Etiopathogenesis and Emerging Methods for Treatment of Vitiligo
Abstract
1. Introduction
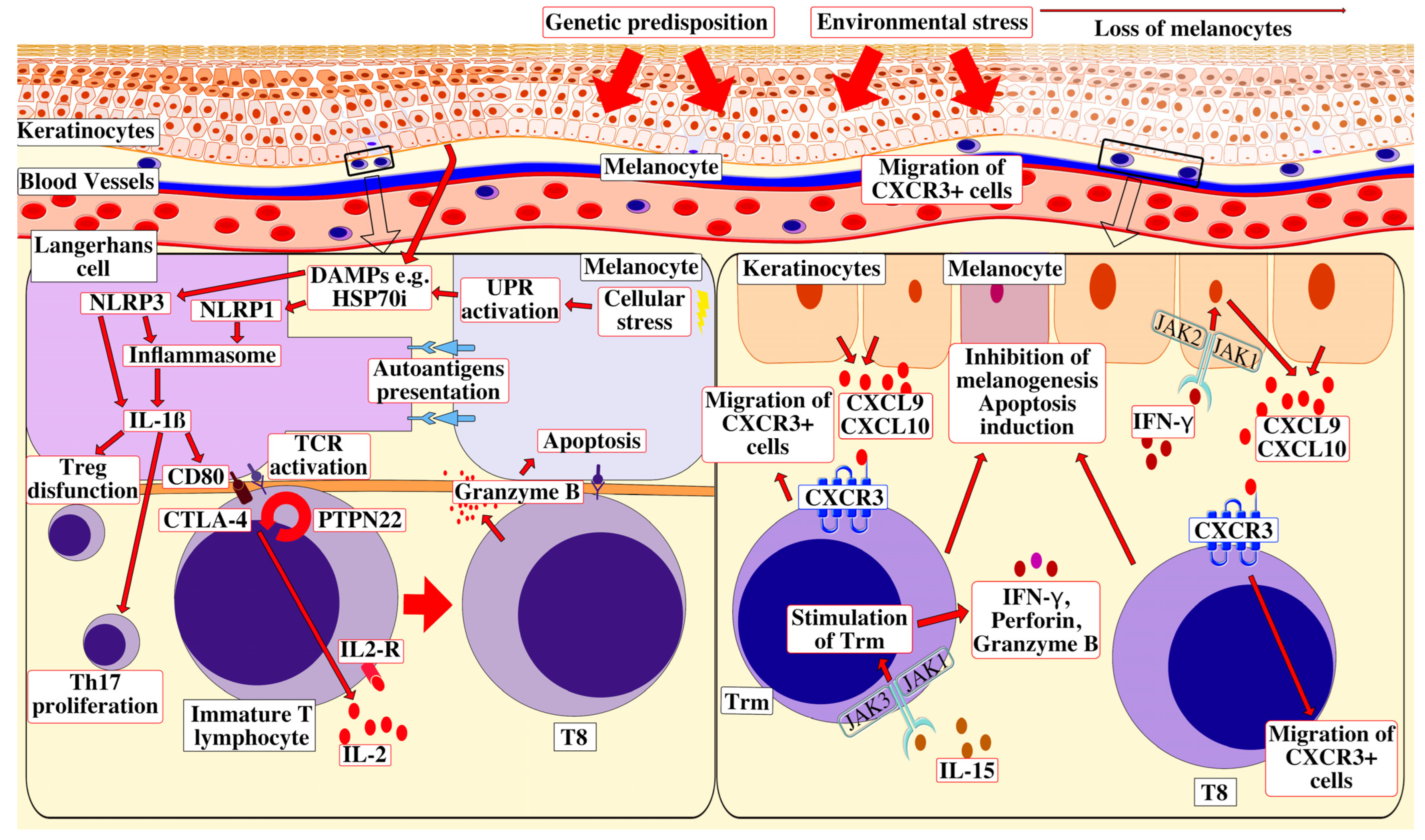
2. Etiopathogenesis
2.1. Genetics of Vitiligo
2.2. Oxidative Stress Leading to Autoimmunity
2.3. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs)
2.4. The Role of CD8+ T-Cells
2.5. The Role of Trm Cells
3. Treatment
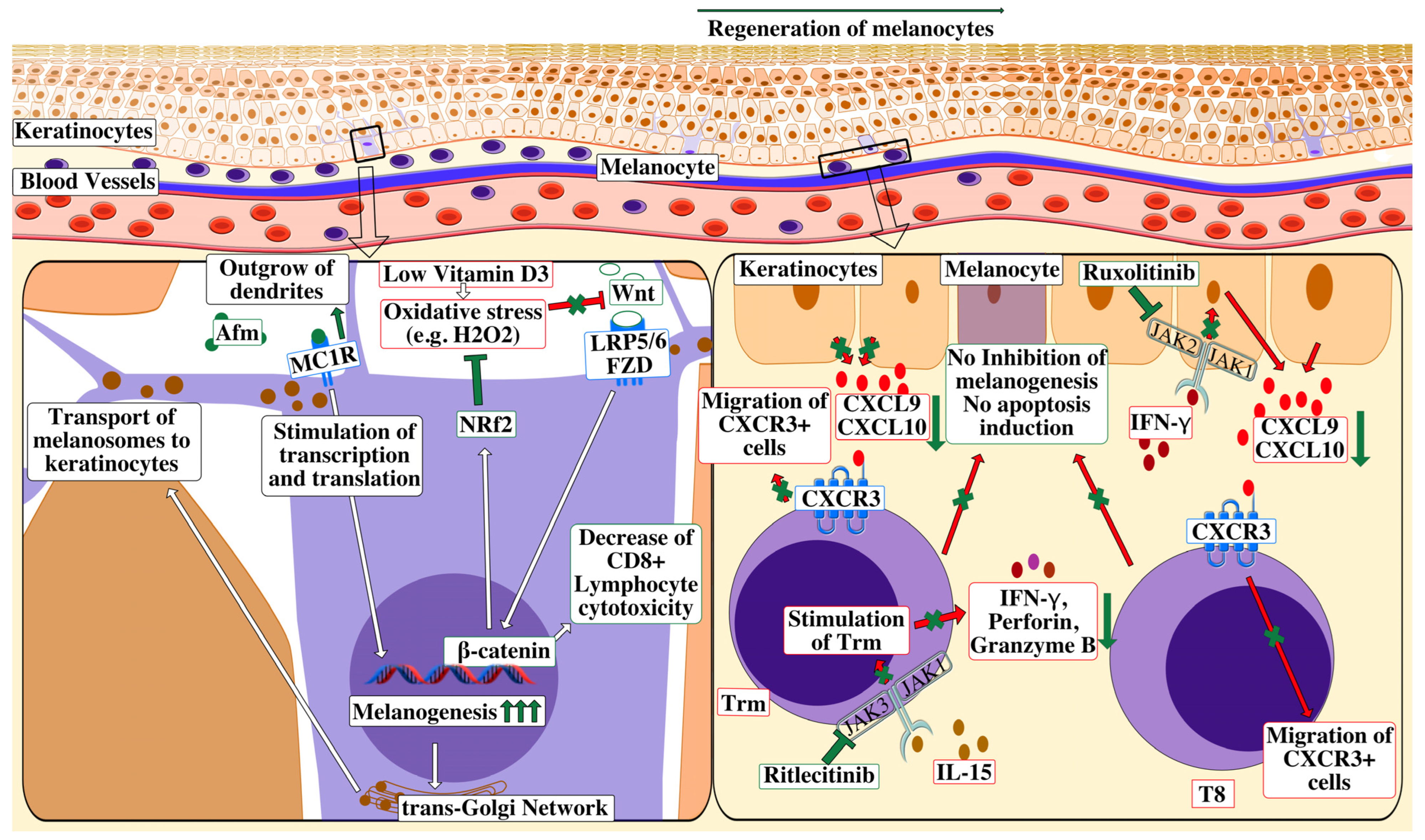
3.1. JAK Inhibitors
3.1.1. Topical Ruxolitinib
3.1.2. Oral JAK Inhibitors
3.2. Prostaglandins and Analogues
3.3. Afamelanotide
3.4. Other Potential Treatments
3.4.1. Cell-Based Therapies
3.4.2. Wnt/β-Catenin-Signaling Agonists
4. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Shi, M.; Jiang, S.; Cui, S.; Wu, Y.; Gao, X.H.; Chen, H.D. The Prevalence of Vitiligo: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanowski, T.; Szlązak, P.; Zabłotna, M.; Olszewska, B.; Sokołowska-Wojdyło, M. Translation, Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Validation of the Vitiligo-Specific Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument (VitiQoL) into Polish. Postep. Dermatologii i Alergol. 2021, 38, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linthorst Homan, M.W.; Spuls, P.I.; de Korte, J.; Bos, J.D.; Sprangers, M.A.; van der Veen, J.P.W. The Burden of Vitiligo: Patient Characteristics Associated with Quality of Life. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 61, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzes, C.; Abadie, S.; Seneschal, J.; Whitton, M.; Meurant, J.M.; Jouary, T.; Ballanger, F.; Boralevi, F.; Taieb, A.; Taieb, C.; et al. The Vitiligo Impact Patient Scale (VIPs): Development and Validation of a Vitiligo Burden Assessment Tool. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzedine, K.; Eleftheriadou, V.; Whitton, M.; Van Geel, N. Vitiligo. Lancet 2015, 386, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Wang, Q.Q.; Wu, J.Q.; Jiang, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.F.; Xiang, L.H. Increased Expression of CXCR3 and Its Ligands in Patients with Vitiligo and CXCL10 as a Potential Clinical Marker for Vitiligo. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, A.; Fain, P.R.; Thody, A.; Bennett, D.C.; Spritz, R.A. Epidemiology of Vitiligo and Associated Autoimmune Diseases in Caucasian Probands and Their Families. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, A.; Wei, X.; Ouyang, J.; Lu, L.; Chen, M.; Zhang, D. Genetic Epidemiology of Vitiligo: A Study of 815 Probands and Their Families from South China. Int. J. Dermatol. 2006, 45, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Andersen, G.; Yorgov, D.; Ferrara, T.M.; Ben, S.; Brownson, K.M.; Holland, P.J.; Birlea, S.A.; Siebert, J.; Hartmann, A.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Autoimmune Vitiligo Identify 23 New Risk Loci and Highlight Key Pathways and Regulatory Variants. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Birlea, S.A.; Fain, P.R.; Ferrara, T.M.; Ben, S.; Riccardi, S.L.; Cole, J.B.; Gowan, K.; Holland, P.J.; Bennett, D.C.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analyses Identify 13 New Susceptibility Loci for Generalized Vitiligo. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Birlea, S.A.; Fain, P.R.; Gowan, K.; Riccardi, S.L.; Holland, P.J.; Mailloux, C.M.; Sufit, A.J.D.; Hutton, S.M.; Amadi-Myers, A.; et al. Variant of TYR and Autoimmunity Susceptibility Loci in Generalized Vitiligo. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, N.; Mojamdar, M.; Ramaiah, A. In Vitro Growth Characteristics of Melanocytes Obtained from Adult Normal and Vitiligo Subjects. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1987, 88, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schallreuter, K.U.; Moore, J.; Wood, J.M.; Beazley, W.D.; Gaze, D.C.; Tobin, D.J.; Marshall, H.S.; Panske, A.; Panzig, E.; Hibberts, N.A. In Vivo and in Vitro Evidence for Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Accumulation in the Epidermis of Patients with Vitiligo and Its Successful Removal by a UVB-Activated Pseudocatalase. J. Investig. Dermatology Symp. Proc. 1999, 4, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Lian, G. ROS and Diseases: Role in Metabolism and Energy Supply. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2020, 467, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakubo, Y.; Merk, H.F.; Masaoudi, T.A.; Sieben, S.; Blomeke, B. N-Acetylation of paraphenylenediamine in human skin and keratinocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Thier, R.; Brüning, T.; Roos, P.H.; Rihs, H.P.; Golka, K.; Ko, Y.; Bolt, H.M. Markers of Genetic Susceptibility in Human Environmental Hygiene and Toxicology: The Role of Selected CYP, NAT and GST Genes. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2003, 206, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chuang, C.C.; Kandaswamy, E.; Zhou, T.; Zuo, L. Role of ROS and Nutritional Antioxidants in Human Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, S.J.; Kikuchi, D.S.; Hernandes, M.S.; Xu, Q.; Griendling, K.K. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, C. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Vitiligo: A Culprit for Melanocyte Death. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 8498472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dai, W.; Wang, S.; Kang, P.; Ye, Z.; Han, P.; Zeng, K.; Li, C. Clinical Significance of Serum Oxidative Stress Markers to Assess Disease Activity and Severity in Patients With Non-Segmental Vitiligo. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 739413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Wei, G.; Mao, H.; Liu, R.; He, Y. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Vitiligo: Igniter Fuse from Oxidative Stress to Melanocyte Loss. Redox Rep. 2022, 27, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, R.; Nillegoda, N.B.; Mayer, M.P.; Bukau, B. The Hsp70 Chaperone Network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sá, D.C.; Festa Neto, C. Inflammasomes and Dermatology. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2016, 91, 566–578. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, J.A.; Susanto, O.; Jenkins, M.R.; Lukoyanova, N.; Sutton, V.R.; Law, R.H.P.; Johnston, A.; Bird, C.H.; Bird, P.I.; Whisstock, J.C.; et al. Perforin Forms Transient Pores on the Target Cell Plasma Membrane to Facilitate Rapid Access of Granzymes during Killer Cell Attack. Blood 2013, 121, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wei, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, W.