IL-18 in Autoinflammatory Diseases: Focus on Adult Onset Still Disease and Macrophages Activation Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
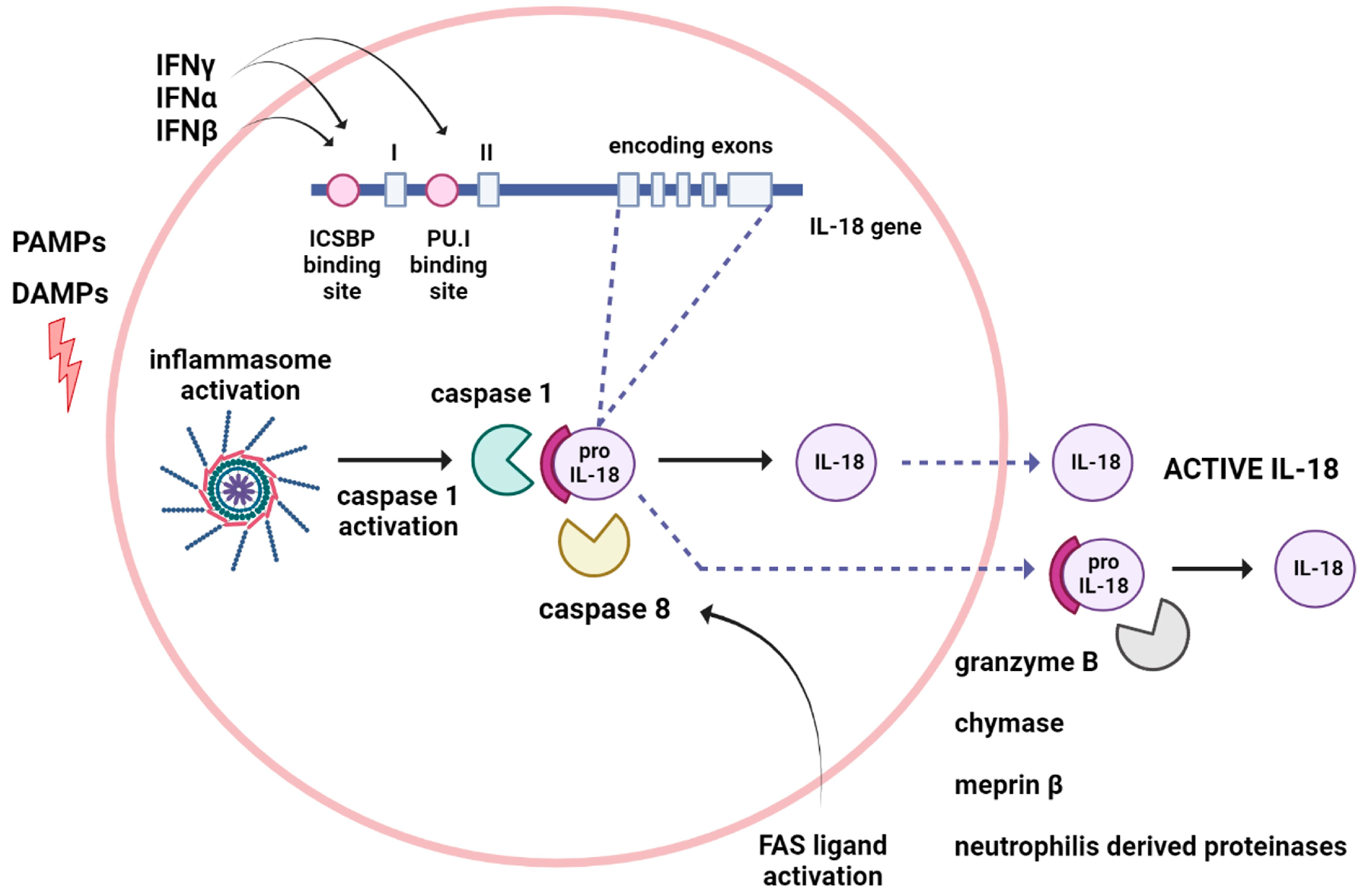
2. Mechanism of IL-18 Formation and Release
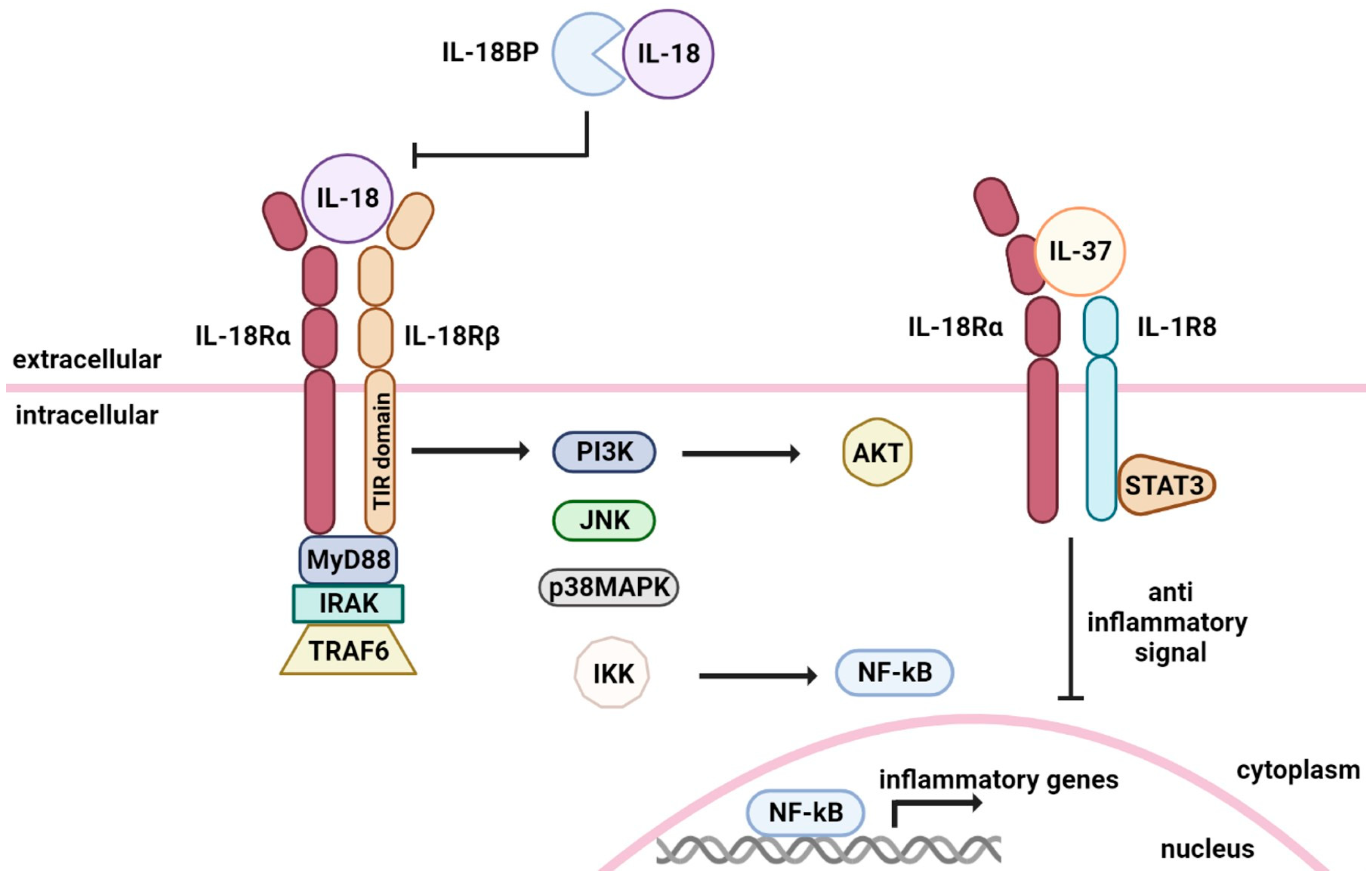
3. IL-18 Signal Transduction
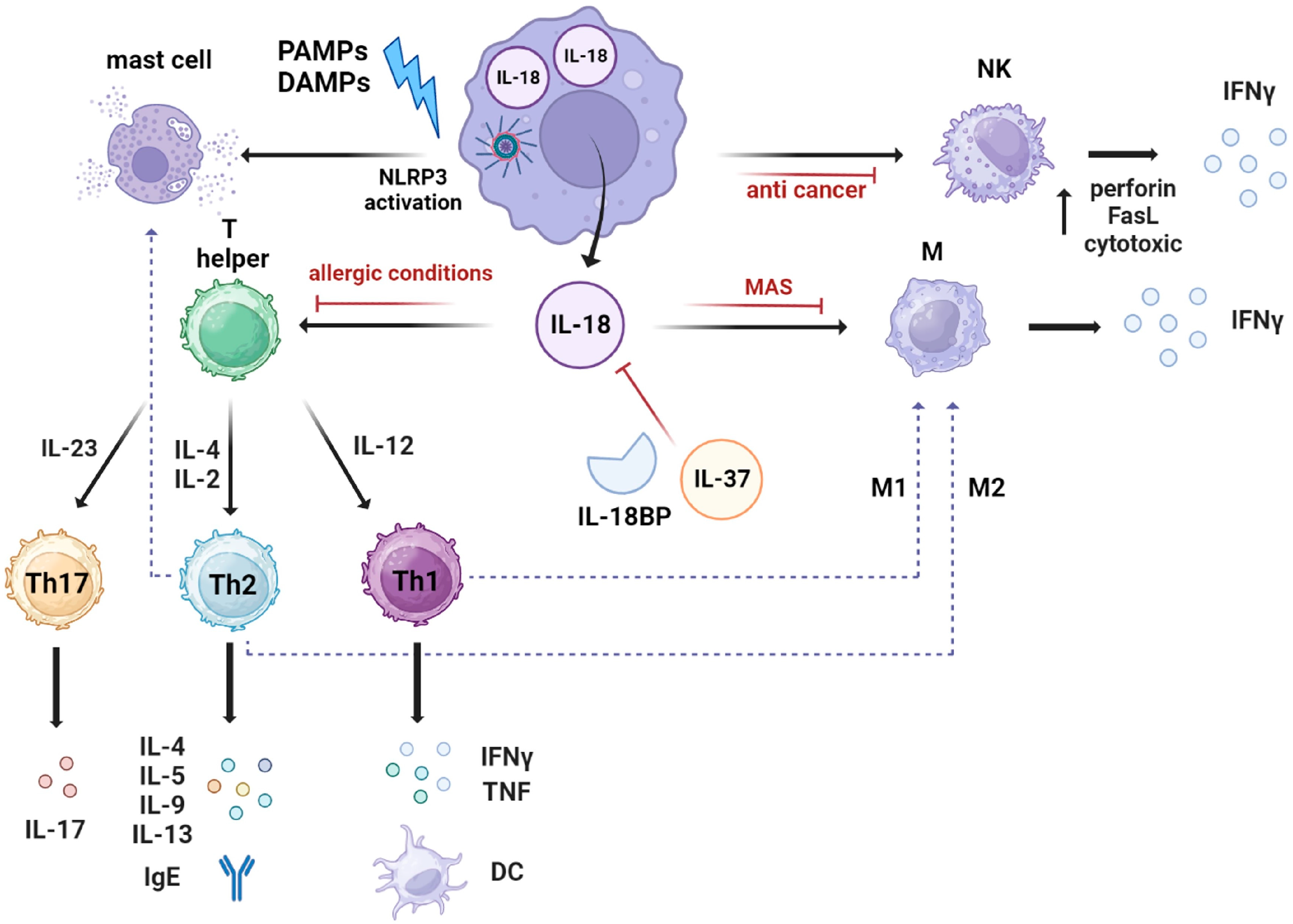
4. IL-18 Mechanism of Action
5. Role of IL-18 Binding Protein and IL-37 in Inhibiting IL-18 Signaling
6. IL-18 in Autoinflammatory Diseases
6.1. The Role of IL-18 in sJIA/AOSD
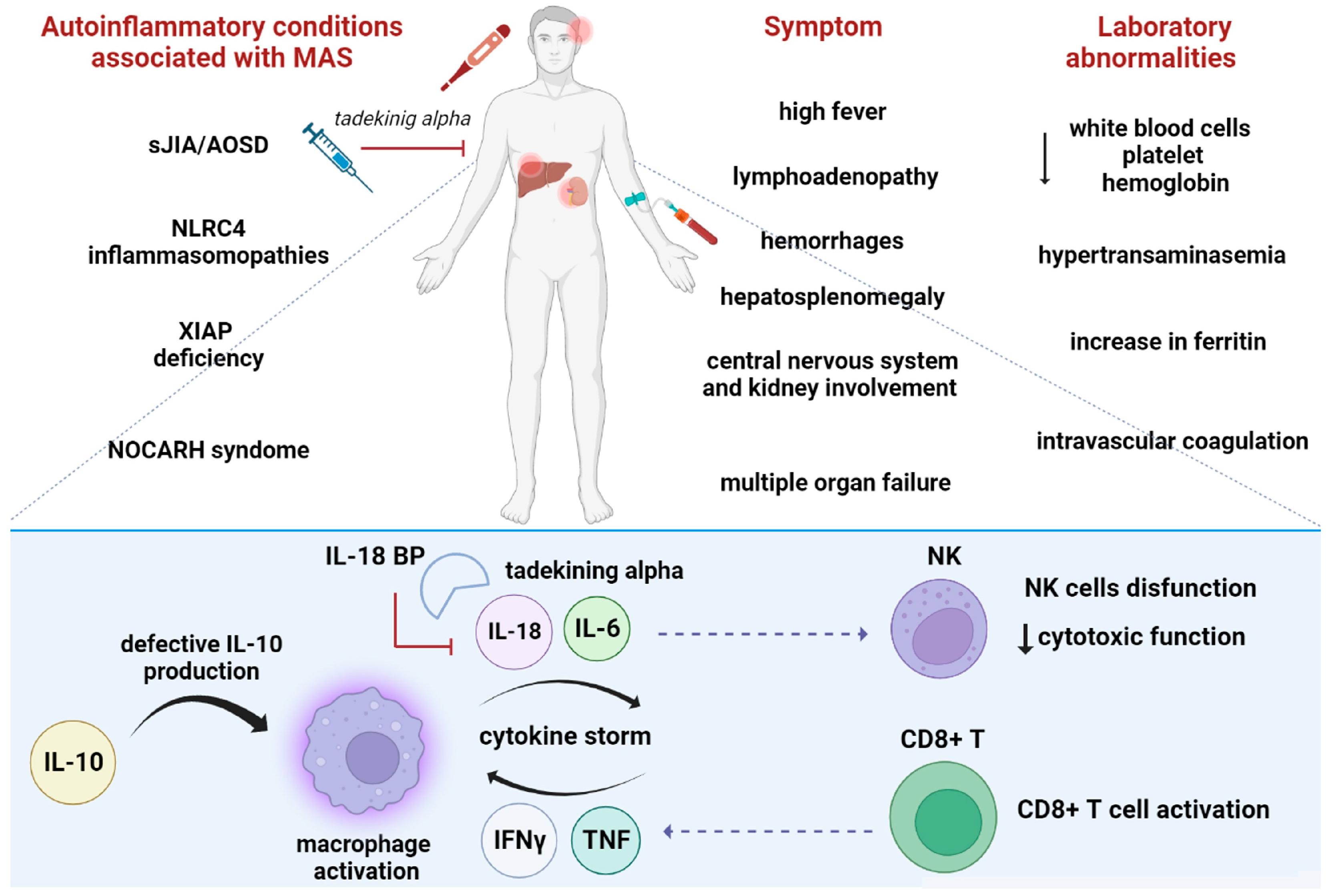
6.2. The Role of IL-18 in Macrophages Activated Syndrome
6.3. Role of IL-18 as Biomarker
6.4. Other Autoinflammatory Conditions Associated with High IL-18 Levels
6.5. IL-18 as a Therapeutic Target
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hurgin, V.; Novick, D.; Rubinstein, M. The promoter of IL-18 binding protein: Activation by an IFN-γ-induced complex of IFN regulatory factor 1 and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16957–16962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Takei, S.; Mori, M.; Yachie, A. Pathogenic roles and diagnostic utility of interleukin-18 in autoinflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 951535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18: Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puren, A.J.; Fantuzzi, G.; Dinarello, C.A. Gene expression, synthesis, and secretion of interleukin 18 and interleukin 1β are differentially regulated in human blood mononuclear cells and mouse spleen cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 2256–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, D.L.; Ombrello, A.; Arostegui, J.I.; Schneider, C.; Dang, V.; de Jesus, A.; Girard-Guyonvarc’H, C.; Gabay, C.; Lee, W.; Chae, J.J.; et al. Excess Serum Interleukin-18 Distinguishes Patients With Pathogenic Mutations in PSTPIP1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Tsutsui, H. Interleukin-18 in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Okamura, H. Interleukin-18 is a unique cytokine that stimulates both Th1 and Th2 responses depending on its cytokine milieu. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001, 12, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Novick, D.; Kim, S.; Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18 and IL-18 Binding Protein. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, H.; Kayagaki, N.; Kuida, K.; Nakano, H.; Hayashi, N.; Takeda, K.; Matsui, K.; Kashiwamura, S.; Hada, T.; Akira, S.; et al. Caspase-1-independent, Fas/Fas ligand-mediated IL-18 secretion from macrophages causes acute liver injury in mice. Immunity 1999, 11, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossaller, L.; Chiang, P.-I.; Schmidt-Lauber, C.; Ganesan, S.; Kaiser, W.J.; Rathinam, V.A.K.; Mocarski, E.S.; Subramanian, D.; Green, D.R.; Silverman, N.; et al. Cutting Edge: FAS (CD95) Mediates Noncanonical IL-1β and IL-18 Maturation via Caspase-8 in an RIP3-Independent Manner. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5508–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, K.; Ohtsuki, T.; Nukada, Y.; Tanimoto, T.; Namba, M.; Okura, T.; Takakura-Yamamoto, R.; Torigoe, K.; Gu, Y.; Su, M.S.-S.; et al. Involvement of Caspase-1 and Caspase-3 in the Production and Processing of Mature Human Interleukin 18 in Monocytic THP.1 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26595–26603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoto, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; Tokime, K.; Kitano, S.; Kakeda, M.; Akeda, T.; Kurokawa, I.; Gabazza, E.C.; Tsutsui, H.; Katayama, N.; et al. Granzyme B is a novel interleukin-18 converting enzyme. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 59, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Bond, J.S. Prointerleukin-18 is activated by meprin beta in vitro and in vivo in intestinal inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31371–31377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahira, M.; Tomura, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Ahn, H.J.; Bian, Y.; Hamaoka, T.; Ohta, T.; Kurimoto, M.; Fujiwara, H. An absolute requirement for STAT4 and a role for IFN-γ as an amplifying factor in IL-12 induction of the functional IL-18 receptor complex. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, S.; Paananen, A.; Miettinen, M.; Kurimoto, M.; Timonen, T.; Julkunen, I.; Sareneva, T. IFN-α and IL-18 synergistically enhance IFN-γ production in human NK cells: Differential regulation of Stat4 activation and IFN-γ gene expression by IFN-α and IL-12. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 2236–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K. Unique Action of Interleukin-18 on T Cells and Other Immune Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, S.; Uehara, A.; Nochi, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ueda, H.; Sugiyama, A.; Hanzawa, K.; Kumagai, K.; Okamura, H.; Takada, H. Neutrophil Proteinase 3-Mediated Induction of Bioactive IL-18 Secretion by Human Oral Epithelial Cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 6568–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Shibuya, K.; Mui, A.; Zonin, F.; Murphy, E.; Sana, T.; Hartley, S.B.; Menon, S.; Kastelein, R.; Bazan, F.; et al. IGIF does not drive Th1 development but synergizes with IL-12 for interferon-γ production and activates IRAK and NFκB. Immunity 1997, 7, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, U.; Kauschat, D.; Koyama, N.; Nuernberger, H.; Ballas, K.; Koschmieder, S.; Bug, G.; Hofmann, W.K.; Hoelzer, D.; Ottmann, O.G. IL-18 activates STAT3 in the natural killer cell line 92, augments cytotoxic activity, and mediates IFN-γ production by the stress kinase p38 and by the extracellular regulated kinases p44erk-1 and p42erk-21. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Darawish, Y.; Li, W.; Yamanishi, K.; Pencheva, M.; Oka, N.; Yamanishi, H.; Matsuyama, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Minato, N.; Okamura, H. Frontline Science: IL-18 primes murine NK cells for proliferation by promoting protein synthesis, survival, and autophagy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ping, F.F.; Lv, W.T.; Feng, J.Y.; Shang, J. Interleukin-18 directly protects cortical neurons by activating PI3K/AKT/NF-κB/CREB pathways. Cytokine 2014, 69, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosotani, Y.; Kashiwamura, S.-I.; Kimura-Shimmyo, A.; Sekiyama, A.; Ueda, H.; Ikeda, T.; Mimura, O.; Okamura, H. Interleukin-18 prevents apoptosis via PI3K/Akt pathway in normal human keratinocytes. J. Dermatol. 