Anti-Islet Autoantibodies in Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
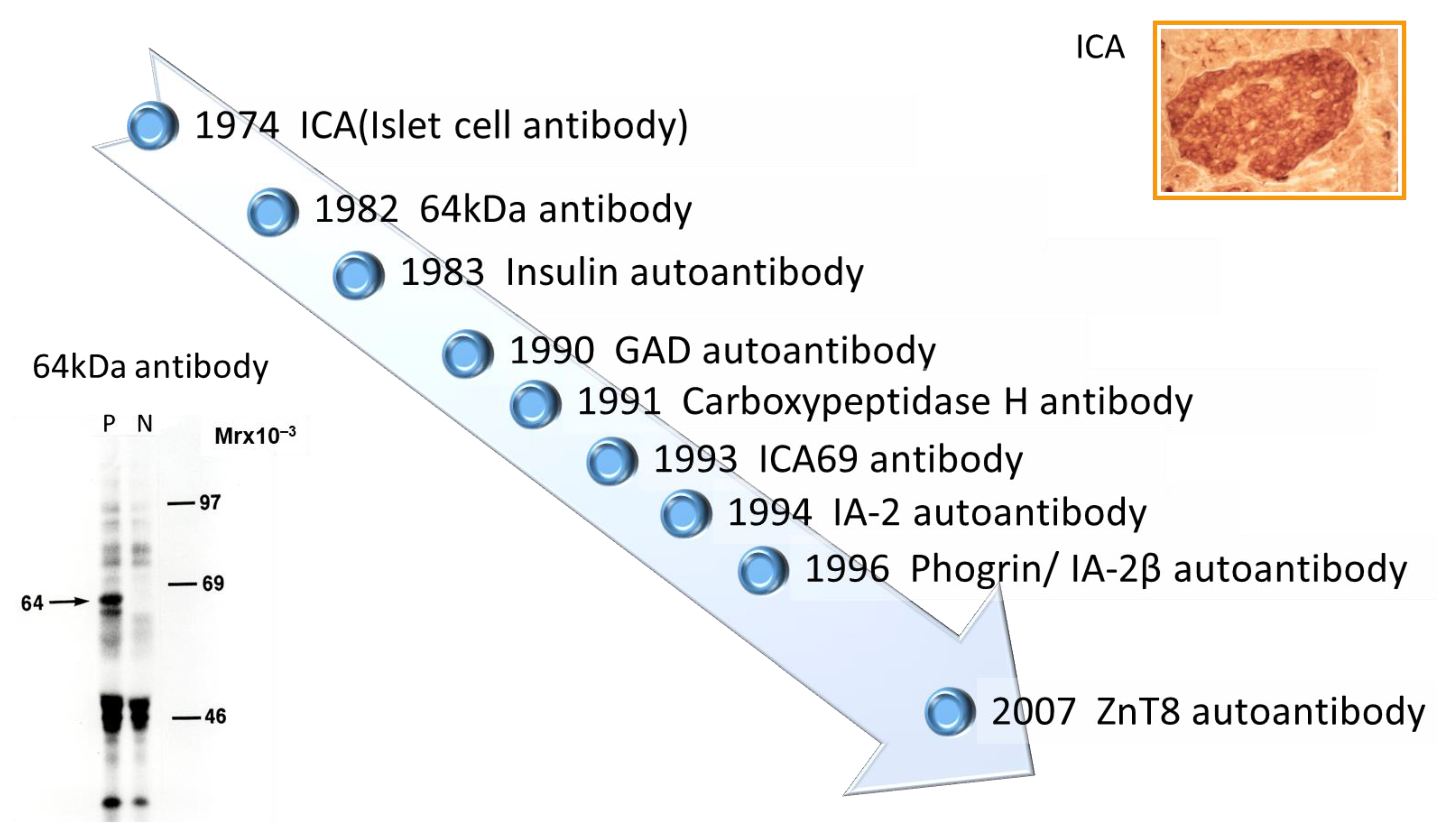
2. History of Anti-Islet Autoantibody Discovery
3. Pathophysiology of the Generation of Anti-Islet Autoantibodies
4. Localization and Function of Autoantigens against Anti-Islet Autoantibodies
- (1)
- Insulin
- (2)
- GAD 65 and GAD67
- (3)
- IA-2 and IA-2β/phogrin
- (4)
- ZnT8
- (5)
- Carboxypeptidase H
- (6)
- ICA69
- (7)
- GM2-1 ganglioside
- (8)
- Heat shock protein 60
- (9)
- GLUT2
- (10)
- Tetraspanin-7
- (11)
- ICA12/SOX13
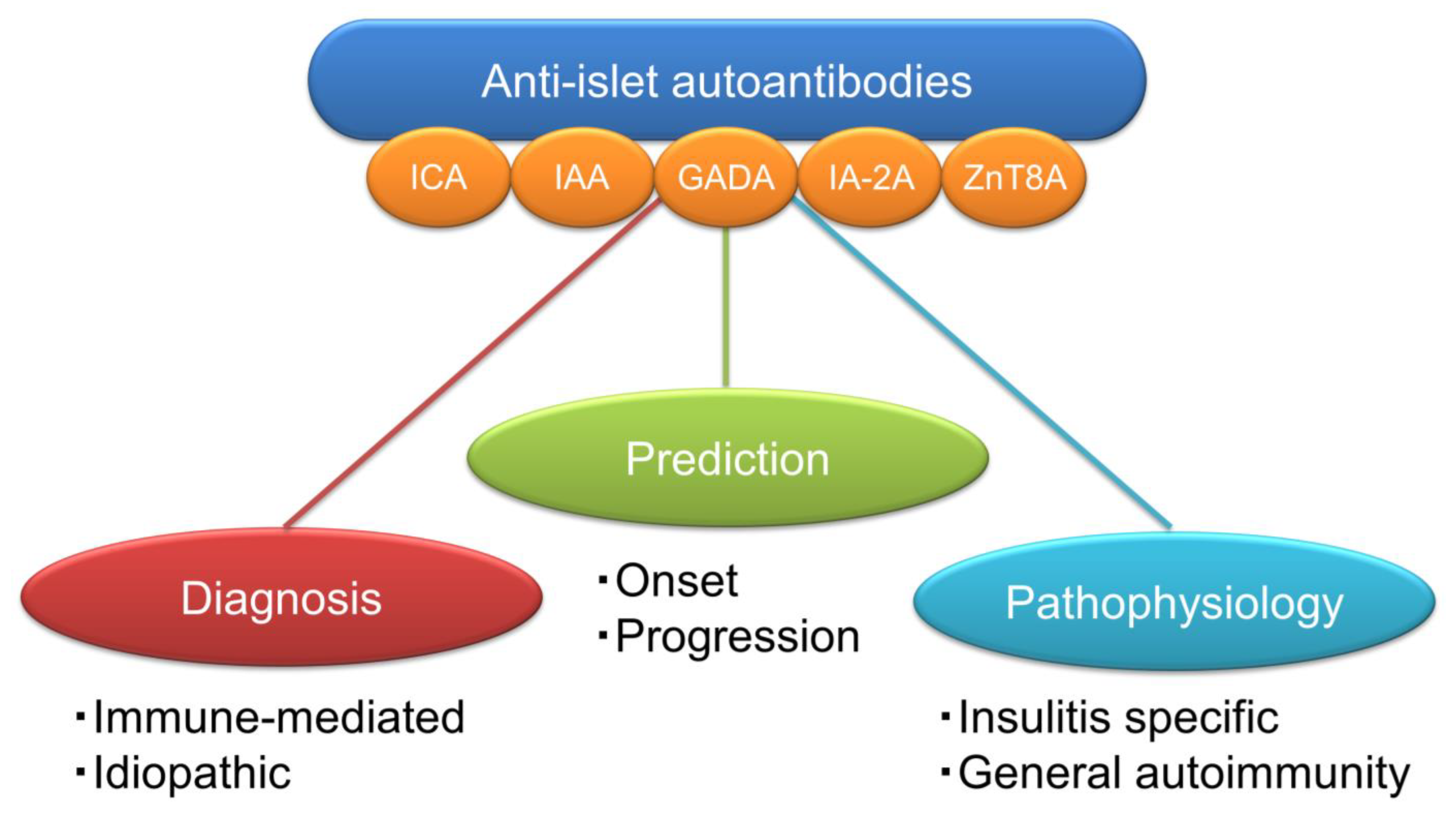
5. Significance of Anti-Islet Autoantibodies in the Pathophysiology of T1D
6. Role of Anti-Islet Autoantibodies in the Diagnosis of T1D
7. Epitopes for Anti-Islet Autoantibodies and Their Clinical Relevance
7.1. Insulin Autoantibodies
7.2. GAD Autoantibodies
7.3. IA-2 Autoantibodies
7.4. ZnT8 Autoantibodies
7.5. Other Anti-Islet Autoantibodies
8. Prediction of Future Insulin Deficiency in Patients with SPIDDM (LADA)
9. Type 1 Diabetes and Associated Autoimmune Diseases
10. Recent Advances in Anti-Islet Autoantibody Assay
11. Anti-Islet Autoantibodies in Trials of Novel Therapeutic Approaches for the Preservation of β-Cell Function
12. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| AITD | autoimmune thyroid disease |
| APS3v | autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 3 variant |
| ECL | electrochemiluminescence |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| HSP | heat shock protein |
| GAD | glutamic acid decarboxylase |
| IA-2 | tyrosine phosphatase-like protein IA-2 |
| IAA | insulin autoantibodies |
| ICA | islet cell antibodies |
| ICA12 | islet cell antigen 12 |
| JDRF | Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation |
| JM | juxta-membrane |
| LADA | latent-autoimmune diabetes in adults |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex |
| NOD | non-obese diabetic |
| PTP | protein tyrosine phosphatase |
| RBA | radio-ligand binding assay |
| RIA | radioimmunoassay |
| SOX13 | sex-determining region-type high mobility group box 13 |
| SPIDDM | slowly progressive type 1 diabetes |
| T1D | type 1 diabetes |
| T2D | type 2 diabetes |
| UKPDS | United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study |
| ZnT8 | zinc transporter 8 |
References
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46 (Suppl. S1), S19–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roep, B.O.; Thomaidou, S.; van Tienhoven, R.; Zaldumbide, A. Type 1 diabetes mellitus as a disease of the β-cell (do not blame the immune system?). Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvonen, M.; Viik-Kajander, M.; Moltchanova, E.; Libman, I.; LaPorte, R.; Tuomilehto, J. Incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes worldwide. Diabetes Mondiale (DiaMond) Project Group. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, E.; Matsuura, N.; Eguchi, K. Type 1 diabetes in Japan. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottazzo, G.F.; Florin-Christensen, A.; Doniach, D. Islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. Lancet 1974, 2, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baekkeskov, S.; Nielsen, J.H.; Marner, B.; Bilde, T.; Ludvigsson, J.; Lernmark, Å. Autoantibodies in newly diagnosed diabetic children immunoprecipitate human pancreatic islet cell proteins. Nature 1982, 298, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.P.; Asplin, C.M.; Clemons, P.; Lyen, K.; Tatpati, O.; Raghu, P.K.; Paquette, T.L. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science 1983, 222, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baekkeskov, S.; Aanstoot, H.J.; Christgau, S.; Reetz, A.; Solimena, M.; Cascalho, M.; Folli, F.; Richter-Olesen, H.; De Camilli, P. Identification of the 64 K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature 1990, 347, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, M.S.; Lu, J.; Goto, Y.; Notkins, A.L. Molecular cloning and identification of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, IA-2, from human insulinoma. DNA Cell. Biol. 1994, 13, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzlau, J.M.; Juhl, K.; Yu, L.; Moua, O.; Sarkar, S.A.; Gottlieb, P.; Rewers, M.