Novel Vaccine against Pathological Pyroglutamate-Modified Amyloid Beta for Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
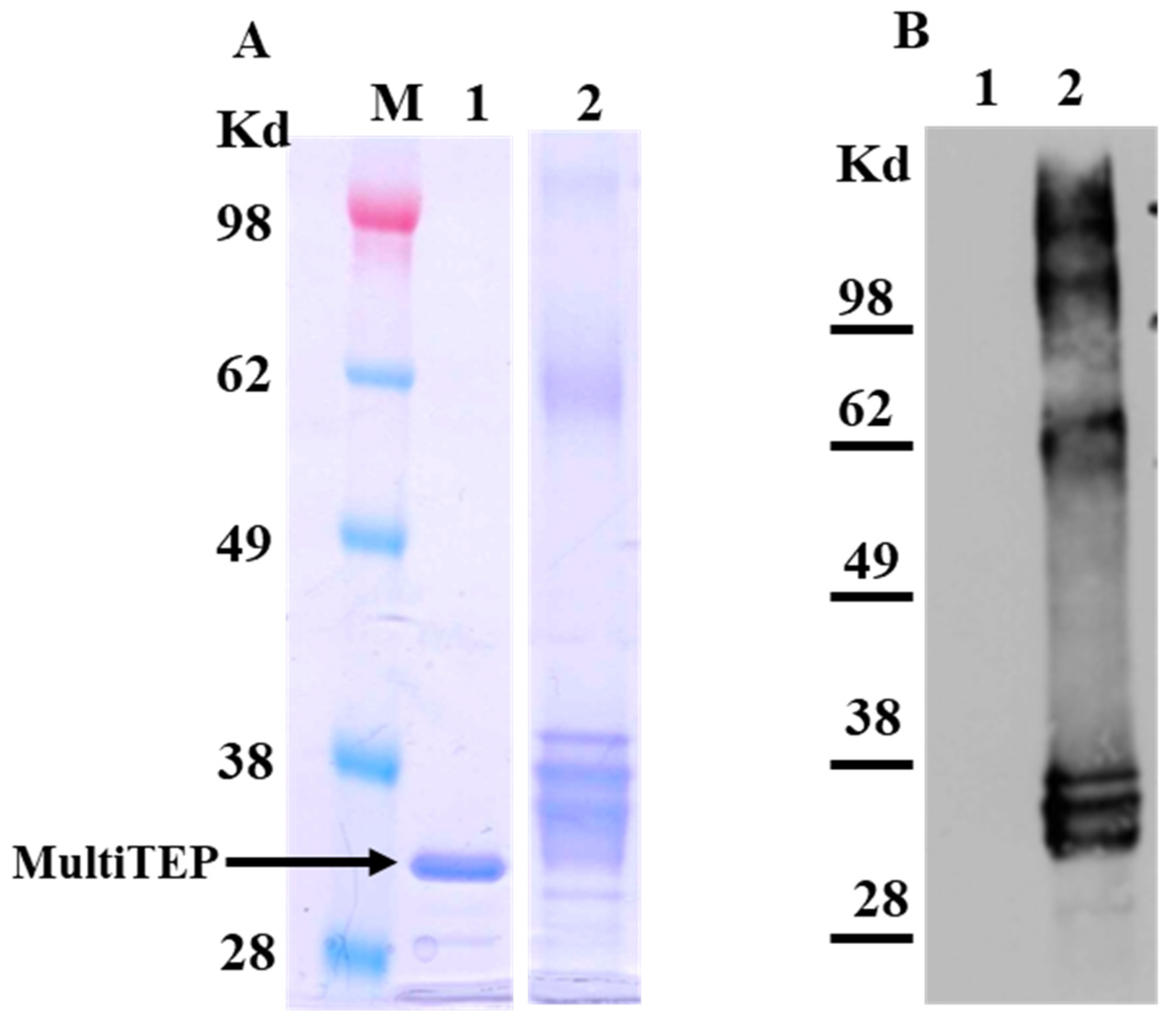
2.1. Preparation of the MultiTEP-Based Carrier Protein for Bioconjugation
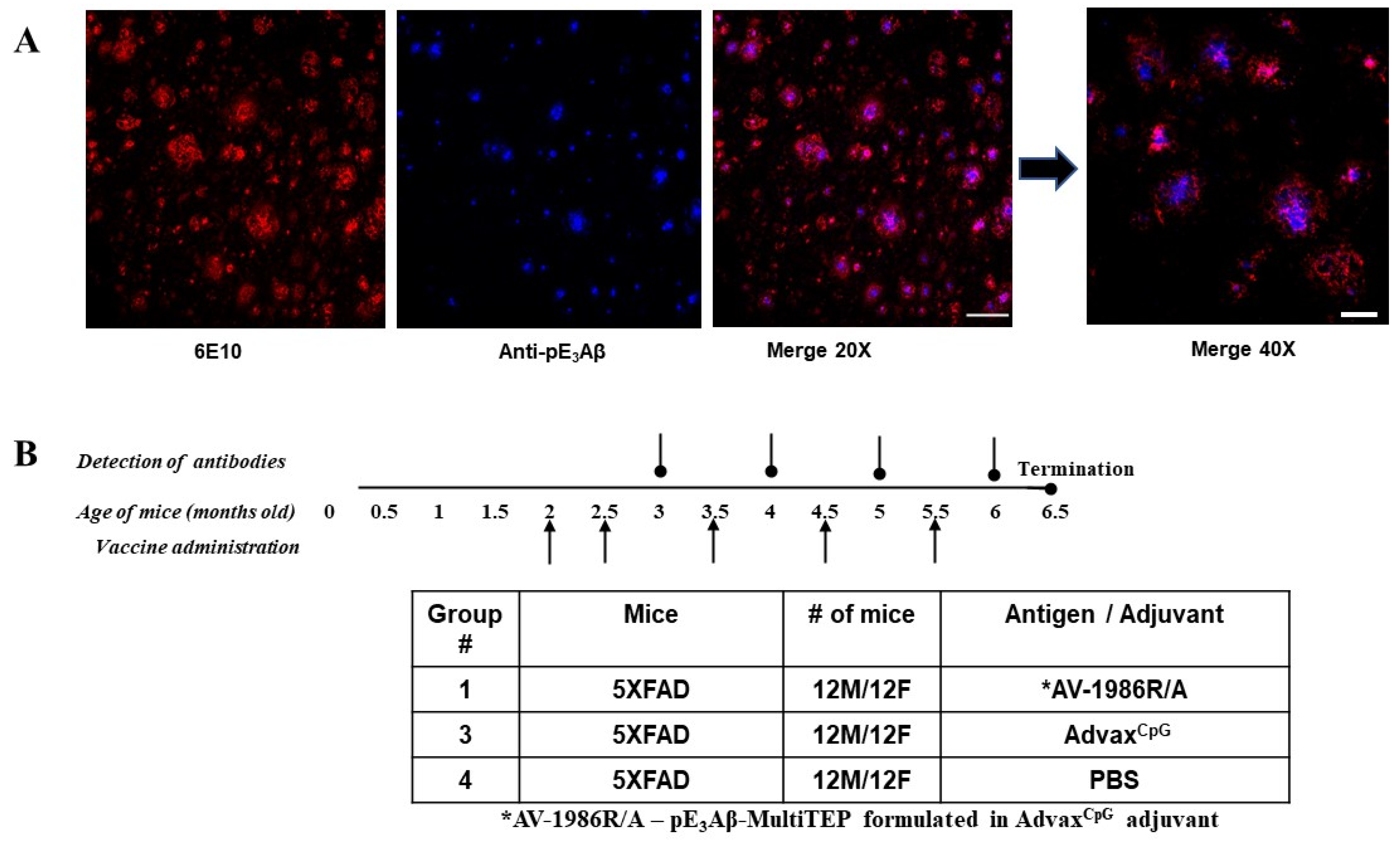
2.2. Choosing the Mouse Model of AD
2.3. Immunogenicity and Selectivity of the AV-1986R/A Vaccine in 5XFAD Mice
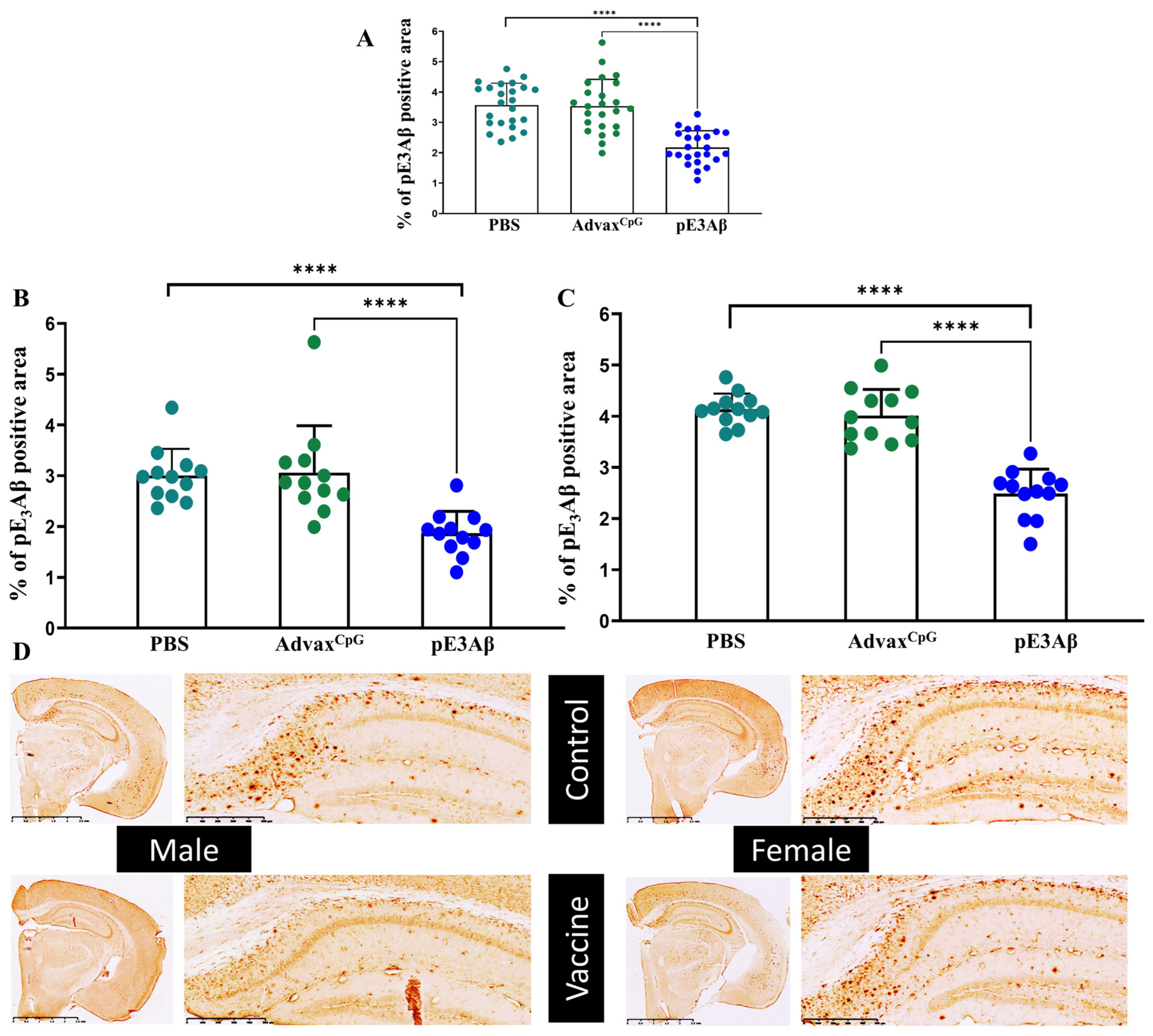
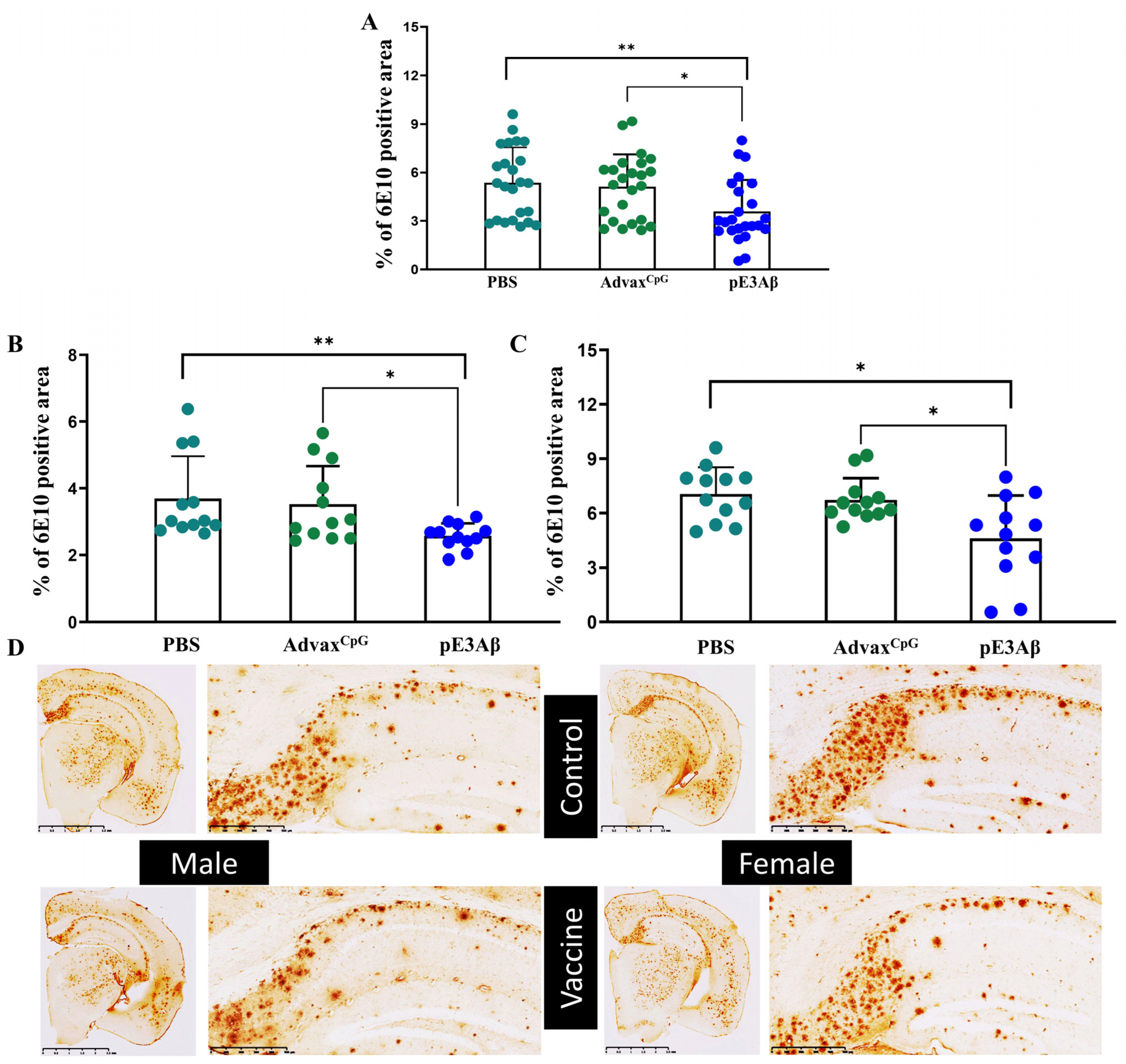
2.4. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Plaque-Clearing in 5XFAD Mice
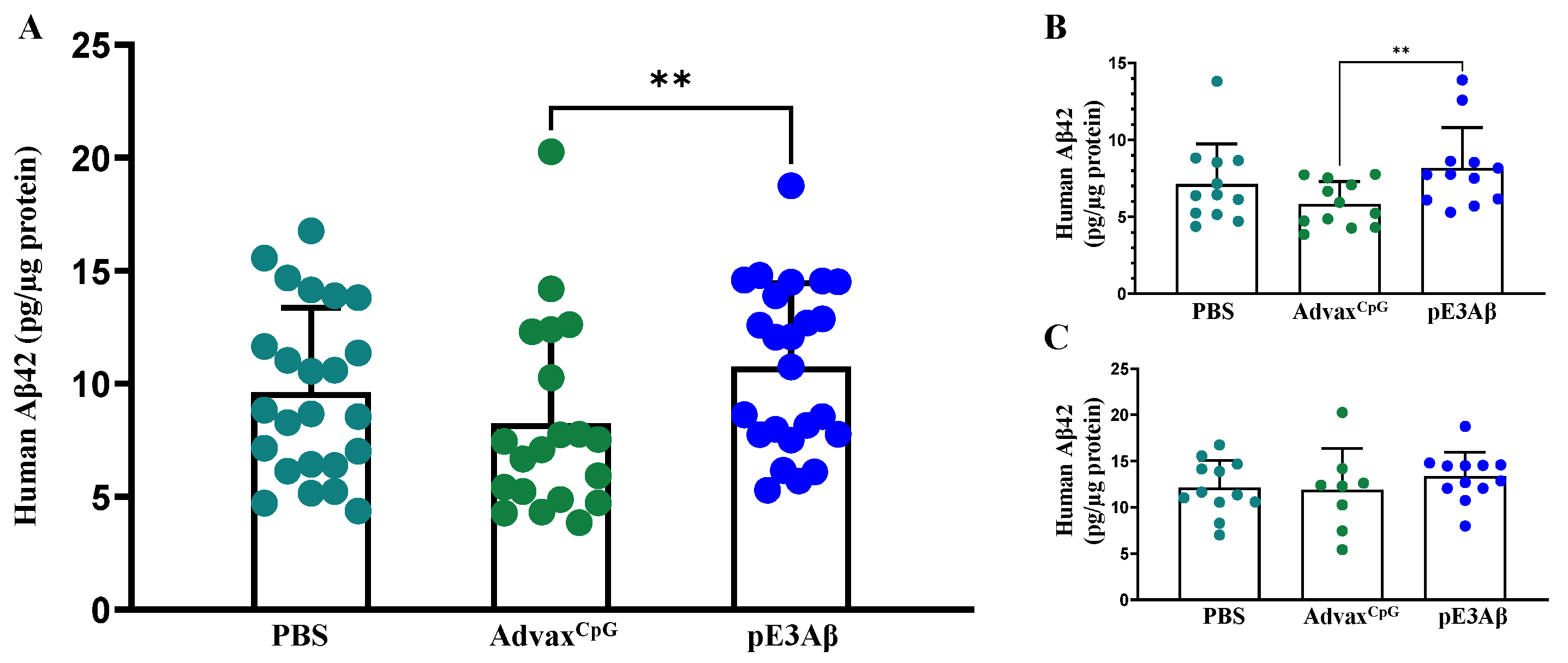
2.5. Aβ Content of 5XFAD Mouse Brain Extracts by ECLIA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of the MultiTEP-Based Vaccine for pE3Aβ by Click Chemistry
4.2. Mouse Model Selection
4.3. Experimental Protocols
4.4. ELISA
4.5. Brain Extraction
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Whole-Slide Imaging and Data Analysis
4.8. Confocal Microscopy
4.9. Data Analysis and Graphing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| pE3Aβ | N-terminally truncated amyloid beta peptides with a cyclized glutamate at position 3 |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ECLIA | Electrochemiluminescent Immunoassay |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| KLH | Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay |
References
- Schenk, D.; Barbour, R.; Dunn, W.; Gordon, G.; Grajeda, H.; Guido, T.; Hu, K.; Huang, J.; Johnson-Wood, K.; Khan, K.; et al. Immunization with amyloid-beta attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 1999, 400, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, P.; Konno, H.; Chan, K.Y.; Baum, L. Rationale for the development of an Alzheimer’s disease vaccine. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agadjanyan, M.G.; Petrovsky, N.; Ghochikyan, A. A fresh perspective from immunologists and vaccine researchers: Active vaccination strategies to prevent and reverse Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vermunt, L.; Sikkes, S.A.M.; van den Hout, A.; Handels, R.; Bos, I.; van der Flier, W.M.; Kern, S.; Ousset, P.J.; Maruff, P.; Skoog, I.; et al. Duration of preclinical, prodromal, and dementia stages of Alzheimer’s disease in relation to age, sex, and APOE genotype. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019, 15, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karran, E.; Mercken, M.; De Strooper, B. The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: An appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, K.L.; Klein, W.L. Amyloid beta oligomers in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis, treatment, and diagnosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafi, J.N.; Leng, M.; Arbanas, J.C.; Tseng, C.H.; Damberg, C.L.; Sarkisian, C.; Landon, B.E. Estimated Annual Spending on Aducanumab in the US Medicare Program. JAMA Health Forum 2022, 3, e214495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciani, D.J. Promising Results from Alzheimer’s Disease Passive Immunotherapy Support the Development of a Preventive Vaccine. Research 2019, 2019, 5341375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, C.P.; Berg, E.A.; Elliott-Bryant, R.; Fishman, J.B.; McKee, A.C.; Morin, P.J.; Shia, M.A.; Fine, R.E. Pyroglutamate-Abeta 3 and 11 colocalize in amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease cerebral cortex with pyroglutamate-Abeta 11 forming the central core. