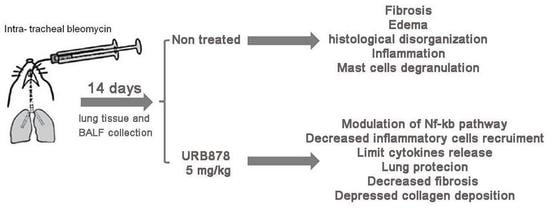
Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) Regulates NF-kb Pathways Reducing Bleomycin-Induced Chronic Lung Inflammation and Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. URB878 Reduced Bleomycin-Induced Mortality, Body Weight Decreases, and Histological Damage
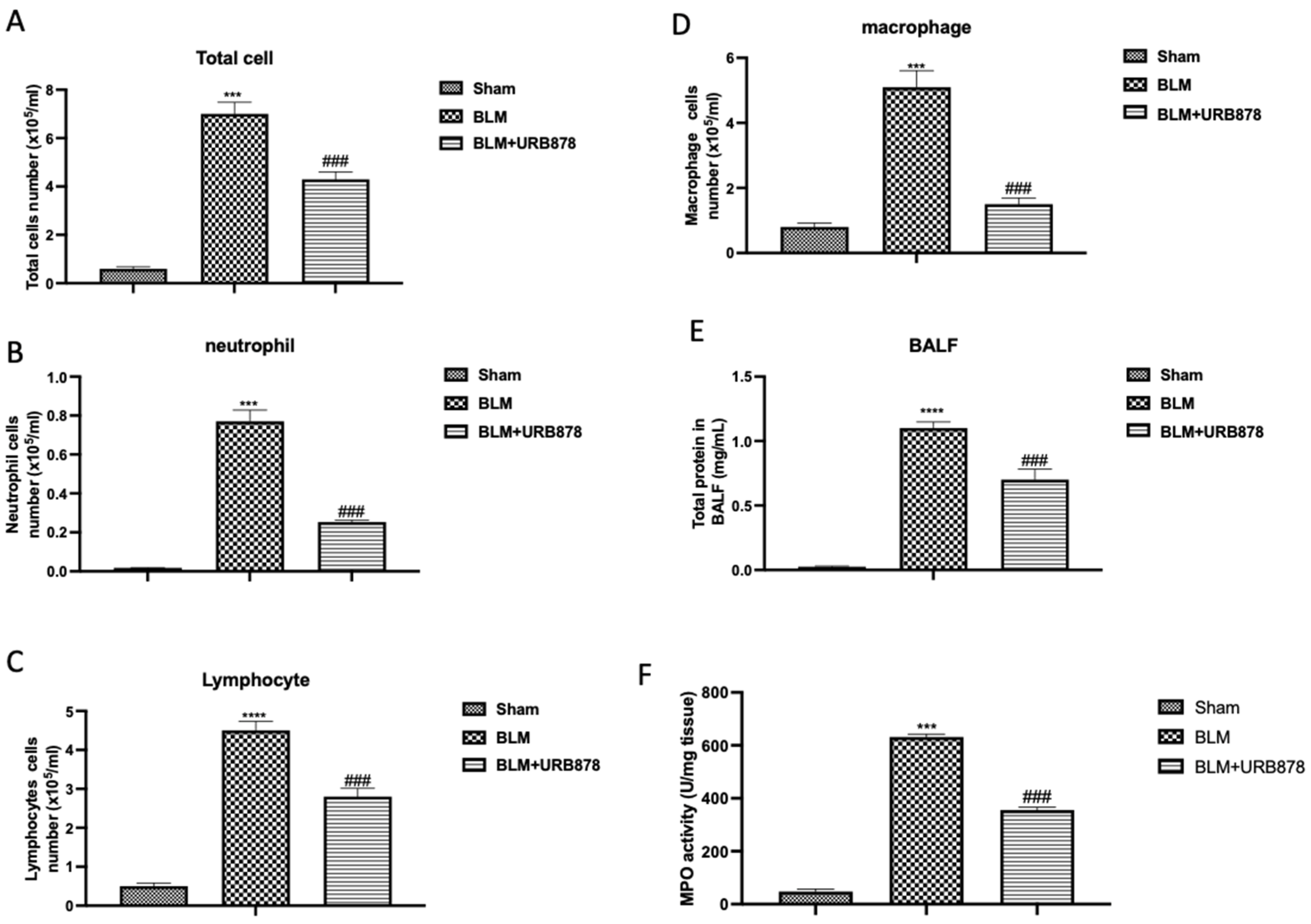
2.2. URB878 Administration Reduced Bleomycin-Induced Inflammatory Cell Migration
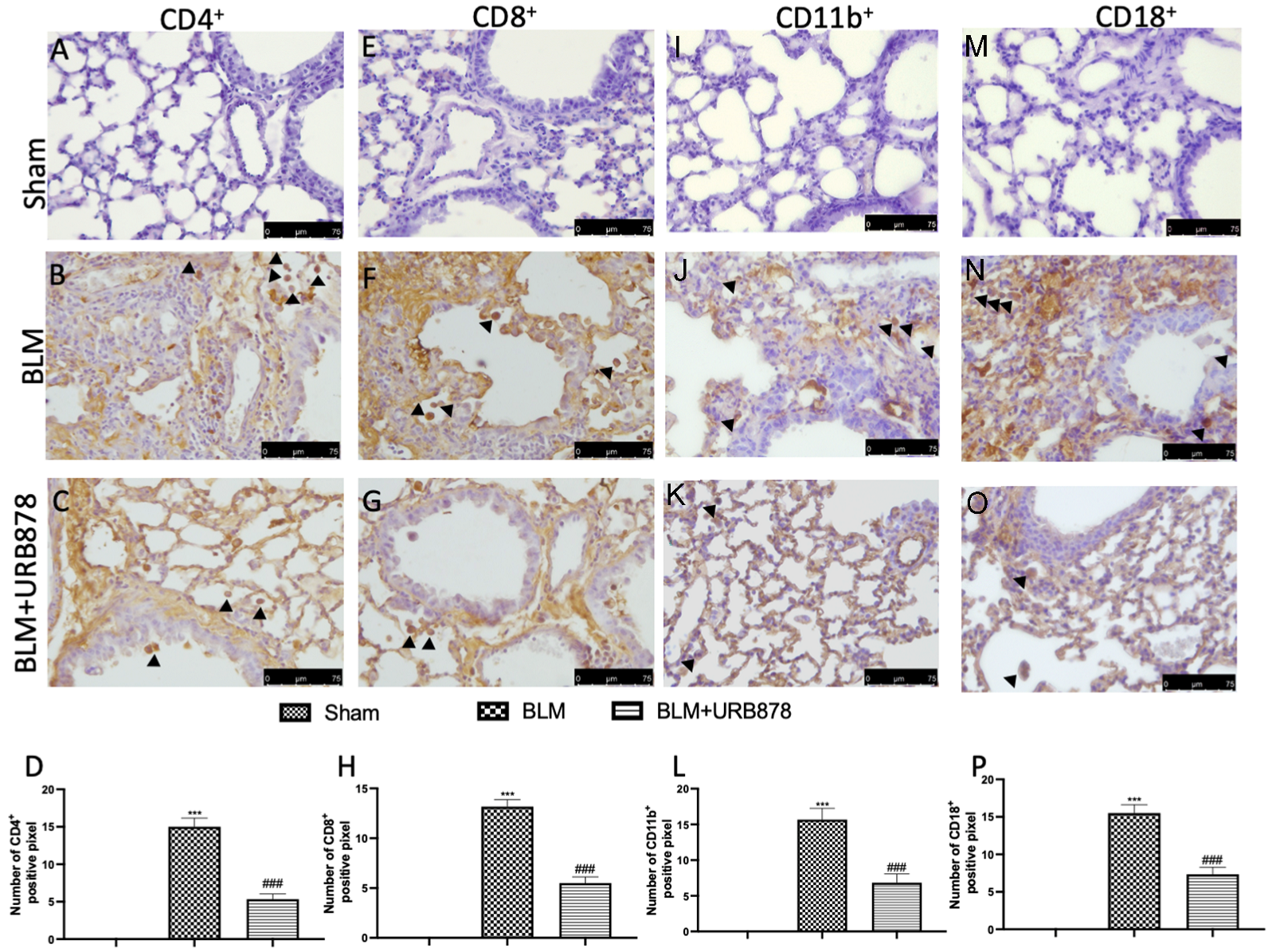
2.3. URB878 Administration Reduced Cell Infiltration
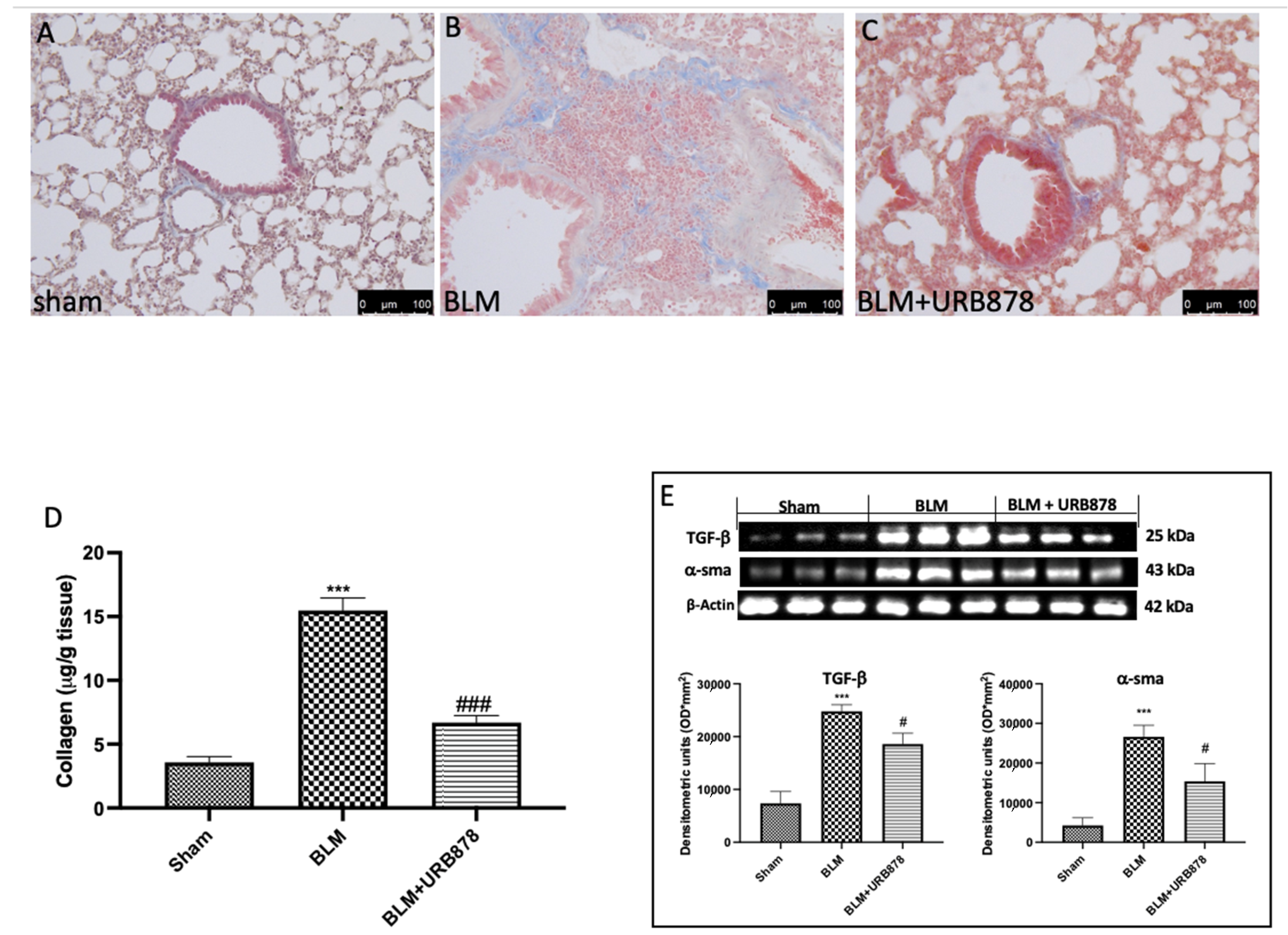
2.4. URB878 Decreased Bleomycin-Induced Fibrosis
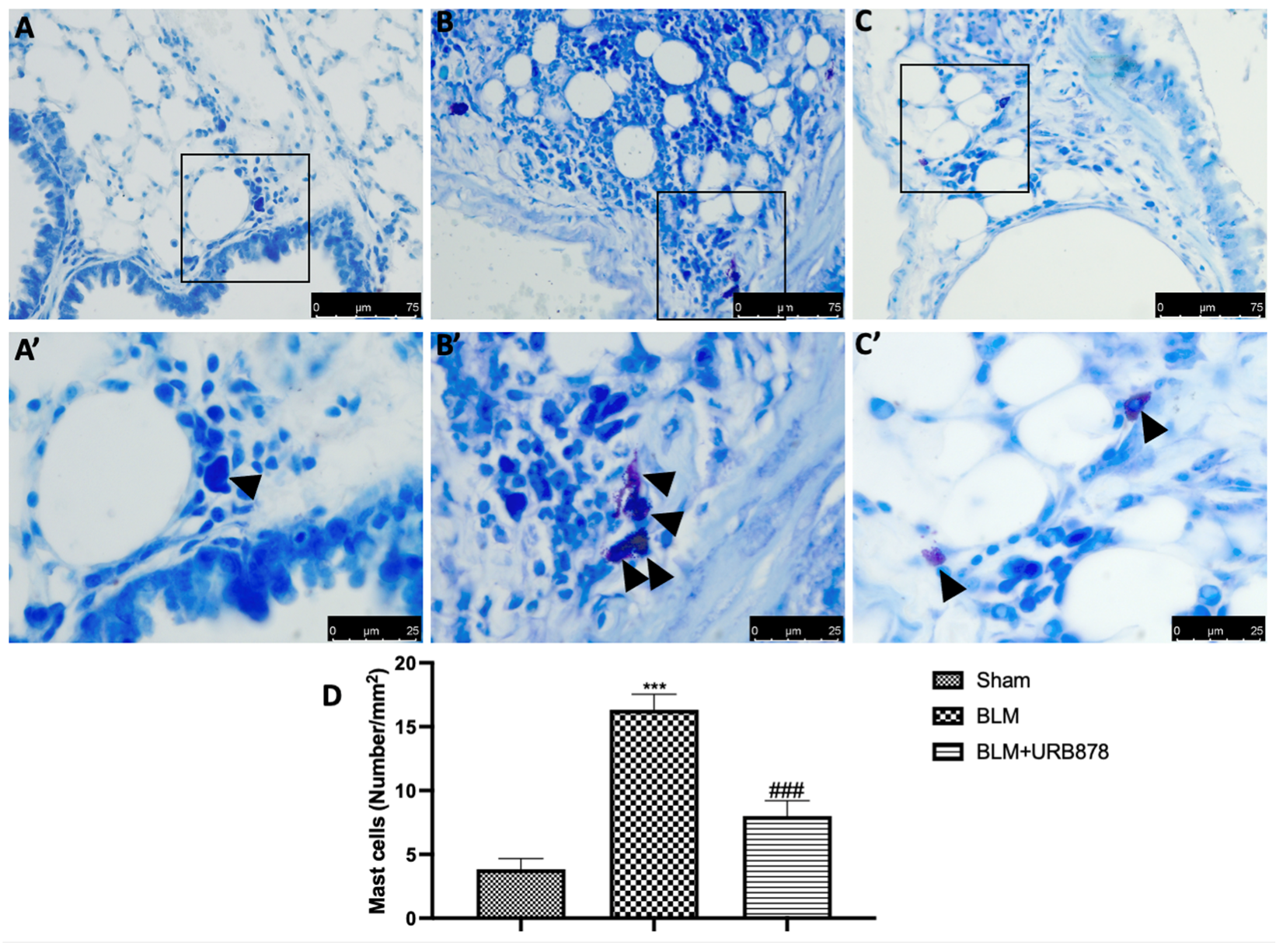