2008, 35, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohka, H.; Yoshino, T.; Iwagaki, H.; Sakuma, I.; Tanimoto, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Kurimoto, M.; Orita, K.; Akagi, T.; Tanaka, N. Interleukin-18/interferon-γ-inducing factor, a novel cytokine, up-regulates ICAM-1 (CD54) expression in KG-1 cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 64, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, J.C.; Park, C.C.; Woods, J.M.; Koch, A.E. A novel role for interleukin-18 in adhesion molecule induction through NF kappa B and phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase-dependent signal transduction pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37069–37075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitzler, I.; Sayi, A.; Kohler, E.; Engler, D.B.; Koch, K.N.; Hardt, W.D.; Müller, A. Caspase-1 has both proinflammatory and regulatory properties in Helicobacter infections, which are differentially mediated by its substrates IL-1β and IL-18. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3594–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuzzi, G.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-18 and interleukin-1β: Two cytokine substrates for ICE (caspase-1). J. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Matsui, K.; Higashino, K.; Okamura, H.; Miyazawa, Y.; Kaneda, K. IFN-γ-inducing factor up-regulates Fas ligand-mediated cytotoxic activity of murine natural killer cell clones. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 3967–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellora, F.; Castriconi, R.; Doni, A.; Cantoni, C.; Moretta, L.; Mantovani, A.; Moretta, A.; Bottino, C. M-CSF induces the expression of a membrane-bound form of IL-18 in a subset of human monocytes differentiating in vitro toward macrophages. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, Y.; Akita, K.; Taniai, M.; Torigoe, K.; Mori, T.; Nishida, Y.; Ushio, S.; Nukada, Y.; Tanimoto, T.; Ikegami, H.; et al. Cloning and expression of interleukin-18 binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1999, 445, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggioni, R.; Cattley, R.C.; Guo, J.; Flores, S.; Brown, H.; Qi, M.; Yin, S.; Hill, D.; Scully, S.; Chen, C.; et al. IL-18-binding protein protects against lipopolysaccharide- induced lethality and prevents the development of Fas/Fas ligand-mediated models of liver disease in mice. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5913–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, B.; Sennello, J.A.; Lehr, H.A.; Senaldi, G.; Dinarello, C.A.; Fantuzzi, G. Frontline: Interferon regulatory factor-1 as a protective gene in intestinal inflammation: Role of TCR γ δ T cells and interleukin-18-binding protein. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 2356–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, N.K.; Vondracek, A.; Kraus, D.; Dinarello, C.A.; Kim, S.H.; Bendele, A.; Senaldi, G.; Arend, W.P. Mechanisms of inhibition of collagen-induced arthritis by murine IL-18 binding protein. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 2100–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccone, P.; Phillips, J.; Conget, I.; Cooke, A.; Nicoletti, F. IL-18 binding protein fusion construct delays the development of diabetes in adoptive transfer and cyclophosphamide-induced diabetes in NOD mouse. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold-Petry, C.A.; Lehrnbecher, T.; Jarisch, A.; Schwabe, D.; Pfeilschifter, J.M.; Muhl, H.; Nold, M.F. Failure of interferon γ to induce the anti-inflammatory interleukin 18 binding protein in familial hemophagocytosis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, D.; Elbirt, D.; Miller, G.; Dinarello, C.A.; Rubinstein, M.; Sthoeger, Z.M. High circulating levels of free interleukin-18 in patients with active SLE in the presence of elevated levels of interleukin-18 binding protein. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colafrancesco, S.; Priori, R.; Alessandri, C.; Perricone, C.; Pendolino, M.; Picarelli, G.; Valesini, G. IL-18 Serum Level in Adult Onset Still’s Disease: A Marker of Disease Activity. Int. J. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 156890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C.; Fautrel, B.; Rech, J.; Spertini, F.; Feist, E.; Kötter, I.; Hachulla, E.; Morel, J.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Hamidou, M.A.; et al. Open-label, multicentre, dose-escalating phase II clinical trial on the safety and efficacy of tadekinig alfa (IL-18BP) in adult-onset Still’s disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canna, S.W.; Girard, C.; Malle, L.; de Jesus, A.; Romberg, N.; Kelsen, J.; Surrey, L.F.; Russo, P.; Sleight, A.; Schiffrin, E.; et al. Life-threatening NLRC4-associated hyperinflammation successfully treated with IL-18 inhibition. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 139, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufler, P.; Azam, T.; Gamboni-Robertson, F.; Reznikov, L.L.; Kumar, S.; Dinarello, C.A.; Kim, S.-H. A complex of the IL-1 homologue IL-1F7b and IL-18-binding protein reduces IL-18 activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13723–13728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubartelli, A. Autoinflammatory diseases. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 161, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Okajima, M.; Toma, T.; Yachie, A.; Wada, T. Role of E148Q in familial Mediterranean fever with an exon 10 mutation in MEFV. Pediatr. Int. 2022, 64, e14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellins, E.D.; Macaubas, C.; Grom, A.A. Pathogenesis of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Some answers, more questions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, N.; Shimizu, M.; Tsunoda, S.; Kawano, M.; Matsumura, M.; Yachie, A. Cytokine profile in adult-onset Still’s disease: Comparison with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 169, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Cho, Y.N.; Kim, T.J.; Park, S.C.; Park, D.J.; Jin, H.M.; Lee, S.S.; Kee, S.J.; Kim, N.; Yoo, D.H.; et al. Natural killer T cell deficiency in active adult-onset Still’s Disease: Correlation of deficiency of natural killer T cells with dysfunction of natural killer cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2868–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grom, A.A.; Villanueva, J.; Lee, S.; Goldmuntz, E.A.; Passo, M.H.; Filipovich, A. Natural killer cell dysfunction in patients with systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and macrophage activation syndrome. J. Pediatr. 2003, 142, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, M.; Yamamura, M.; Taniai, M.; Yamauchi, H.; Tanimoto, T.; Kurimoto, M.; Miyawaki, S.; Amano, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Makino, H. Levels of interleukin-18 and its binding inhibitors in the blood circulation of patients with adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, M.; Shimizu, M.; Yakoyama, T.; Mizuta, M.; Yachie, A. Transient natural killer cell dysfunction associated with interleukin-18 overproduction in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 984–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibatomi, K.; Ida, H.; Yamasaki, S.; Nakashima, T.; Origuchi, T.; Kawakami, A.; Migita, K.; Kawabe, Y.; Tsujihata, M.; Anderson, P.; et al. A novel role for interleukin-18 