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 505, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Solano, I.; Mann, D.; Lemere, C.; Mercken, M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Characterization of Abeta11-40/42 peptide deposition in Alzheimer’s disease and young Down’s syndrome brains: Implication of N-terminally truncated Abeta species in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2006, 112, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirths, O.; Erck, C.; Martens, H.; Harmeier, A.; Geumann, C.; Jawhar, S.; Kumar, S.; Multhaup, G.; Walter, J.; Ingelsson, M.; et al. Identification of low molecular weight pyroglutamate A{beta} oligomers in Alzheimer disease: A novel tool for therapy and diagnosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 41517–41524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thal, D.R.; Walter, J.; Saido, T.C.; Fandrich, M. Neuropathology and biochemistry of Abeta and its aggregates in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandler, M.; Rockenstein, E.; Ubhi, K.; Hansen, L.; Adame, A.; Michael, S.; Galasko, D.; Santic, R.; Mattner, F.; Masliah, E. Detection of peri-synaptic amyloid-beta pyroglutamate aggregates in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease and in AbetaPP transgenic mice using a novel monoclonal antibody. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 28, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schilling, S.; Zeitschel, U.; Hoffmann, T.; Heiser, U.; Francke, M.; Kehlen, A.; Holzer, M.; Hutter-Paier, B.; Prokesch, M.; Windisch, M.; et al. Glutaminyl cyclase inhibition attenuates pyroglutamate Abeta and Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harigaya, Y.; Saido, T.C.; Eckman, C.B.; Prada, C.M.; Shoji, M.; Younkin, S.G. Amyloid beta protein starting pyroglutamate at position 3 is a major component of the amyloid deposits in the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, A.P.; Wong, B.X.; Johanssen, T.; Griffith, J.C.; Masters, C.L.; Bush, A.I.; Barnham, K.J.; Duce, J.A.; Cherny, R.A. Amyloid-beta Peptide Abeta3pE-42 Induces Lipid Peroxidation, Membrane Permeabilization, and Calcium Influx in Neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 6134–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portelius, E.; Lashley, T.; Westerlund, A.; Persson, R.; Fox, N.C.; Blennow, K.; Revesz, T.; Zetterberg, H. Brain amyloid-beta fragment signatures in pathological ageing and Alzheimer’s disease by hybrid immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry. Neurodegener. Dis. 2015, 15, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portelius, E.; Bogdanovic, N.; Gustavsson, M.K.; Volkmann, I.; Brinkmalm, G.; Zetterberg, H.; Winblad, B.; Blennow, K. Mass spectrometric characterization