2.5. URB878 Reduced Mast Cells Degranulation
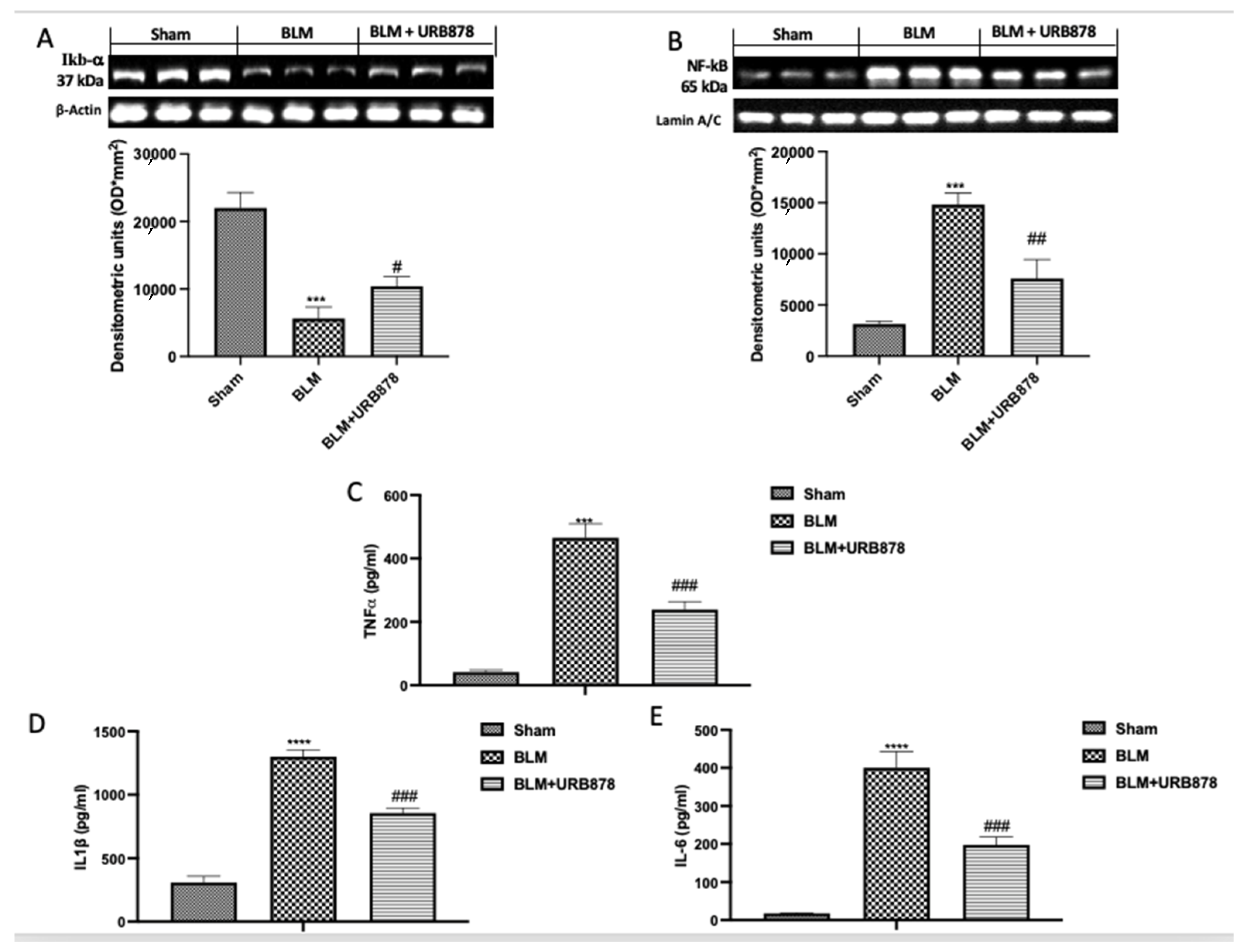
2.6. URB878 Administration Decreased Bleomycin-Induced Inflammation
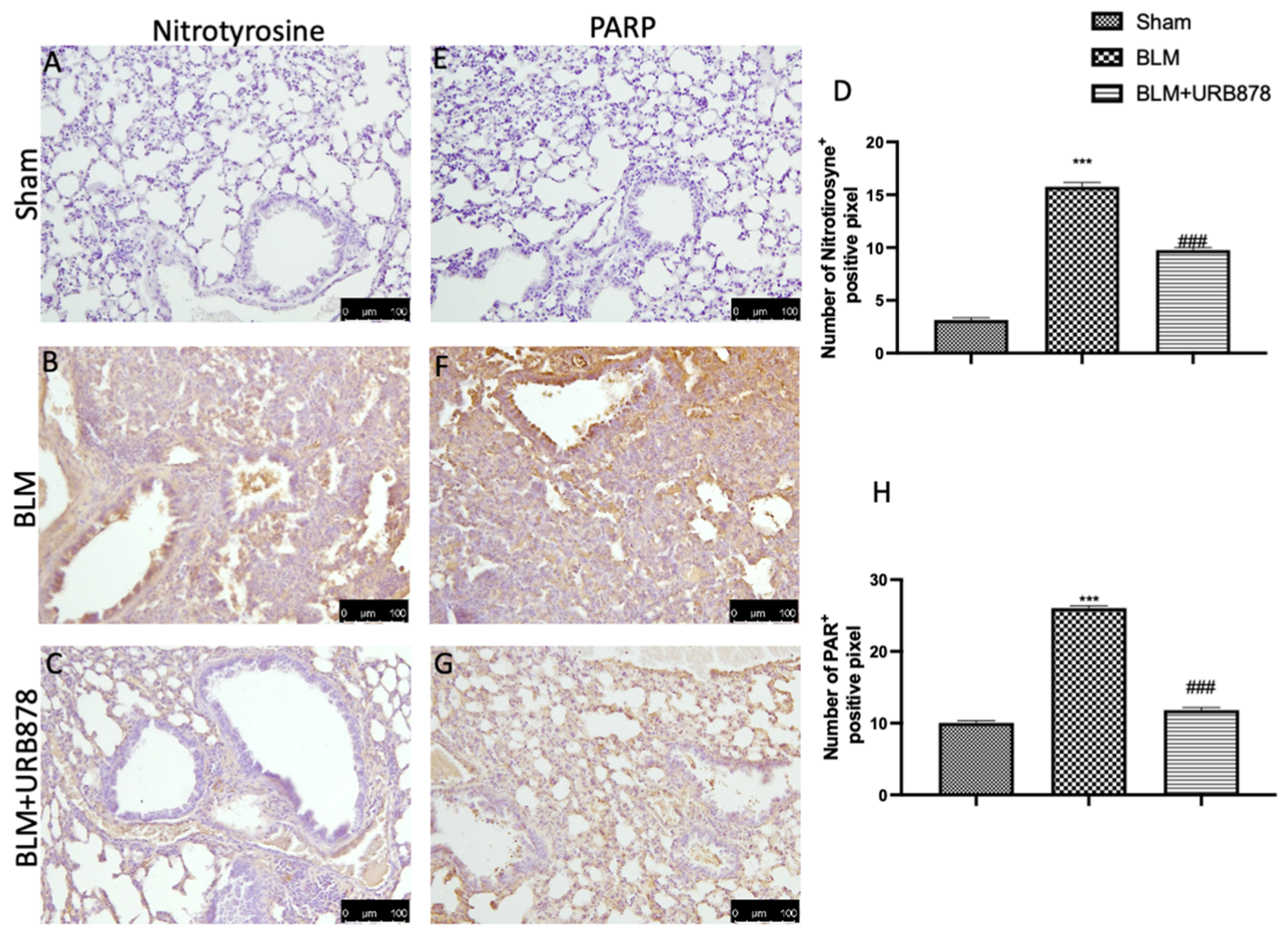
2.7. URB878 Administration Reduced Nitrosative Stress and DNA Damage
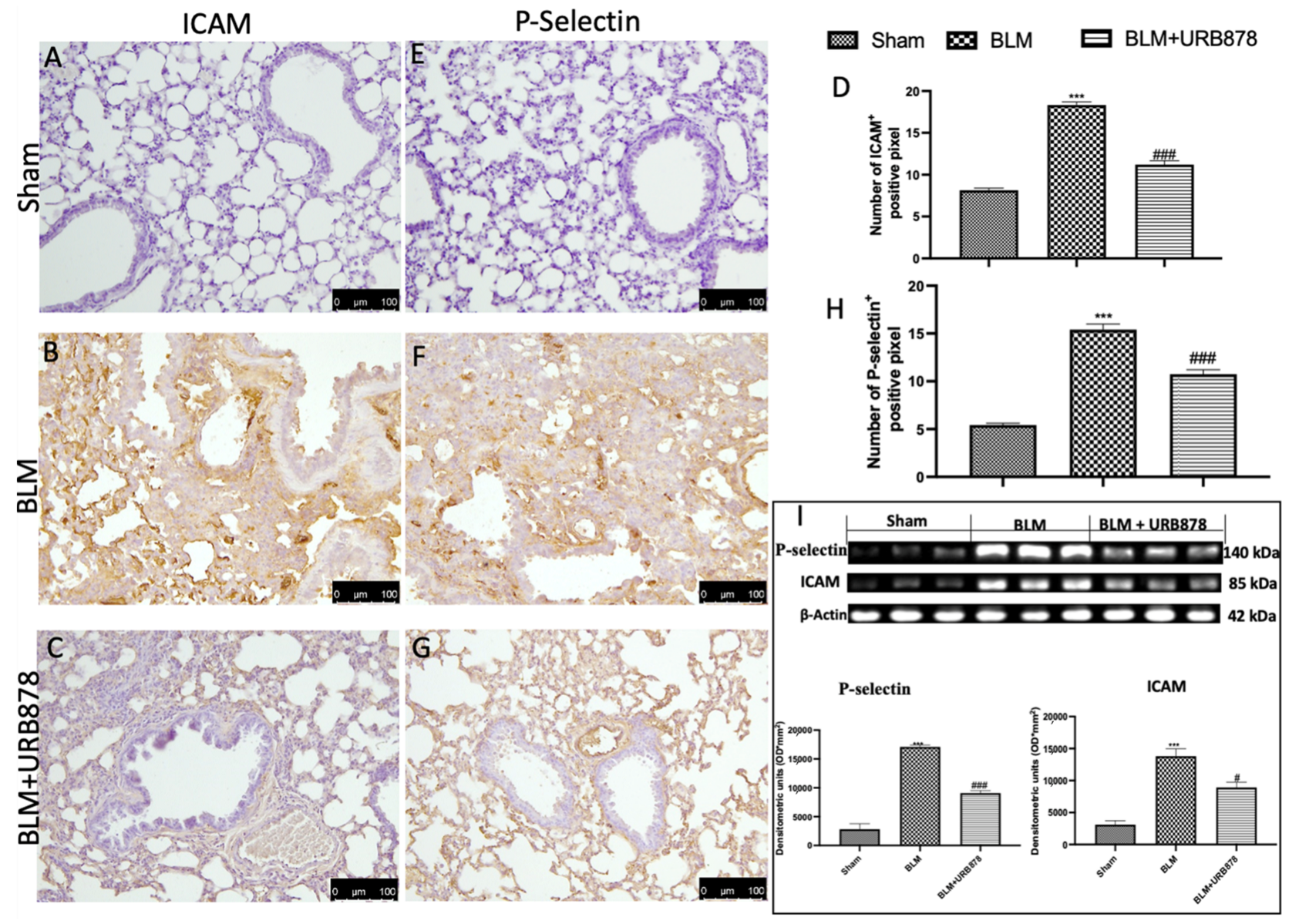
2.8. URB878 Reduced Adhesion Molecule Expression That Bleomycin Induced
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Design and Groups
- (I)
- Bleomycin: animals that receive one injection of bleomycin at time 0.
- (II)
- Bleomycin+URB878: mice were subjected to the bleomycin injection described above and treated orally with URB878 at the dose of 5 mg/kg dissolved in a vehicle consisting of 10% PEG-400, 10% Tween-80, and 80% saline for the first time 1 h after bleomycin injection and once a day for 14 days.
- (III)
- Sham: animals that were exposed to the vehicle.
- (IV)
- Sham groups+URB878: animals received URB878 dissolved in a vehicle for 14 days at the dose of 5 mg/kg.
