Extracellular Vesicle Depletion Protocols of Foetal Bovine Serum Influence Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Phenotype, Immunomodulation, and Particle Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
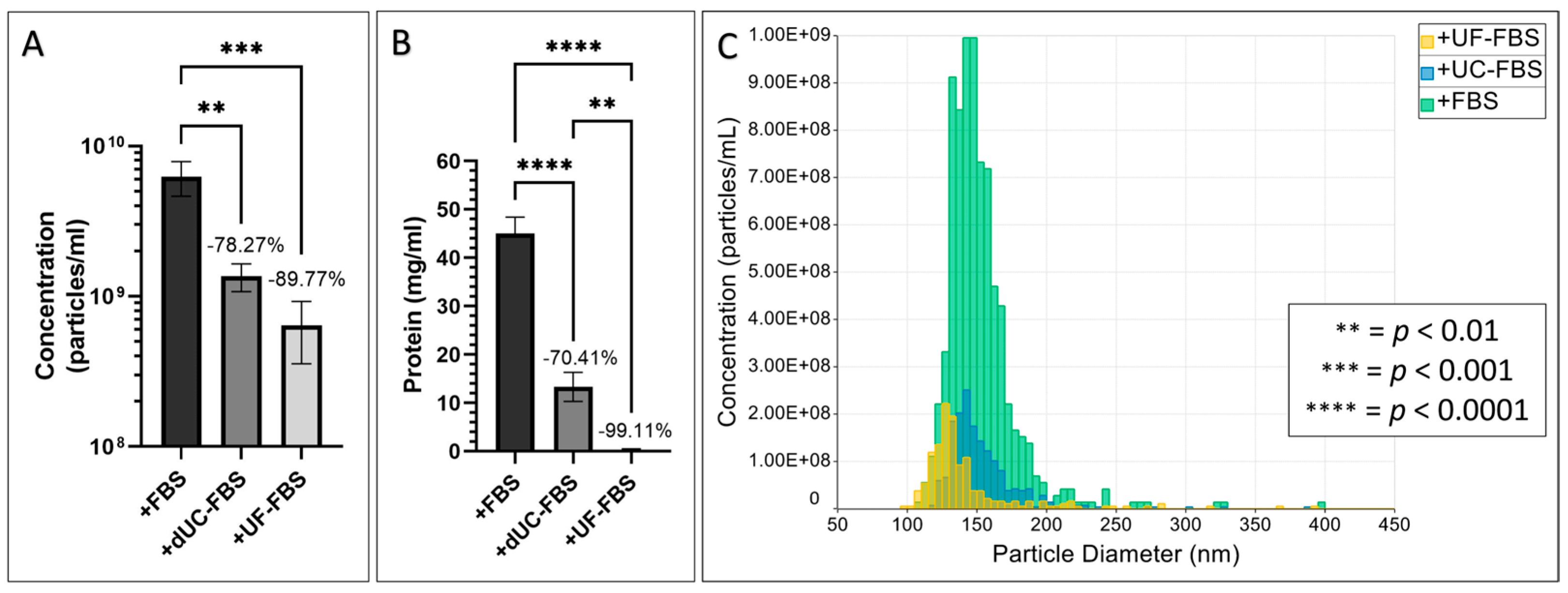
2.1. Efficiency of FBS EV Depletion Protocols
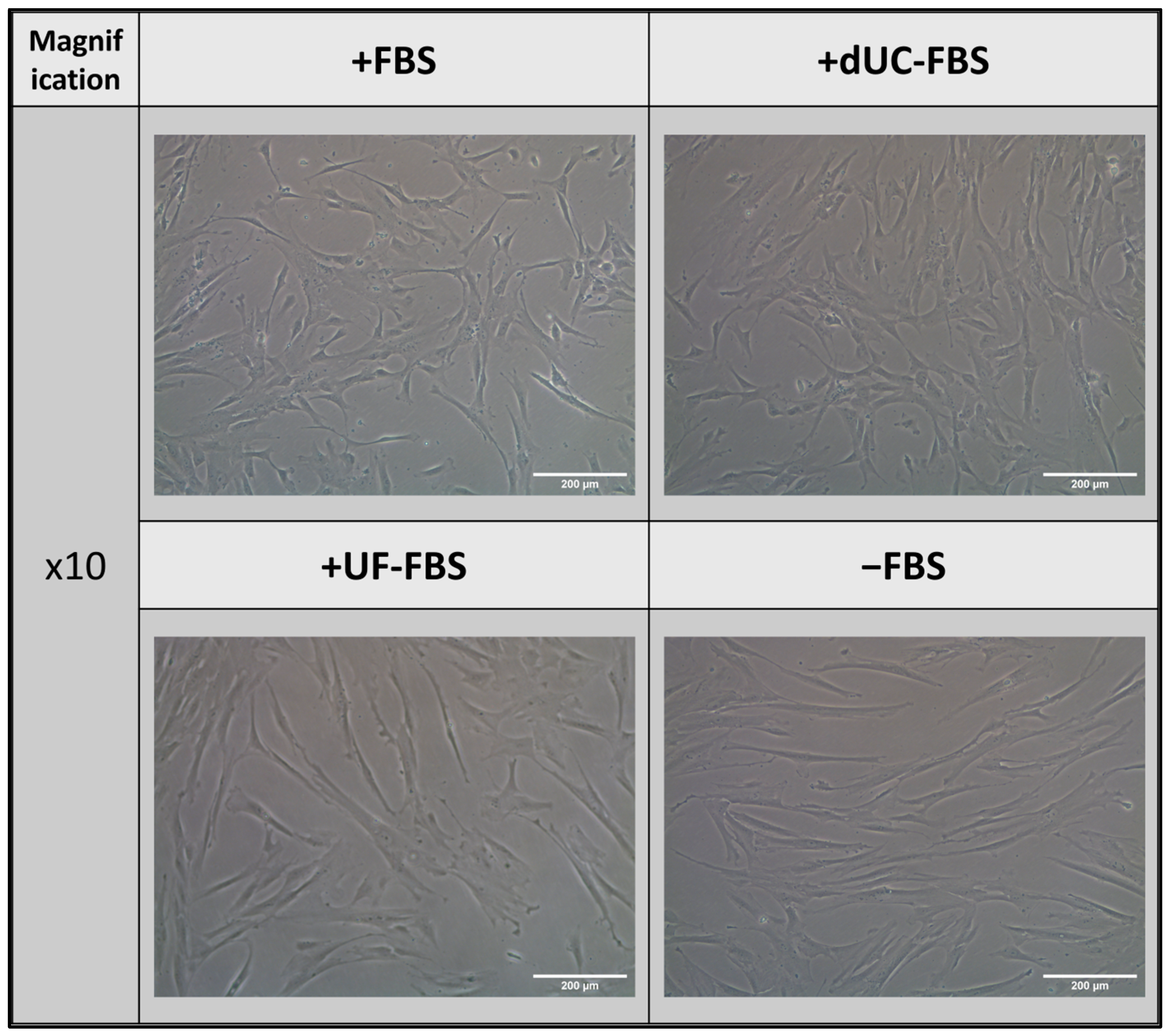
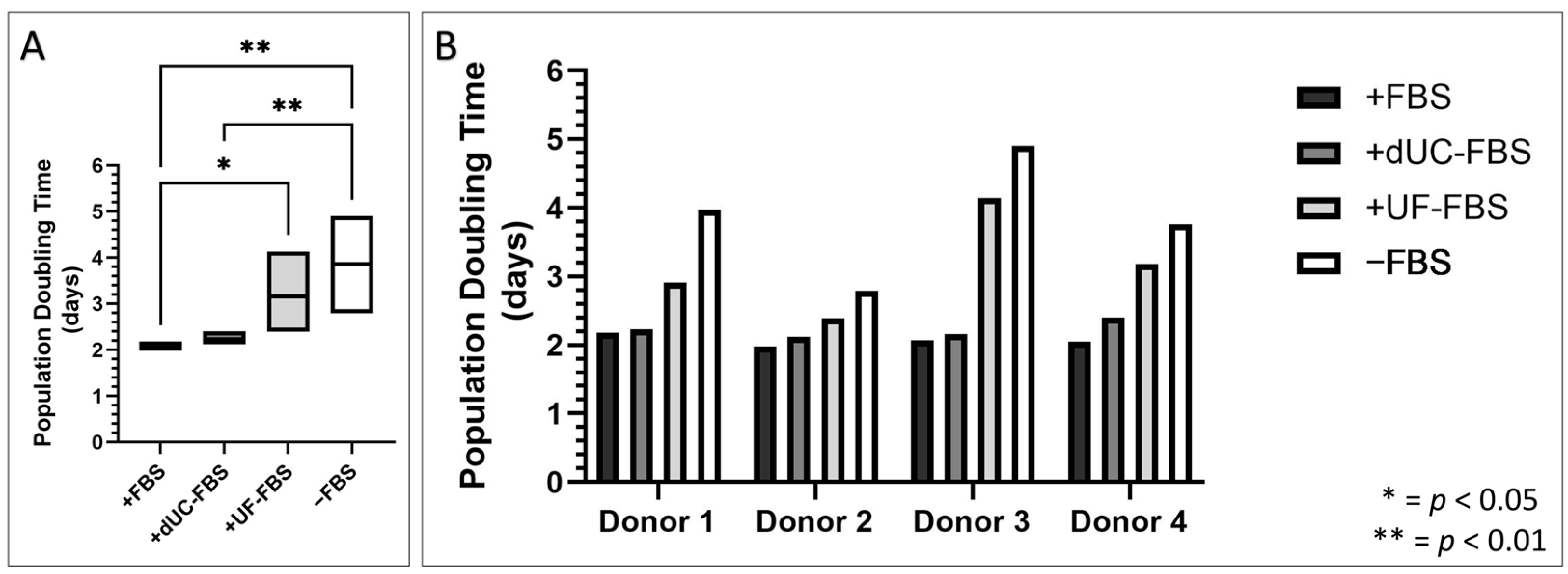
2.2. Morphology of UC-MSCs after Incubation with EV-Depleted Medias
2.3. Phenotype of UC-MSCs after Incubation with EV-Depleted Medias
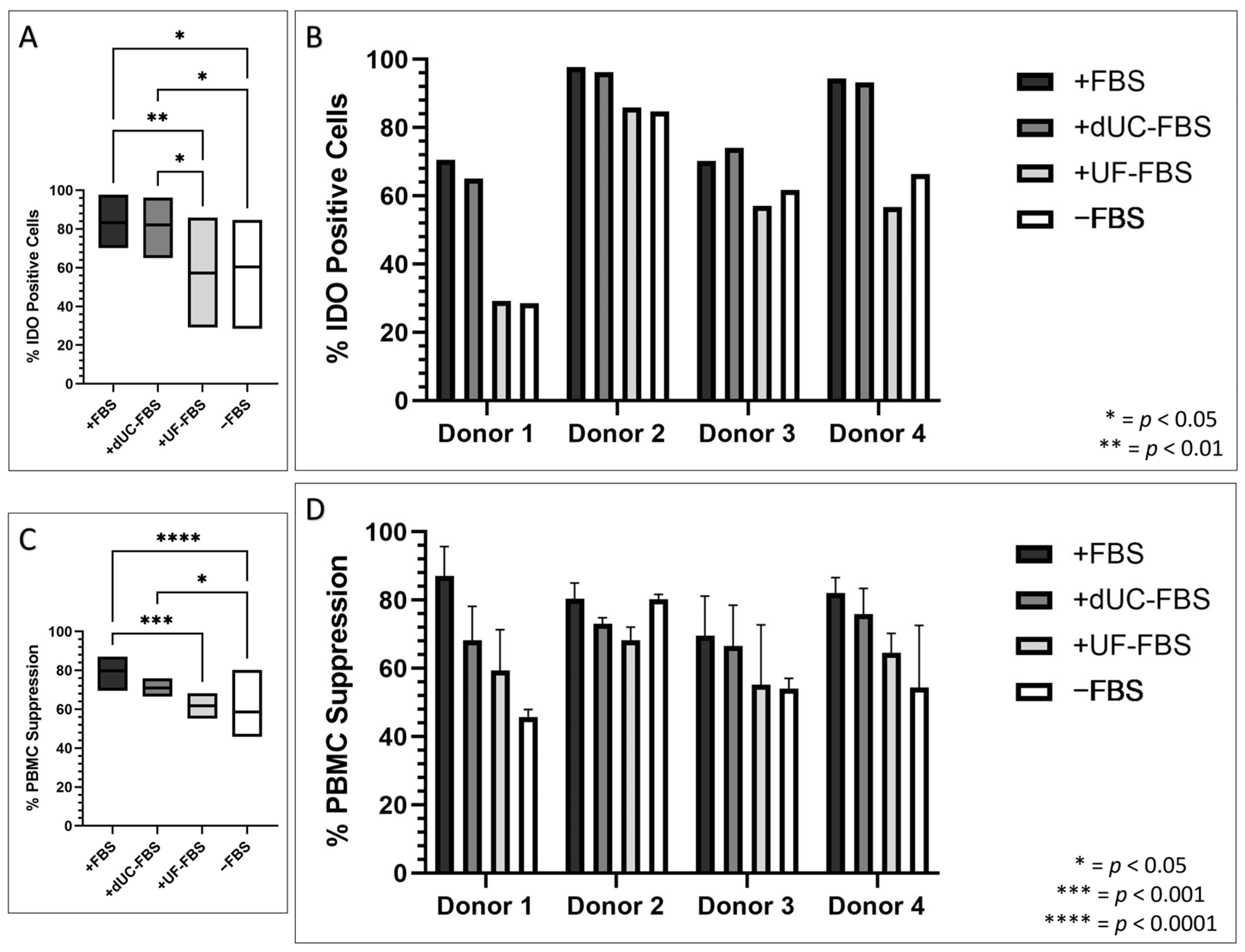
2.4. Immunomodulatory Properties of UC-MSCs after Incubation with EV-Depleted Medias
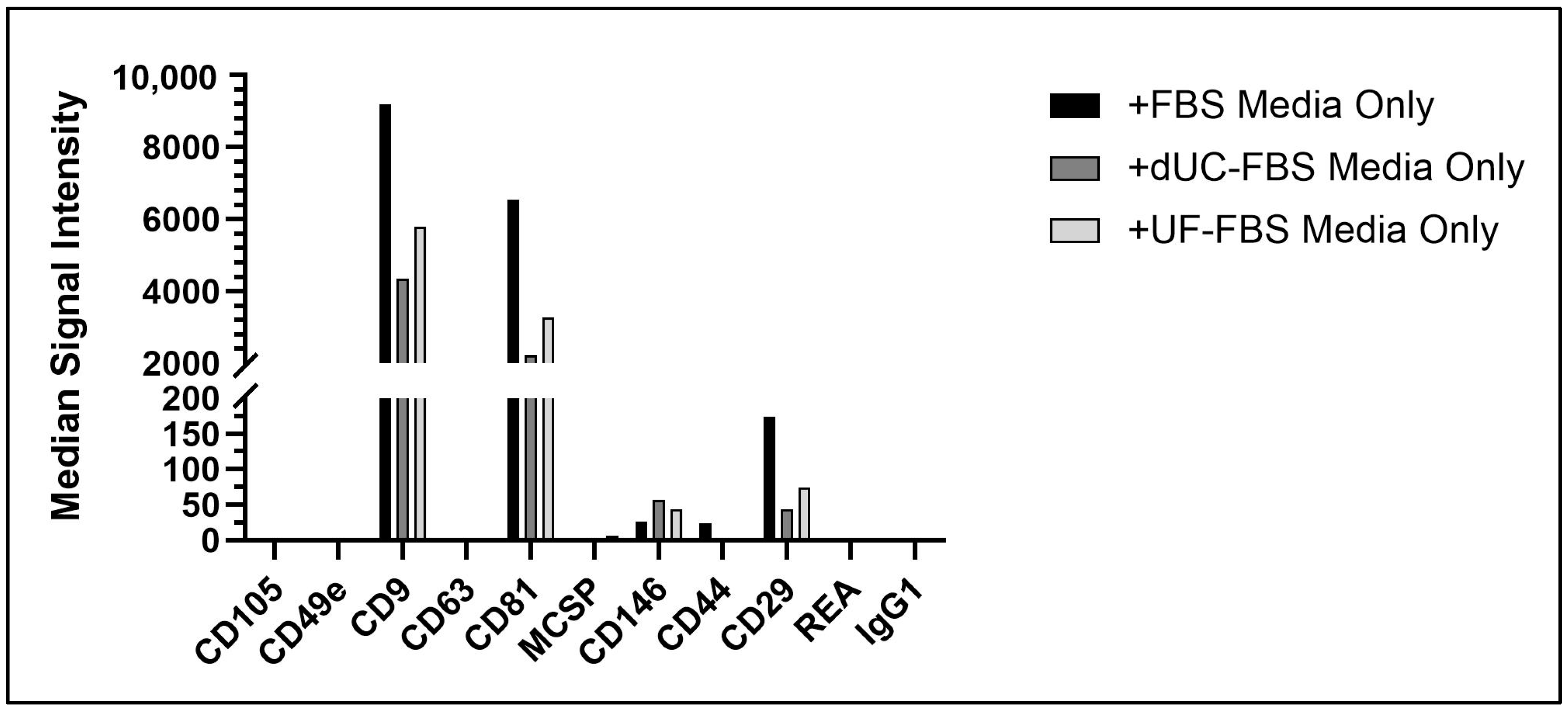
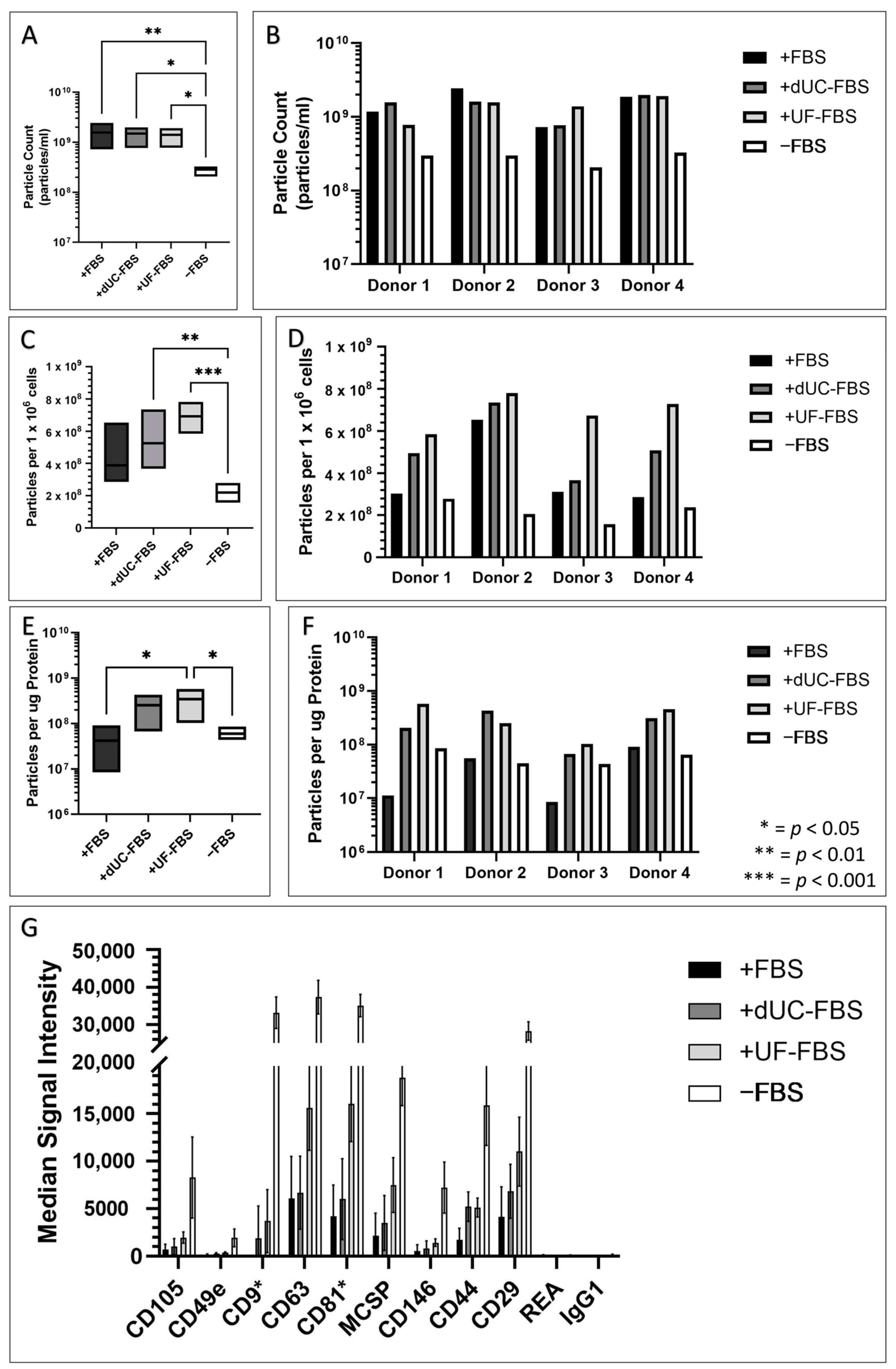
2.5. UC-MSC EV Enriched Conditioned Media Attributes after Incubation with EV-Depleted Media
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Umbilical Cord MSCs
4.2. FBS EV Depletion by Differential Ultracentrifugation (dUC)
4.3. FBS EV Depletion by Ultrafiltration (UF)
4.4. Light Microscopy
4.5. Population Doubling Time (PDT)
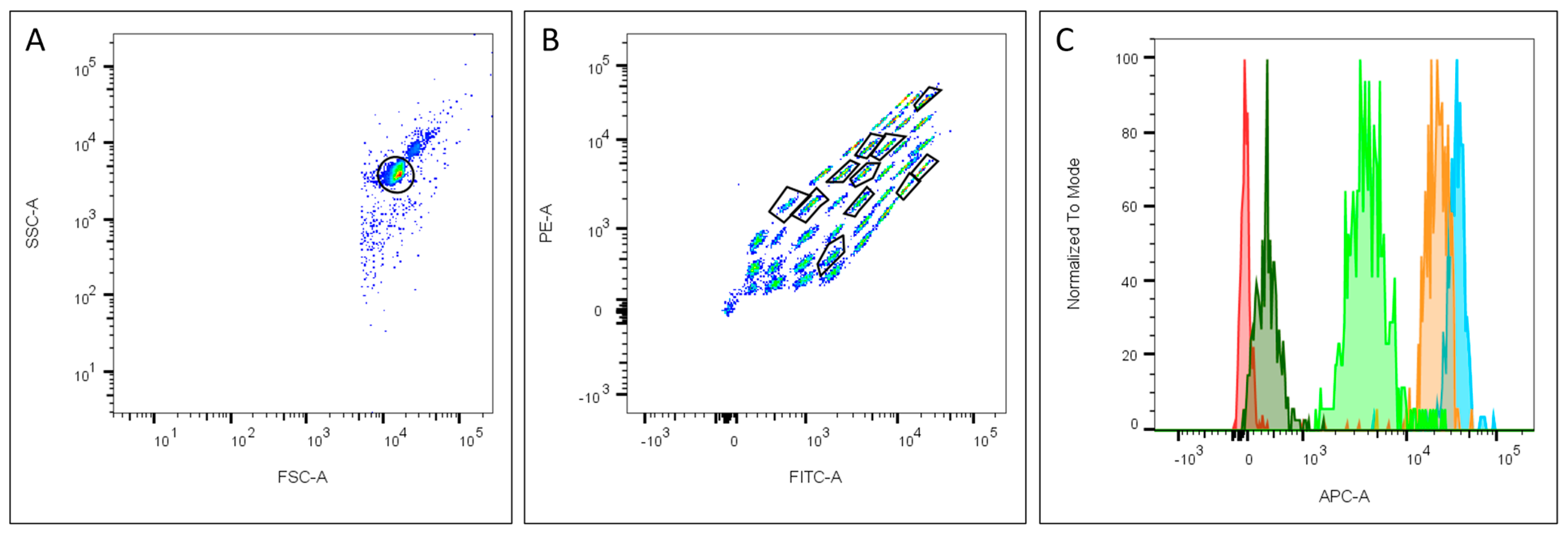
4.6. Flow Cytometry for MSC Characterisation
4.7. PBMC Isolation
4.8. PBMC Suppression Assay
4.9. Extracellular Vesicle Enrichment by Differential Ultracentrifugation
4.10. Particle Concentration
4.11. Protein Concentration
4.12. Flow Cytometry for Extracellular Vesicle Characterisation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nicola, M.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Magni, M.; Milanesi, M.; Longoni, P.D.; Matteucci, P.; Grisanti, S.; Gianni, A.M. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood 2002, 99, 3838–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, A.G.; Long, G.; Tyler, G.; Stefan, A.; Broadfoot, S.J.; Piccinini, A.M.; Middleton, J.; Kehoe, O. Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium reduces disease severity and immune responses in inflammatory arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Trapani, M.; Bassi, G.; Midolo, M.; Gatti, A.; Kamga, P.T.; Cassaro, A.; Carusone, R.; Adamo, A.; Krampera, M. Differential and transferable modulatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles on T, B and NK cell functions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordelas, L.; Schwich, E.; Dittrich, R.; Horn, P.A.; Beelen, D.W.; Börger, V.; Giebel, B.; Rebmann, V. Individual immune-modulatory capabilities of MSC-derived extracellular vesicle (EV) preparations and recipient-dependent responsiveness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, Y.; Han, J.; Yu, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Shi, C.; Duan, F. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosome. Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fattore, A.; Luciano, R.; Pascucci, L.; Goffredo, B.M.; Giorda, E.; Scapaticci, M.; Fierabracci, A.; Muraca, M. Immunoregulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles on T lymphocytes. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 2615–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Cao, L.; He, X.; Li, S.; Yang, M.; Yang, C.; Rong, P.; Yi, S.; Ghimire, K. Enhancing and stabilization of cord blood regulatory T-cell suppressive function by human mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 208, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.; Miura, Y.; Fujishiro, A.; Shindo, T.; Shimazu, Y.; Hirai, H.; Tahara, H.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Ichinohe, T.; Maekawa, T. Graft-versus-host disease amelioration by human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles is associated with peripheral preservation of naive T cell populations. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaro, E.; Carpanetto, A.; Lamorte, S.; Fusco, A.; Caorsi, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bruno, S.; Amoroso, A.; Giovarelli, M.; Porta, M. Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles modulate T cell response to islet antigen glutamic acid decarboxylase in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, A.G.; Treadwell, K.; Roach, P.; Morgan, R.; Lodge, R.; Hyland, M.; Piccinini, A.M.; Forsyth, N.R.; Kehoe, O. Therapeutic Effects of Hypoxic and Pro-Inflammatory Priming of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Inflammatory Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordelas, L.; Rebmann, V.; Ludwig, A.; Radtke, S.; Ruesing, J.; Doeppner, T.; Epple, M.; Horn, P.; Beelen, D.; Giebel, B. MSC-derived exosomes: A novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2014, 28, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, W.; El-Ansary, M.; Sabry, D.; Mostafa, M.A.; Fayad, T.; Kotb, E.; Temraz, M.; Saad, A.-N.; Essa, W.; Adel, H. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles can safely ameliorate the progression of chronic kidney diseases. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Fussenegger, M. Shedding light on extracellular vesicle biogenesis and bioengineering. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, G.V.; Lässer, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Lötvall, J. Importance of exosome depletion protocols to eliminate functional and RNA-containing extracellular vesicles from fetal bovine serum. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, D.; Frank, J.; Appl, H.; Schöffl, H.; Pfaller, W.; Gstraunthaler, G. The serum-free media interactive online database. ALTEX-Altern. Anim. Exp. 2010, 27, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bobis-Wozowicz, S.; Kmiotek, K.; Kania, K.; Karnas, E.; Labedz-Maslowska, A.; Sekula, M.; Kedracka-Krok, S.; Kolcz, J.; Boruczkowski, D.; Madeja, Z. Diverse impact of xeno-free conditions on biological and regenerative properties of hUC-MSCs and their extracellular vesicles. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.T.H.; Nguyen, L.T.; Than, U.T.T. Influences of xeno-free media on mesenchymal stem cell expansion for clinical application. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzás, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lässer, C.; Lötvall, J.; Nolte-‘t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrich, B.M.; Liang, Y.; Khosravi, P.; Federoff, H.J.; Fiandaca, M.S. Fetal bovine serum-derived extracellular vesicles persist within vesicle-depleted culture media. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Batagov, A.O.; Carter, D.R.; Krichevsky, A.M. Fetal bovine serum RNA interferes with the cell culture derived extracellular RNA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosar, J.P.; Cayota, A.; Eitan, E.; Halushka, M.K.; Witwer, K.W. Ribonucleic artefacts: Are some extracellular RNA discoveries driven by cell culture medium components? J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1272832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornilov, R.; Puhka, M.; Mannerström, B.; Hiidenmaa, H.; Peltoniemi, H.; Siljander, P.; Seppänen-Kaijansinkko, R.; Kaur, S. Efficient ultrafiltration-based protocol to deplete extracellular vesicles from fetal bovine serum. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1422674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- François, M.; Romieu-Mourez, R.; Li, M.; Galipeau, J. Human MSC suppression correlates with cytokine induction of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase and bystander M2 macrophage differentiation. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Li, Y.; Shpiruk, T.; Bhagwat, S.; Wall, D.A. Inducible indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 and programmed death ligand 1 expression as the potency marker for mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy 2018, 20, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.V.; Midge, S.; Barua, H.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, T.N.G.; Barrero, R.A.; Duan, A.; Yin, W.; Jiang, G.; Hou, Y.; et al. Bovine extracellular vesicles contaminate human extracellular vesicles produced in cell culture conditioned medium when ‘exosome-depleted serum’ is utilised. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 708, 108963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannerström, B.; Paananen, R.O.; Abu-Shahba, A.G.; Moilanen, J.; Seppänen-Kaijansinkko, R.; Kaur, S. Extracellular small non-coding RNA contaminants in fetal bovine serum and serum-free media. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighitalab, A.; Matin, M.; Khakrah, F.; Asoodeh, A.; Bahrami, A.R. Cost-effective Strategies for Depletion of Endogenous Extracellular Vesicles from Fetal Bovine Serum. J. Cell Mol. Res. 2020, 11, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Yoshizaki, K.; Nishida, H.; Kamishina, H.; Maeda, S.; Takano, K.; Fujita, N.; Nishimura, R.; Jo, J.I.; Tabata, Y.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from canine mesenchymal stromal cells in serum free culture medium have anti-inflammatory effect on microglial cells. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 633426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khasawneh, R.R.; Al Sharie, A.H.; Rub, A.-E.; Serhan, A.O.; Obeidat, H.N. Addressing the impact of different fetal bovine serum percentages on mesenchymal stem cells biological performance. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 4437–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Han, Z.-B.