of brain amyloid beta isoform signatures in familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piccini, A.; Russo, C.; Gliozzi, A.; Relini, A.; Vitali, A.; Borghi, R.; Giliberto, L.; Armirotti, A.; D’Arrigo, C.; Bachi, A.; et al. beta-amyloid is different in normal aging and in Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 34186–34192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, C.; Violani, E.; Salis, S.; Venezia, V.; Dolcini, V.; Damonte, G.; Benatti, U.; D’Arrigo, C.; Patrone, E.; Carlo, P.; et al. Pyroglutamate-modified amyloid beta-peptides–AbetaN3(pE)–strongly affect cultured neuron and astrocyte survival. J. Neurochem. 2002, 82, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Barrow, C.J. The A beta 3-pyroglutamyl and 11-pyroglutamyl peptides found in senile plaque have greater beta-sheet forming and aggregation propensities in vitro than full-length A beta. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 10871–10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirths, O.; Breyhan, H.; Cynis, H.; Schilling, S.; Demuth, H.U.; Bayer, T.A. Intraneuronal pyroglutamate-Abeta 3-42 triggers neurodegeneration and lethal neurological deficits in a transgenic mouse model. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grochowska, K.M.; Yuanxiang, P.; Bar, J.; Raman, R.; Brugal, G.; Sahu, G.; Schweizer, M.; Bikbaev, A.; Schilling, S.; Demuth, H.U.; et al. Posttranslational modification impact on the mechanism by which amyloid-beta induces synaptic dysfunction. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 962–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, L.C.; Schoneck, M.; Sangarapillai, N.; Honold, D.; Shah, N.J.; Langen, K.J.; Willbold, D.; Kutzsche, J.; Schemmert, S.; Willuweit, A. PEAbeta Triggers Cognitive Decline and Amyloid Burden in a Novel Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kimpe, L.; van Haastert, E.S.; Kaminari, A.; Zwart, R.; Rutjes, H.; Hoozemans, J.J.; Scheper, W. Intracellular accumulation of aggregated pyroglutamate amyloid beta: Convergence of aging and Abeta pathology at the lysosome. Age 2013, 35, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar-Singh, S.; De Jonghe, C.; Cruts, M.; Kleinert, R.; Wang, R.; Mercken, M.; De Strooper, B.; Vanderstichele, H.; Lofgren, A.; Vanderhoeven, I.; et al. Nonfibrillar diffuse amyloid deposition due to a gamma(42)-secretase site mutation points to an essential role for N-truncated A beta(42) in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 2589–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lalowski, M.; Golabek, A.; Lemere, C.A.; Selkoe, D.J.; Wisniewski, H.M.; Beavis, R.C.; Frangione, B.; Wisniewski, T. The “nonamyloidogenic” p3 fragment (amyloid beta17-42) is a major constituent of Down’s syndrome cerebellar preamyloid. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 33623–33631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saido, T.C.; Iwatsubo, T.; Mann, D.M.; Shimada, H.; Ihara, Y.; Kawashima, S. Dominant and differential deposition of distinct beta-amyloid peptide species, A beta N3(pE), in senile plaques. Neuron 1995, 14, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nussbaum, J.M.; Schilling, S.; Cynis, H.; Silva, A.; Swanson, E.; Wangsanut, T.; Tayler, K.; Wiltgen, B.; Hatami, A.; Ronicke, R.; et al. Prion-like behaviour and tau-dependent cytotoxicity of pyroglutamylated amyloid-beta. Nature 2012, 485, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayer, T.A. Pyroglutamate Abeta cascade as drug target in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1880–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintun, M.A.; Lo, A.C.; Duggan Evans, C.; Wessels, A.M.; Ardayfio, P.A.; Andersen, S.W.; Shcherbinin, S.; Sparks, J.; Sims, J.R.; Brys, M.; et al. Donanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Eng. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demattos, R.B.; Lu, J.; Tang, Y.; Racke, M.M.; Delong, C.A.; Tzaferis, J.A.; Hole, J.T.; Forster, B.M.; McDonnell, P.C.; Liu, F.; et al. A plaque-specific antibody clears existing beta-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Neuron 2012, 76, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aduhelm. ADUHELM™ (Aducanumab-Avwa) Injection, for Intravenous Use. Initial U.S. Approval: 2021. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/761178s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Lowe, S.L.; Willis, B.A.; Hawdon, A.; Natanegara, F.; Chua, L.; Foster, J.; Shcherbinin, S.; Ardayfio, P.; Sims, J.R. Donanemab (LY3002813) dose-escalation study in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 7, e12112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisman-Mentesh, A.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, M.; DeKosky, B.J.; Wine, Y. The Molecular Mechanisms That Underlie the Immune Biology of Anti-drug Antibody Formation following Treatment with Monoclonal Antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, G.; Manoutcharian, K.; Vasilevko, V.; Munguia, M.E.; Govezensky, T.; Coronas, G.; Luz-Madrigal, A.; Cribbs, D.H.; Gevorkian, G. Immunodominant epitope and properties of pyroglutamate-modified Abeta-specific antibodies produced in rabbits. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 213, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cynis, H.; Frost, J.L.; Crehan, H.; Lemere, C.A. Immunotherapy targeting pyroglutamate-3 Abeta: Prospects and challenges. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Hu, Z.W.; Chen, P.G.; Sun, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.F.; Li, Y.M. Prophylactic Vaccine Based on Pyroglutamate-3 Amyloid beta Generates Strong Antibody Response and Rescues Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukicevic, M.; Fiorini, E.; Siegert, S.; Carpintero, R.; Rincon-Restrepo, M.; Lopez-Deber, P.; Piot, N.; Ayer, M.; Rentero, I.; Babolin, C.; et al. An amyloid beta vaccine that safely drives immunity to a key pathological species in Alzheimer’s disease: Pyroglutamate amyloid beta. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakrania, P.; Hall, G.; Bouter, Y.; Bouter, C.; Beindorff, N.; Cowan, R.; Davies, S.; Price, J.; Mpamhanga, C.; Love, E.; et al. Discovery of a novel pseudo beta-hairpin structure of N-truncated amyloid-beta for use as a vaccine against Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrushina, I.; Hovakimyan, A.; Harahap-Carrillo, I.S.; Davtyan, H.; Antonyan, T.; Chailyan, G.; Kazarian, K.; Antonenko, M.; Jullienne, A.; Hamer, M.M.; et al. Characterization and preclinical evaluation of the cGMP grade DNA based vaccine, AV-1959D to enter the first-in-human clinical trials. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 139, 104823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Hovakimyan, A.; Zagorski, K.; Antonyan, T.; Petrushina, I.; Davtyan, H.; Chailyan, G.; Hasselmann, J.; Iba, M.; Adame, A.; et al. Efficacy and immunogenicity of MultiTEP-based DNA vaccines targeting human alpha-synuclein: Prelude for IND enabling studies. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovakimyan, A.; Antonyan, T.; Shabestari, S.K.; Svystun, O.; Chailyan, G.; Coburn, M.A.; Carlen-Jones, W.; Petrushina, I.; Chadarevian, J.P.; Zagorski, K.; et al. A MultiTEP platform-based epitope vaccine targeting the phosphatase activating domain (PAD) of tau: Therapeutic efficacy in PS19 mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovakimyan, A.; Zagorski, K.; Chailyan, G.; Antonyan, T.; Melikyan, L.; Petrushina, I.; Batt, D.G.; King, O.; Ghazaryan, M.; Donthi, A.; et al. Immunogenicity of MultiTEP platform technology-based Tau vaccine in non-human primates. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davtyan, H.; Ghochikyan, A.; Petrushina, I.; Hovakimyan, A.; Davtyan, A.; Cribbs, D.H.; Agadjanyan, M.G. The MultiTEP platform-based Alzheimer’s disease epitope vaccine activates a broad repertoire of T helper cells in nonhuman primates. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davtyan, H.; Hovakimyan, A.; Kiani Shabestari, S.; Antonyan, T.; Coburn, M.A.; Zagorski, K.; Chailyan, G.; Petrushina, I.; Svystun, O.; Danhash, E.; et al. Testing a MultiTEP-based combination vaccine to reduce Abeta and tau pathology in Tau22/5xFAD bigenic mice. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neddens, J.; Daurer, M.; Flunkert, S.; Beutl, K.; Loeffler, T.; Walker, L.; Attems, J.; Hutter-Paier, B. Correlation of pyroglutamate amyloid beta and ptau Ser202/Thr205 levels in Alzheimer’s disease and related murine models. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eimer, W.A.; Vassar, R. Neuron loss in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease correlates with intraneuronal Abeta42 accumulation and Caspase-3 activation. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wittnam, J.L.; Portelius, E.; Zetterberg, H.; Gustavsson, M.K.; Schilling, S.; Koch, B.; Demuth, H.U.; Blennow, K.; Wirths, O.; Bayer, T.A. Pyroglutamate amyloid beta (Abeta) aggravates behavioral deficits in transgenic amyloid mouse model for Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 8154–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S.L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L.; et al. Intraneuronal beta-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10129–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guntert, A.; Dobeli, H.; Bohrmann, B. High sensitivity analysis of amyloid-beta peptide composition in amyloid deposits from human and PS2APP mouse brain. Neuroscience 2006, 143, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Tan, M.S.; Yu, J.T.; Zhang, W.