Rapid and Cost-Efficient Detection of RET Rearrangements in a Large Consecutive Series of Lung Carcinomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
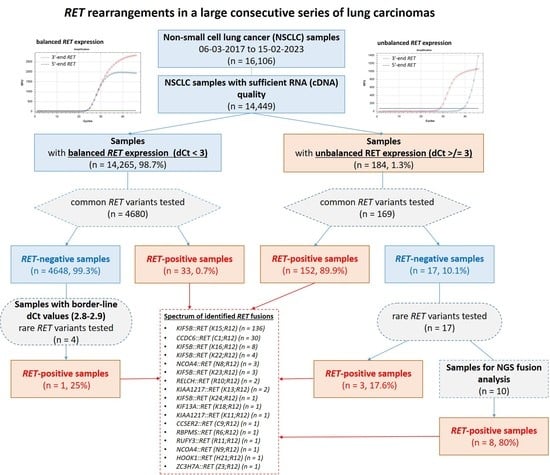
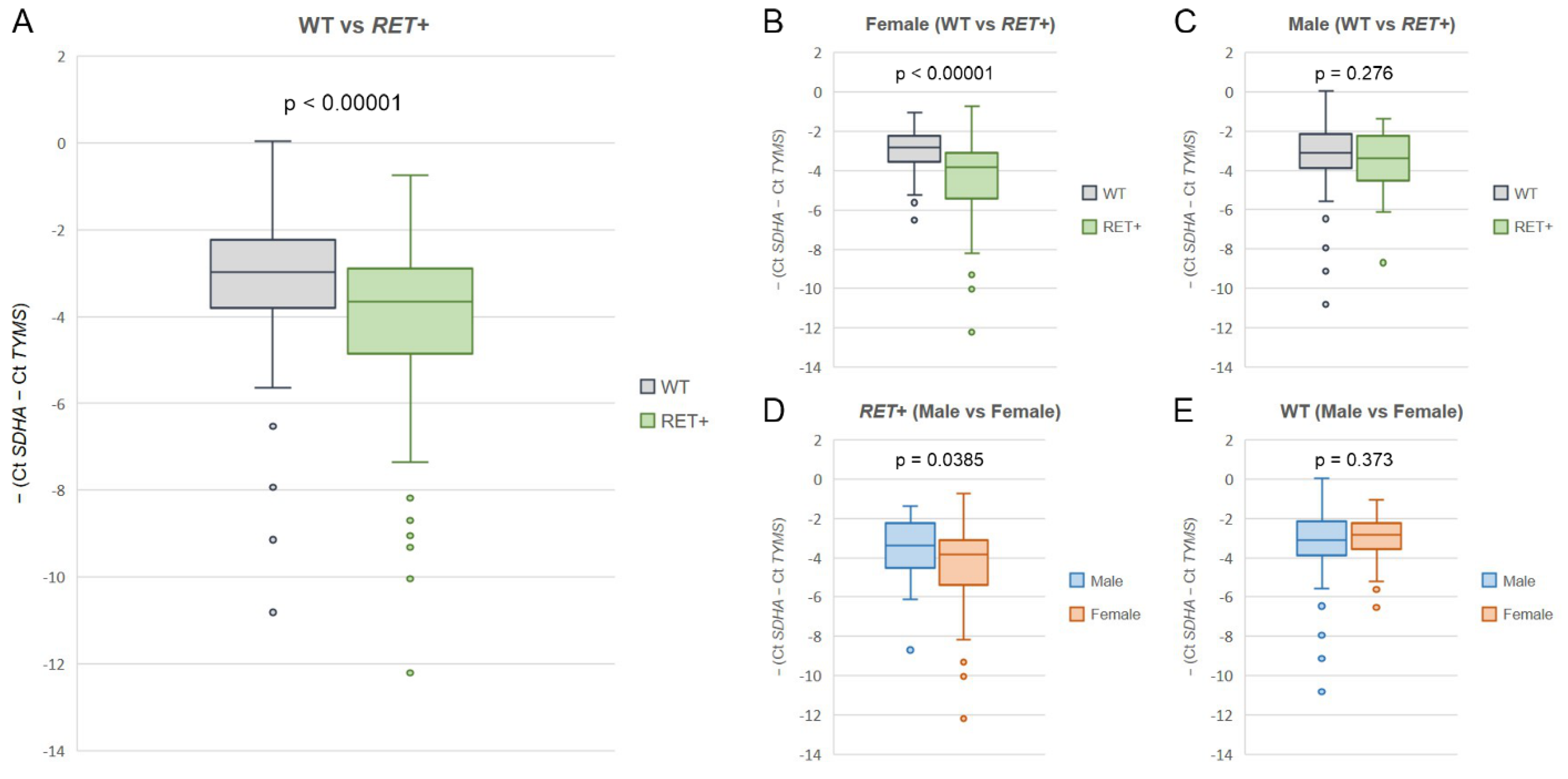
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herbst, R.S.; Aisner, D.L.; Sonett, J.R.; Turk, A.T.; Weintraub, J.L.; Lindeman, N.I. Practical Considerations Relating to Routine Clinical Biomarker Testing for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Focus on Testing for RET Fusions. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 562480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.W.; Loong, H.H.F.; Johnson, M.; Gainor, J.; McCoach, C.E.; Gautschi, O.; Besse, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Curigliano, G.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, D.H.; Besse, B.; Baik, C.S.; Doebele, R.C.; Cassier, P.A.; Lopes, G.; Tan, D.S.W.; et al. Pralsetinib for RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARROW): A multi-cohort, open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novello, S.; Califano, R.; Reinmuth, N.; Tamma, A.; Puri, T. RET Fusion-Positive Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: The Evolving Treatment Landscape. Oncologist 2023, 28, oyac264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautschi, O.; Milia, J.; Filleron, T.; Wolf, J.; Carbone, D.P.; Owen, D.; Camidge, R.; Narayanan, V.; Doebele, R.C.; Besse, B.; et al. Targeting RET in Patients with RET-Rearranged Lung Cancers: Results from the Global, Multicenter RET Registry. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrara, R.; Auger, N.; Auclin, E.; Besse, B. Clinical and Translational Implications of RET Rearrangements in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhury, N.J.; Drilon, A. Decade in review: A new era for RET-rearranged lung cancers. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, D.; Sapio, L.; Della Gravara, L.; Naviglio, S.; Gridelli, C. Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with RET Fusions: Reality and Hopes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imyanitov, E.N.; Iyevleva, A.G.; Levchenko, E.V. Molecular testing and targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Current status and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 157, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.R.; Aypar, U.; Rosen, E.Y.; Mata, D.A.; Benayed, R.; Mullaney, K.; Jayakumaran, G.; Zhang, Y.; Frosina, D.; Drilon, A.; et al. A Performance Comparison of Commonly Used Assays to Detect RET Fusions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.A.; Sireci, A.N.; Marella, N.; Cannon, H.K.; Marquart, T.J.; Holzer, T.R.; Reising, L.O.; Cook, J.D.; Wijayawardana, S.R.; Bodo, J.; et al. Analytical Accuracy of RET Fusion Detection by Break-Apart Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2022, 146, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belli, C.