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Jensen, J.; Davidson, H.W.; et al. The cation efflux transporter ZnT8 (Slc30A8) is a major autoantigen in human type 1 diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17040–17045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christgau, S.; Schierbeck, H.; Aanstoot, H.J.; Aagaard, L.; Begley, K.; Kofod, H.; Hejnaes, K.; Baekkeskov, S. Pancreatic beta cells express two autoantigenic forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase, a 65-kDa hydrophilic form and a 64-kDa amphiphilic form which can be both membrane-bound and soluble. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 21257–21264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harashima, S.; Clark, A.; Christie, M.R.; Notkins, A.L. The dense core transmembrane vesicle protein IA-2 is a regulator of vesicle number and insulin secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8704–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, E.; Hutton, J.C.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase homologue, phogrin, an autoantigen of type 1 diabetes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 227, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Hirai, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, M.; Takahashi, N.; Kasai, H.; Satin, L.S.; Leapman, R.D.; Notkins, A.L. Deletion of IA-2 and/or IA-2β in mice decreases insulin secretion by reducing the number of dense core vesicles. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2347–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Diosdado, M.; Parkinson, D.; Corbett, J.A.; Kwon, G.; Marshall, C.A.; Gingerich, R.L.; Santiago, J.V.; McDaniel, M.L. Potential autoantigens in IDDM. Expression of carboxypeptidase-H and insulin but not glutamate decarboxylase on the β-cell surface. Diabetes 1994, 43, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzenberger, F.; Pietropaolo, S.; Verkade, P.; Habermann, B.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Mziaut, H.; Pietropaolo, M.; Solimena, M. Islet cell autoantigen of 69 kDa is an arfaptin-related protein associated with the Golgi complex of insulinoma INS-1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26166–26173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, O.P.; Lehtovirta, M.; Hastoy, B.; Chandra, V.; Krentz, N.A.J.; Kleiner, S.; Jain, D.; Richard, A.M.; Abaitua, F.; Beer, N.L.; et al. Loss of ZnT8 function protects against diabetes by enhanced insulin secretion. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1596–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, T.J.; Bellomo, E.A.; Wijesekara, N.; Loder, M.K.; Baldwin, J.M.; Gyulkhandanyan, A.V.; Koshkin, V.; Tarasov, A.I.; Carzaniga, R.; Kronenberger, K.; et al. Insulin storage and glucose homeostasis in mice null for the granule zinc transporter ZnT8 and studies of the type 2 diabetes-associated variants. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2070–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotta, F.; Previti, M.; Neerman-Arbez, M.; Dionisi, S.; Cucinotta, D.; Lenti, L.; Di Mario, U.; Halban, P.A. The GM2-1 ganglioside islet autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is expressed in secretory granules and is not β-cell specific. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, Y.; Kasuga, A.; Nomaguchi, H.; Maruyama, T.; Kasatani, T.; Shimada, A.; Takei, I.; Miyazaki, J.; Saruta, T. Detection of autoantibodies to the pancreatic islet heat shock protein 60 in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Autoimmun. 1996, 9, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, L.R.; McAllister, C.T.; Chen, L.; Hughes, S.; Newgard, C.B.; Kettman, J.R.; Unger, R.H.; Johnson, J.H. Autoantibodies to the GLUT-2 glucose transporter of β cells in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus of recent onset. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, D.; Eugster, A.; Jergens, S.; Gavrisan, A.; Weinzierl, C.; Telieps, T.; Winkler, C.; Ziegler, A.G.; Bonifacio, E. Tetraspanin 7 autoantibodies in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasimiotis, H.; Myers, M.A.; Argentaro, A.; Mertin, S.; Fida, S.; Ferraro, T.; Olsson, J.; Rowley, M.J.; Harley, V.R. Sex-determining region Y-related protein SOX13 is a diabetes autoantigen expressed in pancreatic islets. Diabetes 2000, 49, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fousteri, G.; Ippolitoa, E.; Ahmedb, R.; Hamad, A.R.A. Beta-cell specific autoantibodies: Are they just an indicator of type 1 diabetes? Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2017, 13, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallone, R.; Brezar, V. To B or not to B: (anti)bodies of evidence on the crime scene of type 1 diabetes? Diabetes 2011, 60, 2020–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.I.; Smith, J.; Kissack, M.R.; Hogg, K.G.; Green, E.A. Thymic B cell-mediated attack of thymic stroma precedes type 1 diabetes development. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, R.A.; Dunne, J.L.; Atkinson, M.A.; Chiang, J.L.; Dabelea, D.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Herold, K.C.; Krischer, J.P.; Lernmark, Å.; et al. Staging presymptomatic type 1 diabetes: A scientific statement of JDRF, the Endocrine Society, and the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1964–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, A.G.; Rewers, M.; Simell, O.; Simell, T.; Lempainen, J.; Steck, A.; Winkler, C.; Ilonen, J.; Veijola, R.; Knip, M.; et al. Seroconversion to multiple islet autoantibodies and risk of progression to diabetes in children. JAMA 2013, 309, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krischer, J.P. Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Study Group. The use of intermediate endpoints in the design of type 1 diabetes prevention trials. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verge, C.F.; Gianani, R.; Kawasaki, E.; Yu, L.; Pietropaolo, M.; Jackson, R.A.; Chase, H.P.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Prediction of type 1 diabetes in first-degree relatives using a combination of insulin, GAD, and ICA512bdc/IA-2 autoantibodies. Diabetes 1996, 45, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Rewers, M.; Gianani, R.; Kawasaki, E.; Zhang, Y.; Verge, C.; Chase, P.; Klingensmith, G.; Erlich, H.; Norris, J.; et al. Antiislet autoantibodies usually develop sequentially rather than simultaneously. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 4264–4267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Kawasaki, E.; Abiru, N.; Jo, O.; Fukushima, K.; Satoh, T.; Kuriya, G.; Kobayashi, M.; Kuwahara, H.; Yamasaki, H.; et al. Trajectories of anti-islet autoantibodies before development of type 1 diabetes in interferon-treated hepatitis C patients. Case reports and a literature review. Endocr. J. 2010, 57, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E.; Yu, L.; Rewers, M.J.; Hutton, J.C.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Definition of multiple ICA512/phogrin autoantibody epitopes and detection of intramolecular epitope spreading in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 1998, 47, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E.; Yasui, J.; Tsurumaru, M.; Takashima, H.; Ikeoka, T.; Mori, F.; Akazawa, S.; Ueki, I.; Kobayashi, M.; Kuwahara, H.; et al. Sequential elevation of autoantibodies to thyroglobulin and glutamic acid decarboxylase in type 1 diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2013, 4, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, E.; Nakamura, K.; Kuriya, G.; Satoh, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kuwahara, H.; Abiru, N.; Yamasaki, H.; Matsuura, N.; Miura, J.; et al. Differences in the humoral autoreactivity to zinc transporter 8 between childhood- and adult-onset type 1 diabetes in Japanese patients. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 138, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achenbach, P.; Lampasona, V.; Landherr, U.; Koczwara, K.; Krause, S.; Grallert, H.; Winkler, C.; Pflüger, M.; Illig, T.; Bonifacio, E.; et al. Autoantibodies to zinc transporter 8 and SLC30A8 genotype stratify type 1 diabetes risk. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzlau, J.M.; Frisch, L.M.; Hutton, J.C.; Fain, P.R.; Davidson, H.W. Changes in zinc transporter 8 autoantibodies following type 1 diabetes onset: The type 1 diabetes genetics consortium autoantibody workshop. Diabetes Care 2015, 38 (Suppl. S2), S14–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, I.; Weets, I.; Asanghanwa, M.; Ruige, J.; Van Gaal, L.; Mathieu, C.; Keymeulen, B.; Lampasona, V.; Wenzlau, J.M.; Hutton, J.C.; et al. Contribution of antibodies against IA-2β and zinc transporter 8 to classification of diabetes diagnosed under 40 years of age. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño, L.; Ziegler, A.G.; Ziegler, R.; Shoelson, S.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Characterization of insulin autoantibodies in relatives of patients with type I diabetes. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoa, C.J.; Crowther, N.J.; Thomas, J.W.; Hall, T.R.; Bekris, L.M.; Torn, C.; Landin-Olsson, M.; Ortqvist, E.; Palmer, J.P.; Lernmark, A.; et al. Epitope analysis of insulin autoantibodies using recombinant Fab. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 140, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.R.; Thomas, J.W.; Padoa, C.J.; Torn, C.; Landin-Olsson, M.; Ortqvist, E.; Hampe, C.S. Longitudinal epitope analysis of insulin-binding antibodies in type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 146, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devendra, D.; Galloway, T.S.; Horton, S.J.; Evenden, A.; Keller, U.; Wilkin, T.J. The use of phage display to distinguish insulin autoantibody (IAA) from insulin antibody (IA) idiotypes. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tree, T.I.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Duhindan, N.; Hicks, K.E.; Madec, A.M.; Scherbaum, W.A.; Banga, J.P. Two amino acids in glutamic acid decarboxylase act in concert for maintenance of conformational determinants recognised by type 1 diabetic autoantibodies. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E.; Yano, M.; Abiru, N.; Akazawa, S.; Nagataki, S. Detection of recombinant GAD65 and GAD67 antibodies using a simple radioimmunoassay. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1996, 32, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakrishnan, B.; Hoke, D.E.; Langendorf, C.G.; Buckle, A.M.; Rowley, M.J. An analysis of the cross-reactivity of autoantibodies to GAD65 and GAD67 in diabetes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daw, K.; Powers, A.C. Two distinct glutamic acid decarboxylase auto-antibody specificities in IDDM target different epitopes. Diabetes 1995, 44, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampe, C.S.; Hammerle, L.P.; Bekris, L.; Ortqvist, E.; Kockum, I.; Rolandsson, O.; Landin-Olsson, M.; Törn, C.; Persson, B.; Lernmark, A. Recognition of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) by autoantibodies from different GAD antibody-positive phenotypes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 4671–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, E.; Abiru, N.; Ide, A.; Sun, F.; Fukushima, T.; Takahashi, R.; Kuwahara, H.; Fujita, N.; Kita, A.; Oshima, K.; et al. Epitope analysis of GAD65 autoantibodies in Japanese patients with autoimmune diabetes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1005, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, M.; Banga, J.P.; Madec, A.M.; Binder, K.A.; Strebelow, M.; Rjasanowski, I.; Wassmuth, R.; Gilliam, L.K.; Luo, D.; Hampe, C.S. Dynamic changes of GAD65 autoantibody epitope specificities in individuals at risk of developing type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, D.U.; Pleasic, S.M.; Palmer-Crocker, R.; Shapiro, J.A. Cloning and expression of IDDM-specific human autoantigens. Diabetes 1992, 41, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E.; Yu, L.; Gianani, R.; Verge, C.F.; Babu, S.; Bonifacio, E.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Evaluation of islet cell antigen (ICA) 512/IA-2 autoantibody radioassays using overlapping ICA512/IA-2 constructs. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Calado, M.; James, E.A.; Morran, M.P.; Pietropaolo, S.L.; Ouyang, Q.; Arribas-Layton, D.; Songini, M.; Liguori, M.; Casu, A.; Auchus, R.J.; et al. Identification of unique antigenic determinants in the amino terminus of IA-2 (ICA512) in childhood and adult autoimmune diabetes: New biomarker development. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, E.; Sera, Y.; Fujita, N.; Yamauchi, M.; Ozaki, M.; Abe, T.; Yamakawa, K.; Uotani, S.; Takino, H.; Yamasaki, H.; et al. Association between IA-2 autoantibody epitope specificities and age of onset in Japanese patients with autoimmune diabetes. J. Autoimmun. 2001, 17, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sladek, R.; Rocheleau, G.; Rung, J.; Dina, C.; Shen, L.; Serre, D.; Boutin, P.; Vincent, D.; Belisle, A.; Hadjadj, S.