Bypass of Abasic Site–Peptide Cross-Links by Human Repair and Translesion DNA Polymerases
Abstract
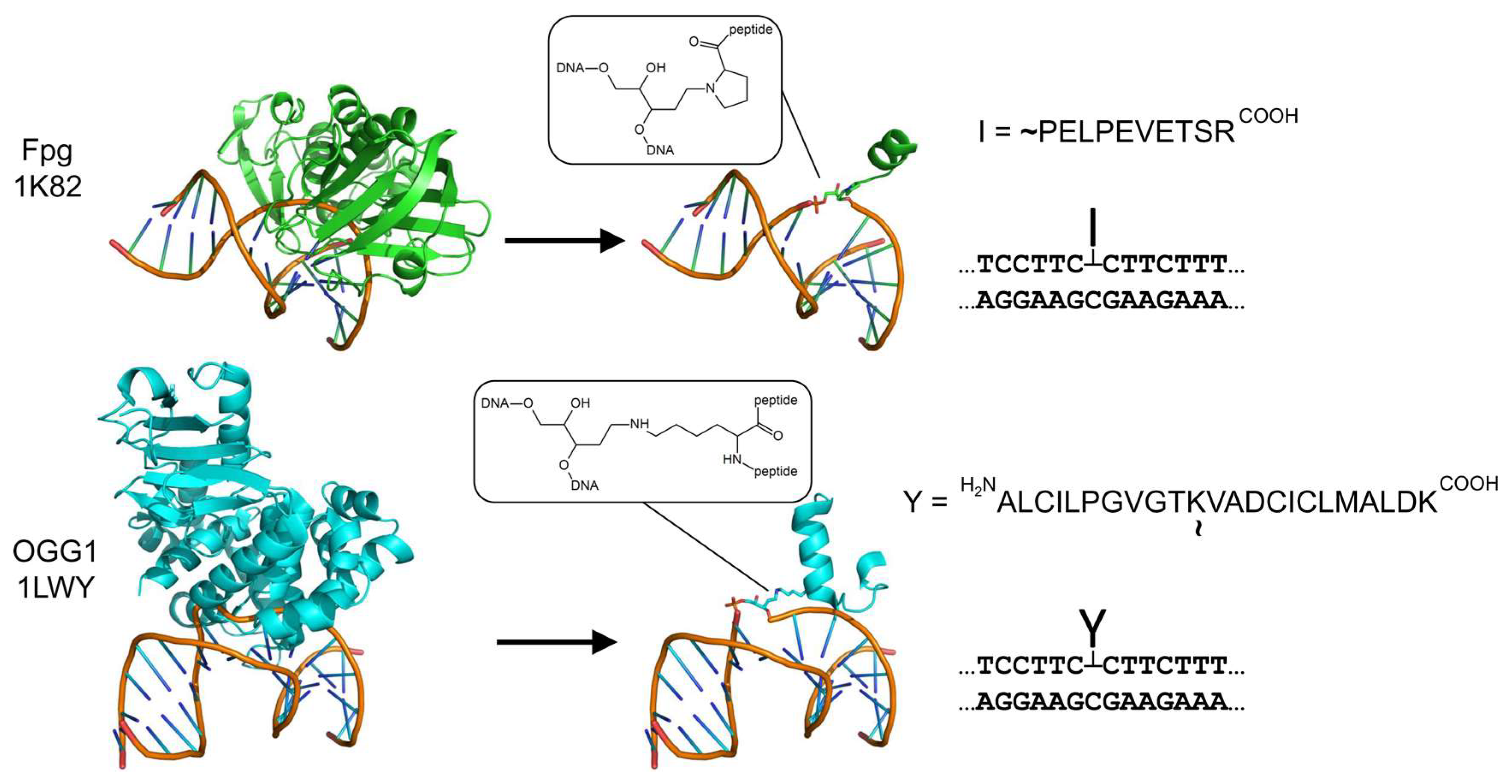
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Repair DNA Polymerases POLβ and POLλ Are Blocked by AP Site–Peptide Cross-Links
2.2. POLβ and POLλ Use dNTP-Stabilized Misalignment to Incorporate Nucleotides Opposite AP Site–Peptide Cross-Links
2.3. POLκ Can Bypass AP Site–Peptide Cross-Links
2.4. POLη Can Bypass AP Site–Peptide Cross-Links with Indiscriminate dNMP Incorporation
2.5. PrimPOL Does Not Bypass AP Site–Peptide Cross-Links but Incorporates dNMPs in a Mn2+-Facilitated Manner
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Oligonucleotides and Enzymes
4.2. Model AP Site–Peptide Conjugates’ Preparation
4.3. Running Start Assay
4.4. Standing Start Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindahl, T.; Nyberg, B. Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 3610–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atamna, H.; Cheung, I.; Ames, B.N. A method for detecting abasic sites in living cells: Age-dependent changes in base excision repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Greenberg, M.M. DNA interstrand cross-link formation by the 1,4-dioxobutane abasic lesion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15225–15231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Greenberg, M.M. Correlation of thermal stability and structural distortion of DNA interstrand cross-links produced from oxidized abasic sites with their selective formation and repair. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 6274–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, M.M.; Weledji, Y.N.; Kroeger, K.M.; Kim, J. In vitro replication and repair of DNA containing a C2′-oxidized abasic site. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 15217–15222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, M.S.; Beyret, E.; Wong, D.; Bales, B.C.; Hwang, J.-T.; Greenberg, M.M.; Demple, B. Covalent trapping of human DNA polymerase β by the oxidative DNA lesion 2-deoxyribonolactone. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7637–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.M. Abasic and oxidized abasic site reactivity in DNA: Enzyme inhibition, cross-linking, and nucleosome catalyzed reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Greenberg, M.M. Irreversible inhibition of DNA polymerase β by an oxidized abasic lesion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5004–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Bebenek, K.; Kunkel, T.A.; Greenberg, M.M. Inhibition of short patch and long patch base excision repair by an oxidized abasic site. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9904–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Greenberg, M.M.; Kow, Y.W.; Hwang, J.-T.; Cunningham, R.P. The 2-deoxyribonolactone lesion produced in DNA by neocarzinostatin and other damaging agents forms cross-links with the base-excision repair enzyme endonuclease III. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 3161–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeger, K.M.; Hashimoto, M.; Kow, Y.W.; Greenberg, M.M. Cross-linking of 2-deoxyribonolactone and its β-elimination product by base excision repair enzymes. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 2449–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodke, P.P.; Matse, J.H.; Dawson, S.; Guengerich, F.P. Nucleophilic thiol proteins bind covalently to abasic sites in DNA. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 1805–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogenhagen, D.F.; Pinz, K.G. The action of DNA ligase at abasic sites in DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7888–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sczepanski, J.T.; Wong, R.S.; McKnight, J.N.; Bowman, G.D.; Greenberg, M.M. Rapid DNA–protein cross-linking and strand scission by an abasic site in a nucleosome core particle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22475–22480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sczepanski, J.T.; Zhou, C.; Greenberg, M.M. Nucleosome core particle-catalyzed strand scission at abasic sites. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachva, M.C.; Kisselev, A.F.; Matkarimov, B.T.; Saparbaev, M.; Groisman, R. DNA-histone cross-links: Formation and repair. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 607045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, R.A.; Zaika, E.I.; Xie, W.; Johnson, F.; Grollman, A.P.; Iden, C.R.; Zharkov, D.O. Proteomic approach to identification of proteins reactive for abasic sites in DNA. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2006, 5, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosheva, A.S.; Zharkov, D.O.; Stahl, J.; Gopanenko, A.V.; Tupikin, A.E.; Kabilov, M.R.; Graifer, D.M.; Karpova, G.G. Recognition but no repair of abasic site in single-stranded DNA by human ribosomal uS3 protein residing within intact 40S subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 3833–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.; Ham, Y.-H.; Jin, L.; Chan, H.W.; Wong, Y.-L.; Chan, C.-K.; Chung, P.-Y. Quantification of a novel DNA–protein cross-link product formed by reacting apurinic/apyrimidinic sites in DNA with cysteine residues in protein by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with the stable isotope-dilution method. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4987–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.; Jin, L. DNA–protein cross-links formed by reacting lysine with apurinic/apyrimidinic sites in DNA and human cells: Quantitative analysis by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry coupled with stable isotope dilution. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESCODD (European Standards Committee on Oxidative DNA Damage); Gedik, C.M.; Collins, A. Establishing the background level of base oxidation in human lymphocyte DNA: Results of an interlaboratory validation study. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duxin, J.P.; Dewar, J.M.; Yardimci, H.; Walter, J.C. Repair of a DNA-protein crosslink by replication-coupled proteolysis. Cell 2014, 159, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stingele, J.; Schwarz, M.S.; Bloemeke, N.; Wolf, P.G.; Jentsch, S. A DNA-dependent protease involved in DNA-protein crosslink repair. Cell 2014, 158, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, B.; Popovic, M.; Newman, J.A.; Fielden, J.; Aitkenhead, H.; Halder, S.; Singh, A.N.; Vendrell, I.; Fischer, R.; Torrecilla, I.; et al. Metalloprotease SPRTN/DVC1 orchestrates replication-coupled DNA-protein crosslink repair. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 704–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, N.B.; Gao, A.O.; Sparks, J.L.; Gallina, I.; Wu, R.A.; Mann, M.; Räschle, M.; Walter, J.C.; Duxin, J.P. Replication-coupled DNA-protein crosslink repair by SPRTN and the proteasome in Xenopus egg extracts. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 574–588.e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühbacher, U.; Duxin, J.P. How to fix DNA-protein crosslinks. DNA Repair 2020, 94, 102924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minko, I.G.; Yamanaka, K.; Kozekov, I.D.; Kozekova, A.; Indiani, C.; O’Donnell, M.E.; Jiang, Q.; Goodman, M.F.; Rizzo, C.J.; Lloyd, R.S. Replication bypass of the acrolein-mediated deoxyguanine DNA-peptide cross-links by DNA polymerases of the DinB family. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Minko, I.G.; Takata, K.-I.; Kolbanovskiy, A.; Kozekov, I.D.; Wood, R.D.; Rizzo, C.J.; Lloyd, R.S. Novel enzymatic function of DNA polymerase ν in translesion DNA synthesis past major groove DNA−peptide and DNA−DNA cross-links. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.E.; Wickramaratne, S.; Khatwani, S.; Wang, Y.