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.F.; Jiang, T.; Tan, L. Toll-like receptor 9 promoter polymorphism is associated with decreased risk of Alzheimer’s disease in Han Chinese. J. Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.M.; Miao, D.; Cao, X.P.; Tan, L.; Tan, L. Innate immune activation in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selles, M.C.; Fortuna, J.T.S.; Santos, L.E. Immunomodulation via Toll-like Receptor 9: An Adjunct Therapy Strategy against Alzheimer’s Disease? J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 4864–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venegas, C.; Heneka, M.T. Danger-associated molecular patterns in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benbenishty, A.; Gadrich, M.; Cottarelli, A.; Lubart, A.; Kain, D.; Amer, M.; Shaashua, L.; Glasner, A.; Erez, N.; Agalliu, D.; et al. Prophylactic TLR9 stimulation reduces brain metastasis through microglia activation. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e2006859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Dementia Key Fact. 2021. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs362/en/ (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures; Alzheimer’s Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Panza, F.; Lozupone, M.; Logroscino, G.; Imbimbo, B.P. A critical appraisal of amyloid-beta-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, M.A.; Sousa, E. BACE-1 and gamma-Secretase as Therapeutic Targets for Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Xia, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. Targeting Amyloidogenic Processing of APP in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayev, R.; D’Adamio, L. Inhibition of gamma-secretase worsens memory deficits in a genetically congruous mouse model of Danish dementia. Mol. Neurodegener. 2012, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panza, F.; Lozupone, M.; Watling, M.; Imbimbo, B.P. Do BACE inhibitor failures in Alzheimer patients challenge the amyloid hypothesis of the disease? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloway, S.; Farlow, M.; McDade, E.; Clifford, D.B.; Wang, G.; Llibre-Guerra, J.J.; Hitchcock, J.M.; Mills, S.L.; Santacruz, A.M.; Aschenbrenner, A.J.; et al. A trial of gantenerumab or solanezumab in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puzzo, D.; Arancio, O. Amyloid-beta peptide: Dr. Jekyll or Mr. Hyde? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 33 (Suppl. S1), S111–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, H.A.; Peers, C. Physiological roles for amyloid beta peptides. J. Physiol. 