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 2007, 445, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzlau, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Moua, O.; Fowler, K.T.; Rangasamy, S.; Walters, J.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Davidson, H.W.; Hutton, J.C. A common nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphism in the SLC30A8 gene determines ZnT8 autoantibody specificity in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2693–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E.; Uga, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kuriya, G.; Satoh, T.; Fujishima, K.; Ozaki, M.; Abiru, N.; Yamasaki, H.; Wenzlau, J.M.; et al. Association between anti-ZnT8 autoantibody specificities and SLC30A8 Arg325Trp variant in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 2299–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzlau, J.M.; Frisch, L.M.; Hutton, J.C.; Davidson, H.W. Mapping of conformational autoantibody epitopes in ZnT8. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, L.; Cervenak, L.; Oroszlán, M.; Prohászka, Z.; Uray, K.; Hudecz, F.; Baranyi, E.; Madácsy, L.; Singh, M.; Romics, L.; et al. Antibodies against different epitopes of heat-shock protein 60 in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Immunol. Lett. 2002, 80, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, A.; Kraus, G.; Lidzba, V.; Müller, D.; Jolink, M.; Ziegler, A.G.; Bonifacio, E. Cytoplasmic ends of tetraspanin 7 harbour epitopes recognised by autoantibodies in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, R.; Tuomi, T.; Mauricio, D.; Pietropaolo, M.; Zhou, Z.; Pozzilli, P.; Leslie, R.D. Management of latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: A consensus statement from an international expert panel. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A.; Kawasaki, E.; Abiru, N.; Awata, T.; Oikawa, Y.; Osawa, H.; Kajio, H.; Ozawa, J.; Takahashi, K.; Chujo, D.; et al. New diagnostic criteria (2023) of slowly progressive type 1 diabetes (SPIDDM) -Report from Committee of type 1 diabetes in Japan Diabetes Society. J. Japan Diab. Soc. 2023. in press. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga, A.; Maruyama, T.; Nakamoto, S.; Ozawa, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Saruta, T. High-titer autoantibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase plus autoantibodies against insulin and IA-2 predicts insulin requirement in adult diabetic patients. J. Autoimmun. 1999, 12, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takino, H.; Yamasaki, H.; Abiru, N.; Sera, Y.; Abe, T.; Kawasaki, E.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Eguchi, K.; Kanazawa, Y.; Nagataki, S. Antibodies to GAD in Japanese patients classified as Type 2 diabetes at diagnosis. High titre of GADAb is a predictive marker for early insulin treatment--report of west Japan (Kyushu, Yamaguchi, Osaka) study for GAD Ab(+) diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2002, 19, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, E.; Nakamura, K.; Kuriya, G.; Satoh, T.; Kuwahara, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Abiru, N.; Yamasaki, H.; Eguchi, K. Autoantibodies to insulin, insulinoma-associated antigen-2, and zinc transporter 8 improve the prediction of early insulin requirement in adult-onset autoimmune diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.; Stratton, I.; Horton, V.; Manley, S.; Zimmet, P.; Mackay, I.R.; Shattock, M.; Bottazzo, G.F.; Holman, R. UKPDS 25: Autoantibodies to islet-cell cytoplasm and glutamic acid decarboxylase for prediction of insulin requirement in type 2 diabetes. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Lancet 1997, 350, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, J.; Kawasaki, E.; Tanaka, S.; Awata, T.; Ikegami, H.; Imagawa, A.; Uchigata, Y.; Osawa, H.; Kajio, H.; Kawabata, Y.; et al. Clinical and genetic characteristics of non-insulin-requiring glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) autoantibody-positive diabetes: A nationwide survey in Japan. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederstigt, C.; Uitbeijerse, B.S.; Janssen, L.G.M.; Corssmit, E.P.M.; de Koning, E.J.P.; Dekkers, O.M. Associated autoimmune disease in type 1 diabetes patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakleas, K.; Soldatou, A.; Karachaliou, F.; Karavanaki, K. Associated autoimmune diseases in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E. Type 1 diabetes and autoimmunity. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2014, 23, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordonouri, O.; Klinghammer, A.; Lang, E.B.; Grüters-Kieslich, A.; Grabert, M.; Holl, R.W. Thyroid autoimmunity in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A multicenter survey. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierrez, G.E.; Latif, K.A.; Murphy, M.B.; Lambeth, H.C.; Stentz, F.; Bush, A.; Kitabchi, A.E. Thyroid dysfunction in patients with type 1 diabetes: A longitudinal study. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glastras, S.J.; Craig, M.E.; Verge, C.F.; Chan, A.K.; Cusumano, J.M.; Donaghue, K.C. The role of autoimmunity at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in the development of thyroid and celiac disease and microvascular complications. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2170–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordonouri, O.; Klingensmith, G.; Knip, M.; Holl, R.W.; Aanstoot, H.J.; Menon, P.S.; Craig, M.E.; International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2014. Other complications and diabetes-associated conditions in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Diabetes 2014, 20 (Suppl. S15), 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, I.; Kawasaki, E.; Ando, T.; Kuwahara, H.; Abiru, N.; Usa, T.; Yamasaki, H.; Ejima, E.; Kawakami, A. Clinical and genetic characteristics of autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 3 variant in the Japanese population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1043–E1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E.; Abiru, N.; Yano, M.; Uotani, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsuo, H.; Yamasaki, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Akazawa, S.; et al. Autoantibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease: Relation to competitive insulin autoantibodies. J. Autoimmun. 1995, 8, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakhadze, M.; Giorgadze, E.; Lomidze, M. The frequency of Langerhans islets β-cells autoantibodies (Anti-GAD) in Georgian children and adolescents with chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 6597091, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Maugendre, D.; Vérité, F.; Guilhem, I.; Genetet, B.; Allannic, H.; Delamaire, M. Anti-pancreatic autoimmunity and Graves’ disease: Study of a cohort of 600 Caucasian patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 137, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lethagen, Å.L.; Ericsson, U.B.; Hallengren, B.; Groop, L.; Tuomi, T. Glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody positivity is associated with an impaired insulin response to glucose and arginine in nondiabetic patients with autoimmune thyroiditis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsdottir, B.; Jönsson, I.; Lantz, M. Prevalence of diabetes and presence of autoantibodies against zinc transporter 8 and glutamic decarboxylase at diagnosis and at follow up of Graves’ disease. Endocrine 2019, 64, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdö, S.L.; Wolff, J.R. γ-aminobutyric acid outside the mammalian brain. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, M.R.; Brown, T.J.; Cassidy, D. Binding of antibodies in sera from Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients to glutamate decarboxylase from rat tissues. Evidence for antigenic and non-antigenic forms of the enzyme. Diabetologia 1992, 35, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottazzo, G.F.; Gleichmann, H. Immunology and Diabetes Workshops: Report of the first international workshop on the standardisation of cytoplasmic islet cell antibodies. Diabetologia 1986, 29, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifacio, E.; Dawkins, R.L.; Lernmark, Å. Immunology and Diabetes Workshops: Report of the second international workshop on the standardisation of cytoplasmic islet cell antibodies. Diabetologia 1987, 30, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, G.V.; Tappaz, M.L.; Braghi, S.; Dozio, N.; Canal, N.; Pozza, G.; Bottazzo, G.F.; Grimaldi, L.M.; Bosi, E. Autoantibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) detected by an immuno-trapping enzyme activity assay: Relation to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and islet cell antibodies. J. Autoimmun. 