The Proteome and Lipidome of Extracellular Vesicles from Haemonchus contortus to Underpin Explorations of Host–Parasite Cross–Talk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterisation of H. contortus EVs
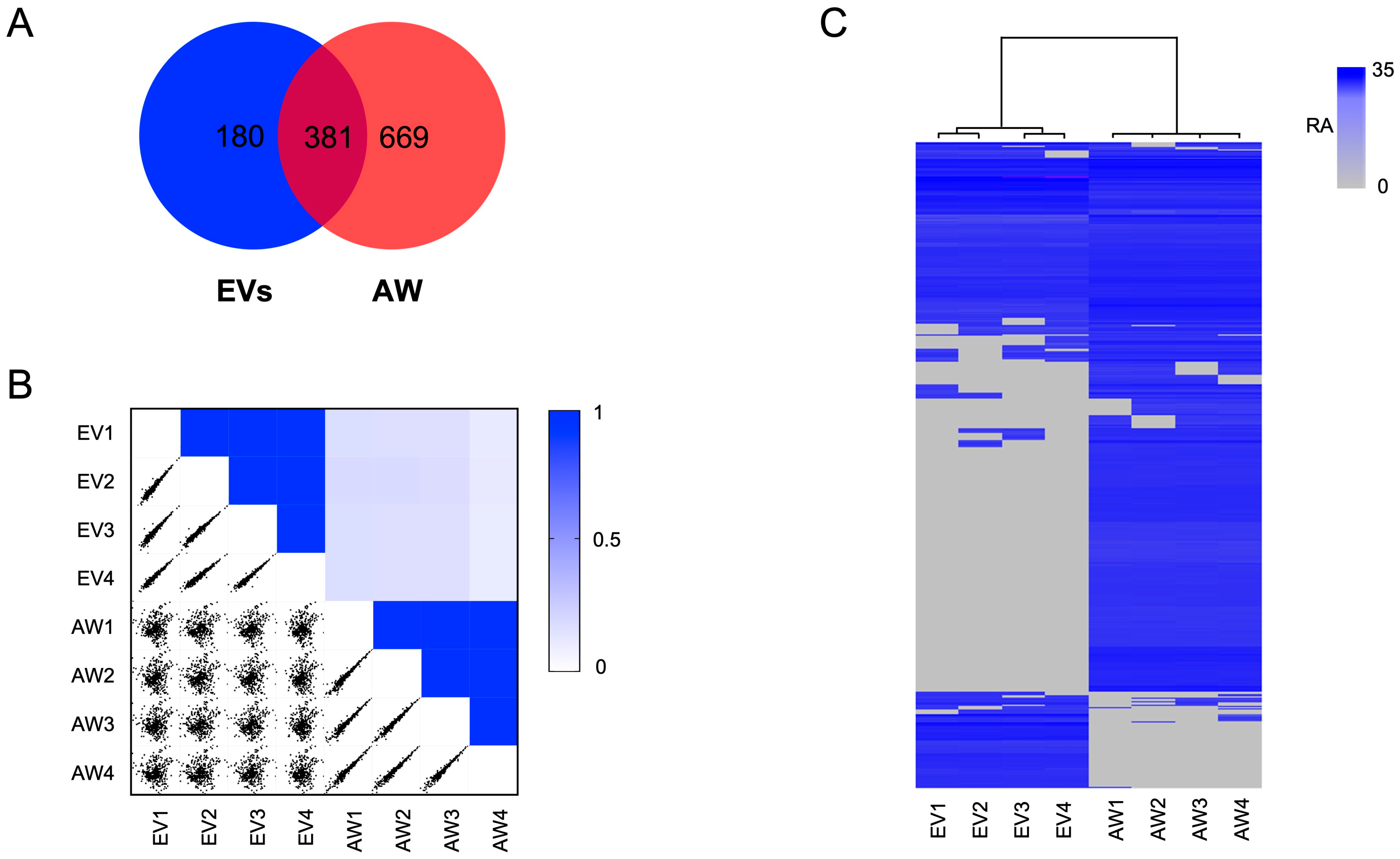
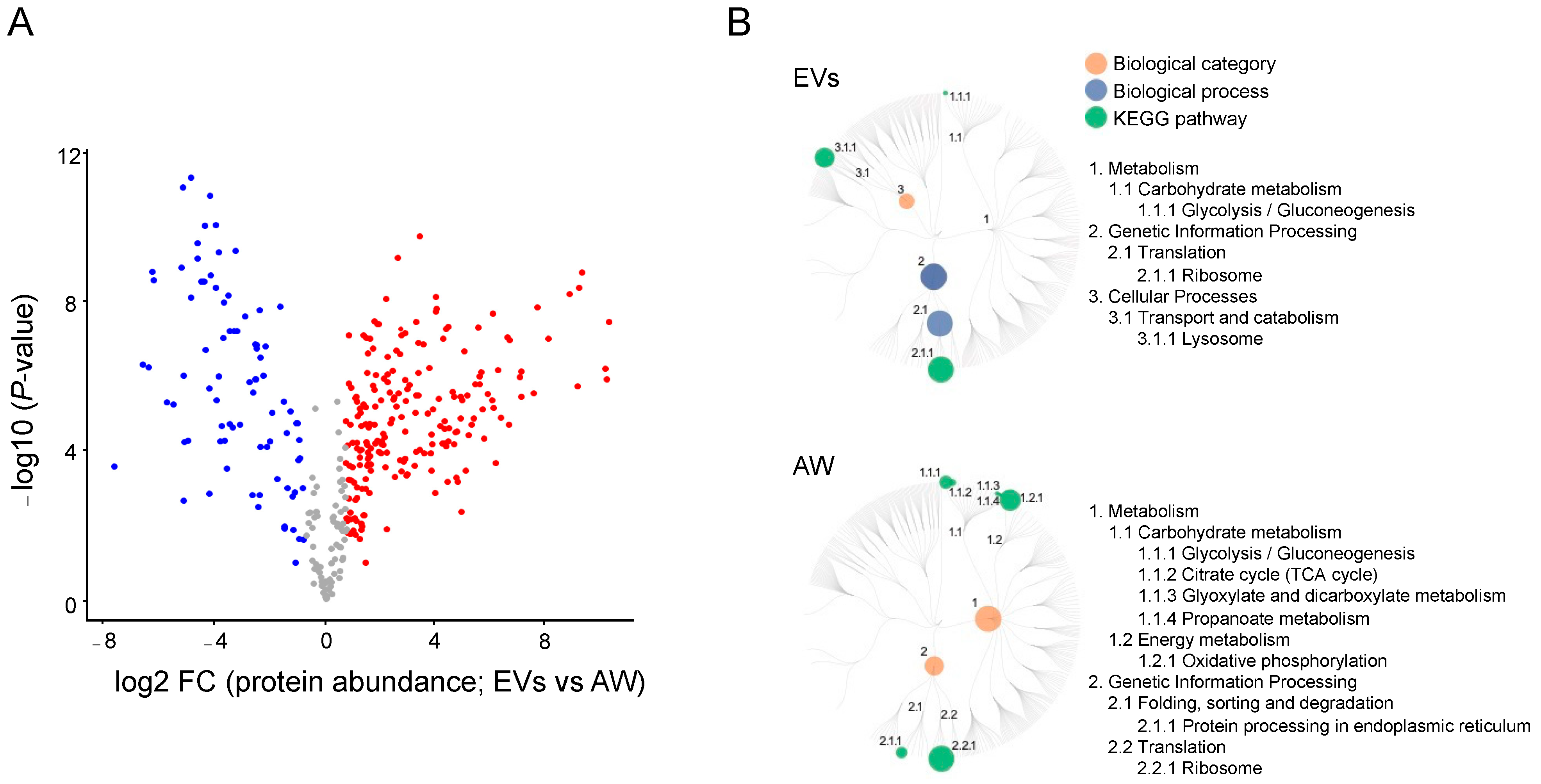
2.2. The EV Proteome for Adult H. contortus
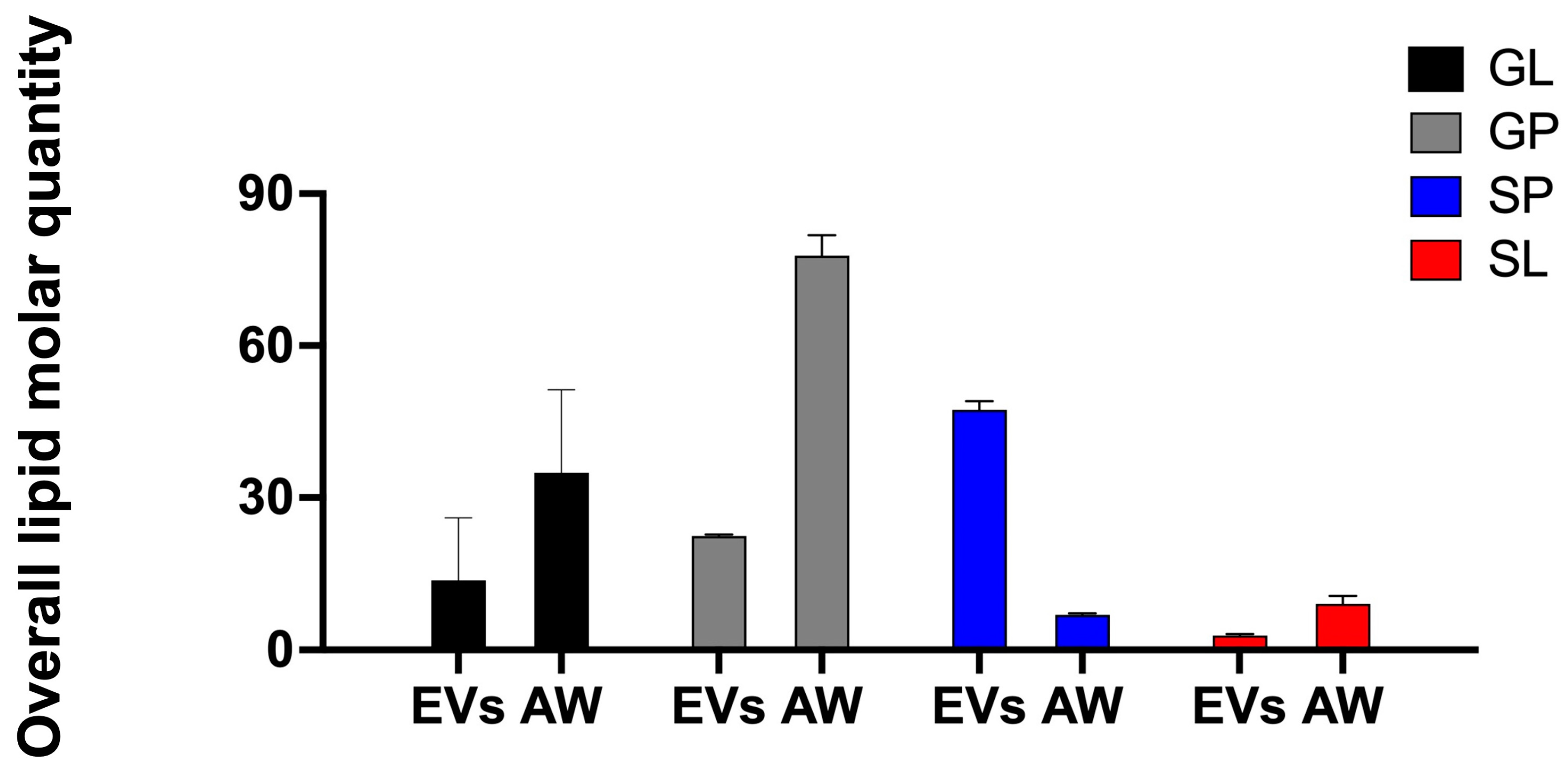
2.3. The EV Lipidome for Adult H. contortus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Parasite Stages
4.2. Preparation of ES Products
4.3. EV Enrichment
4.4. NTA
4.5. TEM
4.6. Extraction of Proteins and Proteomic Analysis by LC-MS/MS
4.7. Protein Identification and Quantification
4.8. Extraction of Lipids and Lipidomic Analysis by HPLC-MS/MS
4.9. Identification and Quantification of Lipids and Statistical Analysis
4.10. Bioinformatic Analyses of Data Sets
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jourdan, P.M.; Lamberton, P.H.L.; Fenwick, A.; Addiss, D.G. Soil-transmitted helminth infections. Lancet 2017, 391, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleard, J.S.; Kotze, A.C.; Leathwick, D.; Nisbet, A.J.; McNeilly, T.N.; Besier, B. A journey through 50 years of research relevant to the control of gastrointestinal nematodes in ruminant livestock and thoughts on future directions. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 1133–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.M. Drug resistance in nematodes of veterinary importance: A status report. Trends Parasitol. 2004, 20, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.M.; Vidyashankar, A.N. An inconvenient truth: Global worming and anthelmintic resistance. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, T.G. Are new anthelmintics needed to eliminate human helminthiases? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taki, A.C.; Byrne, J.J.; Wang, T.; Sleebs, B.E.; Nguyen, N.; Hall, R.S.; Korhonen, P.K.; Chang, B.C.H.; Jackson, P.; Jabbar, A.; et al. High-throughput phenotypic assay to screen for anthelmintic activity on Haemonchus contortus. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clare, R.H.; Bardelle, C.; Harper, P.; Hong, W.D.; Borjesson, U.; Johnston, K.L.; Collier, M.; Myhill, L.; Cassidy, A.; Plant, D.; et al. Industrial scale high-throughput screening delivers multiple fast acting macrofilaricides. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, A.C.; Wang, T.; Nguyen, N.N.; Ang, C.S.; Leeming, M.G.; Nie, S.; Byrne, J.J.; Young, N.D.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, G.; et al. Thermal proteome profiling reveals Haemonchus orphan protein HCO_011565 as a target of the nematocidal small molecule UMW-868. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1014804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnett, W. Secretory products of helminth parasites as immunomodulators. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 195, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drurey, C.; Maizels, R.M. Helminth extracellular vesicles: Interactions with the host immune system. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 137, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotillo, J.; Robinson, M.W.; Kimber, M.J.; Cucher, M.; Ancarola, M.E.; Nejsum, P.; Marcilla, A.; Eichenberger, R.M.; Tritten, L. The protein and microRNA cargo of extracellular vesicles from parasitic helminths–current status and research priorities. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coakley, G.; Maizels, R.M.; Buck, A.H. Exosomes and other extracellular vesicles: The new communicators in parasite infections. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coakley, G.; McCaskill, J.L.; Borger, J.G.; Simbari, F.; Robertson, E.; Millar, M.; Harcus, Y.; McSorley, H.J.; Maizels, R.M.; Buck, A.H. Extracellular vesicles from a helminth parasite suppress macrophage activation and constitute an fffective vaccine for protective immunity. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deatherage, B.L.; Cookson, B.T. Membrane vesicle release in bacteria, eukaryotes, and archaea: A conserved yet underappreciated aspect of microbial life. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.P.; Fromm, B.; Andersen, S.D.; Marcilla, A.; Andersen, K.L.; Borup, A.; Williams, A.R.; Jex, A.R.; Gasser, R.B.; Young, N.D.; et al. Exploration of extracellular vesicles from Ascaris suum provides evidence of parasite-host cross talk. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1578116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harischandra, H.; Yuan, W.; Loghry, H.J.; Zamanian, M.; Kimber, M.J. Profiling extracellular vesicle release by the filarial nematode Brugia malayi reveals sex-specific differences in cargo and a sensitivity to ivermectin. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, A.H.; Coakley, G.; Simbari, F.; McSorley, H.J.; Quintana, J.F.; Le Bihan, T.; Kumar, S.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Lear, M.; Harcus, Y.; et al. Exosomes secreted by nematode parasites transfer small RNAs to mammalian cells and modulate innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenberger, R.M.; Ryan, S.; Jones, L.; Buitrago, G.; Polster, R.; Montes de Oca, M.; Zuvelek, J.; Giacomin, P.R.; Dent, L.A.; Engwerda, C.R.; et al. Hookworm secreted extracellular vesicles interact with host cells and prevent inducible colitis in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenberger, R.M.; Talukder, M.H.; Field, M.A.; Wangchuk, P.; Giacomin, P.; Loukas, A.; Sotillo, J. Characterization of Trichuris muris secreted proteins and extracellular vesicles provides new insights into host-parasite communication. