Genome-Wide Identification of the MYB and bHLH Families in Carnations and Expression Analysis at Different Floral Development Stages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of DcaMYBs and DcabHLHs
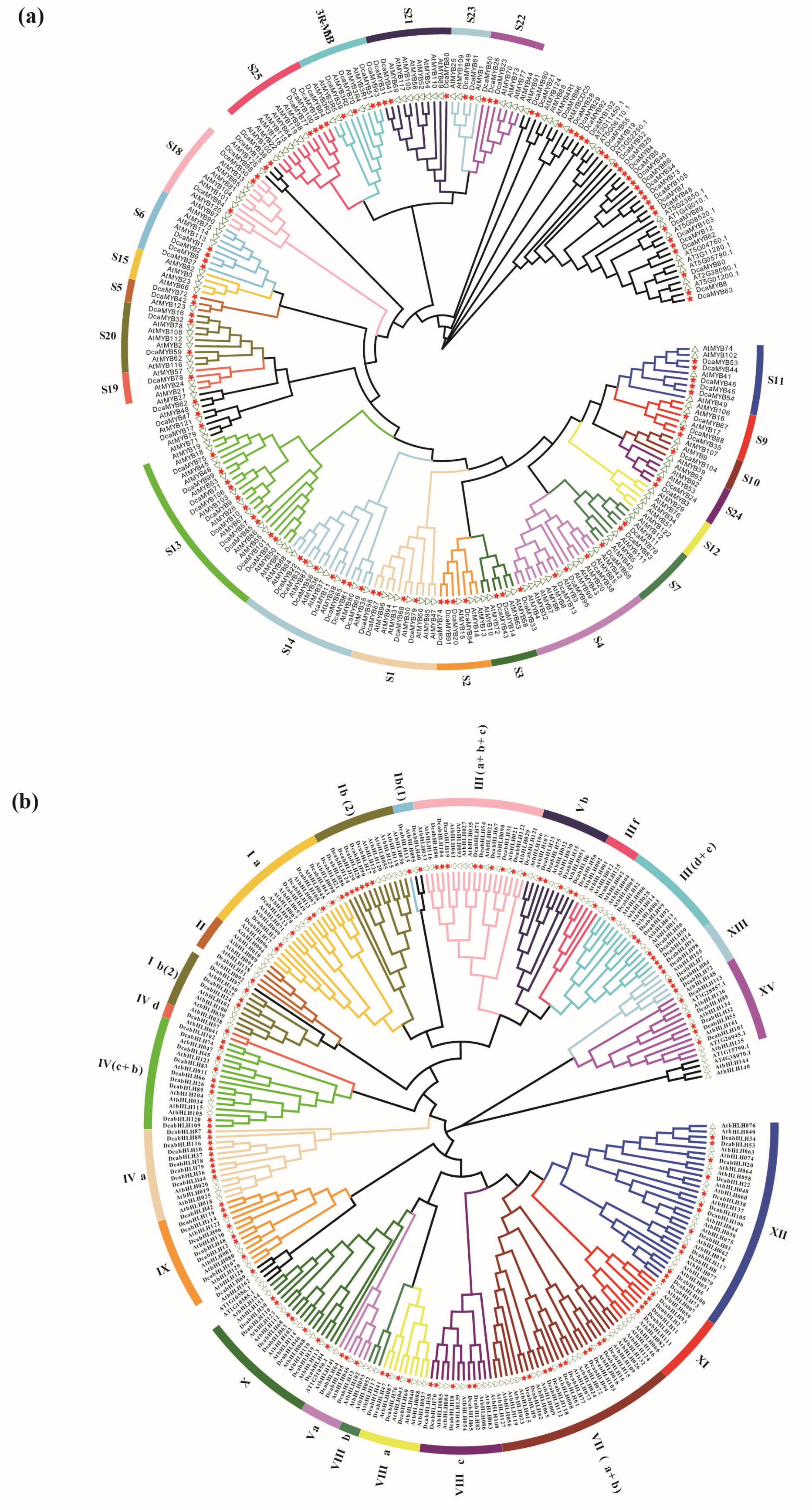
2.2. Phylogenetic Analyses of Carnation MYBs and bHLHs with A. thaliana
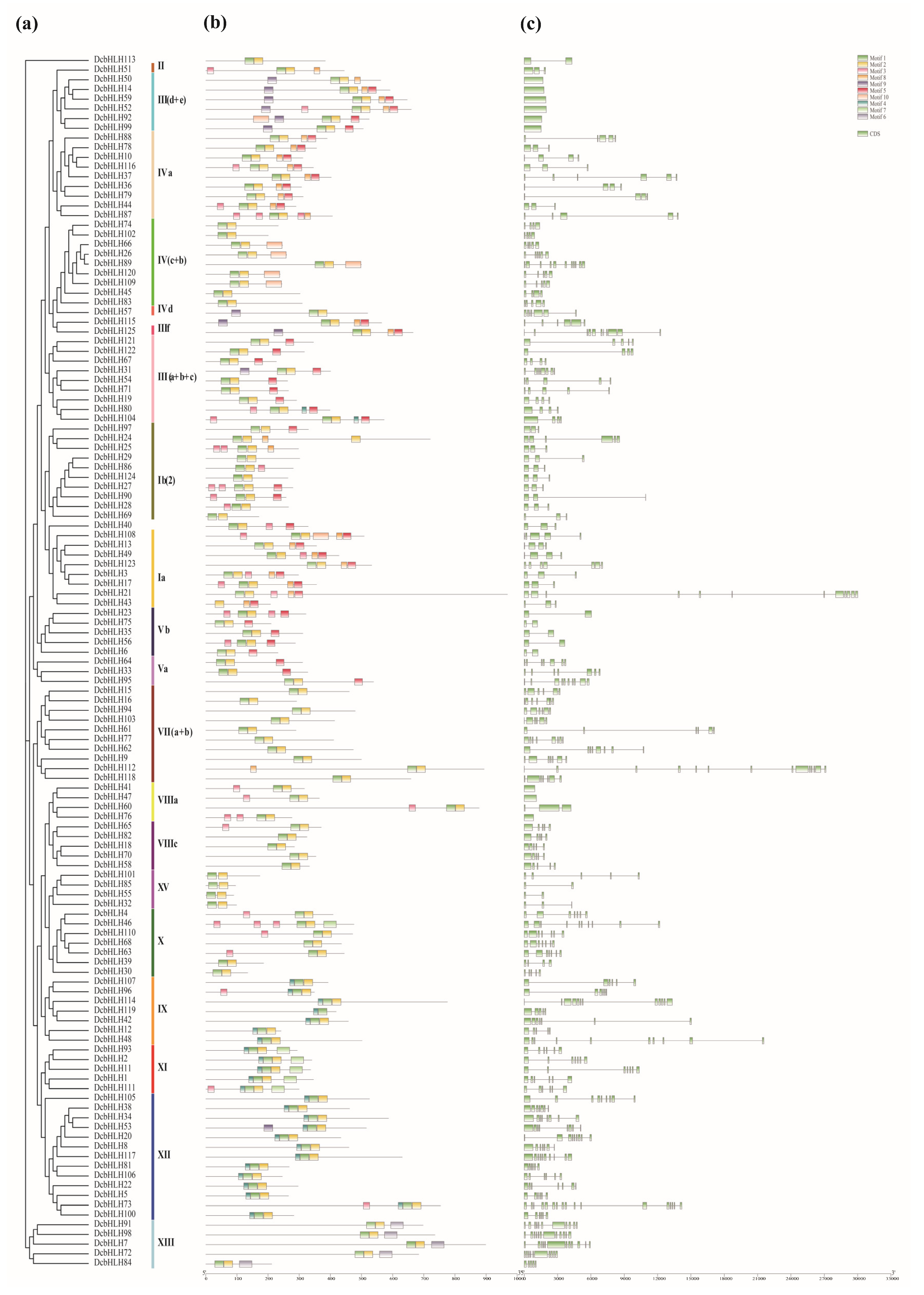
2.3. Gene Structure and Motif Analysis of DcaMYBs and DcabHLHs
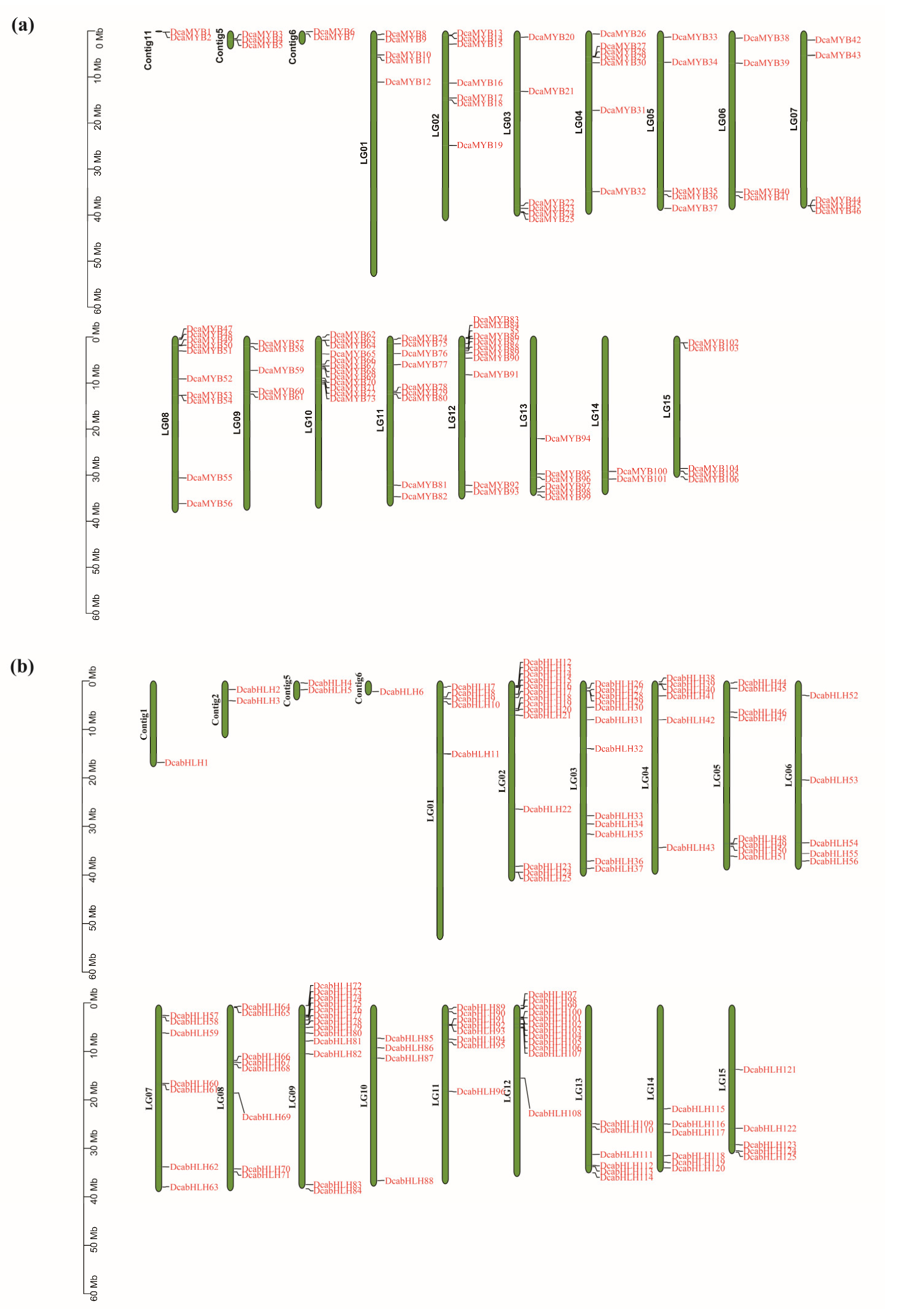
2.4. Chromosomal Locations of DcaMYBs and DcabHLHs
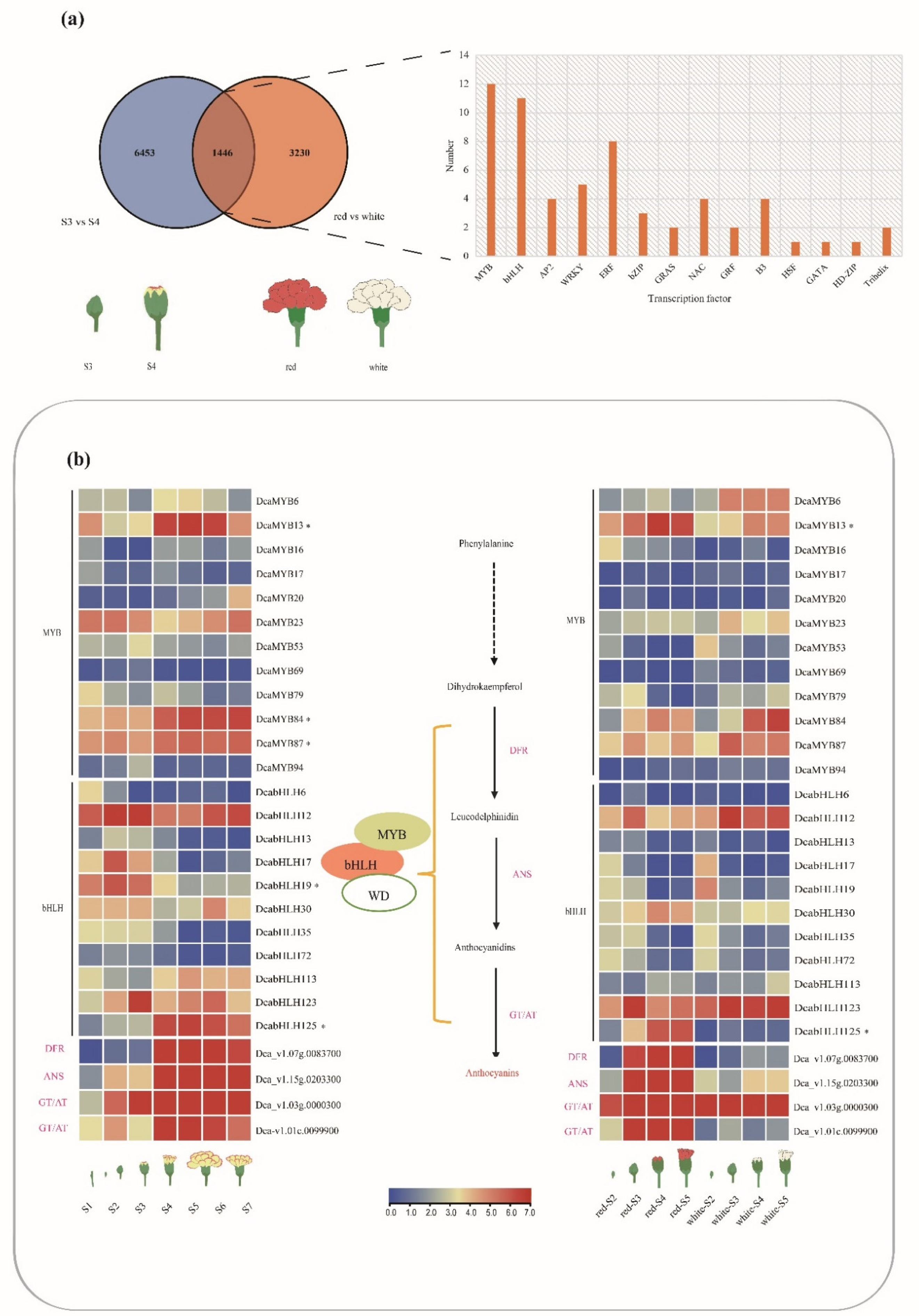
2.5. Expression Profiles of DcaMYBs and DcabHLHs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of MYB and bHLH Family Members in the Carnation Genome
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Classification of Carnation DcaMYBs and DcabHLHs
4.3. Gene Structure and Conserved Motif Analysis of DcaMYBs and DcabHLHs
4.4. Chromosomal Locations of DcaMYBs and DcabHLHs
4.5. RNA-Sequencing (RNA-seq) Data Analysis of DcaMYBs and DcabHLHs
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- İNce, A.G.; Karaca, M. Td-DAMD-PCR assays for fingerprinting of commercial carnations. Turk. J. Biol. 2015, 39, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, H.; Ando, Y.; Sugihara, H.; Narumi-Kawasaki, T.; Takamura, T.; Fukai, S. Information on Flower Coloration and Pigmentation in Current Carnation Cultivars for Use in Future Flower-color Breeding. Hortic. J. 2021, 90, 428–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, L.; Kishimoto, S.; Ohmiya, A.; Yagi, M.; Okamoto, E.; Miyahara, T.; Tsujimoto, T.; Ozeki, Y.; Uchiyama, N.; Hakamatsuka, T.; et al. Esterified carotenoids are synthesized in petals of carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus) and accumulate in differentiated chromoplasts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Ohmiya, A. Biosynthesis of plant pigments: Anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant J. 2008, 54, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M. Flower Pigments Responsible for Cyanic, Yellow, and Cream-White Coloration in Carnation. In The Carnation Genome; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwal, T.; Singh, G.; Jeandet, P.; Pandey, A.; Giri, L.; Ramola, S.; Bhatt, I.D.