1991, 4, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, M.J.; Mackay, I.R.; Chen, Q.Y.; Knowles, W.J.; Zimmet, P.Z. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase discriminate major types of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1992, 41, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E.; Takino, H.; Yano, M.; Uotani, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Takao, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Akazawa, S.; Nagataki, S. Autoantibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase in patients with IDDM and autoimmune thyroid disease. Diabetes 1994, 43, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidli, R.S.; Colman, P.G.; Bonifacio, E.; Bottazzo, G.F.; Harrison, L.C. High level of concordance between assays for glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies. The first international glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody workshop. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidli, R.S.; Colman, P.G.; Bonifacio, E. Disease sensitivity and specificity of 52 assays for glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies. The second international GADAb Workshop. Diabetes 1995, 44, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E.; Tanaka, M.; Miwa, M.; Abiru, N.; Kawakami, A. Novel enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for bivalent ZnT8 autoantibodies. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab, J.; Haupt, F.; Scholz, M.; Matzke, C.; Warncke, K.; Lange, K.; Assfalg, R.; Weininger, K.; Wittich, S.; Löbner, S.; et al. Capillary blood islet autoantibody screening for identifying pre-type 1 diabetes in the general population: Design and initial results of the Fr1da study. BMJ Open. 2016, 6, e011144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, A.; de Jesus Cortez, F.; Ramelius, A.; Bennet, R.; Robinson, P.V.; Seftel, D.; Gebhart, D.; Tandel, D.; Maziarz, M.; Agardh, D.; et al. Multiplex agglutination-PCR (ADAP) autoantibody assays compared to radiobinding autoantibodies in type 1 diabetes and celiac disease. J. Immunol. Methods 2022, 506, 113265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Yu, L. Effective assay technologies fit for large-scale population screening of type 1 diabetes. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2023, 3, 1034698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orban, T.; Bundy, B.; Becker, D.J.; Dimeglio, L.A.; Gitelman, S.E.; Goland, R.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Marks, J.B.; Monzavi, R.; et al. Costimulation modulation with abatacept in patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes: Follow-up 1 year after cessation of treatment. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, M.R.; Harris, K.M.; Pinckney, A.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Rendell, M.S.; Felner, E.I.; Dostou, J.M.; Gitelman, S.E.; Griffin, K.J.; Tsalikian, E.; et al. Alefacept provides sustained clinical and immunological effects in new-onset type 1 diabetes patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescovitz, M.D.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Krause-Steinrauf, H.; Becker, D.J.; Gitelman, S.E.; Goland, R.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Marks, J.B.; McGee, P.F.; Moran, A.M.; et al. Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Anti-CD20 Study Group. Rituximab, B-lymphocyte depletion, and preservation of β-cell function. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, M.J.; Long, S.A.; Blanchfield, J.L.; Schatz, D.A.; Skyler, J.S.; Krischer, J.P.; Bundy, B.N.; Geyer, S.M.; Warnock, M.V.; Miller, J.L.; et al. Low-dose anti-thymocyte globulin preserves C-peptide, reduces HbA1c, and increases regulatory to conventional T-cell ratios in new-onset type 1 diabetes: Two-year clinical trial data. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, K.C.; Bundy, B.N.; Long, S.A.; Bluestone, J.A.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Dufort, M.J.; Gitelman, S.E.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Krischer, J.P.; Linsley, P.S.; et al. Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Study Group. An anti-CD3 antibody, Teplizumab, in relatives at risk for type 1 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, E.K.; Bundy, B.N.; Stier, K.; Serti, E.; Lim, N.; Long, S.A.; Geyer, S.M.; Moran, A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Evans-Molina, C.; et al. Teplizumab improves and stabilizes beta cell function in antibody-positive high-risk individuals. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabc8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Name of Antigen | Localization | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin | Insulin secretory granules | Regulate glucose levels in the blood and induce glucose storage in the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue | [7] |