-C.; Vervacke, J.; Distefano, M.D.; Tretyakova, N.Y. Synthesis of site-specific DNA–protein conjugates and their effects on DNA replication. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramaratne, S.; Boldry, E.J.; Buehler, C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Distefano, M.D.; Tretyakova, N.Y. Error-prone translesion synthesis past DNA-peptide cross-links conjugated to the major groove of DNA via C5 of thymidine. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Fu, I.; Naldiga, S.; Shao, H.; Basu, A.K.; Broyde, S.; Tretyakova, N.Y. 5-Formylcytosine mediated DNA–protein cross-links block DNA replication and induce mutations in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 6455–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldiga, S.; Ji, S.; Thomforde, J.; Nicolae, C.M.; Lee, M.; Zhang, Z.; Moldovan, G.-L.; Tretyakova, N.Y.; Basu, A.K. Error-prone replication of a 5-formylcytosine-mediated DNA-peptide cross-link in human cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10619–10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marians, K.J. Lesion bypass and the reactivation of stalled replication forks. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinet, A.; Tirman, S.; Cybulla, E.; Meroni, A.; Vindigni, A. To skip or not to skip: Choosing repriming to tolerate DNA damage. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Minko, I.G.; Finkel, S.E.; Goodman, M.F.; Lloyd, R.S. Role of high-fidelity Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I in replication bypass of a deoxyadenosine DNA-peptide cross-link. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3815–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodke, P.P.; Gonzalez-Vasquez, G.; Wang, H.; Johnson, K.M.; Sedgeman, C.A.; Guengerich, F.P. Enzymatic bypass of an N6-deoxyadenosine DNA-ethylene dibromide-peptide crosslink by translesion DNA polymerases. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minko, I.G.; Kurtz, A.J.; Croteau, D.L.; Van Houten, B.; Harris, T.M.; Lloyd, R.S. Initiation of repair of DNA–polypeptide cross-links by the UvrABC nuclease. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, P.; Ji, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Schärer, O.D.; Tretyakova, N.Y.; Basu, A.K. Mutagenicity of a model DNA-peptide cross-link in human cells: Roles of translesion synthesis DNA polymerases. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudkina, A.V.; Bulgakov, N.A.; Kim, D.V.; Baranova, S.V.; Ishchenko, A.A.; Saparbaev, M.K.; Koval, V.V.; Zharkov, D.O. Abasic site–peptide cross-links are blocking lesions repaired by AP endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, R.; Zharkov, D.O.; Golan, G.; Fernandes, A.S.; Gerchman, S.E.; Matz, E.; Kycia, J.H.; Grollman, A.P.; Shoham, G. Structure of formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase covalently complexed to DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19811–19816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, J.C.; Bruner, S.D.; Yang, W.; Karplus, M.; Verdine, G.L. Product-assisted catalysis in base-excision DNA repair. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikazono, N.; Noguchi, M.; Fujii, K.; Urushibara, A.; Yokoya, A. The yield, processing, and biological consequences of clustered DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation. J. Radiat. Res. 2009, 50, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiken, Y.; Kanayeva, D.; Taipakova, S.; Groisman, R.; Ishchenko, A.A.; Begimbetova, D.; Matkarimov, B.; Saparbaev, M. Role of base excision repair pathway in the processing of complex DNA damage generated by oxidative stress and anticancer drugs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 617884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiala, K.A.; Hypes, C.D.; Suo, Z. Mechanism of abasic lesion bypass catalyzed by a Y-family DNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8188–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrer, S.M.; Fiala, K.A.; Fowler, J.D.; Newmister, S.A.; Pryor, J.M.; Suo, Z. Quantitative analysis of the efficiency and mutagenic spectra of abasic lesion bypass catalyzed by human Y-family DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudkina, A.V.; Zharkov, D.O. Miscoding and DNA polymerase stalling by methoxyamine-adducted abasic sites. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagovetz, A.M.; Sweasy, J.B.; Preston, B.D. Increased activity and fidelity of DNA polymerase β on single-nucleotide gapped DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27501–27504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianov, G.L.; Prasad, R.; Wilson, S.H.; Bohr, V.A. Role of DNA polymerase β in the excision step of long patch mammalian base excision repair. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13741–13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, N.A.; Rechkunova, N.I.; Dezhurov, S.V.; Khodyreva, S.N.; Favre, A.; Blanco, L.; Lavrik, O.I. Comparison of functional properties of mammalian DNA polymerase λ and DNA polymerase β in reactions of DNA synthesis related to DNA repair. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1751, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duym, W.W.; Fiala, K.A.; Bhatt, N.; Suo, Z. Kinetic effect of a downstream strand and its 5′-terminal moieties on single nucleotide gap-filling synthesis catalyzed by human DNA polymerase λ. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35649–35655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebenek, K.; Garcia-Diaz, M.; Blanco, L.; Kunkel, T.A. The frameshift infidelity of human DNA polymerase λ: Implications for function. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34685–34690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanca, G.; Villani, G.; Shevelev, I.; Ramadan, K.; Spadari, S.; Hübscher, U.; Maga, G. Human DNA polymerases λ and β show different efficiencies of translesion DNA synthesis past abasic sites and alternative mechanisms for frameshift generation. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11605–11615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tippin, B.; Kobayashi, S.; Bertram, J.G.; Goodman, M.F. To slip or skip, visualizing frameshift mutation dynamics for error-prone DNA polymerases. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45360–45368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Pence, M.G.; Eoff, R.L.; Yuan, S.; Fercu, C.A.; Guengerich, F.P. Elucidation of kinetic mechanisms of human translesion DNA polymerase κ using tryptophan mutants. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4394–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, P.; Lu, X.; Zhang, K.; Engen, J.R.; Beuning, P.J. Noncognate DNA damage prevents the formation of the active conformation of the Y-family DNA polymerases DinB and DNA polymerase κ. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 2646–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, H.R.; Sefcikova, J.; Chaparro, V.E.; Beuning, P.J. Mammalian DNA polymerase kappa activity and specificity. Molecules 2019, 24, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisman, A.; Woodgate, R. Translesion DNA polymerases in eukaryotes: What makes them tick? Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 52, 274–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.V.; Guainazzi, A.; Derkunt, S.B.; Enoiu, M.; Schärer, O.D. Structure-dependent bypass of DNA interstrand crosslinks by translesion synthesis polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7455–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.E.; Prakash, S.; Prakash, L. Efficient bypass of a thymine-thymine dimer by yeast DNA polymerase, Polη. Science 1999, 283, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masutani, C.; Kusumoto, R.; Yamada, A.; Dohmae, N.; Yokoi, M.; Yuasa, M.; Araki, M.; Iwai, S.; Takio, K.; Hanaoka, F. The XPV (xeroderma pigmentosum variant) gene encodes human DNA polymerase η. Nature 1999, 399, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masutani, C.; Kusumoto, R.; Iwai, S.; Hanaoka, F. Mechanisms of accurate translesion synthesis by human DNA polymerase η. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rechkoblit, O.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, D.; Wang, Z.; Amin, S.; Krzeminsky, J.; Louneva, N.; Geacintov, N.E. trans-Lesion synthesis past bulky benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide N2-dG and N6-dA lesions catalyzed by DNA bypass polymerases. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30488–30494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klarer, A.C.; Stallons, L.J.; Burke, T.J.; Skaggs, R.L.; McGregor, W.G. DNA polymerase eta participates in the mutagenic bypass of adducts induced by benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide in mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Rajpal, D.K.; Wu, X.; Guo, D.; Wang, M.; Taylor, J.-S.; Wang, Z. Specificity of DNA lesion bypass by the yeast DNA polymerase η. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8233–8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Wu, X.; Rechkoblit, O.; Taylor, J.-S.; Geacintov, N.E.; Wang, Z. Error-prone lesion bypass by human DNA polymerase η. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 4717–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Xie, Z.; Shen, H.; Wang, Z. Role of DNA polymerase η in the bypass of abasic sites in yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 3984–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlwraith, M.J.; Vaisman, A.; Liu, Y.; Fanning, E.; Woodgate, R.; West, S.C. Human DNA polymerase η promotes DNA synthesis from strand invasion intermediates of homologous recombination. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, J.; Rudd, S.G.; Jozwiakowski, S.K.; Bailey, L.J.; Soura, V.; Taylor, E.; Stevanovic, I.; Green, A.J.; Stracker, T.H.; Lindsay, H.D.; et al. PrimPol bypasses UV photoproducts during eukaryotic chromosomal DNA replication. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gómez, S.; Reyes, A.; Martínez-Jiménez, M.I.; Chocrón, E.S.; Mourón, S.; Terrados, G.; Powell, C.; Salido, E.; Méndez, J.; Holt, I.J.; et al. PrimPol, an archaic primase/polymerase operating in human cells. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.K.; Ketkar, A.; Lodeiro, M.F.; Cameron, C.E.; Eoff, R.L. Kinetic analysis of human PrimPol DNA polymerase activity reveals a generally error-prone enzyme capable of accurately bypassing 7,8-dihydro-8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 6584–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.V.; Boldinova, E.O.; Belousova, E.A.; Lavrik, O.I. In vitro lesion bypass by human PrimPol. DNA Repair 2018, 70, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldinova, E.O.; Yudkina, A.V.; Shilkin, E.S.; Gagarinskaya, D.I.; Baranovskiy, A.G.; Tahirov, T.H.; Zharkov, D.O.; Makarova, A.V. Translesion activity of PrimPol on DNA with cisplatin and DNA–protein cross-links. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldinova, E.O.; Belousova, E.A.; Gagarinskaya, D.I.; Maltseva, E.A.; Khodyreva, S.N.; Lavrik, O.I.; Makarova, A.V. Strand displacement activity of PrimPol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohni, K.N.; Wessel, S.R.; Zhao, R.; Wojciechowski, A.C.; Luzwick, J.W.; Layden, H.; Eichman, B.F.; Thompson, P.S.; Mehta, K.P.M.; Cortez, D. HMCES maintains genome integrity by shielding abasic sites in single-strand DNA. Cell 2019, 176, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halabelian, L.; Ravichandran, M.; Li, Y.; Zeng, H.; Rao, A.; Aravind, L.; Arrowsmith, C.H. Structural basis of HMCES interactions with abasic DNA and multivalent substrate recognition. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.S.; Amidon, K.M.; Mohni, K.N.; Cortez, D.; Eichman, B.F. Protection of abasic sites during DNA replication by a stable thiazolidine protein-DNA cross-link. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Su, D.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Tang, M.; Nie, L.; Chen, J. HMCES safeguards replication from oxidative stress and ensures error-free repair. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Wu, X.; Wang, M.; Rechkoblit, O.; Taylor, J.-S.; Geacintov, N.E.; Wang, Z. Error-free and error-prone lesion bypass by human DNA polymerase κ in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 4138–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoska, R.J.; McCulloch, S.D.; Kunkel, T.A. The efficiency and specificity of apurinic/apyrimidinic site bypass by human DNA polymerase η and Sulfolobus solfataricus Dpo4. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50537–50545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Lim, S.; Kim, E.-J.; Jo, A.; Guengerich, F.P. Translesion synthesis across abasic lesions by human B-family and Y-family DNA polymerases α, δ, η, ι, κ, and REV1. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 404, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrati, E.; Tocco, G.; Eritja, R.; Wilson, S.H.; Goodman, M.F. Abasic translesion synthesis by DNA polymerase β violates the “A-rule”: Novel types of nucleotide incorporation by human DNA polymerase β at an abasic lesion in different sequence contexts. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2559–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.; Batra, V.K.; Yang, X.-P.; Krahn, J.M.; Pedersen, L.C.; Beard, W.A.; Wilson, S.H. Structural insight into the DNA polymerase β deoxyribose phosphate lyase mechanism. DNA Repair 2005, 4, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Diaz, M.; Bebenek, K.; Krahn, J.M.; Pedersen, L.C.; Kunkel, T.A. Role of the catalytic metal during polymerization by DNA polymerase lambda. DNA Repair 2007, 6, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rechkoblit, O.; Gupta, Y.K.; Malik, R.; Rajashankar, K.R.; Johnson, R.E.; Prakash, L.; Prakash, S.; Aggarwal, A.K. Structure and mechanism of human PrimPol, a DNA polymerase with primase activity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechkoblit, O.; Johnson, R.E.; Gupta, Y.K.; Prakash, L.; Prakash, S.; Aggarwal, A.K. Structural basis of DNA synthesis opposite 8-oxoguanine by human PrimPol primase-polymerase. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, L.; Su, Y.; Egli, M.; Guengerich, F.P. Structural and kinetic analysis of nucleoside triphosphate incorporation opposite an abasic site by human translesion DNA polymerase η. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 8028–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Bian, C.; Xing, G.; Ling, H. Structure and mechanism of error-free replication past the major benzo[a]pyrene adduct by human DNA polymerase κ. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4957–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibutani, S.; Takeshita, M.; Grollman, A.P. Translesional synthesis on DNA templates containing a single abasic site: A mechanistic study of the “A rule”. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 13916–13922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, M.; Wallace, S.S.; Doublié, S. Crystallographic snapshots of a replicative DNA polymerase encountering an abasic site. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, B.S. The ‘A rule’ of mutagen specificity: A consequence of DNA polymerase bypass of non-instructional lesions? Bioessays 1991, 13, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudkina, A.V.; Dvornikova, A.P.; Zharkov, D.O. Variable termination sites of DNA polymerases encountering a DNA–protein cross-link. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudkina, A.V.; Shilkin, E.S.; Makarova, A.V.; Zharkov, D.O. Stalling of eukaryotic translesion DNA polymerases at DNA-protein cross-links. Genes 2022, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegler, J.; Bittner, D.; Boiteux, S.; Epe, B. Quantification of oxidative DNA modifications in mitochondria. Carcinogenesis 1993, 14, 2309–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Sumberaz, P. Mitochondrial DNA damage: Prevalence, biological consequence, and emerging pathways. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tang, J.; Zhao, L. DNA–protein cross-links between abasic DNA damage and mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM). Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesner, L.N.; Essawy, M.; Warner, C.; Campbell, C. DNA-protein crosslinks are repaired via homologous recombination in mammalian mitochondria. DNA Repair 2021, 97, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkovič, G.; Makarova, A.V.; Wanrooij, P.H.; Forslund, J.; Burgers, P.M.; Wanrooij, S. Oxidative DNA damage stalls the human mitochondrial replisome. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.A.O.; Wilson, D.M., III; Wong, D.; Demple, B. Interaction of human apurinic endonuclease and DNA polymerase β in the base excision repair pathway. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7166–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.E.; Boiteux, S.; Hickson, I.D.; Radicella, J.P. XRCC1 coordinates the initial and late stages of DNA abasic site repair through protein–protein interactions. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6530–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamori, T.; DeRicco, J.; Naqvi, A.; Hoffman, T.A.; Mattagajasingh, I.; Kasuno, K.; Jung, S.-B.; Kim, C.-S.; Irani, K. SIRT1 deacetylates APE1 and regulates cellular base excision repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Kim, K.; Hurwitz, J.; Gary, R.; Levin, D.S.; Tomkinson, A.E.; Park, M.S. Reconstitution of proliferating cell nuclear antigen-dependent repair of apurinic/apyrimidinic sites with purified human proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33703–33708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianova, I.I.; Bohr, V.A.; Dianov, G.L. Interaction of human AP endonuclease 1 with flap endonuclease 1 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen involved in long-patch base excision repair. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 12639–12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniali, G.; Serra, F.; Lirussi, L.; Tanaka, M.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Zhang, S.; Radovic, S.; Dalla, E.; Ciani, Y.; Scaloni, A.; et al. Mammalian APE1 controls miRNA processing and its interactome is linked to cancer RNA metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, N.A.; Koval, V.V.; Zharkov, D.O.; Nevinsky, G.A.; Douglas, K.T.; Fedorova, O.S. Kinetics of substrate recognition and cleavage by human 8-oxoguanine-DNA glycosylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 3919–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, E.; Ogi, T.; Kusumoto, R.; Iwai, S.; Masutani, C.; Hanaoka, F.; Ohmori, H. Error-prone bypass of certain DNA lesions by the human DNA polymerase κ. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endutkin, A.V.; Yudkina, A.V.; Zharkov, T.D.; Kim, D.V.; Zharkov, D.O. Recognition of a clickable abasic site analog by DNA polymerases and DNA repair enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Diaz, M.; Bebenek, K.; Krahn, J.M.; Blanco, L.; Kunkel, T.A.; Pedersen, L.C. A structural solution for the DNA polymerase λ-dependent repair of DNA gaps with minimal homology. Mol. Cell 2004, 13, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.; Stith, C.M.; Majka, J.; Burgers, P.M.J. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen promotes translesion synthesis by DNA polymerase ζ. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 23446–23450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burak, M.J.; Guja, K.E.; Garcia-Diaz, M. Nucleotide binding interactions modulate dNTP selectivity and facilitate 8-oxo-dGTP incorporation by DNA polymerase lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8089–8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Polymerase | Pyrimidine-Rich Template | Purine-Rich Template | Suggested Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| POLβ | G > A > C > T | C > A > T > G | +1 dNTP-stabilized misalignment > “A rule”. |