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Ladanyi, M.; Normanno, N.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Lacroix, L.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Subbiah, V.; Gainor, J.; Endris, V.; et al. ESMO recommendations on the standard methods to detect RET fusions and mutations in daily practice and clinical research. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, B.; Guo, L.; Li, W.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Sun, R.; et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and diagnostic methods of RET rearrangement in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radonic, T.; Geurts-Giele, W.R.R.; Samsom, K.G.; Roemen, G.M.J.M.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; Thunnissen, E.; Meijssen, I.C.; Sleddens, H.F.B.M.; Dinjens, W.N.M.; Boelens, M.C.; et al. RET Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Analysis Is a Sensitive but Highly Unspecific Screening method for RET Fusions in Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Pan, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. The use of quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase PCR for 5′ and 3′ portions of ALK transcripts to detect ALK rearrangements in lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4725–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drilon, A.; Bergagnini, I.; Delasos, L.; Sabari, J.; Woo, K.M.; Plodkowski, A.; Wang, L.; Hellmann, M.D.; Joubert, P.; Sima, C.S.; et al. Clinical outcomes with pemetrexed-based systemic therapies in RET-rearranged lung cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, T.; Pu, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Song, Z.; et al. Association between RET Fusions and Efficacy of Pemetrexed-based Chemotherapy for Patients with Advanced NSCLC in China: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, e349–e354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Clinicopathologic characteristics, genetic variability and therapeutic options of RET rearrangements patients in lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2016, 101, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imyanitov, E.N.; Iyevleva, A.G. Molecular tests for prediction of tumor sensitivity to cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Lett. 2022, 526, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitiushkina, N.V.; Romanko, A.