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, M. Interferon-Gamma Inhibits Melanogenesis and Induces Apoptosis in Melanocytes: A Pivotal Role of CD8+ Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes in Vitiligo. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2015, 95, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, K.; Vincenti, I.; Merkler, D. Resident-Memory T Cells in Tissue-Restricted Immune Responses: For Better or Worse? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Qiao, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Q. Effect of Narrow Band Ultraviolet B Phototherapy as Monotherapy or Combination Therapy for Vitiligo: A Meta-Analysis. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2017, 33, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Liu, F.; Gao, L. Janus Kinase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Vitiligo: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 790125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanowski, T.; Szlązak, P.; Rustowska, A.; Sokołowska-Wojdyło, M. Eficacy of Suction Blister Epidermal Grafting with Concomitant Phototherapy in Vitiligo Treatment. Postep. Dermatologii i Alergol. 2018, 35, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topham, D.J.; Reilly, E.C. Tissue-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells: From Phenotype to Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, A.G. Advances in the Treatment of Vitiligo with JAK Inhibitors. In Proceedings of the AAD Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–26 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Janus Kinase Inhibitors (JAKi)|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/referrals/janus-kinase-inhibitors-jaki (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Bosworth, T.; King, B.A.; Guttman-Yassky, E. JAK Inhibitor Safety Warnings Drawn from Rheumatologic Data May Be Misleading in Dermatology. Medscape, 18 March 2023. Available online: https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/989840 (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Rosmarin, D.; Passeron, T.; Pandya, A.G.; Grimes, P.; Harris, J.E.; Desai, S.R.; Lebwohl, M.; Ruer-Mulard, M.; Seneschal, J.; Wolkerstorfer, A.; et al. Two Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trials of Ruxolitinib Cream for Vitiligo. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzavi, I.; Rosmarin, D.; Harris, J.E.; Pandya, A.G.; Lebwohl, M.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Butler, K.; Kuo, F.I.; Sun, K.; Grimes, P. Efficacy of Ruxolitinib Cream in Vitiligo by Patient Characteristics and Affected Body Areas: Descriptive Subgroup Analyses from a Phase 2, Randomized, Double-Blind Trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosmarin, D.; Pandya, A.G.; Lebwohl, M.; Grimes, P.; Hamzavi, I.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Butler, K.; Kuo, F.; Sun, K.; Ji, T.; et al. Ruxolitinib Cream for Treatment of Vitiligo: A Randomised, Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, K.N.; Rosmarin, D. Vitiligo Treatments: Review of Current Therapeutic Modalities and JAK Inhibitors. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 24, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, A.G.; Harris, J.E.; Lebwohl, M.; Hamzavi, I.H.; Butler, K.; Kuo, F.I.; Wei, S.; Rosmarin, D. Addition of Narrow-Band UVB Phototherapy to Ruxolitinib Cream in Patients With Vitiligo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 3352–3355.