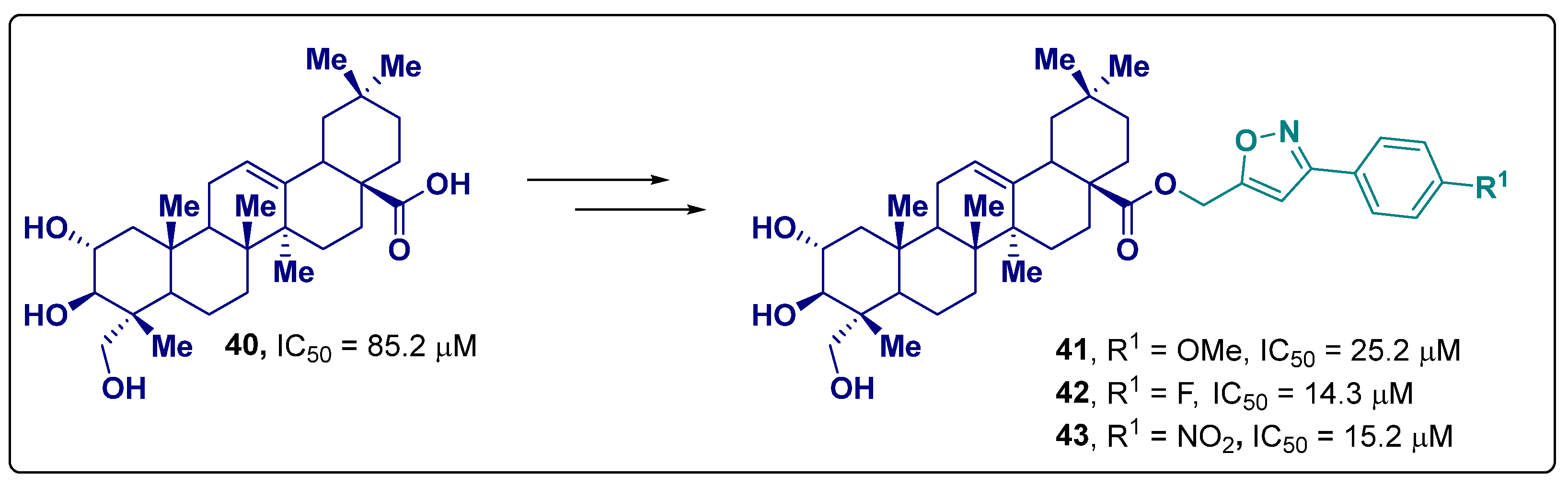
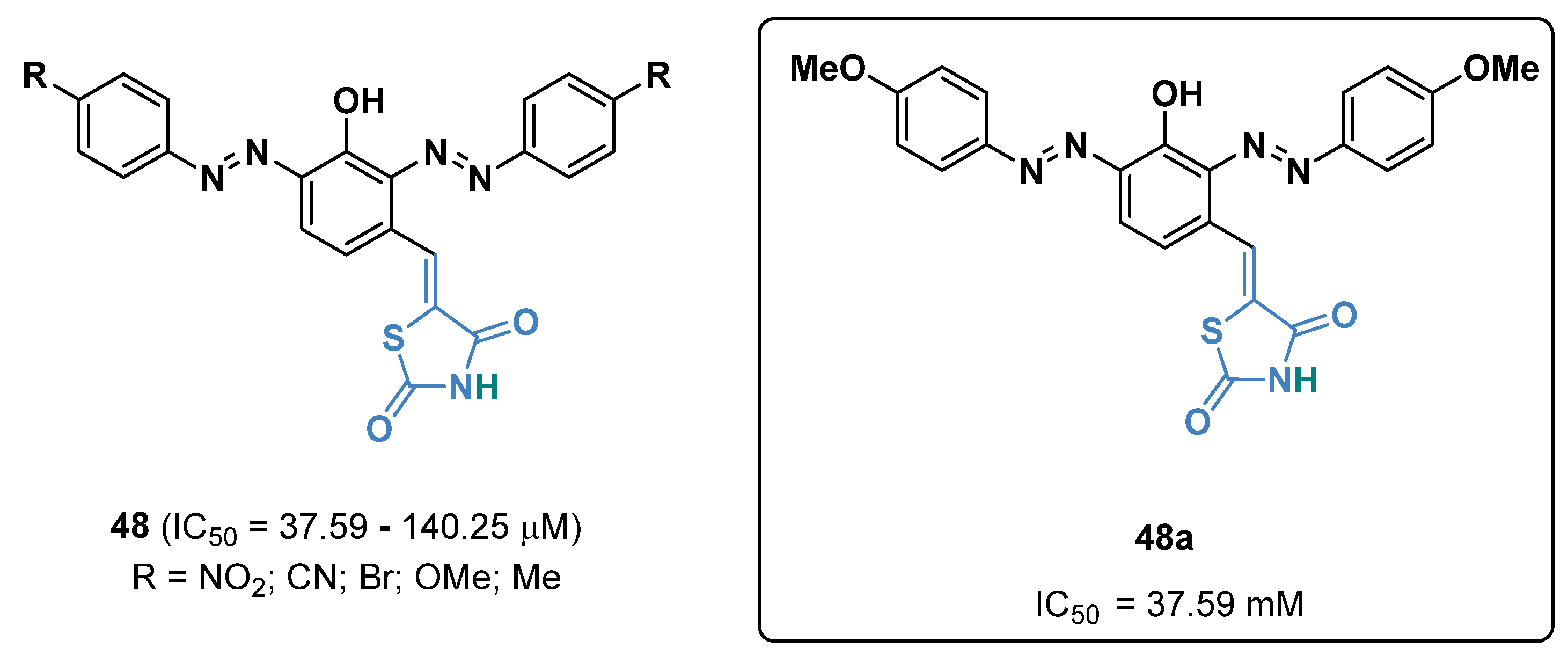
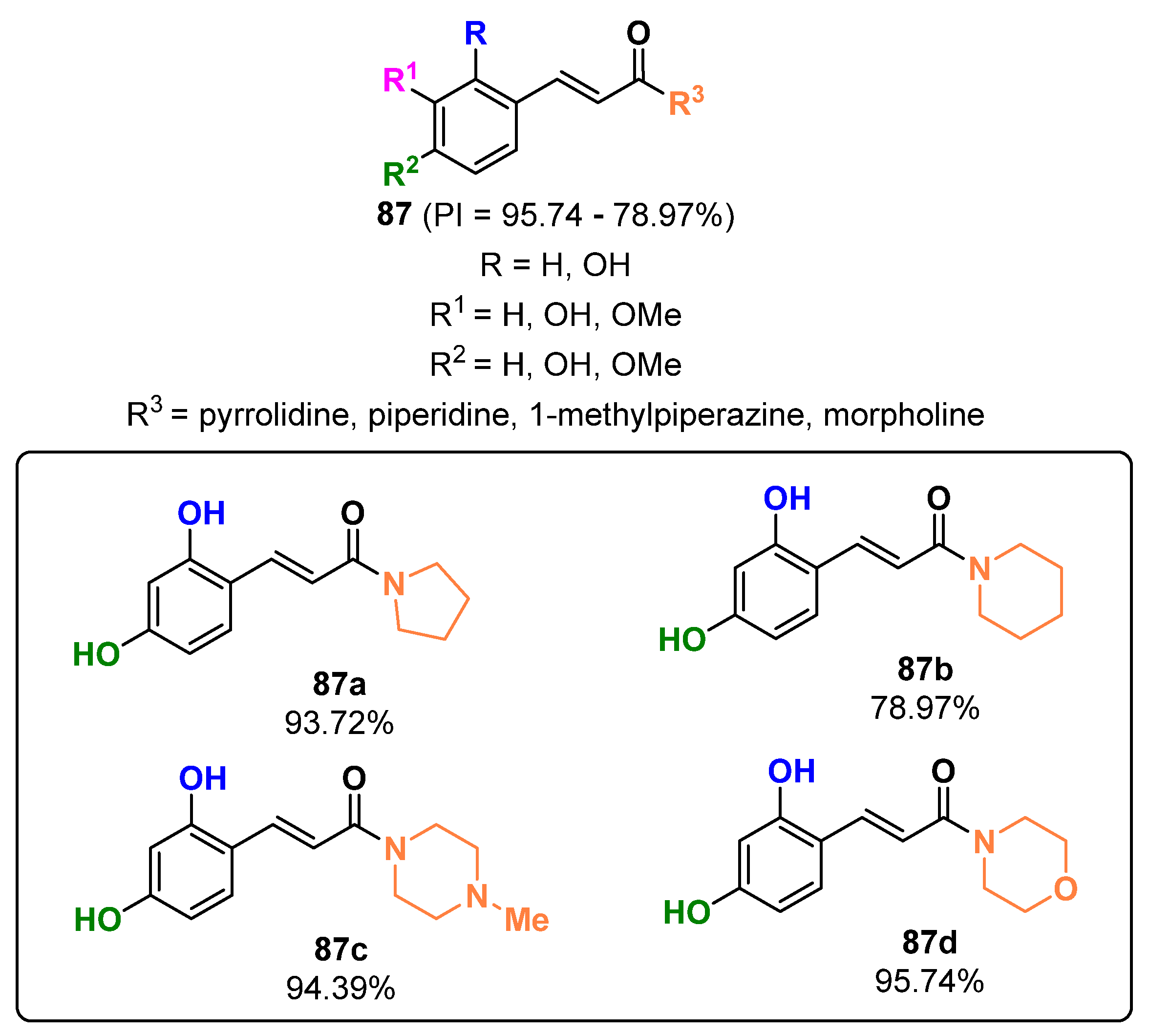
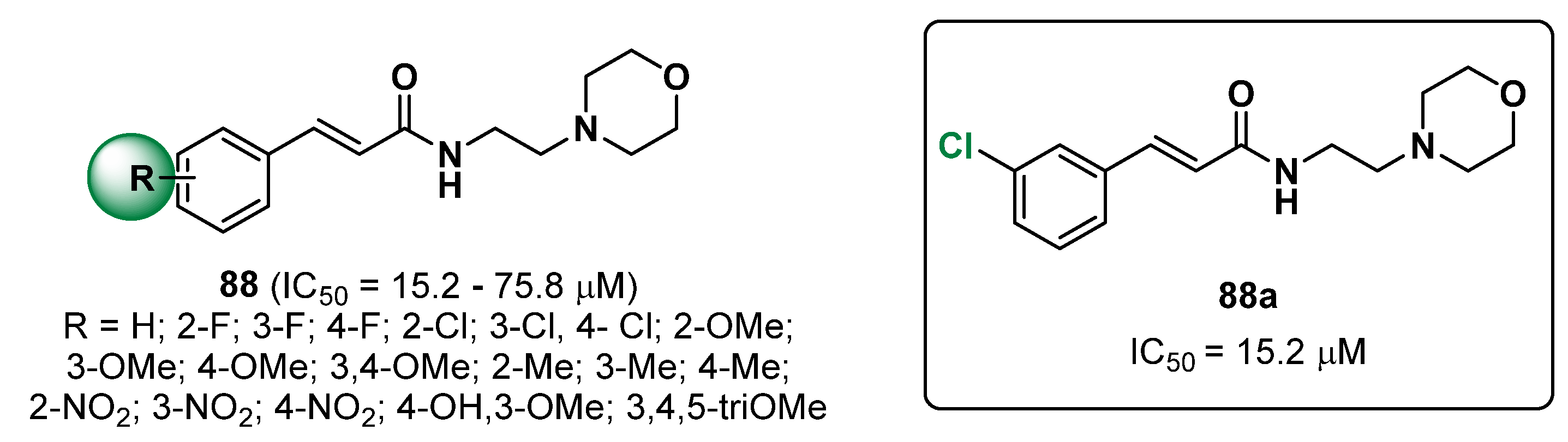
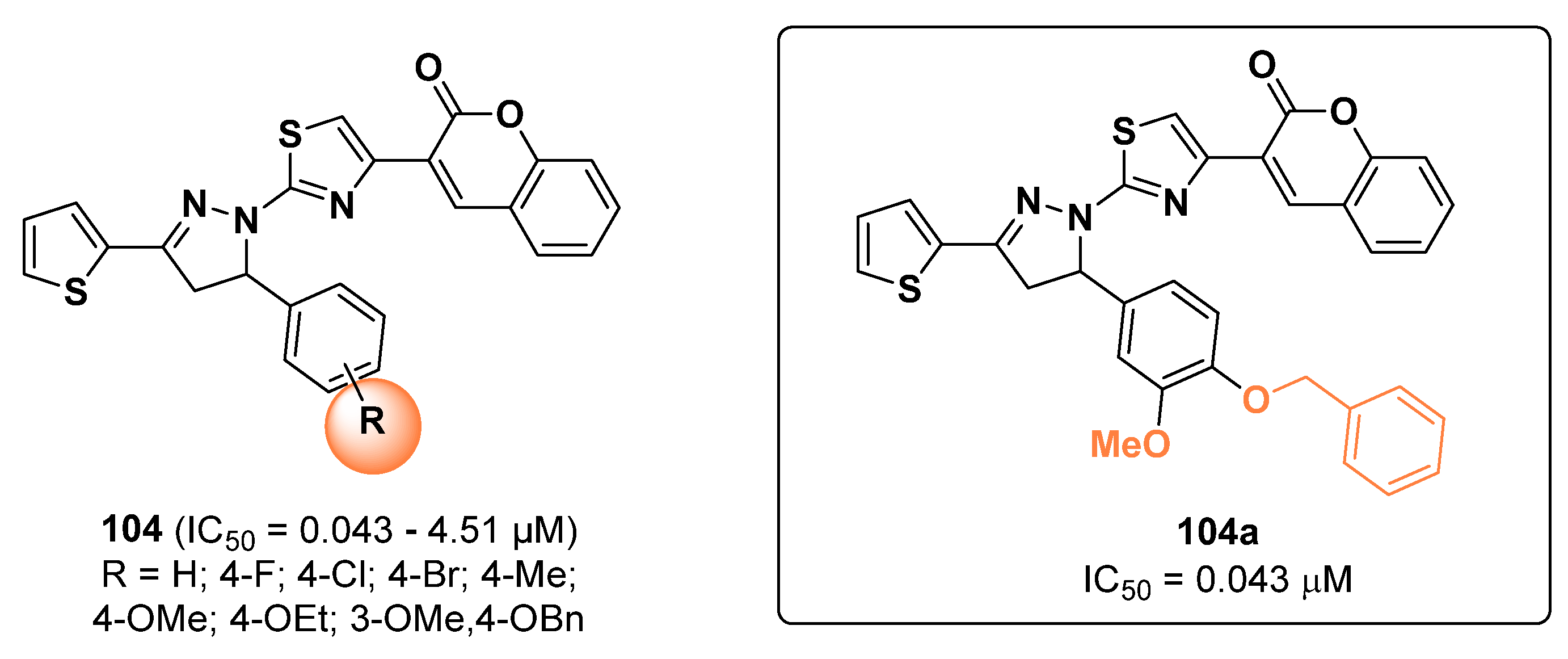
2.20. Miscellaneous
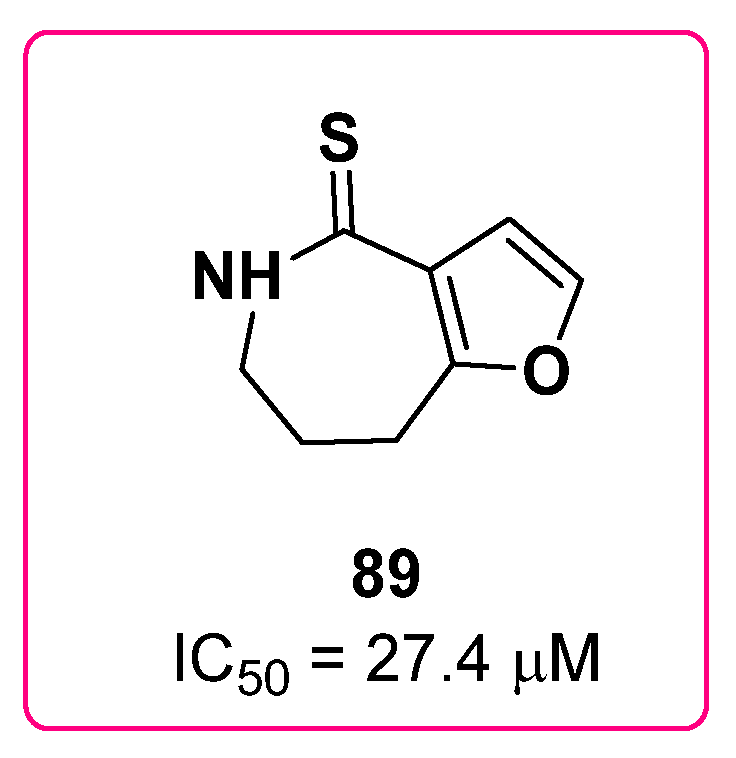
2.21. Azepines
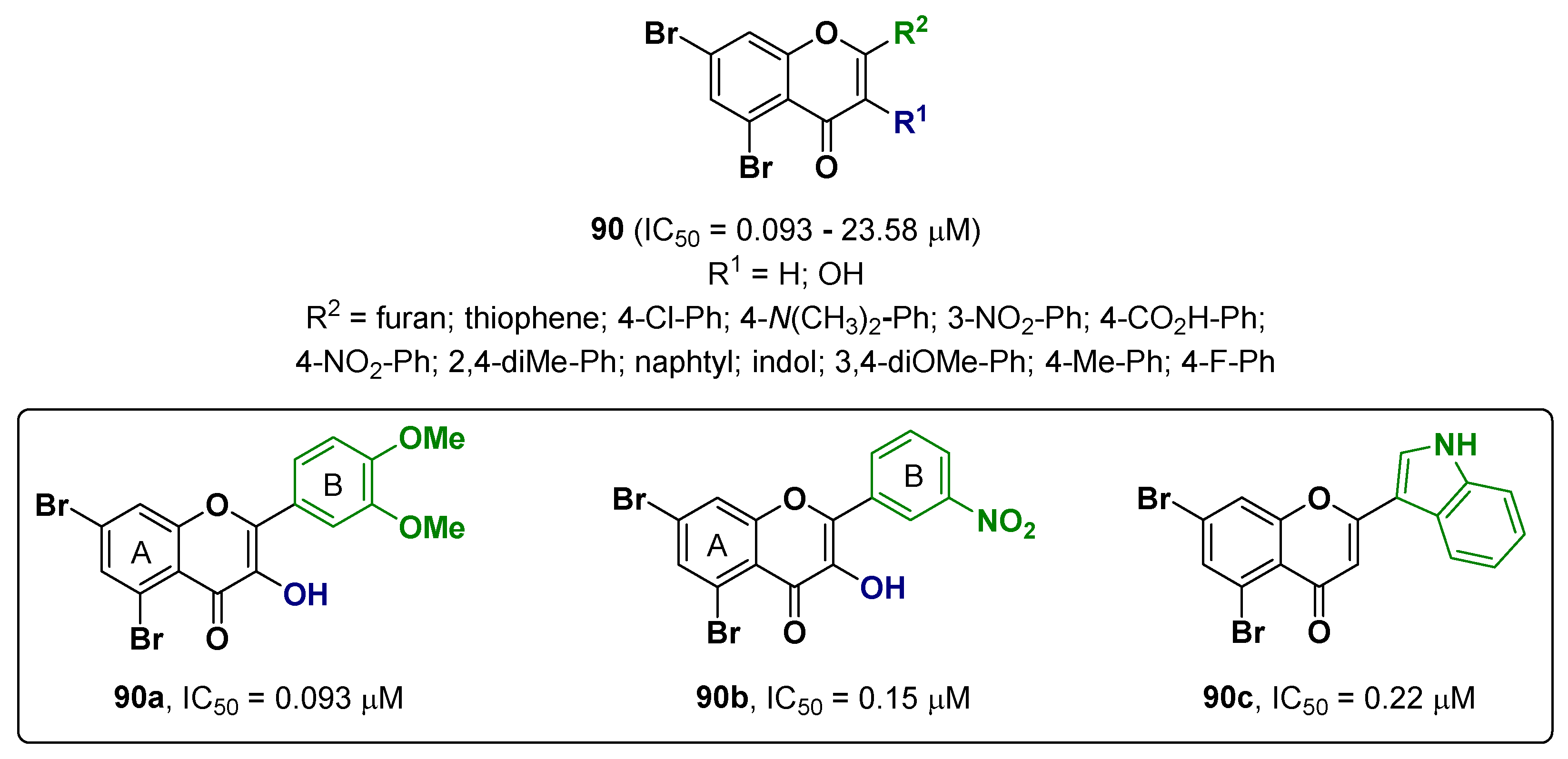
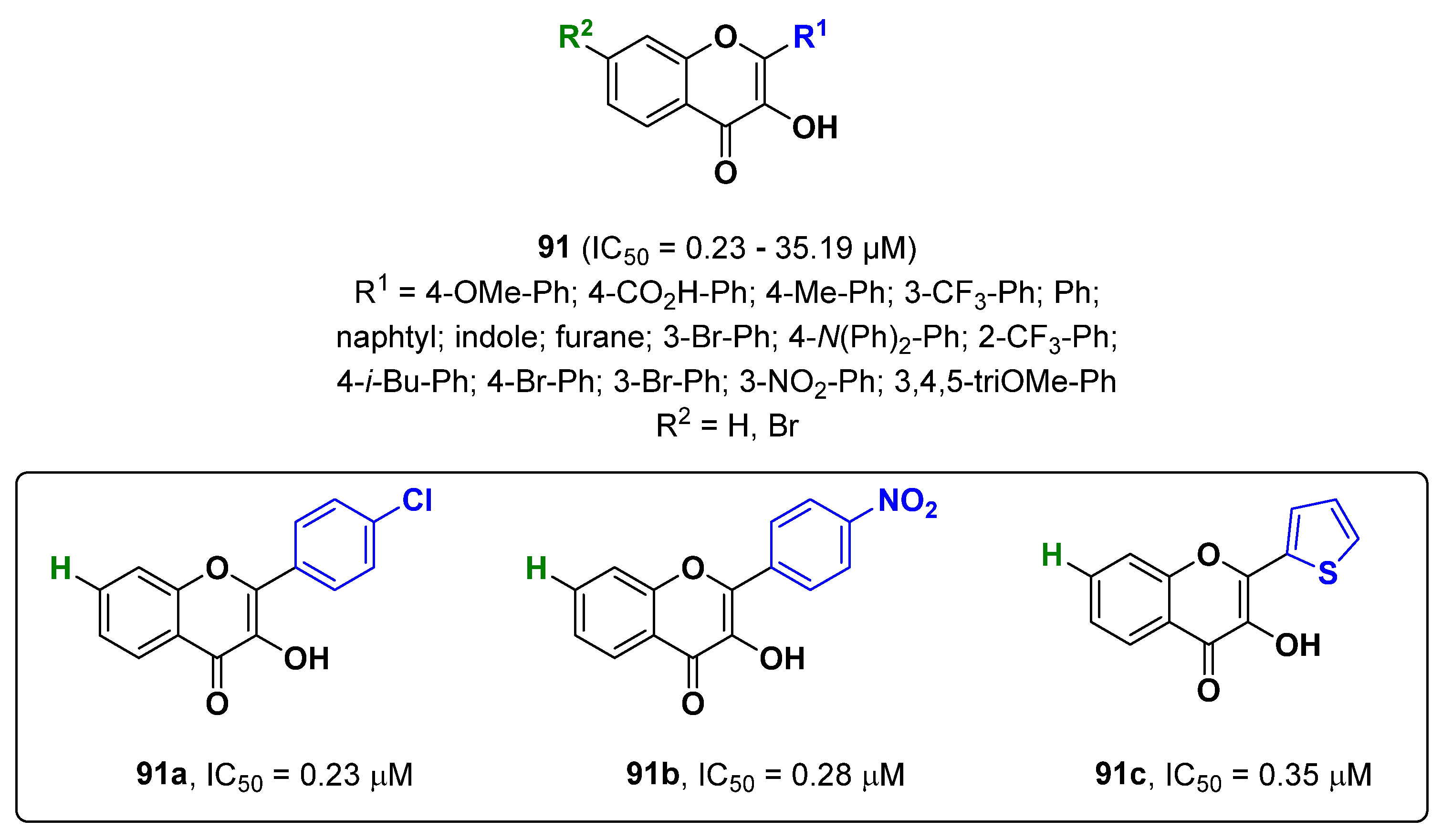
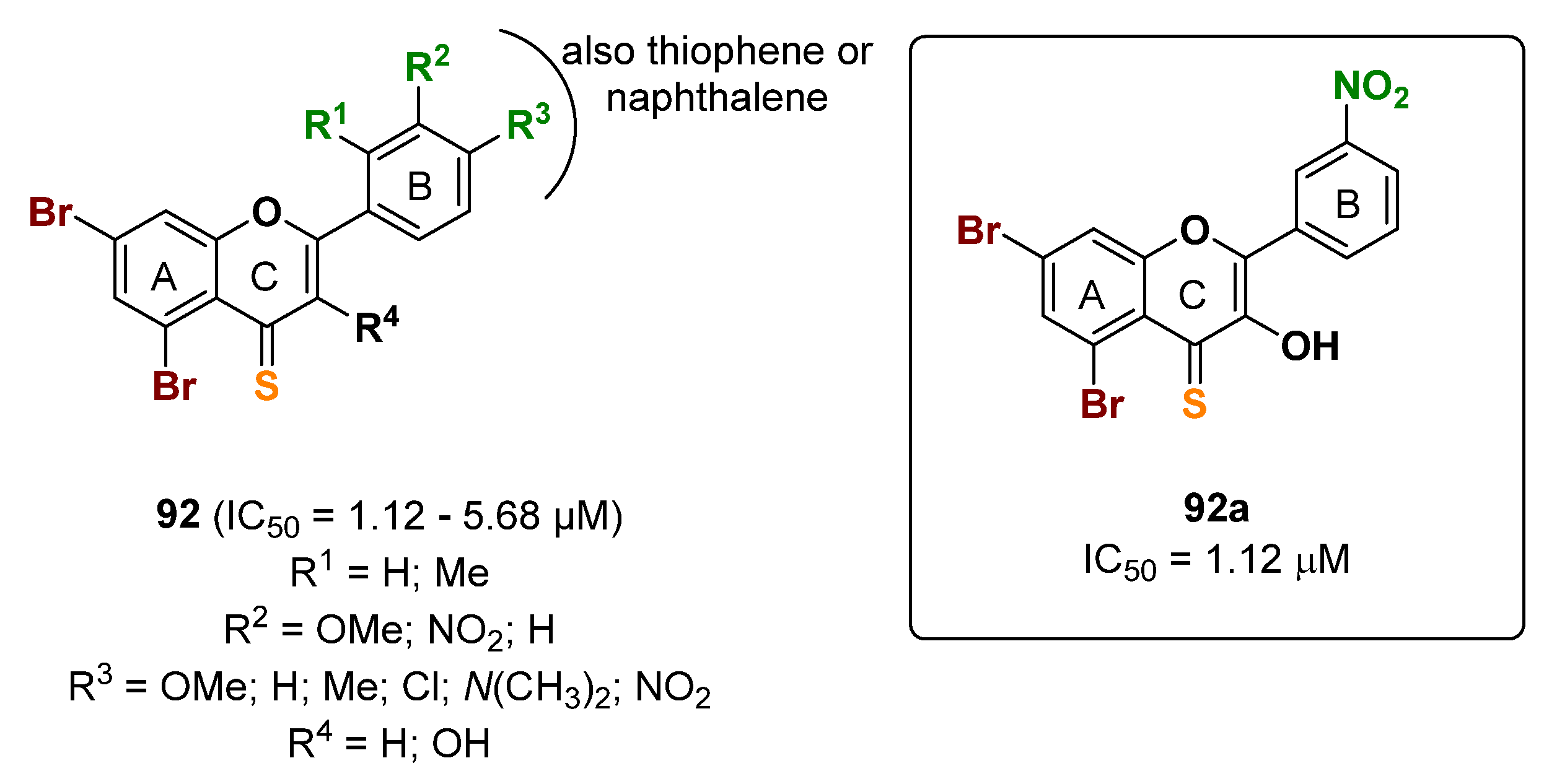
2.22. Chromone Derivatives
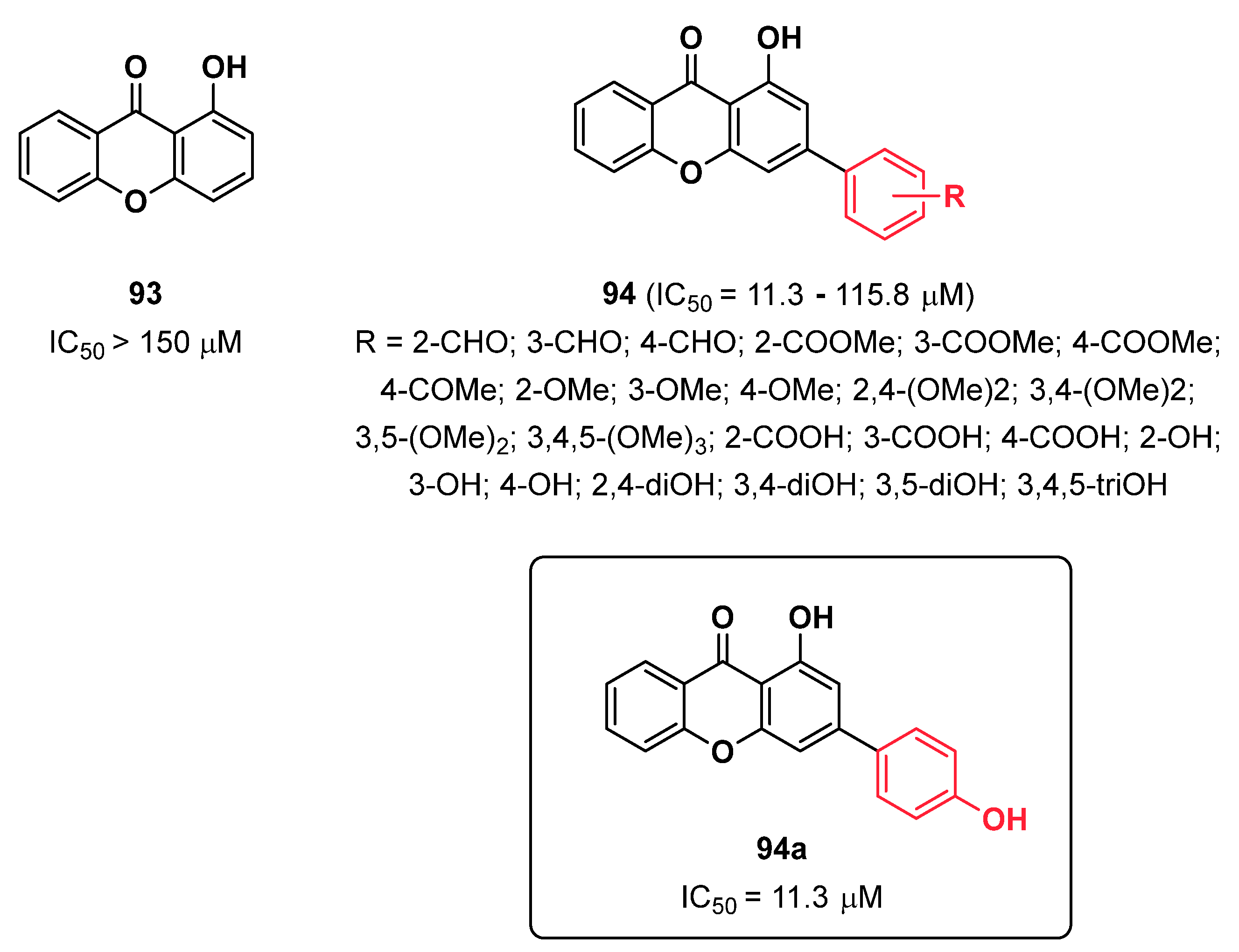
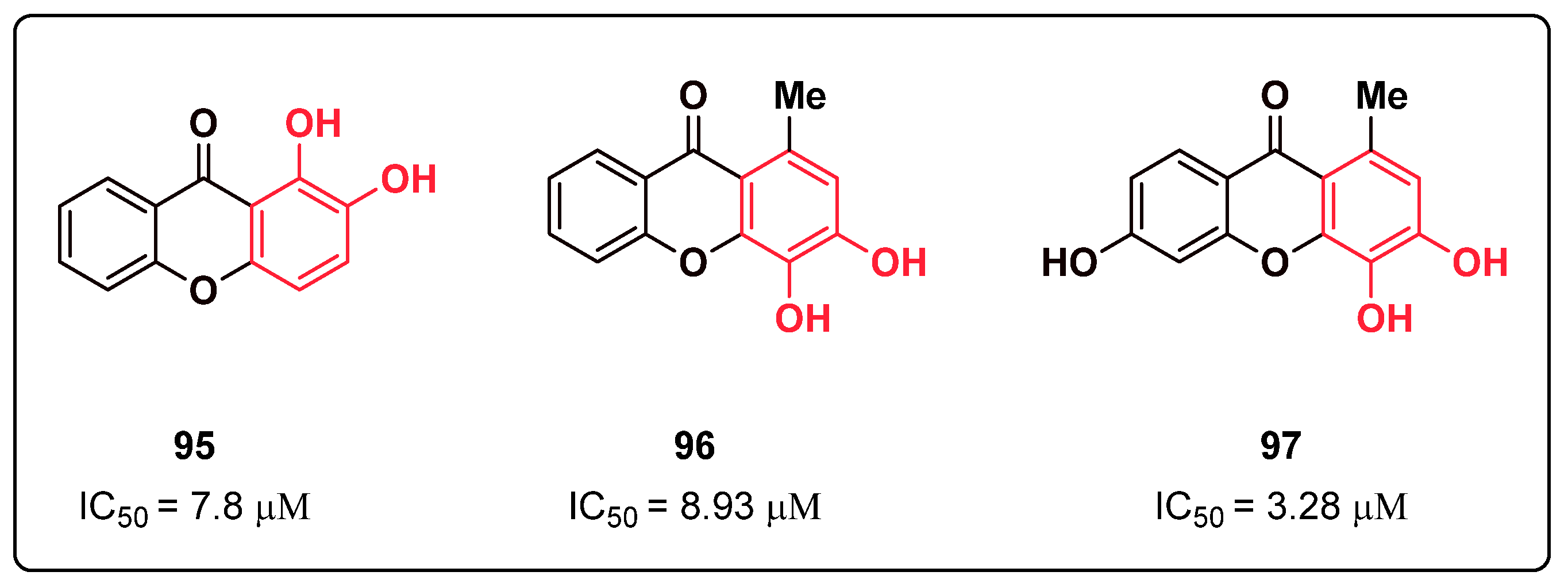
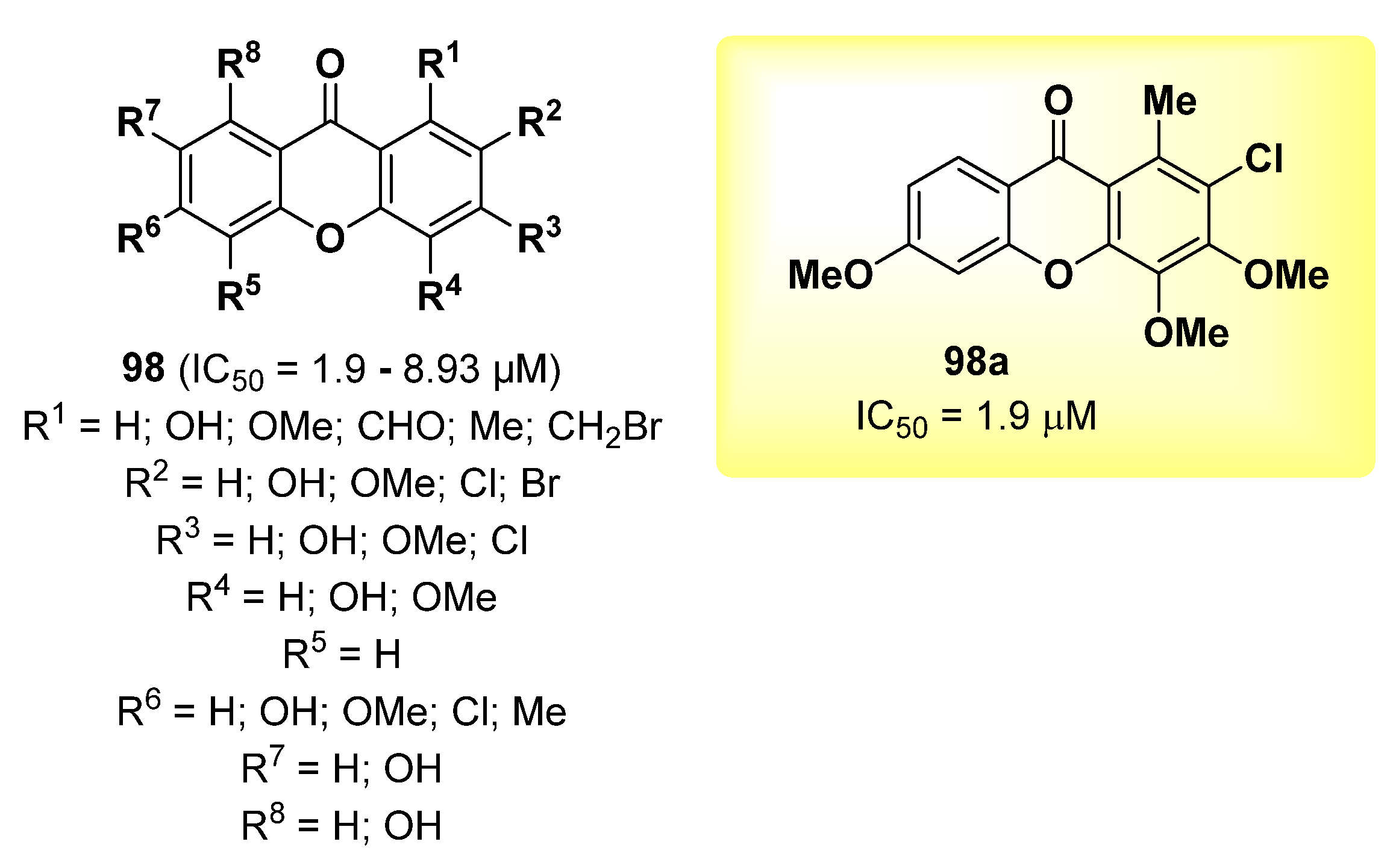
2.23. Xanthone Derivatives
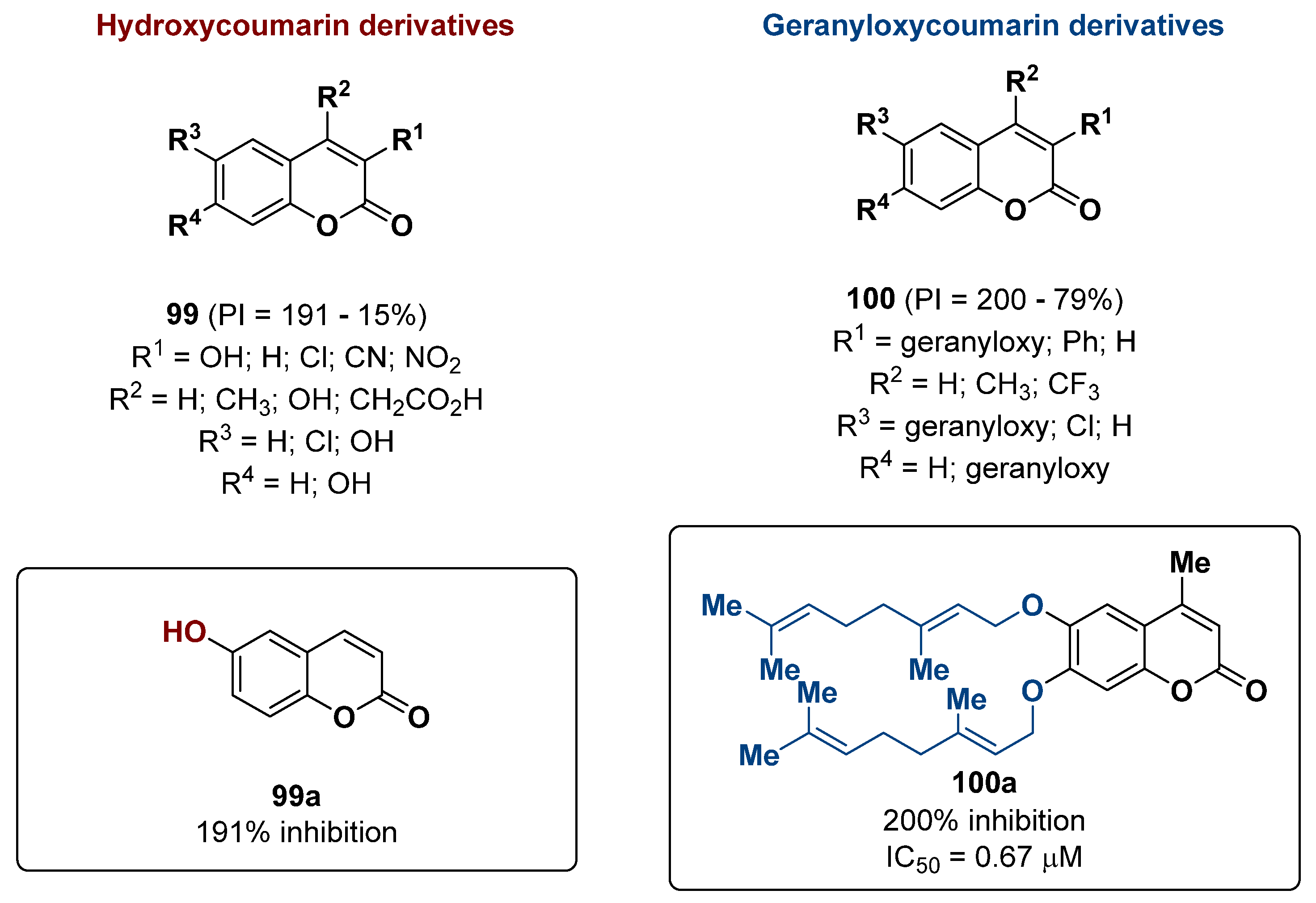
2.24. Coumarin Derivatives
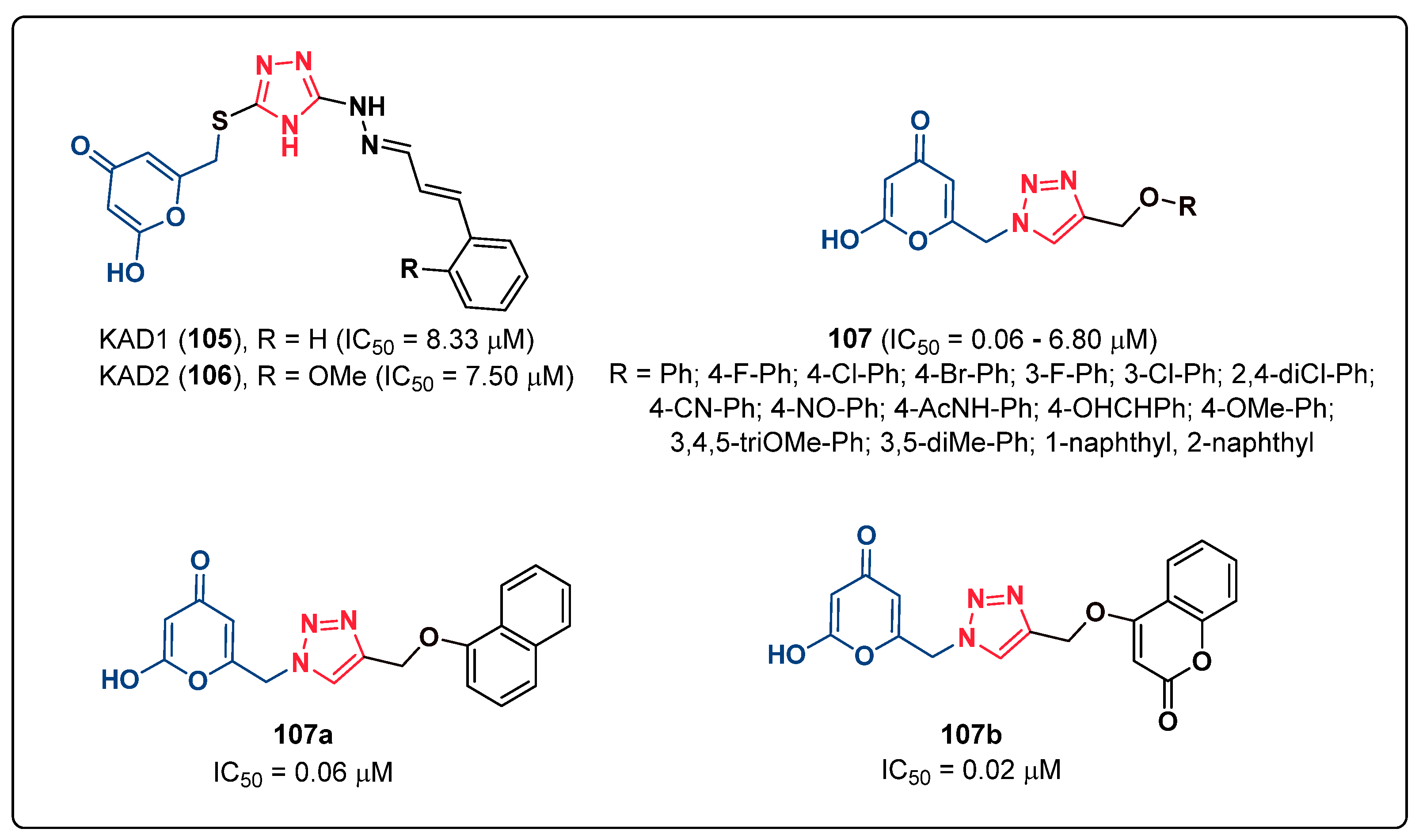
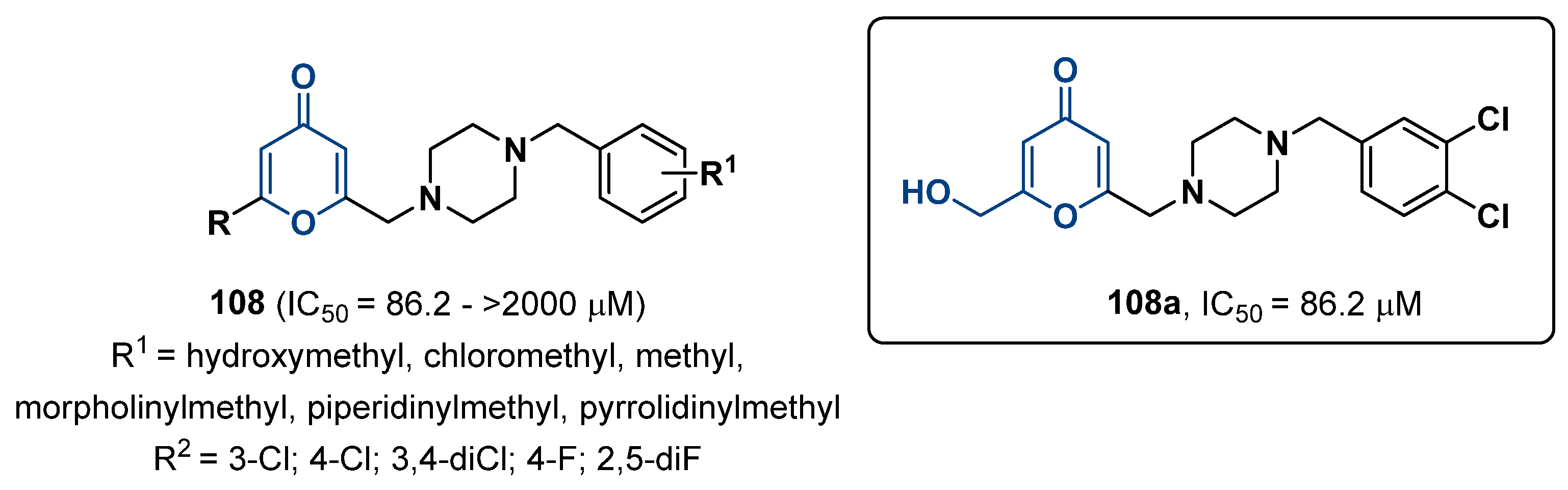
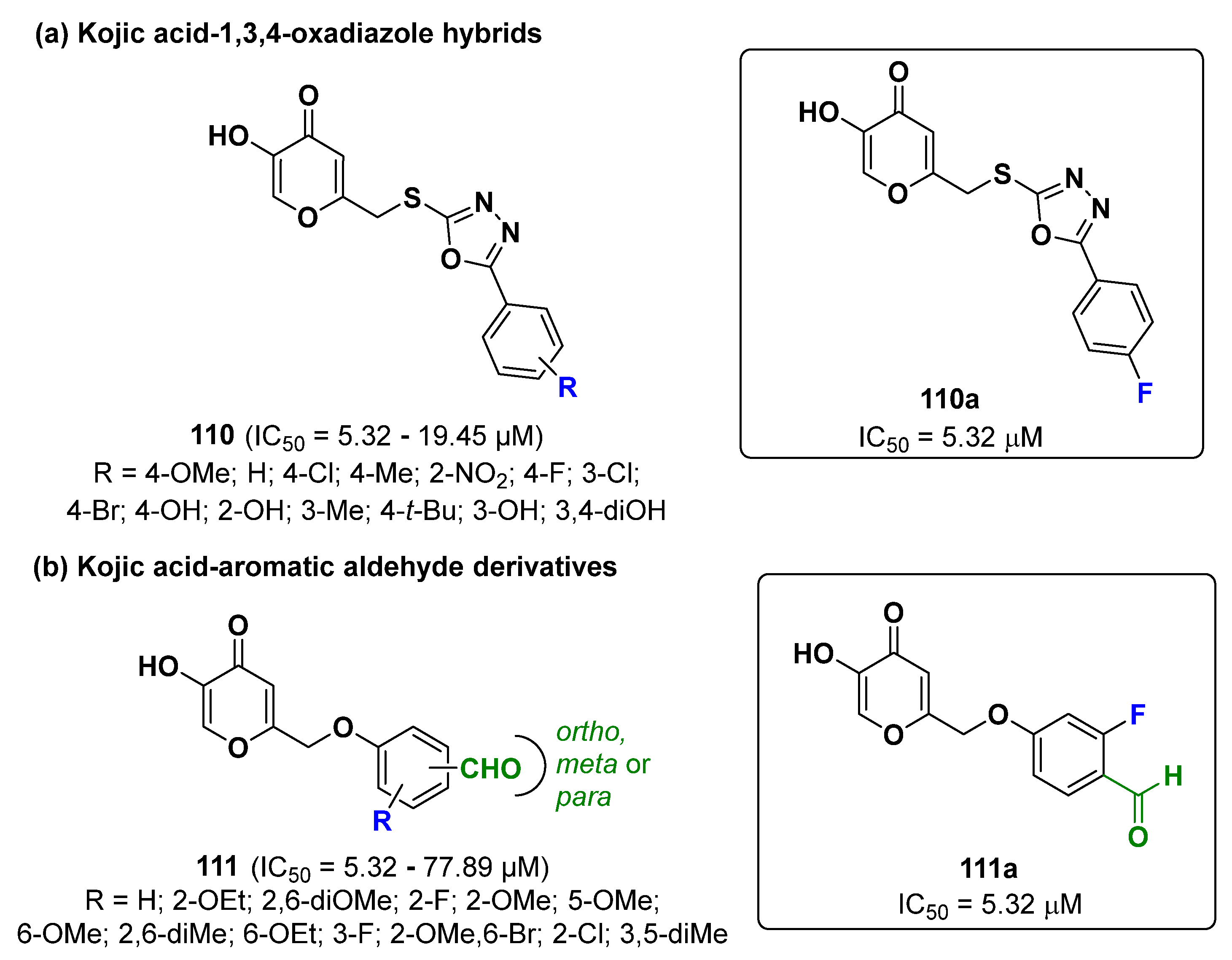
2.25. Kojic Acid Derivatives
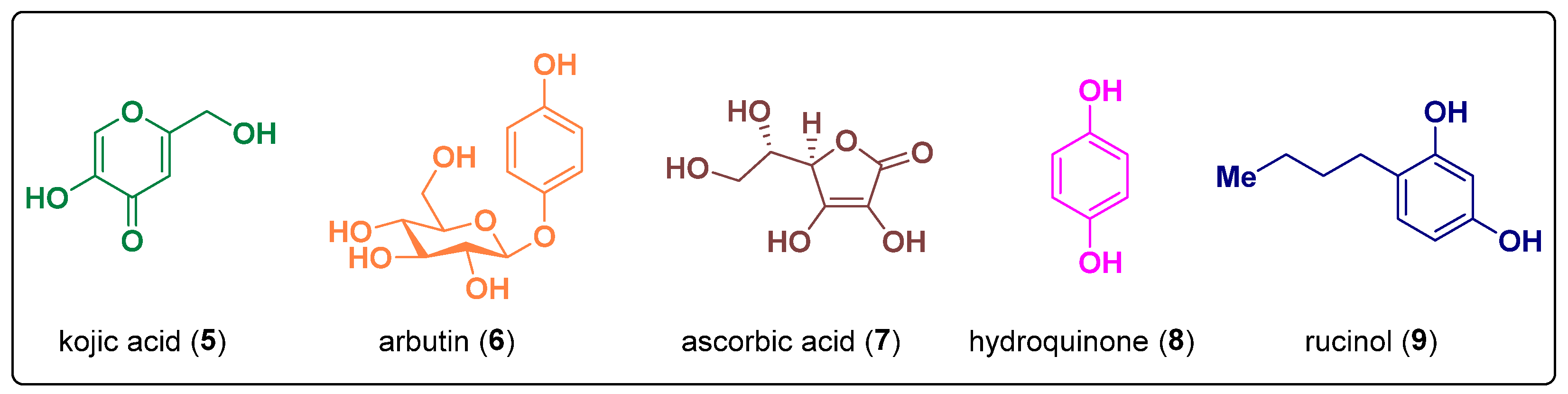
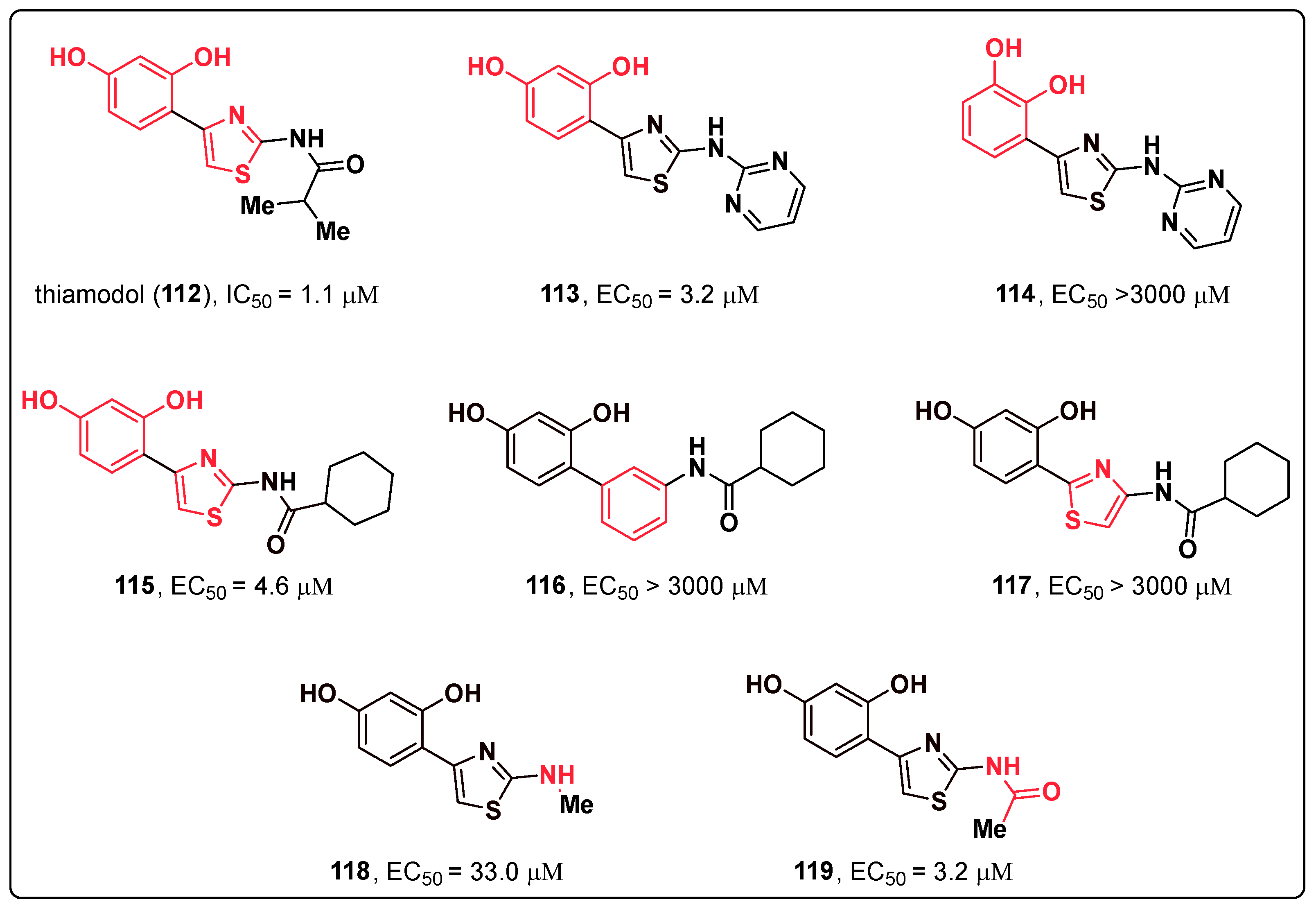
3. Human Tyrosinase Inhibitors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solano, F. On the metal cofactor in the tyrosinase family. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanteev, M.; Goldfeder, M.; Fishman, A. Structure–Function correlations in tyrosinases. Protein Sci. 2015, 24, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatsu, T.; Nakashima, A.; Watanabe, H.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Zucca, F.A.; Zecca, L.; Youdim, M.; Wulf, M.; Riederer, P.; et al. The role of tyrosine hydroxylase as a key player in neuromelanin synthesis and the association of neuromelanin with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2023, 130, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, A.; Wang, J.; Huang, D.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qu, Q.; Ma, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhu, M.; et al. Potential application of natural bioactive compounds as skin-whitening agents: A review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 6669–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Ouyang, L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, G. Recent advances in the design and discovery of synthetic tyrosinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, G.; Zeng, Q.-H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.J.; Zhao, Y. A systematic review of synthetic tyrosinase inhibitors and their structure-activity relationship. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4053–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chib, S.; Jamwal, V.L.; Kumar, V.; Gandhi, S.G.; Saran, S. Fungal production of kojic acid and its industrial applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 2111–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Builla, J.; Barluenga, J. Heterocyclic Compounds: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kabir, E.; Uzzaman, M. A review on biological and medicinal impact of heterocyclic compounds. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favi, G. Modern Strategies for Heterocycle Synthesis. Molecules 2020, 25, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, M.; Spanò, V.; Raimondi, M.V.; Tarantelli, C.; Spriano, F.; Bertoni, F.; Barraja, P.; Montalbano, A. Recurrence of the oxazole motif in tubulin colchicine site inhibitors with anti-tumor activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghour, M.S.; Elkady, H.; Eldehna, W.M.; El-Deeb, N.; Kenawy, A.M.; Elkaeed, E.B.; Alsfouk, B.A.; Alesawy, M.S.; Husein, D.Z.; Metwaly, A.M. Design, synthesis, anti-proliferative evaluation, docking, and MD simulations studies of new thiazolidine-2, 4-diones targeting VEGFR-2 and apoptosis pathway. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotb, A.R.; Bakhotmah, D.A.; Abdallah, A.E.; Elkady, H.; Taghour, M.S.; Eissa, I.H.; El-Zahabi, M.A. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel bioactive thalidomide analogs as anticancer immunomodulatory agents. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 33525–33539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Qiu, R.-Z.; Sun, S.-L.; Zhao, C.; Fan, T.-Y.; Chen, M.; Li, N.-G.; Shi, Z.-H. Small-molecule fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitors: An attractive and efficient method for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12403–12428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, M.; Ingarra, A.M.; Raimondi, M.V.; Spanò, V.; Piccionello, A.P.; De Franco, M.; Menilli, L.; Gandin, V.; Miolo, G.; Barraja, P. New tricyclic systems as photosensitizers towards triple negative breast cancer cells. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2022, 45, 806–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, I.H.; Dahab, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.K.; Alsaif, N.A.; Alanazi, A.; Eissa, S.I.; Mehany, A.B.; Beauchemin, A.M. Design and discovery of new antiproliferative 1, 2, 4-triazin-3 (2H)-ones as tubulin polymerization inhibitors targeting colchicine binding site. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 112, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariganti, N.; Loke, S.K.; Pagadala, E.; Chinta, P.; Poola, B.; Chetti, P.; Bansal, A.; Ramachandran, B.; Srinivasadesikan, V.; Kottalanka, R.K. Design, synthesis, anticancer activity of new amide derivatives derived from 1, 2, 3-triazole-benzofuran hybrids: An insights from molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation and DFT studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1273, 134250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampilek, J. Heterocycles in medicinal chemistry. Molecules 2019, 24, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaya, W.T.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Weijn, A.; Mes, J.J.; Fusetti, F.; Wichers, H.J.