4.3. Measurement of Lung Edema
4.4. Histopathological Evaluation with Hematoxylin/Eosin, Toluidine Blue, and Masson
4.5. Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL)
4.6. Western Blot Analysis of Cytosolic and Nuclear Extracts
4.7. Cytokine Measurement
4.8. Immunohistochemical Localization of Nitrotyrosine, Poly(ADP-Ribose), CD4, CD8, CD11b, CD18, ICAM, and P-Selectin
4.9. Soluble Collagen Assay
4.10. Survival Rate
4.11. Mieloperoxidase (MPO) Evaluation
4.12. Materials
4.13. Synthesis of URB878
4.14. Statistical Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, E.S.; Lazar, M.H.; Thannickal, V.J. Pathogenetic mechanisms in usual interstitial pneumonia/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2003, 201, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E., Jr.; Tooze, J.A.; Schwarz, M.I.; Brown, K.R.; Cherniack, R.M. Predicting survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Scoring system and survival model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, T.; Di Paola, R.; Mazzon, E.; Muia, C.; Caputi, A.P.; Cuzzocrea, S. Melatonin limits lung injury in bleomycin treated mice. J. Pineal. Res. 2005, 39, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Ma, T.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Xiang, Z.; Han, X. TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation promotes myofibroblast differentiation of LR-MSCs and exacerbates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Jiang, J.; Ma, T.; Xie, J.; Duan, L.; Chen, R.; Song, P.; Yu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Pathogenesis pathways of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in bleomycin-induced lung injury model in mice. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2014, 190, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, N.I.; Schnapp, A.; Park, J.E. Pharmacologic differentiation of inflammation and fibrosis in the rat bleomycin model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, M.; Ambrozewicz, E.; Gegotek, A.; Toczek, M.; Skrzydlewska, E. Long-term administration of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor (URB597) to rats with spontaneous hypertension disturbs liver redox balance and phospholipid metabolism. Adv. Med. Sci. 2019, 64, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, M.; Baranowska-Kuczko, M.; Niklinska, G.N.; Skrzydlewska, E. The FAAH Inhibitor URB597 Modulates Lipid Mediators in the Brain of Rats with Spontaneous Hypertension. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, M.; Luczaj, W.; Gegotek, A.; Toczek, M.; Bielawska, K.; Skrzydlewska, E. Crosstalk between liver antioxidant and the endocannabinoid systems after chronic administration of the FAAH inhibitor, URB597, to hypertensive rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 301, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, M.; Luczaj, W.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Ambrozewicz, E.; Toczek, M.; Skrzydlewska, E. The Effect of Long-Term Administration of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Inhibitor URB597 on Oxidative Metabolism in the Heart of Rats with Primary and Secondary Hypertension. Molecules 2018, 23, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mor, M.; Rivara, S.; Lodola, A.; Plazzi, P.V.; Tarzia, G.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Piersanti, G.; Kathuria, S.; Piomelli, D. Cyclohexylcarbamic acid 3’- or 4’-substituted biphenyl-3-yl esters as fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors: Synthesis, quantitative structure-activity relationships, and molecular modeling studies. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 4998–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kathuria, S.; Gaetani, S.; Fegley, D.; Valino, F.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Tarzia, G.; La Rana, G.; Calignano, A.; et al. Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbi, G.; Bambico, F.R.; Mangieri, R.; Bortolato, M.; Campolongo, P.; Solinas, M.; Cassano, T.; Morgese, M.G.; Debonnel, G.; Duranti, A.; et al. Antidepressant-like activity and modulation of brain monoaminergic transmission by blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18620–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alteba, S.; Mizrachi Zer-Aviv, T.; Tenenhaus, A.; Ben David, G.; Adelman, J.; Hillard, C.J.; Doron, R.; Akirav, I. Antidepressant-like effects of URB597 and JZL184 in male and female rats exposed to early life stress. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 39, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedse, G.; Colangeli, R.; Lavecchia, A.M.; Romano, A.; Altieri, F.; Cifani, C.; Cassano, T.; Gaetani, S. Role of the basolateral amygdala in mediating the effects of the fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 on HPA axis response to stress. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska-Kuczko, M.; Kozlowska, H.; Kloza, M.; Harasim-Symbor, E.; Biernacki, M.; Kasacka, I.; Malinowska, B. Beneficial Changes in Rat Vascular Endocannabinoid System in Primary Hypertension and under Treatment with Chronic Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase by URB597. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska-Kuczko, M.; Kozlowska, H.; Kloza, M.; Karpinska, O.; Toczek, M.; Harasim, E.; Kasacka, I.; Malinowska, B. Protective role of cannabinoid CB1 receptors and vascular effects of chronic administration of FAAH inhibitor URB597 in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Life Sci. 2016, 151, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, M.; Ambrozewicz, E.; Gegotek, A.; Toczek, M.; Bielawska, K.; Skrzydlewska, E. Redox system and phospholipid metabolism in the kidney of hypertensive rats after FAAH inhibitor URB597 administration. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambico, F.R.; Duranti, A.; Nobrega, J.N.; Gobbi, G. The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 modulates serotonin-dependent emotional behaviour, and serotonin1A and serotonin2A/C activity in the hippocampus. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Ghiri, M.; Shahini, F.; Zarrindast, M.R. The effect of URB597, exercise or their combination on the performance of 6-OHDA mouse model of Parkinson disease in the elevated plus maze, tail suspension test and step-down task. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Loverme, J.; La Rana, G.; Compton, T.R.; Parrott, J.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Tarzia, G.; Calignano, A.; et al. The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 (cyclohexylcarbamic acid 3’-carbamoylbiphenyl-3-yl ester) reduces neuropathic pain after oral administration in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piomelli, D.; Tarzia, G.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Compton, T.R.; Dasse, O.; Monaghan, E.P.; Parrott, J.A.; Putman, D. Pharmacological profile of the selective FAAH inhibitor KDS-4103 (URB597). CNS Drug Rev. 2006, 12, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, D.; Matthey, M.; Bindila, L.; Lerner, R.; Lutz, B.; Zimmer, A.; Fleischmann, B.K. Endocannabinoid anandamide mediates hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18710–18715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkler, K.; Ramer, R.; Dithmer, S.; Ivanov, I.; Merkord, J.; Hinz, B. Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors confer anti-invasive and antimetastatic effects on lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15047–15064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravi, J.; Sneh, A.; Shilo, K.; Nasser, M.W.; Ganju, R.K. FAAH inhibition enhances anandamide mediated anti-tumorigenic effects in non-small cell lung cancer by downregulating the EGF/EGFR pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2475–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bedse, G.; Romano, A.; Tempesta, B.; Lavecchia, M.A.; Pace, L.; Bellomo, A.; Duranti, A.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Cifani, C.; Cassano, T.; et al. Inhibition of anandamide hydrolysis enhances noradrenergic and GABAergic transmission in the prefrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala of rats subjected to acute swim stress. J. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 93, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacobbe, J.; Marrocu, A.; Di Benedetto, M.G.; Pariante, C.M.; Borsini, A. A systematic, integrative review of the effects of the endocannabinoid system on inflammation and neurogenesis in animal models of affective disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 93, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegley, D.; Gaetani, S.