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, E.V.; Tiurin, V.I.; Ermachenkova, T.I.; Martianov, A.S.; Mulkidjan, R.S.; Sokolova, T.N.; Kholmatov, M.M.; Bizin, I.V.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the test for 5′-/3′-end mRNA unbalanced expression as a screening tool for ALK and ROS1 fusions in lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 3226–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuta, K.; Kohno, T.; Yoshida, A.; Shimada, Y.; Asamura, H.; Furuta, K.; Kushima, R. RET-rearranged non-small-cell lung carcinoma: A clinicopathological and molecular analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Guo, L.; Gu, Y.; Huang, T.; Liu, M.; Zou, X.; Yang, B.; Huang, P.; Wen, C.; Yi, L.; et al. The genomic characteristics of RET fusion positive tumors in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, C.; Yin, W.; Wang, G.; Mao, X.; Xiang, J.; Li, B.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Molecular Patterns of RET-Rearranged Lung Cancer in Chinese Patients. Oncol. Res. 2019, 27, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preobrazhenskaya, E.; Zagrebin, F.; Mulkidzhan, R.; Krivosheeva, E.; Saitova, E.; Raskin, G.; Bizin, I.; Imyanitov, E. Novel kinase-activating fusions in lung adenocarcinomas. In Proceedings of the 35st European Congress of Pathology, Dublin, Ireland, 9–13 September 2023. Abstracts; Virchows Arch 2023 (in press). [Google Scholar]
- Hess, L.M.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Y.E.; Bhandari, N.R.; Sireci, A. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with RET-fusion positive non-small lung cancer in real-world practice in the United States. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Ye, T.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. ALK, ROS1 and RET fusions in 1139 lung adenocarcinomas: A comprehensive study of common and fusion pattern-specific clinicopathologic, histologic and cytologic features. Lung Cancer 2014, 84, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, S.; Scheel, A.H.; Scheffler, M.; Schultheis, A.M.; Gautschi, O.; Aebersold, F.; Diebold, J.; Pall, G.; Rothschild, S.; Bubendorf, L.; et al. Clinicopathological Characteristics of RET Rearranged Lung Cancer in European Patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reguart, N.; Teixidó, C.; Giménez-Capitán, A.; Paré, L.; Galván, P.; Viteri, S.; Rodríguez, S.; Peg, V.; Aldeguer, E.; Viñolas, N.; et al. Identification of ALK, ROS1, and RET Fusions by a Multiplexed mRNA-Based Assay in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Samples from Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piton, N.; Ruminy, P.; Gravet, C.; Marchand, V.; Colasse, É.; Lamy, A.; Mear, C.L.N.; Bibeau, F.; Marguet, F.; Guisier, F.; et al. Ligation-dependent RT-PCR: A new specific and low-cost technique to detect ALK, ROS, and RET rearrangements in lung adenocarcinoma. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldea, M.; Marinello, A.; Duruisseaux, M.; Zrafi, W.; Conci, N.; Massa, G.; Metro, G.; Monnet, I.; Iranzo, P.G.; Tabbo, F.; et al. RET-MAP: An International Multicenter Study on Clinicobiologic Features and Treatment Response in Patients with Lung Cancer Harboring a RET Fusion. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.I.; Zhu, V.W. Catalog of 5′ fusion partners in RET+ NSCLC Circa 2020. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2020, 1, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitiushkina, N.V.; Iyevleva, A.G.; Poltoratskiy, A.N.; Ivantsov, A.O.; Togo, A.V.; Polyakov, I.S.; Orlov, S.V.; Matsko, D.E.; Novik, V.I.; Imyanitov, E.N. Detection of EGFR mutations and EML4-ALK rearrangements in lung adenocarcinomas using archived cytological slides. Cancer Cytopathol. 2013, 121, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitiushkina, N.V.; Kholmatov, M.; Tiurin, V.I.; Romanko, A.A.; Yatsuk, O.S.; Sokolova, T.N.; Ivantsov, A.O.; Kuligina, E.S.; Stepanov, I.A.; Belyaev, A.M.; et al. Comparative analysis of expression of mutant and wild-type alleles is essential for reliable PCR-based detection of MET exon 14 skipping. Biochimie 2019, 165, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martianov, A.S.; Mitiushkina, N.V.; Ershova, A.N.; Martynenko, D.E.; Bubnov, M.G.; Amankwah, P.; Yanus, G.A.; Aleksakhina, S.N.; Tiurin, V.I.; Venina, A.R.; et al. KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, HER2 and MSI Status in a Large Consecutive Series of Colorectal Carcinomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
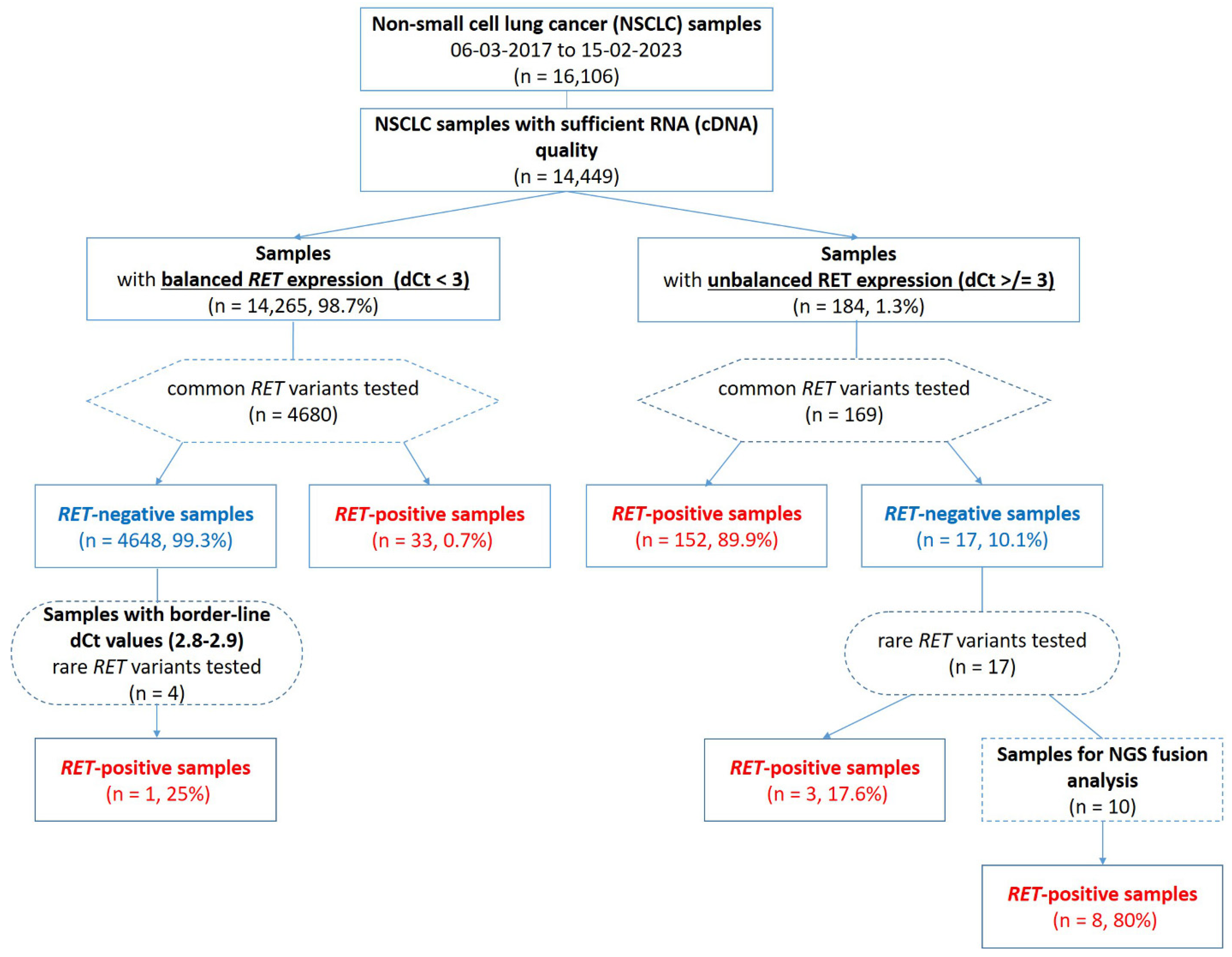
| Cases with Unbalanced 5′/3′-End Expression of RET | Cases with Balanced 5′/3′-End Expression of RET | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fusions detected via PCR for common variants | 152 (82.2%) | 33 (17.8%) | 185 |
| Fusions detected via PCR for rare variants | 3 (75.0%) | 1 (25.0%) | 4 |
| Fusions detected via NGS | 8 (100%) (6–rare, 2–novel) | - | 8 |
| Total RET-fusion-positive cases (n = 197) | 163 (82.7%) | 34 (17.3%) | 197 |
| Fusion | Number of Cases |
|---|---|
| KIF5B::RET (K15;R12) | 136 (69.1%) |
| CCDC6::RET (C1;R12) | 30 (15.1%) |
| KIF5B::RET (K16;R12) | 8 (4.1%) |
| KIF5B::RET (K22;R12) | 4 (2.0%) |