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.C.; Xu, X.L.; Lou, X.F.; Du, Y.Z. Recent Progress and Future Directions: The Nano-Drug Delivery System for the Treatment of Vitiligo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3267–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boca, S.; Berce, C.; Jurj, A.; Petrushev, B.; Pop, L.; Gafencu, G.A.; Selicean, S.; Moisoiu, V.; Temian, D.; Micu, W.T.; et al. Ruxolitinib-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles for Topical Administration: An Alternative for Treating Alopecia? Med. Hypotheses 2017, 109, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruxolitinib Drug Label. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215309s001lbl.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, F.; Ding, X. Excellent Repigmentation of Generalized Vitiligo with Oral Baricitinib Combined with NB-UVB Phototherapy. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, M.; Heyes, C.; Robertson, S.J.; Varigos, G.A.; Ross, G. Oral Tofacitinib: A Promising Treatment in Atopic Dermatitis, Alopecia Areata and Vitiligo. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 42, 942–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craiglow, B.G.; King, B.A. Tofacitinib Citrate for the Treatment of Vitiligo a Pathogenesis-Directed Therapy. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komnitski, M.; Komnitski, A.; Komnitski Junior, A.; Silva de Castro, C.C. Partial Repigmentation of Vitiligo with Tofacitinib, without Exposure to Ultraviolet Radiation. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2020, 95, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.Y.; Cepica, T.; Maberry, S. Amelioration of Unstable Vitiligo and Normalization of Thryroglobulin Antibodies with Oral Tofacitinib. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 23, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Huang, X.; Ma, L.P.; Qi, F.; Wang, S.N.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wei, S.N.; Gao, L.; Liu, F. Baricitinib Is Effective in Treating Progressing Vitiligo in Vivo and in Vitro. Dose-Response 2022, 20, 15593258221105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumford, B.P.; Gibson, A.; Chong, A.H. Repigmentation of Vitiligo with Oral Baricitinib. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2020, 61, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.E.; Rashighi, M.; Nguyen, N.; Jabbari, A.; Ulerio, G.; Clynes, R.; Christiano, A.M.; Mackay-Wiggan, J. Rapid Skin Repigmentation on Oral Ruxolitinib in a Patient with Coexistent Vitiligo and Alopecia Areata (AA). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perche, P.; Purvis, C.; Pichardo, R. Refractory Alopecia Areata and Vitiligo Responding to Tofacitinib Monotherapy. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1366–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzedine, K.; Peeva, E.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Cox, L.A.; Banerjee, A.; Han, G.; Hamzavi, I.; Ganesan, A.K.; Picardo, M.; Thaçi, D.