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystal Structure of Agaricus bisporus Mushroom Tyrosinase: Identity of the Tetramer Subunits and Interaction with Tropolone. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5477–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittorio, S.; Seidel, T.; Germanò, M.P.; Gitto, R.; Ielo, L.; Garon, A.; Rapisarda, A.; Pace, V.; Langer, T.; De Luca, L. A Combination of pharmacophore and docking-based virtual screening to discover new tyrosinase inhibitors. Mol. Inform. 2020, 39, 1900054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Laughter, M.R.; Anderson, J.B.; Sadeghpour, M. Emerging topical therapies to treat pigmentary disorders: An evidence-based approach. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, U. Carbazole and hydrazone derivatives as new competitive inhibitors of tyrosinase: Experimental clues to binuclear copper active site binding. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 83, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, N.; Hossein Sayahi, M.; Iraji, A.; Yazzaf, R.; Moazzam, A.; Mobaraki, K.; Adib, M.; Attarroshan, M.; Larijani, B.; Rastegar, H.; et al. Evaluating the effects of disubstituted 3-hydroxy-1H-pyrrol-2(5H)-one analog as novel tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 126, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-G.; Gao, Z.-P.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; Hu, C.-M.; Lin, J.; Wu, X.-Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.-S.; Xiong, Z.; Zhu, D.-Y. Synthesis and Biological Activity Evaluation of 2-Cyanopyrrole Derivatives as Potential Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 914944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iraji, A.; Sheikhi, N.; Attarroshan, M.; Reaz Sharifi Ardani, G.; Kabiri, M.; Naghibi Bafghi, A.; Kobarfard, F.; Rezaei, Z.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Foroumadi, A.; et al. Design, synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, in vitro tyrosinase inhibition, antioxidant evaluation, in silico and kinetic studies of substituted indole-carbohydrazides. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 129, 106140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari Boroujeni, S.; Haghighijoo, Z.; Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani, M.; Mosadeghkhah, A.; Moazzam, A.; Yavari, A.; Hajimahmoodi, M.; Sabourian, R.; Hosseini, S.; Larijani, B. Design, Synthesis, in Vitro, and in Silico Evaluation of N-Phenylacetamide-Oxindole-Thiosemicarbazide Hybrids as New Potential Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channar, P.A.; Saeed, A.; Larik, F.A.; Batool, B.; Kalsoom, S.; Hasan, M.; Erben, M.F.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Ali, M.; Ashraf, Z. Synthesis of aryl pyrazole via Suzuki coupling reaction, in vitro mushroom tyrosinase enzyme inhibition assay and in silico comparative molecular docking analysis with Kojic acid. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 79, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekir, S.; Debbabi, M.; Regazzetti, A.; Dargère, D.; Laprévote, O.; Jannet, H.B.; Gharbi, R. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 1, 2, 3-triazole linked coumarinopyrazole conjugates as potent anticholinesterase, anti-5-lipoxygenase, anti-tyrosinase and anti-cancer agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Mo, J.; Xiong, B.; Liao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xing, S.; He, S.; Lyu, W.; Zhang, N.; et al. Discovery of Resorcinol-Based Polycyclic Structures as Tyrosinase Inhibitors for Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.-M.; Yu, Z.-Y.; Lin, M.-Z.; Wei, Q.-M.; Song, S. 5-Methoxy-2-mercaptobenzimidazole as an efficient inhibitor on tyrosinase: Inhibitory activity and mechanism. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 131, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Wang, Y. Recent researches in triazole compounds as medicinal drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 239–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, M.M.; Matin, P.; Rahman, M.R.; Ben Hadda, T.; Almalki, F.A.; Mahmud, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alruwaily, M.; Alshehri, S. Triazoles and Their Derivatives: Chemistry, Synthesis, and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 864286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, H.C.; Sharpless, K.B. The growing impact of click chemistry on drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, M.; Ashtari, A.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Ranjbar, S.; Dehghani, A.; Akbarzadeh, T.; Larijani, B.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Saeedi, M. Synthesis of New Benzimidazole-1,2,3-triazole Hybrids as Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1800120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.R.S.; Abbasi, M.A.; Rehman, A.U.; Siddiqui, S.Z.; Raza, H.; Hassan, M.; Shah, S.A.A.; Shahid, M.; Seo, S.-Y. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of tyrosinase inhibiting novel bi-heterocyclic acetamides: Mechanistic insights through enzyme inhibition, kinetics and computational studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 86, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanjare, B.D.; Mahajan, P.G.; Dige, N.C.; Raza, H.; Hassan, M.; Han, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Seo, S.-Y.; Lee, K.H. Novel 1,2,4-triazole analogues as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors: Synthesis, kinetic mechanism, cytotoxicity and computational studies. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 2089–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, A.; Ghani, U.; Ali Syed, S.; Riazullah. Thiosemicarbazide binds with the dicopper center in the competitive inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase enzyme: Synthesis and molecular modeling of theophylline analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 127826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hałdys, K.; Goldeman, W.; Anger-Góra, N.; Rossowska, J.; Latajka, R. Monosubstituted Acetophenone Thiosemicarbazones as Potent Inhibitors of Tyrosinase: Synthesis, Inhibitory Studies, and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekier, A.; Węglińska, L.; Paneth, A.; Paneth, P.; Dzitko, K. 4-Arylthiosemicarbazide derivatives as a new class of tyrosinase inhibitors and anti-Toxoplasma gondii agents. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 1145–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezudo, I.; Ayelen Ramallo, I.; Alonso, V.L.; Furlan, R.L.E. Effect directed synthesis of a new tyrosinase inhibitor with anti-browning activity. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpoor, H.; Moghadam Farid, S.; Iraji, A.; Asgari, M.S.; Edraki, N.; Hosseini, S.; Jamshidzadeh, A.; Larijani, B.; Attarroshan, M.; Pirhadi, S.; et al. Anti-melanogenesis and anti-tyrosinase properties of aryl-substituted acetamides of phenoxy methyl triazole conjugated with thiosemicarbazide: Design, synthesis and biological evaluations. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultekin, E.; Bekircan, O.; Kolcuoğlu, Y.; Akdemir, A. Synthesis of new 1, 2, 4-triazole–(thio) semicarbazide hybrid molecules: Their tyrosinase inhibitor activities and molecular docking analysis. Arch. Pharm. 2021, 354, 2100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Vanjare, B.D.; Sim, K.-Y.; Raza, H.; Lee, K.H.; Shahzadi, S.; Kloczkowski, A. Biological and Cheminformatics Studies of Newly Designed Triazole Based Derivatives as Potent Inhibitors against Mushroom Tyrosinase. Molecules 2022, 27, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, G.; Zeng, Q.-H.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.J.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis, antioxidant and anti-tyrosinase activity of 1,2,4-triazole hydrazones as antibrowning agents. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bimoussa, A.; Oubella, A.; Bamou, F.Z.; Khdar, Z.A.; Fawzi, M.; Laamari, Y.; Ait Itto, M.Y.; Morjani, H.; Auhmani, A. New 1, 3, 4-thiadiazoles derivatives: Synthesis, antiproliferative activity, molecular docking and molecular dynamics. Future Med. Chem. 2022, 14, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Noh, S.G.; Park, Y.; Kang, D.; Chun, P.; Chung, H.Y.; Jung, H.J.; Moon, H.R. A potent tyrosinase inhibitor,(E)-3-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-(thiophen-2-yl) prop-2-en-1-one, with anti-melanogenesis properties in α-MSH and IBMX-induced B16F10 melanoma cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.R.S.; Abbasi, M.A.; Siddiqui, S.Z.; Raza, H.; Hassan, M.; Shah, S.A.A.; Seo, S.-Y. Synthesis, Kinetics, Binding Conformations and Structure-activity Relationship of Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Aralkylated 2-aminothiazole-ethyltriazole Hybrids. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 20, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, R.; Saeed, A.; Larik, F.A.; Abbas, Q.; Hassan, M.; Raza, H.; Seo, S.-Y. Novel 1,3-oxazine-tetrazole hybrids as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors and free radical scavengers: Synthesis, kinetic mechanism, and molecular docking studies. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.R.; Menezes, T.M.; da Silva, L.P.; Pires, D.S.; Princival, J.L.; Seabra, G.; Neves, J.L. Furan inhibitory activity against tyrosinase and impact on B16F10 cell toxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.J.; Noh, S.G.; Ryu, I.Y.; Park, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R.; Chung, H.Y. (E)-1-(Furan-2-yl)-(substituted phenyl)prop-2-en-1-one Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitors and Melanogenesis Inhibition: An In Vitro and In Silico Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.A.T.; Guedes, I.A.; Pereira, W.L.; Teixeira, R.R.; Dardenne, L.E.; Nascimento, C.J.; Figueroa-Villar, J.D. Isobenzofuran-1(3H)-ones as new tyrosinase inhibitors: Biological activity and interaction studies by molecular docking and NMR. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2021, 1869, 140580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaye, N.A.; Mughal, E.U.; Elkaeed, E.B.; Ashraf, Z.; Kehili, S.; Nazir, Y.; Naeem, N.; Abdul Majeed, N.; Sadiq, A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted aurone derivatives as potential tyrosinase inhibitors: In vitro, kinetic, QSAR, docking and drug-likeness studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Yang, J.; Lee, S.; Park, C.; Kang, D.; Akter, J.; Ullah, S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R. The tyrosinase inhibitory effects of isoxazolone derivatives with a (Z)-β-phenyl-α, β-unsaturated carbonyl scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 3882–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanipekun, B.E.; Ponnapalli, M.G.; Patel, H.K.; Munipalle, K.; Shaik, K. Design, synthesis of new phenyl acetylene and isoxazole analogues of arjunolic acid as potent tyrosinase and alpha glucosidase inhibitors. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 37, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanipekun, B.E.; Ponnapalli, M.G.; Shaik, K.; Nanubolu, J.B.; Kommalapati, V.K.; Tangutur, A.D. α-Glucosidase inhibitory isomeric corniculatolides from the stems of the indian mangrove plant, Xylocarpus granatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.; Park, Y.; Ryu, I.Y.; Jung, H.J.; Ullah, S.; Choi, H.; Park, C.; Kang, D.; Lee, S.; Chun, P.; et al. In silico and in vitro insights into tyrosinase inhibitors with a 2-thioxooxazoline-4-one template. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanjare, B.D.; Choi, N.G.; Mahajan, P.G.; Raza, H.; Hassan, M.; Han, Y.; Yu, S.-M.; Kim, S.J.; Seo, S.-Y.; Lee, K.H. Novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole compounds inhibit the tyrosinase and melanin level: Synthesis, in-vitro, and in-silico studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 41, 116222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, H.; Rehman Sadiq Butt, A.; Athar Abbasi, M.; Zahra Siddiqui, S.; Hassan, M.; Adnan Ali Shah, S.; Ja Kim, S. 2-Aminothiazole-Oxadiazole Bearing N-Arylated Butanamides: Convergent Synthesis, Tyrosinase Inhibition, Kinetics, Structure-Activity Relationship, and Binding Conformations. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202201019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, G.; Türe, A.; Ercan, A.; Öncül, S.; Aytemir, M.D. Synthesis, computational molecular docking analysis and effectiveness on tyrosinase inhibition of kojic acid derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Mohammadi, H.T.; Mahdavi, A.; Shourian, M.; Ghafouri, H. Evaluation of thiazolidinone derivatives as a new class of mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, E.; Lee, E.K.; Noh, S.G.; Jung, H.J.; Moon, K.M.; Park, M.H.; Park, Y.J.; Hyun, M.K.; Lee, A.K.; Kim, S.J. In vitro and in vivo evidence of tyrosinase inhibitory activity of a synthesized (Z)-5-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one (5-HMT). Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechowska, K.; Świtalska, M.; Cytarska, J.; Jaroch, K.; Łuczykowski, K.; Chałupka, J.; Wietrzyk, J.; Misiura, K.; Bojko, B.; Kruszewski, S. Discovery of tropinone-thiazole derivatives as potent caspase 3/7 activators, and noncompetitive tyrosinase inhibitors with high antiproliferative activity: Rational design, one-pot tricomponent synthesis, and lipophilicity determination. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 175, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piechowska, K.; Mizerska-Kowalska, M.; Zdzisińska, B.; Cytarska, J.; Baranowska-Łączkowska, A.; Jaroch, K.; Łuczykowski, K.; Płaziński, W.; Bojko, B.; Kruszewski, S. Tropinone-derived alkaloids as potent anticancer agents: Synthesis, tyrosinase inhibition, mechanism of action, DFT calculation, and molecular docking studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujan, R.; Saeed, A.; Ashraf, S.; Channar, P.A.; Abbas, Q.; Rind, M.A.; Hassan, M.; Raza, H.; Seo, S.-Y.; El-Seedi, H.R. Synthesis, computational studies and enzyme inhibitory kinetics of benzothiazole-linked thioureas as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 7035–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.M.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.-A.; Park, D.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Moon, H.R.; Chung, H.Y. Design and synthesis of 5-(substituted benzylidene) thiazolidine-2, 4-dione derivatives as novel tyrosinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 49, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.M.; Park, J.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Park, D.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, E.K.; Han, Y.K.; Kim, J.-A.; Lee, J.Y. Synthesis and biological activity of hydroxy substituted phenyl-benzo [d] thiazole analogues for antityrosinase activity in B16 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 21, 2445–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, E.; Noh, S.-G.; Ha, S.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, A.K.; Hyun, M.K.; Kang, D.; Lee, S.; Park, C. Evaluation of the novel synthetic tyrosinase inhibitor (Z)-3-(3-bromo-4-hydroxybenzylidene) thiochroman-4-one (MHY1498) in vitro and in silico. Molecules 2018, 23, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Ryu, I.Y.; Choi, I.; Ullah, S.; Jung, H.J.; Park, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Hong, S.; Yoon, I.-S.; et al. Novel Anti-Melanogenic Compounds, (Z)-5-(Substituted Benzylidene)-4-thioxothiazolidin-2-one Derivatives: In Vitro and In Silico Insights. Molecules 2021, 26, 4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Hong, S.; Jung, H.J.; Ullah, S.; Hwang, Y.; Choi, H.; Ko, J.; Lee, J.; Chun, P.; Chung, H.Y.; et al. Identification of a Novel Class of Anti-Melanogenic Compounds, (Z)-5-(Substituted benzylidene)-3-phenyl-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one Derivatives, and Their Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Activities. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, J.; Jung, H.J.; Ullah, S.; Ko, J.; Jeong, Y.; Park, Y.J.; Kang, M.K.; Yun, H.; Kim, M.-S.; et al. A Novel Class of Potent Anti-Tyrosinase Compounds with Antioxidant Activity, 2-(Substituted phenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)benzo[d]thiazoles: In Vitro and In Silico Insights. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Ryu, I.Y.; Choi, I.; Ullah, S.; Jung, H.J.; Park, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Hong, S.; Chun, P.; et al. Identification of (Z)-2-benzylidene-dihydroimidazothiazolone derivatives as tyrosinase inhibitors: Anti-melanogenic effects and in silico studies. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, Y.J.; Jung, H.J.; Ullah, S.; Yoon, D.