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Tarzia, G.; Piomelli, D. Characterization of the fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor cyclohexyl carbamic acid 3’-carbamoyl-biphenyl-3-yl ester (URB597): Effects on anandamide and oleoylethanolamide deactivation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 313, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clapper, J.R.; Vacondio, F.; King, A.R.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Silva, C.; Sanchini, S.; Tarzia, G.; Mor, M.; Piomelli, D. A second generation of carbamate-based fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors with improved activity in vivo. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vacondio, F.; Silva, C.; Lodola, A.; Carmi, C.; Rivara, S.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Sanchini, S.; Clapper, J.R.; Piomelli, D.; et al. Biphenyl-3-yl alkylcarbamates as fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitors: Steric effects of N-alkyl chain on rat plasma and liver stability. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4466–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mor, M.; Lodola, A.; Rivara, S.; Vacondio, F.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Sanchini, S.; Piersanti, G.; Clapper, J.R.; King, A.R.; et al. Synthesis and quantitative structure-activity relationship of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors: Modulation at the N-portion of biphenyl-3-yl alkylcarbamates. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3487–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hay, J.; Shahzeidi, S.; Laurent, G. Mechanisms of bleomycin-induced lung damage. Arch. Toxicol. 1991, 65, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Mora, A.L.; LaVoy, J.; Brigham, K.L.; Rojas, M. Increased bleomycin-induced lung injury in mice deficient in the transcription factor T-bet. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L658–L667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bantsimba-Malanda, C.; Marchal-Somme, J.; Goven, D.; Freynet, O.; Michel, L.; Crestani, B.; Soler, P. A role for dendritic cells in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komura, K.; Yanaba, K.; Horikawa, M.; Ogawa, F.; Fujimoto, M.; Tedder, T.F.; Sato, S. CD19 regulates the development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 3574–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Zhang, K.; Karmiol, S.; Phan, S.H. Lung fibroblast alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and contractile phenotype in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 148, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Conte, E.; Fagone, E.; Gili, E.; Fruciano, M.; Iemmolo, M.; Pistorio, M.P.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Vancheri, C. Preventive and therapeutic effects of thymosin beta4 N-terminal fragment Ac-SDKP in the bleomycin model of pulmonary fibrosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33841–33854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reber, L.L.; Daubeuf, F.; Pejler, G.; Abrink, M.; Frossard, N. Mast cells contribute to bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and injury in mice through a chymase/mast cell protease 4-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Bassouny, D.R.; Omar, N.M.; Khalaf, H.A.; Al-Salam, R.A.A. Role of nuclear factor-kappa B in bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis and the probable alleviating role of ginsenoside: Histological, immunohistochemical, and biochemical study. Anat. Cell Biol. 2021, 54, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, T.; Mazzon, E.; Di Paola, R.; Muia, C.; Threadgill, M.D.; Caputi, A.P.; Thiemermann, C.; Cuzzocrea, S. Inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase modulate signal transduction pathways and the development of bleomycin-induced lung injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 313, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidot, D.M.; Folkesson, H.G.; Jain, L.; Sznajder, J.I.; Pittet, J.F.; Matthay, M.A. Integrating acute lung injury and regulation of alveolar fluid clearance. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L301–L306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanos, S.E.; Mavrommati, I.; Korovesi, I.; Roussos, C. Pulmonary endothelium in acute lung injury: From basic science to the critically ill. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 1702–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inghilleri, S.; Morbini, P.; Oggionni, T.; Barni, S.; Fenoglio, C. In situ assessment of oxidant and nitrogenic stress in bleomycin pulmonary fibrosis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 125, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, W.; Hu, D.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, W.; Chen, C. Resveratrol efficiently improves pulmonary function via stabilizing mast cells in a rat intestinal injury model. Life Sci. 2017, 185, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, T.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Interdonato, L.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Paola, R.D.; et al. Acai (Euterpe Oleraceae Mart.) Seeds Regulate NF-kappaB and Nrf2/ARE Pathways Protecting Lung against Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 56, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, R.; Monaco, F.; Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Atrazine Inhalation Worsen Pulmonary Fibrosis Regulating the Nuclear Factor-Erythroid 2-Related Factor (Nrf2) Pathways Inducing Brain Comorbidities. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 55, 704–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma Translocation 1 Inhibitor as a Novel Therapeutic Tool for Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Adelmidrol: A New Promising Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Tool in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, C.M.; Puddington, L.; Wu, C.; Guernsey, L.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Phan, S.H.; Thrall, R.S. Chronic inhaled ovalbumin exposure induces antigen-dependent but not antigen-specific inhalational tolerance in a murine model of allergic airway disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaughan, R.P.; Szewczyk, M.T., Jr.; Lanosa, M.J.; Desesa, C.R.; Gianutsos, G.; Morris, J.B. Adenosine sensory transduction pathways contribute to activation of the sensory irritation response to inspired irritant vapors. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 93, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’amico, R.; Monaco, F.; Fusco, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Crupi, R.; Interdonato, L.; Sforza, A.M.; Gugliandolo, E.; et al. Exposure to Atrazine Induces Lung Inflammation through Nrf2-HO1 and Beclin 1/LC3 Pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 55, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, T.; Duranti, A.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) Inhibition Plays a Key Role in Counteracting Acute Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Xia, J.; Zhao, H.S.; Hou, R.; Talukder, M.; Yu, L.; Guo, J.Y.; Li, J.L. Lycopene Triggers Nrf2-AMPK Cross Talk to Alleviate Atrazine-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12385–12394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Du, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, D.; Liang, D.; Zhao, L.; Shang, J. Effects of atrazine on the oxidative damage of kidney in Wister rats. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 3235–3243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Gao, S.; Ren, R.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y. Atrazine-induced apoptosis of splenocytes in BALB/C mice. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Bi, H.; Ma, K.; Li, B. Developmental Exposure to Atrazine Impairs Spatial Memory and Downregulates the Hippocampal D1 Dopamine Receptor and cAMP-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y. Oral Exposure to Atrazine Induces Oxidative Stress and Calcium Homeostasis Disruption in Spleen of Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7978219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Paola, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide (PEA-um((R))) in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Talero, E.; Siracusa, R.; Alcaide, A.; Cordaro, M.; Maria Zubelia, J.; Bruschetta, G.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Protective effect of polyphenols in an inflammatory process associated with experimental pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manitsopoulos, N.; Nikitopoulou, I.; Maniatis, N.A.; Magkou, C.; Kotanidou, A.; Orfanos, S.E. Highly Selective Endothelin-1 Receptor A Inhibition Prevents Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice. Respiration 2018, 95, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Inui, N.; Hakamata, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Enomoto, N.