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, J.Z.; Li, C.T.; Xin, P.L.; Han, Z.C.; Zhu, X.P. Serum-free media and the immunoregulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells in vivo and in vitro. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrikoski, M.; Sivula, J.; Huhtala, H.; Helminen, M.; Salo, F.; Mannerström, B.; Miettinen, S. Different culture conditions modulate the immunological properties of adipose stem cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomopoulos, A.; van Deen, W.K.; Manansala, A.-R.; Lacey, P.N.; Tomakili, T.A.; Ziman, A.; Hommes, D.W. Optimization of human mesenchymal stem cell manufacturing: The effects of animal/xeno-free media. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, J.P.; Saher, O.; Hagey, D.; Mamand, D.R.; Liang, X.; Zheng, W.; Corso, G.; Gustafsson, O.; Görgens, A.; Smith, C.E. Growth media conditions influence the secretion route and release levels of engineered extracellular vesicles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lee, Y.; Johansson, H.J.; Mäger, I.; Vader, P.; Nordin, J.Z.; Wiklander, O.P.; Lehtiö, J.; Wood, M.J.; Andaloussi, S.E. Serum-free culture alters the quantity and protein composition of neuroblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coller, H.A.; Sang, L.; Roberts, J.M. A new description of cellular quiescence. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forteza-Genestra, M.A.; Antich-Rosselló, M.; Calvo, J.; Gayà, A.; Monjo, M.; Ramis, J.M. Purity determines the effect of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stromal cells. Cells 2020, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennan, C.; Garcia, J.; Roberts, S.; Hulme, C.; Wright, K. A comprehensive characterisation of large-scale expanded human bone marrow and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennan, C.; Wright, K.