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Ritlecitinib for the Treatment of Active Nonsegmental Vitiligo: A Randomized Phase 2b Clinical Trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 88, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotallevi, F.; Gioacchini, H.; De Simoni, E.; Marani, A.; Candelora, M.; Paolinelli, M.; Molinelli, E.; Offidani, A.; Simonetti, O. Vitiligo, from Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Advances: State of the Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagui, N.A.; El-Tartoushy, S.A.; Rashed, L.A.; Elmasry, M.F. Assessment of Prostaglandin F2-Alpha (PGF2α) in Lesional and Nonlesional Skin of Vitiligo Patients. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsad, D.; Pandhi, R.; Dogra, S.; Kumar, B. Topical Prostaglandin Analog (PGE2) in Vitiligo—A Preliminary Study. In Proceedings of the International Journal of Dermatology. Int. J. Dermatol. 2002, 41, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanokrungsee, S.; Pruettivorawongse, D.; Rajatanavin, N. Clinical Outcomes of Topical Bimatoprost for Nonsegmental Facial Vitiligo: A Preliminary Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Prasad, S.; Sinha, R. Bimatoprost Ophthalmic Solution in Facial Vitiligo. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbar, T.S.; El-Ammawi, T.S.; Abdel-Rahman, A.T.; Hanna, M.R. The Effect of Latanoprost on Vitiligo: A Preliminary Comparative Study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korobko, I.V.; Lomonosov, K.M. A Pilot Comparative Study of Topical Latanoprost and Tacrolimus in Combination with Narrow-Band Ultraviolet B Phototherapy and Microneedling for the Treatment of Nonsegmental Vitiligo. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 29, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neinaa, Y.M.E.H.; Lotfy, S.S.; Ghaly, N.R.; Doghaim, N.N. A Comparative Study of Combined Microneedling and Narrowband Ultraviolet B Phototherapy versus Their Combination with Topical Latanoprost in the Treatment of Vitiligo. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanokrungsee, S.; Khunkhet, S.; Rojhirunsakool, S.; Thadvibun, K.; Sahaspot, T. Triple Combination Therapy of Narrowband Ultraviolet B, Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser and Topical Bimatoprost 0.01% for Non-Segmental Vitiligo on Non-Facial Areas: A Randomized Half-Body, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Comparative Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minder, E.I.; Barman-Aksoezen, J.; Schneider-Yin, X. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Afamelanotide and Its Clinical Use in Treating Dermatologic Disorders. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.W.; Grimes, P.E.; Agbai, O.; Hamzavi, I.; Henderson, M.; Haddican, M.; Linkner, R.V.; Lebwohl, M. Afamelanotide and Narrowband UV-B Phototherapy for the Treatment of Vitiligo a Randomized Multicenter Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, J.J.H.; Chuah, S.Y.; Jhingan, A.; Chong, W.S.; Thng, S.T.G. Afamelanotide Implants and Narrow-Band Ultraviolet B Phototherapy for the Treatment of Nonsegmental Vitiligo in Asians. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaszewska-Szostek, A.; Polak, A.; Słupecka-Ziemilska, M.; Krzyżanowska, M.; Puzianowska-Kuźnicka, M. Current Status of Cell-Based Therapies for Vitiligo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Ezzedine, K.; Hamzavi, I.; Pandya, A.G.; Harris, J.E. Current and Emerging Treatments for Vitiligo. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Meng, X.; Lin, J. The Possible Role of Wnt/Β-catenin Signaling in Vitiligo Treatment. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderweil, S.G.; Amano, S.; Ko, W.C.; Richmond, J.M.; Kelley, M.; Senna, M.M.; Pearson, A.; Chowdary, S.; Hartigan, C.; Barton, B.; et al. A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase-II Clinical Trial to Evaluate Oral Simvastatin as a Treatment for Vitiligo. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 150–151.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, E.S.E.; Allam, S.H.; Mabrouk, M.M.; Elgharbawy, N.M.; Salaam, S.F.A. Simvastatin and Non-Segmental Vitiligo: A New Potential Treatment Option? Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Lu, Y. Advances in Vitiligo: Update on Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 986918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migayron, L.; Boniface, K.; Seneschal, J. Vitiligo, From Physiopathology to Emerging Treatments: A Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 10, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frączek, A.; Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Placek, W. The Role of TRM Cells in the Pathogenesis of Vitiligo—A Review of the Current State-of-the-Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.; Charlton, O.; Smith, S.D. New Onset Vitiligo in a Patient with Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treated with Adalimumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luber, R.P.; Chamberlain, A.J.; Sparrow, M.P. New Onset Vitiligo Following Commencement of Infliximab in Crohn Disease. Intern. Med. J. 2017, 47, 972–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méry-Bossard, L.; Bagny, K.; Chaby, G.; Khemis, A.; Maccari, F.; Marotte, H.; Perrot, J.L.; Reguiai, Z.; Sigal, M.L.; Avenel-Audran, M.; et al. New-Onset Vitiligo and Progression of Pre-Existing Vitiligo during Treatment with Biological Agents in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiong, X.; He, Y.; Xu, J. Role of HMGB1 in Vitiligo: Current Perceptions and Future Perspectives. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellei, B.; Migliano, E.; Picardo, M. Therapeutic potential of adipose tissue-derivatives in modern dermatology. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 12, 1837–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwanowski, T.; Kołkowski, K.; Nowicki, R.J.; Sokołowska-Wojdyło, M. Etiopathogenesis and Emerging Methods for Treatment of Vitiligo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119749
Iwanowski T, Kołkowski K, Nowicki RJ, Sokołowska-Wojdyło M. Etiopathogenesis and Emerging Methods for Treatment of Vitiligo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119749
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwanowski, Tomasz, Karol Kołkowski, Roman Janusz Nowicki, and Małgorzata Sokołowska-Wojdyło. 2023. "Etiopathogenesis and Emerging Methods for Treatment of Vitiligo" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119749
APA StyleIwanowski, T., Kołkowski, K., Nowicki, R. J., & Sokołowska-Wojdyło, M. (2023). Etiopathogenesis and Emerging Methods for Treatment of Vitiligo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119749