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1428004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, S.R.; Laing, R.; Bartley, D.J.; Britton, C.; Chaudhry, U.; Gilleard, J.S.; Holroyd, N.; Mable, B.K.; Maitland, K.; Morrison, A.A.; et al. A genome resequencing-based genetic map reveals the recombination landscape of an outbred parasitic nematode in the presence of polyploidy and polyandry. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gao, W.; Yan, S.; Zhu, X.; Suo, X.; Liu, X.; Gupta, N.; Hu, M. N-glycome and N-glycoproteome of a hematophagous parasitic nematode Haemonchus. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, R.; Kikuchi, T.; Martinelli, A.; Tsai, I.J.; Beech, R.N.; Redman, E.; Holroyd, N.; Bartley, D.J.; Beasley, H.; Britton, C.; et al. The genome and transcriptome of Haemonchus contortus, a key model parasite for drug and vaccine discovery. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Wang, T.; Korhonen, P.K.; Ang, C.S.; Williamson, N.A.; Young, N.D.; Stroehlein, A.J.; Hall, R.S.; Koehler, A.V.; Hofmann, A.; et al. Molecular alterations during larval development of Haemonchus contortus in vitro are under tight post-transcriptional control. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Korhonen, P.K.; Campbell, B.E.; Young, N.D.; Jex, A.R.; Jabbar, A.; Hall, R.S.; Mondal, A.; Howe, A.C.; Pell, J.; et al. The genome and developmental transcriptome of the strongylid nematode Haemonchus contortus. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Nie, S.; Ma, G.; Korhonen, P.K.; Koehler, A.V.; Ang, C.S.; Reid, G.E.; Williamson, N.A.; Gasser, R.B. The developmental lipidome of Haemonchus contortus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Ma, G.; Nie, S.; Williamson, N.A.; Reid, G.E.; Gasser, R.B. Lipid composition and abundance in the reproductive and alimentary tracts of female Haemonchus contortus. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Ma, G.; Ang, C.S.; Korhonen, P.K.; Xu, R.; Nie, S.; Koehler, A.V.; Simpson, R.J.; Greening, D.W.; Reid, G.E.; et al. Somatic proteome of Haemonchus contortus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ma, G.; Ang, C.S.; Korhonen, P.K.; Stroehlein, A.J.; Young, N.D.; Hofmann, A.; Chang, B.C.H.; Williamson, N.A.; Gasser, R.B. The developmental phosphoproteome of Haemonchus contortus. J. Proteom. 2020, 213, 103615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ma, G.; Ang, C.S.; Korhonen, P.K.; Koehler, A.V.; Young, N.D.; Nie, S.; Williamson, N.A.; Gasser, R.B. High throughput LC-MS/MS-based proteomic analysis of excretory-secretory products from short-term in vitro culture of Haemonchus contortus. J. Proteom. 2019, 204, 103375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, S.R.; Tracey, A.; Laing, R.; Holroyd, N.; Bartley, D.; Bazant, W.; Beasley, H.; Beech, R.; Britton, C.; Brooks, K.