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Georgiev, M.I.; Clement, C.; et al. Anthocyanins, multi-functional natural products of industrial relevance: Recent biotechnological advances. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourcel, L.; Irani, N.G.; Lu, Y.; Riedl, K.; Schwartz, S.; Grotewold, E. The formation of Anthocyanic Vacuolar Inclusions in Arabidopsis thaliana and implications for the sequestration of anthocyanin pigments. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, D.; Hou, M.; Fu, G.; Tan, J.; Zhao, J.-L.; Jiang, R.; Xu, Y.; et al. The genomic and bulked segregant analysis of Curcuma alismatifolia revealed its diverse bract pigmentation. aBIOTECH 2022, 3, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, N.W.; Davies, K.M.; Lewis, D.H.; Zhang, H.; Montefiori, M.; Brendolise, C.; Boase, M.R.; Ngo, H.; Jameson, P.E.; Schwinn, K.E. A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pigmentation in eudicots. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 962–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moglia, A.; Florio, F.E.; Iacopino, S.; Guerrieri, A.; Milani, A.M.; Comino, C.; Barchi, L.; Marengo, A.; Cagliero, C.; Rubiolo, P.; et al. Identification of a new R3 MYB type repressor and functional characterization of the members of the MBW transcriptional complex involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in eggplant (S. melongena L.). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.; Brockman, A.; Aguirre, L.; Campbell, A.; Bean, A.; Cantero, A.; Gonzalez, A. Advances in the MYB-bHLH-WD Repeat (MBW) Pigment Regulatory Model: Addition of a WRKY Factor and Co-option of an Anthocyanin MYB for Betalain Regulation. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.S.; Yang, Q.Q.; Feng, K.; Xiong, A.S. Changing Carrot Color: Insertions in DcMYB7 Alter the Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis and Modification. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Dubos, C.; Lepiniec, L. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, S.; Xie, C.H.; Yuan, L. The interaction domains of the plant Myc-like bHLH transcription factors can regulate the transactivation strength. Planta 2008, 227, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Pei, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Chiang, V.L.; Sederoff, R.R.; Zhao, X. MYB-Mediated Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Dong, W.; Liu, S.; Tian, L.; Li, J.; Du, H. MYB Transcription Factors Becoming Mainstream in Plant Roots. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Vasudev, P.G. MYB transcription factors and their role in Medicinal plants. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 10995–11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L. MYB Transcription Factors as Regulators of Secondary Metabolism in Plants. Biology 2020, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zong, X.; Ren, P.; Qian, Y.; Fu, A. Basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) Transcription Factors Regulate a Wide Range of Functions in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Jalmi, S.K.; Bhagat, P.K.; Verma, N.; Sinha, A.K. A bHLH transcription factor, MYC2, imparts salt intolerance by regulating proline biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 2560–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Sun, J.; Yan, P.; Sun, Y.; Wan, P.; Ye, W.; Fan, B. DcTT8, a bHLH transcription factor, regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in Dendrobium candidum. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Ni, J.; Yin, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Bai, S.; Teng, Y. Light-Induced Basic/Helix-Loop-Helix64 Enhances Anthocyanin Biosynthesis and Undergoes CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1-Mediated Degradation in Pear. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 1684–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, L.; Gu, H.; Cheng, D.; Guo, X.; Chen, R.