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Balain, B.; Richardson, J.; Roberts, S. Isolation and characterisation of mesenchymal stem cells from different regions of the human umbilical cord. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 916136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, B.E.; Amilon, K.R.; Esteves, C.L.; French, H.M.; Watson, E.; Aurich, C.; Donadeu, F.X. Isolation and characterization of equine endometrial mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, M.C.; Delavan, C.P.; Jensen, K.J.; Cantu, C.; Montgomery, R.K.; Christy, B.A.; Cap, A.P.; Bynum, J.A. A streamlined proliferation assay using mixed lymphocytes for evaluation of human mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulation activity. J. Immunol. Methods 2021, 488, 112915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deun, J.; Mestdagh, P.; Agostinis, P.; Akay, Ö.; Anand, S.; Anckaert, J.; Martinez, Z.A.; Baetens, T.; Beghein, E.; Bertier, L. EV-TRACK: Transparent reporting and centralizing knowledge in extracellular vesicle research. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 228–232. [Google Scholar]
| MSC Marker | +FBS | +dUC-FBS | +UF-FBS | −FBS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD73 | 99.85 ± 0.13 | 99.93 ± 0.15 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 99.93 ± 0.10 |
| CD90 | 99.55 ± 0.31 | 99.43 ± 0.78 | 99.95 ± 0.10 | 99.63 ± 0.49 |
| CD105 | 99.68 ± 0.47 | 99.70 ± 0.48 | 99.98 ± 0.05 | 99.78 ± 0.39 |
| CD14 | 0.81 ± 0.35 | 0.62 ± 0.31 | 1.24 ± 0.47 | 1.20 ± 0.46 |
| CD19 | 1.40 ± 0.59 | 1.26 ± 0.37 | 0.32 ± 0.15 | 1.23 ± 0.47 |
| CD34 | 0.33 ± 0.44 | 1.07 ± 0.73 | 0.84 ± 0.67 | 1.44 ± 0.44 |
| CD45 | 1.18 ± 0.62 | 1.65 ± 0.34 | 1.83 ± 0.06 | 1.38 ± 0.67 |
| HLA-DR | 0.18 ± 0.16 | 0.54 ± 0.31 | 0.07 ± 0.13 | 0.33 ± 0.30 |
| Viability | 98.45 ± 0.82 | 98.62 ± 0.80 | 98.68 ± 0.59 | 98.57 ± 0.61 |