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Kang, M.K.; Kang, D.; Park, Y.; et al. Design and Synthesis of (Z)-2-(Benzylamino)-5-benzylidenethiazol-4(5H)-one Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitors and Their Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Effects. Molecules 2023, 28, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehzadi, S.A.; Saeed, A.; Perveen, F.; Channar, P.A.; Arshad, I.; Abbas, Q.; Kalsoom, S.; Yousaf, S.; Simpson, J. Identification of two novel thiazolidin-2-imines as tyrosinase inhibitors: Synthesis, crystal structure, molecular docking and DFT studies. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.-F.; Hu, P.-P.; Liu, M.-S.; Kong, X.-L.; Zhang, J.-C.; Hider, R.C.; Zhou, T. Design and synthesis of hydroxypyridinone-L-phenylalanine conjugates as potential tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6597–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.-Y.; Zhang, M.-X.; Dong, X.-W.; Hu, Y.-Z.; Dai, X.-Y.; Wei, X.; Hider, R.C.; Zhang, J.-C.; Zhou, T. Design and synthesis of novel hydroxypyridinone derivatives as potential tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 26, 3103–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.-L.; Wang, X.-L.; Chen, K.; Dong, X.-W.; Kong, L.-M.; Zhao, D.-Y.; Hider, R.C.; Zhou, T. Novel hydroxypyridinone derivatives containing an oxime ether moiety: Synthesis, inhibition on mushroom tyrosinase and application in anti-browning of fresh-cut apples. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, N.; Hong, G.; Jun, K. Synthesis and evaluation of 2′,4′,6′-trihydroxychalcones as a new class of tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerya, O.; Musa, R.; Khatib, S.; Tamir, S.; Vaya, J. Chalcones as potent tyrosinase inhibitors: The effect of hydroxyl positions and numbers. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-Z.; Chen, K.; Chen, Y.-L.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Hider, R.C.; Zhou, T. Design and synthesis of novel stilbene-hydroxypyridinone hybrids as tyrosinase inhibitors and their application in the anti-browning of freshly-cut apples. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Kang, D.; Lee, S.; Ikram, M.; Park, C.; Park, Y.; Yoon, S.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R. Synthesis of cinnamic amide derivatives and their anti-melanogenic effect in α-MSH-stimulated B16F10 melanoma cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapasam, A.; Kollipara, M.R. A survey of crystal structures and biological activities of platinum group metal complexes containing N-acylthiourea ligands. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2020, 195, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, M.; Sabourian, R.; Tasharoie, A.; Safavi, M.; Iraji, A.; Khalili Ghomi, M.; Dastyafteh, N.; Irajie, C.; Zarenezhad, E.; Mostafavi Pour, S.M. Thioquinoline derivatives conjugated to thiosemicarbazide as potent tyrosinase inhibitors with anti-melanogenesis properties. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larik, F.A.; Saeed, A.; Channar, P.A.; Muqadar, U.; Abbas, Q.; Hassan, M.; Seo, S.-Y.; Bolte, M. Design, synthesis, kinetic mechanism and molecular docking studies of novel 1-pentanoyl-3-arylthioureas as inhibitors of mushroom tyrosinase and free radical scavengers. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 141, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, M.N.; Saeed, A.; Channar, P.A.; Larik, F.A.; Zain-ul abideen, M.; Shabir, G.; Abbas, Q.; Hassan, M.; Raza, H.; Seo, S.-Y. Synthesis, molecular docking and kinetic studies of novel quinolinyl based acyl thioureas as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors and free radical scavengers. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 90, 103063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmortazavi, S.S.; Farvandi, M.; Ghafouri, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Shourian, M. Evaluation of novel pyrimidine derivatives as a new class of mushroom tyrosinase inhibitor. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbabi, M.; Nimbarte, V.D.; Chekir, S.; Chortani, S.; Romdhane, A.; Ben Jannet, H. Design and synthesis of novel potent anticoagulant and anti-tyrosinase pyranopyrimidines and pyranotriazolopyrimidines: Insights from molecular docking and SAR analysis. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 82, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Ejaz, S.A.; Khalid, A.; Channar, P.A.; Aziz, M.; Abbas, Q.; Wani, T.A.; Alsaif, N.A.; Alanazi, M.M.; Al-Hossaini, A.M.; et al. Acetophenone-Based 3,4-Dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-Thione as Potential Inhibitor of Tyrosinase and Ribonucleotide Reductase: Facile Synthesis, Crystal Structure, In-Vitro and In-Silico Investigations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriapkin, A.; Kodonidi, I.; Pozdnyakov, D. Targeted Synthesis and Study of Anti-tyrosinase Activity of 2-Substituted Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]Thieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-4(3H)-One. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2022, 21, e126557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dige, N.C.; Mahajan, P.G.; Raza, H.; Hassan, M.; Vanjare, B.D.; Hong, H.; Hwan Lee, K.; Latip, J.; Seo, S.-Y. Ultrasound mediated efficient synthesis of new 4-oxoquinazolin-3(4H)-yl)furan-2-carboxamides as potent tyrosinase inhibitors: Mechanistic approach through chemoinformatics and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 92, 103201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, S.; Deri, B.; Germanò, M.P.; Gitto, R.; Ielo, L.; Buemi, M.R.; Certo, G.; Vittorio, S.; Rapisarda, A.; Pazy, Y. Targeting tyrosinase: Development and structural insights of novel inhibitors bearing arylpiperidine and arylpiperazine fragments. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3908–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielo, L.; Deri, B.; Germano, M.P.; Vittorio, S.; Mirabile, S.; Gitto, R.; Rapisarda, A.; Ronsisvalle, S.; Floris, S.; Pazy, Y. Exploiting the 1-(4-fluorobenzyl) piperazine fragment for the development of novel tyrosinase inhibitors as anti-melanogenic agents: Design, synthesis, structural insights and biological profile. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 178, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittorio, S.; Ielo, L.; Mirabile, S.; Gitto, R.; Fais, A.; Floris, S.; Rapisarda, A.; Germanò, M.P.; De Luca, L. 4-Fluorobenzylpiperazine-containing derivatives as efficient inhibitors of mushroom tyrosinase. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabile, S.; Vittorio, S.; Paola Germanò, M.; Adornato, I.; Ielo, L.; Rapisarda, A.; Gitto, R.; Pintus, F.; Fais, A.; De Luca, L. Evaluation of 4-(4-Fluorobenzyl)piperazin-1-yl]-Based Compounds as Competitive Tyrosinase Inhibitors Endowed with Antimelanogenic Effects. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 3083–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.A.; Rehman, Z.U.; Rehman, A.U.; Siddiqui, S.Z.; Nazir, M.; Hassan, M.; Raza, H.; Shah, S.A.A. Synthesis of bi-heterocyclic sulfonamides as tyrosinase inhibitors: Lineweaver–Burk plot evaluation and computational ascriptions. Acta Chim. Slov. 2020, 67, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, L.; Germanò, M.P.; Fais, A.; Pintus, F.; Buemi, M.R.; Vittorio, S.; Mirabile, S.; Rapisarda, A.; Gitto, R. Discovery of a new potent inhibitor of mushroom tyrosinase (Agaricus bisporus) containing 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl) piperazin-1-yl moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabile, S.; Germanò, M.P.; Fais, A.; Lombardo, L.; Ricci, F.; Floris, S.; Cacciola, A.; Rapisarda, A.; Gitto, R.; De Luca, L. Design, Synthesis, and in Vitro Evaluation of 4-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)piperazine-Based Compounds Targeting Tyrosinase. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202200305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, H.; Abbasi, M.A.; Siddiqui, S.Z.; Hassan, M.; Abbas, Q.; Hong, H.; Shah, S.A.A.; Shahid, M.; Seo, S.-Y. Synthesis, molecular docking, dynamic simulations, kinetic mechanism, cytotoxicity evaluation of N-(substituted-phenyl)-4-{(4-[(E)-3-phenyl-2-propenyl]-1-piperazinyl} butanamides as tyrosinase and melanin inhibitors: In vitro, in vivo and in silico approaches. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, 103445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, R.; Oliva, P.; Prencipe, F.; Manfredini, S.; Germanò, M.P.; De Luca, L.; Ricci, F.; Corallo, D.; Aveic, S.; Mariotto, E.; et al. Cinnamic acid derivatives linked to arylpiperazines as novel potent inhibitors of tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 231, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimiri, M.; Khosravikia, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Pedrood, K.; Hosseini, S.Z.; Asgari, M.S.; Pirhadi, S.; Attarroshan, M.; Mobaraki, K.; Hosseini, S. Rational Design, Synthesis, in Vitro, and in Silico Studies of Chlorophenylquinazolin-4 (3H)-One Containing Different Aryl Acetohydrazides as Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202100964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chi, Y.; Gong, C.; Yang, H.; Zeng, F.; Gao, F.; Hua, X.; Wang, Z. Newly Designed Quinazolinone Derivatives as Novel Tyrosinase Inhibitor: Synthesis, Inhibitory Activity, and Mechanism. Molecules 2022, 27, 5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, Q.-X.; Wang, Q.; Song, K.-K.; Qiu, L. Inhibitory effects of cinnamic acid and its derivatives on the diphenolase activity of mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) tyrosinase. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Ishiguro, K.; Kubo, I. Tyrosinase inhibitory p-Coumaric acid from Ginseng leaves. Phytother. Res. 1999, 13, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S. Tyrosinase inhibitors of Pulsatilla cernua root-derived materials. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1400–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Park, Y.; Ikram, M.; Lee, S.; Park, C.; Kang, D.; Yang, J.; Akter, J.; Yoon, S.; Chun, P. Design, synthesis and anti-melanogenic effect of cinnamamide derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5672–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Park, C.; Ikram, M.; Kang, D.; Lee, S.; Yang, J.; Park, Y.; Yoon, S.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R. Tyrosinase inhibition and anti-melanin generation effect of cinnamamide analogues. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafary, S.; Ranjbar, S.; Larijani, B.; Amini, M.; Biglar, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Bakhshaei, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Sakhteman, A.; Khoshneviszadeh, M. Novel morpholine containing cinnamoyl amides as potent tyrosinase inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okajima, S.; Hamamoto, A.; Asano, M.; Isogawa, K.; Ito, H.; Kato, S.; Hirata, Y.; Furuta, K.; Takemori, H. Azepine derivative T4FAT, a new copper chelator, inhibits tyrosinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-H.; Yang, S.-H.; Kim, D.-S.; Kim, N.D.; Shin, H.