in human natural killer cell death: High serum levels and low natural killer cell numbers in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, W.; Vastert, S.J.; Beekman, J.M.; Wulffraat, N.M.; Kuis, W.; Coffer, P.J.; Prakken, B.J. Defective phosphorylation of interleukin-18 receptor beta causes impaired natural killer cell function in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2782–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, T.; Nishimura, K.; Murase, A.; Hattori, S.; Ohara, A.; Nozawa, T.; Hara, R.; Ito, S. Impaired Interleukin-18 Signaling in Natural Killer Cells From Patients With Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022, 4, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.-L.; Chen, Y.-M.; Hsieh, C.-W.; Chen, H.-H.; Lee, H.-C.; Hung, W.-T.; Tang, K.-T.; Chen, D.-Y. Upregulation of circulating microRNA-134 in adult-onset Still’s disease and its use as potential biomarker. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puren, A.J.; Fantuzzi, G.; Gu, Y.; Su, M.S.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-18 (IFNγ-inducing factor) induces IL-8 and IL-1β via TNFα production from non-CD14+ human blood mononuclear cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Put, K.; Avau, A.; Brisse, E.; Mitera, T.; Put, S.; Proost, P.; Bader-Meunier, B.; Westhovens, R.; Eynde, B.J.V.D.; Orabona, C.; et al. Cytokines in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Tipping the balance between interleukin-18 and interferon-γ. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crayne, C.B.; Albeituni, S.; Nichols, K.E.; Cron, R.Q. The Immunology of Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avčin, T.; Tse, S.M.; Schneider, R.; Ngan, B.; Silverman, E.D. Macrophage activation syndrome as the presenting manifestation of rheumatic diseases in childhood. J. Pediatr. 2006, 148, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulert, G.S.; Grom, A.A. Pathogenesis of Macrophage Activation Syndrome and Potential for Cytokine-Directed Therapies. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumegi, J.; Barnes, M.G.; Nestheide, S.V.; Molleran-Lee, S.; Villanueva, J.; Zhang, K.; Risma, K.A.; Grom, A.A.; Filipovich, A.H. Gene expression profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from children with active hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2011, 117, e151–e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E.S.; Girard-Guyonvarc’h, C.; Holzinger, D.; de Jesus, A.A.; Tariq, Z.; Picarsic, J.; Schiffrin, E.J.; Foell, D.; Grom, A.A.; Ammann, S.; et al. Interleukin-18 diagnostically distinguishes and pathogenically promotes human and murine macrophage activation syndrome. Blood 2018, 131, 1442–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvie, E.M.; Khan, A.; Hubank, M.; Kellam, P.; Woo, P. Specific gene expression profiles in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 1954–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Kullberg, B.J.; Verschueren, I.; Van Der Meer, J.W. Interleukin-18 induces production of proinflammatory cytokines in mice: No intermediate role for the cytokines of the tumor necrosis factor family and interleukin-1β. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 3057–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard-Guyonvarc′H, C.; Palomo, J.; Martin, P.; Rodriguez, E.; Troccaz, S.; Palmer, G.; Gabay, C. Unopposed IL-18 signaling leads to severe TLR9-induced macrophage activation syndrome in mice. Blood 2018, 131, 1430–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grom, A.A.; Ilowite, N.T.; Pascual, V.; Brunner, H.I.; Martini, A.; Lovell, D.; Ruperto, N.; Leon, K.; Lheritier, K.; Abrams, K.; et al. Rate and Clinical Presentation of Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Patients with Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Treated With Canakinumab. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Sakakibara, Y.; Kawano, M.; Yachie, A. Transient impairment of NK cell function in an infant born to a mother with adult-onset Still’s disease: Perinatal effect of maternal IL-18. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 143, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, S.; Itoh, Y.; Morio, T.; Sumitomo, N.; Daimaru, K.; Minota, S. Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Patients with Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis under Treatment with Tocilizumab. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Nakagishi, Y.; Inoue, N.; Mizuta, M.; Ko, G.; Saikawa, Y.; Kubota, T.; Yamasaki, Y.; Takei, S.; Yachie, A. Interleukin-18 for predicting the development of macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 160, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.Y.; Schulert, G.S.; Canna, S.W.; Huang, Y.; Sundel, J.; Li, Y.; Hoyt, K.J.; Blaustein, R.B.; Wactor, A.; Do, T.; et al. Adenosine deaminase 2 as a biomarker of macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessel, C.; Fall, N.; Grom, A.; de Jager, W.; Vastert, S.; Strippoli, R.; Bracaglia, C.; Sundberg, E.; Horne, A.; Ehl, S.; et al. Definition and validation of serum biomarkers for optimal differentiation of hyperferritinaemic cytokine storm conditions in children: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e563–e573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, M.; Shimizu, M.; Inoue, N.; Ikawa, Y.; Nakagishi, Y.; Yasuoka, R.; Iwata, N.; Yachie, A. Clinical significance of interleukin-18 for the diagnosis and prediction of disease course in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2421–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeno, N.; Takei, S.; Nomura, Y.; Imanaka, H.; Hokonohara, M.; Miyata, K. Highly elevated serum levels of interleukin-18 in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis but not in other juvenile idiopathic arthritis subtypes or in Kawasaki disease: Comment on the article by Kawashima et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2539–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard-Guyonvarc’H, C.; Rech, J.; Brown, M.; Allali, D.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Spertini, F.; Schiffrin, E.J.; Schett, G.; Manger, B.; Bas, S.; et al. Elevated serum levels of free interleukin-18 in adult-onset Still’s disease. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 2237–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelušić, M.; Lukić, I.K.; Tambić-Bukovac, L.; Dubravčić, K.; Malčić, I.; Rudan, I.; Batinić, D. Interleukin-18 as a mediator of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 1332–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feist, E.; Mitrovic, S.; Fautrel, B. Mechanisms, biomarkers and targets for adult-onset Still’s disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrovic, S.; Fautrel, B. New Markers for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 85, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudela, H.; Drynda, S.; Lux, A.; Horneff, G.; Kekow, J. Comparative study of Interleukin-18 (IL-18) serum levels in adult onset Still’s disease (AOSD) and systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) and its use as a biomarker for diagnosis and evaluation of disease activity. BMC Rheumatol. 