| Media Condition | Protocol | Composition |
|---|---|---|
| +FBS | DMEM-F12 + 10% FBS + 1% P/S | |
| +dUC-FBS | FBS was centrifuged at 120,000× g for 18 h at 4 °C. The supernatant was collected, avoiding the last ½ cm of liquid to not disturb the pellet. | DMEM-F12 + 10% dUC-FBS + 1% P/S |
| +UF-FBS | FBS was loaded onto Amicon ultra-15, 100 kDa filters and spun for 3000× g for 55 min at 4 °C. The filtrate was collected. | DMEM-F12 + 10% UF-FBS + 1% P/S |
| −FBS | DMEM-F12 + 1% P/S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davies, R.; Allen, S.; Mennan, C.; Platt, M.; Wright, K.; Kehoe, O. Extracellular Vesicle Depletion Protocols of Foetal Bovine Serum Influence Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Phenotype, Immunomodulation, and Particle Release. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119242
Davies R, Allen S, Mennan C, Platt M, Wright K, Kehoe O. Extracellular Vesicle Depletion Protocols of Foetal Bovine Serum Influence Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Phenotype, Immunomodulation, and Particle Release. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119242
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavies, Rebecca, Shannen Allen, Claire Mennan, Mark Platt, Karina Wright, and Oksana Kehoe. 2023. "Extracellular Vesicle Depletion Protocols of Foetal Bovine Serum Influence Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Phenotype, Immunomodulation, and Particle Release" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119242
APA StyleDavies, R., Allen, S., Mennan, C., Platt, M., Wright, K., & Kehoe, O. (2023). Extracellular Vesicle Depletion Protocols of Foetal Bovine Serum Influence Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Phenotype, Immunomodulation, and Particle Release. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119242








