A Role for Advanced Glycation End Products in Molecular Ageing
Abstract
1. Introduction
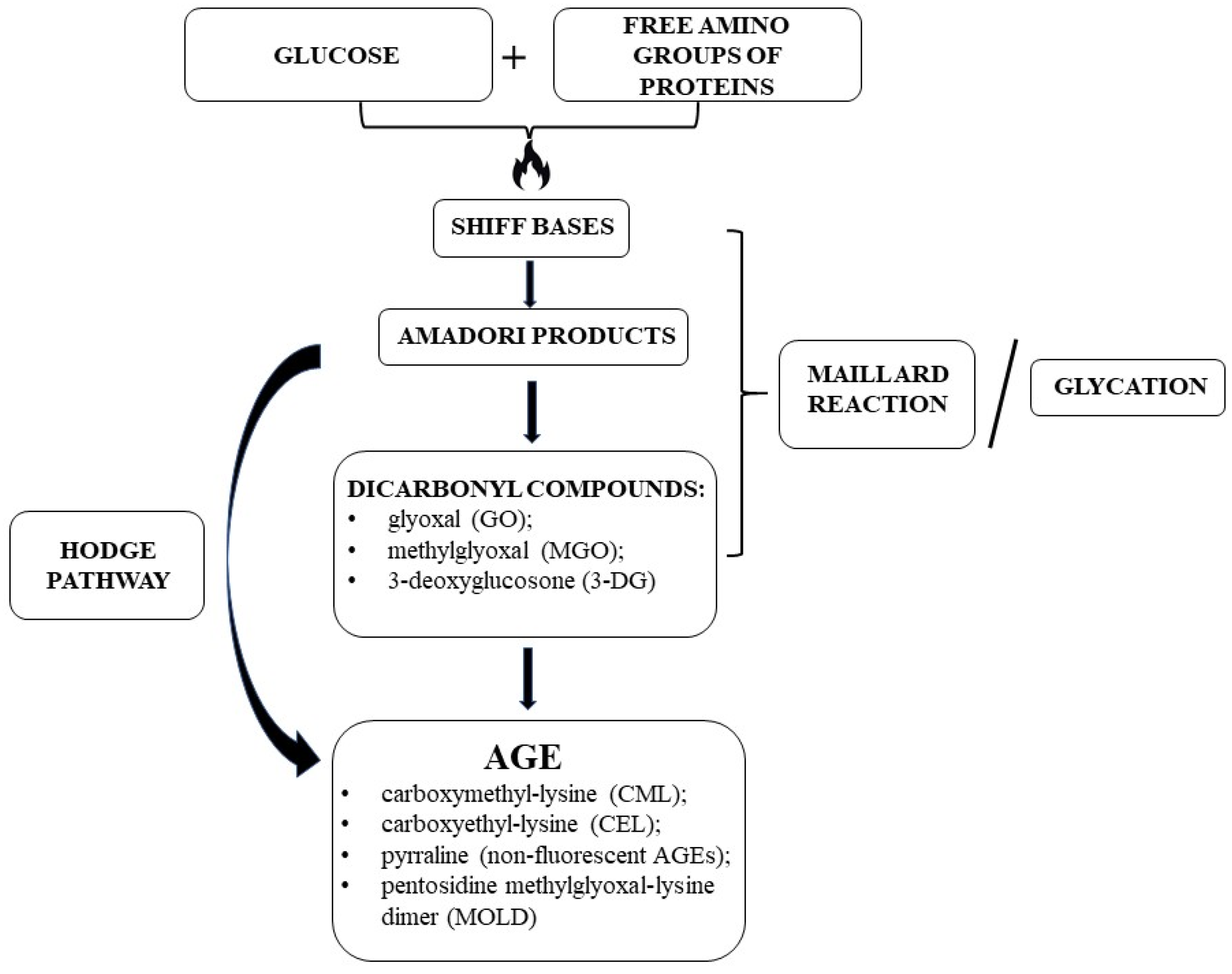
2. AGEs
2.1. AGE Formation and Biochemistry
2.2. Endogenous and Exogenous AGEs: Balancing the AGE Content
3. AGEs: Mechanism of Action
3.1. The AGE–RAGE Interaction
3.2. AGEs Trigger Oxidative Stress
3.3. Impact of AGEs on the ECM and Ageing
3.4. Inhibitors and Decoy Receptors for AGEs
4. The Role of AGEs in Modulating the Immune System
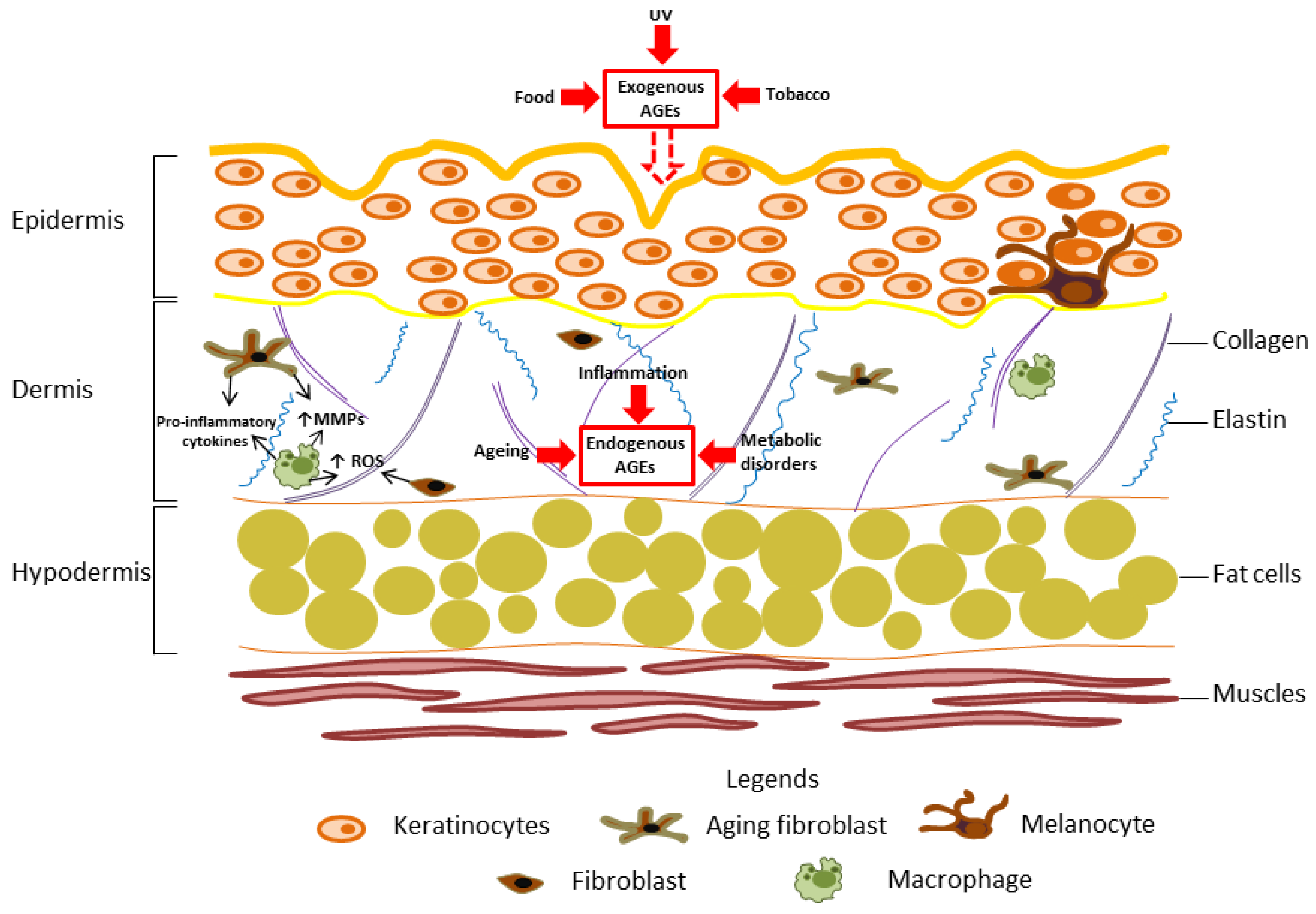
5. AGEs in Ageing Skin
6. AGEs and Vascular Dysfunction
7. AGEs in Ageing Ocular System
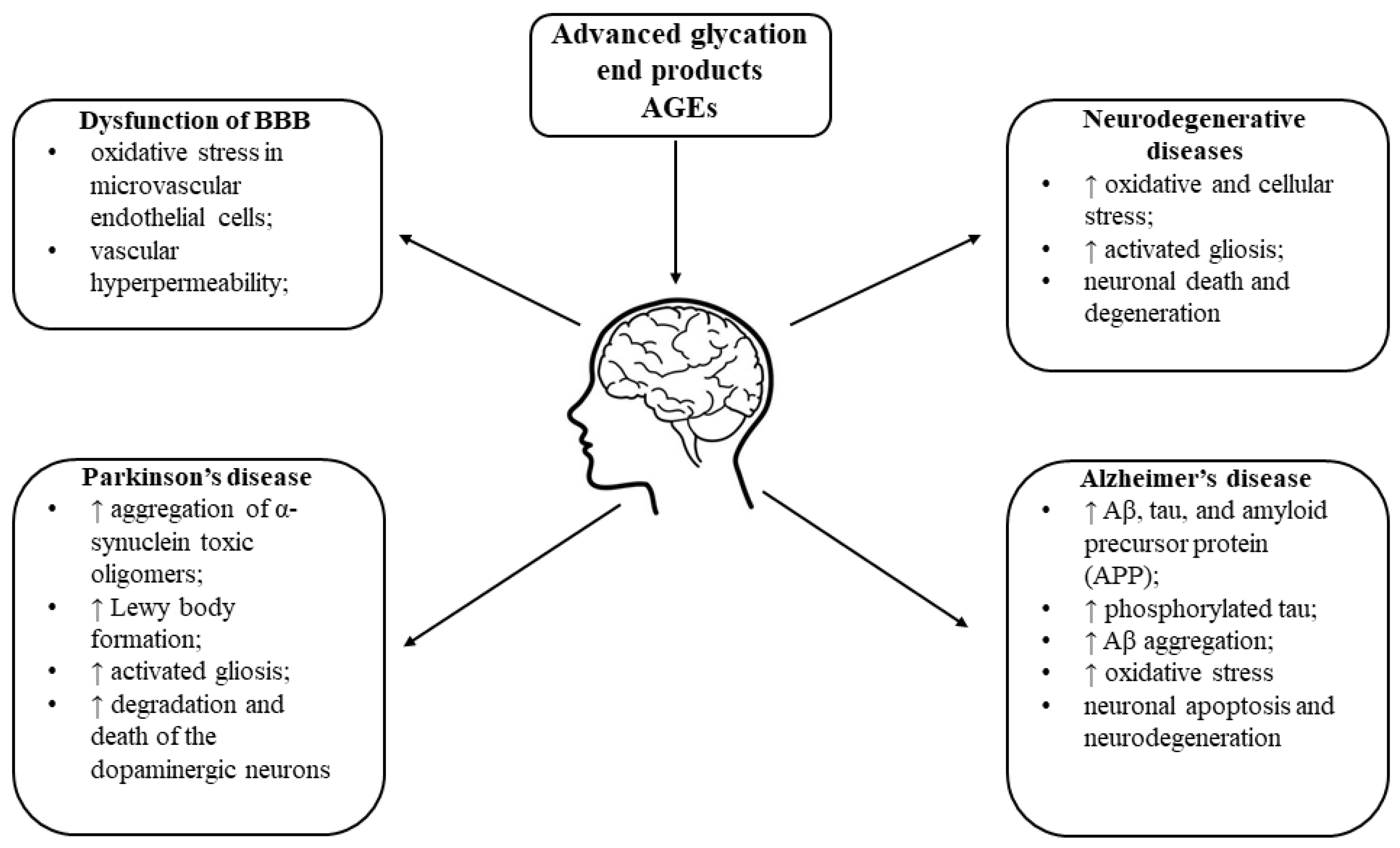
8. AGEs in Brain Ageing
9. AGEs and Their Impact on Ageing-Related Changes in Pancreatic β-Cells
10. AGEs and Deterioration of Kidney Function with Ageing
11. AGEs and Cancer
12. AGE and Muscle Ageing
13. Anti-AGEs Strategies
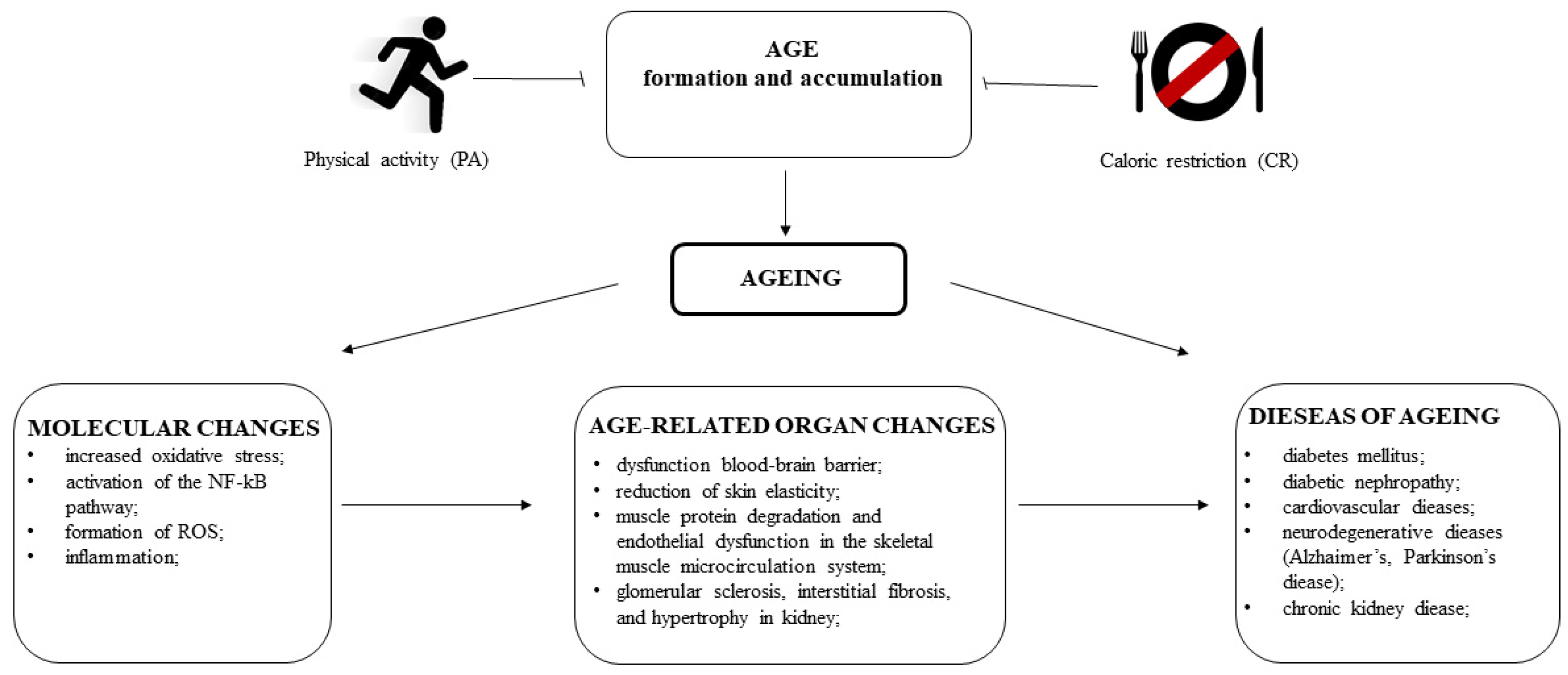
14. Lifestyle Interventions and AGEs
14.1. The Relationship between PA and AGEs
14.2. CR as a Way to Reduce the Effects of AGEs
15. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zong, H.; Ward, M.; Stitt, A.W. AGEs, RAGE, and diabetic retinopathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2011, 11, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Yee Ooi, X.; Parvus, M.; Valdez, L.; Tsin, A. Advanced Glycation End Products: Formation, Role in Diabetic Complications, and Potential in Clinical Applications. In The Eye and Foot in Diabetes; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semba, R.D.; Nicklett, E.J.; Ferrucci, L. Does accumulation of advanced glycation end products contribute to the aging phenotype? J. Gerontol. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribarri, J.; Cai, W.; Peppa, M.; Goodman, S.; Ferrucci, L.; Striker, G.; Vlassara, H. Circulating glycotoxins and dietary advanced glycation endproducts: Two links to inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and aging. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2007, 62, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.; Mishra, M. AGE-RAGE stress, stressors, and antistressors in health and disease. Int. J. Angiol. 2018, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen, M.W.; Hedegaard, R.V.; Andersen, J.M.; de Courten, B.; Bügel, S.; Nielsen, J.; Skibsted, L.H.; Dragsted, L.O. Advanced glycation endproducts in food and their effects on health. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Niu, L.; Tay, F.R. Clinical/Translational Aspects of Advanced Glycation End-Products. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, T.L. Dietary Advanced Glycation End-Products Elicit Toxicological Effects by Disrupting Gut Microbiome and Immune Homeostasis. J. Immunotoxicol. 2021, 18, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twarda-Clapa, A.; Olczak, A.; Białkowska, A.M.; Koziołkiewicz, M. Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs): Formation, Chemistry, Classification, Receptors, and Diseases Related to AGEs. Cells 2022, 11, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournet, M.; Bonté, F.; Desmoulière, A. Glycation Damage: A Possible Hub for Major Pathophysiological Disorders and Aging. Aging Dis. 2018, 1, 880–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottum, M.S.; Mistry, A.M. Advanced glycation endproducts: Modifiable environmental factors profoundly mediate insulin resistance. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Liu, J.; Dong, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Novel advances in inhibiting advanced glycation end product formation using natural compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, K.; Yoo, Y.; Son, M.; Lee, J.; Jeong, G.B.; Park, Y.M.; Salekdeh, G.H.; Lee, B. Advanced glycation end-products produced systemically and by macrophages: A common contributor to inflammation and degenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 177, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, V.; Kumar, V.; Singh, K.; Kumar, A.; Kim, J.J. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) may be a striking link between modern diet and health. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalkwijk, C.G.; Miyata, T. Early- and advanced non-enzymatic glycation in diabetic vascular complications: The search for therapeutics. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.B.; Hogger, P. Dietary polyphenols and type 2 diabetes: Current insights and future perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xia, Y.; Zeng, M.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Liu, J. Caffeic acid inhibits the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and mitigates the ages-induced oxidative stress and inflammation reaction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Hsieh, W.T.; Chen, S.U.; Chiang, B.H. Hematopoietic and myeloprotective activities of an acidic Angelica sinensis polysaccharide on human CD34+ stem cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Do, M.; Lee, J.; Jeong, M.; Lim, O.; Kim, S. Inhibitory effect of arachis hypogaea (peanut) and its phenolics against methylglyoxal-derived advanced glycation end product toxicity. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, M.; Yamagishi, S. Possible involvement of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 973–978.21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy Addi, U.; Jakhotia, S.; Reddy, S.S.; Reddy, G.B. Age-related neuronal damage by advanced glycation end products through altered proteostasis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 355, 109840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröter, D.; Höhn, A. Role of Advanced Glycation End Products in Carcinogenesis and their Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 5245–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosato, M.; Zamboni, V.; Ferrini, A.; Cesari, M. The aging process and potential interventions to extend life expectancy. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gladyshev, V.N.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Clarke, S.G.; Cuervo, A.M.; Fiehn, O.; de Magalhães, J.P.; Mau, T.; Maes, M.; Moritz, R.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; et al. Molecular damage in aging. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.F.L.; Schumacher, B. Principles of the Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Aging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, A.J.; Walker, A.E.; Magerko, K.A.; Bramwell, R.C.; Black, A.D.; Henson, G.D.; Lawson, B.R.; Lesniewski, L.A.; Seals, D.R. Life-long caloric restriction reduces oxidative stress and preserves nitric oxide bioavailability and function in arteries of old mice. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Brown, K.; Hirschey, M.D.; Verdin, E.; Chen, D. Calorie restriction reduces oxidative stress by SIRT3-mediated SOD2 activation. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 662–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinmura, K. Effects of caloric restriction on cardiac oxidative stress and mitochondrial bioenergetics: Potential role of cardiac sirtuins. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 528935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungvari, Z.; Parrado-Fernandez, C.; Csiszar, A.; de Cabo, R. Mechanisms underlying caloric restriction and lifespan regulation: Implications for vascular aging. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luevano-Contreras, C.; Chapman-Novakofski, K. Dietary advanced glycation end products and aging. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, S. Potential clinical utility of advanced glycation end product cross-link breakers in age- and diabetes-associated disorders. Rejuvenation Res. 2012, 15, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, C.; Davis, K.E.; Imrhan, V.; Juma, S.; Vijayagopal, P. Advanced Glycation End Products and Risks for Chronic Diseases: Intervening Through Lifestyle Modification. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2017, 13, 384–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordain, L.; Eaton, S.B.; Sebastian, A.; Mann, N.; Lindeberg, S.; Watkins, B.A.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Brand-Miller, J. Origins and evolution of the western diet: Health implications for the 21st century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M.; Vlassara, H.; Cerami, A. Nonenzymatic glycosylation and the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Ann. Intern. Med. 1984, 101, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.; Jacobs, K.; Haucke, E.; Navarrete Santos, A.; Grune, T.; Simm, A. Role of advanced glycation end products in cellular signaling. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nursten, H.E. The Maillard Reaction. Chemistry, Biochemistry and Implications; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, S.R.; Baynes, J.W. Maillard reaction products in tissue proteins: New products and new perspectives. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, A.; Giovino, A.; Benny, J.; Martinelli, F. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs): Biochemistry, Signaling, Analytical Methods, and Epigenetic Effects. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Parravano, M.; Micheli, A.; Gaddini, L.; Matteucci, A.; Mallozzi, C.; Facchiano, F.; Malchiodi-Albedi, F.; Pricci, F. A quick, simple method for detecting circulating fluorescent advanced glycation end-products: Correlation with in vitro and in vivo non-enzymatic glycation. Metabolism 2017, 71, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, S.; Blumenfeld, O.; Ranney, H.M. Studies of an Unusual Hemoglobin in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1969, 36, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corica, D.; Pepe, G.; Currò, M.; Aversa, T.; Tropeano, A.; Ientile, R.; Wasniewska, M. Methods to investigate advanced glycation end-product and their application in clinical practice. Methods 2022, 203, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, T.; Cai, W.; Peppa, M.; Dardaine, V.; Baliga, B.; Uribarri, J.; Vlassara, H. Advanced glycoxidation end products in commonly consumed foods. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2004, 104, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowotny, K.; Schroter, D.; Schreiner, M.; Grune, T. Dietary advanced glycation end products and their relevance for human health. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 47, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribarri, J.; Woodruff, S.; Goodman, S.; Cai, W.; Chen, X.; Pyzik, R.; Yong, A.; Striker, G.E.; Vlassara, H. Advanced glycation end products in foods and a practical guide to their reduction in the diet. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwabara, S.; Hosoe, H.; Ohno, R.I.; Nagai, R.; Shiraki, M. Development and evaluation of novel ELISA for determination of urinary pentosidine. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Nakamura, K.; Kanai, M.; Nagayama, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Saito, N.; Nagata, M. Determination of urinary and serum pentosidine and its application to elder patients. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 21, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Ohishi, T.; Aoshima, H.; Kawana, K.; Kushida, K.; Inoue, T.; Horiuchi, K. The Maillard protein cross-link pentosidine in urine from diabetic patients. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, T.H.; Humpert, P.M.; Nawroth, P.P.; Bierhaus, A. Reactive metabolites and AGE/RAGE-mediated cellular dysfunction affect the aging process: A mini-review. Gerontology 2011, 57, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapos, M.P. Methylglyoxal in living organisms—Chemistry, biochemistry, toxicology and biological implications. Toxicol. Lett. 1999, 110, 145–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisswenger, P.J.; Howell, S.K.; Nelson, R.G.; Mauer, M.; Szwergold, B.S. Alpha-oxoaldehyde metabolism and diabetic complications. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaman, I.; Bélanger, M.; Magistretti, P.J. Methylglyoxal, the dark side of glycolysis. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Battah, S.; Karachalias, N.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Horanyi, M.; Baroti, K.; Hollan, S.; Thornalley, P.J. Increased formation of methylglyoxal and protein glycation, oxidation and nitrosation in triosephosphate isomerase deficiency. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1639, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, N.; Thornalley, P.J. Methylglyoxal, glyoxalase 1 and the dicarbonyl proteome. Amino Acids 2010, 42, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koschinsky, T.; He, C.J.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Bucala, R.; Liu, C.; Buenting, C.; Heitmann, K.; Vlassara, H. Orally absorbed reactive glycation products (glycotoxins): An environmental risk factor in diabetic nephropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6474–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheijen, J.L.J.M.; Hanssen, N.M.J.; van Greevenbroek, M.M.; Van der Kallen, C.J.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Schalkwijk, C.G. Dietary Intake of Advanced Glycation Endproducts Is Associated with Higher Levels of Advanced Glycation Endproducts in Plasma and Urine: The CODAM Study. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, T.; Wada, Y.; Cai, Z.; Iida, Y.; Horie, K.; Yasuda, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kurokawa, K.; van Ypersele de Strihou, C. Implication of an increased oxidative stress in the formation of advanced glycation end products in patients with end-stage renal failure. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makita, Z.; Bucala, R.; Rayfield, E.J.; Friedman, E.A.; Kaufman, A.M.; Korbet, S.M.; Barth, R.H.; Winston, J.A.; Fuh, H.; Manogue, K.R.; et al. Reactive glycosylation endproducts in diabetic uraemia and treatment of renal failure. Lancet 1994, 343, 1519–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Ueda, Y.; Shinzato, T.; Iida, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Kurokawa, K.; van Ypersele de Strihou, C.; Maeda, K. Accumulation of albumin-linked and free-form pentosidine in the circulation of uremic patients with end-stage renal failure: Renal implications in the pathophysiology of pentosidine. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1996, 7, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawada, A.; Machowiak, A.; Rychter, A.M.; Ratajczak, A.E.; Szymczak-Tomczak, A.; Dobrowolska, A.; Krela-Kaźmierczak, I. Accumulation of Advanced Glycation End-Products in the Body and Dietary Habits. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, C.; Founds, H.; Nicholl, I.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Giordano, D.; Vanpatten, S.; Lee, A.; Al-Abed, Y.; Vlassara, H.; Bucala, R.; et al. Tobacco smoke is a source of toxic reactive glycation products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13915–13920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, R.D.; Beyan, H.; Sawtell, P.; Boehm, B.O.; Spector, T.D.; Snieder, H. Level of an advanced glycated end product is genetically determined: A study of normal twins. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2441–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Rabbani, N.; Thornalley, P.J. Glyoxalase in ageing. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornalley, P.J. The glyoxalase system in health and disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 1993, 14, 287–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga da-Cunha, M.; Jacquemin, P.; Delpierre, G.; Godfraind, C.; Théate, I.; Vertommen, D.; Clotman, F.; Lemaigre, F.; Devuyst, O.; Van Schaftingen, E. Increased protein glycation in fructosamine 3-kinase-deficient mice. Biochem. J. 2006, 399, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, J.R.; Beisswenger, P.J.; Szwergold, B.S. Some clues as to the regulation, expression, function, and distribution of fructosamine-3-kinase and fructosamine-3-kinase-related protein. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H.; Uribarri, J. Glycoxidation and diabetic complications: Modern lessons and a warning? Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2004, 5, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Lüthen, R.; Häussinger, D.; Sebeková, K.; Schinzel, R.; Voelker, W.; Heidland, A.; Thornalley, P.J. Increased Protein Glycation in Cirrhosis and Therapeutic Strategies to Prevent It. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisugi, R.; Kouzuma, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Akizuki, S.; Miyamoto, H.; Someya, Y.; Yokoyama, J.; Abe, I.; Hirai, N.; Ohnishi, A. Structural and Glycation Site Changes of Albumin in Diabetic Patient with Very High Glycated Albumin. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 382, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, G. Receptor for advanced glycation end products and athero¬sclerosis: From basic mechanisms to clinical implications. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, L.; Gatti, E.; Zeni, F.; Antonelli, A.; Catucci, A.; Koch, M.; Pompilio, G.; Fritz, G.; Raucci, A.; Bianchi, M.E. The receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) is only present in mammals, and belongs to a family of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo-Stella, N.; Bozzini, S.; De Silvestri, A.; Sbarsi, I.; Pizzochero, C.; Lorusso, L.; Martinetti, M.; Cuccia, M. Molecular study of receptor for advanced glycation end product gene promoter and identification of specific HLA haplotypes possibly involved in chronic fatigue syndrome. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattilo, B.M.; Fritz, G.; Leclerc, E.; Vander Kooi, C.W.; Heizmann, C.W.; Chazin, W.J. The extracellular region of the receptor for advanced glycation end products is composed of two independent structural units. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 6957–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.R.; Lue, L.; Paul, G.; Patel, A.; Sabbagh, M.N. Receptor for advanced glycation endproduct modulators: A new therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2015, 24, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, F.; Rabizadeh, S.; Mansournia, M.A.; Mirmiranpoor, H.; Salehi, S.S.; Akhavan, S.; Esteghamati, A.; Nakhjavani, M. Inflammatory, oxidative stress and anti-oxidative markers in patients with endometrial carcinoma and diabetes. Cytokine 2019, 120, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlmann, M.; Okhrimenko, A.; Marcinkowski, P.; Osterland, M.; Herrmann, P.; Smith, J.; Heizmann, C.W.; Schlag, P.M.; Stein, U. RAGE mediates S100A4-induced cell motility via MAPK/ERK and hypoxia signaling and is a prognostic biomarker for human colorectal cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 3220–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Sakoda, M.; Ueno, S.; Hiwatashi, K.; Iino, S.; Minami, K.; Kawasaki, Y.; Hashiguchi, M.; Tanoue, K.; Mataki, Y.; et al. Clinical implication of the relationship between high mobility group box-1 and tumor differentiation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3411–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Yamagishi, S. Involvement of toxic AGEs (TAGE) in the pathogenesis of diabetic vascular complications and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2009, 16, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Giambanco, I.; Donato, R. RAGE in tissue homeostasis, repair and regeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadipooya, K.; Uy, E.M. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), receptor for AGEs, diabetes, and bone: Review of the literature. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1799–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislinger, T.; Fu, C.; Huber, B.; Qu, W.; Taguchi, A.; Du Yan, S.; Hofmann, M.; Yan, S.F.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Stern, D.; et al. Ne-(carboxymethyl)lysine adducts of proteins are ligands for receptor for advanced glycation end prod¬ucts that activate cell signaling pathways and modulate gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31740–31749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.S.; Schmidt, A.M.; Banes, A.K.; Wang, X.; Stern, D.M.; Marrero, M.B. S100b-RAGE-mediated augmentation of angiotensin II-induced activation of JAK2 in vascular smooth muscle cells is dependent on PLD2. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavakis, T.; Bierhaus, A.; Nawroth, P. RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation end products): A central player in the inflammatory response. Microbes Infect. 2004, 6, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Liu, N.; Wang, C.; Qin, B.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, M.; Chang, L.; Yan, L.J.; Zhao, B. Role of RAGE in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuah, Y.K.; Basir, R.; Talib, H.; Tie, T.H.; Nordin, N. Receptor for advanced glycation end products and its involvement in inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Inflam. 2013, 403460, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; He, J.C.; Zhu, L.; Peppa, M.; Lu, C.; Uribarri, J.; Vlassara, H. High levels of dietary advanced glycation end products transform low-density lipoprotein into a potent redox-sensitive mitogen-activated protein kinase stimulant in diabetic patients. Circulation 2004, 110, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Baker, N.L.; Hunt, K.J. Baseline markers of inflammation are associated with progression to macroalbuminuria in type 1 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Yang, X.; Qin, J.; Ye, K.; Wang, X.; Shi, H.; Jiang, M.; Liu, X.; Lu, X. Glyoxalase-1 overexpression reverses defective proangiogenic function of diabetic adipose-derived stem cells in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice model of critical limb ischemia. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, D.; Bansal, S.; Banerjee, B.D.; Madhu, S.V.; Kalra, O.P.; Tripathi, A.K. Role of advanced glycation end product (AGE)-induced receptor (RAGE) expression in diabetic vascular complications. Microvasc. Res. 2014, 95, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, V.M.; Mustata, G.T.; Biemel, K.L.; Reihl, O.; Lederer, M.O.; Zhenyu, D.; Sell, D.R. Cross-linking of the extracellular matrix by the Maillard reaction in aging and diabetes: An update on “a puzzle nearing resolution. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzijl, N.; DeGroot, J.; Thorpe, S.R.; Bank, R.A.; Shaw, J.N.; Lyons, T.J.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Lafeber, F.P.; Baynes, J.W.; TeKoppele, J.M. Effect of collagen turnover on the accumulation of advanced glycation end products. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39027–39031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Hasu, M.; Popov, D.; Zhang, J.H.; Chen, J.; Yan, S.D.; Brett, J.; Cao, R.; Kuwabara, K.; Costache, G. Receptor for advanced glyca¬tion end products (AGEs) has a central role in vessel wall interac¬tions and gene activation in response to circulating AGE proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8807–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.V.; Mahaff, H.; Wu, K.; Smith, G.; Nagai, R.; Simpson, D.A.; Boulton, M.E.; Stitt, A.W. Advanced glycation end product (AGE) accumulation on Bruch’s membrane: Links to age-related RPE dysfunction. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Bae, E.; Amin, S.; Kim, D. Extracellular matrix, gap junctions, and retinal vascular homeostasis in diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 133, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striker, L.J.; Striker, G.E. Administration of AGEs in vivo induces extracellular matrix gene expression. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1996, 11 (Suppl. 5), 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwald, S.E. Ageing of the conduit arteries. J. Pathol. 2007, 211, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholl, I.D.; Stitt, A.W.; Moore, J.E.; Ritchie, A.J.; Archer, D.B.; Bucala, R. Increased levels of advanced glycation endproducts in the lenses and blood vessels of cigarette smokers. Mol. Med. 1998, 4, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Makita, Z.; Horii, Y.; Brunelle, S.; Cerami, A.; Sehajpal, P.; Suthanthiran, M.; Vlassara, H. Two novel rat liver membrane proteins that bind advanced glycosylation end products: Relationship to macrophage receptor for glucose modified proteins. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politz, O.; Gratchev, A.; McCourt, P.A.G.; Schledzewski, K.; Guillot, P.; Johansson, S.; Svineng, G.; Franke, P.; Kannicht, C.; Kzhyshkowska, J.; et al. Stabilin-1 and -2 Constitute a Novel Family of Fasciclin-like Hyaluronan Receptor Homologues. Biochem. J. 2002, 362, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Adachi, H.; Osuga, J.I.; Ohashi, K.; Yahagi, N.; Sekiya, M.; Okazaki, H.; Tomita, S.; Iizuka, Y.; Shimano, H.; et al. FEEL-1 and FEEL-2 Are Endocytic Receptors for Advanced Glycation End Products. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12613–12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, D.J.; Kreibich, G.; Gilmore, R. Oligosaccharyltransferase activity is associated with a protein complex composed of ribophorins I and II and a 48 kd protein. Cell 1992, 69, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H.; Li, Y.M.; Imani, F.; Wojciechowicz, D.; Yang, Z.; Liu, F.T.; Cerami, A. Identification of galectin-3 as a high-affinity binding protein for advanced glycation end products (AGE): A new member of the AGE-receptor complex. Mol. Med. 1995, 1, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; Sakai, M. Scavenger receptors for oxidized and glycated proteins. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jono, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Nagai, R.; Sawamura, T.; Kitamura, T.; Horiuchi, S. Lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) serves as an endothelial receptor for advanced glycation end products (AGE). FEBS Lett. 2002, 511, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Nagase, M.; Fujita, T.; Narumiya, S.; Masaki, T.; Sawamura, T. Diabetes enhances lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1) expression in the vascular endothelium: Possible role of LOX-1 ligand and AGE. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 287, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; He, J.C.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Striker, G.E.; Vlassara, H. AGE-receptor-1 counteracts cellular oxidant stress induced by AGEs via negative regulation of p66shc-dependent FKHRL1 phosphorylation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 294, C145–C152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, A.; Nakayama, H.; Horiuchi, S. Scavenger receptors that recognize advanced glycation end products. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2002, 12, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; He, J.C.; Zhu, L.; Lu, C.; Vlassara, H. Advanced glycation end product (AGE) receptor 1 suppresses cell oxidant stress and activation signaling via EGF receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13801–13806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.J.; Zheng, F.; Stitt, A.; Striker, L.; Hattori, M.; Vlassara, H. Differential expression of renal AGE-receptor genes in NOD mice: Possible role in nonobese diabetic renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, A.; Forbes, J.M. Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Role for Advanced Glycation End-Product Receptor 1 (AGE-R1)? Glycoconj. J. 2016, 33, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.L.Y.; Forbes, J.M.; Cooper, M.E. AGE, RAGE, and ROS in Diabetic Nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, F.; Vlassara, H. Overexpression of AGE-Receptor-1 (AGE-R1) in Mice Prevent AGE Accumulation and Delays Diabetic Renal Injury. Diabetes 2005, 54, A21-B. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.A.; Chitra, P.S.; Reddy, G.B. Advanced Glycation End Products Mediated Cellular and Molecular Events in the Pathology of Diabetic Nephropathy. Biomol. Concepts 2016, 7, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stitt, A.W.; Bucala, R.; Vlassara, H. Atherogenesis and Advanced Glycation: Promotion, Progression, and Prevention. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 811, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, G.; Pricci, F.; Iacobini, C.; Leto, G.; Amadio, L.; Barsotti, P.; Frigeri, L.; Hsu, D.K.; Vlassara, H.; Liu, F.T.; et al. Accelerated diabetic glomerulopathy in galectin-3/AGE receptor 3 knockout mice. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.M. Soluble RAGEs-prospects for treating & tracking metabolic and inflammatory disease. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Maillard-Lefebvre, H.; Boulanger, E.; Daroux, M.; Gaxatte, C.; Hudson, B.I.; Lambert, M. Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products: A new biomarker in diagnosis and prognosis of chronic inflammatory diseases. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bukulin, M.; Kojro, E.; Roth, A.; Metz, V.V.; Fahrenholz, F.; Nawroth, P.P.; Bierhaus, A.; Postina, R. Receptor for advanced glycation end products is subjected to protein ectodomain shedding by metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 35507–35516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucci, A.; Cugusi, S.; Antonelli, A.; Barabino, S.M.; Monti, L.; Bierhaus, A.; Reiss, K.; Saftig, P.; Bianchi, M.E. A soluble form of the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) is produced by proteolytic cleavage of the membrane-bound form by the sheddase a disintegrin and metalloprotease 10 (ADAM10). FASEB J. 2008, 22, 3716–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, A.; Koyama, S.; Sasagawa-Monden, M.; Kadoya, M.; Konishi, K.; Shoji, T.; Inaba, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Koyama, H. JNK and ATF4 as two important platforms for tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated shedding of receptor for advanced glycation end products. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 3575–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalea, A.Z.; Schmidt, A.M.; Hudson, B.I. Alternative Splicing of RAGE: Roles in Biology and Disease. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2011, 16, 2756–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancovsky-Wajcman, D.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Isakov, N.F.; Webb, M.; Zemel, M.; Shibolet, O.; Kariv, R. Serum Soluble Receptor for AGE (sRAGE) Levels Are Associated With Unhealthy Lifestyle and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciarelli, L.G.; Wendt, T.; Qu, W.; Lu, Y.; Lalla, E.; Rong, L.L.; Goova, M.T.; Moser, B.; Kislinger, T.; Lee, D.C.; et al. RAGE blockade stabilizes established atherosclerosis in diabetic apolipoprotein E-null mice. Circulation 2002, 106, 2827–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, G.R.; Pachydaki, S.I.; Tari, S.R.; Lee, S.E.; Donmoyer, C.M.; Ma, W.; Rong, L.L.; Buciarelli, L.G.; Wendt, T.; Hörig, H.; et al. The RAGE axis in early diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 2916–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wear-Maggitti, K.; Lee, J.; Conejero, A.; Schmidt, A.M.; Grant, R.; Breitbart, A. Use of topical sRAGE in diabetic wounds increases neovascularization and granulation tissue formation. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2004, 52, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goova, M.T.; Li, J.; Kislinger, T.; Qu, W.; Lu, Y.; Bucciarelli, L.G.; Nowygrod, S.; Wolf, B.M.; Caliste, X.; Yan, S.F.; et al. Blockade of receptor for advanced glycation end-products restores effective wound healing in diabetic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, S.; Matsui, T. Soluble form of a receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE) as a biomarker. Front. Biosci. 2010, 1, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Yamagishi, S.; Adachi, H.; Kurita-Nakamura, Y.; Matsui, T.; Yoshida, T.; Imaizumi, T. Serum levels of sRAGE, the soluble form of receptor for advanced glycation end products, are associated with inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colhoun, H.M.; Betteridge, D.J.; Durrington, P.; Hitman, G.; Neil, A.; Livingstone, S.; Charlton-Menys, V.; Bao, W.; Demicco, D.A.; Preston, G.M.; et al. Total soluble and endogenous secretory receptor for advanced glycation end products as predictive biomarkers of coronary heart disease risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: An analysis from the CARDS trial. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2379–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, S.J.; Chen, Y.; Sacks, D.B.; Christenson, E.S.; Christenson, R.H.; Rebholz, C.M.; Selvin, E. Cross-sectional analysis of AGE-CML, sRAGE, and esRAGE with diabetes and cardiometabolic risk factors in a community-based cohort. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semba, R.D.; Ferrucci, L.; Fink, J.C.; Sun, K.; Beck, J.; Dalal, M.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fried, L.P. Advanced glycation end products and their circulating receptors and level of kidney function in older community-dwelling women. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Welsh, P.; Papacosta, O.; Ellins, E.A.; Halcox, J.P.J.; Whincup, P.H.; Sattar, N. Circulating soluble receptor for advanced glycation end product: Cross-sectional associations with cardiac markers and subclinical vascular disease in older men with and without diabetes. Atherosclerosi 2017, 264, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, F.; Vazzana, N.; Iodice, P.; Lattanzio, S.; Liani, R.; Bellomo, R.G.; Lessiani, G.; Perego, F.; Saggini, R.; Davi, G. Effects of high-amount-high-intensity exercise on in vivo platelet activation: Modulation by lipid peroxidation and AGE/RAGE axis. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 110, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, C.; Bozzini, S.; Guasti, L.; D’Angelo, A.; Capettini, A.C.; Paganini, E.M.; Falcone, R.; Moia, R.; Gazzaruso, C.; Pelissero, G. Soluble RAGE plasma levels in patients with coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease. Sci. World J. 2013, 9, 584504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, P.; Rutten, E.P.A.; Dentener, M.A.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Reynaert, N.L. Decreased plasma sRAGE levels in COPD: Influence of oxygen therapy. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K. Low levels of serum soluble receptors for advanced glycation end products, biomarkers for disease state: Myth or reality. J. Angiol. 2014, 23, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erusalimsky, J.D. The use of the soluble receptor for advanced glycation-end products (sRAGE) as a potential biomarker of disease risk and adverse outcomes. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimaru, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Inoue, T.; Nishida, S.; Ra, C. Extracellular superoxide released from mitochondria mediates mast cell death by advanced glycation end products. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, R.S.; Mockett, R.J.; Orr, W.C. Current issues concerning the role of oxidative stress in aging: A perspective. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2000, 29, 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.Q.; Gong, Z.J.; Xu, S.Q.; Li, X.; Wang, L.K.; Wu, S.M.; Wu, J.H.; Yang, H.F. Advanced glycation end products promote differentiation of CD4(+) T helper cells toward pro-inflammatory response. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2014, 34, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhle, F.; Weiterer, S.; Siegler, B.H.; Brenner, T.; Lichtenstern, C.; Weigand, M.A. Advanced glycation endproducts induce self- and cross-tolerance in monocytes. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaura, A.; Nishinaka, T.; Hamasaki, S.; Hatipoglu, O.F.; Wake, H.; Nishibori, M.; Mori, S.; Nakao, S.; Takahashi, H. Advanced glycation end-products reduce lipopolysaccharide uptake by macrophages. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Siddarth, M.; Chawla, D.; Banerjee, B.D.; Madhu, S.V.; Tripathi, A.K. Advanced glycation end products enhance reactive oxygen and nitrogen species generation in neutrophils in vitro. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2012, 361, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Ye, J.; Song, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Tian, M.; Dong, J.; Lu, S. Effects of advanced glycation end products on neutrophil migration and aggregation in diabetic wounds. Aging 2021, 13, 12143–12159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.L.; Sharp, P.S.; North, M.E.; Rainbow, S.J.; Knight, S.C. Advanced glycation end products modulate the maturation and function of peripheral blood dendritic cells. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almajwal, A.M.; Alam, I.; Abulmeaty, M.; Razak, S.; Pawelec, G.; Alam, W. Intake of dietary advanced glycation end products influences inflammatory markers, immune phenotypes, and antiradical capacity of healthy elderly in a little-studied population. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipkiss, A.R. Accumulation of altered proteins and ageing: Causes and effects. Exp. Gerontol. 2006, 41, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Katta, R. Sugar Sag: Glycation and the Role of Diet in Aging Skin. Ski. Ther. Lett. 2015, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Li, L.; Guo, M.M.; He, Y.F.; Dong, Y.M.; Meng, H.; Yi, F. Advanced Glycation End Products in the Skin: Molecular Mechanisms, Methods of Measurement, and Inhibitory Pathways. Front. Med. 2022, 11, 837222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Waqas, K.; Tan, R.C.; Voortman, T.; Ikram, M.A.; Nijsten, T.E.C.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Zillikens, M.C. The association between dietary and skin advanced glycation end products: The Rotterdam Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 1, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisan, M.; Taulescu, M.; Crisan, D.; Cosgarea, R.; Parvu, A.; Cãtoi, C.; Drugan, T. Expression of advanced glycation end-products on sun-exposed and non-exposed cutaneous sites during the ageing process in humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 7, 75003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ge, C. Diet and Skin Aging-From the Perspective of Food Nutrition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, T.J.; Janda, K.D. A previously undescribed chemical link between smoking and metabolic disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 12, 15084–15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellow, N.J.; Coughlan, M.T.; Reid, C.M. Association between habitual dietary and lifestyle behaviours and skin autofluorescence (SAF), a marker of tissue accumulation of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs), in healthy adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2209–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, G.; Gori, M.; Randazzo, E.; Vierucci, F. Skin advanced glycation end-products evaluation in infants according to the type of feeding and mother’s smoking habits. SAGE Open Med. 2016, 9, 2050312116682126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, B.; Yang, S. Correlation analysis between advanced glycation end products detected noninvasively and skin aging factors. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, N.C.; Bailey, A.J. The effects of the Maillard reaction on the physical properties and cell interactions of collagen. Pathol. Biol. 2006, 54, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinaga, E.; Kawada, A.; Ono, K.; Fujimoto, E.; Wachi, H.; Harumiya, S.; Nagai, R.; Tajima, S. N(ε)-(carboxymethyl)lysine modification of elastin alters its biological properties: Implications for the accumulation of abnormal elastic fibers in actinic elastosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhani, M.; Maclellan, C.M.; Raptis, M.; Vora, S.; Trackman, P.C.; Graves, D.T. Advanced glycation end products induce apoptosis in fibroblasts through activation of ROS, MAP kinases, and the FOXO1 transcription factor. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C850–C856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueper, T.; Grune, T.; Prahl, S.; Lenz, H.; Welge, V.; Biernoth, T.; Vogt, Y.; Muhr, G.M.; Gaemlich, A.; Jung, T.; et al. Vimentin is the specific target in skin glycation. Structural prerequisites, functional consequences, and role in skin aging. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 10, 23427–23436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pageon, H.; Zucchi, H.; Ricois, S.; Bastien, P.; Asselineau, D. UVA Exposure Combined with Glycation of the Dermis Are Two Catalysts for Skin Aging and Promotes a Favorable Environment to the Appearance of Elastosis. J. Aging Res. 2021, 26, 6647773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagrigoraki, A.; Del Giglio, M.; Cosma, C.; Maurelli, M.; Girolomoni, G.; Lapolla, A. Advanced Glycation End Products are Increased in the Skin and Blood of Patients with Severe Psoriasis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 6, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, I.M.; van de Zande, S.C.; Westra, J.; Zwerver, J.; Smit, A.J.; Mulder, D.J. The AGE Reader: A non-invasive method to assess long-term tissue damage. Methods 2022, 203, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gursinsky, T.; Ruhs, S.; Friess, U.; Diabaté, S.; Krug, H.F.; Silber, R.E.; Simm, A. Air pollution-associated fly ash particles induce fibrotic mechanisms in primary fibroblasts. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Yang, C.; Chen, L.H.; Ren, M.; Lao, G.J.; Yan, L. Impairment of human keratinocyte mobility and proliferation by advanced glycation end products-modified BSA. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laina, A.; Stellos, K.; Stamatelopoulos, K. Vascular ageing: Underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 109, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Canteli, M.; Iadecola, C. Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Aging: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 3, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.; Montezano, A.C.; Touyz, R.M. Vascular biology of ageing-Implications in hypertension. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2015, 83, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatta, E.G. The reality of aging viewed from the arterial wall. Artery Res. 2013, 1, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frimat, M.; Daroux, M.; Litke, R.; Nevière, R.; Tessier, F.J.; Boulanger, E. Kidney, heart and brain: Three organs targeted by ageing and glycation. Clin. Sci. 2017, 1, 1069–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhu, Y.J.; Li, C.G.; Tang, Y.Z.; Jiang, Z.H.; Yang, M.; Ni, C.L.; Chen, L.M.; Niu, W.Y. The relationship between circulating irisin levels and tissues AGE accumulation in type 2 diabetes patients. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yun, J.S.; Ko, S.H. Advanced Glycation End Products and Their Effect on Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takino, J.I.; Sato, T.; Kanetaka, T.; Okihara, K.; Nagamine, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Hori, T. RasGRP2 inhibits glyceraldehyde-derived toxic advanced glycation end-products from inducing permeability in vascular endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henning, R.J. Type-2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Future Cardiol. 2018, 14, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirban, A.; Kotsi, P.; Franke, K.; Strijowski, U.; Cai, W.; Götting, C.; Tschoepe, D. Acute macrovascular dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes induced by ingestion of advanced glycated β-lactoglobulins. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avagimyan, A.; Popov, S.; Shalnova, S. The Pathophysiological Basis of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Development. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 47, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, S.L.; Sonmez, H.; Basman, C.; Singh, V.; Poretsky, L. The role of advanced glycation end-products in the development of coronary artery disease in patients with and without diabetes mellitus: A review. Mol. Med. 2018, 23, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deluyker, D.; Ferferieva, V.; Noben, J.P.; Swennen, Q.; Bronckaers, A.; Lambrichts, I.; Rigo, J.M.; Bito, V. Cross-linking versus RAGE: How do high molecular weight advanced glycation products induce cardiac dysfunction? Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 1, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Egan, J.; Vasan, S.; Jyothirmayi, G.N.; Masurekar, M.R.; Lopez, S.; Williams, C.; Torres, R.L.; Wagle, D.; Ulrich, P.; et al. An advanced glycation endproduct cross-link breaker can reverse age-related increases in myocardial stiffness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 14, 2809–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, S.Y.; Xu, P.; Babcock, S.A.; Dolence, E.K.; Brownlee, M.; Li, J.; Ren, J. Advanced glycation endproduct (AGE) accumulation and AGE receptor (RAGE) up-regulation contribute to the onset of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Liu, D.; Yu, L.; Zhan, L.; Li, X.J.; Peng, H.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Yuan, X.C. Advanced glycation end-products impair Na+/K+-ATPase activity in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Role of the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/sirtuin 1 pathway. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 41, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.B.; Swensen, A.C.; Winden, D.R.; Bodine, J.S.; Bikman, B.T.; Reynolds, P.R. Cardiomyocyte mitochondrial respiration is reduced by receptor for advanced glycation end-product signaling in a ceramide-dependent manner. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 1, H63–H69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, G.W., 2nd. Mitochondrial dynamism and heart disease: Changing shape and shaping change. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seals, D.R.; Alexander, L.M. Vascular aging. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 1, 1841–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamwal, S.; Sharma, S. Vascular endothelium dysfunction: A conservative target in metabolic disorders. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, T.; Yan, S.F.; Yan, S.D.; Belov, D.; Rong, L.L.; Sousa, M.; Andrassy, M.; Marso, S.P.; Duda, S.; Arnold, B.; et al. Central role of RAGE-dependent neointimal expansion in arterial restenosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmopoulos, M.; Drekolias, D.; Zavras, P.D.; Piperi, C.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Impact of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) signaling in coronary artery disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, K.; Martínez, F.; Beltrán, A.; González, D.; Herrera, B.; Quintero, G.; Delgado, R.; Rojas, A. Albumin-derived advanced glycation end-products trigger the disruption of the vascular endothelial cadherin complex in cultured human and murine endothelial cells. Biochem. J. 2001, 1, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, H.H.; Ramasamy, R.; Schmidt, A.M. Advanced Glycation End Products: Building on the Concept of the “Common Soil” in Metabolic Disease. Endocrinology 2020, 1, bqz006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Koyama, H.; Morioka, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kizu, A.; Motoyama, K.; Mori, K.; Fukumoto, S.; Shioi, A.; Shimogaito, N.; et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products is involved in impaired angiogenic response in diabetes. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2245–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Hurtado del Pozo, C.; Rosario, R.; Zou, Y.S.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Xu, X.; Patel, P.R.; Benoit, V.M.; Yan, S.F.; Li, H.; et al. RAGE regulates the metabolic and inflammatory response to high-fat feeding in mice. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1948–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, B.I.; Dong, C.; Gardener, H.; Elkind, M.S.; Wright, C.B.; Goldberg, R.; Sacco, R.L.; Rundek, T. Serum levels of soluble receptor for advanced glycation end-products and metabolic syndrome: The Northern Manhattan Study. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozio, E.; Corradi, V.; Vianello, E.; Scalzotto, E.; de Cal, M.; Corsi Romanelli, M.M.; Ronco, C. Increased Levels of sRAGE in Diabetic CKD-G5D Patients: A Potential Protective Mechanism against AGE-Related Upregulation of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9845175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhuri, S.; Dutta, D.; Sen, A.; Chowdhury, I.H.; Mitra, B.; Mondal, L.K.; Saha, A.; Bhadhuri, G.; Bhattacharya, B. Role of N-ε- carboxy methyl lysine, advanced glycation end products and reactive oxygen species for the development of nonproliferative and proliferative retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.P.; Bali, A.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. Advanced glycation end products and diabetic complications. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, R.H.; Linetsky, M.; Stitt, A.W. The pathogenic role of Maillard reaction in the aging eye. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1205–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, S.; Bejarano, E.; Taylor, A. Mechanistic targeting of advanced glycation end-products in age-related diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3631–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrigglesworth, J.; Ward, P.; Harding, I.H.; Nilaweera, D.; Wu, Z.; Woods, R.L.; Ryan, J. Factors associated with brain ageing—A systematic review. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, F.; Chen, D.; Akhter, A.; Yan, S.F. Age-dependent accumulation of dicarbonyls and advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) associates with mitochondrial stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 164, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Ahmed, U.; Thornalley, P.J.; Hager, K.; Fleischer, G.; Münch, G. Protein glycation, oxidation and nitration adduct residues and free adducts of cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer’s disease and link to cognitive impairment. J. Neurochem. 2005, 92, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungratanawanich, W.; Qu, Y.; Wang, X.; Essa, M.M.; Song, B.J. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and other adducts in aging-related diseases and alcohol-mediated tissue injury. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 168–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Weber, D.; Raupbach, J.; Dakal, T.C.; Fließbach, K.; Ramirez, A.; Grune, T.; Wüllner, U. Advanced glycation end products and protein carbonyl levels in plasma reveal sex-specific differences in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.; Franke, S.; Rüster, C.; Wolf, G. Advanced glycation end-products and the kidney. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 40, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Byun, K.; Bayarsaikhan, E.; Kim, D.; Kim, C.Y.; Mook-Jung, I.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, S.U.; Yamamoto, T.; Won, M.H.; Song, B.J.; et al. Induction of neuronal death by microglial AGE-albumin: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37917. [Google Scholar]
- Dobi, A.; Rosanaly, S.; Devin, A.; Baret, P.; Meilhac, O.; Harry, G.J.; d’Hellencourt, C.L.; Rondeau, P. Activated microglial cells synthesize and secrete AGE-albumin, Advanced glycation end-products disrupt brain microvascular endothelial cell barrier: The role of mitochondria and oxidative stress. Microvasc. Res. 2021, 133, 104098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Song, P.; Chen, W.; Xie, X.; Luo, R.; Su, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, R.; Zhu, P.; et al. Inhibition of Caspase-1 Ameliorates Ischemia-Associated Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction and Integrity by Suppressing Pyroptosis Activation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 11, 540669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratna, D.; Fan, X.; Leung, W.; Lok, J.; Guo, S.; Xing, C.; Wang, X.; Lo, E.H. Cerebrovascular degradation of TRKB by MMP9 in the diabetic brain. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3373–3377. [Google Scholar]
- Rom, S.; Heldt, N.A.; Gajghate, S.; Seliga, A.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Persidsky, Y. Hyperglycemia and advanced glycation end products disrupt BBB and promote occludin and claudin-5 protein secretion on extracellular microvesicles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 28, 18828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jia, W.; Tian, X.; Jiang, P.; Cheng, Z.; Li, J. AGEs/RAGE blockade downregulates Endothenin-1 (ET-1), mitigating Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) injury in deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Bioengineered 2012, 12, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Shu, T.; Lin, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; Han, X. Inhibition of the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) protects pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, A.; Storace, D.; Odetti, P.; Viviani, G.L. Advanced glycation end-products affect transcription factors regulating insulin gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 395, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Ma, Z.; Han, X. AGEs decrease insulin synthesis in pancreatic beta-cell by repressing Pdx-1 protein expression at the post-translational level. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, S.M.; Dong, H.J.; Li, Z.; Cai, W.; Altomonte, J.; Thung, S.N.; Zeng, F.; Fisher, E.A.; Vlassara, H. Improved insulin sensitivity is associated with restricted intake of dietary glycoxidation products in the db/db mouse. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, S. Role of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and receptor for AGEs (RAGE) in vascular damage in diabetes. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Saxena, A.; Mishra, A.; Natu, S.M. Advanced glycation end products and diabetic retinopathy. J. Ocul. Biol. Dis. Informat. 2012, 5, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Moldogazieva, N.T.; Mokhosoev, I.M.; Mel’nikova, T.I.; Porozov, Y.B.; Terentiev, A.A. Oxidative Stress and Advanced Lipoxidation and Glycation End Products (ALEs and AGEs) in Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 14, 3085756. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, M.; Park, L.; Shin, G.; Hong, H.; Kang, I.; Park, Y. Induction of apoptosis of Beta cells of the pancreas by advanced glycation end-products, important mediators of chronic complications of diabetes mellitus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1150, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Lu, A.L.; Yao, X.M.; Hua, Q.; Li, X.Y.; Qin, L.; Zhang, H.M.; Meng, G.X.; Su, Q. Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome by Advanced Glycation End Products Promotes Pancreatic Islet Damage. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 9692546. [Google Scholar]
- Sergi, D.; Naumovski, N.; Heilbronn, L.K.; Abeywardena, M.; O’Callaghan, N.; Lionetti, L.; Luscombe-Marsh, N. Mitochondrial (Dys)function and insulin resistance: From pathophysiological molecular mechanisms to the impact of diet. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gurbuz, O.; Yorgancı, A.; Ozgu-Erdinc, A.S.; Tasci, Y. First trimester screening of serum advanced glycation end products levels of pregnant women who have risk factors for gestational diabetes and their obstetric outcomes: A preliminary case-control study. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2022, 42, 3048–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera Fernández, S.; Martín Martínez, M.D.; De Francisco Montero, C.; Gabaldón Rodríguez, I.; Vilches Arenas, Á.; Ortega Calvo, M. Modelos predictivos de diabetes gestacional, un nuevo modelo de predicción [Predictive models of gestational diabetes, a new prediction mode]. Semergen 2021, 47, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Kitai, Y.; Nangaku, M.; Yanagita, M. Aging-Related Kidney Diseases. Contrib. Nephrol. 2021, 199, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley, P.J.; Battah, S.; Ahmed, N.; Karachalias, N.; Agalou, S.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Dawnay, A. Quantitative screening of advanced glycation endproducts in cellular and extracellular proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Biochem. J. 2003, 375, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotheringham, A.K.; Gallo, L.A.; Borg, D.J.; Forbes, J.M. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) and Chronic Kidney Disease: Does the Modern Diet AGE the Kidney. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semba, R.D.; Fink, J.C.; Sun, K.; Windham, B.G.; Ferrucci, L. Serum Carboxymethyl-lysine, a Dominant Advanced Glycation End Product, is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease: The Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. J. Ren. Nutr. 2010, 20, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, R.J.H.; Broers, N.J.H.; Canaud, B.; Christiaans, M.H.L.; Cornelis, T.; Gauly, A.; Hermans, M.M.H.; Konings, C.J.A.M.; van der Sande, F.M.; Scheijen, J.L.J.M.; et al. Advanced glycation endproducts and dicarbonyls in end-stage renal disease: Associations with uraemia and courses following renal replacement therapy. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semba, R.D.; Fink, J.C.; Sun, K.; Bandinelli, S.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. Carboxymethyl-lysine, an advanced glycation end product, and decline of renal function in older community-dwelling adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2009, 48, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makita, Z.; Radoff, S.; Rayfield, E.J.; Yang, Z.; Skolnik, E.; Delaney, V.; Friedman, E.A.; Cerami, A.; Vlassara, H. Advanced glycosylation end products in patients with diabetic nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.J.; Hyon, J.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Han, E.H.; Kim, Y.; Cha, Y.S.; Ha, S.K. Glycolaldehyde, an Advanced Glycation End Products Precursor, Induces Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Renal Mesangial Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 934. [Google Scholar]