| GAD65 | Synaptic-like vesicles in the cytoplasm of β-cells | Rate-limiting enzyme engaged in the synthesis of the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid from L-glutamate | [8] |
| GAD67 | Cytosol of β-cells | Rate-limiting enzyme engaged in the synthesis of the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid from L-glutamate | [11] |
| IA-2 | Insulin secretory granule membrane | Regulate insulin secretory granule content and β-cell growth | [9,12] |
| Phogrin/IA-2β | Insulin secretory granule membrane | Regulate insulin secretory granule content and β-cell growth | [13,14] |
| Carboxypeptidase H | Insulin secretory granules and granule membrane | Convert proinsulin into insulin and C-peptide by catalyzing the release of C-terminal arginine or lysine residues from polypeptides | [15] |
| ICA69 | Insulin secretory granule membrane | Dense-core vesicles signaling and maturation | [16] |
| ZnT8 | Insulin secretory granule membrane | Transport zinc ion from the cytosol into the insulin secretory granules | [17,18] |
| GM2-1 ganglioside | Secretory granules in β-cells and non-β-cells | unknown | [19] |
| Heat shock protein 60 | Insulin secretory granules | Assist correct folding of partially folded polypeptides and presentation of antigen to MHC molecules | [20] |
| GLUT2 | β-cell surface membrane | Uptake glucose from the blood into β-cells | [21] |
| Tetraspanin-7 | Insulin secretory granule membrane | Regulate Ca2+-dependent insulin exocytosis | [22] |
| ICA12/SOX13 | Cytoplasm and nucleus in β-cells and non-β-cells | Transcription factor (Function in the islets is unknown) | [23] |
| Subject | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Healthy control | <1% |
| Acute-onset type 1 diabetes (at onset) | 60–80% |
| Fulminant type 1 diabetes | 5–9% |
| LADA (SPIDDM) | 100% |
| Type 2 diabetes (diet/OHA) | 4–5% |
| Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome, type 1 | 30–40% |
| Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome, type 2 | 30–50% |
| Autoimmune thyroid disease | 6–8% |
| Stiff-person syndrome | 60–70% |
| Required Item: |
| (1) The presence of anti-islet autoantibodies at some time point during the disease course a; |
| (2) The absence of ketosis or ketoacidosis at the diagnosis of diabetes and the unnecessity for insulin treatment to correct hyperglycemia immediately after diagnosis in principle; |
| (3) The gradual decrease in insulin secretion overtime, requirement of insulin treatment more than 3 months b after diagnosis of diabetes, and exhausted endogenous insulin secretion (fasting serum C-peptide immunoreactivity < 0.6 ng/mL) at last observed time point. |
| Judgement: |
| When the case fulfills the criteria of all of the three described above ((1), (2), and (3)), the case is diagnosed with “slowly progressive type 1 diabetes (definite)”; when the case fulfills the criteria only (1) and (2), but not (3), the case is diagnosed with “slowly progressive type 1 diabetes (probable)”. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawasaki, E. Anti-Islet Autoantibodies in Type 1 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210012
Kawasaki E. Anti-Islet Autoantibodies in Type 1 Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):10012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210012
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawasaki, Eiji. 2023. "Anti-Islet Autoantibodies in Type 1 Diabetes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 10012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210012
APA StyleKawasaki, E. (2023). Anti-Islet Autoantibodies in Type 1 Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 10012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210012