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Suda, T. Changes in pulmonary endothelial cell properties during bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordaro, M.; Paterniti, I.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. KU0063794, a Dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 Inhibitor, Reduces Neural Tissue Damage and Locomotor Impairment after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2415–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Petrosino, S.; Cuzzocrea, S. Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Co-UltraPEALut in a Mouse Model of Vascular Dementia. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campolo, M.; Esposito, E.; Ahmad, A.; Di Paola, R.; Paterniti, I.; Cordaro, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Wallace, J.L.; Cuzzocrea, S. Hydrogen sulfide-releasing cyclooxygenase inhibitor ATB-346 enhances motor function and reduces cortical lesion volume following traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paterniti, I.; Di Paola, R.; Campolo, M.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Tremolada, G.; Maestroni, A.; Bandello, F.; Esposito, E.; et al. Palmitoylethanolamide treatment reduces retinal inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 769, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordaro, M.; Impellizzeri, D.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Adelmidrol, a Palmitoylethanolamide Analogue, as a New Pharmacological Treatment for the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Paola, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; Campolo, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Fusco, R.; Pugliatti, P.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Protective Effects of Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA-um) in Myocardial Ischaemia and Reperfusion Injury in VIVO. Shock 2016, 46, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Impellizzeri, D.; Bruschetta, G.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. A new co-micronized composite containing palmitoylethanolamide and polydatin shows superior oral efficacy compared to their association in a rat paw model of carrageenan-induced inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 782, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Crupi, R.; Pascali, J.; Alfonsi, D.; Marcolongo, G.; Cuzzocrea, S. 2-pentadecyl-2-oxazoline: Identification in coffee, synthesis and activity in a rat model of carrageenan-induced hindpaw inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 108, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Absence of formyl peptide receptor 1 causes endometriotic lesion regression in a mouse model of surgically-induced endometriosis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 31355–31366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Effect of PEA-OXA on neuropathic pain and functional recovery after sciatic nerve crush. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. The Role of Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts on an Experimental Model of Painful Degenerative Joint Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Britti, D.; Morittu, V.M.; Evangelista, M.; Cuzzocrea, S. Adelmidrol, in combination with hyaluronic acid, displays increased anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects against monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Wu, S.; Xie, W.; He, H. Ketamine ameliorates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in experimental traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2 pathway. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiang, J. Tenacissoside H Promotes Neurological Recovery of Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Injury in Mice by Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative stress via TrkB Pathway. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 48, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.D.; Huang, Y.H.; Lai, C.S.W.; Dong, C.M.; Ho, L.C.; Wu, E.X.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.M.; Chung, S.K.; Sham, P.C.; et al. Chemotherapy-Induced Cognitive Impairment Is Associated with Cytokine Dysregulation and Disruptions in Neuroplasticity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Liang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yin, X.; Yang, H.; Zhi, Y.; Ying, G.; Zou, J.; Chen, L.; Yao, X.; et al. Astaxanthin protects cognitive function of vascular dementia. Behav. Brain Funct. 2020, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Paracetamol, a New Association to Relieve Hyperalgesia and Pain in a Sciatic Nerve Injury Model in Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Cordaro, M.; D’Amico, R.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Smeriglio, A.; Mandalari, G.; et al. The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Anacardium occidentale L. Cashew Nuts in a Mouse Model of Colitis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Paola, R.; Crisafulli, C.; Mazzon, E.; Genovese, T.; Paterniti, I.; Bramanti, P.; Cuzzocrea, S. Effect of PD98059, a selective MAPK3/MAPK1 inhibitor, on acute lung injury in mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Paola, R.; Mazzon, E.; Muia, C.; Genovese, T.; Menegazzi, M.; Zaffini, R.; Suzuki, H.; Cuzzocrea, S. Green tea polyphenol extract attenuates lung injury in experimental model of carrageenan-induced pleurisy in mice. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. 2-Pentadecyl-2-Oxazoline Reduces Neuroinflammatory Environment in the MPTP Model of Parkinson Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 9251–9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrosino, S.; Campolo, M.; Impellizzeri, D.; Paterniti, I.; Allara, M.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Esposito, E.; et al. 2-Pentadecyl-2-Oxazoline, the Oxazoline of Pea, Modulates Carrageenan-Induced Acute Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordaro, M.; Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Fusco, R.; Inferrera, A.; Esposito, E.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Effects of a co-micronized composite containing palmitoylethanolamide and polydatin in an experimental model of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 329, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crupi, R.; Cordaro, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Impellizzeri, D. Management of Traumatic Brain Injury: From Present to Future. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Scuto, M.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Di Paola, R.; et al. The Role of Annexin A1 and Formyl Peptide Receptor 2/3 Signaling in Chronic Corticosterone-Induced Depression-Like behaviors and Impairment in Hippocampal-Dependent Memory. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 19, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Therapeutic potential of dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS)-induced colitis in mice by targeting IL-1beta and IL-18. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullane, K.M.; Kraemer, R.; Smith, B. Myeloperoxidase activity as a quantitative assessment of neutrophil infiltration into ischemic myocardium. J. Pharmacol. Methods 1985, 14, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Genovese, T.; Duranti, A.; Monaco, F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) Regulates NF-kb Pathways Reducing Bleomycin-Induced Chronic Lung Inflammation and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210125
Genovese T, Duranti A, Monaco F, Siracusa R, Fusco R, Impellizzeri D, D’Amico R, Cordaro M, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R. Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) Regulates NF-kb Pathways Reducing Bleomycin-Induced Chronic Lung Inflammation and Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):10125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210125
Chicago/Turabian StyleGenovese, Tiziana, Andrea Duranti, Francesco Monaco, Rosalba Siracusa, Roberta Fusco, Daniela Impellizzeri, Ramona D’Amico, Marika Cordaro, Salvatore Cuzzocrea, and Rosanna Di Paola. 2023. "Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) Regulates NF-kb Pathways Reducing Bleomycin-Induced Chronic Lung Inflammation and Pulmonary Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 10125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210125
APA StyleGenovese, T., Duranti, A., Monaco, F., Siracusa, R., Fusco, R., Impellizzeri, D., D’Amico, R., Cordaro, M., Cuzzocrea, S., & Di Paola, R. (2023). Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) Regulates NF-kb Pathways Reducing Bleomycin-Induced Chronic Lung Inflammation and Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 10125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210125