- Thieme, K.; Pereira, B.M.V.; da Silva, K.S.; Fabre, N.T.; Catanozi, S.; Passarelli, M.; Correa-Giannella, M.L. Chronic advanced-glycation end products treatment induces TXNIP expression and epigenetic changes in glomerular podocytes in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci. 2021, 270, 118997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Welsh, G.I.; Raghu, G.; Menon, R.K.; Saleem, M.A.; Reddy, G.B. Carboxymethyl lysine induces EMT in podocytes through transcription factor ZEB2: Implications for podocyte depletion and proteinuria in diabetes mellitus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 15, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.R.; Lee, K.W. Methylglyoxal-Derived Advanced Glycation End Product (AGE4)-Induced Apoptosis Leads to Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress through the RAGE/JNK Pathway in Kidney Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6530. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; Peng, H.; Li, C.; Ye, Z.; Tang, H.; Tang, Y.; Chen, C.; Lou, T. Advanced glycation end products induce glomerular endothelial cell hyperpermeability by upregulating matrix metalloproteinase activity. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 4447–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.; Han, Y.; Ren, W.; Jiang, J.; Wang, P.; Hu, Z. Advanced glycation end-products affect the cytoskeletal structure of rat glomerular endothelial cells via the Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 4321–4326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, S.; Inagaki, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Amano, S.; Koga, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Makita, Z. Advanced glycation end product-induced apoptosis and overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human-cultured mesangial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20309–20315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, A.; Yap, F.Y.T.; Borg, D.J.; McCarthy, D.; Fotheringham, A.; Leung, S.; Penfold, S.A.; Sourris, K.C.; Coughlan, M.T.; Schulz, B.L.; et al. The AGE receptor, OST48 drives podocyte foot process effacement and basement membrane expansion (alters structural composition). Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 4, e00278. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.C.; Kuo, P.L. The Role of Galectin-3 in the Kidneys. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heijst, J.W.; Niessen, H.W.; Hoekman, K.; Schalkwijk, C.G. Advanced glycation end products in human cancer tissues: Detection of Nepsilon-(carboxymethyl)lysine and argpyrimidine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, H.; Matou-Nasri, S.; Wang, Q.; Rabhan, Z.; Al-Eidi, H.; Al Abdulrahman, A.; Ahmed, N. Advanced glycation endproducts increase proliferation, migration and invasion of the breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 429–441. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, P.; Chaudhry, N.; Mittal, R.; Mukherjee, T.K. Role of receptor for advanced glycation end products in the complication and progression of various types of cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar]
- Cepas, V.; Collino, M.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M. Redox Signaling and Advanced Glycation Endproducts (AGEs) in Diet-Related Diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi, S.; Nakamura, K.; Inoue, H.; Kikuchi, S.; Takeuchi, M. Possible participation of advanced glycation end products in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer in diabetic patients. Med. Hypotheses 2005, 64, 1208–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Ballotari, P.; Vicentini, M.; Manicardi, V.; Gallo, M.; Chiatamone Ranieri, S.; Greci, M.; Giorgi Rossi, P. Diabetes and risk of cancer incidence: Results from a population-based cohort study in northern Italy. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 703. [Google Scholar]
- Jee, S.H.; Ohrr, H.; Sull, J.W.; Yun, J.E.; Ji, M.; Samet, J.M. Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women. JAMA 2005, 293, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lega, I.C.; Lipscombe, L.L. Review: Diabetes, Obesity, and Cancer-Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, bnz014. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Kartsonaki, C.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Bian, Z.; Bragg, F.; Millwood, I.Y.; Shen, L.; Zhou, S.; et al. Diabetes, plasma glucose and incidence of colorectal cancer in Chinese adults: A prospective study of 0.5 million people. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2018, 72, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.L.; Rojna, M. Diabetes and risk of cancer. ISRN Oncol. 2013, 2013, 583786. [Google Scholar]
- Granic, A.; Hurst, C.; Dismore, L.; Dodds, R.M.; Witham, M.D.; Robinson, S.M.; Sayer, A.A. Advanced glycation end products in skeletal muscle health and sarcopenia: A systematic review of observational studies. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 209, 111744. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.M.; Vandervoort, A.A.; Lexell, J. Aging of human muscle: Structure, function and adaptability. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 1995, 5, 129–142. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, W.K.; Williams, J.; Atherton, P.; Larvin, M.; Lund, J.; Narici, M. Sarcopenia, dynapenia, and the impact of advancing age on human skeletal muscle size and strength; a quantitative review. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, G.W. Effect of inflammation on the aging microcirculation: Impact on skeletal muscle blood flow control. Microcirculation 2006, 13, 343–352. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, L.C.; Redden Schwartz, Z.; Cohen, D.J.; McClure, M.J. Advanced Glycation End-Products in Skeletal Muscle Aging. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Egawa, T.; Tsuda, S.; Goto, A.; Ohno, Y.; Yokoyama, S.K.; Hayashi, G.T. Potential involvement of dietary advanced glycation end products in impairment of skeletal muscle growth and muscle contractile function in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, A.R.; Lieber, R.L. Structure and Function of the Skeletal Muscle Extracellular Matrix. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Momma, H.; Niu, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Guan, L.; Sato, M.; Guo, H.; Chujo, M.; Otomo, A.; Yufei, C.; Tadaura, H.; et al. Skin advanced glycation end product accumulation and muscle strength among adult men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019, 393, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, S.; Ochi, M.; Akechi, Y.; Takei, S.; Senzaki, K.; Okada, Y.; Miura, S.; Ochi, H.; Igase, M.; Ohyagi, Y. Dermal advanced glycation end-product accumulation is associated with sarcopenia-related measures in middle-aged and older men. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2022, 101, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Kubo, A.; Sugioka, Y.; Mitsui, R.; Fukuhara, N.; Nihei, F.; Takeda, Y. Relationship between advanced glycation end-product accumulation and low skeletal muscle mass in Japanese men and women. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabara, Y.; Ikezoe, T.; Yamanaka, M.; Setoh, K.; Segawa, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kosugi, S.; Nakayama, T.; Ichihashi, N.; Tsuboyama, T.; et al. Advanced Glycation End Product Accumulation Is Associated With Low Skeletal Muscle Mass, Weak Muscle Strength, and Reduced Bone Density: The Nagahama Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, Y.; Toyoguchi, T.; Inage, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Orita, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kanamoto, H.; Abe, K.; Norimoto, M.; Umimura, T.; et al. Advanced glycation end products are associated with sarcopenia in older women: Aging marker dynamics. J. Women Aging 2021, 33, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, P.; Njemini, R.; Vantieghem, S.; Gorus, E.; Pool-Goudzwaard, A.; Buyl, R.; Bautmans, I. Reaction time in healthy elderly is associated with chronic low-grade inflammation and advanced glycation end product. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 108, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, S.; Khan, S.; Almatroudi, A.; Khan, A.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Rahmani, A.H. A review on mechanism of inhibition of advanced glycation end products formation by plant derived polyphenolic compounds. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 787–805. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, A.H.; Anwar, S.; Raut, R.; Almatroudi, A.; Babiker, A.Y.; Khan, A.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Almatroodi, S.A. Therapeutic Potential of Myrrh, a Natural Resin, in Health Management through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Advanced Glycation End Products Formation Using In Vitro and In Silico Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, H.; Anwar, S. Prevention of non-enzymatic glycosylation (glycation): Implication in the treatment of diabetic complication. Int. J. Health Sci. 2016, 10, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goon, J.A.; Noor Aini, A.H.; Musalmah, M.; Yasmin Anum, M.Y.; Nazaimoon, W.M.; Ngah, W.Z. Effect of Tai Chi exercise on DNA damage, antioxidant enzymes, and oxidative stress in middle-age adults. J. Phys. Act. Health 2009, 6, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, G.; Cai, J.; Dang, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, W.; Duan, W.; et al. Inhibitory Effects of Myriocin on Non-Enzymatic Glycation of Bovine Serum Albumin. Molecules 2022, 27, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenth, H.; Zuidema, S.U.; Krijnen, W.P.; Bautmans, I.; Smit, A.J.; van der Schans, C.; Hobbelen, H. Advanced Glycation End Products Are Associated With Physical Activity and Physical Functioning in the Older Population. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Cao, P.; Kakihana, T.; Sato, E.; Suda, C.; Muroya, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Hu, G.; Ishii, T.; Ito, O.; et al. Chronic Running Exercise Alleviates Early Progression of Nephropathy with Upregulation of Nitric Oxide Synthases and Suppression of Glycation in Zucker Diabetic Rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbin, M.A.; Davel, A.P.; Couto, G.K.; de Araújo, G.G.; Rossoni, L.V.; Antunes, E.; Zanesco, A. Interaction between advanced glycation end products formation and vascular responses in femoral and coronary arteries from exercised diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e53318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramita, N.; Puspasari, B.C.; Arrody, R.; Kartinah, N.T.; Andraini, T.; Mardatillah, J.; Rusli, H.; Santoso, D.I.S. Protective Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training (MICT) against Vascular Dysfunction in Hyperglycemic Rats. J. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 3, 5631488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Fujimoto, S. Decrease in serum levels of advanced glycation end-products by short-term lifestyle modification in non-diabetic middle-aged females. Med. Sci. Monit. 2009, 15, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Egawa, T.; Hayashi, T. Association of Glycative Stress With Motor and Muscle Function. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 855358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda-Sobczak, A.; Falkowski, B.; Araszkiewicz, A.; Zozulinska-Ziolkiewicz, D. Association Between Self-reported Physical Activity and Skin Autofluorescence, a Marker of Tissue Accumulation of Advanced Glycation End Products in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-sectional Study. Clin. Ther. 2018, 40, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, K.L.; Borges, J.P.; Lopes, G.O.; Pereira, E.; Mediano, M.F.F.; Farinatti, P.; Tibiriça, E.; Daliry, A. Influence of Physical Exercise on Advanced Glycation End Products Levels in Patients Living With the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotani, K.; Caccavello, R.; Sakane, N.; Yamada, T.; Taniguchi, N.; Gugliucci, A. Influence of Physical Activity Intervention on Circulating Soluble Receptor for Advanced Glycation end Products in Elderly Subjects. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2011, 3, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sponder, M.; Campean, I.A.; Emich, M.; Fritzer-Szekeres, M.; Litschauer, B.; Graf, S.; Dalos, D.; Strametz-Juranek, J. Long-term physical activity leads to a significant increase in serum sRAGE levels: A sign of decreased AGE-mediated inflammation due to physical activity? Heart Vessel. 2018, 33, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshiar, S.H.; Helia, E.H.; Taherian, A.M.; Jafarnejad, S. Exercise, Advanced Glycation End Products, and Their Effects on Cardiovascular Disorders: A Narrative Review. Heart Mind 2020, 6, 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Farinha, J.B.; Ramis, T.R.; Vieira, A.F.; Macedo, R.C.; Rodrigues-Krause, J.; Boeno, F.P.; Schroeder, H.T.; Müller, C.H.; Boff, W.; Krause, M.; et al. Glycemic, inflammatory and oxidative stress responses to different high-intensity training protocols in type 1 diabetes: A randomized clinical trial. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.M.; Han, K.A.; Ahn, H.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Hong, H.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Yang, S.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, D.S.; et al. Effects of exercise on sRAGE levels and cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3751–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgutka, K.; Piotrowska, K. Ograniczenie kaloryczne a proces starzenia się organizmu. Post Biol. Kom. 2021, 48, 249–364. [Google Scholar]
- Teillet, L.; Verbeke, P.; Gouraud, S.; Bakala, H.; Borot-Laloi, C.; Heudes, D.; Bruneval, P.; Corman, B. Food restriction prevents advanced glycation end product accumulation and retards kidney aging in lean rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teillet, L.; Ribière, P.; Gouraud, S.; Bakala, H.; Corman, B. Cellular signaling, AGE accumulation and gene expression in hepatocytes of lean aging rats fed ad libitum or food-restricted. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2002, 123, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, D.R.; Lane, M.A.; Obrenovich, M.E.; Mattison, J.A.; Handy, A.; Ingram, D.K.; Cutler, R.G.; Roth, G.S.; Monnier, V.M. The effect of caloric restriction on glycation and glycoxidation in skin collagen of nonhuman primates. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2003, 58, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashige, K.; Kouda, K.; Kouda, M.; Horiuchi, K.; Takahashi, M.; Nagano, A.; Tanaka, T.; Takeuchi, H. Calorie restricted diet and urinary pentosidine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Physiol. Anthropol. Appl. Hum. Sci. 2004, 23, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugliucci, A.; Kotani, K.; Taing, J.; Matsuoka, Y.; Sano, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Egawa, K.; Horikawa, C.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kiso, Y.; et al. Short-term low calorie diet intervention reduces serum advanced glycation end products in healthy overweight or obese adults. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 54, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; He, J.C.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Zheng, F.; Striker, G.E.; Vlassara, H. Oral glycotoxins determine the effects of calorie restriction on oxidant stress, age-related diseases, and lifespan. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, R.; Sedaghat, M.; Hedayati, M.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Sohrab, G. Low advanced Glycation end product diet improves the central obesity, insulin resistance and inflammatory profiles in Iranian patients with metabolic syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggerio, A.; Strunz, C.M.C.; Pacanaro, A.P.; Leal, D.P.; Takada, J.Y.; Avakian, S.D.; Mansur, A.P. Gene Expression of Sirtuin-1 and Endogenous Secretory Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products in Healthy and Slightly Overweight Subjects after Caloric Restriction and Resveratrol Administration. Nutrients 2018, 10, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhou, M.; Ge, Y.; Wang, X. SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 187, 111215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Uribarri, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Swamy, S.; Zhao, Z.; Grosjean, F.; Simonaro, C.; Kuchel, G.A.; Schnaider-Beeri, M.; et al. Oral glycotoxins are a modifiable cause of dementia and the metabolic syndrome in mice and humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4940–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribarri, J.; Cai, W.; Pyzik, R.; Goodman, S.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Ramdas, M.; Striker, G.E.; Vlassara, H. Suppression of native defense mechanisms, SIRT1 and PPARγ, by dietary glycoxidants precedes disease in adult humans; relevance to lifestyle-engendered chronic diseases. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Cell | Molecular Mechanisms | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Endothelial cells | Aberrant angiogenesis [227]; ↑ permeability of glomerular filtration barrier [233,234]. | |
| Podocytes |
| Induces apoptosis [203]; oxidative stress, fibrosis; EMT [230]. |
| Mesangial cells |
| Hyperfiltration and microalbuminuria; promote proliferative inhibition, hypertrophy, and apoptosis [235]. |
| Effects of AGEs on Muscles | Description of the Research Group | References |
|---|---|---|
| Decreased grip strength and thigh cross-sectional area in men | 240 middle-aged and elderly people (120 women and 120 men) | [257] |
| Decreased grip strength and leg extension power | 232 men were selected to measure grip strength and 138 men to measure leg extension strength | [255] |
| Decreased skeletal muscle index | 132 participants (70 men, 62 women) | [258] |
| Decreased skeletal muscle index, grip strength, hip flexion strength | 9203 participants | [259] |
| Decreased appendicular lean mass and percentage of lean body mass | 47 women with sarcopenia, 23 healthy volunteers | [260] |
| Decreased muscle mass | mice with low and high AGEs diets | [253] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zgutka, K.; Tkacz, M.; Tomasiak, P.; Tarnowski, M. A Role for Advanced Glycation End Products in Molecular Ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129881
Zgutka K, Tkacz M, Tomasiak P, Tarnowski M. A Role for Advanced Glycation End Products in Molecular Ageing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):9881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129881
Chicago/Turabian StyleZgutka, Katarzyna, Marta Tkacz, Patrycja Tomasiak, and Maciej Tarnowski. 2023. "A Role for Advanced Glycation End Products in Molecular Ageing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 9881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129881
APA StyleZgutka, K., Tkacz, M., Tomasiak, P., & Tarnowski, M. (2023). A Role for Advanced Glycation End Products in Molecular Ageing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 9881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129881