2006, 575, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brothers, H.M.; Gosztyla, M.L.; Robinson, S.R. The Physiological Roles of Amyloid-beta Peptide Hint at New Ways to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zagorski, K.; Chailyan, G.; Hovakimyan, A.; Antonyan, T.; Kiani Shabestari, S.; Petrushina, I.; Davtyan, H.; Cribbs, D.H.; Blurton-Jones, M.; Masliah, E.; et al. Immunogenicity of MultiTEP-Platform-Based Recombinant Protein Vaccine, PV-1950R, Targeting Three B-Cell Antigenic Determinants of Pathological alpha-Synuclein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.J.; Lee, J.K.; Shin, O.S. Aging and the Immune System: The Impact of Immunosenescence on Viral Infection, Immunity and Vaccine Immunogenicity. Immune Netw. 2019, 19, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran Terol, P.; Kumita, J.R.; Hook, S.C.; Dobson, C.M.; Esbjorner, E.K. Solvent exposure of Tyr10 as a probe of structural differences between monomeric and aggregated forms of the amyloid-beta peptide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coles, M.; Bicknell, W.; Watson, A.A.; Fairlie, D.P.; Craik, D.J. Solution structure of amyloid beta-peptide(1–40) in a water-micelle environment. Is the membrane-spanning domain where we think it is? Biochemistry 1998, 37, 11064–11077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.E.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M. Improved method for predicting linear B-cell epitopes. Immunome Res. 2006, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, R.J. Rapid coomassie blue staining of protein gels. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2010, 2010, pdb.prot5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, X.N.; Wang, H.F.; Chen, S.D.; Zhang, Y.R.; Chen, S.F.; Cui, M.; Cheng, W.; Dong, Q.; Ma, T.; et al. The dynamics of plasma biomarkers across the Alzheimer’s continuum. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.B.; Janelidze, S.; Stomrud, E.; Palmqvist, S.; van Westen, D.; Dage, J.L.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Hansson, O. Plasma markers predict changes in amyloid, tau, atrophy and cognition in non-demented subjects. Brain 2021, 144, 2826–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.K. An Algorithm for Preclinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelemy, N.R.; Li, Y.; Joseph-Mathurin, N.; Gordon, B.A.; Hassenstab, J.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Buckles, V.; Fagan, A.M.; Perrin, R.J.; Goate, A.M.; et al. A soluble phosphorylated tau signature links tau, amyloid and the evolution of stages of dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Thijssen, E.H.; Vermunt, L.; Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H.; van der Flier, W.M.; Mielke, M.M.; Del Campo, M. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: Towards clinical implementation. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chetelat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttinen, M.; Paananen, J.; Neme, A.; Mitra, V.; Takalo, M.; Natunen, T.; Paldanius, K.M.A.; Makinen, P.; Bremang, M.; Kurki, M.I.; et al. A multiomic approach to characterize the temporal sequence in Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 124, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ” presents endpoint titers of Antibodies in the sera of an individual mouse.