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Fan, X.; Chen, J. Genome-wide characterization and analysis of bHLH transcription factors related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in spine grapes (Vitis davidii). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelemen, Z.; Sebastian, A.; Xu, W.; Grain, D.; Salsac, F.; Avon, A.; Berger, N.; Tran, J.; Dubreucq, B.; Lurin, C.; et al. Analysis of the DNA-Binding Activities of the Arabidopsis R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Family by One-Hybrid Experiments in Yeast. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleindt, C.K.; Stracke, R.; Mehrtens, F.; Weisshaar, B. Expression analysis of flavonoid biosynthesis genes during Arabidopsis thaliana silique and seed development with a primary focus on the proanthocyanidin biosynthetic pathway. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepiniec, L.; Debeaujon, I.; Routaboul, J.M.; Baudry, A.; Pourcel, L.; Nesi, N.; Caboche, M. Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.; Du, L.N.; Rui, L.; Bing, H.; Su, W.B.; Qin, Y.H.; Zhao, J.T.; Wang, H.C.; Hu, G.B. Two LcbHLH Transcription Factors Interacting with LcMYB1 in Regulating Late Structural Genes of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Nicotiana and Litchi chinensis During Anthocyanin Accumulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracke, R.; Werber, M.; Weisshaar, B. The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001, 4, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.; Dolan, L. Origin and diversification of basic-helix-loop-helix proteins in plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, H.; Narumi-Kawasaki, T.; Takamura, T.; Fukai, S. Analysis of Flower Color Variation in Carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus L.) Cultivars Derived from Continuous Bud Mutations. Hortic. J. 2019, 88, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, Y.; Iijima, L.; Higuchi, K.; Miyahara, T.; Sasaki, N.; Tsujimoto, T.; Abe, Y.; Matsuba, Y.; Nishizaki, Y.; Suzuki-Wagner, A.