| NCOA4::RET (N8;R12) | 3 (1.5%) |
| KIF5B::RET (K23;R12) | 3 (1.5%) |
| RELCH::RET (R10;R12) | 2 (1.0%) |
| KIAA1217::RET (K13;R12) | 2 (1.0%) |
| KIF5B::RET (K24;R12) | 1 (0.5%) |
| KIF13A::RET (K18;R12) | 1 (0.5%) |
| KIAA1217::RET (K11;R12) | 1 (0.5%) |
| CCSER2::RET (C9;R12) | 1 (0.5%) |
| RBPMS::RET (R6;R12) | 1 (0.5%) |
| RUFY3::RET (R11;R12) | 1 (0.5%) |
| NCOA4::RET (N9;R12) | 1 (0.5%) |
| ZC3H7A::RET (Z3;R12) | 1 (0.5%) |
| HOOK1::RET (H21;R12) | 1 (0.5%) |
| Total | 197 |
| dCt >/= 3 | dCt >/= 2 | dCt >/= 1 | dCT < 1 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases tested for common variants | 169 | 224 | 376 | 4473 | 4849 |
| RET-positive (8 common variants) | 152/169 (89.9%) | 170/224 (75.9%) | 176/376 (46.8%) | 9/4473 (0.2%) | 185/4849 (3.8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiurin, V.I.; Preobrazhenskaya, E.V.; Mitiushkina, N.V.; Romanko, A.A.; Anuskina, A.A.; Mulkidjan, R.S.; Saitova, E.S.; Krivosheyeva, E.A.; Kharitonova, E.D.; Shevyakov, M.P.; et al. Rapid and Cost-Efficient Detection of RET Rearrangements in a Large Consecutive Series of Lung Carcinomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310530
Tiurin VI, Preobrazhenskaya EV, Mitiushkina NV, Romanko AA, Anuskina AA, Mulkidjan RS, Saitova ES, Krivosheyeva EA, Kharitonova ED, Shevyakov MP, et al. Rapid and Cost-Efficient Detection of RET Rearrangements in a Large Consecutive Series of Lung Carcinomas. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):10530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310530
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiurin, Vladislav I., Elena V. Preobrazhenskaya, Natalia V. Mitiushkina, Aleksandr A. Romanko, Aleksandra A. Anuskina, Rimma S. Mulkidjan, Evgeniya S. Saitova, Elena A. Krivosheyeva, Elena D. Kharitonova, Mikhail P. Shevyakov, and et al. 2023. "Rapid and Cost-Efficient Detection of RET Rearrangements in a Large Consecutive Series of Lung Carcinomas" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 10530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310530
APA StyleTiurin, V. I., Preobrazhenskaya, E. V., Mitiushkina, N. V., Romanko, A. A., Anuskina, A. A., Mulkidjan, R. S., Saitova, E. S., Krivosheyeva, E. A., Kharitonova, E. D., Shevyakov, M. P., Tryakin, I. A., Aleksakhina, S. N., Venina, A. R., Sokolova, T. N., Martianov, A. S., Shestakova, A. D., Ivantsov, A. O., Iyevleva, A. G., & Imyanitov, E. N. (2023). Rapid and Cost-Efficient Detection of RET Rearrangements in a Large Consecutive Series of Lung Carcinomas. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 10530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310530