” presents endpoint titers of Antibodies in the sera of an individual mouse.
 ” presents endpoint titers of Antibodies in the sera of an individual mouse.
” presents endpoint titers of Antibodies in the sera of an individual mouse.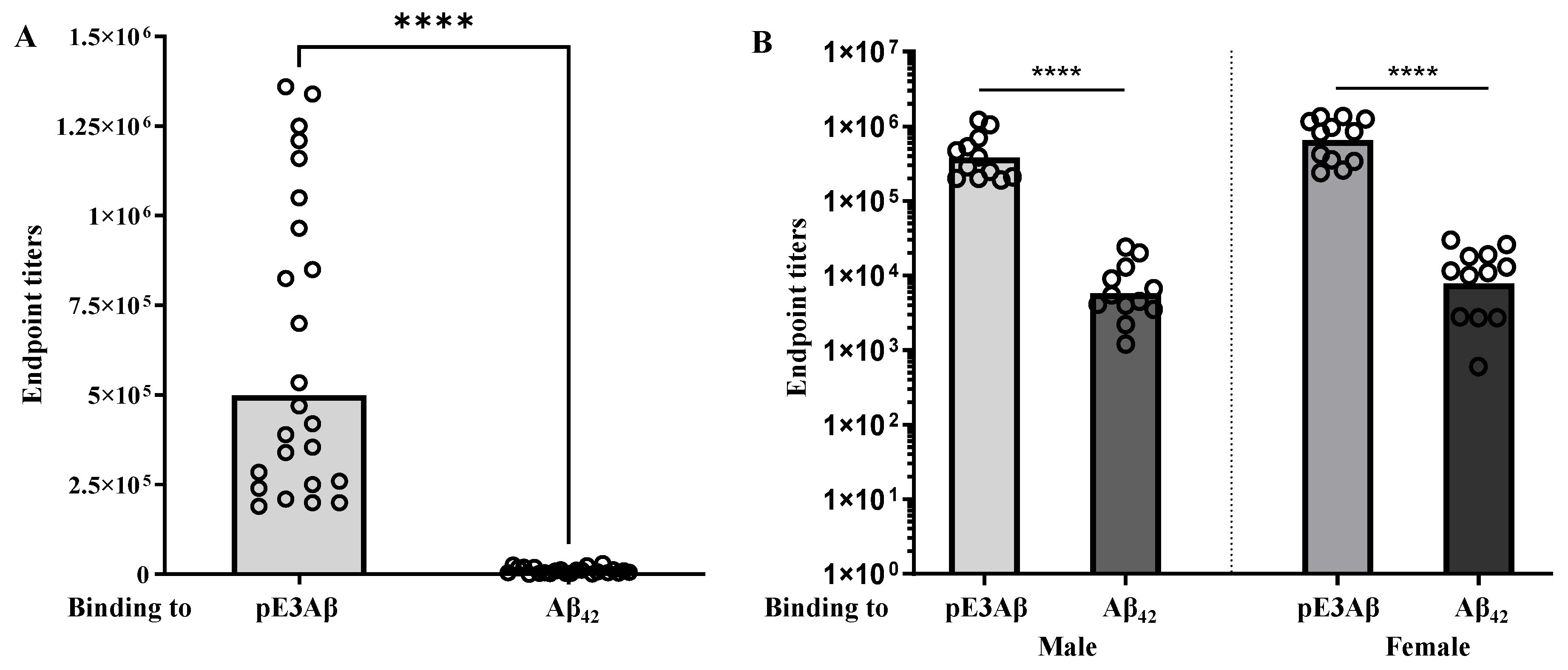

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zagorski, K.; King, O.; Hovakimyan, A.; Petrushina, I.; Antonyan, T.; Chailyan, G.; Ghazaryan, M.; Hyrc, K.L.; Chadarevian, J.P.; Davtyan, H.; et al. Novel Vaccine against Pathological Pyroglutamate-Modified Amyloid Beta for Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129797
Zagorski K, King O, Hovakimyan A, Petrushina I, Antonyan T, Chailyan G, Ghazaryan M, Hyrc KL, Chadarevian JP, Davtyan H, et al. Novel Vaccine against Pathological Pyroglutamate-Modified Amyloid Beta for Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129797
Chicago/Turabian StyleZagorski, Karen, Olga King, Armine Hovakimyan, Irina Petrushina, Tatevik Antonyan, Gor Chailyan, Manush Ghazaryan, Krzysztof L. Hyrc, Jean Paul Chadarevian, Hayk Davtyan, and et al. 2023. "Novel Vaccine against Pathological Pyroglutamate-Modified Amyloid Beta for Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129797