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Carnation Flower Colors via Anthocyanin and Flavonoid Biosynthetic Pathways. In The Carnation Genome; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M.; Kosugi, S.; Hirakawa, H.; Ohmiya, A.; Tanase, K.; Harada, T.; Kishimoto, K.; Nakayama, M.; Ichimura, K.; Onozaki, T.; et al. Sequence analysis of the genome of carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus L.). DNA Res. 2014, 21, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Anwar, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, J. Impact of inorganic salts on vase life and postharvest qualities of the cut flower of Perpetual Carnation. Braz. J. Biol. 2020, 81, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onozaki, T. Breeding of carnations (Dianthus caryophyllus L.) for long vase life. Breed. Sci. 2018, 68, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Shao, D.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; et al. A MYB transcription factor containing fragment introgressed from Gossypium bickii confers pink flower on Gossypium hirsutum L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 192, 116121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchio, F.; Wing, J.F.; van der Woude, K.; Mol, J.N.; Koes, R. Analysis of bHLH and MYB domain proteins: Species-specific regulatory differences are caused by divergent evolution of target anthocyanin genes. Plant J. 1998, 13, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, A.; Machemer, K.; Braun, E.L.; Grotewold, E. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. 2011, 66, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Osbourn, A.; Ma, P. MYB Transcription Factors as Regulators of Phenylpropanoid Metabolism in Plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.P.; Wang, Z.Z. The Arabidopsis PAP1 Transcription Factor Plays an Important Role in the Enrichment of Phenolic Acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12168–12175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Zhao, M.; Leavitt, J.M.; Lloyd, A.M. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J. 2008, 53, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Putterill, J.; Stevenson, D.E.; Kutty-Amma, S.; Allan, A.C. Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J. 2007, 49, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagné, D.; Lin-Wang, K.; Espley, R.V.; Volz, R.K.; How, N.M.; Rouse, S.; Brendolise, C.; Carlisle, C.M.; Kumar, S.; Silva, N.D. An Ancient Duplication of Apple MYB Transcription Factors Is Responsible for Novel Red Fruit-Flesh Phenotypes. Am. Soc. Plant Biol. 2012, 161, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Hirochika, H. Association of VvmybA1 Gene Expression with Anthocyanin Production in Grape (Vitis vinifera) Skin-color Mutants. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2005, 74, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Hirochika, H. Retrotransposon-Induced Mutations in Grape Skin Color. Science 2004, 304, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFountain, A.M.; Yuan, Y.W. Repressors of anthocyanin biosynthesis. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, B.; Qin, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhao, J. Advance of the negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by MYB transcription factors. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, A.; De Vos, C.H.; Wein, M.; Sun, Z.; Greco, R.; Kroon, A.; Mol, J.N.; O’Connell, A.P. The strawberry FaMYB1 transcription factor suppresses anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. 2001, 28, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, K.; Qi, Y.; Lv, G.; Ren, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, F. Transcriptional Regulation of Anthocyanin Synthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR Complexes in Kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3677–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Peng, D.; Wu, Q.; Liao, X.; Xiang, K.; Wang, Z.; Tembrock, L.R.; Bendahmane, M.; Bao, M.; et al. Integrated multi-omic data and analyses reveal the pathways underlying key ornamental traits in carnation flowers. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1182–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Yang, D.-C.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Jin, J.; Gao, G. PlantRegMap: Charting functional regulatory maps in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D1104–D1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, A.; Smita, S.; Lenka, S.K.; Rajwanshi, R.; Chinnusamy, V.; Bansal, K.C. Genome-wide classification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S.; Battistuzzi, F.U. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Hu, S.; Chen, W.-H. Evolview v3: A webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totsuka, A.; Okamoto, E.; Miyahara, T.; Kouno, T.; Cano, E.A.; Sasaki, N.; Watanabe, A.; Tasaki, K.; Nishihara, M.; Ozeki, Y. Repressed expression of a gene for a basic helix-loop-helix protein causes a white flower phenotype in carnation. Breed Sci. 2018, 68, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leng, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Wu, Z. Genome-Wide Identification of the MYB and bHLH Families in Carnations and Expression Analysis at Different Floral Development Stages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119499
Leng L, Zhang X, Liu W, Wu Z. Genome-Wide Identification of the MYB and bHLH Families in Carnations and Expression Analysis at Different Floral Development Stages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119499
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeng, Luhong, Xiaoni Zhang, Weichao Liu, and Zhiqiang Wu. 2023. "Genome-Wide Identification of the MYB and bHLH Families in Carnations and Expression Analysis at Different Floral Development Stages" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119499
APA StyleLeng, L., Zhang, X., Liu, W., & Wu, Z. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification of the MYB and bHLH Families in Carnations and Expression Analysis at Different Floral Development Stages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119499