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic variation defines the chromosome-scale assembly of Haemonchus contortus, a model gastrointestinal worm. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.; Preston, S.; Jabbar, A.; Garcia-Bustos, J.; Addison, R.S.; Hayes, S.; Rali, T.; Wang, T.; Koehler, A.V.; Chang, B.C.H.; et al. Selected alpha-pyrones from the plants Cryptocarya novoguineensis (Lauraceae) and Piper methysticum (Piperaceae) with activity against Haemonchus contortus in vitro. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2019, 9, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Preston, S.; Garcia-Bustos, J.F.; Baell, J.B.; Ventura, S.; Le, T.; McNamara, N.; Nguyen, N.; Botteon, A.; Skinner, C.; et al. Tetrahydroquinoxalines induce a lethal evisceration phenotype in Haemonchus contortus in vitro. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2019, 9, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, A.J.; Meeusen, E.N.; Gonzalez, J.F.; Piedrafita, D.M. Immunity to Haemonchus contortus and vaccine development. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 353–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, B.; Antonopoulos, A.; Haslam, S.M.; Dicker, A.J.; McNeilly, T.N.; Johnston, S.L.; Dell, A.; Knox, D.P.; Britton, C. Novel expression of Haemonchus contortus vaccine candidate aminopeptidase H11 using the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilleard, J.S. Haemonchus contortus as a paradigm and model to study anthelmintic drug resistance. Parasitology 2013, 140, 1506–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.; Sotillo, J.; Ancarola, M.E.; Borup, A.; Boysen, A.T.; Brindley, P.J.; Buzas, E.I.; Cavallero, S.; Chaiyadet, S.; Chalmers, I.W.; et al. Special considerations for studies of extracellular vesicles from parasitic helminths: A community-led roadmap to increase rigour and reproducibility. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.Y.; Marks, N.D.; Winter, A.D.; Weir, W.; Tzelos, T.; McNeilly, T.N.; Britton, C.; Devaney, E. Conservation of a microRNA cluster in parasitic nematodes and profiling of miRNAs in excretory-secretory products and microvesicles of Haemonchus contortus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyadet, S.; Sotillo, J.; Smout, M.; Cantacessi, C.; Jones, M.K.; Johnson, M.S.; Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Potriquet, J.; Laohaviroj, M.; et al. Carcinogenic liver fluke secretes extracellular vesicles that promote cholangiocytes to adopt a tumorigenic phenotype. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwiklinski, K.; de la Torre-Escudero, E.; Trelis, M.; Bernal, D.; Dufresne, P.J.; Brennan, G.P.; O’Neill, S.; Tort, J.; Paterson, S.; Marcilla, A.; et al. The extracellular vesicles of the helminth pathogen, Fasciola hepatica: Biogenesis pathways and cargo molecules involved in parasite pathogenesis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 3258–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacki, F.C.; Swain, M.T.; Klychnikov, O.I.; Niazi, U.; Ivens, A.; Quintana, J.F.; Hensbergen, P.J.; Hokke, C.H.; Buck, A.H.; Hoffmann, K.F. Protein and small non-coding RNA-enriched extracellular vesicles are released by the pathogenic blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 28665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbari, F.; McCaskill, J.; Coakley, G.; Millar, M.; Maizels, R.M.; Fabrias, G.; Casas, J.; Buck, A.H. Plasmalogen enrichment in exosomes secreted by a nematode parasite versus those derived from its mouse host: Implications for exosome stability and biology. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 30741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, Z.; Yanez-Mo, M. Tetraspanins in extracellular vesicle formation and function. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Torre-Escudero, E.; Bennett, A.P.S.; Clarke, A.; Brennan, G.P.; Robinson, M.W. Extracellular vesicle biogenesis in helminths: More than one route to the surface? Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantacessi, C.; Campbell, B.E.; Visser, A.; Geldhof, P.; Nolan, M.J.; Nisbet, A.J.; Matthews, J.B.; Loukas, A.; Hofmann, A.; Otranto, D.; et al. A portrait of the “SCP/TAPS” proteins of eukaryotes—Developing a framework for fundamental research and biotechnological outcomes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauters, L.; Naalden, D.; Gheysen, G. The distribution of lectins across the phylum nematoda: A genome-wide search. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbers, R.H.P.; Schneiter, R.; Holterman, M.H.M.; Drurey, C.; Smant, G.; Asojo, O.A.; Maizels, R.M.; Lozano-Torres, J.L. Secreted venom allergen-like proteins of helminths: Conserved modulators of host responses in animals and plants. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuda, A.P.; Krijgsveld, J.; Cornelissen, A.W.; Heck, A.J.; de Vries, E. Comprehensive analysis of the secreted proteins of the parasite Haemonchus contortus reveals extensive sequence variation and differential immune recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16941–16951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asojo, O.A.; Darwiche, R.; Gebremedhin, S.; Smant, G.; Lozano-Torres, J.L.; Drurey, C.; Pollet, J.; Maizels, R.M.; Schneiter, R.; Wilbers, R.H.P. Heligmosomoides polygyrus venom allergen-like protein-4 (HpVAL-4) is a sterol binding protein. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, A.; Darwiche, R.; Rezende, W.C.; Farias, L.P.; Leite, L.C.; Schneiter, R.; Asojo, O.A. Schistosoma mansoni venom allergen-like protein 4 (SmVAL4) is a novel lipid-binding SCP/TAPS protein that lacks the prototypical CAP motifs. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 2186–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotland, T.; Hessvik, N.P.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Exosomal lipid composition and the role of ether lipids and phosphoinositides in exosome biology. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, R.S.; Kulkarni, A.; Becker, M.W.; Lei, X.; Sarkar, S.; Ramanadham, S.; Phelps, E.A.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Sims, E.K.; Mirmira, R.G. Extracellular vesicles in beta cell biology: Role of lipids in vesicle biogenesis, cargo, and intercellular signaling. Mol. Metab. 2022, 63, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixson, A.C.; Dawson, T.R.; Di Vizio, D.; Weaver, A.M. Context-specific regulation of extracellular vesicle biogenesis and cargo selection. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 454–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deehan, M.R.; Frame, M.J.; Parkhouse, R.M.; Seatter, S.D.; Reid, S.D.; Harnett, M.M.; Harnett, W. A phosphorylcholine-containing filarial nematode-secreted product disrupts B lymphocyte activation by targeting key proliferative signaling pathways. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kleij, D.; Latz, E.; Brouwers, J.F.; Kruize, Y.C.; Schmitz, M.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Espevik, T.; de Jong, E.C.; Kapsenberg, M.L.; Golenbock, D.T.; et al. A novel host-parasite lipid cross-talk. Schistosomal lyso-phosphatidylserine activates toll-like receptor 2 and affects immune polarization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48122–48129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, K.; Almeida, P.E.; Atella, G.; Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.; Pelajo-Machado, M.; Lenzi, H.L.; Bozza, M.T.; Bozza, P.T. Schistosomal-derived lysophosphatidylcholine are involved in eosinophil activation and recruitment through Toll-like receptor-2-dependent mechanisms. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaffoni, F.; Tatti, M.; Boe, A.; Salvioli, R.; Fluharty, A.; Sonnino, S.; Vaccaro, A.M. Saposin B binds and transfers phospholipids. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, S.; Hartman, D.; Presidente, P.J.; Newton, S.E.; Gasser, R.B. HcSTK, a Caenorhabditis elegans PAR-1 homologue from the parasitic nematode, Haemonchus contortus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulkens, J.; De Wever, O.; Hendrix, A. Analyzing bacterial extracellular vesicles in human body fluids by orthogonal biophysical separation and biochemical characterization. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 40–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Turchinovich, A.; Mahairaki, V.; Troncoso, J.C.; Pletnikova, O.; Haughey, N.J.; Vella, L.J.; Hill, A.F.; Zheng, L.; et al. Influence of species and processing parameters on recovery and content of brain tissue-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1785746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, C.S.; Binos, S.; Knight, M.I.; Moate, P.J.; Cocks, B.G.; McDonagh, M.B. Global survey of the bovine salivary proteome: Integrating multidimensional prefractionation, targeted, and glycocapture strategies. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 5059–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Brown, G.R.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI Reference Sequences (RefSeq): Current status, new features and genome annotation policy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D130–D135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Rustam, Y.H.; Masters, C.L.; Makalic, E.; McLean, C.A.; Hill, A.F.; Barnham, K.J.; Reid, G.E.; Vella, L.J. Characterization of brain-derived extracellular vesicle lipids in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, G.; Fahy, E.; Aoki, J.; Dennis, E.A.; Durand, T.; Ejsing, C.S.; Fedorova, M.; Feussner, I.; Griffiths, W.J.; Kofeler, H.; et al. Update on LIPID MAPS classification, nomenclature, and shorthand notation for MS-derived lipid structures. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Chang, H.Y.; Daugherty, L.; Fraser, M.; Hunter, S.; Lopez, R.; McAnulla, C.; McMenamin, C.; Nuka, G.; Pesseat, S.; et al. The InterPro protein families database: The classification resource after 15 years. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D213–D221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Cox, J. Perseus: A bioinformatics platform for integrative analysis of proteomics data in cancer research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1711, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Irie, M.; Mori, H.; Kurokawa, K.; Yamada, T. FuncTree: Functional analysis and visualization for large-scale omics data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Protein | Accession Code |
|---|---|
| Saposin | HCON_00047370; HCON_00047380 |
| Nematode fatty acid retinoid-binding proteins | HCON_00092780; HCON_00092800; HCON_00092810 |
| Fatty acid-binding proteins | HCON_00169150 |
| SCP/TAPS proteins | HCON_00100510; HCON_00137280; HCON_00140240; HCON_00146300; HCON_00148510; HCON_00192680 |
| Vitellogenin | HCON_00188470 |
| Lipid Category/Class | EVs | Adult Worms | Shared by EVs and Adult Worms | Total Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerolipids | ||||
| DG | 11 | 22 | 11 | 22 |
| TG | 39 | 189 | 39 | 189 |
| Glycerophospholipids | ||||
| PC | 51 | 54 | 51 | 54 |
| PE | 99 | 106 | 99 | 106 |
| PG | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| PI | 12 | 18 | 12 | 18 |