2019, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, S.; Solomon, K.; Canna, S.W.; Girard-Guyonvarc’h, C.; Gabay, C.; Schiffrin, E.; Sleight, A.; A Grom, A.; Schulert, G.S. IL-18 as therapeutic target in a patient with resistant systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and recurrent macrophage activation syndrome. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, O.; Shan, N.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, P.; Wei, D.; Sun, R. The imbalance of IL-18/IL-18BP in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Yamada, K.; Kaneda, H.; Wada, H.; Wada, T.; Toma, T.; Ohta, K.; Kasahara, Y.; Yachie, A. Distinct cytokine profiles of systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated macrophage activation syndrome with particular emphasis on the role of interleukin-18 in its pathogenesis. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazodier, K.; Marin, V.; Novick, D.; Farnarier, C.; Robitail, S.; Schleinitz, N.; Veit, V.; Paul, P.; Rubinstein, M.; Dinarello, C.A.; et al. Severe imbalance of IL-18/IL-18BP in patients with secondary hemophagocytic syndrome. Blood 2005, 106, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canna, S.W.; A de Jesus, A.; Gouni, S.; Brooks, S.R.; Marrero, B.; Liu, Y.; A DiMattia, M.; Zaal, K.J.M.; Sanchez, G.A.M.; Kim, H.; et al. An activating NLRC4 inflammasome mutation causes autoinflammation with recurrent macrophage activation syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaud, S.; Fondanèche, M.-C.; Lambert, N.; Pasquier, B.; Mateo, V.; Soulas, P.; Galicier, L.; Le Deist, F.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Revy, P.; et al. XIAP deficiency in humans causes an X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Nature 2006, 444, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Kanegane, H.; Ohta, K.; Katoh, F.; Imamura, T.; Nakazawa, Y.; Miyashita, R.; Hara, J.; Hamamoto, K.; Yang, X.; et al. Sustained elevation of serum interleukin-18 and its association with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in XIAP deficiency. Cytokine 2014, 65, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.T.; Coppola, S.; Krumbach, O.H.; Prencipe, G.; Insalaco, A.; Cifaldi, C.; Brigida, I.; Zara, E.; Scala, S.; DI Cesare, S.; et al. A novel disorder involving dyshematopoiesis, inflammation, and HLH due to aberrant CDC42 function. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2778–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, S.; Insalaco, A.; Zara, E.; Di Rocco, M.; Marafon, D.P.; Spadaro, F.; Pannone, L.; Farina, L.; Pasquini, L.; Martinelli, S.; et al. Mutations at the C-terminus of CDC42 cause distinct hematopoietic and autoinflammatory disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhns, D.B.; Fink, D.L.; Choi, U.; Sweeney, C.; Lau, K.; Priel, D.L.; Riva, D.; Mendez, L.; Uzel, G.; Freeman, A.F.; et al. Cytoskeletal abnormalities and neutrophil dysfunction in WDR1 deficiency. Blood 2016, 128, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, H.; Wada, T. Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases with chronic excess of serum interleukin-18. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 930141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.L.; Chae, J.J.; Park, Y.H.; De Nardo, D.; Stirzaker, R.A.; Ko, H.