| POLλ | G >> A > C > T | C >> T > A > G | +1 dNTP-stabilized misalignment >> +2 dNTP-stabilized misalignment. |
| POLκ | A > G,C > T | C > A,T > G | +1 dNTP-stabilized misalignment >> +2 dNTP-stabilized misalignment, “A rule”. |
| hPOLη | A,G > T,C (APPXL-I) | A,G,C > T (APPXL-I) | Inaccurate. Likely several mechanisms. |
| G > T,C,A (APPXL-Y) | C >> A > G > T (APPXL-Y) | ||
| yPOLη | G >> A > T >> C (APPXL-I) | A,G,C > T (APPXL-I) | |
| G > T,C,A (APPXL-Y) | C >> A > G > T (APPXL-Y) | ||
| PrimPOL | A ~ G > C > T (APPXL-I/Mg2+) | C > A,G,T (APPXL-I/Mg2+) | Size dependent: “A rule” for APPXL-I, +1 dNTP-stabilized misalignment for APPXL-Y. |
| G >> A,T,C (APPXL-Y/Mg2+) | C >> A,G,T (APPXL-Y/Mg2+) | ||
| A ~ G ~ C ~ T (APPXL-I/Mn2+) | C >> A > T,G (APPXL-I/Mn2+) | ||
| G > A,C > T (APPXL-Y/Mn2+) | C >> A > T,G (APPXL-Y/Mn2+) |
| ID | Sequence, 5′→3′ | Length | Modification (X) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40oG | GCTCTGGAATTCCTTCXCTTCTTTCCTCTCGACGGTCTCG | 40 | 8-oxoguanine |
| 40U | GCTCTGGAATTCCTTCXCTTCTTTCCTCTCGACGGTCTCG | 40 | uracil |
| 28down | GAGGAAAGAAGCGAAGGAATTCCAGAGC | 28 | |
| 28oG | GAGGAAAGAAGXGAAGGAATTCCAGAGC | 28 | 8-oxoguanine |
| 40temp | GCTCTGGAATTCCTTCCCTTCTTTCCTCTCGACGGTCTCG | 40 | |
| 40comp; 40marker | CGAGACCGTCGAGAGGAAAGAAGCGAAGGAATTCCAGAGC | 40 | |
| 21comp | GGAATTCCTTCCCTTCTTTCC | 21 | |
| 23marker | CGAGACCGTCGAGAGGAAAGAAG | 23 | |
| run_pri; 11marker | CGAGACCGTCG | 11 | |
| stand_pri_1 | GAGAGGAAAGAAG | 13 | |
| stand_pri_2 | GCTCTGGAATTCCTTC | 16 |
| Enzyme | Concentration in Running Start Assay, nM | Concentration in Standing Start Assay, nM | Reaction Buffer | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POLβ | 200 | 300 | 20 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.6), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT | [46] |
| POLλ | 200 | 200 | 50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.5), 2.5 mM MgCl2, 2% glycerol, 1 mM DTT, 100 µg/mL BSA | [46], modified after [109] |
| POLκ | 100 | 100 | 50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5), 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT | [46] |
| hPOLη, yPOLη | 50 | 120 | 30 mM HEPES–NaOH (pH 7.4), 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 100 µg/mL BSA | [92] |
| PrimPOL | 200 | 500 | 30 mM HEPES (pH 7.2), 10 mM MgCl2 or 0.5 mM MnCl2, 5% glycerol, 100 µg/mL BSA | [72] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yudkina, A.V.; Barmatov, A.E.; Bulgakov, N.A.; Boldinova, E.O.; Shilkin, E.S.; Makarova, A.V.; Zharkov, D.O. Bypass of Abasic Site–Peptide Cross-Links by Human Repair and Translesion DNA Polymerases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310877
Yudkina AV, Barmatov AE, Bulgakov NA, Boldinova EO, Shilkin ES, Makarova AV, Zharkov DO. Bypass of Abasic Site–Peptide Cross-Links by Human Repair and Translesion DNA Polymerases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):10877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310877
Chicago/Turabian StyleYudkina, Anna V., Alexander E. Barmatov, Nikita A. Bulgakov, Elizaveta O. Boldinova, Evgeniy S. Shilkin, Alena V. Makarova, and Dmitry O. Zharkov. 2023. "Bypass of Abasic Site–Peptide Cross-Links by Human Repair and Translesion DNA Polymerases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 10877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310877
APA StyleYudkina, A. V., Barmatov, A. E., Bulgakov, N. A., Boldinova, E. O., Shilkin, E. S., Makarova, A. V., & Zharkov, D. O. (2023). Bypass of Abasic Site–Peptide Cross-Links by Human Repair and Translesion DNA Polymerases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 10877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310877