| PS | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| CL | 5 | 12 | 5 | 12 |
| LPC | 16 | 18 | 16 | 18 |
| LPE | 18 | 19 | 18 | 19 |
| LPI | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| LPS | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| Sphingolipids | ||||
| SM | 70 | 63 | 63 | 79 |
| Cer | 80 | 73 | 73 | 80 |
| HexCer | 26 | 21 | 21 | 26 |
| ShexCer | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Sterol lipids | ||||
| CE | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| In total | 446 | 615 | 423 | 638 |
| Lipid Category (EVs/Adult Worms) | Saturated (%) | Unsaturated (%) | Odd-Chain FA (%) | Even-Chain FA (%) | Total No. of FA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-Chain FA | Long-Chain FA | Medium-Chain FA | Long-Chain FA | ||||
| Glycerolipids | ND/0.4 | 7.8/19.5 | ND/ND | 8.2/25.8 | 2.3/6.7 | 13.7/39.0 | 138/651 |
| Glycerophospholipids | 0.1/0.1 | 21.1/13.5 | ND/ND | 25.9/20.3 | 8.7/5.7 | 38.4/28.2 | 406/482 |
| Sphingolipids | ND/ND | 21.2/11.4 | ND/ND | 15.2/8.7 | 16.1/9.3 | 20.3/10.8 | 314/286 |
| Sterol lipids | ND/ND | ND/ND | ND/ND | 0.5/0.3 | ND/ND | 0.5/0.3 | 4/4 |
| Total | 0.1/0.5 | 50.1/44.4 | ND/ND | 49.8/55.1 | 27.1/21.7 | 72.9/78.3 | 862/1423 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Koukoulis, T.F.; Vella, L.J.; Su, H.; Purnianto, A.; Nie, S.; Ang, C.-S.; Ma, G.; Korhonen, P.K.; Taki, A.C.; et al. The Proteome and Lipidome of Extracellular Vesicles from Haemonchus contortus to Underpin Explorations of Host–Parasite Cross–Talk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310955
Wang T, Koukoulis TF, Vella LJ, Su H, Purnianto A, Nie S, Ang C-S, Ma G, Korhonen PK, Taki AC, et al. The Proteome and Lipidome of Extracellular Vesicles from Haemonchus contortus to Underpin Explorations of Host–Parasite Cross–Talk. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):10955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310955
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tao, Tiana F. Koukoulis, Laura J. Vella, Huaqi Su, Adityas Purnianto, Shuai Nie, Ching-Seng Ang, Guangxu Ma, Pasi K. Korhonen, Aya C. Taki, and et al. 2023. "The Proteome and Lipidome of Extracellular Vesicles from Haemonchus contortus to Underpin Explorations of Host–Parasite Cross–Talk" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 10955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310955
APA StyleWang, T., Koukoulis, T. F., Vella, L. J., Su, H., Purnianto, A., Nie, S., Ang, C.-S., Ma, G., Korhonen, P. K., Taki, A. C., Williamson, N. A., Reid, G. E., & Gasser, R. B. (2023). The Proteome and Lipidome of Extracellular Vesicles from Haemonchus contortus to Underpin Explorations of Host–Parasite Cross–Talk. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 10955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310955