-J.; Tye, H.; Cengia, L.; DiRago, L.; Metcalf, D.; et al. Aberrant actin depolymerization triggers the pyrin inflammasome and autoinflammatory disease that is dependent on IL-18, not IL-1β. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satış, H.; Özger, H.S.; Aysert Yıldız, P.; Hızel, K.; Gulbahar, Ö.; Erbaş, G.; Aygencel, G.; Guzel Tunccan, O.; Öztürk, M.A.; Dizbay, M.; et al. Prognostic value of interleukin-18 and its association with other inflammatory markers and disease severity in COVID-19. Cytokine 2021, 137, 155302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Bacchi, M.; Bertolino, M. Pharmacokinetics of IL-18 binding protein in healthy volunteers and subjects with rheumatoid arthritis or plaque psoriasis. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 31, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geerlinks, A.V.; Dvorak, A.M.; Jordan, M.B.; Schiffrin, E.J.; Behrens, E.M.; Marsh, R. XIAP Deficiency Treatment Consortium A Case of XIAP Deficiency Successfully Managed with Tadekinig Alfa (rhIL-18BP). J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 901–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindoli, S.; Doria, A.; Sfriso, P. Progress in Biological Therapies for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Biol. Targets Ther. 2022, 16, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Rood, J.E.; Rezk, A.; Pogoriler, J.; Finn, L.S.; Burnham, J.M.; Josephson, M.B.; Bar-Or, A.; Behrens, E.M.; Canna, S.W. Improvement of Refractory Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis-Associated Lung Disease with Single-Agent Blockade of IL-1β and IL-18. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M.J.; Mier, J.W.; Logan, T.; Atkins, M.; Koon, H.; Koch, K.M.; Kathman, S.; Pandite, L.N.; Oei, C.; Kirby, L.C.; et al. Clinical and Biological Effects of Recombinant Human Interleukin-18 Administered by Intravenous Infusion to Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4265–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihim, S.A.; Abubakar, S.D.; Zian, Z.; Sasaki, T.; Saffarioun, M.; Maleknia, S.; Azizi, G. Interleukin-18 cytokine in immunity, inflammation, and autoimmunity: Biological role in induction, regulation, and treatment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 919973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baggio, C.; Bindoli, S.; Guidea, I.; Doria, A.; Oliviero, F.; Sfriso, P. IL-18 in Autoinflammatory Diseases: Focus on Adult Onset Still Disease and Macrophages Activation Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311125
Baggio C, Bindoli S, Guidea I, Doria A, Oliviero F, Sfriso P. IL-18 in Autoinflammatory Diseases: Focus on Adult Onset Still Disease and Macrophages Activation Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):11125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311125
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaggio, Chiara, Sara Bindoli, Irina Guidea, Andrea Doria, Francesca Oliviero, and Paolo Sfriso. 2023. "IL-18 in Autoinflammatory Diseases: Focus on Adult Onset Still Disease and Macrophages Activation Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 11125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311125
APA StyleBaggio, C., Bindoli, S., Guidea, I., Doria, A., Oliviero, F., & Sfriso, P. (2023). IL-18 in Autoinflammatory Diseases: Focus on Adult Onset Still Disease and Macrophages Activation Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 11125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311125