-J.; Liu, K. Novel Quercetin Derivative of 3,7-Dioleylquercetin Shows Less Toxicity and Highly Potent Tyrosinase Inhibition Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, S.; Ranjbar, S.; Dadfar, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Gholampour, M.; Sakhteman, A.; Khoshneviszadeh, M. 4 H-benzochromene derivatives as novel tyrosinase inhibitors and radical scavengers: Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular docking analysis. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, J.; Mughal, E.U.; Sadiq, A.; Bibi, M.; Naeem, N.; Ali, A.; Massadaq, A.; Fatima, N.; Javid, A.; Zafar, M.N.; et al. Exploring 3-hydroxyflavone scaffolds as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors: Synthesis, X-ray crystallography, antimicrobial, fluorescence behaviour, structure-activity relationship and molecular modelling studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 7107–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, J.; Mughal, E.U.; Alsantali, R.I.; Obaid, R.J.; Sadiq, A.; Naeem, N.; Ali, A.; Massadaq, A.; Javed, Q.; Javid, A.; et al. Structure-based designing and synthesis of 2-phenylchromone derivatives as potent tyrosinase inhibitors: In vitro and in silico studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 35, 116057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, E.U.; Ashraf, J.; Hussein, E.M.; Nazir, Y.; Alwuthaynani, A.S.; Naeem, N.; Sadiq, A.; Alsantali, R.I.; Ahmed, S.A. Design, Synthesis, and Structural Characterization of Thioflavones and Thioflavonols as Potential Tyrosinase Inhibitors: In Vitro and In Silico Studies. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 17444–17461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagufta; Ahmad, I. Recent insight into the biological activities of synthetic xanthone derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 116, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Chen, L.; Luo, G.; Liu, L.; Zhu, W.; Yan, P.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W. Study on synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-aryl substituted xanthone derivatives as novel and potent tyrosinase inhibitors. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 67, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, D.I.; Almeida, M.C.; Maciel, B.; Carmo, H.; Sousa Lobo, J.; Dal Pozzo, C.; Cravo, S.M.; Rosa, G.P.; Kane-Pagès, A.; do Carmo Barreto, M. Efficacy, stability, and safety evaluation of new polyphenolic xanthones towards identification of bioactive compounds to fight skin photoaging. Molecules 2020, 25, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, G.P.; Palmeira, A.; Resende, D.I.S.P.; Almeida, I.F.; Kane-Pagès, A.; Barreto, M.C.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M.M.M. Xanthones for melanogenesis inhibition: Molecular docking and QSAR studies to understand their anti-tyrosinase activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 29, 115873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, E.-J. Inhibitory Effects of Coumarin Derivatives on Tyrosinase. Molecules 2021, 26, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintus, F.; Floris, S.; Fais, A.; Era, B.; Kumar, A.; Gatto, G.; Uriarte, E.; Matos, M.J. Hydroxy-3-Phenylcoumarins as Multitarget Compounds for Skin Aging Diseases: Synthesis, Molecular Docking and Tyrosinase, Elastase, Collagenase and Hyaluronidase Inhibition, and Sun Protection Factor. Molecules 2022, 27, 6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuri, S.; Era, B.; Pintus, F.; Cadoni, E.; Cabiddu, M.G.; Fais, A.; Pivetta, T. Hydroxylated Coumarin-Based Thiosemicarbazones as Dual Antityrosinase and Antioxidant Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasab, N.H.; Raza, H.; Eom, Y.S.; Hassan, M.; Kloczkowski, A.; Kim, S.J. Synthesis and discovery of potential tyrosinase inhibitor of new coumarin-based thiophenyl-pyrazolylthiazole nuclei: In-vitro evaluation, cytotoxicity, kinetic and computational studies. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2023, 101, 1262–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Le, T.; Xue, J.; Engelhardt, U.H.; Jiang, H. Kojic Acid Showed Consistent Inhibitory Activity on Tyrosinase from Mushroom and in Cultured B16F10 Cells Compared with Arbutins. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-S. An Updated Review of Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2440–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.; Kishore, B.; Bhat, R.; Sukumar, D.; Martis, J.; Ganesh, H. A comparative study of the efficacy of 4% hydroquinone vs 0.75% Kojic acid cream in the treatment of facial melasma. Indian J. Dermatol. 2013, 58, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.-M.; Kwak, S.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, Y.-S. Kojic acid–tripeptide amide as a new tyrosinase inhibitor. Peptide Sci. 2007, 88, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefnejad, F.; Iraji, A.; Sabourian, R.; Moazzam, A.; Tasharoie, S.; Sara Mirfazli, S.; Zomorodian, K.; Alireza Akhlagh, S.; Hosseini, S.; Larijani, B. Ugi Bis-Amide Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitor; Synthesis, Biology Assessment, and in Silico Analysis. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202200607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Su, W.-C.; Li, C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Q.-X.; Zheng, J.; Tang, D.-L.; Chen, S.-M.; Wang, Q. Anti-melanogenesis of novel kojic acid derivatives in B16F10 cells and zebrafish. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.-J.; Shi, Y.; Wen, Z.-J.; Chen, Q.-X.; Wang, Q. Kinetic and computational molecular docking simulation study of novel kojic acid derivatives as anti-tyrosinase and antioxidant agents. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashooriha, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Moradi, S.E.; Rafiei, A.; Kardan, M.; Emami, S. 1, 2, 3-Triazole-based kojic acid analogs as potent tyrosinase inhibitors: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 82, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashooriha, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Rafiei, A.; Kardan, M.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Emami, S. Kojic acid–natural product conjugates as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 201, 112480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri, N.; Iraji, A.; Yavari, A.; Asgari, M.S.; Zamani, S.; Hosseini, S.; Bahadorikhalili, S.; Pirhadi, S.; Larijani, B.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; et al. The natural-based optimization of kojic acid conjugated to different thio-quinazolinones as potential anti-melanogenesis agents with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 116044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; He, M.; Huang, Y.; Peng, Z. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new kojic acid-1,3,4-oxadiazole hybrids as tyrosinase inhibitors and their application in the anti-browning of fresh-cut mushrooms. Food Chem. 2023, 409, 135275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, G.; He, Y.; Wang, J.J.; Zhao, Y. Tyrosinase inhibitory mechanism and anti-browning properties of novel kojic acid derivatives bearing aromatic aldehyde moiety. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulier, B.; Pérès, B.; Haudecoeur, R. Advances in the Design of Genuine Human Tyrosinase Inhibitors for Targeting Melanogenesis and Related Pigmentations. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13428–13443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, M.; Bassi, G.; Rotondi, G.; Khettabi, L.; Dichiara, M.; Murer, P.; Scheuermann, J.; Soler-Lopez, M.; Neri, D. Discovery, affinity maturation and multimerization of small molecule ligands against human tyrosinase and tyrosinase-related protein 1. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Na, J.H.; Chang, P.-S.; Han, J. Protection of Grain Products from Sitophilus oryzae (L.) Contamination by Anti-Insect Pest Repellent Sachet Containing Allyl Mercaptan Microcapsule. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, T.; Scherner, C.; Röhm, K.-H.; Kolbe, L. Structure-Activity Relationships of Thiazolyl Resorcinols, Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Human Tyrosinase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
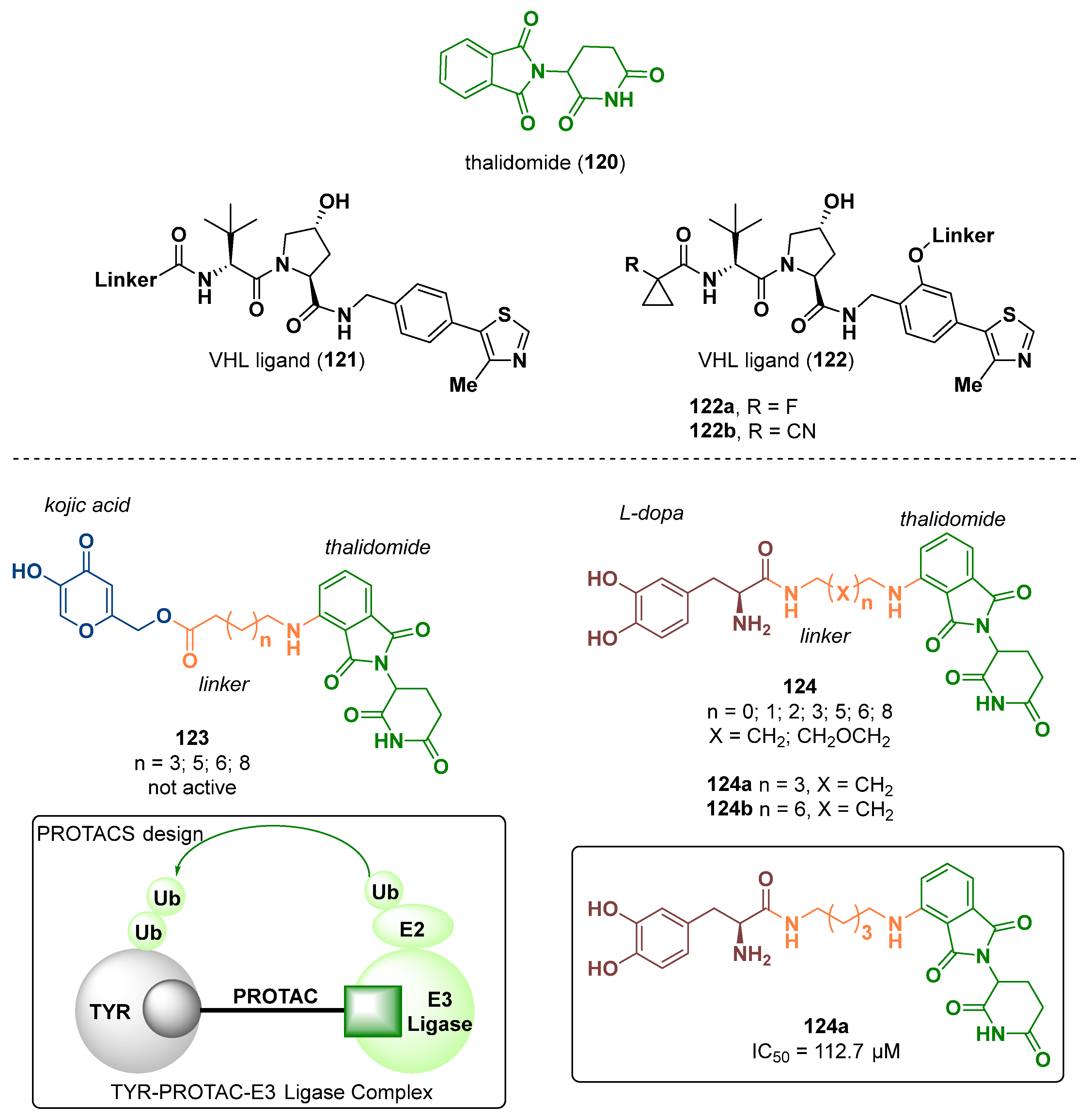
- Fu, D.; Yuan, Y.; Qin, F.; Xu, Y.; Cui, X.; Li, G.; Yao, S.; Deng, Y.; Tang, Z. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of tyrosinase-targeting PROTACs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 226, 113850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burslem, G.M.; Crews, C.M. Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras as Therapeutics and Tools for Biological Discovery. Cell 2020, 181, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popow, J.; Arnhof, H.; Bader, G.; Berger, H.; Ciulli, A.; Covini, D.; Dank, C.; Gmaschitz, T.; Greb, P.; Karolyi-Özguer, J.; et al. Highly Selective PTK2 Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras to Probe Focal Adhesion Kinase Scaffolding Functions. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2508–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnaby, W.; Koegl, M.; Roy, M.J.; Whitworth, C.; Diers, E.; Trainor, N.; Zollman, D.; Steurer, S.; Karolyi-Oezguer, J.; Riedmueller, C.; et al. BAF complex vulnerabilities in cancer demonstrated via structure-based PROTAC design. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luh, L.M.; Scheib, U.; Juenemann, K.; Wortmann, L.; Brands, M.; Cromm, P.M. Prey for the Proteasome: Targeted Protein Degradation—A Medicinal Chemist’s Perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15448–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.L.; Grant, N.J.; Temperley, N.D.; Patton, E.E. Small molecule screening in zebrafish: An in vivo approach to identifying new chemical tools and drug leads. Cell Commun. Signal. 2010, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
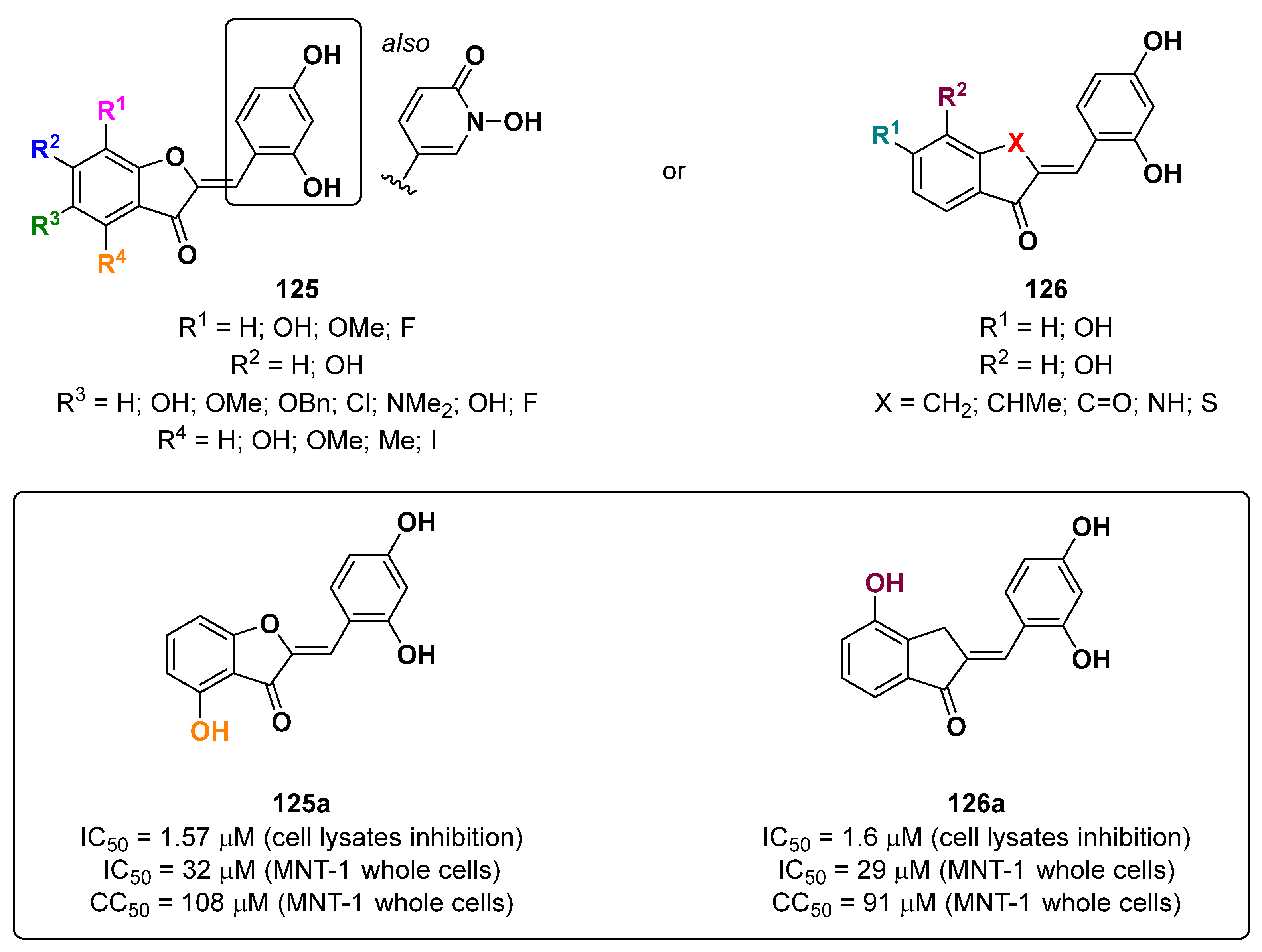
- Roulier, B.; Rush, I.; Lazinski, L.M.; Pérès, B.; Olleik, H.; Royal, G.; Fishman, A.; Maresca, M.; Haudecoeur, R. Resorcinol-based hemiindigoid derivatives as human tyrosinase inhibitors and melanogenesis suppressors in human melanoma cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 246, 114972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vittorio, S.; Dank, C.; Ielo, L. Heterocyclic Compounds as Synthetic Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Recent Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24109097
Vittorio S, Dank C, Ielo L. Heterocyclic Compounds as Synthetic Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Recent Advances. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):9097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24109097
Chicago/Turabian StyleVittorio, Serena, Christian Dank, and Laura Ielo. 2023. "Heterocyclic Compounds as Synthetic Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Recent Advances" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 9097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24109097
APA StyleVittorio, S., Dank, C., & Ielo, L. (2023). Heterocyclic Compounds as Synthetic Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Recent Advances. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 9097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24109097








